Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān;
alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by
Protestant missions) is a
province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
in
Southwest China occupying most of the
Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the
Tibetan Plateau between the
Jinsha River on the west, the
Daba Mountains in the north and the
Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
to the northwest,
Gansu to the north,
Shaanxi to the northeast,
Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
to the east,
Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to t ...
to the southeast,
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
to the south, and the
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of ...
to the west.
In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the
ancient states of
Ba and
Shu. Their conquest by
Qin strengthened it and paved the way for
Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of "king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Emperor ( ...
's
unification of China under the
Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
. During the
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and wa ...
era,
Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative of the H ...
's state of
Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by
Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent
Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Q ...
conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
,
Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
served as the temporary capital of the
Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northea ...
, making it the focus of the
Japanese bombing. It was one of the last
mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or dem ...
areas captured by the
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
during the
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on main ...
and was divided into four parts from 1949 to 1952, with Chongqing restored two years later. It suffered gravely during the
Great Chinese Famine of 1959–61 but remained China's
most populous province until
Chongqing Municipality was again separated from it in 1997.
The
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of proper ...
of Sichuan speak distinctive
Sichuanese dialects of
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
. The spicy
Sichuan pepper is prominent in modern
Sichuan cuisine, featuring dishes—including
Kung Pao chicken and
mapo tofu—that have become staples of Chinese cuisine around the world. In 1950, the province of
Xikang was dissolved and its territory was later split between the newly established
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of ...
and the Province of Sichuan. The western and northwestern part of Sichuan is made up of
Tibetan and
Qiang autonomous areas.
Sichuan is the
6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in
Western China and the second largest among inland provinces after
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
. As of 2021, its nominal GDP was 5,385 billion yuan (US$847.68 billion), ahead of the GDP of Turkey of 815 billion.
Compared to a country, it would be the
18th-largest economy as well as the
19th most populous as of 2021.
There are many
panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear (or simply the panda), is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its bold black-and-white coat and rotund body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes use ...
stations in the province and large reserves for these creatures, such as Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda.
Names
It is commonly believed that the name ''Sichuan'' means "four
rivers", and in
folk etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
, this is usually taken to mean four of the province's major rivers: the
Jialing,
Jinsha (or
Wu),
Min, and
Tuo.
According to
historical geographer Tan Qixiang, "four rivers" is an erroneous interpretation of the place's name.
The name of the province is a contraction of the phrases ''Sì Chuānlù'' "Four Plain
Circuits") and ''Chuānxiá Sìlù'' "Four Circuits of Chuanxia"),
[''Si'' (四) means "four", ''Chuan'' (川) means "plain", and ''Xia'' ("峡") could be understood as "gorge". ''Sì Chuānlù'' and ''Chuānxiá Sìlù'' are general names for the Four Circuits,.] referring to the division of the existing
imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texas
...
administrative circuit in the area into four during the
Northern Song dynasty
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ...
, which was
Yizhou,
Lizhou,
Zizhou, and
Kuizhou. The word ''chuan'' () here means "
plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands. ...
", not its normal meaning of "river" as popularly assumed. In addition to its
postal map and
Wade-Giles forms, the name has also been irregularly romanized as Szű-chuan and Szechuan.
In antiquity, the area of modern Sichuan including the now separated Chongqing Municipality was known to the
Chinese as , in reference to the
ancient states of
Ba and
Shu that once occupied the
Sichuan Basin. Shu continued to be used to refer to the Sichuan region all through its history right up to the present day; several states formed in the area used the same name, for example, the
Shu of the
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and wa ...
period, and
Former Shu
Great Shu (Chinese: 大蜀, Pinyin: Dàshǔ) called in retrospect Former Shu (Chinese: 前蜀, Pinyin: Qiánshǔ) or occasionally Wang Shu (王蜀), was one of the Ten Kingdoms formed during the chaotic period between the rules of the Tang dyna ...
and
Later Shu of the
Ten Kingdoms period. Currently, both the characters for ''Shu'' and ''Chuan'' are commonly used as abbreviations for Sichuan.
History
Prehistory
The
Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas of the
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
watershed were a cradle of indigenous civilizations dating back to at least the 15th century BC, coinciding with the
Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and f ...
in northern China. The region had its own distinct religious beliefs and worldview. The earliest culture found in the region through archaeological investigation is the
Baodun culture (2700–1750 BC) excavated in the
Chengdu Plain.
Ba and Shu Kingdoms
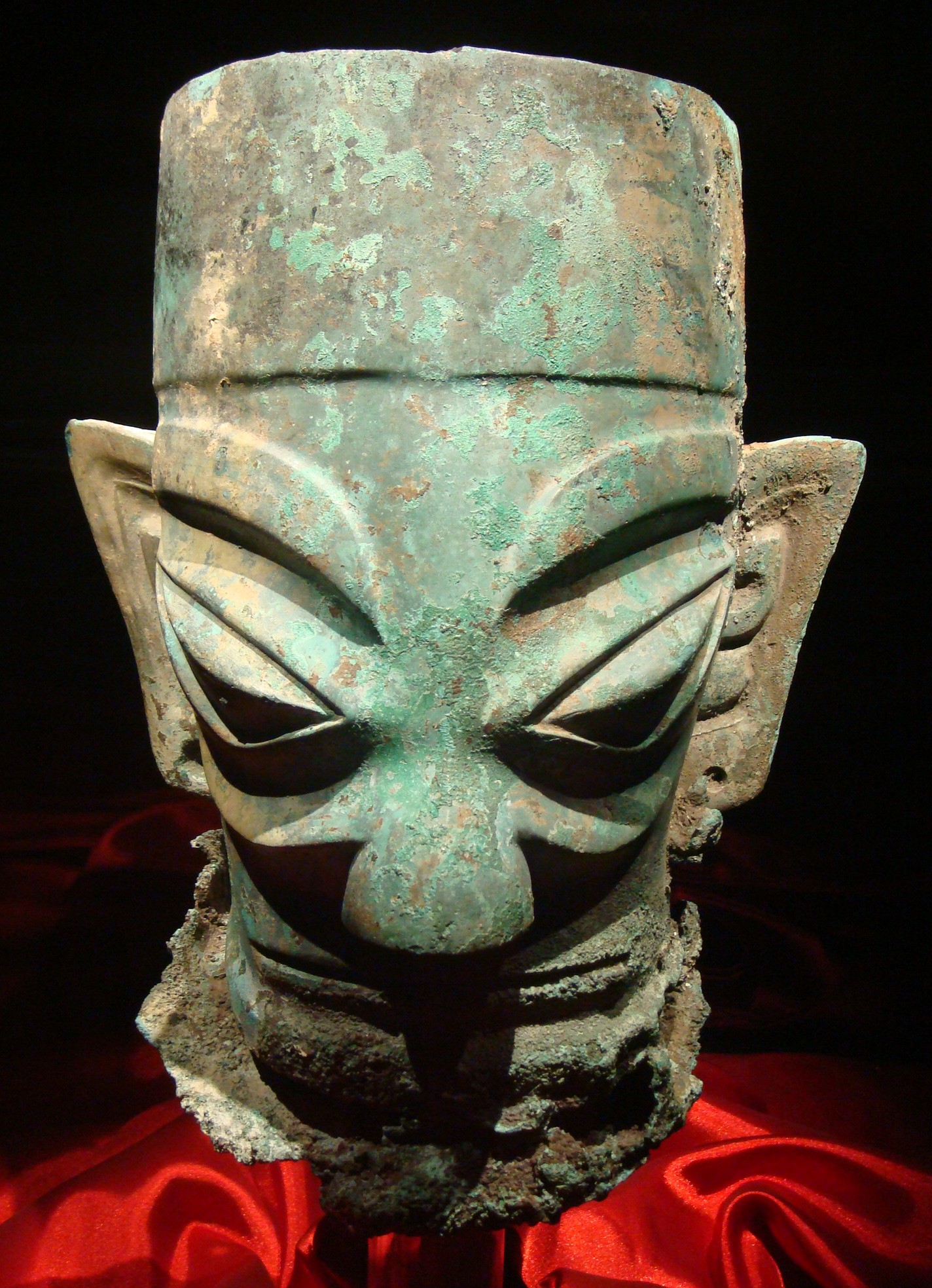

The most important native states were those of Ba and Shu.
Ba stretched into Sichuan from the
Han Valley in
Shaanxi and
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The pr ...
down the
Jialing River as far as its confluence with the
Yangtze
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
at
Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
.
occupied the valley of the
Min, including
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
and other areas of western Sichuan.
[ The existence of the early state of Shu was poorly recorded in the main historical records of China. It was, however, referred to in the '']Book of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shūjīng'', earlier ''Shu King'') or ''Classic of History'', also known as the ''Shangshu'' (“Venerated Documents”), is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetoric ...
'' as an ally of the Zhou. Accounts of Shu exist mainly as a mixture of mythological stories and historical legends recorded in local annals such as the '' Chronicles of Huayang'' compiled in the Jin dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty (; ) or the Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the (司馬晉) or the (兩晉), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Sima Yan (Emperor Wu), eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had p ...
,Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan ...
valley of north-central China.
Qin dynasty
The rulers of the expansionist state of Qin, based in present-day Gansu and Shaanxi, were the first strategists to realize that the area's military importance matched its commercial and agricultural significance. The Sichuan basin is surrounded by the Hengduan Mountains to the west, the Qin Mountains to the north, and Yungui Plateau to the south. Since the Yangtze flows through the basin and then through the perilous Three Gorges to eastern and southern China, Sichuan was a staging area for amphibious military forces and a haven for political refugees.
Qin armies finished their conquest of the kingdoms of Shu and Ba by 316 BC. Any written records and civil achievements of earlier kingdoms were destroyed. Qin administrators introduced improved agricultural technology. Li Bing, engineered the Dujiangyan irrigation system to control the Min River, a major tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
of the Yangtze. This innovative hydraulic system was composed of movable weirs which could be adjusted for high or low water flow according to the season, to either provide irrigation or prevent floods. The increased agricultural output and taxes made the area a source of provisions and men for Qin's unification of China.
Han dynasty
 Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. Following the declining central government of the
Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. Following the declining central government of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
in the second century, the Sichuan basin, surrounded by mountains and easily defensible, became a popular place for upstart generals to found kingdoms that challenged the authority of Yangtze Valley emperors over China.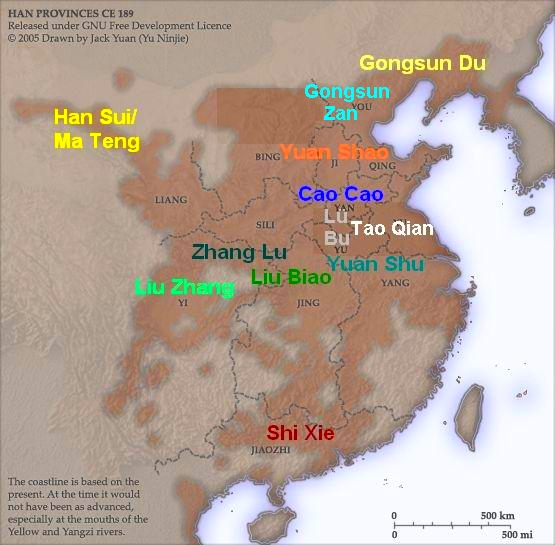
Three Kingdoms
In 221, during the partition following the fall of the Eastern Han – the era of the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and wa ...
– Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative of the H ...
founded the southwest kingdom of Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was one of the three major states that compet ...
(; 221–263) in parts of Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan, with Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
as its capital. Shu-Han claimed to be the successor to the Han dynasty.conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
the Kingdom of Shu-Han as a step on the path to reuniting China. Salt production becomes a major business in Ziliujing District
Ziliujing District, formerly romanized as Tzuliutsing, is a district of Zigong in Sichuan Province, China. The district covers and had a population of 330,000 people in 2005.
History
According to Fang, China has always managed salt and iron, w ...
. During the Six Dynasties period of Chinese disunity, Sichuan began to be populated by non- Han ethnic minority peoples, owing to the migration of Gelao people
The Gelao people (also spelled Gelo) ( Gelao: ''Klau'', ) are an ethnic group of China and Vietnam. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. However, many Gelao are also variously classified ...
from the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the Sichuan basin.
Tang dynasty
Sichuan came under the firm control of a Chinese central government during the Sui dynasty, but it was during the subsequent Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
that Sichuan regained its previous political and cultural prominence for which it was known during the Han. Chengdu became nationally known as a supplier of armies and the home of Du Fu, who is sometimes called China's greatest poet. During the An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general off ...
(755–763), Emperor Xuanzong of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was the seventh emperor of the Tang dynasty in China, reigning from 712 to 756 CE. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. In the ear ...
fled from Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
to Sichuan which became his refuge. The region was torn by constant warfare and economic distress as it was besieged by the Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (, ; ) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of imperial expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. The empire further expanded under the ...
.
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms
In the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, Sichuan became the centre of the Shu kingdom with its capital in Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
founded by Wang Jian. In 925 the kingdom was absorbed into Later Tang but would regain independence under Meng Zhixiang who founded Later Shu in 934. Later Shu would continue until 965 when it was absorbed by the Song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetiti ...
.
Song dynasty
During the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
(960–1279), Sichuanese Sichuanese, Szechuanese or Szechwanese may refer to something of, from, or related to the Chinese province and region of Sichuan (Szechwan/Szechuan) (historically and culturally including Chongqing), especially:
*Sichuanese people, a subgroup of the ...
was able to protect themselves from Tibetan attacks with the help of the central government. There were rebellions against the Song by Li Shun in 994 and Wang Jun in 1000. Sichuan also saw cultural revivals like the great poets Su Xun
Su Xun (; 22 May 1009 – 21 May 1066) was a Chinese writer during the Song dynasty, best known for his essays. He is considered one of the Eight Masters of the Tang and Song, along with his sons Su Shi and Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), ...
(), Su Shi
Su Shi (; 8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), courtesy name Zizhan (), art name Dongpo (), was a Chinese calligrapher, essayist, gastronomer, pharmacologist, poet, politician, and travel writer during the Song dynasty. A major personality of t ...
, and Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), or Su Che, courtesy names Ziyou and Tongshu , was a Chinese essayist, historian, poet, and politician from Meishan, located in modern-day Sichuan Province, China.
Su was highly honored as a politician and essayist in ...
.Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
.
It was also during the Song dynasty that the bulk of the native Ba people
Ba () was an ancient state in eastern Sichuan, China. Its original capital was Yicheng (Enshi City), Hubei. Ba was conquered by Qin in 316 BC. The historical Bo people and the modern Tujia people trace some of their origins back to the people of ...
of eastern Sichuan assimilated into the Han Chinese ethnicity.
