|
Paraceratherium
''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinoceros. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 million years ago). The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. It is classified as a member of the family Paraceratheriidae. ''Paraceratherium'' means "near the hornless beast", in reference to ''Aceratherium'', the genus in which the type species ''P. bugtiense'' was originally placed. The exact size of ''Paraceratherium'' is unknown because of the incompleteness of the fossils. The shoulder height was about , and the length about . Its weight is estimated to have been about . The long neck supported a skull that was about long. It had large, tusk-like incisors and a nasal incision that suggests it had a prehensile upper lip or proboscis (trunk). The legs were long and pillar-like. The lifestyle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ... Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraceratheriidae
Paraceratheriidae is an extinct family of long-limbed, hornless rhinocerotoids, commonly known as paraceratheres or indricotheres, that originated in the Eocene epoch and lived until the early Miocene. The first paraceratheres were only about the size of large dogs, growing progressively larger in the late Eocene and Oligocene. They were most common in the rainforest floodplain region which is now Kazakhstan, India, and southwest China, and lived further inland throughout northern and central Asia as well. The paraceratheres reached the peak of their evolution from the middle Oligocene to the early Miocene, where they became very large, herbivorous mammals. Most genera were about the size of modern draft horses and the extinct giant horse ''Equus giganteus'', with some growing significantly larger. The largest genus was ''Paraceratherium'', which was more than twice as heavy as a bull African elephant, and was one of the largest land mammals that ever lived. However, they remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
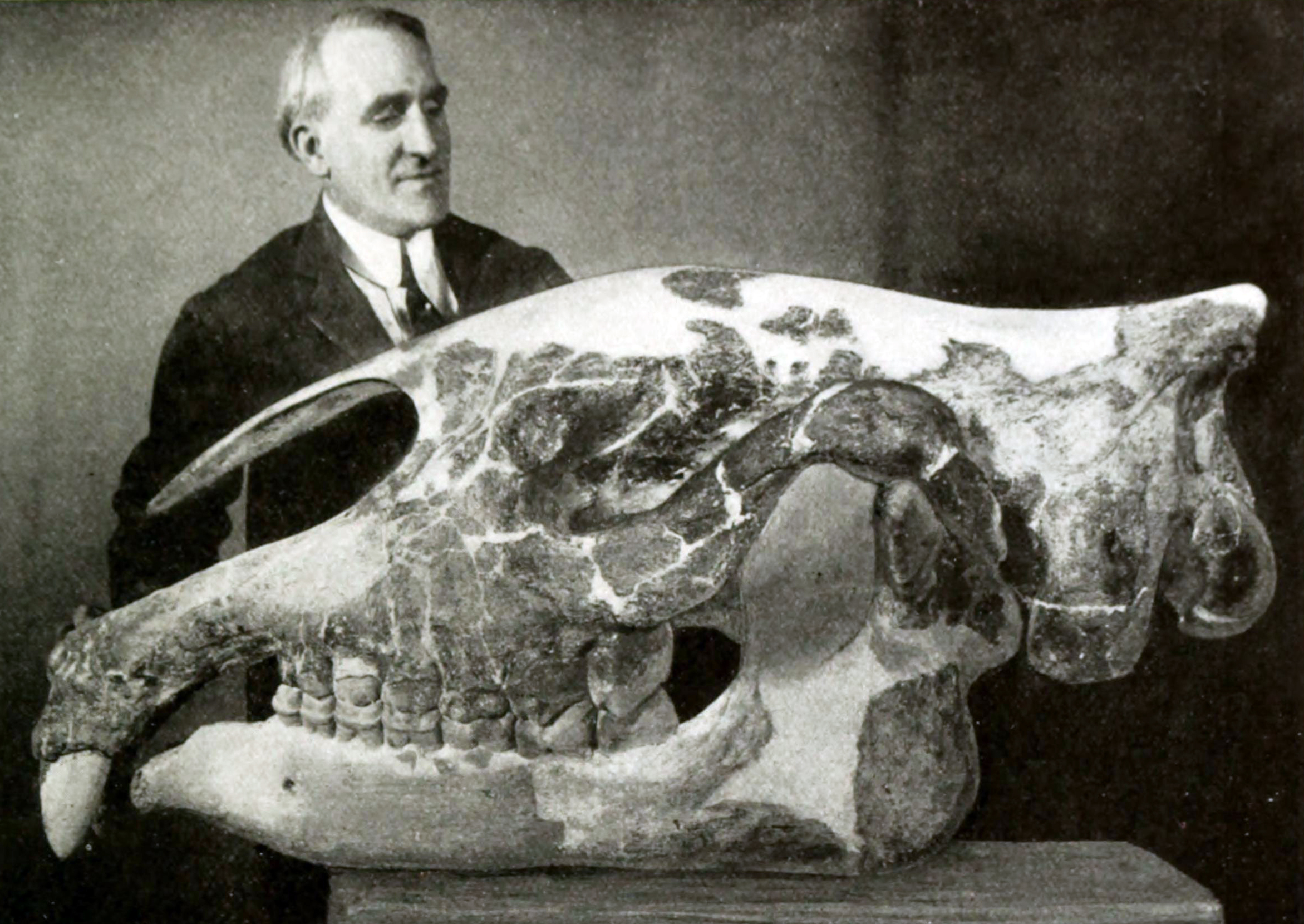
Clive Forster-Cooper
Sir Clive Forster Cooper, FRS (3 April 1880 – 23 August 1947) was an English palaeontologist and Director of the Cambridge University Museum of Zoology and Natural History Museum in London. He was the first to describe ''Paraceratherium'', also commonly known as ''Indricotherium'' or ''Baluchitherium'', the largest known land mammal. Early life He was born on 3 April 1880 in Hampstead, London, the second child and only son of John Forster Cooper and his wife Mary Emily Miley. His maternal grandfather, Miles Miley, was an amateur botanist and naturalist, and encouraged Clive Forster-Cooper in his interest in natural history. He was educated at Summer Fields School, Oxford, Rugby School.'Forster-Cooper, Sir Clive', in ''Who Was Who'' In 1897 he went up to Trinity College, Cambridge, and took a BA in 1901 and MA in 1904. Early career In 1900, Forster Cooper travelled with John Stanley Gardiner to the Maldive and Laccadive Islands to undertake collections and study the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinocerotoidea
Rhinocerotoidea is a superfamily consisting of three family groups of odd-toed ungulates, three of which, the Amynodontidae, Hyracodontidae, and Paraceratheriidae, are extinct. The only extant family group is the Rhinocerotidae (true rhinoceroses), which survives as five living species. The extinct members of this superfamily are often called "rhinoceroses" alongside members of the family Rhinocerotidae, though they include genera, such as ''Paraceratherium'', which do not closely resemble modern rhinoceroses. Taxonomy The cladogram below follows a phylogenetic analysis In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... by Bai ''et al.'' (2020): References {{Taxonbar, from=Q15487229 Odd-toed ungulates Mammal superfamilies Taxa named by John Edward Gray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Nature And Science
The is in the northeast corner of Ueno Park in Tokyo. The museum has exhibitions on pre- Meiji science in Japan. It is the venue of the taxidermied bodies of the legendary dogs Hachikō and Taro and Jiro. A life-size blue whale model and a steam locomotive are also on display outside. History Blue whale Life size model. Opened in 1871, it has had several names, including Ministry of Education Museum, Tokyo Museum, Tokyo Science Museum, the National Science Museum of Japan, and the National Museum of Nature and Science as of 2007. It was renovated in the 1990s and 2000s, and offers a wide variety of natural history exhibitions and interactive scientific experiences. It was completed as the main building of the Tokyo Science Museum in September 1931 as part of the reconstruction project after the Great Kanto Earthquake. Neo-Renaissance style. Designed by Kenzo Akitani, an engineer of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Building Division. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Pavlova
Maria Vasilievna Pavlova ( rus, Мария Васильевна Павлова; ''née'' Gortynskaia (); June 26, 1854 – December 23, 1938) was a Ukrainian who became a paleontologist and academician in Moscow during the Russian Empire and Soviet era. She is known for her research on the fossils of and the naming of hoofed-mammals of the Tertiary period. She was a professor at Moscow State University. She also made great efforts to establish the Museum of Paleontology at the university. In 1926, the museum was named after her and her second husband, Alexei Petrovich Pavlov, a geologist, paleontologist, and academician who made a significant contribution in the field of stratigraphy. Early life Maria Vasillievna Gortynskaia was born in Kozelets, Ukraine in 1854. She was schooled at home until the age of eleven in 1865. Her secondary education was at the Institute for Noble Maidens in Kiev, which she completed in 1870 at the age of sixteen. Her first marriage was to Illich-Shish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Browsing (herbivory)
Browsing is a type of herbivory in which a herbivore (or, more narrowly defined, a folivore) feeds on leaves, soft shoots, or fruits of high-growing, generally woody plants such as shrubs. This is contrasted with grazing, usually associated with animals feeding on grass or other lower vegetations. Alternatively, grazers are animals eating mainly grass, and browsers are animals eating mainly non-grasses, which include both woody and herbaceous dicots. In either case, an example of this dichotomy are goats (which are primarily browsers) and sheep (which are primarily grazers). Browse The plant material eaten is known as ''browse'' and is in nature taken directly from the plant, though owners of livestock such as goats and deer may cut twigs or branches for feeding to their stock. In temperate regions, owners take browse before leaf fall, then dry and store it as a winter feed supplement. In time of drought, herdsmen may cut branches from beyond the reach of their stock, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |