|
Su Zhe
Su Zhe (; 1039–1112), or Su Che, courtesy names Ziyou and Tongshu , was a Chinese essayist, historian, poet, and politician from Meishan, located in modern-day Sichuan Province, China. Su was highly honored as a politician and essayist in the Song Dynasty, as were his father Su Xun and his elder brother Su Shi. All of them were among " The Eight Great Men of Letters of the Tang and Song Dynasties". Sansu temple where they lived was rebuilt into Sansu Museum in 1984, and this building has been one of the most famous cultural attractions. Su Zhe left many fine works and most of them have been widely read. Su died in 1112, at the age of 74. Life Su Zhe was born on 20 February 1039 in Meishan, which now belongs to Sichuan Province. At the age of 18, he and his brother Su Shi passed the highest level civil service examination to attain the degree of jinshi, a prerequisite of high government office. In 1070, Su Zhe wrote a letter to the emperor to point out that it was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su (surname)
Su is the pinyin romanization of the common Chinese surname written in simplified characters and traditionally. It was listed 42nd among the Song-era list of the ''Hundred Family Surnames''. In 2019 it was the 46th most common surname in mainland China. Romanizations The Wade form of the name is identical to the pinyin, but it is also sometimes irregularly romanized as Soo. and are also romanized So and Sou in Cantonese; Soh and Souw in Southern Min dialects; Soh in Teochew; and Thu in Gan. This Chinese name is also the source of the Vietnamese surname Tô (Chữ Nôm: ); the Korean surname , which is romanized So; the Japanese surname , which is also romanized So; and the Filipino/Tagalog surname So. Also, the Filipino family name "Solon" is a Hispanicized version of So. The Solon clan coming from Cebu are famous for their ancestors who were government officials. The Solons were originally from Canton. Distribution Su was the 41st-most-common Chinese surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
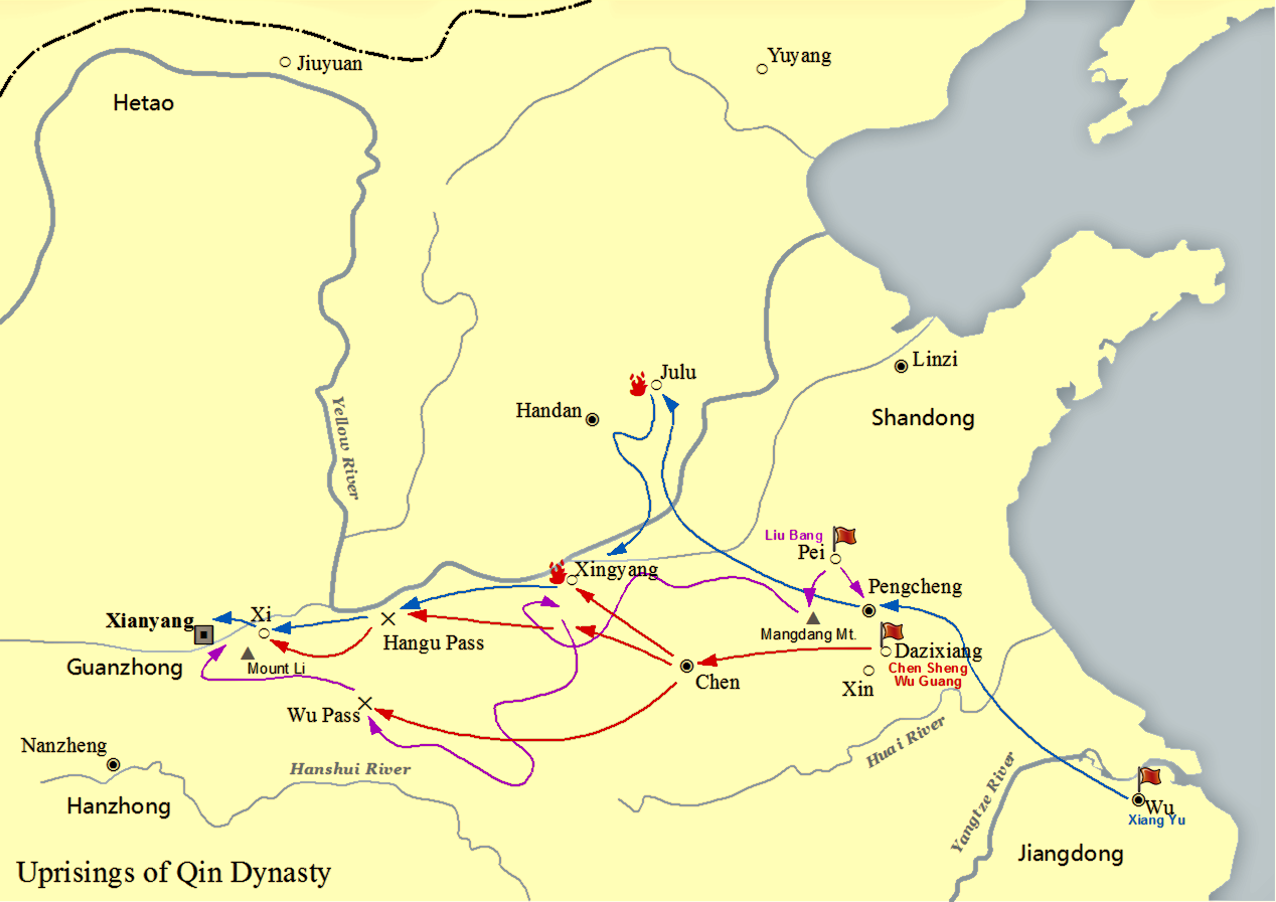
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politicians From Meishan
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking, a politician can be anyone who seeks to achieve political power in a government. Identity Politicians are people who are politically active, especially in party politics. Political positions range from local governments to state governments to federal governments to international governments. All ''government leaders'' are considered politicians. Media and rhetoric Politicians are known for their rhetoric, as in speeches or campaign advertisements. They are especially known for using common themes that allow them to develop their political positions in terms familiar to the voters. Politicians of necessity become expert users of the media. Politicians in the 19th century made heavy use of newspapers, magazines, and pamphlets, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poets From Sichuan
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems ( oral or written), or they may also perform their art to an audience. The work of a poet is essentially one of communication, expressing ideas either in a literal sense (such as communicating about a specific event or place) or metaphorically. Poets have existed since prehistory, in nearly all languages, and have produced works that vary greatly in different cultures and periods. Throughout each civilization and language, poets have used various styles that have changed over time, resulting in countless poets as diverse as the literature that (since the advent of writing systems) they have produced. History In Ancient Rome, professional poets were generally sponsored by patrons, wealthy supporters including nobility and military officials. For ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historians From Sichuan
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity During the '' Irving v Penguin Books and Lipstadt'' trial, people became aware that the court needed to identify what was an "objective historian" in the same vein as the reasonable person, and reminiscent of the standard traditionally used in English law of "the man on the Clapham omnibus". This was necessary so that there would be a legal benchmark to compare and contrast the schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th-century Chinese Historians
The 11th century is the period from 1001 ( MI) through 1100 ( MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium. In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early part of the High Middle Ages. There was, after a brief ascendancy, a sudden decline of Byzantine power and a rise of Norman domination over much of Europe, along with the prominent role in Europe of notably influential popes. Christendom experienced a formal schism in this century which had been developing over previous centuries between the Latin West and Byzantine East, causing a split in its two largest denominations to this day: Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. In Song dynasty China and the classical Islamic world, this century marked the high point for both classical Chinese civilization, science and technology, and classical Islamic science, philosophy, technology and literature. Rival political factions at the Song dynasty court created strife amongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1112 Deaths
111 may refer to: *111 (number) *111 BC * AD 111 *111 (emergency telephone number) *111 (Australian TV channel) * Swissair Flight 111 * ''111'' (Her Majesty & the Wolves album) * ''111'' (Željko Joksimović album) * NHS 111 *(111) a Miller index for the crystal face plane formed by cutting off the corner equally along each axis *111 (MBTA bus) *111 (New Jersey bus) * ''111'' (Pabllo Vittar album) See also * III (other) * List of highways numbered 111 *1/11 (other) 1/11 may refer to: *January 11 (month-day date notation) *November 1 (day-month date notation) *1st Battalion, 11th Marines 1st Battalion 11th Marines (1/11) is an artillery battalion comprising four firing batteries and a Headquarters battery. T ... * 11/1 (other) * Roentgenium, synthetic chemical element with atomic number 111 {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1039 Births
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu (poetry)
''Fu'' (), often translated "rhapsody" or "poetic exposition", is a form of Chinese rhymed prose that was the dominant literary form during the Han dynasty (206AD220). ''Fu'' are intermediary pieces between poetry and prose in which a place, object, feeling, or other subject is described and rhapsodized in exhaustive detail and from as many angles as possible. Features characteristic of ''fu'' include alternating rhyme and prose, varying line length, close alliteration, onomatopoeia, loose parallelism, and extensive cataloging of their topics. ''Fu'' composers usually strove to use as wide a vocabulary as possible, and classical ''fu'' often contain many rare and archaic Chinese words. They were not sung like songs, but were recited or chanted. The ''fu'' genre came into being around the 3rd to 2nd centuries BC and continued to be regularly used into the Song dynasty (9601279). ''Fu'' were used as grand praises for the imperial courts, palaces, and cities, but were also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ci (poetry)
CI or Ci may refer to: Business terminology * Customer intelligence, a discipline in marketing * Competitive intelligence * Corporate identity * Continual improvement * Confidential information Businesses and organisations Academia and education * California State University, Channel Islands * Channel Islands High School * Collegium Invisibile * Confucius Institute Religion * Josephites of Belgium, a Catholic congregation * Christian Identity * Christian Institute, a British charity which promotes Christian values Other businesses and organizations * Charity Intelligence Canada * China Airlines (IATA code) * Cigna health services (NYSE symbol) * Consumers International * Cycling Ireland * CI Records, a music record label * Cambria and Indiana Railroad * CANZUK International, organisation which promotes cooperation between Canada, Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom * Conservation International, an international environmental non-governmental organization * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi (poetry)
''Shi'' and ''shih''Based on the Wade-Giles system formerly used by Taiwan and English-speaking countries. are romanizations of the character /, the Chinese word for all poetry generally and across all languages. In Western analysis of the styles of Chinese poetry, ''shi'' is also used as a term of art for a specific poetic tradition, modeled after the Old Chinese works collected in the Confucian ''Classic of Poetry''. This anthology included both aristocratic poems (the "Hymns" and "Eulogies") and more rustic works believed to have derived from Huaxia folk songs (the "Odes"). They are composed in ancient Chinese, mostly in four-character lines. In such analysis, "''shi''" poetry is contrasted with other forms such as the Chu-derived "'' cí''" and the Han-era "'' fu''".Watson, Burton. ''Chinese Lyricism: Shih Poetry from the Second to the Twelfth Century''. Columbia Univ. Press (New York), 1971. .Frankel, Hans. ''The Flowering Plum and the Palace Lady''. Yale Univ. Press (New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuzhou
Xuzhou (徐州), also known as Pengcheng (彭城) in ancient times, is a major city in northwestern Jiangsu province, China. The city, with a recorded population of 9,083,790 at the 2020 census (3,135,660 of which lived in the built-up area made of Quanshan, Gulou, Yunlong and Tongshan urban Districts and Jiawang District not being conurbated), is a national complex transport hub and an important gateway city in East China. Xuzhou is a central city of Huaihai Economic Zone and Xuzhou metropolitan area. Xuzhou is an important node city of the country's Belt and Road Initiative, and an international new energy base. Xuzhou has won titles such as the National City of Civility (全国文明城市) and the United Nations Habitat Scroll of Honour award. The city is designated as National Famous Historical and Cultural City since 1986 for its relics, especially the terracotta armies, the Mausoleums of the princes and the art of relief of Han dynasty. Xuzhou is a major city among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |