photosynthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Photosynthesis is a process used by
Photosynthesis is a process used by
 Most photosynthetic organisms are
Most photosynthetic organisms are
 In photosynthetic bacteria, the proteins that gather light for photosynthesis are embedded in
In photosynthetic bacteria, the proteins that gather light for photosynthesis are embedded in
 In the
In the
 In plants,
In plants,

 In hot and dry conditions, plants close their
In hot and dry conditions, plants close their
 Several groups of animals have formed
Several groups of animals have formed
 Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-17th century when he carefully measured the
Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-17th century when he carefully measured the
 There are three main factors affecting photosynthesis and several corollary factors. The three main are:
* Light
There are three main factors affecting photosynthesis and several corollary factors. The three main are:
* Light
 The process of photosynthesis provides the main input of free energy into the biosphere, and is one of four main ways in which radiation is important for plant life.
The radiation climate within plant communities is extremely variable, in both time and space.
In the early 20th century,
The process of photosynthesis provides the main input of free energy into the biosphere, and is one of four main ways in which radiation is important for plant life.
The radiation climate within plant communities is extremely variable, in both time and space.
In the early 20th century,
 As carbon dioxide concentrations rise, the rate at which sugars are made by the light-independent reactions increases until limited by other factors.
As carbon dioxide concentrations rise, the rate at which sugars are made by the light-independent reactions increases until limited by other factors.
A collection of photosynthesis pages for all levels from a renowned expert (Govindjee)
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20090428090455/http://scienceaid.co.uk/biology/biochemistry/photosynthesis.html Science Aid: PhotosynthesisArticle appropriate for high school science
Metabolism, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis – The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
* ttp://www.life.uiuc.edu/govindjee/photosynBook.html Overall Energetics of Photosynthesis
The source of oxygen produced by photosynthesis
Interactive animation, a textbook tutorial *
Photosynthesis – Light Dependent & Light Independent Stages
Khan Academy, video introduction
{{Authority control Agronomy Biological processes Botany Cellular respiration Ecosystems Metabolism Plant nutrition Plant physiology Quantum biology
 Photosynthesis is a process used by
Photosynthesis is a process used by plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s and other organisms
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fungi; ...
to convert
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* "Conversion" (''Stargate Atlantis''), an episode of the television series
* "The Conversion" ...
light energy
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahe ...
into chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
that, through cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
molecules, such as sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
s and starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
es, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a ...
– hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs Photoautotrophs are organisms that use light energy and inorganic carbon to produce organic materials. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb energy through the chlorophyll molecules in their chloroplasts while prokaryotic photoautotrophs use chlorophyll ...
. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.
Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s called reaction center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or t ...
s that contain green chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
(and other colored) pigments/chromophores. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s called chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
s from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. The hydrogen freed by the splitting of water is used in the creation of two further compounds that serve as short-term stores of energy, enabling its transfer to drive other reactions: these compounds are reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid synth ...
(NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of ...
(ATP), the "energy currency" of cells.
In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are synthesized by a subsequent sequence of reactions called the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) is an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis, notably as the principal acceptor in plants. It is a colourless anion, a double phosphate ester of the ketopentose (ketone-containing sugar with five car ...
(RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
. In other bacteria, different mechanisms such as the reverse Krebs cycle
The reverse Krebs cycle (also known as the reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle, the reverse TCA cycle, or the reverse citric acid cycle, or the reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle, or the reductive TCA cycle)
is a sequence of chemical reactions that ...
are used to achieve the same end.
The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
early in the evolutionary history of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest #Origins of life on Earth, emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', fo ...
and most likely used reducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are commonly reducing agents include the Earth meta ...
s such as hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
or hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
, rather than water, as sources of electrons. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed directly to the oxygenation of the Earth, which rendered the evolution of complex life
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni ...
possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt ...
, which is about eight times the current power consumption of human civilization
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food.
This art ...
. Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 billion ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
s (91–104 Pg petagrams, or billion metric tons), of carbon into biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
per year. That plants receive some energy from light – in addition to air, soil, and water – was first discovered in 1779 by Jan Ingenhousz
Jan (or John) Ingenhousz or Ingen-Housz FRS (8 December 1730 – 7 September 1799) was a Dutch-born British physiologist, biologist and chemist.
He is best known for discovering photosynthesis by showing that light is essential to the process ...
.
Photosynthesis is vital for climate processes, as it captures carbon dioxide from the air and then binds carbon in plants and further in soils and harvested products. Cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s alone are estimated to bind 3,825 Tg (teragrams) or 3.825 Pg (petagrams) of carbon dioxide every year, i.e. 3.825 billion metric tons.
Overview
photoautotroph Photoautotrophs are organisms that use light energy and inorganic carbon to produce organic materials. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb energy through the chlorophyll molecules in their chloroplasts while prokaryotic photoautotrophs use chlorophyll ...
s, which means that they are able to synthesize food directly from carbon dioxide and water using energy from light. However, not all organisms use carbon dioxide as a source of carbon atoms to carry out photosynthesis; photoheterotroph
Photoheterotrophs ('' Gk'': ''photo'' = light, ''hetero'' = (an)other, ''troph'' = nourishment) are heterotrophic phototrophs – that is, they are organisms that use light for energy, but cannot use carbon dioxide as their sole carbon source. Cons ...
s use organic compounds, rather than carbon dioxide, as a source of carbon. In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, photosynthesis releases oxygen. This oxygenic photosynthesis is by far the most common type of photosynthesis used by living organisms. Although there are some differences between oxygenic photosynthesis in plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
, algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, the overall process is quite similar in these organisms. There are also many varieties of anoxygenic photosynthesis
Bacterial anoxygenic photosynthesis differs from the better known oxygenic photosynthesis in plants by the reductant used (e.g. hydrogen sulfide instead of water) and the byproduct generated (e.g. elemental sulfur instead of molecular oxygen).
Ba ...
, used mostly by bacteria, which consume carbon dioxide but do not release oxygen.
Carbon dioxide is converted into sugars in a process called carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
; photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s. Carbon fixation is an endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. p. ...
redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
reaction. In general outline, photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
: while photosynthesis is a process of reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates, cellular respiration is the oxidation of carbohydrates or other nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s to carbon dioxide. Nutrients used in cellular respiration include carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids. These nutrients are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide and water, and to release chemical energy to drive the organism's metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are distinct processes, as they take place through different sequences of chemical reactions and in different cellular compartment
Cellular compartments in cell biology comprise all of the closed parts within the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell, usually surrounded by a single or double lipid layer membrane. These compartments are often, but not always, defined as membrane-bo ...
s.
The general equation
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in ...
for photosynthesis as first proposed by Cornelis van Niel is:
: + + → + +
Since water is used as the electron donor in oxygenic photosynthesis, the equation for this process is:
: + + → + +
This equation emphasizes that water is both a reactant in the light-dependent reaction
Light-dependent reactions is jargon for certain photochemical reactions that are involved in photosynthesis, the main process by which plants acquire energy. There are two light dependent reactions, the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and ...
and a product of the light-independent reaction
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
, but canceling ''n'' water molecules from each side gives the net equation:
: + + → +
Other processes substitute other compounds (such as arsenite
In chemistry, an arsenite is a chemical compound containing an arsenic oxyanion where arsenic has oxidation state +3. Note that in fields that commonly deal with groundwater chemistry, arsenite is used generically to identify soluble AsIII anions. ...
) for water in the electron-supply role; for example some microbes use sunlight to oxidize arsenite to arsenate
The arsenate ion is .
An arsenate (compound) is any compound that contains this ion. Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid.
The arsenic atom in arsenate has a valency of 5 and is also known as pentavalent arsenic or As(V).
Arsenate resem ...
: The equation for this reaction is:
: + + → + (used to build other compounds in subsequent reactions)
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first stage, ''light-dependent reactions'' or ''light reactions'' capture the energy of light and use it to make the hydrogen carrier NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
and the energy-storage molecule ATP. During the second stage, the ''light-independent reactions'' use these products to capture and reduce carbon dioxide.
Most organisms that use oxygenic photosynthesis use visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
for the light-dependent reactions, although at least three use shortwave infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
or, more specifically, far-red radiation.
Some organisms employ even more radical variants of photosynthesis. Some archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
use a simpler method that employs a pigment similar to those used for vision in animals. The bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin is a protein used by Archaea, most notably by haloarchaea, a class of the Euryarchaeota. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move protons across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting ...
changes its configuration in response to sunlight, acting as a proton pump. This produces a proton gradient more directly, which is then converted to chemical energy. The process does not involve carbon dioxide fixation and does not release oxygen, and seems to have evolved separately from the more common types of photosynthesis.
Photosynthetic membranes and organelles
cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s. In its simplest form, this involves the membrane surrounding the cell itself. However, the membrane may be tightly folded into cylindrical sheets called thylakoid
Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thyl ...
s, or bunched up into round vesicles
Vesicle may refer to:
; In cellular biology or chemistry
* Vesicle (biology and chemistry), a supramolecular assembly of lipid molecules, like a cell membrane
* Synaptic vesicle
; In human embryology
* Vesicle (embryology), bulge-like features o ...
called ''intracytoplasmic membranes''. These structures can fill most of the interior of a cell, giving the membrane a very large surface area and therefore increasing the amount of light that the bacteria can absorb.
In plants and algae, photosynthesis takes place in organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the ...
s called chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s. A typical plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capabi ...
contains about 10 to 100 chloroplasts. The chloroplast is enclosed by a membrane. This membrane is composed of a phospholipid inner membrane, a phospholipid outer membrane, and an intermembrane space. Enclosed by the membrane is an aqueous fluid called the stroma. Embedded within the stroma are stacks of thylakoids (grana), which are the site of photosynthesis. The thylakoids appear as flattened disks. The thylakoid itself is enclosed by the thylakoid membrane, and within the enclosed volume is a lumen or thylakoid space. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are integral and peripheral membrane protein
Peripheral membrane proteins, or extrinsic membrane proteins, are membrane proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. These proteins attach to integral membrane proteins, or penetrate the periph ...
complexes of the photosynthetic system.
Plants absorb light primarily using the pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compo ...
chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
. The green part of the light spectrum is not absorbed but is reflected which is the reason that most plants have a green color. Besides chlorophyll, plants also use pigments such as carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the exc ...
s and xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek (, "yellow") and (, "l ...
s. Algae also use chlorophyll, but various other pigments are present, such as phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist wi ...
, carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the exc ...
s, and xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek (, "yellow") and (, "l ...
s in green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
, phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin (PE) is a red protein-pigment complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and cryptophytes, accessory to the main chlorophyll pigments responsible for photosynthesis.The red pigmen ...
in red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority ...
(rhodophytes) and fucoxanthin
Fucoxanthin is a xanthophyll, with formula C42H58O6. It is found as an accessory pigment in the chloroplasts of brown algae and most other heterokonts, giving them a brown or olive-green color. Fucoxanthin absorbs light primarily in the blue-green ...
in brown algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and po ...
and diatoms
A diatom (New Latin, Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group com ...
resulting in a wide variety of colors.
These pigments are embedded in plants and algae in complexes called antenna proteins. In such proteins, the pigments are arranged to work together. Such a combination of proteins is also called a light-harvesting complex
A light-harvesting complex consists of a number of chromophores which are complex subunit proteins that may be part of a larger super complex of a photosystem, the functional unit in photosynthesis. It is used by plants and photosynthetic bacteria ...
.
Although all cells in the green parts of a plant have chloroplasts, the majority of those are found in specially adapted structures called leaves
A leaf (plural, : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant plant stem, stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", wh ...
. Certain species adapted to conditions of strong sunlight and arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
ity, such as many ''Euphorbia
''Euphorbia'' is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae. "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae (in deference to t ...
'' and cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek ...
species, have their main photosynthetic organs in their stems. The cells in the interior tissues of a leaf, called the mesophyll
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, ste ...
, can contain between 450,000 and 800,000 chloroplasts for every square millimeter of leaf. The surface of the leaf is coated with a water-resistant wax
Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low ...
y cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
that protects the leaf from excessive evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
of water and decreases the absorption of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
or blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when obs ...
light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
to minimize heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is al ...
ing. The transparent epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rele ...
layer allows light to pass through to the palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a fence or defensive wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks, and used as a defensive structure or enclosure. Palisades can form a stockade.
Etymology
''Palisade' ...
mesophyll cells where most of the photosynthesis takes place.
Light-dependent reactions
light-dependent reactions
Light-dependent reactions is jargon for certain photochemical reactions that are involved in photosynthesis, the main process by which plants acquire energy. There are two light dependent reactions, the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and ...
, one molecule of the pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compo ...
chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
absorbs one photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
and loses one electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
. This electron is taken up by a modified form of chlorophyll called pheophytin
Pheophytin or phaeophytin is a chemical compound that serves as the first electron carrier intermediate in the electron transfer pathway of Photosystem II (PS II) in plants, and the type II photosynthetic reaction center (RC P870) found in purpl ...
, which passes the electron to a quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds
molecule, starting the flow of electrons down an uch as benzene or naphthalene
Uch ( pa, ;
ur, ), frequently referred to as Uch Sharīf ( pa, ;
ur, ; ''"Noble Uch"''), is a historic city in the southern part of Pakistan's Punjab province. Uch may have been founded as Alexandria on the Indus, a town founded by Alexand ...
by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double ...electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
that leads to the ultimate reduction of NADP
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
to NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
. In addition, this creates a proton gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and th ...
(energy gradient) across the chloroplast membrane
Chloroplasts contain several important membranes, vital for their function. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have a double-membrane envelope, called the chloroplast envelope, but unlike mitochondria, chloroplasts also have internal membrane structu ...
, which is used by ATP synthase
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation ...
in the synthesis of ATP. The chlorophyll molecule ultimately regains the electron it lost when a water molecule is split in a process called photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. ...
, which releases oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
.
The overall equation for the light-dependent reactions under the conditions of non-cyclic electron flow in green plants is:
Not all wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
s of light can support photosynthesis. The photosynthetic action spectrum depends on the type of accessory pigment Accessory pigments are light-absorbing compounds, found in photosynthetic organisms, that work in conjunction with chlorophyll ''a''. They include other forms of this pigment, such as chlorophyll ''b'' in green algal and higher plant antennae, wh ...
s present. For example, in green plants, the action spectrum
An action spectrum is a graph of the rate of biological effectiveness plotted against wavelength of light. It is related to absorption spectrum in many systems. Mathematically, it describes the inverse quantity of light required to evoke a const ...
resembles the absorption spectrum
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating f ...
for chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
s and carotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpki ...
s with absorption peaks in violet-blue and red light. In red algae, the action spectrum is blue-green light, which allows these algae to use the blue end of the spectrum to grow in the deeper waters that filter out the longer wavelengths (red light) used by above-ground green plants. The non-absorbed part of the light spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequency, frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energy, photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with f ...
is what gives photosynthetic organisms their color (e.g., green plants, red algae, purple bacteria) and is the least effective for photosynthesis in the respective organisms.
Z scheme
 In plants,
In plants, light-dependent reaction
Light-dependent reactions is jargon for certain photochemical reactions that are involved in photosynthesis, the main process by which plants acquire energy. There are two light dependent reactions, the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and ...
s occur in the thylakoid membrane
Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thyl ...
s of the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s where they drive the synthesis of ATP and NADPH. The light-dependent reactions are of two forms: cyclic and non-cyclic.
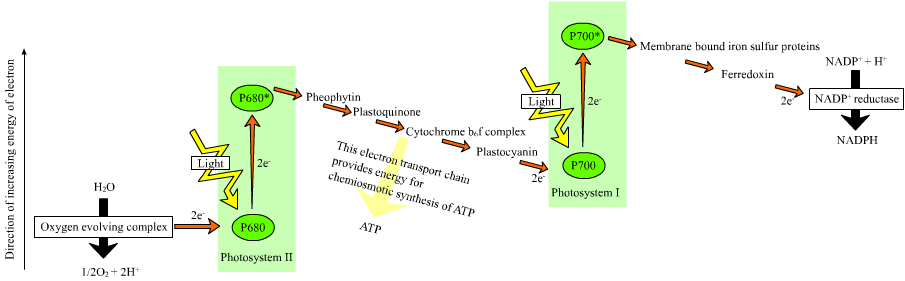
In the non-cyclic reaction, the photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
s are captured in the light-harvesting antenna complex
The light-harvesting complex (or antenna complex; LH or LHC) is an array of protein and chlorophyll molecules embedded in the thylakoid membrane of plants and cyanobacteria, which transfer light energy to one chlorophyll ''a'' molecule at the Phot ...
es of photosystem II
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem ...
by chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
and other accessory pigments Accessory pigments are light-absorbing compounds, found in photosynthetic organisms, that work in conjunction with chlorophyll ''a''. They include other forms of this pigment, such as chlorophyll ''b'' in green algal and higher plant antennae, w ...
(see diagram at right). The absorption of a photon by the antenna complex loosens an electron by a process called photoinduced charge separation
Photoinduced charge separation is the process of an electron in an atom or molecule, being excited to a higher energy level by the absorption of a photon and then leaving the atom or molecule to a nearby electron acceptor.
Rutherford model
An atom ...
. The antenna system is at the core of the chlorophyll molecule of the photosystem II reaction center. That loosened electron is taken up by the primary electron-acceptor molecule, pheophytin. As the electrons are shuttled through an electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
(the so-called ''Z-scheme'' shown in the diagram), a chemiosmotic potential
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and th ...
is generated by pumping proton cations (H+) across the membrane and into the thylakoid space. An ATP synthase
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation ...
enzyme uses that chemiosmotic potential to make ATP during photophosphorylation In the process of photosynthesis, the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation. Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, driven by the main primary source of ...
, whereas NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
is a product of the terminal redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
reaction in the ''Z-scheme''. The electron enters a chlorophyll molecule in Photosystem I
Photosystem I (PSI, or plastocyanin–ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses ...
. There it is further excited by the light absorbed by that photosystem
Photosystems are functional and structural units of protein complexes involved in photosynthesis. Together they carry out the primary photochemistry of photosynthesis: the absorption of light and the transfer of energy and electrons. Photosystems ...
. The electron is then passed along a chain of electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process. Electron acceptors are sometimes mista ...
s to which it transfers some of its energy. The energy delivered to the electron acceptors is used to move hydrogen ions across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen. The electron is eventually used to reduce the co-enzyme NADP with a H+ to NADPH (which has functions in the light-independent reaction); at that point, the path of that electron ends.
The cyclic reaction is similar to that of the non-cyclic but differs in that it generates only ATP, and no reduced NADP (NADPH) is created. The cyclic reaction takes place only at photosystem I. Once the electron is displaced from the photosystem, the electron is passed down the electron acceptor molecules and returns to photosystem I, from where it was emitted, hence the name ''cyclic reaction''.
Water photolysis
Linear electron transport through a photosystem will leave the reaction center of that photosystem oxidized. Elevating another electron will first require re-reduction of the reaction center. The excited electrons lost from the reaction center (P700) ofphotosystem I
Photosystem I (PSI, or plastocyanin–ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses ...
are replaced by transfer from plastocyanin
Plastocyanin is a copper-containing protein that mediates electron-transfer. It is found in a variety of plants, where it participates in photosynthesis. The protein is a prototype of the blue copper proteins, a family of intensely blue-colored m ...
, whose electrons come from electron transport through photosystem II
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem ...
. Photosystem II, as the first step of the ''Z-scheme'', requires an external source of electrons to reduce its oxidized chlorophyll ''a'' reaction center. The source of electrons for photosynthesis in green plants and cyanobacteria is water. Two water molecules are oxidized by the energy of four successive charge-separation reactions of photosystem II to yield a molecule of diatomic oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
and four hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
ions. The electrons yielded are transferred to a redox-active tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
residue that is oxidized by the energy of P680. This resets the ability of P680 to absorb another photon and release another photo-dissociated electron. The oxidation of water is catalyzed
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
in photosystem II by a redox-active structure that contains four manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
ions and a calcium ion; this oxygen-evolving complex
The oxygen-evolving complex (OEC), also known as the water-splitting complex, is the portion of photosystem II where photo-oxidation of water occurs during the light reactions of photosynthesis. The OEC is surrounded by four core protein subuni ...
binds two water molecules and contains the four oxidizing equivalents that are used to drive the water-oxidizing reaction (Kok's S-state diagrams). The hydrogen ions are released in the thylakoid lumen and therefore contribute to the transmembrane chemiosmotic potential that leads to ATP synthesis. Oxygen is a waste product of light-dependent reactions, but the majority of organisms on Earth use oxygen and its energy for cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
, including photosynthetic organisms.
Light-independent reactions
Calvin cycle
In the light-independent (or "dark") reactions, theenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
RuBisCO
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is con ...
captures CO2 from the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
and, in a process called the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
, uses the newly formed NADPH and releases three-carbon sugars, which are later combined to form sucrose and starch. The overall equation for the light-independent reactions in green plants is
Carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
produces the three-carbon sugar intermediate, which is then converted into the final carbohydrate products. The simple carbon sugars produced by photosynthesis are then used to form other organic compounds, such as the building material cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, the precursors for lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
and amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
biosynthesis, or as a fuel in cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
. The latter occurs not only in plants but also in animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s when the carbon and energy from plants is passed through a food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), det ...
.
The fixation or reduction of carbon dioxide is a process in which carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
combines with a five-carbon sugar, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) is an organic substance that is involved in photosynthesis, notably as the principal acceptor in plants. It is a colourless anion, a double phosphate ester of the ketopentose (ketone-containing sugar with five car ...
, to yield two molecules of a three-carbon compound, glycerate 3-phosphate
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. Th ...
, also known as 3-phosphoglycerate. Glycerate 3-phosphate, in the presence of ATP and NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
produced during the light-dependent stages, is reduced to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, also known as triose phosphate or 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and abbreviated as G3P, GA3P, GADP, GAP, TP, GALP or PGAL, is a metabolite that occurs as an intermediate in several central pathways of all organisms.Nelson, D ...
. This product is also referred to as 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, also known as triose phosphate or 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and abbreviated as G3P, GA3P, GADP, GAP, TP, GALP or PGAL, is a metabolite that occurs as an intermediate in several central pathways of all organisms.Nelson, D ...
) or, more generically, as triose
A triose is a monosaccharide, or simple sugar, containing three carbon atoms. There are only three possible trioses (including dihydroxyacetone): L-glyceraldehyde and D-glyceraldehyde, the two enantiomers of glyceraldehyde, which are aldotriose ...
phosphate. Most (5 out of 6 molecules) of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate produced are used to regenerate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate so the process can continue. The triose phosphates not thus "recycled" often condense to form hexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
phosphates, which ultimately yield sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
and cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
. The sugars produced during carbon metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
yield carbon skeletons that can be used for other metabolic reactions like the production of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
.
Carbon concentrating mechanisms
On land
stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
to prevent water loss. Under these conditions, will decrease and oxygen gas, produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis, will increase, causing an increase of photorespiration
Photorespiration (also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle or C2 cycle) refers to a process in plant metabolism where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP, wasting some of the energy produced by photosynthesis. The desired reaction i ...
by the oxygenase
An oxygenase is any enzyme that oxidizes a substrate by transferring the oxygen from molecular oxygen O2 (as in air) to it. The oxygenases form a class of oxidoreductases; their EC number is EC 1.13 or EC 1.14.
Discoverers
Oxygenases were disco ...
activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is co ...
and decrease in carbon fixation. Some plants have evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
mechanisms to increase the concentration in the leaves under these conditions.
Plants that use the C4 carbon fixation process chemically fix carbon dioxide in the cells of the mesophyll by adding it to the three-carbon molecule phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate (2-phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP) is the ester derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate. It exists as an anion. PEP is an important intermediate in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found (−61.9 kJ/ ...
(PEP), a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme called PEP carboxylase PEP carboxylase may refer to:
* Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (also known as PEP carboxylase, PEPCase, or PEPC; , PDB ID: 3ZGE) is an enzyme in the family of carboxy-lyases found in plants and some bacteria that ...
, creating the four-carbon organic acid oxaloacetic acid
Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes ...
. Oxaloacetic acid or malate
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms (L ...
synthesized by this process is then translocated to specialized bundle sheath
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will inclu ...
cells where the enzyme RuBisCO
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is con ...
and other Calvin cycle enzymes are located, and where released by decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is t ...
of the four-carbon acids is then fixed by RuBisCO activity to the three-carbon 3-phosphoglyceric acid
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. The ...
s. The physical separation of RuBisCO from the oxygen-generating light reactions reduces photorespiration and increases fixation and, thus, the photosynthetic capacity
Photosynthetic capacity (Amax) is a measure of the maximum rate at which leaves are able to fix carbon during photosynthesis. It is typically measured as the amount of carbon dioxide that is fixed per metre squared per second, for example as μmo ...
of the leaf. plants can produce more sugar than plants in conditions of high light and temperature. Many important crop plants are plants, including maize, sorghum, sugarcane, and millet. Plants that do not use PEP-carboxylase in carbon fixation are called C3 plants because the primary carboxylation reaction, catalyzed by RuBisCO, produces the three-carbon 3-phosphoglyceric acids directly in the Calvin-Benson cycle. Over 90% of plants use carbon fixation, compared to 3% that use carbon fixation; however, the evolution of in over 60 plant lineages makes it a striking example of convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
. C2 photosynthesis, which involves carbon-concentration by selective breakdown of photorespiratory glycine, is both an evolutionary precursor to and a useful CCM in its own right.
Xerophytes
A xerophyte (from Greek ξηρός ''xeros'' 'dry' + φυτόν ''phuton'' 'plant') is a species of plant that has adaptations to survive in an environment with little liquid water, such as a desert such as the Sahara or places in the Alps or the ...
, such as cacti
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek ...
and most succulents
In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word ''succulent'' comes from the Latin word ''sucus'', meani ...
, also use PEP carboxylase to capture carbon dioxide in a process called Crassulacean acid metabolism
Crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as CAM photosynthesis, is a carbon fixation pathway that evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions that allows a plant to photosynthesize during the day, but only exchange gases at night. ...
(CAM). In contrast to metabolism, which ''spatially'' separates the fixation to PEP from the Calvin cycle, CAM ''temporally'' separates these two processes. CAM plants have a different leaf anatomy from plants, and fix the at night, when their stomata are open. CAM plants store the mostly in the form of malic acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms ...
via carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate (2-phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP) is the ester derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate. It exists as an anion. PEP is an important intermediate in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found (−61.9 kJ/ ...
to oxaloacetate, which is then reduced to malate. Decarboxylation of malate during the day releases inside the leaves, thus allowing carbon fixation to 3-phosphoglycerate by RuBisCO. CAM is used by 16,000 species of plants.
Calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate ...
accumulating plants, such as ''Amaranthus hybridus
''Amaranthus hybridus'', commonly called green amaranth, slim amaranth, smooth amaranth, smooth pigweed, or red amaranth, is a species of annual flowering plant. It is a weedy species found now over much of North America and introduced into Europ ...
'' and ''Colobanthus quitensis
''Colobanthus quitensis'', the Antarctic pearlwort, is one of two native flowering plants found in the Antarctic region. It has yellow flowers and grows about 5 cm (two inches) tall, with a cushion-like growth habit that gives it a moss-like appe ...
,'' show a variation of photosynthesis where calcium oxalate crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
function as dynamic carbon pools, supplying carbon dioxide ( CO2) to photosynthetic cells when stoma
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bor ...
ta are partially or totally closed. This process was named Alarm photosynthesis Alarm photosynthesis is a variation of photosynthesis where calcium oxalate Druse (botany), crystals function as dynamic carbon pools, supplying carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide, CO2) to photosynthetic cells when Stoma, stomata are partially or totall ...
. Under stress conditions (e.g. water deficit) oxalate released from calcium oxalate crystals is converted to CO2 by an oxalate oxidase
In enzymology, an oxalate oxidase () is an oxalate degrading enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
:oxalate + O2 + 2 H+ \rightleftharpoons 2 CO2 + H2O2
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are oxalate, O2, and H+, whereas its two products a ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
and the produced CO2 can support the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
reactions. Reactive hydrogen peroxide ( H2O2), the byproduct of oxalate oxidase reaction, can be neutralized by catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
. Alarm photosynthesis represents a photosynthetic variant to be added to the well-known C4 and CAM
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the bind ...
pathways. However, alarm photosynthesis, in contrast to these pathways, operates as a biochemical pump that collects carbon from the organ interior (or from the soil) and not from the atmosphere.
In water
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
possess carboxysome
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) consisting of polyhedral protein shells filled with the enzymes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO)—the predominant enzyme in carbon fixation and the rate limiting e ...
s, which increase the concentration of around RuBisCO to increase the rate of photosynthesis. An enzyme, carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate and hydrogen ions). The active site ...
, located within the carboxysome releases CO2 from dissolved hydrocarbonate ions (HCO). Before the CO2 diffuses out it is quickly sponged up by RuBisCO, which is concentrated within the carboxysomes. HCO ions are made from CO2 outside the cell by another carbonic anhydrase and are actively pumped into the cell by a membrane protein. They cannot cross the membrane as they are charged, and within the cytosol they turn back into CO2 very slowly without the help of carbonic anhydrase. This causes the HCO ions to accumulate within the cell from where they diffuse into the carboxysomes. Pyrenoid
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Bio ...
s in algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
and hornwort
Hornworts are a group of non-vascular Embryophytes (land plants) constituting the division Anthocerotophyta (). The common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte. As in mosses and liverworts, hornworts have a ...
s also act to concentrate around RuBisCO.
Order and kinetics
The overall process of photosynthesis takes place in four stages:Efficiency
Plants usually convert light intochemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
with a photosynthetic efficiency The photosynthetic efficiency is the fraction of light energy converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis in green plants and algae. Photosynthesis can be described by the simplified chemical reaction
:6 H2O + 6 CO2 + energy → C6H12O6 + ...
of 3–6%.
Absorbed light that is unconverted is dissipated primarily as heat, with a small fraction (1–2%) re-emitted as chlorophyll fluorescence
Chlorophyll fluorescence is light re-emitted by chlorophyll molecules during return from excited to non-excited states. It is used as an indicator of photosynthetic energy conversion in plants, algae and bacteria. Excited chlorophyll dissipates ...
at longer (redder) wavelengths. This fact allows measurement of the light reaction of photosynthesis by using chlorophyll fluorometers.
Actual plants' photosynthetic efficiency varies with the frequency of the light being converted, light intensity, temperature and proportion of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and can vary from 0.1% to 8%. By comparison, solar panels
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a phot ...
convert light into electric energy
Electrical energy is energy related to forces on electrically charged particles and the movement of electrically charged particles (often electrons in wires, but not always). This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electr ...
at an efficiency of approximately 6–20% for mass-produced panels, and above 40% in laboratory devices.
Scientists are studying photosynthesis in hopes of developing plants with increased yield.
The efficiency of both light and dark reactions can be measured but the relationship between the two can be complex. For example, the ATP and NADPH energy molecules, created by the light reaction, can be used for carbon fixation or for photorespiration in C3 plants. Electrons may also flow to other electron sinks. For this reason, it is not uncommon for authors to differentiate between work done under non-photorespiratory conditions and under photorespiratory conditions.
Chlorophyll fluorescence of photosystem II can measure the light reaction, and infrared gas analyzers can measure the dark reaction. It is also possible to investigate both at the same time using an integrated chlorophyll fluorometer and gas exchange system, or by using two separate systems together. Infrared gas analyzers and some moisture sensors are sensitive enough to measure the photosynthetic assimilation of CO2, and of ΔH2O using reliable methods CO2 is commonly measured in μmols/(m2/s), parts per million or volume per million and H2O is commonly measured in mmol/(m2/s) or in mbars. By measuring CO2 assimilation, ΔH2O, leaf temperature, barometric pressure, leaf area, and photosynthetically active radiation or PAR, it becomes possible to estimate, "A" or carbon assimilation, "E" or transpiration, "gs" or stomatal conductance, and Ci or intracellular CO2. However, it is more common to used chlorophyll fluorescence for plant stress measurement, where appropriate, because the most commonly used parameters FV/FM and Y(II) or F/FM' can be measured in a few seconds, allowing the investigation of larger plant populations.
Gas exchange systems that offer control of CO2 levels, above and below ambient, allow the common practice of measurement of A/Ci curves, at different CO2 levels, to characterize a plant's photosynthetic response.
Integrated chlorophyll fluorometer – gas exchange systems allow a more precise measure of photosynthetic response and mechanisms. While standard gas exchange photosynthesis systems can measure Ci, or substomatal CO2 levels, the addition of integrated chlorophyll fluorescence measurements allows a more precise measurement of CC to replace Ci. The estimation of CO2 at the site of carboxylation in the chloroplast, or CC, becomes possible with the measurement of mesophyll conductance or gm using an integrated system.
Photosynthesis measurement systems are not designed to directly measure the amount of light absorbed by the leaf. But analysis of chlorophyll-fluorescence, P700- and P515-absorbance and gas exchange measurements reveal detailed information about e.g. the photosystems, quantum efficiency and the CO2 assimilation rates. With some instruments, even wavelength-dependency of the photosynthetic efficiency can be analyzed.
A phenomenon known as quantum walk
Quantum walks are quantum analogues of classical random walks. In contrast to the classical random walk, where the walker occupies definite states and the randomness arises due to stochastic transitions between states, in quantum walks randomness ...
increases the efficiency of the energy transport of light significantly. In the photosynthetic cell of an alga, bacterium, or plant, there are light-sensitive molecules called chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color.
The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molec ...
s arranged in an antenna-shaped structure named a photocomplex. When a photon is absorbed by a chromophore, it is converted into a quasiparticle
In physics, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related emergent phenomena arising when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum.
For exam ...
referred to as an exciton
An exciton is a bound state of an electron and an electron hole which are attracted to each other by the electrostatic Coulomb force. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists in insulators, semiconductors and some liquids. The ...
, which jumps from chromophore to chromophore towards the reaction center of the photocomplex, a collection of molecules that traps its energy in a chemical form accessible to the cell's metabolism. The exciton's wave properties enable it to cover a wider area and try out several possible paths simultaneously, allowing it to instantaneously "choose" the most efficient route, where it will have the highest probability of arriving at its destination in the minimum possible time.
Because that quantum walking takes place at temperatures far higher than quantum phenomena usually occur, it is only possible over very short distances. Obstacles in the form of destructive interference cause the particle to lose its wave properties for an instant before it regains them once again after it is freed from its locked position through a classic "hop". The movement of the electron towards the photo center is therefore covered in a series of conventional hops and quantum walks.
Evolution
Early photosynthetic systems, such as those ingreen
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
and purple sulfur
The purple sulfur bacteria (PSB) are part of a group of Pseudomonadota capable of photosynthesis, collectively referred to as purple bacteria. They are anaerobic or microaerophilic, and are often found in stratified water environments including ...
and green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
and purple nonsulfur bacteria, are thought to have been anoxygenic, and used various other molecules than water as electron donor
In chemistry, an electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process.
Typical reducing agents undergo permanent chem ...
s. Green and purple sulfur bacteria are thought to have used hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
and sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
as electron donors. Green nonsulfur bacteria used various amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent s ...
and other organic acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are rel ...
s as electron donors. Purple nonsulfur bacteria used a variety of nonspecific organic molecules. The use of these molecules is consistent with the geological evidence that Earth's early atmosphere was highly reducing at that time
''For the song "That Time" by Regina Spektor see Begin to Hope''
''That Time'' is a one-act play by Samuel Beckett, written in English between 8 June 1974 and August 1975. The play was specially written for actor Patrick Magee, who delivered it ...
.
Fossils of what are thought to be filamentous
The word filament, which is descended from Latin ''filum'' meaning " thread", is used in English for a variety of thread-like structures, including:
Astronomy
* Galaxy filament, the largest known cosmic structures in the universe
* Solar filament ...
photosynthetic organisms have been dated at 3.4 billion years old. More recent studies also suggest that photosynthesis may have begun about 3.4 billion years ago.
The main source of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
in the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
derives from oxygenic photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in ...
, and its appearance is sometimes referred to as the oxygen catastrophe
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), also called the Great Oxygenation Event, the Oxygen Catastrophe, the Oxygen Revolution, the Oxygen Crisis, or the Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere ...
. Geological evidence suggests that oxygenic photosynthesis, such as that in cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
, became important during the Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
era around 2 billion years ago. Modern photosynthesis in plants and most photosynthetic prokaryotes is oxygenic, using water as an electron donor, which is oxidized
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
to molecular oxygen in the photosynthetic reaction center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or t ...
.
Symbiosis and the origin of chloroplasts
 Several groups of animals have formed
Several groups of animals have formed symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
relationships with photosynthetic algae. These are most common in coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...
s, sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through t ...
s and sea anemone
Sea anemones are a group of predation, predatory marine invertebrates of the order (biology), order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the ''Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classifi ...
s. It is presumed that this is due to the particularly simple body plan
A body plan, ( ), or ground plan is a set of morphological features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many.
This term, usually applied to animals, envisages a "blueprin ...
s and large surface areas of these animals compared to their volumes. In addition, a few marine mollusks
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is esti ...
''Elysia viridis
''Elysia viridis'', the sap-sucking slug, is a small-to-medium-sized species of green sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusc in the family Plakobranchidae.
This sea slug resembles a nudibranch, but it is not closely related to th ...
'' and ''Elysia chlorotica
''Elysia chlorotica'' (common name the eastern emerald elysia) is a small-to-medium-sized species of green sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusc. This sea slug superficially resembles a nudibranch, yet it does not belong to that clad ...
'' also maintain a symbiotic relationship with chloroplasts they capture from the algae in their diet and then store in their bodies (see Kleptoplasty
Kleptoplasty or kleptoplastidy is a symbiosis, symbiotic phenomenon whereby plastids, notably chloroplasts from algae, are sequestered by host organisms. The word is derived from ''Kleptes'' (κλέπτης) which is Greek language, Greek for thie ...
). This allows the mollusks to survive solely by photosynthesis for several months at a time. Some of the genes from the plant cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
have even been transferred to the slugs, so that the chloroplasts can be supplied with proteins that they need to survive.
An even closer form of symbiosis may explain the origin of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts have many similarities with photosynthetic bacteria, including a circular chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
, prokaryotic-type ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to ...
, and similar proteins in the photosynthetic reaction center. The endosymbiotic theory
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory,) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibl ...
suggests that photosynthetic bacteria were acquired (by endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. E ...
) by early eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
cells to form the first plant cells. Therefore, chloroplasts may be photosynthetic bacteria that adapted to life inside plant cells. Like mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
, chloroplasts possess their own DNA, separate from the nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It ...
of their plant host cells and the genes in this chloroplast DNA resemble those found in cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
. DNA in chloroplasts codes for redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
proteins such as those found in the photosynthetic reaction centers. The CoRR Hypothesis
The CoRR hypothesis states that the location of genetic information in cytoplasmic organelles permits regulation of its expression by the reduction-oxidation ("redox") state of its gene products.
CoRR is short for "co-location for redox regulation ...
proposes that this co-location of genes with their gene products is required for redox regulation of gene expression, and accounts for the persistence of DNA in bioenergetic organelles.
Photosynthetic eukaryotic lineages
Symbiotic and kleptoplastic organisms excluded: *Theglaucophyte
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of spe ...
s and the red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
—clade Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae ''sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced /ɑːrkɪ'plastɪdə/) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group ...
(uni- and multicellular)
*The cryptophytes—clade Cryptista
Cryptista is a clade of algae-like eukaryotes. It is most likely related to Archaeplastida which includes plants and many algae, within the larger group Diaphoretickes.
Although it has sometimes placed along with Haptista in the group Hacrobia, ...
(unicellular)
*The haptophyte
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for ''Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae.
The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at t ...
s—clade Haptista
Haptista is a proposed group of protists made up of centrohelids and haptophytes. Phylogenomic studies indicate that Haptista, together with ''Ancoracysta twista'', forms a sister clade to the SAR+Telonemia supergroup, but it may also be sister t ...
(unicellular)
*The dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are ...
s and chromerids in the superphylum Myzozoa
Myzozoa is a grouping of specific phyla within Alveolata, that either feed through myzocytosis, or were ancestrally capable of feeding through myzocytosis.
Many protozoan orders are included within Myzozoa.
It is sometimes described as a phyl ...
, and Pseudoblepharisma
''Pseudoblepharisma'' is a genus of heterotrich ciliates inhabiting oxygen depleted freshwater habitats. Most sources report that it contains one species, ''Pseudoblepharisma tenue'', but at least four have been seen in literature.
''P. tenue'' wa ...
in the phylum Ciliophora
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different ...
—clade Alveolata (unicellular)
*The ochrophytes—clade Heterokont
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which ...
a (uni- and multicellular)
*The chlorarachniophyte
The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally the ...
s and 3 species of Paulinella
''Paulinella'' is a genus of at least eleven
species including both freshwater and marine amoeboids.
Its most famous members are the three photosynthetic species ''P. chromatophora'', ''P. micropora'' and ''P. longichromatophora'', the first tw ...
in the phylum Cercozoa
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eu ...
—clade Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foramini ...
(unicellular)
*The euglenid
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical ...
s—clade Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
(unicellular)
Except for the euglenids, which are found within the Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
, all of these belong to the Diaphoretickes
Diaphoretickes () is a major group of eukaryotic organisms, with over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes.
Diaphoretickes includes:
* Archaeplastida (comprising red alg ...
. Archaeplastida and the photosynthetic Paulinella got their plastids, which are surrounded by two membranes, through primary endosymbiosis
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
in two separate events, by engulfing a cyanobacterium. The plastids in all the other groups have either a red or green algal origin, and are referred to as the "red lineages" and the "green lineages". The only known exception is the ciliate ''Pseudoblepharisma tenue'', which in addition to its plastids that originated from green algae also has a purple sulfur bacterium as symbiont. In dinoflagellates and euglenids the plastids are surrounded by three membranes, and in the remaining lines by four. A nucleomorph
Nucleomorphs are small, vestigial eukaryotic nuclei found between the inner and outer pairs of membranes in certain plastids. They are thought to be vestiges of primitive red and green algal nuclei that were engulfed by a larger eukaryote. Becaus ...
, remnants of the original algal nucleus located between the inner and outer membranes of the plastid, is present in the cryptophytes (from a red alga) and chlorarachniophytes (from a green alga).
Some dinoflagellates that lost their photosynthetic ability later regained it again through new endosymbiotic events with different algae.
While able to perform photosynthesis, many of these eukaryotic groups are mixotroph A mixotroph is an organism that can use a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode on the continuum from complete autotrophy at one end to heterotrophy at the other. It is estimated that mixotrophs comp ...
s and practice heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
y to various degrees.
Cyanobacteria and the evolution of photosynthesis
The biochemical capacity to use water as the source for electrons in photosynthesis evolved once, in acommon ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
of extant cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
(formerly called blue-green algae), which are the only prokaryotes performing oxygenic photosynthesis. The geological record indicates that this transforming event took place early in Earth's history, at least 2450–2320 million years ago (Ma), and, it is speculated, much earlier. Because the Earth's atmosphere contained almost no oxygen during the estimated development of photosynthesis, it is believed that the first photosynthetic cyanobacteria did not generate oxygen. Available evidence from geobiological studies of Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
(>2500 Ma) sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s indicates that life existed 3500 Ma, but the question of when oxygenic photosynthesis evolved is still unanswered. A clear paleontological window on cyanobacterial evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
opened about 2000 Ma, revealing an already-diverse biota of cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria remained the principal primary producers
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", ...
of oxygen throughout the Proterozoic Eon
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided i ...
(2500–543 Ma), in part because the redox structure of the oceans favored photoautotrophs capable of nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular nitrogen (), with a strong triple covalent bond, in the air is converted into ammonia () or related nitrogenous compounds, typically in soil or aquatic systems but also in industry. Atmo ...
. Green algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as ...
joined cyanobacteria as the major primary producers of oxygen on continental shelves
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
near the end of the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
, but only with the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
(251–66 Ma) radiations of dinoflagellates, coccolithophorids, and diatoms did the primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
of oxygen in marine shelf waters take modern form. Cyanobacteria remain critical to marine ecosystem
Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surf ...
s as primary producers of oxygen in oceanic gyres, as agents of biological nitrogen fixation, and, in modified form, as the plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosy ...
s of marine algae.
Experimental history
Discovery
Although some of the steps in photosynthesis are still not completely understood, the overall photosynthetic equation has been known since the 19th century. Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-17th century when he carefully measured the
Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-17th century when he carefully measured the mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
of the soil used by a plant and the mass of the plant as it grew. After noticing that the soil mass changed very little, he hypothesized that the mass of the growing plant must come from the water, the only substance he added to the potted plant. His hypothesis was partially accurate – much of the gained mass comes from carbon dioxide as well as water. However, this was a signaling point to the idea that the bulk of a plant's biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
comes from the inputs of photosynthesis, not the soil itself.
Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
, a chemist and minister, discovered that when he isolated a volume of air under an inverted jar and burned a candle in it (which gave off CO2), the candle would burn out very quickly, much before it ran out of wax. He further discovered that a mouse could similarly "injure" air. He then showed that the air that had been "injured" by the candle and the mouse could be restored by a plant.
In 1779, Jan Ingenhousz
Jan (or John) Ingenhousz or Ingen-Housz FRS (8 December 1730 – 7 September 1799) was a Dutch-born British physiologist, biologist and chemist.
He is best known for discovering photosynthesis by showing that light is essential to the process ...
repeated Priestley's experiments. He discovered that it was the influence of sunlight on the plant that could cause it to revive a mouse in a matter of hours.
In 1796, Jean Senebier
Jean Senebier (6 or 25 May 1742 – 22 July 1809) was a Genevan Calvinist pastor and naturalist. He was chief librarian of the Republic of Geneva. A pioneer in the field of photosynthesis research, he provided extensive evidence that plants co ...
, a Swiss pastor, botanist, and naturalist, demonstrated that green plants consume carbon dioxide and release oxygen under the influence of light. Soon afterward, Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure showed that the increase in mass of the plant as it grows could not be due only to uptake of CO2 but also to the incorporation of water. Thus, the basic reaction by which photosynthesis is used to produce food (such as glucose) was outlined.
Refinements
Cornelis Van Niel made key discoveries explaining the chemistry of photosynthesis. By studying purple sulfur bacteria and green bacteria he was the first to demonstrate that photosynthesis is a light-dependent redox reaction, in which hydrogen reduces (donates its atoms as electrons and protons to) carbon dioxide. Robert Emerson discovered two light reactions by testing plant productivity using different wavelengths of light. With the red alone, the light reactions were suppressed. When blue and red were combined, the output was much more substantial. Thus, there were two photosystems, one absorbing up to 600 nm wavelengths, the other up to 700 nm. The former is known as PSII, the latter is PSI. PSI contains only chlorophyll "a", PSII contains primarily chlorophyll "a" with most of the available chlorophyll "b", among other pigments. These include phycobilins, which are the red and blue pigments of red and blue algae, respectively, and fucoxanthol for brown algae and diatoms. The process is most productive when the absorption of quanta is equal in both PSII and PSI, assuring that input energy from the antenna complex is divided between the PSI and PSII systems, which in turn powers the photochemistry. Robert Hill thought that a complex of reactions consisted of an intermediate to cytochrome b6 (now a plastoquinone), and that another was from cytochrome f to a step in the carbohydrate-generating mechanisms. These are linked by plastoquinone, which does require energy to reduce cytochrome f. Further experiments to prove that the oxygen developed during the photosynthesis of green plants came from water were performed by Hill in 1937 and 1939. He showed that isolatedchloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s give off oxygen in the presence of unnatural reducing agents like iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl o ...
, ferricyanide
Ferricyanide is the anion e(CN)6sup>3−. It is also called hexacyanoferrate(III) and in rare, but systematic nomenclature, hexacyanidoferrate(III). The most common salt of this anion is potassium ferricyanide, a red crystalline material that i ...
or benzoquinone Benzoquinone (C6H4O2) is a quinone with a single benzene ring. There are 2 (out of 3 hypothetical) benzoquinones:
* 1,4-Benzoquinone, most commonly, right image (also ''para''-benzoquinone, ''p''-benzoquinone, ''para''-quinone, or just quinone)
* 1 ...
after exposure to light. In the Hill reaction:
:2 H2O + 2 A + (light, chloroplasts) → 2 AH2 + O2
A is the electron acceptor. Therefore, in light, the electron acceptor is reduced and oxygen is evolved. Samuel Ruben
Samuel Ruben (14 July 1900 – 16 July 1988) was an American inventor who made lasting contributions to electrochemistry and solid-state technology, including the founding of Duracell. He is listed as an inventor in ove200 patents. Early life
Born ...
and Martin Kamen
Martin David Kamen (August 27, 1913, Toronto – August 31, 2002, Montecito, California) was an American chemist who, together with Sam Ruben, co-discovered the synthesis of the isotope carbon-14 on February 27, 1940, at the University of C ...
used radioactive isotopes
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
to determine that the oxygen liberated in photosynthesis came from the water.

Melvin Calvin
Melvin Ellis Calvin (April 8, 1912 – January 8, 1997) was an American biochemist known for discovering the Calvin cycle along with Andrew Benson and James Bassham, for which he was awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He spent most of hi ...
and Andrew Benson
Andrew Alm Benson (September 24, 1917 – January 16, 2015) was an American biologist and a professor of biology at the University of California, San Diego, until his retirement in 1989. He is known for his work in understanding the carbon cy ...
, along with James Bassham
James Alan Bassham (November 26, 1922 – November 19, 2012) was an American scientist known for his work on photosynthesis.
He received a B.S. degree in chemistry in 1945 from the University of California, Berkeley, earning his Ph.D. degree ...
, elucidated the path of carbon assimilation (the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle) in plants. The carbon reduction cycle is known as the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
, but many scientists refer to it as the Calvin-Benson, Benson-Calvin, or even Calvin-Benson-Bassham (or CBB) Cycle.
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
-winning scientist Rudolph A. Marcus
Rudolph Arthur Marcus (born July 21, 1923) is a Canadian-born chemist who received the 1992 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his contributions to the theory of electron transfer reactions in chemical systems". Marcus theory, named after him, provide ...
was later able to discover the function and significance of the electron transport chain.
Otto Heinrich Warburg
Otto Heinrich Warburg (, ; 8 October 1883 – 1 August 1970), son of physicist Emil Warburg, was a German physiologist, medical doctor, and Nobel laureate. He served as an officer in the elite Uhlan (cavalry regiment) during the First World War ...
and Dean Burk
Dean Turner Burk (March 21, 1904 – October 6, 1988) was an American biochemist, medical researcher, and a cancer researcher at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute and the National Cancer Institute. In 1934, he developed the Lineweaver–Burk plot toge ...
discovered the I-quantum photosynthesis reaction that splits CO2, activated by the respiration.
In 1950, first experimental evidence for the existence of photophosphorylation In the process of photosynthesis, the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight is called photophosphorylation. Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, driven by the main primary source of ...
''in vivo'' was presented by Otto Kandler
Otto Kandler (23 October 1920 in Deggendorf – 29 August 2017 in Munich, Bavaria)
was a German botanist and microbiologist. Until his retirement in 1986 he was professor of botany at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
His most importa ...
using intact ''Chlorella
''Chlorella'' is a genus of about thirteen species of single-celled green algae belonging to the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain the ...
'' cells and interpreting his findings as light-dependent ATP formation.
In 1954, Daniel I. Arnon et al. discovered photophosphorylation ''in vitro'' in isolated chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s with the help of P32.
Louis N.M. Duysens and Jan Amesz
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to:
Acronyms
* Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN
* Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code
* Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group
* Japanese Article Numb ...
discovered that chlorophyll "a" will absorb one light, oxidize cytochrome f, while chlorophyll "a" (and other pigments) will absorb another light but will reduce this same oxidized cytochrome, stating the two light reactions are in series.
Development of the concept
In 1893,Charles Reid Barnes
Charles Reid Barnes (1858–1910) was an American botanist specializing in bryophytes ( mosses, liverworts and hornworts). He was co-editor of the '' Botanical Gazette'' for over 25 years.
Barnes was born at Madison, Indiana, September 7, 1858. ...
proposed two terms, ''photosyntax'' and ''photosynthesis'', for the biological process of ''synthesis of complex carbon compounds out of carbonic acid, in the presence of chlorophyll, under the influence of light''. Over time, the term ''photosynthesis'' came into common usage. Later discovery of anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria and photophosphorylation necessitated redefinition of the term.
C3 : C4 photosynthesis research
In the late 1940s at theUniversity of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
, the details of photosynthetic carbon metabolism were sorted out by the chemists Melvin Calvin
Melvin Ellis Calvin (April 8, 1912 – January 8, 1997) was an American biochemist known for discovering the Calvin cycle along with Andrew Benson and James Bassham, for which he was awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He spent most of hi ...
, Andrew Benson, James Bassham and a score of students and researchers utilizing the carbon-14 isotope and paper chromatography techniques. The pathway of CO2 fixation by the algae ''Chlorella'' in a fraction of a second in light resulted in a 3 carbon molecule called phosphoglyceric acid (PGA). For that original and ground-breaking work, a Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
was awarded to Melvin Calvin in 1961. In parallel, plant physiologists studied leaf gas exchanges using the new method of infrared gas analysis and a leaf chamber where the net photosynthetic rates ranged from 10 to 13 μmol CO2·m−2·s−1, with the conclusion that all terrestrial plants have the same photosynthetic capacities, that are light saturated at less than 50% of sunlight.
Later in 1958–1963 at Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach an ...
, field grown maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
was reported to have much greater leaf photosynthetic rates of 40 μmol CO2·m−2·s−1 and not be saturated at near full sunlight. This higher rate in maize was almost double of those observed in other species such as wheat and soybean, indicating that large differences in photosynthesis exist among higher plants. At the University of Arizona, detailed gas exchange research on more than 15 species of monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of ...
and dicot
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, t ...
uncovered for the first time that differences in leaf anatomy are crucial factors in differentiating photosynthetic capacities among species. In tropical grasses, including maize, sorghum, sugarcane, Bermuda grass and in the dicot amaranthus, leaf photosynthetic rates were around 38−40 μmol CO2·m−2·s−1, and the leaves have two types of green cells, i. e. outer layer of mesophyll cells surrounding a tightly packed cholorophyllous vascular bundle sheath cells. This type of anatomy was termed Kranz anatomy in the 19th century by the botanist Gottlieb Haberlandt
Gottlieb Haberlandt (28 November 1854 – 30 January 1945) was an Austrian botanist. He was the son of European 'soybean' pioneer Professor Friedrich J. Haberlandt. His son Ludwig Haberlandt was an early reproductive physiologist now given credi ...
while studying leaf anatomy of sugarcane. Plant species with the greatest photosynthetic rates and Kranz anatomy showed no apparent photorespiration, very low CO2 compensation point, high optimum temperature, high stomatal resistances and lower mesophyll resistances for gas diffusion and rates never saturated at full sun light. The research at Arizona was designated a Citation Classic in 1986. These species were later termed C4 plants as the first stable compound of CO2 fixation in light has 4 carbons as malate and aspartate. Other species that lack Kranz anatomy were termed C3 type such as cotton and sunflower, as the first stable carbon compound is the 3-carbon PGA. At 1000 ppm CO2 in measuring air, both the C3 and C4 plants had similar leaf photosynthetic rates around 60 μmol CO2·m−2·s−1 indicating the suppression of photorespiration in C3 plants.
Factors
 There are three main factors affecting photosynthesis and several corollary factors. The three main are:
* Light
There are three main factors affecting photosynthesis and several corollary factors. The three main are:
* Light irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
and wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
* Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', ''molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', an ...
* Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
.
Total photosynthesis is limited by a range of environmental factors. These include the amount of light available, the amount of leaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, ste ...
area a plant has to capture light (shading by other plants is a major limitation of photosynthesis), the rate at which carbon dioxide can be supplied to the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s to support photosynthesis, the availability of water, and the availability of suitable temperatures for carrying out photosynthesis.
Light intensity (irradiance), wavelength and temperature
Frederick Blackman
Frederick Frost Blackman FRS (25 July 1866 – 30 January 1947) was a British plant physiologist.
Frederick Blackman was born in Lambeth, London to a doctor. He studied medicine at St. Bartholomew's Hospital, graduating MA. In the subsequent yea ...
and Gabrielle Matthaei
Gabrielle Louise Caroline Howard (née Matthaei; 3 October 1876 – 18 August 1930), usually cited as G. L. C. Matthaei, was an English plant physiologist and economic botanist who advocated organic farming.
Education and photosynthesis ...
investigated the effects of light intensity (irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
) and temperature on the rate of carbon assimilation.
* At constant temperature, the rate of carbon assimilation varies with irradiance, increasing as the irradiance increases, but reaching a plateau at higher irradiance.
* At low irradiance, increasing the temperature has little influence on the rate of carbon assimilation. At constant high irradiance, the rate of carbon assimilation increases as the temperature is increased.
These two experiments illustrate several important points: First, it is known that, in general, photochemical
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet (wavelength from 100 to 400 nm), visible light (400–7 ...
reactions are not affected by temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
. However, these experiments clearly show that temperature affects the rate of carbon assimilation, so there must be two sets of reactions in the full process of carbon assimilation. These are the light-dependent 'photochemical' temperature-independent stage, and the light-independent, temperature-dependent stage. Second, Blackman's experiments illustrate the concept of limiting factor
A limiting factor is a variable of a system that causes a noticeable change in output or another measure of a type of system. The limiting factor is in a pyramid shape of organisms going up from the producers to consumers and so on. A factor not l ...
s. Another limiting factor is the wavelength of light. Cyanobacteria, which reside several meters underwater, cannot receive the correct wavelengths required to cause photoinduced charge separation in conventional photosynthetic pigments. To combat this problem, a series of proteins with different pigments surround the reaction center. This unit is called a phycobilisome
Phycobilisomes are light harvesting antennae of photosystem II in cyanobacteria, red algae and glaucophytes. It was lost in the plastids of green algae / plants (chloroplasts).
General structure
Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 ...
.
Carbon dioxide levels and photorespiration
RuBisCO
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations RuBisCo, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme () involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is con ...
, the enzyme that captures carbon dioxide in the light-independent reactions, has a binding affinity for both carbon dioxide and oxygen. When the concentration of carbon dioxide is high, RuBisCO will fix carbon dioxide. However, if the carbon dioxide concentration is low, RuBisCO will bind oxygen instead of carbon dioxide. This process, called photorespiration
Photorespiration (also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle or C2 cycle) refers to a process in plant metabolism where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP, wasting some of the energy produced by photosynthesis. The desired reaction i ...
, uses energy, but does not produce sugars.
RuBisCO oxygenase activity is disadvantageous to plants for several reasons:
# One product of oxygenase activity is phosphoglycolate (2 carbon) instead of 3-phosphoglycerate
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. Th ...
(3 carbon). Phosphoglycolate cannot be metabolized by the Calvin-Benson cycle and represents carbon lost from the cycle. A high oxygenase activity, therefore, drains the sugars that are required to recycle ribulose 5-bisphosphate and for the continuation of the Calvin-Benson cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
.
# Phosphoglycolate is quickly metabolized to glycolate that is toxic to a plant at a high concentration; it inhibits photosynthesis.
# Salvaging glycolate is an energetically expensive process that uses the glycolate pathway, and only 75% of the carbon is returned to the Calvin-Benson cycle as 3-phosphoglycerate. The reactions also produce ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
(NH3), which is able to diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
out of the plant, leading to a loss of nitrogen.
::A highly simplified summary is:
:::2 glycolate + ATP → 3-phosphoglycerate + carbon dioxide + ADP + NH3
The salvaging pathway for the products of RuBisCO oxygenase activity is more commonly known as photorespiration, since it is characterized by light-dependent oxygen consumption and the release of carbon dioxide.
See also
*Jan Anderson (scientist)
Joan Mary "Jan" Anderson FAA FRS (13 May 1932 – 28 August 2015) was a New Zealand scientist who worked in Canberra, Australia, distinguished by her investigation of photosynthesis.
Life
Joan Mary Anderson was born in 1932 in Queenstown, ...
* Artificial photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that biomimics the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term artificial photosynthesis is commonly used to refer to ...
* Calvin-Benson cycle
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into ...
* Carbon fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as ...
* Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
* Chemosynthesis
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
* Daily light integral
* Hill reaction The Hill reaction is the light-driven transfer of electrons from water to Hill reagents (non-physiological oxidants) in a direction against the chemical potential gradient as part of photosynthesis. Robin Hill discovered the reaction in 1937. H ...
* Integrated fluorometer
Photosynthesis systems are electronic scientific instruments designed for non-destructive measurement of photosynthetic rates in the field. Photosynthesis systems are commonly used in agronomic and environmental research, as well as studies of the ...
* Light-dependent reaction
Light-dependent reactions is jargon for certain photochemical reactions that are involved in photosynthesis, the main process by which plants acquire energy. There are two light dependent reactions, the first occurs at photosystem II (PSII) and ...
* Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, Mechanistic Organ ...
* Photobiology Photobiology is the scientific study of the beneficial and harmful interactions of light (technically, non-ionizing radiation) in living organisms. The field includes the study of photophysics, photochemistry, photosynthesis, photomorphogenesis, vis ...
* Photoinhibition
Photoinhibition is light-induced reduction in the photosynthetic capacity of a plant, alga, or cyanobacterium. Photosystem II (PSII) is more sensitive to light than the rest of the photosynthetic machinery, and most researchers define the term as ...
* Photosynthetic reaction center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or t ...
* Photosynthetically active radiation Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis. This spectral region corresponds more o ...
* Photosystem
Photosystems are functional and structural units of protein complexes involved in photosynthesis. Together they carry out the primary photochemistry of photosynthesis: the absorption of light and the transfer of energy and electrons. Photosystems ...
* Photosystem I
Photosystem I (PSI, or plastocyanin–ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses ...
* Photosystem II
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem ...
* Quantasome
Quantasomes are particles found in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts in which photosynthesis takes place. They are embedded in a paracrystalline array on the surface of thylakoid discs in chloroplasts. They are composed of lipids and proteins ...
* Quantum biology
Quantum biology is the study of applications of quantum mechanics and theoretical chemistry to aspects of biology that cannot be accurately described by the classical laws of physics. An understanding of fundamental quantum interactions is importan ...
* Radiosynthesis
* Red edge
Red edge refers to the region of rapid change in reflectance of vegetation in the near infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Chlorophyll contained in vegetation absorbs most of the light in the visible part of the spectrum but becomes al ...
* Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
References
Further reading
Books
* * * *Papers
* *External links
A collection of photosynthesis pages for all levels from a renowned expert (Govindjee)
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20090428090455/http://scienceaid.co.uk/biology/biochemistry/photosynthesis.html Science Aid: PhotosynthesisArticle appropriate for high school science
Metabolism, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis – The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
* ttp://www.life.uiuc.edu/govindjee/photosynBook.html Overall Energetics of Photosynthesis
The source of oxygen produced by photosynthesis
Interactive animation, a textbook tutorial *
Photosynthesis – Light Dependent & Light Independent Stages
Khan Academy, video introduction
{{Authority control Agronomy Biological processes Botany Cellular respiration Ecosystems Metabolism Plant nutrition Plant physiology Quantum biology