|
Phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin (PE) is a red protein-pigment complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and Cryptomonad, cryptophytes, accessory to the main chlorophyll pigments responsible for photosynthesis.The red pigment is due to the prosthetic group, phycoerythrobilin, which gives phycoerythrin its red color. Like all phycobiliproteins, it is composed of a protein part covalently binding chromophores called phycobilins. In the phycoerythrin family, the most known phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore. Phycoerythrobilin is a linear tetrapyrrole molecule found in cyanobacteria, red algae, and cryptomonads. Together with other bilins such as phycocyanobilin it serves as a light-harvesting pigment in the photosynthetic light-harvesting structures of cyanobacteria called phycobilisomes. Phycoerythrins are composed of (αβ) monomers, usually organised in a disk-shaped Protein quaternary structure, trim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycobiliprotein
Phycobiliproteins are water-soluble proteins present in cyanobacteria and certain algae (rhodophytes, cryptomonads, glaucocystophytes). They capture light energy, which is then passed on to chlorophylls during photosynthesis. Phycobiliproteins are formed of a complex between proteins and covalently bound phycobilins that act as chromophores (the light-capturing part). They are most important constituents of the phycobilisomes. Major phycobiliproteins Characteristics Phycobiliproteins demonstrate superior fluorescent properties compared to small organic fluorophores, especially when high sensitivity or multicolor detection required : * Broad and high absorption of light suits many light sources * Very intense emission of light: 10-20 times brighter than small organic fluorophores * Relative large Stokes shift gives low background, and allows multicolor detections. * Excitation and emission spectra do not overlap compared to conventional organic dyes. * Can be used in tandem (si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
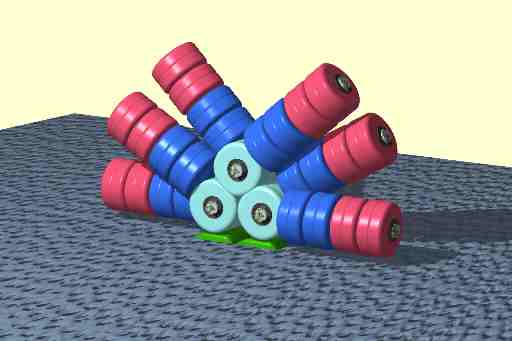
Phycobilisome
Phycobilisomes are light-harvesting antennae that transmit the energy of harvested photons to photosystem II and photosystem I in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae and glaucophytes. They were lost during the evolution of the chloroplasts of green algae and plants. General structure Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 polypeptides) anchored to thylakoid membranes. They are made of stacks of chromophorylated proteins, the phycobiliproteins, and their associated linker polypeptides. Each phycobilisome consists of a core made of allophycocyanin, from which several outwardly oriented rods made of stacked disks of phycocyanin and (if present) phycoerythrin(s) or phycoerythrocyanin. The spectral property of phycobiliproteins are mainly dictated by their prosthetic groups, which are linear tetrapyrroles known as phycobilins including phycocyanobilin, phycoerythrobilin, phycourobilin and phycobiliviolin. The spectral properties of a given phyco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycourobilin
Phycourobilin is an orange tetrapyrrole involved in photosynthesis in cyanobacteria and red algae. This chromophore is bound to the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, the distal component of the light-harvesting system of cyanobacteria and red algae (phycobilisome). When bound to phycoerythrin, phycourobilin shows an absorption maximum around 495 nm. This chromophore is always a donor chromophore of phycoerythrins, since their acceptor chromophore is always phycoerythrobilin Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of w .... It can also be linked to the linker polypeptides of the phycobilisome, in which its precise role remains unclear. Phycourobilin is found in marine phycobilisome containing organisms, allowing them to efficiently absorb blue-green light. In the ubiquitous marine c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycobilisomes
Phycobilisomes are light-harvesting antennae that transmit the energy of harvested photons to photosystem II and photosystem I in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae and glaucophytes. They were lost during the evolution of the chloroplasts of green algae and plants. General structure Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 polypeptides) anchored to thylakoid membranes. They are made of stacks of chromophorylated proteins, the phycobiliproteins, and their associated linker polypeptides. Each phycobilisome consists of a core made of allophycocyanin, from which several outwardly oriented rods made of stacked disks of phycocyanin and (if present) phycoerythrin(s) or phycoerythrocyanin. The spectral property of phycobiliproteins are mainly dictated by their prosthetic groups, which are linear tetrapyrroles known as phycobilins including phycocyanobilin, phycoerythrobilin, phycourobilin and phycobiliviolin. The spectral properties of a given phycobilin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrobilin2
Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. The amount of phycoerythrobilin in phycoerythrins varies a lot, depending on the considered organism. In some Rhodophytes and oceanic cyanobacteria, phycoerythrobilin is also present in the phycocyanin Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist ..., then termed R-phycocyanin. Like all phycobilins, phycoerythrobilin is covalently linked to these phycobiliproteins by a thioether bond. References External links Chemical Structure of phycoerythrobilin Tetrapyrroles Photosynthetic pigments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxonomic revisions. The majority of species (6,793) are Florideophyceae, and mostly consist of multicellular, ocean, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, no terrestrial species exist, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity. Red algae form a distinct group characterized by eukaryotic cells without flagella and centrioles, chloroplasts without external endoplasmic reticulum or unstack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a superclass of algae, most of which have plastids. They are traditionally considered a division of algae among phycologists, under the name of Cryptophyta. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. They are classified as superclass Cryptomonada, which is divided into two classes: heterotrophic Goniomonadea and phototrophic Cryptophyceae. The two groups are united under three shared morphological characteristics: presence of a periplast, ejectisomes with secondary scroll, and mitochondrial cristae with flat tubules. Genetic studies as early as 1994 also supported the hypothesis that ''Goniomonas'' was sister to Cryptophyceae. A study in 2018 found strong evidence that the common ancestor of Crypto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. The amount of phycoerythrobilin in phycoerythrins varies a lot, depending on the considered organism. In some Rhodophytes and oceanic cyanobacteria, phycoerythrobilin is also present in the phycocyanin Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist ..., then termed R-phycocyanin. Like all phycobilins, phycoerythrobilin is covalently linked to these phycobiliproteins by a thioether bond. References External links Chemical Structure of phycoerythrobilin Tetrapyrroles Photosynthetic pigment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which capture the Radiant energy, energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy and release oxygen. The chemical energy created is then used to make sugar and other organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process called the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in some unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulate and are moved around within cells. Their behavior is strongly influenced by environmental factors like light color and intensity. Chloroplasts cannot be made anew by the plant cell and must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |