|
Elasmotherium
''Elasmotherium'' is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during Late Miocene through the Pleistocene, existing at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. A more recent date of 26,000 BP is considered less reliable. It was the last surviving member of Elasmotheriinae, a distinctive group of rhinoceroses separate from the group that contains living rhinoceros (Rhinocerotinae). The two groups are estimated to have split at least 35 million years ago according to fossils and molecular evidence. Five species are recognised. The genus first appeared in the Late Miocene in China, likely having evolved from '' Sinotherium'', before spreading to the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. The best known, ''E. sibiricum'', sometimes called the Siberian unicorn, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead (though see below). Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
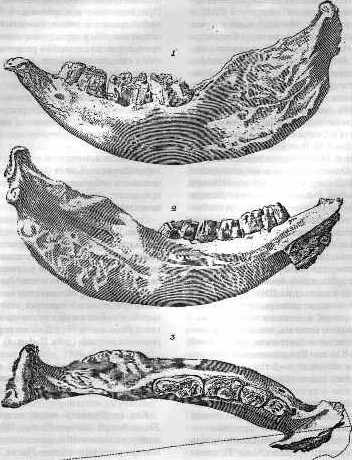
Elasmotherium Mandible
''Elasmotherium'' is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during Late Miocene through the Pleistocene, existing at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. A more recent date of 26,000 BP is considered less reliable. It was the last surviving member of Elasmotheriinae, a distinctive group of rhinoceroses separate from the group that contains living rhinoceros (Rhinocerotinae). The two groups are estimated to have split at least 35 million years ago according to fossils and molecular evidence. Five species are recognised. The genus first appeared in the Late Miocene in China, likely having evolved from '' Sinotherium'', before spreading to the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Caucasus and Central Asia. The best known, ''E. sibiricum'', sometimes called the Siberian unicorn, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead (though see below). Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinotherium
''Sinotherium'' (" Chinese Beast") is a genus of single-horned elasmotheriine rhinoceros that lived from the late Miocene (Tortonian - Messinian) to Early Pliocene. It was ancestral to ''Elasmotherium,'' demonstrating a very important evolutionary transition from nasal-horned elasmotheriines to frontal-horned elasmotheriines. Its fossils have been found in the Karabulak Formation of Kazakhstan, lower jaw and teeth have been found in Mongolia, and a partial skull is known from the upper part of the Liushu Formation of western China. ''Sinotherium'' diverged from the ancestral genus, '' Iranotherium'', first found in Iran, during the early Pliocene. Some experts prefer to lump ''Sinotherium'', and '' Iranotherium'' into ''Elasmotherium''. Discovery, History and Taxonomy Species The type species of ''Sinotherium'' is ''S. lagrelii''. It is also known to have an additional species from the Zaisan depression of Kazakhstan called ''S. zaisanensis'', however, doubt has been raised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family (biology), family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South Asia, South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivore, herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a crystal structure, lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their colon (anatomy), hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azov Museum Of History, Archaeology And Palaeontology
The Azov Museum of History, Archaeology and Palaeontology (russian: Азовский историко-археологический и палеонтологический музей-заповедник) in Azov, Rostov oblast, is one of the largest museums in the south of Russia, particularly notable for its palaeontological collection. History The museum was first opened on 17 May 1917 by the efforts of Mikhail Aronovich Makarovskiy and the town's civic society, and displayed small items given by the local population (old coins, postage stamps, bullets and so on), but was destroyed shortly afterwards in the Russian Revolution. It was reopened in 1937 but the collections were lost during the occupation by German troops in World War II. After the war the local people tried to revive the museum, but to do so took until 1960. The museum occupies the premises of the old town hall. It also administers the Powder Cellar Museum. Exhibits The palaeontological collection is of par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notoungulata
Notoungulata is an extinct order of mammalian ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the Holocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resembling animals as disparate as rabbits and rhinoceroses. Notoungulata are the largest group of South American native ungulates, with over 150 genera in 14 families having been described, divided into two major subgroupings, Typotheria and Toxodontia. Notoungulates first diversified during the Eocene. Their diversity declined during the Late Neogene, with only the large toxodontids persisting until the end of the Pleistocene. Collagen analysis suggests that notoungulates are closely related to litopterns, another group of South American ungulates, and their closest living relatives being perissodactyls (odd-toed ungulates), including rhinoceroses, tapirs and equines. but their relationships to other South American ungulates are uncert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar Tooth
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called '' gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow University
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU; russian: Московский государственный университет имени М. В. Ломоносова) is a public research university in Moscow, Russia and the most prestigious university in the country. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches (including five foreign ones in the Commonwealth of Independent States countries). Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner had been affiliated with the university. The university was ranked 18th by ''The Three University Missions Ranking'' in 2022, and 76th by the ''QS World University Rankings'' in 2022, #293 in the world by the global ''Times Higher World University Rankings'', and #326 by ''U.S. News & World Report'' in 2022. It was the highest-ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Society Of Naturalists
Moscow Society of Naturalists (russian: Московское общество испытателей природы (MOIP)) is one of Russia's oldest learned societies. In 1805 it was founded as the Imperial Society of Naturalists of Moscow (''Société Impériale des Naturalistes de Moscou'') under the auspices of two noblemen, Mikhail Muravyov and Alexis Razumovsky, by Johann Fischer von Waldheim in 1805. Princess Zenaǐde Wolkonsky made a gift of her own library to the society.'' Ю. В. Чайковский''Старейшее общество и его библиотека.Москва научная. — М.: Янус-К, 1997. — С. 392—415. It was organised under the auspices of the Moscow State University (MSU) and included many members of the university staff amongst its members. The tasks of the society were considered to be the development of general scientific problems of natural science, the study of the natural resources of Russia, including "the discovery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekaterina Dashkova
Yekaterina Romanovna Vorontsova (russian: Екатери́на Рома́новна Воронцо́ва) (28 March, 1743 – 15 January, 1810) This source reports that Prince Dashkov died in 1761. was an influential noblewoman, a major figure of the Russian Enlightenment and a close friend of Empress Catherine the Great. She was part of the ''coup d'état'' that placed Catherine on the throne, the first woman in the world to head a national academy of sciences, the first woman in Europe to hold a government office and the president of the Russian Academy, which she helped found. She also published prolifically, with original and translated works on many subjects, and was invited by Benjamin Franklin to become the first female member of the American Philosophical Society. Early life and education Born Countess Yekaterina Romanovna Vorontsova, she was the daughter of Count Roman Vorontsov, a member of the Senate, and his wife Marfa Surmina. Her uncle Mikhail Illarionovich and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |