|
EP300
Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 (where E1A = adenovirus early region 1A) also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''EP300'' gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth. The EP300 gene is located on the long (q) arm of the human chromosome 22 at position 13.2. This gene encodes the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. EP300 is closely related to another gene, CREB binding protein, which is found on human chromosome 16. Function p300 HAT functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 22 (human)
Chromosome 22 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. Humans normally have two copies of chromosome 22 in each cell. Chromosome 22 is the second smallest human chromosome, spanning about 49 million DNA base pairs and representing between 1.5 and 2% of the total DNA in cells. In 1999, researchers working on the Human Genome Project announced they had determined the sequence of base pairs that make up this chromosome. Chromosome 22 was the first human chromosome to be fully sequenced. Human chromosomes are numbered by their apparent size in the karyotype, with Chromosome 1 being the largest and Chromosome 22 having originally been identified as the smallest. However, genome sequencing has revealed that Chromosome 21 is actually smaller than Chromosome 22. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 22. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation, their predictions of the number of genes on e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivator
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in all li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
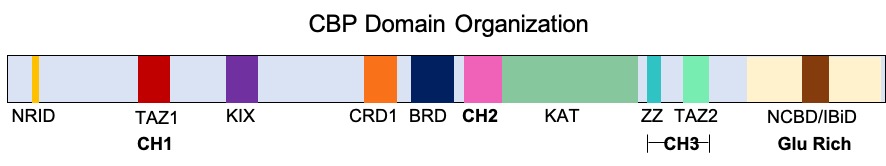
CREB Binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromodomain
A bromodomain is an approximately 110 amino acid protein domain that recognizes acetylated lysine residues, such as those on the ''N''-terminal tails of histones. Bromodomains, as the "readers" of lysine acetylation, are responsible in transducing the signal carried by acetylated lysine residues and translating it into various normal or abnormal phenotypes. Their affinity is higher for regions where multiple acetylation sites exist in proximity. This recognition is often a prerequisite for protein-histone association and chromatin remodeling. The domain itself adopts an all-α protein fold, a bundle of four alpha helices each separated by loop regions of variable lengths that form a hydrophobic pocket that recognizes the acetyl lysine. Discovery The bromodomain was identified as a novel structural motif by John W. Tamkun and colleagues studying the drosophila gene ''Brahma''/''brm'', and showed sequence similarity to genes involved in transcriptional activation. The name "bromo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KIX Domain
In biochemistry, the KIX domain (kinase-inducible domain (KID) interacting domain) or CREB binding domain is a protein domain of the eukaryotic transcriptional coactivators CBP and P300. It serves as a docking site for the formation of heterodimers between the coactivator and specific transcription factors. Structurally, the KIX domain is a globular domain consisting of three α-helices and two short 310-helices. The KIX domain was originally discovered in 1996 as the specific and minimal region in CBP that binds and interacts with phosphorylated CREB to activate transcription. It was thus first termed CREB-binding domain. However, when it was later discovered that it also binds many other proteins, the more general name KIX domain became favoured. The KIX domain contains two separate binding sites: the "c-Myb site", named after the oncoprotein c-Myb, and the "MLL site", named after the proto-oncogene MLL (Mixed Lineage Leukemia, KMT2A). The paralogous coactivators CBP (CREBBP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIF1A
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, also known as HIF-1-alpha, is a subunit of a heterodimeric transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) that is encoded by the ''HIF1A'' gene. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019 was awarded for the discovery of HIF. HIF1A is a basic helix-loop-helix PAS domain containing protein, and is considered as the master transcriptional regulator of cellular and developmental response to hypoxia. The dysregulation and overexpression of ''HIF1A'' by either hypoxia or genetic alternations have been heavily implicated in cancer biology, as well as a number of other pathophysiologies, specifically in areas of vascularization and angiogenesis, energy metabolism, cell survival, and tumor invasion. Two other alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified. Structure HIF1 is a heterodimeric basic helix-loop-helix structure that is composed of HIF1A, the alpha subunit (this protein), and the aryl hydrocarbon rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism. Nuclear receptors bind directly to DNA regulating the expression of adjacent genes; hence these receptors are classified as transcription factors. The regulation of gene expression by nuclear receptors often occurs in the presence of a ligand—a molecule that affects the receptor's behavior. Ligand binding to a nuclear receptor results in a conformational change activating the receptor. The result is up- or down-regulation of gene expression. A unique property of nuclear receptors that differentiates them from other classes of receptors is their direct control of genomic DNA. Nuclear receptors play key roles in both embryonic development a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYB (gene)
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains. Function Viral The Myb gene family is named after the eponymous gene in Avian myeloblastosis virus. The viral Myb (v-Myb, ) recognizes the sequence 5'-YAACKG-3'. It causes myeloblastosis (myeloid leukemia) in chickens. Compared to the normal animal cellular Myb (c-myb), v-myb contains deletions in the C-terminal regulatory domain, leading to aberrant activation of other oncogenes. Animals Myb proto-oncogene protein is a member of the MYB (myeloblastosis) family of transcription factors. The protein contains three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central transcriptional activation domain and a C-terminal domain involved in transcriptional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Sven Gustaf Hedin in 1896. It is also a precursor to histamine, a vital inflammatory agent in immune responses. The acyl radical is histidyl. Properties of the imidazole side chain The conjugate acid (protonated form) of the imidazole side chain in histidine has a p''K''a of approximately 6.0. Thus, below a pH of 6, the imidazole ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |