Rhino Entertainment Video Albums on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five
Javan Rhinoceros
/ref> Male horns can reach 26 cm in length, while in females they are knobs or altogether absent. These animals prefer dense lowland rain forest, tall grass and reed beds that are plentiful with large floodplains and mud wallows. Though once widespread throughout Asia, by the 1930s they were nearly hunted to extinction in Nepal, India, Burma, Peninsular Malaysia, and

 Rhinocerotoids diverged from other perissodactyls by the early Eocene. Fossils of '' Hyrachyus eximus'' found in North America date to this period. This small hornless ancestor resembled a tapir or small horse more than a rhino. Four families, sometimes grouped together as the
Rhinocerotoids diverged from other perissodactyls by the early Eocene. Fossils of '' Hyrachyus eximus'' found in North America date to this period. This small hornless ancestor resembled a tapir or small horse more than a rhino. Four families, sometimes grouped together as the
 Cladogram showing the relationships of recent and Late Pleistocene rhinoceros species (minus ''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus)'' based on whole nuclear genomes, after Liu et al., 2021:
denotes extinct taxa
* Family Rhinocerotidae
** †'' Teletaceras''
** †''
Cladogram showing the relationships of recent and Late Pleistocene rhinoceros species (minus ''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus)'' based on whole nuclear genomes, after Liu et al., 2021:
denotes extinct taxa
* Family Rhinocerotidae
** †'' Teletaceras''
** †''
 Adult rhinoceros have no real predators in the wild, other than humans. Young rhinos sometimes fall prey to big cats,
Adult rhinoceros have no real predators in the wild, other than humans. Young rhinos sometimes fall prey to big cats,

 Rhinoceros horns develop from subcutaneous tissues, and are made of keratinous mineralized compartments. The horns root in a germinative layer.
Rhinoceros horns are used in traditional medicines in parts of Asia, and for dagger handles in Yemen and Oman. Esmond Bradley Martin has reported on the trade for dagger handles in Yemen. In Europe, it was historically believed that rhino horns could purify water and could detect poisoned liquids, and likely as an aphrodisiac and an antidote to poison.
It is a common misconception that rhinoceros horn in powdered form is used as an aphrodisiac or a cure for cancer in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as ''Cornu Rhinoceri Asiatici'' (犀角, ''xījiǎo'', "rhinoceros horn"); no TCM text in history has ever mentioned such prescriptions. In TCM, rhino horn is sometimes prescribed for fevers and convulsions, a treatment not supported by
Rhinoceros horns develop from subcutaneous tissues, and are made of keratinous mineralized compartments. The horns root in a germinative layer.
Rhinoceros horns are used in traditional medicines in parts of Asia, and for dagger handles in Yemen and Oman. Esmond Bradley Martin has reported on the trade for dagger handles in Yemen. In Europe, it was historically believed that rhino horns could purify water and could detect poisoned liquids, and likely as an aphrodisiac and an antidote to poison.
It is a common misconception that rhinoceros horn in powdered form is used as an aphrodisiac or a cure for cancer in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as ''Cornu Rhinoceri Asiatici'' (犀角, ''xījiǎo'', "rhinoceros horn"); no TCM text in history has ever mentioned such prescriptions. In TCM, rhino horn is sometimes prescribed for fevers and convulsions, a treatment not supported by
 Greek historian and geographer Agatharchides (2nd century BC) mentions the rhinoceros in his book ''On the Erythraean Sea''.
Greek historian and geographer Agatharchides (2nd century BC) mentions the rhinoceros in his book ''On the Erythraean Sea''.
White Rhinoceros, White Rhinoceros Profile, Facts, Information, Photos, Pictures, Sounds, Habitats, Reports, News – National Geographic
* Laufer, Berthold. 1914. "History of the Rhinoceros". In: ''Chinese Clay Figures, Part I: Prolegomena on the History of Defence Armour''. Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago, pp. 73–173. * * * Chapman, January (1999). ''The Art of Rhinoceros Horn Carving in China''. Christies Books, London. . * * * *
Rhino Species
Rhino Images
page on th
Rhino Resource Center
Rhinoceros entry
on World Wide Fund for Nature website.
International Anti Poaching Foundation
Free To Use Rhino Images
Rhinoceros Resources & Photos
on African Wildlife Foundation website * UK Times article: "South African spy chief linked to rhino horn trade
South African spy chief linked to rhino horn trade
* Video on South African government minister's alleged involvement in illegal rhino horn trade
VIDEO: Rhino poacher says Mahlobo is his 'mate'
People Not Poaching: The Communities and IWT Learning Platform
{{Authority control Extant Eocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Taxa named by John Edward Gray Unicorns
extant
Extant is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Extant taxon, a taxon which is not extinct, ...
species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and Southeast Asia.
Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut
The hindgut (or epigaster) is the posterior ( caudal) part of the alimentary canal. In mammals, it includes the distal one third of the transverse colon and the splenic flexure, the descending colon, sigmoid colon and up to the ano-rectal juncti ...
allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips to pluck food.
Rhinoceros are killed by poachers for their horns, which are bought and sold on the black market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the se ...
for high prices, leading to most living rhinoceros species being considered endangered. The contemporary market for rhino horn is overwhelmingly driven by China and Vietnam, where it is bought by wealthy consumers to use in traditional Chinese medicine, among other uses. Rhino horns are made of keratin, the same material as hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
and fingernails, and there is no good evidence of any health benefits. A market also exists for rhino horn dagger handles in Yemen, which was the major source of demand for rhino horn in the 1970s and 1980s.
Taxonomy and naming
The word ''rhinoceros'' is derived through Latin from the grc, ῥῑνόκερως, which is composed of (''rhino-'', " nose") and (''keras'', " horn") with a horn on the nose. The plural in English is ''rhinoceros'' or ''rhinoceroses''. The collective noun for a group of rhinoceroses is ''crash'' or ''herd''. The name has been in use since the 14th century. The family Rhinocerotidae consists of only four extant genera: ''Ceratotherium
''Ceratotherium'' (Greek: "horn" (keratos), "beast" (therion)) is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the white rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium ...
'' (white rhinoceros), ''Diceros
''Diceros'' (Greek: "two" (dio), "horn" (keratos)) is a genus of rhinoceros containing the living black rhinoceros ''(Diceros bicornis)'' and at least one extinct species.
Taxonomy
''Diceros'' is generally believed to have branched off from an ...
'' (black rhinoceros), '' Dicerorhinus'' (Sumatran rhinoceros), and '' Rhinoceros'' (Indian and Javan rhinoceros). The living species fall into three categories. The two African species, the white rhinoceros and the black rhinoceros, belong to the tribe Dicerotini, which originated in the middle Miocene, about 14.2 million years ago. The species diverged during the early Pliocene (about 5 million years ago). The main difference between black and white rhinos is the shape of their mouths – white rhinos have broad flat lips for grazing, whereas black rhinos have long pointed lips for eating foliage. There are two living Rhinocerotini species, the Indian rhinoceros and the Javan rhinoceros, which diverged from one another about 10 million years ago. The Sumatran rhinoceros is the only surviving representative of the Dicerorhinini.
A subspecific hybrid white rhino (''Ceratotherium s. simum'' × ''C. s. cottoni'') was bred at the Dvůr Králové Zoo (Zoological Garden Dvur Kralove nad Labem) in the Czech Republic in 1977. Interspecific hybridisation of black and white rhinoceros has also been confirmed.
While the black rhinoceros has 84 chromosomes (diploid number, 2N, per cell), all other rhinoceros species have 82 chromosomes. Chromosomal polymorphism might lead to varying chromosome counts. For instance, in a study there were three northern white rhinoceroses with 81 chromosomes.
Species
White
There are twosubspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of white rhinoceros: the southern white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum simum'') and the northern white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum cottoni''). As of 2013, the southern subspecies has a wild population of 20,405—making them the most abundant rhino subspecies in the world. The northern subspecies is critically endangered, with all that is known to remain being two captive females. There is no conclusive explanation of the name "white rhinoceros". A popular idea that "white" is a distortion of either the Afrikaans word ''wyd'' or the Dutch word
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German lan ...
''wijd'' (or its other possible spellings ''whyde'', ''weit'', etc.,), meaning "wide" and referring to the rhino's square lips, is not supported by linguistic studies.
The white rhino has an immense body and large head, a short neck and broad chest. Females weigh and males . The head-and-body length is and the shoulder height is . On its snout it has two horns. The front horn is larger than the other horn and averages in length and can reach . The white rhinoceros also has a prominent muscular hump that supports its relatively large head. The colour of this animal can range from yellowish brown to slate grey. Most of its body hair is found on the ear fringes and tail bristles, with the rest distributed rather sparsely over the rest of the body. White rhinos have the distinctive flat broad mouth that is used for grazing.
Black
The name "black rhinoceros" ('' Diceros bicornis'') was chosen to distinguish this species from the white rhinoceros ('' Ceratotherium simum''). This can be confusing, as the two species are not truly distinguishable by color. There are four subspecies of black rhino: South-central (''Diceros bicornis minor
The south-central black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis minor''), also known as the south-central hook-lipped rhinoceros or the lesser black rhino, is a subspecies of the black rhinoceros. In keeping with the rules of zoological nomenclature, the ...
''), the most numerous, which once ranged from central Tanzania south through Zambia, Zimbabwe and Mozambique to northern and eastern South Africa; South-western ('' Diceros bicornis occidentalis'') which are better adapted to the arid and semi-arid savannas of Namibia, southern Angola, western Botswana and western South Africa; East African (''Diceros bicornis michaeli
The eastern black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis michaeli''), also known as the East African black rhinoceros, is a subspecies of the black rhinoceros. Its numbers are very low due to poaching for its horn, and it is listed as critically endanger ...
''), primarily in Tanzania; and West African (''Diceros bicornis longipes
The western black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis longipes'') or West African black rhinoceros is an extinct subspecies of the black rhinoceros. It was declared extinct by the IUCN in 2011. The western black rhinoceros was believed to have been ...
'') which was declared extinct in November 2011. The native Tswanan name ''keitloa'' describes a South African variation of the black rhino in which the posterior horn is equal to or longer than the anterior horn.
An adult black rhinoceros stands high at the shoulder and is in length. An adult weighs from , exceptionally to , with the females being smaller than the males. Two horns on the skull are made of keratin with the larger front horn typically 50 cm long, exceptionally up to 140 cm. Sometimes, a third smaller horn may develop. The black rhino is much smaller than the white rhino, and has a pointed mouth, which it uses to grasp leaves and twigs when feeding.
During the latter half of the 20th century, their numbers were severely reduced from an estimated 70,000 in the late 1960s to a record low of 2,410 in 1995. Since then, numbers have been steadily increasing at a continental level with numbers doubling to 4,880 by the end of 2010. As of 2008, the numbers are still 90% lower than three generations ago.
Indian
The Indian rhinoceros, or greater one-horned rhinoceros, (''Rhinoceros unicornis'') has a single horn 20 to 60 cm long. It is nearly as large as the African white rhino. Its thick, silver-brown skin folds into the shoulder, back, and rump, giving it an armored appearance. Its upper legs and shoulders are covered in wart-like bumps, and it has very little body hair. Grown males are larger than females in the wild, weighing from . Shoulder height is . Females weigh about and are long. The record-sized specimen was approximately . Indian rhinos once inhabited many areas ranging from Pakistan toMyanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, Joh ...
and maybe even parts of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Because of humans, they now exist in only several protected areas of India (in Assam, West Bengal, and a few pairs in Uttar Pradesh) and Nepal, plus a pair in Lal Suhanra National Park in Pakistan reintroduced there from Nepal. They are confined to the tall grasslands and forests in the foothills of the Himalayas. Two-thirds of the world's Indian rhinoceroses are now confined to the Kaziranga National Park situated in the Golaghat district
Golaghat district (Pron:ˌgəʊləˈgɑ:t) is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. It attained district status in 1987. The district headquarters are located at Golaghat. The district occupies an and lies above sea level.
...
of Assam, India.
Javan
The Javan rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros sondaicus'') is one of the most endangered largemammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s in the world. According to 2015 estimates, only about 60 remain, in Java, Indonesia, all in the wild. It is also the least known rhino species. Like the closely related, and larger, Indian rhinoceros, the Javan rhino has a single horn. Its hairless, hazy gray skin falls into folds into the shoulder, back, and rump, giving it an armored appearance. Its length reaches including the head, and its height . Adults are variously reported to weigh 900–1,400 kg or 1,360–2,000 kg.Rhino GuideJavan Rhinoceros
/ref> Male horns can reach 26 cm in length, while in females they are knobs or altogether absent. These animals prefer dense lowland rain forest, tall grass and reed beds that are plentiful with large floodplains and mud wallows. Though once widespread throughout Asia, by the 1930s they were nearly hunted to extinction in Nepal, India, Burma, Peninsular Malaysia, and
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
for the supposed medical powers of their horns and blood. As of 2015, only 58–61 individuals remain in Ujung Kulon National Park, Java, Indonesia. The last known Javan rhino in Vietnam was reportedly killed for its horn in 2011 by Vietnamese poachers. Now only Java contains the last Javan rhinos.
Sumatran
The Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis'') is the smallest extant rhinoceros species, as well as the one with the mosthair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
. It can be found at very high altitudes in Borneo and Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
. Due to habitat loss and poaching, their numbers have declined and it has become the second most threatened rhinoceros. About 275 Sumatran rhinos are believed to remain. There are three subspecies of Sumatran rhinoceros: the Sumatran rhinoceros proper (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis sumatrensis''), the Bornean rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis harrissoni'') and the possibly extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
Northern Sumatran rhinoceros (''Dicerorhinus sumatrensis lasiotis'').
A mature rhino typically stands about high at the shoulder, has a length of and weighs around , though the largest individuals have been known to weigh as much as . Like the African species, it has two horns; the larger is the front (), with the smaller usually less than long. Males have much larger horns than the females. Hair can range from dense (the densest hair in young calves) to sparse. The color of these rhinos is reddish brown. The body is short and has stubby legs. The lip is prehensile.
Sumatran rhinoceros are on the verge of extinction due to loss of habitat and illegal hunting. Once they were spread across South-east Asia, but now they are confined to several parts of Indonesia and Malaysia due to reproductive isolation. There were 320 ''D. sumatrensis'' in 1995, which by 2011 have dwindled to 216. It has been found through DNA comparison that the Sumatran rhinoceros is the most ancient extant rhinoceros and related to the extinct Eurasian woolly rhino species, '' Coelodonta''. In 1994 Alan Rabinowitz publicly denounced governments, non-governmental organizations, and other institutions for lacking in their attempts to conserve the Sumatran rhinoceros. To conserve it, they would have to relocate them from small forests to breeding programs that could monitor their breeding success. To boost reproduction, the Malaysian and Indonesian governments could also agree to exchange the gametes of the Sumatran and (smaller) Bornean subspecies. The Indonesian and Malaysian governments have also proposed a single management unit for these two ancient subspecies.
Plantations for palm oil have taken out the living areas and led to the eradication of the rhino in Sumatra.
Evolution

 Rhinocerotoids diverged from other perissodactyls by the early Eocene. Fossils of '' Hyrachyus eximus'' found in North America date to this period. This small hornless ancestor resembled a tapir or small horse more than a rhino. Four families, sometimes grouped together as the
Rhinocerotoids diverged from other perissodactyls by the early Eocene. Fossils of '' Hyrachyus eximus'' found in North America date to this period. This small hornless ancestor resembled a tapir or small horse more than a rhino. Four families, sometimes grouped together as the superfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
Rhinocerotoidea, evolved in the late Eocene, namely the Hyracodontidae, Amynodontidae, Paraceratheriidae and Rhinocerotidae.
Hyracodontidae
Hyracodontidae, also known as "running rhinos", showed adaptations for speed, and would have looked more like horses than modern rhinos. The smallest hyracodontids were dog-sized. Hyracodontids spread across Eurasia from the mid-Eocene to early Oligocene.Amynodontidae
The Amynodontidae, also known as "aquatic rhinos", dispersed acrossNorth America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and Eurasia, from the late Eocene to early Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
. The amynodontids were hippopotamus-like in their ecology and appearance, inhabiting rivers and lakes, and sharing many of the same adaptations to aquatic life as hippos.Paraceratheriidae
The Paraceratheriidae, also known as paraceratheres or indricotheres, originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the early Miocene. The first paraceratheres were only about the size of large dogs, growing progressively larger in the late Eocene and Oligocene. The largest genus of the family was '' Paraceratherium'', which was more than twice as heavy as a bull African elephant, and was one of the largest land mammals that ever lived.Rhinocerotidae
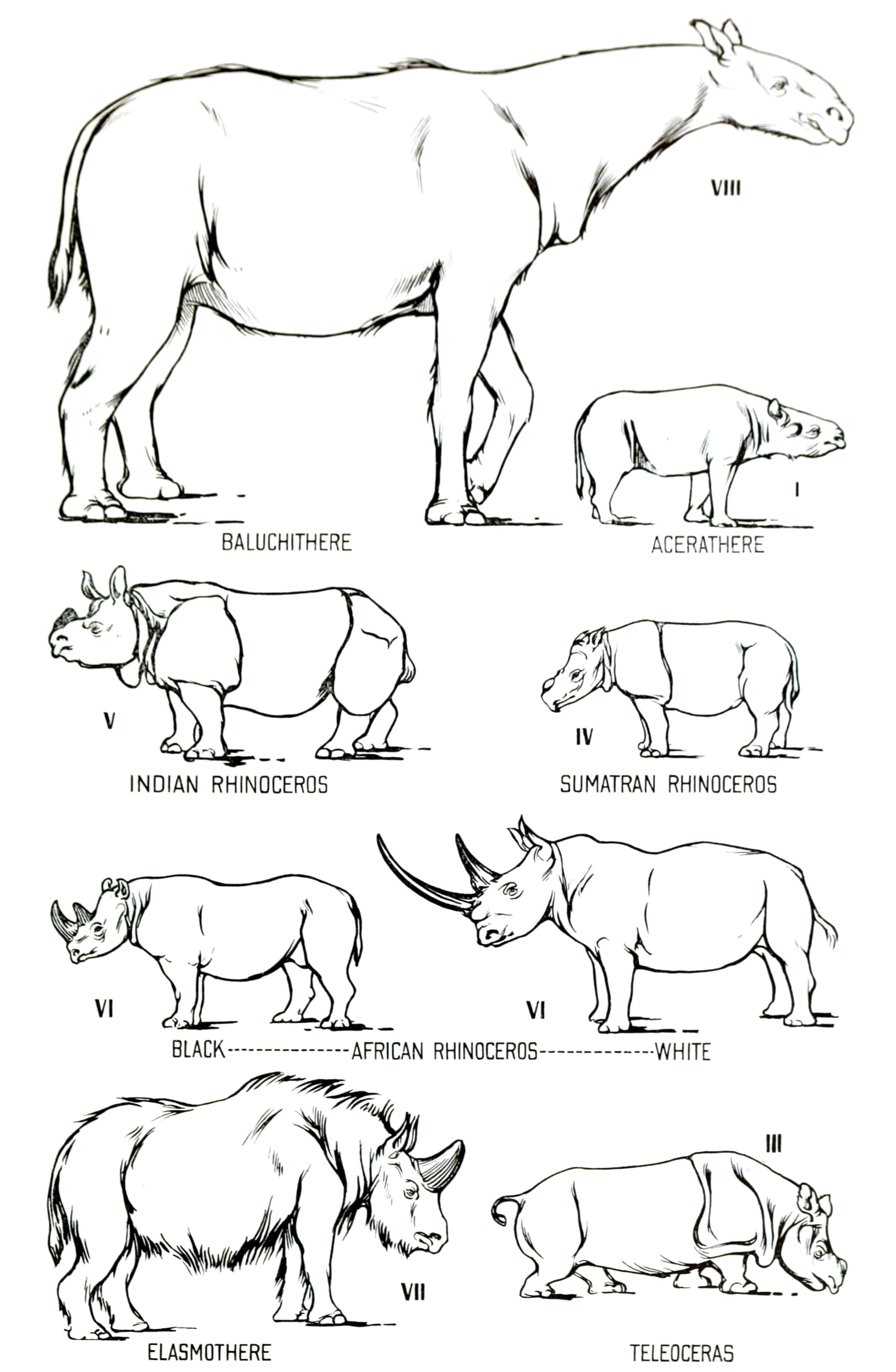
The family of all modern rhinoceros, the Rhinocerotidae, first appeared in the Late Eocene in Eurasia. The earliest members of Rhinocerotidae were small and numerous; at least 26 genera lived in Eurasia and North America until a wave of extinctions in the middle Oligocene wiped out most of the smaller species. Several independent lineages survived. '' Menoceras'', a pig-sized rhinoceros, had two horns side by side. The North American '' Teleoceras'' had short legs, a barrel chest and lived until about five million years ago. The last rhinos in the Americas became extinct during the Pliocene. Modern rhinos are thought to have begun dispersal from Asia during the Miocene. Alongside the extant species, four additional species of rhinoceros survived into the Last Glacial Period: the woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis''), '' Elasmotherium sibiricum'' and two species of '' Stephanorhinus,'' Merck's rhinoceros (''Stephanorhinus kirchbergensis'') and the Narrow-nosed rhinoceros (''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus)''. The woolly rhinoceros appeared inChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
around 1 million years ago and first arrived in Europe around 600,000 years ago. It reappeared 200,000 years ago, alongside the woolly mammoth, and became numerous. ''Elasmotherium'' was two meters tall, five meters long and weighed around five tons, with a single enormous horn, hypsodont teeth and long legs for running. The latest known well dated bones of ''Elasmotherium''in found in the south of Western Siberia (the area that is today Kazakhstan) date as recently as 39,000 years ago.
The origin of the two living African rhinos can be traced to the late Miocene () species ''Ceratotherium neumayri''. The lineages containing the living species diverged by the early Pliocene, when ''Diceros praecox'', the likely ancestor of the black rhinoceros, appears in the fossil record. The black and white rhinoceros remain so closely related that they can still mate and successfully produce offspring.
 Cladogram showing the relationships of recent and Late Pleistocene rhinoceros species (minus ''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus)'' based on whole nuclear genomes, after Liu et al., 2021:
denotes extinct taxa
* Family Rhinocerotidae
** †'' Teletaceras''
** †''
Cladogram showing the relationships of recent and Late Pleistocene rhinoceros species (minus ''Stephanorhinus hemitoechus)'' based on whole nuclear genomes, after Liu et al., 2021:
denotes extinct taxa
* Family Rhinocerotidae
** †'' Teletaceras''
** †''Uintaceras
''Uintaceras'' is an extinct genus of medium-sized rhinoceros that lived in North America (Wyoming and Utah) during the Middle Eocene, with only the type species ''U. radinskyi'', named in 1997, currently contained within the genus.L. T. Holbrook ...
''
** Subfamily Rhinocerotinae
*** Tribe Aceratheriini
**** †
A dagger, obelisk, or obelus is a typographical mark that usually indicates a footnote if an asterisk has already been used. The symbol is also used to indicate death (of people) or extinction (of species). It is one of the modern descendan ...
'' Aceratherium'' lived from 33.9 to 3.4 Ma
**** †''Acerorhinus
''Acerorhinus'' was a genus of rhinoceros of the tribe Aceratheriini endemic to Asia from the Miocene, living from 13.6—7.0 mya existing for approximately .
Among other locations, well-preserved ''Acerorhinus'' skull specimens have been found ...
'' 13.6–7.0 Ma
**** †''Alicornops
''Alicornops'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros belonging to the subfamily Aceratheriinae. It lived in Eurasia during the Miocene and Pliocene.
Four species are known. Two of them, ''Alicornops complanatum'' and ''Alicornops laogouense'' were de ...
'' 13.7–5.3 Ma
**** †'' Aphelops'' 20.43–5.33 Ma
**** †'' Chilotheridium'' 23.0–11.6 Ma
**** †''Chilotherium
''Chilotherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during the Miocene through Pliocene living for 13.7—3.4 mya, existing for approximately .. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
Description
It was a large, robust animal reaching 1.5-1.8 ...
'' 13.7–3.4 Ma
**** †''Floridaceras
''Floridaceras'' is an extinct genus of Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceros) of the Miocene epoch (early Hemingfordian), endemic to North America, living from around ~20.6–16.3 Annum, Ma, existing for approximately .
Taxonomy
''Floridaceras'' was named ...
'' 20.4–16.3 Ma
**** †'' Hoploaceratherium'' 16.9–16.0 Ma
**** †''Mesaceratherium
''Mesaceratherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros.
References
Miocene rhinoceroses
Miocene mammals of Asia
Fossil taxa described in 1969
{{paleo-oddtoedungulate-stub ...
''
**** †'' Peraceras'' 20.6–10.3 Ma
**** †''Plesiaceratherium
''Plesiaceratherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros. It includes two species: ''P. gracile'' from China and ''P. mirallesi'' from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Euro ...
'' 20.0–11.6 Ma
**** †''Ronzotherium
''Ronzotherium'' is an extinct genus of Odd-toed ungulate, perissodactyl mammal from the family Rhinoceros, Rhinocerotidae. The name derives from the hill of 'Ronzon', the French locality near Le Puy-en-Velay at which it was first discovered, and ...
'' 37–23 Ma
**** †''Shansirhinus
''Shansirhinus'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros endemic to China during the Miocene through Pliocene.
Members of ''Shansirhinus'' were originally classified as species of ''Chilotherium
''Chilotherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros en ...
''
**** †'' Sinorhinus''
**** †'' Subchilotherium''
*** Tribe Teleoceratini
**** †'' Aprotodon'' 28.4–5.330 Ma
**** †'' Brachydiceratherium''
**** †'' Brachypotherium'' 20.0–5.33 Ma
**** †'' Diaceratherium'' 28.4–16.0 Ma
**** †''Prosantorhinus
''Prosantorhinus'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros from the lower and middle Miocene. The small teleoceratine rhinocerotid was found in western Europe and Asia.
Description
''Posantorhinus'' was a similarly sized animal to the Sumatran rhino ...
'' 16.9–7.25 Ma
**** †''Shennongtherium
''Shennongtherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros from the Miocene time period. It once roamed in what is now China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous co ...
''
**** †'' Teleoceras'' 16.9–4.9 Ma
*** Rhinocerotina Burdigalian–Present
**** Tribe Rhinocerotini 40.4–11.1 Ma–Present
***** †''Gaindatherium
''Gaindatherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in Asia during the Miocene. It is mainly known from the Siwalik Hills in Pakistan, though its fossils have been found as far west as the Negev desert.
Description
''Gaindatherium'' is ...
'' 11.6–11.1 Ma
***** Subtribe Rhinocerotina 17.5 Ma–Present
****** †'' Nesorhinus'' .70 Ma
****** †'' Rusingaceros'' 17.5 Ma
****** '' Rhinoceros'' – Indian & Javan rhinoceros
**** Tribe Dicerorhinini
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family (biology), family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member ...
***** †'' Coelodonta'' – Woolly rhinoceros
***** '' Dicerorhinus'' – Sumatran rhinoceros
***** †'' Dihoplus'' 11.610–1.810 Ma
***** †''Lartetotherium
''Lartetotherium'' is an extinct species of rhinoceros that lived during the Miocene in Europe.
The species ''Lartetotherium sansaniense'' was a unique cursorial rhinoceros with a distinctly long horn. Its teeth were brachyodont
The mol ...
'' 15.97–8.7 Ma
***** †'' Stephanorhinus'' 9.7–0.04 Ma – Merck's rhinoceros & Narrow-nosed rhinoceros
**** Tribe Dicerotini 23.0–Present
***** ''Ceratotherium
''Ceratotherium'' (Greek: "horn" (keratos), "beast" (therion)) is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the white rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium ...
'' – White rhinoceros 7.25–Present
***** ''Diceros
''Diceros'' (Greek: "two" (dio), "horn" (keratos)) is a genus of rhinoceros containing the living black rhinoceros ''(Diceros bicornis)'' and at least one extinct species.
Taxonomy
''Diceros'' is generally believed to have branched off from an ...
'' – Black rhinoceros 23.0–Present
***** †''Paradiceros
''Paradiceros'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros that lived in east Africa during the Late Miocene, between 10.5 and 9 million years ago.
''Paradiceros'' was a relatively small species once believed to be closely allied to ''Diceros''. It was a ...
'' 15.97–11.61 Ma
**** Rhinocerotinae ''incertae sedis''
***** †''Protaceratherium
''Protaceratherium'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros from the Oligocene and Miocene of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, ...
''
** Subfamily Elasmotheriinae
*** †'' Gulfoceras'' 23.03–20.43 Ma
*** †''Victoriaceros
''Victoriaceros'' is an extinct genus of elasmotheriine rhinoceros known from the Miocene of Maboko Island, Kenya.
Discovery
''Victoriaceros'' is known from the holotype, an almost perfectly preserved skull, which characterized mainly by the la ...
'' 15 Ma
*** Tribe Diceratheriini
**** †''Diceratherium
''Diceratherium'' (meaning "two horned beast") is an extinct genus of rhinoceros endemic to North America, Europe, and Asia during the Oligocene through Miocene living from 33.9 to 11.6 mya, existing for approximately . Mass estimates for the ...
'' 33.9–11.6 Ma
**** †'' Penetrigonias''
**** †''Subhyracodon
''Subhyracodon'' (Latin: "below" (sub), + Greek: "hyrax" (hyrak = 'shrewmouse'), and "tooth" (odontos, referring to the genus ''Hyracodon'')) is an extinct genus of hornless rhinoceroses. With a length of and a weight estimated of (in ''S. mitis ...
'' 38.0–26.3 Ma
**** †'' Trigonias'' 37-34 Ma
*** Tribe Elasmotheriini 20.0–0.1 Ma
**** †''Bugtirhinus
''Bugtirhinus'' was a genus of rhinoceros of the subfamily Elasmotheriinae endemic to Asia during the Miocene living from 20—16.9 mya existing for approximately .
Taxonomy
''Bugtirhinus'' was named by Antoine and Welcomme (2000). Its type is ...
'' 20.0–16.9 Ma
**** †''Caementodon
''Caementodon'' is an extinct genus of rhinoceros of the clade Elasmotheriinae endemic to Europe and Asia during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was na ...
''
**** †'' Elasmotherium'' – Giant rhinoceros
''Elasmotherium'' is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during Late Miocene through the Pleistocene, existing at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. A more recent date of 26,000 BP is consider ...
3.6–0.039 Ma
**** †''Hispanotherium
''Hispanotherium'' was a genus of rhinoceros of the tribe Elasmotheriini endemic to Europe and Asia during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Mioce ...
'' synonymized with ''Huaqingtherium'' 16.0–7.25 Ma
**** †'' Iranotherium''
**** †'' Kenyatherium''
**** †''Meninatherium
''Meninatherium'' is a poorly understood extinct genus of Asian rhinoceros. It is known only from an Upper Oligocene European type specimen which was destroyed during World War II.
References
Oligocene rhinoceroses
Oligocene mammals of ...
''
**** †'' Menoceras'' 23.03–16.3 Ma
**** †'' Ningxiatherium''
**** †'' Ougandatherium'' 20.0–16.9 Ma
**** †'' Parelasmotherium''
**** †'' Procoelodonta''
**** †'' Sinotherium'' 9.0–5.3 Ma
Predators, poaching and hunting
 Adult rhinoceros have no real predators in the wild, other than humans. Young rhinos sometimes fall prey to big cats,
Adult rhinoceros have no real predators in the wild, other than humans. Young rhinos sometimes fall prey to big cats, crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to inclu ...
s, African wild dogs, and hyena
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek , ), are feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the clas ...
s.
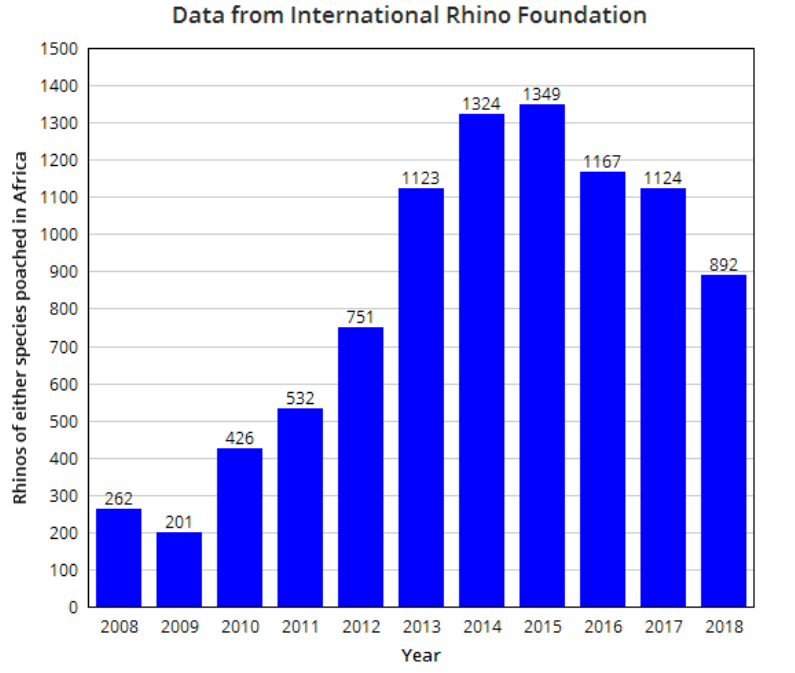
Although rhinos are large and aggressive and have a reputation for being resilient, they are very easily poached; they visit water holes daily and can be easily killed while they drink. As of December 2009, poaching increased globally while efforts to protect the rhino are considered increasingly ineffective. The most serious estimate, that only 3% of poachers are successfully countered, is reported of Zimbabwe, while Nepal has largely avoided the crisis. Poachers have become more sophisticated. South African officials have called for urgent action against poaching after poachers killed the last female rhino in the Krugersdorp Game Reserve near Johannesburg. Statistics from South African National Parks
South African National Parks (SANParks) is the body responsible for managing South Africa's national parks. SANParks was formed in 1926, and currently manages 19 parks consisting of , over 3% of the total area of South Africa.
Many parks offer ...
show that 333 rhinoceros were killed in South Africa in 2010, increasing to 668 by 2012, over 1,004 in 2013, and over 1,338 killed in 2015. In some cases rhinos are drugged and their horns removed, while in other instances more than the horn is taken.
The Namibian government has supported the practice of rhino trophy hunting as a way to raise money for conservation. Hunting licenses for five Namibian Black rhinos are auctioned annually, with the money going to the government's Game Products Trust Fund. Some conservationists and members of the public oppose or question this practice.
Horn use
 Rhinoceros horns develop from subcutaneous tissues, and are made of keratinous mineralized compartments. The horns root in a germinative layer.
Rhinoceros horns are used in traditional medicines in parts of Asia, and for dagger handles in Yemen and Oman. Esmond Bradley Martin has reported on the trade for dagger handles in Yemen. In Europe, it was historically believed that rhino horns could purify water and could detect poisoned liquids, and likely as an aphrodisiac and an antidote to poison.
It is a common misconception that rhinoceros horn in powdered form is used as an aphrodisiac or a cure for cancer in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as ''Cornu Rhinoceri Asiatici'' (犀角, ''xījiǎo'', "rhinoceros horn"); no TCM text in history has ever mentioned such prescriptions. In TCM, rhino horn is sometimes prescribed for fevers and convulsions, a treatment not supported by
Rhinoceros horns develop from subcutaneous tissues, and are made of keratinous mineralized compartments. The horns root in a germinative layer.
Rhinoceros horns are used in traditional medicines in parts of Asia, and for dagger handles in Yemen and Oman. Esmond Bradley Martin has reported on the trade for dagger handles in Yemen. In Europe, it was historically believed that rhino horns could purify water and could detect poisoned liquids, and likely as an aphrodisiac and an antidote to poison.
It is a common misconception that rhinoceros horn in powdered form is used as an aphrodisiac or a cure for cancer in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as ''Cornu Rhinoceri Asiatici'' (犀角, ''xījiǎo'', "rhinoceros horn"); no TCM text in history has ever mentioned such prescriptions. In TCM, rhino horn is sometimes prescribed for fevers and convulsions, a treatment not supported by evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients". The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of t ...
: this treatment has been compared to consuming fingernail clippings in water. In 1993, China signed the CITES treaty and removed rhinoceros horn from the Chinese medicine pharmacopeia, administered by the Ministry of Health. In 2011, the Register of Chinese Herbal Medicine in the United Kingdom issued a formal statement condemning the use of rhinoceros horn. A growing number of TCM educators are also speaking out against the practice, although some TCM practitioners still believe that it is a life-saving medicine.
Vietnam reportedly has the biggest number of rhino horn consumers, with their demand driving most of the poaching, which has risen to record levels. The "Vietnam CITES Management Authority" has claimed that Hanoi recently experienced a 77% drop in the usage of rhino horn, but National Geographic has challenged these claims, noticing that there was no rise in the numbers of criminals who were apprehended or prosecuted. South African rhino poaching's main destination market is Vietnam. An average sized horn can bring in as much as a quarter of a million dollars in Vietnam and many rhino range states have stockpiles of rhino horn.
Horn trade
International trade in rhinoceros horn has been declared illegal by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) since 1977. A proposal bySwaziland
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
to lift the international ban was rejected in October 2016. Domestic sale of rhinoceros horn in South Africa, home of 80% of the remaining rhino population, was banned as of 2009. The ban was overturned in a court case in 2017, and South Africa plans to draft regulations for the sale of rhino horn, possibly including export for "non-commercial purposes". The South African government has proposed that a legal trade of rhino horn be established, arguing that this could reduce poaching and prevent the extinction of this species.
In March 2013, some researchers suggested that the only way to reduce poaching would be to establish a regulated trade based on humane and renewable harvesting from live rhinos. The World Wildlife Fund opposes legalization of the horn trade, as it may increase demand, while IFAW released a report by ''EcoLarge'', suggesting that more thorough knowledge of economic factors is required to justify the pro-trade option.
Conservation
According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, conservation of African rhinoceroses as consumers of large amounts of vegetation is crucial to maintaining the shape of the African landscape and the natural resources of local communities.Ways to prevent poaching
Horn removal
To prevent poaching, in certain areas, rhinos have been tranquillized and their horns removed. Armed park rangers, particularly in South Africa, are also working on the front lines to combat poaching, sometimes killing poachers who are caught in the act. A 2012 spike in rhino killings increased concerns about the future of the species.Horn poisoning
In 2011, the Rhino Rescue Project began a horn-trade control method consisting of infusing the horns of living rhinos with a mixture of a pink dye and an acaricide (to kill ticks) which is safe for rhinos but toxic to humans. The procedure also includes inserting threeRFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electromag ...
identification chips and taking DNA samples. Because of the fibrous nature of rhino horn, the pressurized dye infuses the interior of the horn but does not color the surface or affect rhino behavior. Depending on the quantity of horn a person consumes, experts believe the acaricide would cause nausea, stomach-ache, and diarrhea, and possibly convulsions. It would not be fatal—the primary deterrent is the knowledge that the treatment has been applied, communicated by signs posted at the refuges. The original idea grew out of research into the horn as a reservoir for one-time tick treatments, and experts selected an acaricide they think is safe for the rhino, oxpeckers, vultures, and other animals in the preserve's ecosystem. Proponents claim that the dye cannot be removed from the horns, and remains visible on x-ray scanners even when the horn is ground to a fine powder.
The UK charity organization Save the Rhino
Save the Rhino International (SRI), a United Kingdom, UK-based Wildlife conservation, conservation charity, is Europe's largest single-species Rhinoceros, rhino charity, in terms of funds raised and grants made, and in terms of profile and posi ...
has criticized horn poisoning on moral and practical grounds. The organization questions the assumptions that the infusion technique works as intended, and that even if the poison were effective, whether middlemen in a lucrative, illegal trade would care much about the effect it would have on buyers. Additionally, rhino horn is increasingly purchased for decorative use, rather than for use in traditional medicine. Save the Rhino questions the feasibility of applying the technique to all African rhinos, since workers would have to reapply the acaricide every 4 years. It was also reported that one out of 150 rhinos treated did not survive the anesthesia.
Artificial substitute for rhinoceros horn
Another way to undercut the rhinoceros horn market has been suggested by Matthew Markus of Pembient, a biotechnology firm. He proposes the synthesis of an artificial substitute for rhinoceros horn. To enable authorities to distinguish the bioengineered horn from real rhinoceros horn, the genetic code of the bioengineered horn could be registered, similar to the DNA of living rhinoceros in the RhODIS (Rhino DNA Index System). Initial responses from many conservationists were negative, but a 2016 report from TRAFFIC—which monitors trade in wildlife and animal parts—conceded that it "...would be rash to rule out the possibility that trade in synthetic rhinoceros horn could play a role in future conservation strategies".Historical representations
 Greek historian and geographer Agatharchides (2nd century BC) mentions the rhinoceros in his book ''On the Erythraean Sea''.
Greek historian and geographer Agatharchides (2nd century BC) mentions the rhinoceros in his book ''On the Erythraean Sea''.
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Due ...
created a famous woodcut of a rhinoceros in 1515, based on a written description and brief sketch by an unknown artist of an Indian rhinoceros that had arrived in Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
earlier that year. He never saw the animal itself, so '' Dürer's Rhinoceros'' is a somewhat inaccurate depiction. Rhinoceros are depicted in the Chauvet Cave in France, pictures dated to 10,000–30,000 years ago.
There are legends about rhinoceroses stamping out fire in Burma, India, and Malaysia. The mythical rhinoceros has a special name in Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, ''badak api'', wherein ''badak'' means rhinoceros, and ''api'' means fire. The animal would come when a fire was lit in the forest and stamp it out. There are no recent confirmations of this phenomenon. This legend was depicted in the film '' The Gods Must Be Crazy'' (1980), which shows an African rhinoceros putting out two campfires.
In 1974 a lavender rhinoceros symbol began to be used as a symbol of the gay community in Boston.
See also
Conservation
* Bardiya National Park * Chitwan National Park * International Rhino Foundation * Kaziranga National Park * List of odd-toed ungulates by population * Nicolaas Jan van Strien *Save the Rhino
Save the Rhino International (SRI), a United Kingdom, UK-based Wildlife conservation, conservation charity, is Europe's largest single-species Rhinoceros, rhino charity, in terms of funds raised and grants made, and in terms of profile and posi ...
* TRAFFIC
Individual rhinoceroses
* Abada * Clara * List of fictional pachyderms *Rhinoceros of Versailles
The Rhinoceros of Versailles was a living Indian rhinoceros which was kept in the Palace of Versailles menagerie from 1770 until 1793.
History
The live rhinoceros was a gift from M. Chevalier, French governor of Chandernagor, to Louis XV. It l ...
Literature
* '' Rhinoceros'', 1959 playOther
* Rhinoceroses in ancient ChinaReferences
Further reading
White Rhinoceros, White Rhinoceros Profile, Facts, Information, Photos, Pictures, Sounds, Habitats, Reports, News – National Geographic
* Laufer, Berthold. 1914. "History of the Rhinoceros". In: ''Chinese Clay Figures, Part I: Prolegomena on the History of Defence Armour''. Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago, pp. 73–173. * * * Chapman, January (1999). ''The Art of Rhinoceros Horn Carving in China''. Christies Books, London. . * * * *
External links
Rhino Species
Rhino Images
page on th
Rhino Resource Center
Rhinoceros entry
on World Wide Fund for Nature website.
International Anti Poaching Foundation
Free To Use Rhino Images
Rhinoceros Resources & Photos
on African Wildlife Foundation website * UK Times article: "South African spy chief linked to rhino horn trade
South African spy chief linked to rhino horn trade
* Video on South African government minister's alleged involvement in illegal rhino horn trade
VIDEO: Rhino poacher says Mahlobo is his 'mate'
People Not Poaching: The Communities and IWT Learning Platform
{{Authority control Extant Eocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Taxa named by John Edward Gray Unicorns