In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Southern Song dynasty established coordinated defenses against the Mongolian Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongols, Mongol-led Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the M ...
, in Sichuan and Xiangyang. The Southern Song state monopolized the Sichuan tea industry to pay for warhorses, but this state intervention eventually brought devastation to the local economy. The line of defense was finally broken through after the first use of firearms in history during the six-year Battle of Xiangyang, which ended in 1273. Allegedly there were a million pieces of unspecified types of skeleton bones belonging to war animals and both Song and Yuan soldiers who perished in the fighting over the city, although the figure may have been grossly exaggerated. The recorded number of families in Sichuan dropped from 2,640,000 families, as recorded from the census taken in 1162 AD, to 120,000 families in 1282 AD. Possible causes include forced population transfer to nearby areas, evacuation to nearby provinces, census under-reporting or inaccuracy, and war-related deaths.
One instance of the deportation of Sichuanese civilians to Mongolia occurred in the aftermath of a battle in 1259 when more than 80,000 people were taken captive from one city in Sichuan and moved to Mongolia.
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty defeated Ming Yuzhen's Xia polity which ruled Sichuan.Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, major architectural works were created in Sichuan. Buddhism remained influential in the region. Bao'en Temple is a well-preserved 15th-century monastery complex built between 1440 and 1446 during the Zhengtong Emperor's reign (1427–64). Dabei Hall enshrines a thousand-armed wooden image of Guanyin and Huayan Hall is a repository with a revolving sutra
''Sutra'' ( sa, सूत्र, translit=sūtra, translit-std=IAST, translation=string, thread)Monier Williams, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Oxford University Press, Entry fo''sutra'' page 1241 in Indian literary traditions refers to an a ...
cabinet. The wall paintings, sculptures, and other ornamental details are masterpieces of the Ming period.
Qing dynasty
Sichuan was originally the origin of the Deng lineage until one of them was hired as an official in Guangdong during the Ming dynasty but during the Qing plan to increase the population in 1671 they came to Sichuan again. Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping (22 August 1904 – 19 February 1997) was a Chinese revolutionary leader, military commander and statesman who served as the paramount leader of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) from December 1978 to November 1989. Aft ...
was born in Sichuan.Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, Sichuan was merged with Shaanxi and Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-lev ...
to create "Shenzhuan" during 1680–1731 and 1735–1748.Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
) were established in the early 18th century. In the aftermath of the Sino-Nepalese War on China's southwestern border, the Qing gave Sichuan's provincial government direct control over the minority-inhabited areas of Sichuan west of Kangding, which had previously been handled by an amban.
Republic of China
 In the early 20th century, the newly founded
In the early 20th century, the newly founded Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northea ...
established the Chuanbian Special Administrative District () on the province's territories to the west of the Sichuan Basin. The Special District later became the province of Xikang, incorporating the areas inhabited by Yi, Tibetan, and Qiang ethnic minorities to its west, and eastern part of today's Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of ...
.
In the 20th century, as Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
, Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
, and Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the ninth-most populous Chinese city a ...
had all been occupied by the Japanese during the Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Thea ...
, the capital of the Republic of China had been temporarily relocated to Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
, then a major city in Sichuan. An enduring legacy of this move is those nearby inland provinces, such as Shaanxi, Gansu, and Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to t ...
, which previously never had modern Western-style universities, began to be developed in this regard. The difficulty of accessing the region overland from the eastern part of China and the foggy climate hindering the accuracy of the Japanese bombing of the Sichuan Basin made the region the stronghold of Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
's Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Tai ...
government during 1938–45 and led to the Bombing of Chongqing.
The Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Thea ...
was soon followed by the resumed Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was fought between the Kuomintang-led government of the Republic of China and forces of the Chinese Communist Party, continuing intermittently since 1 August 1927 until 7 December 1949 with a Communist victory on main ...
, and the cities of East China are obtained by the Communists one after another, the Kuomintang government again tried to make Sichuan its stronghold on the mainland, although it already saw some Communist activity since it was one area on the road of the Long March
The Long March (, lit. ''Long Expedition'') was a military retreat undertaken by the Red Army of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the forerunner of the People's Liberation Army, to evade the pursuit of the National Army of the Chinese Nati ...
. Chiang Kai-shek himself flew to Chongqing from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
in November 1949 to lead the defense. But the same month Chongqing switched to the Communists, followed by Chengdu on 10 December. The Kuomintang general Wang Sheng wanted to stay behind with his troops to continue the anticommunist guerilla war in Sichuan, but was recalled to Taiwan. Many of his soldiers made their way there as well, via Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
.
People's Republic of China
The People's Republic of China was founded in 1949, and it split Sichuan into four areas and separated Chongqing municipality. Sichuan was reconstituted in 1952, with Chongqing added in 1954, while the former Xikang province was split between Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
in the west and Sichuan in the east.Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping (22 August 1904 – 19 February 1997) was a Chinese revolutionary leader, military commander and statesman who served as the paramount leader of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) from December 1978 to November 1989. Aft ...
took power, Sichuan was one of the first provinces to experiment with the market economic enterprise.
From 1955 until 1997 Sichuan had been China's most populous province, hitting the 100 million mark shortly after the 1982 census figure of 99,730,000. This changed in 1997 when the Sub-provincial city
A sub-provincial division () in China is a prefecture-level city governed by a province promoted by half a level. Thus, it is half a level under the provincial level (hence the name sub-provincial) but half a level above the prefecture-level.
...
of Chongqing as well as the three surrounding prefectures of Fuling, Wanxian, and Qianjiang were split off into the new Chongqing Municipality. The new municipality was formed to spearhead China's effort to economically develop its western provinces, as well as to coordinate the resettlement of residents from the reservoir areas of the Three Gorges Dam project.
In 1997 when Sichuan split, the sum of the two parts was recorded to be 114,720,000 people. As of 2010, Sichuan ranks as both the 3rd largest (the largest among Chinese provinces with a population greater than 50 million) and 4th most populous province in China.[, and ]
Administrative divisions
Sichuan consists of twenty-one prefecture-level divisions: eighteen prefecture-level cities
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
During the Republican era, many of China' ...
(including a sub-provincial city
A sub-provincial division () in China is a prefecture-level city governed by a province promoted by half a level. Thus, it is half a level under the provincial level (hence the name sub-provincial) but half a level above the prefecture-level.
...
) and three autonomous prefectures:
The twenty prefectures of Sichuan are subdivided into 183 county-level division
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, ther ...
s (53 district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
s, 17 county-level cities, 109 counties, and 4 autonomous counties). At the end of the year 2017, the total population is 83.02 million.
Urban areas
Geography and biodiversity
Sichuan consists of two geographically very distinct parts. The eastern part of the province is mostly within the fertile Sichuan basin (which is shared by Sichuan with Chongqing Municipality). The western Sichuan consists of numerous mountain ranges forming the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau, which are known generically as the Hengduan Mountains. One of these ranges, the Daxue Mountains, contains the highest point of the province Gongga Shan
Mount Gongga (), also known as Minya Konka (Khams Tibetan pinyin: ''Mi'nyâg Gong'ga Riwo'') and colloquially as "The King of Sichuan Mountains", is the highest mountain in Sichuan province, China. It has an elevation of above sea level. This m ...
, at above sea level. The mountains are formed by the collision of the Tibetan Plateau with the Yangtze Plate. Faults here include the Longmenshan Fault which ruptured during the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. Other mountain ranges surround the Sichuan Basin from north, east, and south. Among them are the Daba Mountains, in the province's northeast.
The Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
and its tributaries flow through the mountains of western Sichuan and the Sichuan Basin; thus, the province is upstream of the great cities that stand along the Yangtze River further to the east, such as Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
, Wuhan
Wuhan (, ; ; ) is the capital of Hubei Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the largest city in Hubei and the most populous city in Central China, with a population of over eleven million, the ninth-most populous Chinese city a ...
, Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
, and Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
. One of the major tributaries of the Yangtze within the province is the Min River of central Sichuan, which joins the Yangtze at Yibin. There are also a number of other rivers, such as the Jialing River, Tuo River, Yalong River, Wu River, and Jinsha River, and any four of the various rivers are often grouped as the "four rivers" that the name of Sichuan is commonly and mistakenly believed to mean.monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
al influences, with rainfall heavily concentrated in the summer. Under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, the Sichuan Basin (including Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
) in the eastern half of the province experiences a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cwa'' or ''Cfa''), with long, hot, wet summers and short, mild to cool, dry, and cloudy winters. Consequently, it has China's lowest sunshine totals. The western region has mountainous areas producing a cooler but sunnier climate. Having cool to very cold winters and mild summers, temperatures generally decrease with greater elevation. However, due to its high altitude and its inland location, many areas such as Garze County and Zoige County in Sichuan exhibit a subarctic climate ( Köppen ''Dwc'')- featuring extremely cold winters down to −30 °C and even cold summer nights. The region is geologically active with landslides and earthquakes. Average elevation ranges from 2,000 to 3,500 meters; average temperatures range from 0 to 15 °C.Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
to the east, Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to t ...
to the southeast, Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of ...
to the west.
File:Larix potaninii trees Huluhai.jpg, ''Larix potaninii
''Larix potaninii'' is a species of larch conifer in the family Pinaceae. It is found in China and Nepal. The one of southernmost species of the genus ''Larix'', the range of ''Larix potaninii'' extends southward almost to 27° N.
Varieties
, ...
'' in autumn colour.
File:1 Seda facing south.jpg, Garzê Prefecture
File:Zitong-sichuan-china.jpg, Zitong County
File:A Typical Linpan unit in Pi County.jpg, Linpan in Chengdu Plain is a well-known landmark in Chengdu Plain, Sichuan.
Giant panda

Giant panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear (or simply the panda), is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its bold black-and-white coat and rotund body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes u ...
s live in bamboo forests and low mountainous areas such as the Minshan Mountains in Sichuan. The majority of the panda population lives in Sichuan, with their range spreading into Shaanxi and Gansu. As it is abundant where they live, pandas' diet consists of 99% bamboo, with small other plants, or small animals consisting of the other 1%. As the panda is native to China, they have become a national symbol of China.
Politics
The politics of Sichuan is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater Chin ...
.
The governor of Sichuan is the highest-ranking official in the People's Government of Sichuan. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor has less power than the Sichuan Communist Party of China's Party Committee Secretary, colloquially termed the "Sichuan CPC Party Chief".
Economy

 Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in Western China and the second largest among inland provinces after
Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in Western China and the second largest among inland provinces after Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
. As of 2021, its nominal GDP was 5,385 billion yuan (US$847.68 billion), ahead of the GDP of Turkey of 815 billion.disposable income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current income taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major ...
of the urbanites averaged 41,444 yuan (US$6510).
Sichuan has been historically known as the "Province of Abundance". It is one of the major agricultural production bases of China. Grain, including rice and wheat, is the major product with output that ranked first in China in 1999. Commercial crops include citrus fruits, sugar cane, sweet potatoes, peaches, and grapes. Sichuan also had the largest output of pork among all the provinces and the second largest output of silkworm cocoons in 1999. Sichuan is rich in mineral resources. It has more than 132 kinds of proven underground mineral resources including vanadium, titanium, and lithium is the largest in China. The Panxi region alone possesses 13.3% of the reserves of iron, 93% of titanium, 69% of vanadium, and 83% of cobalt in the whole country. Sichuan also possesses China's largest proven natural gas reserves, the majority of which are transported to more developed eastern regions.Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
and Mianyang are the production centers for textiles and electronics products. Deyang, Panzhihua, and Yibin are the production centers for machinery, metallurgical industries, and wine, respectively. Sichuan's wine production accounted for 21.9% of the country's total production in 2000.
Great strides have been made in developing Sichuan into a modern hi-tech industrial base, by encouraging both domestic and foreign investments in electronics and information technology (such as software), machinery and metallurgy (including automobiles), hydropower, pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries.
The auto industry is an important and key sector of the machinery industry in Sichuan. Most of the auto manufacturing companies are located in Chengdu, Mianyang, Nanchong, and Luzhou.
Other important industries in Sichuan include aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astrona ...
and defense (military) industries. A number of China's rockets ( Long March rockets) and satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
s were launched from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, located in the city of Xichang.
Sichuan's landscapes and rich historical relics have also made the province a center for tourism.
The Three Gorges Dam, the largest dam ever constructed, was built on the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
in nearby Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The pr ...
province to control flooding in the Sichuan Basin, neighboring Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked province in the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the ...
province, and downstream. The plan is hailed by some as China's efforts to shift towards alternative energy sources and to further develop its industrial and commercial bases, but others have criticised it for its potentially harmful effects, such as massive resettlement of residents in the reservoir areas, loss of archeological sites, and ecological damages.
Minimum wage
Starting in 2021, the minimum wage in Sichuan Province will be 2,100 yuan ($330).
Economic development zones
Chengdu Hi-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone
Chengdu Hi-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone was established with the approval of the State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative autho ...
on October 18, 2010, and passed the national acceptance on February 25, 2011. It was officially operated in May 2011. Chengdu High-tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone is integrated and expanded from the former Chengdu Export Processing Zone and Chengdu Bonded Logistics Center. it is located in the Chengdu West High-tech Industrial Development Zone, with an area of 4.68 square kilometers and divided into three areas A, B, and C. The industries focus on notebook computer manufacturing, tablet computer manufacturing, wafer manufacturing, chip packaging testing, electronic components, precision machining, and the biopharmaceutical industry. Chengdu Hi-Tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone has attracted the top 500 multinational enterprises such as Intel, Foxconn, Texas Instruments, Dell, Morse, and so on.
In 2020, the Chengdu Hi-Tech Comprehensive Free Trade Zone achieved a total import and export volume of 549.1 billion yuan (including the Shuangliu Sub-zone), accounting for 68% of the province's total foreign trade import and export volume, ranking first in the national comprehensive insurance zone import and export volume for three consecutive years.
Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone
Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone () was approved as state-level development zone in February 2000. The zone now has a developed area of and a planned area of . Chengdu Economic and Technological Development Zone (CETDZ) lies east of Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan Province and the hub of transportation and communication in southwest China. The zone has attracted investors and developers from more than 20 countries to carry out their projects there. Industries encouraged in the zone include mechanical, electronic, new building materials, medicine, and food processing.
Chengdu Export Processing Zone
Chengdu Export Processing Zone ()) was ratified by the State Council as one of the first 15 export processing zones in the country in April 2000. In 2002, the state ratified the establishment of the Sichuan Chengdu Export Processing West Zone with a planned area of , located inside the west region of the Chengdu Hi-tech Zone.
Chengdu Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
 Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Mianyang Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
Mianyang Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone was established in 1992, with a planned area of . The zone is situated 96 kilometers away from Chengdu and is away from Mianyang Airport. Since its establishment, the zone accumulated 177.4 billion yuan of industrial output, 46.2 billion yuan of gross domestic product, and fiscal revenue of 6.768 billion yuan. There are more than 136 high-tech enterprises in the zone and they accounted for more than 90% of the total industrial output.
The zone is a leader in the electronic information industry, biological medicine, new materials, and the production of motor vehicles and parts.
Transportation
 For millennia, Sichuan's rugged and riverine landscape presented enormous challenges to the development of transportation infrastructure, and the lack of roads out of the Sichuan Basin contributed to the region's isolation. Since the 1950s, numerous highways and railways have been built through the Qinling in the north and the Bashan in the east. Dozens of bridges across the Yangtze and its tributaries to the south and west have brought greater connectivity with Yunnan and Tibet.
For millennia, Sichuan's rugged and riverine landscape presented enormous challenges to the development of transportation infrastructure, and the lack of roads out of the Sichuan Basin contributed to the region's isolation. Since the 1950s, numerous highways and railways have been built through the Qinling in the north and the Bashan in the east. Dozens of bridges across the Yangtze and its tributaries to the south and west have brought greater connectivity with Yunnan and Tibet.
Airports
Chengdu Shuangliu International Airport is the 4th-busiest airport in mainland China. It was among the world's top 30 busiest airports in 2015, and the busiest in western and central China. It was also the fifth-busiest airport in terms of cargo traffic in China in 2013. Chengdu airport is the hub of Sichuan Airlines, Chengdu Airlines, Shenzhen Airlines, Tibet Airlines, China Southern Airlines
China Southern Airlines Company Limited is an airline headquartered in Baiyun District, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province and is the largest airline in China. Established on 1 July 1988 following the restructuring of the CAAC Airlines that acq ...
, China Eastern Airlines
China Eastern Airlines Corporation Limited (), also known as China Eastern, is an airline headquartered in the China Eastern Airlines Building, on the grounds of Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport in Changning District, Shanghai. It is ...
, Lucky Air, and Air China
Air China Limited () is the flag carrier of the People's Republic of China and one of the "Big Three" mainland Chinese airlines (alongside China Southern Airlines and China Eastern Airlines). Air China's headquarters are in Shunyi District, ...
. Alongside Shuangliu Airport, Chengdu Tianfu International Airport has opened in 2021.
Chengdu airports are also 144-hour transit visa-free airports for foreigners from 51 countries including Albania, Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Brunei, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, Mexico, Republic of Montenegro, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, and United States.
Expressways
On 3 November 2007, the Sichuan Transportation Bureau announced that the Suining-Chongqing Expressway was completed after three years of construction. After the completion of the Chongqing section of the road, the expressway connected Chengdu-Nanchong Expressway and formed the shortest expressway from Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
to Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
. The new expressway is shorter than the pre-existing road between Chengdu and Chongqing; thus journey time between the two cities was reduced by an hour, now taking two and a half hours. The Sui-Yu Expressway is a four-lane overpass with a speed limit of . The total investment was 1.045 billion yuan.
Rail
China Railway Chengdu Group is headquartered in Chengdu, the capital of Sichuan Province, managing railway systems in Sichuan, Chongqing, and Guizhou. Sichuan's major railways in Sichuan include the Baoji–Chengdu, Chengdu–Chongqing, Chengdu–Kunming, Neijiang–Kunming, Suining–Chongqing, and Chengdu–Dazhou railways. High-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, line ...
ways in Sichuan include the Chengdu–Chongqing high-speed railway, Xi'an-Chengdu high-speed railway, Chengdu-Guiyang high-speed railway, and Chengdu–Kunming high-speed railway. A suburban railway connects Chengdu and Dujiangyan.
Demographics
 The majority of the province's population is
The majority of the province's population is Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive v ...
(95% of the provincial population), who are found scattered throughout the region except for the far western areas. Thus, significant minorities of Tibetan, Yi, Qiang, and Nakhi people
The Nakhi or Nashi (; Naxi: ; lit.: "Black people") are an East Asian ethnic group inhabiting the foothills of the Himalayas in the northwestern part of Yunnan Province, as well as the southwestern part of Sichuan Province in China.
The Nakh ...
reside in the western portion that is impacted by inclement weather and natural disasters, environmentally fragile, and impoverished. Sichuan's capital of Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
is home to a large community of Tibetans, with 30,000 permanent Tibetan residents and up to 200,000 Tibetan floating population. The Eastern Lipo, included with either the Yi or the Lisu people
The Lisu people ( Lisu: ; my, လီဆူလူမျိုး, ; ; th, ลีสู่) are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group who inhabit mountainous regions of Myanmar (Burma), southwest China, Thailand, and the Indian state of Arunachal Pr ...
, as well as the A-Hmao, also are among the ethnic groups of the provinces.
Sichuan was China's most populous province before Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
became a directly controlled municipality; it is currently the fourth most populous, after Guangdong, Shandong, and Henan. As of 1832, Sichuan was the most populous of the 18 provinces in China, with an estimated population at that time of 21 million.Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
until 1991, when the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
was dissolved. It is also one of the only eight subnational divisions to ever reach 100 million people (Uttar Pradesh, Russian RSFSR, Maharashtra, Sichuan, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
, Shandong, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
, and Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
). It is currently ranked 10th.
Religion
The predominant religions in Sichuan are Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be fill ...
s, Taoist traditions, and Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy ...
. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 10.6% of the population believes and is involved in cults of ancestors, while 0.68% of the population identifies as Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
.Yiguandao
Yiguandao / I-Kuan Tao (),; ko, 일관도, Ilgwando; th, อนุตตรธรรม, . meaning the Consistent Way or Persistent Way, is a Chinese salvationist religious sect that emerged in the late 19th century, in Shandong, to become ...
(Tiandao) in Sichuan, equal to 2.4% of the province's population.[
The reports didn't give figures for other types of religion; the vast majority of the population may be either irreligious or involved in the worship of nature deities, Buddhism, ]Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
, Taoism, folk religious sects, and small minorities of Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
. Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in maj ...
is widespread, especially in areas inhabited by ethnic Tibetans. Sichuan is one of the cradles of the early Heavenly Masters' Taoist religious movements.
File:Huanglong Sichuan China Multicolored-ponds-04.jpg, View of the Temple of the Yellow Dragon (Chinese Buddhism) in Huanglong.
File:Litang8.jpg, Statues of buddhas at Litang Monastery of the Tibetan tradition.
File:Main altar before Shangqing Temple on Qingchengshan, in Chengdu, Sichuan.jpg, A pavilion of the Shangqing Temple (Taoist) in Qingchengshan, Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
.
File:China - Mount Emei - EmeiShan - Sichuan 11.jpg, Golden Temple of Mount Emei
Mount Emei (; ), alternately Mount Omei, is a mountain in Sichuan Province, China, and is the highest of the Four Sacred Buddhist Mountains of China. Mount Emei sits at the western rim of the Sichuan Basin. The mountains west of it are k ...
(Chinese Buddhism).
File:巴巴寺.JPG, , a Chinese Sufi mosque in Langzhong.
File:Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception, Chengdu.png, Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception, Chengdu (Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
)
File:St John's Cathedral, Paoning.jpg, St John's Cathedral, Langzhong ( Anglican)
Culture
 The ''Sichuanese people'' (
The ''Sichuanese people'' (Sichuanese Sichuanese, Szechuanese or Szechwanese may refer to something of, from, or related to the Chinese province and region of Sichuan (Szechwan/Szechuan) (historically and culturally including Chongqing), especially:
*Sichuanese people, a subgroup of the ...
: Ba1su2ren2; IPA
IPA commonly refers to:
* India pale ale, a style of beer
* International Phonetic Alphabet, a system of phonetic notation
* Isopropyl alcohol, a chemical compound
IPA may also refer to:
Organizations International
* Insolvency Practitioner ...
: ; alternatively , , or ) are a subgroup of Han Chinese living in mostly Sichuan province and the neighboring Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
municipality. Beginning from the 9th century BC, Shu (on the Chengdu Plain) and Ba (which had its first capital at Enshi City in Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The pr ...
and controlled part of the Han Valley) emerged as cultural and administrative centers where two rival kingdoms were established. Although eventually, the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
destroyed the kingdoms of Shu and Ba, the Qin government accelerated the technological and agricultural advancements of Sichuan making it comparable to that of the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan ...
Valley. The now-extinct Ba-Shu language was derived from Qin-era settlers and represents the earliest documented division from what is now called Middle Chinese.
During the Yuan and Ming dynasties, the population of the area was reduced through wars and the bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as ...
, and settlers arrived from the area of modern Hubei, replacing the earlier common Chinese with a new standard.
The Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
Memorial, located in Jiangyou, is a museum in memory of Li Bai, a Chinese poet of Tang China (618–907) built at the place where he grew up. The building was begun in 1962 on the occasion of the 1200th anniversary of his death, completed in 1981, and opened to the public in October 1982. The memorial is built in the style of the classic Tang garden.
In 2003, Sichuan had "88 art performing troupes, 185 culture centers, 133 libraries, and 52 museums". Companies based in Sichuan also produced 23 television series and one film.
Languages
 The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the
The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
.
The most widely used variety of Chinese spoken in Sichuan is Sichuanese Sichuanese, Szechuanese or Szechwanese may refer to something of, from, or related to the Chinese province and region of Sichuan (Szechwan/Szechuan) (historically and culturally including Chongqing), especially:
*Sichuanese people, a subgroup of the ...
, which is the lingua franca in Sichuan, Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
, and parts of the Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of ...
. Although Sichuanese is generally classified as a dialect of Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
, it is highly divergent in phonology, vocabulary, and even grammar from Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standa ...
.Tibetans
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans ...
and Qiang people
The Qiang people ( Qiangic: ''Rrmea''; ) are an ethnic group in China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised by the People's Republic of China, with a population of approximately 310,000 in 2000. They live mainly in a ...
. Tibetans speak the Khams and Amdo Tibetan
Amdo Tibetan (; also called ''Am kä'') is the Tibetic language spoken in Amdo (now mostly in Qinghai, some in Ngawa and Gannan). It has two dialects, the farmer dialect and the nomad dialect.
Amdo is one of the three branches of traditional ...
, which are Tibetic languages
The Tibetic languages form a well-defined group of languages descended from Old Tibetan (7th to 9th centuries).Tournadre, Nicolas. 2014. "The Tibetic languages and their classification." In ''Trans-Himalayan linguistics, historical and descriptiv ...
, as well as various Qiangic languages. The Qiang speak Qiangic languages and often Tibetic languages as well. The Yi people
The Yi or Nuosu people,; zh, c=彝族, p=Yízú, l=Yi ethnicity historically known as the Lolo,; vi, Lô Lô; th, โล-โล, Lo-Lo are an ethnic group in China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Numbering nine million people, they are the sev ...
of Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture in southern Sichuan speak the Nuosu language, which is one of the Lolo-Burmese languages
The Lolo-Burmese languages (also Burmic languages) of Burma and Southern China form a coherent branch of the Sino-Tibetan family.
Names
Until ca. 1950, the endonym ''Lolo'' was written with derogatory characters in Chinese, and for this reas ...
; Yi is written using the Yi script, a syllabary standardized in 1974. The Southwest University for Nationalities has one of China's most prominent Tibetology departments and the Southwest Minorities Publishing House prints literature in minority languages. In the minority-inhabited regions of Sichuan, there is bilingual signage and public school instruction in non-Mandarin minority languages.
Cuisine
Sichuan is well known for its spicy cuisine and use of Sichuan peppers due to its humid climate.
The Sichuanese are proud of their cuisine, known as one of the Four Great Traditions of Chinese cuisine. The cuisine here is of "one dish, one shape, hundreds of dishes, hundreds of tastes", as the saying goes, to describe its acclaimed diversity. The most prominent traits of Sichuanese cuisine are described by four words: spicy, hot, fresh, and fragrant. Sichuan cuisine is popular in the whole nation of China, and so are Sichuan chefs. Two well-known Sichuan chefs are Chen Kenmin and his son Chen Kenichi
, whose name is often romanized Chin Kenichi in Japanese sources, is a chef best known for his role as the Iron Chef Chinese on the television series '' Iron Chef'' (料理の鉄人). Nicknamed The Szechuan Sage, he wears a yellow outfit and ri ...
, who was Iron Chef Chinese on the Japanese television series " Iron Chef".
Another famous Sichuan cuisine is hotpot. Hot pot is a Chinese soup containing a variety of East Asian foodstuffs and ingredients, prepared with a simmering pot of soup stock at the dining table. While the hot pot is kept simmering, ingredients are placed into the pot and cooked at the table. Typical hot pot dishes include thinly sliced meat, leaf vegetables, mushrooms, wontons, egg dumplings, tofu, and seafood. The cooked food is usually eaten with a dipping sauce.
File:Kung-pao-shanghai.jpg, Kung Pao chicken, one of the best known dishes of Sichuan cuisine
File:Mapodoufu.jpg, Mapo doufu
File:担担面 Dandan noodles.jpg, Dandan noodles
File:Mixed sauce noodles.JPG, Zha Jiang Noodles ()
Education

Colleges and universities
As of 2022, Sichuan hosts 134 institutions of higher education, ranking first in the Western China region and fifth among all Chinese provinces after Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its c ...
, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
, Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
and Shandong.Sichuan University
Sichuan University (SCU) is a national key public research university in Chengdu, Sichuan, China. The university is wholly funded by the Ministry of Education.
SCU is one of the top universities of China, and a Class A Double First Class Univer ...
(Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
)
*Southwest Jiaotong University
Southwest Jiaotong University () is located in national central city Chengdu, Sichuan Province, affiliated to the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China. It's a national key university co-supported by the Ministry of Educatio ...
(Chengdu)
* University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (Chengdu)
* Southwestern University of Finance and Economics (Chengdu)
* Chengdu University of Technology (Chengdu)
* Chengdu University of Information Technology (Chengdu)
* Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Chengdu)
* Civil Aviation Flight University of China ( Guanghan)
* Southwest University for Nationalities (Chengdu)
* Sichuan Normal University (Chengdu)
* Sichuan Agricultural University ( Ya'an, Chengdu, Dujiangyan)
* Southwest Petroleum University ( Nanchong and Chengdu)
* Xihua University (Chengdu)
* Southwest University of Science and Technology ( Mianyang)
*China West Normal University
China West Normal University (CWNU; ) is a comprehensive normal university featuring teacher education and training in Nanchong, Sichuan, China.
The university was established in 1946. It now has 30,343 students.
History
China West Normal Univer ...
( Nanchong)
* North Sichuan Medical College (Nanchong)
*Panzhihua University (Panzhihua)
*Sichuan Police College ( Luzhou)
* Sichuan University of Science and Engineering ( Zigong and Yibin)
* Chengdu University (Chengdu)
*Xichang University ( Xichang)
*Aba Teachers University ( Ngawa Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture)
Tourism
File:Beauty of Jiuzhaigou National Park - Apr 2017.png, Jiuzhaigou
File:Yading - panoramio (1).jpg, Yading
File:1 huanglong pools aerial 2011.jpg, Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area
Huanglong () is a scenic and historic interest area in the northwest part of Sichuan, China. It is located in the southern part of the Minshan mountain range, north-northwest of the capital Chengdu. This area is known for its colorful travertin ...
File:QinChengHouShan WuLongGou.jpg, Waterfalls at Mount Qincheng
File:畢棚溝 Bipenggou Valley 1.jpg, Bipenggou Valley
File:四姑娘山景区 Mount Siguniang Scenic Area 45.jpg, Mount Siguniang Scenic Area
File:大冰瀑布-Q30023595.jpg, Hailuogou Glacier Forest Park
File:Dujiang Weir.jpg, Dujiangyan irrigation system
File:Mount Emei - Sunrise above the clouds.jpg, alt=, Mount Emei
Mount Emei (; ), alternately Mount Omei, is a mountain in Sichuan Province, China, and is the highest of the Four Sacred Buddhist Mountains of China. Mount Emei sits at the western rim of the Sichuan Basin. The mountains west of it are k ...
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
s in Sichuan province and Chongqing municipality include:
* Dazu Rock Carvings and Wulong Karst (Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a municipality in Southwest China. The official abbreviation of the city, "" (), was approved by the State Cou ...
municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality ...
)
*Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area
Huanglong () is a scenic and historic interest area in the northwest part of Sichuan, China. It is located in the southern part of the Minshan mountain range, north-northwest of the capital Chengdu. This area is known for its colorful travertin ...
* Jiuzhaigou Valley Scenic and Historic Interest Area
*Mount Emei
Mount Emei (; ), alternately Mount Omei, is a mountain in Sichuan Province, China, and is the highest of the Four Sacred Buddhist Mountains of China. Mount Emei sits at the western rim of the Sichuan Basin. The mountains west of it are k ...
Scenic Area, including Leshan Giant Buddha Scenic Area
* Mount Qincheng and the Dujiangyan Irrigation System
* Sichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries
As of July 2013, the world's largest building, the New Century Global Center is located in the city of Chengdu. At high, long, and wide, the Center houses retail outlets, a 14-theater cinema, offices, hotels, the Paradise Island waterpark, an artificial beach, a -long LED screen, skating rink, pirate ship, fake Mediterranean village, 24-hour artificial sun, and 15,000-spot parking area.
Notable individuals
*Bao Sanniang
Bao Sanniang is a possibly fictional character of the Three Kingdoms period of China. She appears primarily in Chinese opera and plays, and is usually portrayed as a brave woman warrior and as the wife of Guan Suo, a possibly fictitious son of ...
(), a possibly fictional woman warrior of the Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty and wa ...
period.
*Li Bai
Li Bai (, 701–762), also pronounced as Li Bo, courtesy name Taibai (), was a Chinese poet, acclaimed from his own time to the present as a brilliant and romantic figure who took traditional poetic forms to new heights. He and his friend Du F ...
(701–762), poet of the Tang dynasty
* Guifeng Zongmi (; 780–841), Tang dynasty Buddhist scholar-monk, fifth patriarch of the Huayan () school as well as a patriarch of the Heze lineage of Southern Chan
* Ouyang Xiu (1007–22 September 1072), Confucian historian, essayist, calligrapher, poet, and official bureaucrat of the Song dynasty
*Su Xun
Su Xun (; 22 May 1009 – 21 May 1066) was a Chinese writer during the Song dynasty, best known for his essays. He is considered one of the Eight Masters of the Tang and Song, along with his sons Su Shi and Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), ...
(), poet and prose-writer of the Song dynasty
*Su Shi
Su Shi (; 8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), courtesy name Zizhan (), art name Dongpo (), was a Chinese calligrapher, essayist, gastronomer, pharmacologist, poet, politician, and travel writer during the Song dynasty. A major personality of t ...
(8 January 1037 – 24 August 1101), Confucian bureaucrat official, poet, artist, calligrapher, pharmacologist, gastronome, and official bureaucrat of the Song dynasty
*Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), or Su Che, courtesy names Ziyou and Tongshu , was a Chinese essayist, historian, poet, and politician from Meishan, located in modern-day Sichuan Province, China.
Su was highly honored as a politician and essayist in ...
(1039–1112), poet and essayist, a Confucian bureaucratic official of the Song dynasty
* Ba Jin (25 November 1904 – 17 October 2005), novelist and writer
*Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping (22 August 1904 – 19 February 1997) was a Chinese revolutionary leader, military commander and statesman who served as the paramount leader of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) from December 1978 to November 1989. Aft ...
, Chinese Paramount Leader during the 1980s, his former residence is now a museum.
* Chen Kenmin (27 June 1912 – 12 May 1990), chef who specialized in Szechwan cuisine. Father of well-known Iron Chef, Chen Kenichi
, whose name is often romanized Chin Kenichi in Japanese sources, is a chef best known for his role as the Iron Chef Chinese on the television series '' Iron Chef'' (料理の鉄人). Nicknamed The Szechuan Sage, he wears a yellow outfit and ri ...
.
* Li Ching-Yuen (; died 6 May 1933), herbalist, martial artist and tactical advisor, also known for extreme longevity claims
*Che Yongli
Che Yongli (born 28 January 1980) is a Chinese actress.
She is noted for her roles as A Mei and Mei Ling in the films '' A Singing Fairy'' and '' All For Love'' respectively.
Life
Early life
Che was born and raised in Chengdu, Sichuan, she gra ...
(28 January 1980), actress
* Xu Yiyang (12 August 1997), singerChen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the ...
, official and writer
*Huang Jiguang
Huang Jiguang (; January 18, 1931 – October 19, 1952) was a highly-decorated Chinese soldier during the Korean War.
Biography
Huang was born in Sichuan Province, his mother is Deng Fangzhi and brother is Huang Jishu. In March 1951, Huang dec ...
, highly decorated soldier during the Korean War
* Zhao Yiman, resistance fighter
* Liu Yonghao, businessman
* GAI, rapper, singer, and songwriter
* Zhang Yong (restaurateur), Singapore's richest man in 2019
* Wang Jianlin, business magnate, investor, and philanthropist
* Jiang Zhuyun, revolutionary martyr
* Zhang Daqian, artists
*Wang Xiaoya
Wang Xiaoya (; born 22 January 1968) is a Chinese television host and media personality.
She won the Golden Mike Award in 2003.
Biography
Wang was born in Zhaojue County, Sichuan in January 1968, her father was an editor in ''Liangshan Daily'' ( ...
, television host and media personality
* Li Yifeng, actor and singer
* Li Yuchun, singer, songwriter, and actress
* Tan Weiwei, singer and actress
* Tang Chun-i, philosopher and scholar
* Luo Ruiqing, army officer and politician
* Zhuo Wenjun, poet
* Yang Xiong, poet, philosopher, and politician
* Zheng Ji, nutritionist, and pioneering biochemist
* Zhu De, general, warlord, politician, and revolutionary
* Zhang Lan, political activist
* Zou Rong, revolutionary martyr
*Guo Moruo
Guo Moruo (; November 16, 1892 – June 12, 1978), courtesy name Dingtang (), was a Chinese author, poet, historian, archaeologist, and government official.
Biography
Family history
Guo Moruo, originally named Guo Kaizhen, was born on November ...
, author, poet, historian, archaeologist, and government official
* Zhang Qun, premier of the Republic of China
* Bai Ling, actress
* Xu Youyu, scholar
* Cheung Chung-kiu, business magnate
* Song Yonghua, scholar
* Sanyu (painter)
* Zhang Aiping, from Tongchuan District, Dazhou City, Vice Premier, State Councilor, and Minister of Defense
* Zhang Liangying, singer and songwriter
* Akio Hong, broadcaster
Sports
Professional sports teams in Sichuan include:
* Chinese Basketball Association
** Sichuan Blue Whales
* China League Two
** Sichuan Jiuniu F.C.
* Chinese Volleyball League
** Sichuan Volleyball Team
* China Table Tennis Super League
**Sichuan Quan-Xing Table-Tennis Team
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
Sister states and regions
* Washington, United States (1982)
* Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, United States (1982)
* Hiroshima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Hiroshima Prefecture has a population of 2,811,410 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 8,479 km² (3,274 sq mi). Hiroshima Prefecture borders Okayama Prefecture to the ...
, Japan (1984)
* Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan (1985)
* South P'yŏngan
South Pyongan Province (Phyŏngannamdo; ) is a province of North Korea. The province was formed in 1896 from the southern half of the former Pyongan Province, remained a province of Korea until 1945, then became a province of North Korea. It ...
, North Korea (1985)
* Midi-Pyrénées, France (1987)
* North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhab ...
, Germany (1988)
* Leicestershire, United Kingdom (1988)
* Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, Italy (1990)
* Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the ...
, Brazil (1992)
* Tolna County
Tolna ( hu, Tolna megye, ; german: Komitat Tolnau) is an administrative county ( comitatus or megye) in present Hungary as it was of the former Kingdom of Hungary. It lies in central Hungary, on the west bank of the river Danube. It shares border ...
, Hungary (1993)
* Valencian Community
The Valencian Community ( ca-valencia, Comunitat Valenciana, es, Comunidad Valenciana) is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous comm ...
, Spain (1994)
* Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium (1995)
* Barinas State, Venezuela (2001)
* Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, Netherlands (2001)
* Almaty Province, Kazakhstan (2001)
* Mpumalanga
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. It ...
, South Africa (2002)
* Suphan Buri
Suphan Buri () is a town (''thesaban mueang'') in central Thailand. It covers ''tambon'' Tha Philiang and parts of ''tambons'' Rua Yai and Tha Rahat, all within the Mueang Suphan Buri District. As of 2006 it had a population of 26,656. The town ...
, Thailand (2010)
* Victoria, Australia (2015)
* Lavalleja, Uruguay (2020)
See also
* 2008 Sichuan earthquake
* Bashu culture
*'' Chronicles of Huayang''
*Eight Immortals from Sichuan
Eight Immortals from Sichuan ({{zh, c=蜀中八仙, p=Shǔ zhōng bāxiān) are eight Sichuanese who supposedly became '' xian'' ("immortals; transcendents; fairies"). The term is first used by Qiao Xiu (譙秀 qiáo xiù) in ''Record of Shu' ...
*''The Good Person of Szechwan
''The Good Person of Szechwan'' (german: Der gute Mensch von Sezuan, first translated less literally as ''The Good Man of Setzuan'') is a play written by the German dramatist Bertolt Brecht, in collaboration with Margarete Steffin and Ruth Ber ...
''
* List of prisons in Sichuan
* Major national historical and cultural sites (Sichuan)
* Qutang Gorge
* Sichuan Airlines
* Sichuan cuisine
* Sichuan dialect
* Sichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries
Notes
References
External links
*
Economic profile for Sichuan
at HKTDC
The Hong Kong Trade Development Council (HKTDC) is a statutory body established in 1966 as the international marketing dedicated to creating opportunities for Hong Kong's businesses. The organisation has 50 offices around the world, including ...
Ancient silver coins of Sichuan
*
{{Authority control
Provinces of the People's Republic of China
Western China
 Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. Following the declining central government of the
Sichuan was subjected to the autonomous control of kings named by the imperial family of the Han dynasty. Following the declining central government of the 
 In the early 20th century, the newly founded
In the early 20th century, the newly founded 


 Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in Western China and the second largest among inland provinces after
Sichuan is the 6th-largest provincial economy of China, the largest in Western China and the second largest among inland provinces after  Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
Established in 1988, Chengdu Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone () was approved as one of the first national hi-tech development zones in 1991. In 2000, it was open to APEC and has been recognized as a national advanced hi-tech development zone in successive assessment activities held by China's Ministry of Science and Technology. It ranks 5th among the 53 national hi-tech development zones in China in terms of comprehensive strength.
Chengdu Hi-tech Development Zone covers an area of , consisting of South Park and West Park. By relying on the city sub-center, which is under construction, South Park is focusing on creating a modernized industrial park of science and technology with scientific and technological innovation, incubation R&D, modern service industry, and Headquarters economy playing leading roles. Priority has been given to the development of the software industry. Located on both sides of the "Chengdu-Dujiangyan-Jiuzhaigou" golden tourism channel, the West Park aims at building a comprehensive industrial park targeting industrial clustering with complete supportive functions. West Park gives priority to three major industries i.e. electronic information, biomedicine, and precision machinery.
 For millennia, Sichuan's rugged and riverine landscape presented enormous challenges to the development of transportation infrastructure, and the lack of roads out of the Sichuan Basin contributed to the region's isolation. Since the 1950s, numerous highways and railways have been built through the Qinling in the north and the Bashan in the east. Dozens of bridges across the Yangtze and its tributaries to the south and west have brought greater connectivity with Yunnan and Tibet.
For millennia, Sichuan's rugged and riverine landscape presented enormous challenges to the development of transportation infrastructure, and the lack of roads out of the Sichuan Basin contributed to the region's isolation. Since the 1950s, numerous highways and railways have been built through the Qinling in the north and the Bashan in the east. Dozens of bridges across the Yangtze and its tributaries to the south and west have brought greater connectivity with Yunnan and Tibet.
 The ''Sichuanese people'' (
The ''Sichuanese people'' ( The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the
The Sichuanese once spoke their variety of Spoken Chinese called Ba-Shu Chinese, or Old Sichuanese before it became extinct during the Ming dynasty. Now most of them speak Sichuanese Mandarin. The Minjiang dialects are thought by some linguists to be a bona fide descendant of Old Sichuanese, but there is no conclusive evidence whether Minjiang dialects are derived from Old Sichuanese or Southwestern Mandarin.
The languages of Sichuan are primarily members of three subfamilies of the 