Pampanga, officially the Province of Pampanga ( pam, Lalawigan ning Pampanga; tl, Lalawigan ng Pampanga ), is a
province in the
Central Luzon region of the
Philippines. Lying on the northern shore of
Manila Bay, Pampanga is bordered by
Tarlac to the north,
Nueva Ecija to the northeast,
Bulacan to the east, the
Manila Bay to the central-south,
Bataan to the southwest and
Zambales to the west. Its capital is the
City of San Fernando.
Angeles City is the largest LGU but while geographically within Pampanga, it is classified as a
first-class, highly urbanized city and has been governed independently of the province since it received its charter in 1964.
The name ''La Pampanga'' was given by the Spaniards, who encountered natives living along the banks (''pampáng'') of the
Pampanga River. Its creation in 1571 makes it the first Spanish province on Luzon Island (
Cebu in
Visayas is older as it was founded by the
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex Hist ...
in 1565). The town of
Villa de Bacolor in the province briefly served as the Spanish colonial capital when
Great Britain invaded Manila as part of the
Seven Years' War. At the eve of the
Philippine Revolution of 1896, Pampanga was one of eight provinces placed under
martial law for rebellion against the
Spanish Empire; it is thus represented on the
Philippine national flag as one of the eight rays of the sun.
Pampanga is served by
Clark International Airport (formerly ''Diosdado Macapagal International Airport''), which is in
Clark Freeport Zone, some north of the provincial capital. The province is home to two
Philippine Air Force
The Philippine Air Force (PAF) ( tgl, Hukbong Himpapawid ng Pilipinas, , Army of the Air of the Philippines) ( es, Ejército Aérea del Filipinas, , Ejército de la Aérea de la Filipinas) is the aerial warfare service branch of the Armed Forc ...
airbase
An air base (sometimes referred to as a military air base, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base) is an aerodrome used as a military base by a military force for the operation ...
s:
Basa Air Base in
Floridablanca and the former United States
Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base on Luzon Island in the Philippines, located west of Angeles City, about northwest of Metro Manila. Clark Air Base was previously a United States military facility, operated by the U.S. Air Forc ...
in Angeles. Due to its growing population and developments, the Clark Global City is now developed and is located in
Clark Freeport Zone. In 2015, the province had 2,198,110 inhabitants, while it had 1,079,532 registered voters.
History
Pampanga during the Philippine colonial era
Ancient Pampanga's Territorial area included portions of the modern provinces of
Tarlac,
Bataan,
Zambales,
Nueva Ecija and
Bulacan. Pampanga was re-organized as a province by the Spaniards on December 11, 1571. For better administration and taxation purposes, the Spanish authorities subdivided Pampanga into ''pueblos'', which were further subdivided into districts (''
barrios
Barrios is a Spanish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Agustín Barrios (1885–1944), Paraguayan guitarist and composer
*Ángel Barrios (1882–1964), Spanish guitarist and composer
*Arturo Barrios (born 1962), Mexican athlet ...
'') and in some cases into royal and private estates (''
encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
''s).
Due to excessive abuses committed by some ''encomenderos'', King
Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
in 1574 prohibited the further awarding of private estates, but this decree was not fully enforced until 1620. In a report of
Philippine encomiendas on June 20, 1591,
Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
Gómez Pérez Dasmariñas reported to the Crown that La Pampanga's encomiendas were Bataan, Betis y Lubao, Macabebe, Candaba, Apalit, Calumpit, Malolos, Binto, Guiguinto, Caluya, Bulacan and
Mecabayan. The encomiendas of La Pampanga at that time had eighteen thousand six hundred and eighty whole tributes.
Pampanga, which is about in area and inhabited by more than 1.5 million people, had its present borders drawn in 1873. During the Spanish regime it was one of the richest Philippine provinces.
Manila and its surrounding region were then primarily dependent on Kapampangan agricultural, fishery and forestry products as well as on the supply of skilled workers. As other Luzon provinces were created due to increases in population, some well-established Pampanga towns were lost to new emerging provinces in Central Luzon.
During the 17th century, The
Dutch recruited men from Pampanga as mercenaries who served the
Royal Netherlands East Indies Army, known as
Papangers part of the larger
Mardijkers
The Mardijker people refers to an ethnic community in the Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) made up of descendants of freed slaves. They could be found at all major trading posts in the East Indies. They were mostly Christian, of various ...
community. Their legacy can be found in
North Jakarta
North Jakarta ( id, Jakarta Utara; bew, Jakarte Belilir) is one of the five administrative cities (''kota administrasi'') which form Special Capital Region of Jakarta, Indonesia. North Jakarta is not self-governed and does not have a city counci ...
, however, there are few traces of their descendants, except for a small community in
Kampung Tugu.
The historic province of Bataan which was founded in 1754 under the administration of Spanish
Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
Pedro Manuel Arandia, absorbed from the province of Pampanga the municipalities of Abucay, Balanga (now a city), Dinalupihan, Llana Hermosa, Orani, Orion, Pilar, and Samal.
During the
British occupation of Manila (1762–1764),
Bacolor
Bacolor, officially the Municipality of Bacolor ( pam, Balen ning Bakúlud; tgl, Bayan ng Bacolor), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 48,066 people.
Bacolor ...
became the provisional Spanish colonial capital and military base.
The old Pampanga towns of Aliaga, Cabiao, Gapan, San Antonio and San Isidro were ceded to the province of Nueva Ecija in 1848 during the term of Spanish Governor-General
Narciso Claveria y Zaldua Narciso may refer to:
Given name
* Narciso Clavería y de Palacios, Spanish architect
* Narciso Clavería y Zaldúa, Governor General of the Philippines
* Narciso dos Santos, Brazilian former footballer
* Narciso Durán, Franciscan friar and missio ...
. The municipality of ''San Miguel de Mayumo'' of Pampanga was yielded to the province of Bulacan in the same provincial boundary configuration in 1848.
In 1860, the northern towns of Bamban, Capas, Concepcion, Victoria, Tarlac, Mabalacat, Magalang, Porac and Floridablanca were separated from Pampanga and were placed under the jurisdiction of a military command called ''Comandancia Militar de Tarlac''. However, in 1873, the four latter towns were returned to Pampanga and the other five became municipalities of the newly created Province of Tarlac.
On December 8, 1941, Japanese planes bombed
Clark Air Base
Clark Air Base is a Philippine Air Force base on Luzon Island in the Philippines, located west of Angeles City, about northwest of Metro Manila. Clark Air Base was previously a United States military facility, operated by the U.S. Air Forc ...
marking the beginning of the invasion of Pampanga. Between 1941 and 1942, occupying Japanese forces began entering Pampanga.
During the counter-insurgencies under the Japanese occupation from 1942 to 1944, Kapampangan guerrilla fighters and the
Hukbalahap Communist guerrillas fought side by side in the province of Pampanga, attacking and retreating the
Japanese Imperial forces
The Imperial Japanese Armed Forces (IJAF) were the combined military forces of the Japanese Empire. Formed during the Meiji Restoration in 1868,"One can date the 'restoration' of imperial rule from the edict of 3 January 1868." p. 334. they ...
for over three years of fighting and invasion.
The establishment of the military general headquarters and military camp bases of the
Philippine Commonwealth Army was active from 1935 to 1946. The
Philippine Constabulary was active from 1935 to 1942 and 1944 to 1946 in the province of Pampanga. During the military engagements of the anti-Japanese Imperial military operations in central Luzon from 1942 to 1945 in the province of Bataan, Bulacan, Northern Tayabas (now Aurora), Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, and Zambales, the local guerrilla resistance fighters and Hukbalahap Communist guerrillas, helped the U.S. military forces fight the Imperial Japanese armed forces.
In the 1945 liberation of Pampanga, Kapampangan guerrilla fighters and the Hukbalahap Communist guerrillas supported combat forces from Filipino and American ground troops in attacking Japanese Imperial forces during the Battle of Pampanga until the end of the Second World War. Local military operations soldiers and officers of the Philippine Commonwealth Army 2nd, 26th, 3rd, 32nd, 33rd, 35th, 36th and 37th Infantry Division and the Philippine Constabulary 3rd Constabulary Regiment recaptured and liberated the province of Pampanga and fought against the Japanese Imperial forces during the Battle of Pampanga.
Pampanga during the Postwar era

After the Second World War, operations in the main province of Pampanga was downfall insurgencies and conflicts between the Philippine Government forces and the Hukbalahap Communist rebels on 1946 to 1954 during the
Hukbalahap Rebellion.
Pampanga during the Marcos martial law era
During the
Marcos dictatorship, thousands of Kapampangans were
tortured and
murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person wit ...
ed by the Marcos regime through various means such as
rape, forced stripping, electric shocks, beatings, and genital mutilations, among many others. Kapampangan religious leaders
rose up against Marcos until the
People Power Revolution occurred, where a Kapampangan,
Corazon Aquino
Maria Corazon "Cory" Sumulong Cojuangco-Aquino (; ; January 25, 1933 – August 1, 2009) was a Filipina politician who served as the 11th president of the Philippines from 1986 to 1992. She was the most prominent figure of the 1986 People P ...
, became president.
Among the most prominent of these victims were the Sapang Bato martyrs -
Claro Cabrera During the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos, Filipino workers in the labor industry experienced the effects of government corruption, crony capitalism, and cheap labor for foreign transnational industries, One of the objectives of Martial Law was to c ...
,
Rolando Castro During the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos, Filipino workers in the labor industry experienced the effects of government corruption, crony capitalism, and cheap labor for foreign transnational industries, One of the objectives of Martial Law was to c ...
and
Pepito Deheran During the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos, Filipino workers in the labor industry experienced the effects of government corruption, crony capitalism, and cheap labor for foreign transnational industries, One of the objectives of Martial Law was to c ...
- who were victims of ‘salvaging’ - the term used as a time for summary executions. The three were members of the Concerned Citizens of Pampanga, a cause-oriented group that denounced the human rights abuses of the martial law regime, and had campaigned for a boycott of the
1984 Batasang Pambansa election
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast As ...
, which the opposition regarded as a Marcos ploy to pacify the Philippines' growing protest movement. The three were abducted by Marcos' soldiers shortly after the elections, and brought to a military camp where they were interrogated, beaten and stabbed. The three were left for dead on the banks of the
Apalit river, where Castro and Cabrera's bodies were discovered later. However, Deheran survived, and was able to name two of their attackers before he was attacked again and killed at the hospital where he had been brought to recuperate.
Another prominent early case was that of
Holy Angel College instructor and former Jesuit seminarian Teresito "Terry" Sison, whose founding of the Salaginto Dramatic Guild and performance of socially relevant plays led to his being attacked by a
local private army who called themselves the Monkees, and for his eventual capture by Marcos' soldiers in 1971, when Marcos had
suspended the Writ of Habeas Corpus as a test-run for Martial Law in 1971. Terry, a diabetic, was tortured at
Camp Crame using methods including the burning of the soles of his feet using a hot iron. Sustaining liver damage due to his torture, he died on National Heroes day, on November 30, 1980.
Cabrera, Castro, Deheran, and Sison are all honored at the Philippines'
Bantayog ng mga Bayani, which honors the martyrs and heroes who fought against Marcos' authoritarian regime.
Contemporary history
The June 15, 1991 eruption of
Mount Pinatubo displaced a large number of people with the submersion of whole towns and villages by massive
lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extreme ...
floods. This led to a large-scale advancement in disaster preparation in government. In 2010, a Kapampangan,
Benigno Aquino III, son of former President
Corazon Aquino
Maria Corazon "Cory" Sumulong Cojuangco-Aquino (; ; January 25, 1933 – August 1, 2009) was a Filipina politician who served as the 11th president of the Philippines from 1986 to 1992. She was the most prominent figure of the 1986 People P ...
, was elected as president.
On April 22, 2019, the province suffered severe damage due to
6.1 magnitude earthquake which originated from
Zambales and was the most affected area by the earthquake due to province sitting on soft sediment and
alluvial soil.
Several structures in the province were damaged by the quake, including a 4-story supermarket in Porac, the
Bataan-Pampanga boundary arch and the main terminal of
Clark International Airport, as well as old churches in
Lubao and
Porac, where the stone bell tower of the 19th-century
Santa Catalina de Alejandria Church collapsed.
Geography
Pampanga covers a total area of occupying the south-central section of the
Central Luzon region. When Angeles is included for geographical purposes, the province's area is . The province is bordered by
Tarlac to the north,
Nueva Ecija to the northeast,
Bulacan to the east, the
Manila Bay to the central-south,
Bataan to the southwest, and
Zambales to the northwest.
Its terrain is relatively flat with one distinct mountain,
Mount Arayat and the notable
Pampanga River. Among its municipalities,
Porac has the largest area with ;
Candaba comes in second with ; followed by
Floridablanca with .
Santo Tomas, with an area of only , is the smallest.
Climate
The province of Pampanga has two distinct climates, rainy and dry. The rainy or wet season normally begins in May and runs through October, while the rest of the year is the dry season. The warmest period of the year occurs between March and April, while the coolest period is from December through February. The wet season will be from June to October and also dry season
will be from November to April in the province of Pampanga.
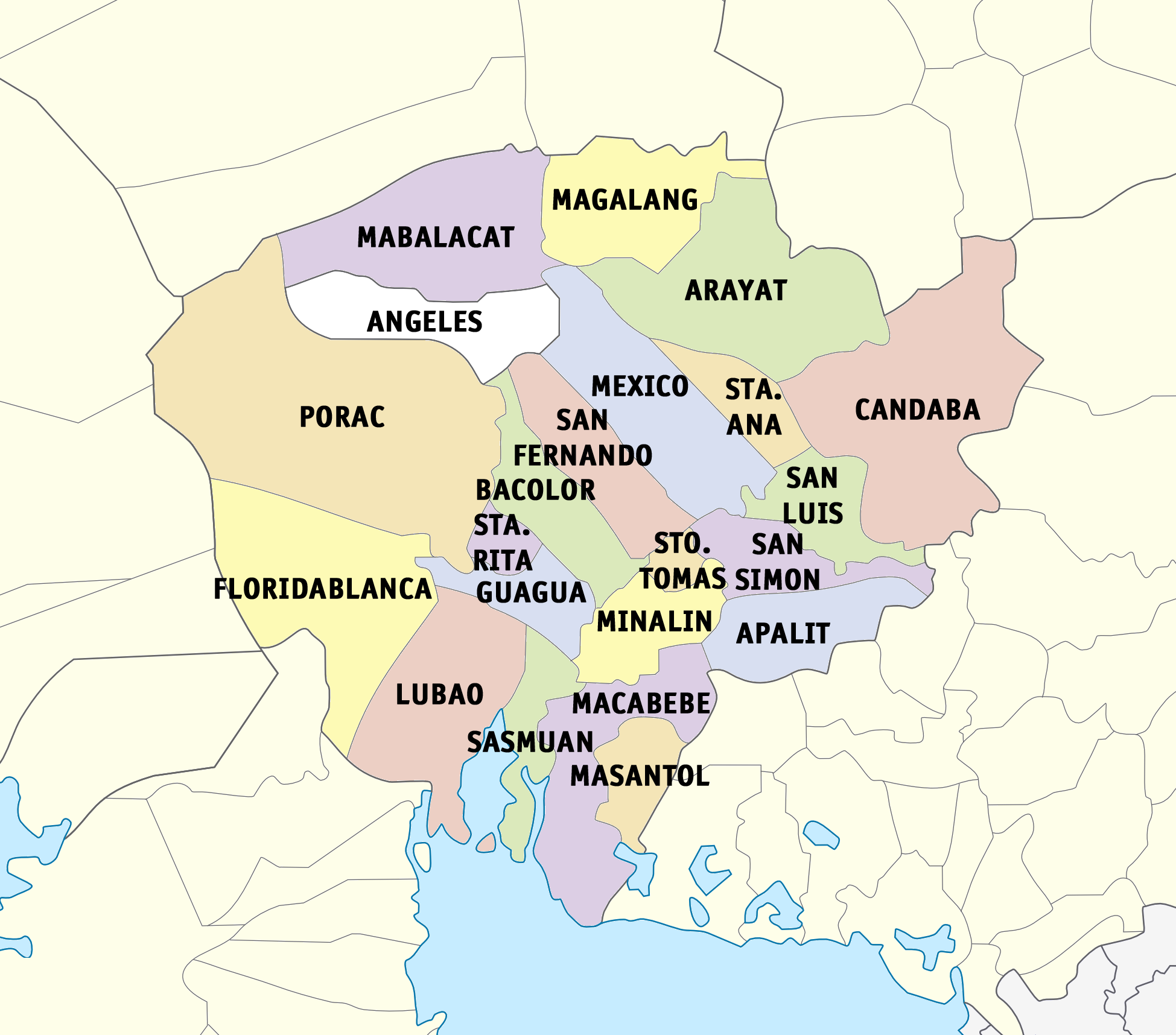
Administrative divisions
Pampanga comprises 19
municipalities and three
cities (one highly urbanized and two component).
Demographics
Population
The population of Pampanga in the 2020 census was 2,437,709 people, with a density of . If Angeles is included for geographical purposes, the population is 2,609,744, with a density of . The native inhabitants of Pampanga are generally referred to as the
Kapampangans
The Kapampangan people ( pam, Taung Kapampangan), Pampangueños or Pampangos, are the sixth largest ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines, numbering about 2,784,526 in 2010. They live mainly in the provinces of Pampanga, Bataan and Tarlac, as ...
(alternatively ''Pampangos'' or ''Pampangueños'').
Languages
The whole population of Pampanga speak
Kapampangan, which is one of the
Central Luzon languages along with the
Sambalic languages.
English and
Tagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
are rather spoken and used as secondary languages. There are a few
Sambal speakers in the province, especially near the border of
Zambales.
Religion
The province of Pampanga is composed of many religious groups, but it is predominantly
Roman Catholic (88.92%).
According to 2010 Census, other prominent Christian groups include the
Iglesia ni Cristo (3.84%),
Evangelicals
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
(1.34%),
Aglipayan Church (0.60%),
Jesus is Lord Church (0.48%),
Baptist Church
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compete ...
(0.39%),
Jehovah’s Witnesses (0.27%), Church of Christ (0.23%), United Church of Christ in the Philippines (0.22%),
Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
(0.18%) and many others.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
(0.017%) is also present in the province, mainly due to migrants originating from
the south, as well as
Buddhism, which is practiced by a few people of
Chinese descent.
Economy
Farming and fishing are the two main industries. Major products include rice, corn, sugarcane, and tilapia. Pampanga is the tilapia capital of the country because of its high production reaching 214,210.12 metric tons in 2015. In addition to farming and fishing, the province supports thriving cottage industries that specialize in wood carving, furniture making, guitars and handicrafts. Every
Christmas season, the province of Pampanga, especially in the capital city of
San Fernando becomes the center of a thriving industry centered on handcrafted lighted lanterns called ''parols'' that display a kaleidoscope of light and color. Other industries include its casket industry and the manufacturing of all-purpose vehicles in the municipality of Santo Tomas.
The province is famous for its sophisticated culinary work. Kapampangans are well known for their culinary creations. Famous food products range from the mundane to the exotic. Roel's Meat Products, Pampanga's Best and Mekeni Food are among the better known meat brands of the country producing Kapampangan favorites such as pork and chicken
tocino
Tocino is bacon in Spanish, typically made from the pork belly and often formed into cubes in Spain. In Caribbean countries, such as Puerto Rico and Cuba, ''tocino'' is made from pork fatback and is neither cured nor smoked but simply fried un ...
s,
beef tapa
''Tapa'' is dried or cured beef, pork, mutton, venison or horse meat, although other meat or even fish may be used. Filipinos prepare ''tapa'' by using thin slices of meat and curing these with salt and spices as a preservation method.
''Tapa' ...
, hotdogs,
longganizas (Philippine-style cured sausages) and
chorizo
Chorizo (, from Spanish ; similar to but distinct from Portuguese ) is a type of pork cured meat originating from the Iberian Peninsula.
In Europe, chorizo is a fermented, cured, smoked meat, which may be sliced and eaten without cooking, or ...
s.
Specialty foods such as the
siopao,
pandesal, tutong,
lechon (roasted pig) and its sarsa (sauce) are popular specialty foods in the region. The more exotic ''betute tugak'' (stuffed frog), ''kamaru'' (mole crickets) cooked adobo, ''bulanglang'' (pork cooked in guava juice), ''
lechon kawali
''Lechon kawali'', also known as ''lechon de carajay'' or ''litsong kawali'' in Tagalog, is a Filipino recipe consisting of pork belly slabs deep-fried in a pan or wok (''kawali''). It is seasoned beforehand, cooked then served in cubes. It ...
'' and ''
bringhe
Paelya () or paella (Spanish), is a Philippine rice dish adapted from the Valencian ''paella''. However, it differs significantly in its use of native glutinous rice (''malagkít''), giving it a soft and sticky texture, unlike the '' al dente' ...
'' (a green sticky rice dish like paella) are a mainstay in Kapampangan feasts.
Native sweets and delicacies like pastillas, turonnes de casuy, buro, are the most sought after by Filipinos including a growing number of tourists who enjoy authentic Kapampangan cuisine. The famous cookie in Mexico, Pampanga, ''Panecillos de San Nicolas'', which is known as the mother of all Philippine cookies, is made here, famously made by Lillian Borromeo. The cookies are made with arrowroot, sugar, coconut milk and butter and are blessed in Catholic parishes every year on the feast of San Nicolas Tolentino.
The cookies are believed to have a healing power and bestow good luck and are sometimes crumbled into rice fields before planting.
Tourism is a growing industry in the province of Pampanga. Clark Freeport Zone is home to
Clark International Airport, designated as the Philippines' future premier gateway. Other developing industries include semiconductor manufacturing for electronics and computers mostly located within the freeport.
Within the Clark Special Economic Zone are well-established hotels and resorts. Popular tourist destinations include St. Peter Shrine in Apalit, Mt. Arayat National Park in San Juan Bano, Mount Arayat, the
Paskuhan Village
The Paskuhan Village, officially known as the Philippine Christmas Village also known as Hilaga, is a Christmas-themed park located in San Fernando, Pampanga, Philippines. It is operational all year-round and is under the management of the Tourism ...
in the City of San Fernando, the Casino Filipino in Angeles and, for nature and wildlife, "Paradise Ranch and Zoocobia Fun Zoo" in Clark. Well-known annual events include the
Giant Lantern Festival
The Giant Lantern Festival (Kapampangan: ''Ligligan Parul'') is an annual festival held in mid-December in the City of San Fernando in the Philippines. The festival features a competition of giant parol lanterns. Because of the popularity of the ...
in December, the
hot air balloon festival in Clarkfield in February and in Lubao in April, the
San Pedro Cutud Lenten Rites
The San Pedro Cutud Lenten Rites is a Holy Week re-enactment of Christ's Passion and Death which takes place in Barangay San Pedro Cutud, City of San Fernando, Pampanga in the Philippines.
It includes a passion play culminating with the actua ...
celebrated two days before Easter, and the Aguman Sanduk in
Minalin celebrated on the afternoon of New Year's Day.
Boat culture
There have been proposals to revitalize the
karakoa shipbuilding tradition of the Kapampangan people in recent years. The karakoa was the warship of the Kapampangan from the classical eras (before 15th century) up to the 16th century. The production of the karakoa and its usage were stopped by the Spanish colonialists to establish the galleon ship-making tradition instead, as a sign of Spanish dominance over the Kapampangan.
Infrastructure
Telecommunication
Telephone services are provided by
PLDT,
Digitel, Converge Telecom, Datelcom, the Evangelista Telephone Company, and the Pampanga Telecom Company in the town of Macabebe. The province has 24 public telegraph offices distributed among its towns while the facilities of PT&T and RCPI were set up to serve the business centers in Angeles, San Fernando City and Guagua.
Several Internet Service provider are available. These include the Angeles Computer Network Specialist, Information Resources Network System, Inc.,
osaic communications Inc., Net Asia Angeles, Phil World On Line and Comclark Network and Technology Corp.
United Parcel Service (UPS) and Federal Express">United Parcel Service">osaic communications Inc., Net Asia Angeles, Phil World On Line and Comclark Network and Technology Corp.
United Parcel Service (UPS) and Federal Express (FedEx) provide international courier services. Their hubs are in the Clark Freeport Zone. They are complemented by four local couriers operating as the communication and baggage of the province. There are three postal district offices and 35 post office stations distributed in the 20 municipalities and two cities of the province.
Water and power

Potable water supply in the province reaches the populace through three levels namely: Level I (point source system), Level II (communal faucet system), and Level III (individual connections). A well or spring is the pinpointed water source in areas where houses are few as the system is only designed to serve 15 to 25 households. As of 1997, there were 128,571 Level I water system users in the province. The communal faucet system (Level II) serves the rural areas while the Level III system is managed by the Local Water Utilities Administration (LWUA). The system provides individual house connections to all second and first class private subdivisions.
Electric power is distributed to the majority of the towns through the distribution centers of the Pampanga Electric Cooperative (PELCO) which include PELCO I, II, III. Small parts of Candaba and Macabebe are also supplied by
Manila Electric Company (Meralco). Angeles and small parts of Mabalacat are supplied by Angeles Electric Corporation (AEC) Villa de Bacolor, Guagua, Sta, Rita, Lubao, Sasmuan, Porac, Mabalacat and small part of Floridablanca are supplied by Pampanga Electric Cooperative II (PELCO II). City of San Fernando and Floridablanca is supplied by San Fernando Electric Company (SFELAPCO).
Power is also transmitted to the province through various transmission lines and substations located within the province, such as the Mexico and Clark substations, and
Hermosa–Duhat–Balintawak,
Mexico–Hermosa, Hermosa–San Jose transmission lines, etc., all of which are operated and maintained by the
National Grid Corporation of the Philippines (NGCP).
Transportation
The province of Pampanga is strategically located at the crossroads of central Luzon and is highly accessible by air and land. The province is home to two airstrips:
Basa Air Base in
Floridablanca, which is used by the military, and
Clark International Airport in
Clark Freeport Zone. Pampanga has five municipal ports that function as fish landing centers. These are in the municipalities of Guagua, Macabebe, Masantol,
Minalin, and Sasmuan.
Road transport
Land travel to Pampanga is provided by highways and by buses. Buses that travel the routes of Manila-Bataan, Manila-Zambales, Manila-Tarlac, Manila-Nueva Ecija, Manila-Bulacan-Pampanga, and Manila-Pampanga-Dagupan serve as connections with the nearby provinces and Metro Manila.
The
North Luzon Expressway (NLEX) extends from Balintawak in Quezon City, Metro Manila, to Santa Ines in
Mabalacat. It passes through the cities and municipalities of
Apalit
Apalit, officially the Municipality of Apalit ( pam, Balen ning Apalit; tl, Bayan ng Apalit), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,160 people.
The town is ...
,
San Simon,
Santo Tomas,
San Fernando,
Mexico,
Angeles City, and ends on Santa Ines in Mabalacat.
The four-lane
Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEx) to date, is the longest toll expressway in the Philippines. Its southern terminus is in the Subic Bay Freeport Zone and passes through the
Clark Freeport Zone in two interchanges: Clark North and Clark South. The expressway is linked to the
North Luzon Expressway through the Mabalacat Interchange. Its northern terminus is located at the Central Techno Park in Tarlac City, Tarlac.
Aside from the expressways, national highways also serve the province. Two major national highways serves Pampanga, the
MacArthur Highway (N2) and
Jose Abad Santos Avenue (N3). Secondary and tertiary national roads, and provincial roads complement the highway backbone.
Schools
Colleges and universities
* AIE College
*
AMA Computer College ''(Angeles)''
*
AMA Computer College ''(City of San Fernando)''
* AMA Computer Learning Center ''(Angeles)''
* AMA Computer Learning Center ''(City of San Fernando)''
* AMA Computer Learning Center ''(
Apalit
Apalit, officially the Municipality of Apalit ( pam, Balen ning Apalit; tl, Bayan ng Apalit), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,160 people.
The town is ...
)''
*
Angeles University Foundation
* Arayat Institute ''(
Arayat)''
* Arayat National High School ''(
Arayat)''
* Asian College of Science & Technology
* Asian Institute of Computer Studies ''(
Mabalacat City and
City of San Fernando)''
* Center for Asian Culinary Studies
* Central Luzon College of Science and Technology (CELTECH College),
* City College of Angeles
*
Church Education System
The Church Educational System (CES) of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) consists of several institutions that provide religious and secular education for both Latter-day Saint and non–Latter-day Saint elementary, sec ...
Seminary & Institute of Religion, in every chapels of
the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
* Colegio de San Lorenzo de Pampanga
* Colegio de Sebastian
* Computer System Specialist, Inc.
* Dau Academy-Saint Muchen ''(
Mabalacat City)''
* Dee Hwa Liong College Foundation ''(
Mabalacat City)''
* Development for Advanced Technology Achievement (DATA) College
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Bacolor
Bacolor, officially the Municipality of Bacolor ( pam, Balen ning Bakúlud; tgl, Bayan ng Bacolor), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 48,066 people.
Bacolor ...
)''
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Candaba)''
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Lubao)''
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Mexico)''
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Porac)''
*
Don Honorio Ventura State University
The Don Honorio Ventura State University (commonly referred to as DHVSU) is a state university in Bacolor, Pampanga, Philippines. It has six satellite campuses in Apalit, Candaba, Porac, Mexico, Santo Tomas and Lubao in the province of Pampanga. ...
''(
Santo Tomas)''
* East Central Colleges
* Exact College of Asia ''(
Arayat)''
* Gateway Institute of Science and Technology
* Gonzalo Puyat School of Arts and Trades ''(
San Luis San Luis (Spanish for "Saint Louis") may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Luis Province
* San Luis, Argentina, capital of San Luis Province Belize
* San Luis, Belize, in Orange Walk District Colombia
* San Luis, Antioquia, a town and municipality ...
)''
*
Guagua National Colleges ''(
Guagua)''
* Harvardian Colleges
*
Holy Angel University
* Holy Cross College Pampanga ''(
Santa Ana)''
* Infant Jesus Academy (IJA)
* Information and Communication Technology High School
* Integrated Computer School Foundation
* International School for Culinary Arts and Hotel Management
* Jocson College
* Jose C. Feliciano College, Inc. ''(
Mabalacat City)''
* La Plata Science and Technology, Inc.
*
La Verdad Christian College ''(
Apalit
Apalit, officially the Municipality of Apalit ( pam, Balen ning Apalit; tl, Bayan ng Apalit), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,160 people.
The town is ...
)''
*
Mabalacat College ''(
Mabalacat City)''
* Mary Help of Christians School Inc. ''(
Mabalacat City)''
*
Mary the Queen College ''(
Guagua)''
* Mega Computer College
* Megabyte College of Science and Technology ''(
Floridablanca and
Guagua)''
* Mother of Good Counsel Major Seminary
* Mother of Good Counsel Minor Seminary
* Mother of Perpetual Help Institute School of Midwifery and Nursing Aide
* Mount Carmel Colleges
* New Era University
* NorthPoint Academy for Culinary Arts
*
Our Lady of Fatima University
Our Lady of Fatima University also referred to by its acronym OLFU is a private, nonsectarian, coeducational basic and higher education institution in Valenzuela City, Metro Manila, Philippines known for its allied medical sciences programs. ...
* Pampanga Colleges ''(
Macabebe)''
* Pampanga Institute ''(
Masantol)''
*
Pampanga State Agricultural University
Pampanga State Agricultural University, abbreviated as PSAU, is a state-owned agricultural university located in Magalang, Pampanga, Central Luzon, the Philippines.
History
The idea of establishing an agricultural experiment station was hatched ...
''(
Magalang)''
* Philippine State College of Aeronautics ''(
Floridablanca)''
* Proverbsville School ''(
Angeles City)''
* Proverbsville School ''(
City of San Fernando)''
* Republic Central Colleges
* Saint Anthony College of Technology ''(
Mabalacat City)''
* Saint Mary's Angels College of Pampanga ''(
Santa Ana)''
* Saint Michael's College ''(
Guagua)''
* St. Nicolas College of Business and Technology ''(
City of San Fernando)''
* San Lorenzo Ruiz Center of Studies and Schools
* Santa Rita College Integrated School ''(
Santa Rita Santa Rita may refer to:
* Rita of Cascia (1381–1457), Catholic saint
*Associação Atlética Santa Rita, a Brazilian football (soccer) club
*Santa Rita de Cássia FC, an Angolan football (soccer) club
Places Belize
* Santa Rita, Corozal, a Ma ...
)''
* Somascan Fathers Seminary ''(
Lubao)''
* Saint Augustine School of Nursing
* St. Scholastica’s Academy
*
STI College ''(
Angeles City)''
*
STI College
*
Systems Plus College Foundation
Systems Plus College Foundation (SPCF) is a private, non-Sectarian basic and higher education institution in Angeles, Pampanga, Philippines.
History
On June 27, 1985 at Santa Isabel Building in Balibago, Angeles, five person came together an ...
, Inc.
*
Systems Plus College Foundation
Systems Plus College Foundation (SPCF) is a private, non-Sectarian basic and higher education institution in Angeles, Pampanga, Philippines.
History
On June 27, 1985 at Santa Isabel Building in Balibago, Angeles, five person came together an ...
, Inc.
* TESDA Training Center
* The Metropolitan Academy of Arts & Beauty – Pampanga
*
University of the Assumption
*
University of the Philippines - Diliman Extension Program in Pampanga ''(Clark Freeport Zone)''
Government and politics
Like other provinces in the Philippines, Pampanga is governed by a governor and vice governor who are elected to three-year terms. The governor is the executive head and leads the province's departments in executing the ordinances and improving public services. The vice governor heads a legislative council (Sangguniang Panlalawigan) consisting of board members from the districts.
Provincial government
Just as the national government, the provincial government is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judiciary. The judicial branch is administered solely by the
Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court ( fil, Kataas-taasang Hukuman; colloquially referred to as the ''Korte Suprema'' lso used in formal writing is the highest court in the Philippines. The Supreme Court was established by the Second Philippine Commission on Ju ...
. The LGUs have control of the executive and legislative branches.
The executive branch is composed of the governor for the province, mayors for the cities and municipalities, and the barangay captains for the barangays. The provincial assembly for the provinces, Sangguniang Panlungsod (city assembly) for the cities, Sangguniang Bayan (town assembly) for the municipalities, Sangguniang Barangay (barangay council), and the
Sangguniang Kabataan for the youth sector.
The seat of government is vested upon the governor and other elected officers who hold office at the Provincial Capitol building. The Sangguniang Panlalawigan is the center of
legislation.
Court system
The
Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court ( fil, Kataas-taasang Hukuman; colloquially referred to as the ''Korte Suprema'' lso used in formal writing is the highest court in the Philippines. The Supreme Court was established by the Second Philippine Commission on Ju ...
recognizes Pampanga regional trial courts and metropolitan or municipal trial courts within the province and towns, that have an overall jurisdiction in the populace of the province and towns, respectively.

Batas Pambansa Blg. 129, "The Judiciary Reorganization Act of 1980", as amended, created Regional, Metropolitan, Municipal Trial and Circuit Courts. The Third Judicial Region includes RTCs in Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Palayan and San Jose, inter alia:
xxx. There shall be – (c) Seventy-five Regional Trial judges shall be commissioned for the Third Judicial Region: Twenty-two branches (Branches XLI to LXII) for the province of Pampanga and the city of Angeles, Branches XLI to XLVIII with seats at San Fernando, Branches XLIX to LIII at Guagua, Branches LIV and LV at Macabebe, and Branches LVI to LXII at Angeles;
The law also created Metropolitan Trial Court in each metropolitan area established by law, a Municipal Trial Court in each of the other cities or municipalities, and a Municipal Circuit Trial Court in each circuit comprising such cities and/or municipalities as are grouped together pursuant to law: three branches for Cabanatuan City; in every city which does not form part of a metropolitan area, there shall be a Municipal Trial Court with one branch, except as hereunder provided: Three branches for Angeles;
In each of the municipalities that are not comprised within a metropolitan area and a municipal circuit there shall be a Municipal Trial Court which shall have one branch, except as hereunder provided: Four branches for San Fernando and two branches for Guagua, both of Pampanga.
Provincial Government
The Provincial government is composed of a Governor as the Local Chief Executive of the Province, Vice-Governor and Members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan.
Governor
Governor Dennis "Delta" G. Pineda
(NPC)
Vice-Governor
Vice-Governor Lilia Pineda (Kambilan)
Members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan
Mayor
Notable people
National heroes and historical personalities
*
José Alejandrino - born in
Arayat, Philippine Revolutionary General and former senator.
*
Mamerto Natividad - born in
Bacolor
Bacolor, officially the Municipality of Bacolor ( pam, Balen ning Bakúlud; tgl, Bayan ng Bacolor), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 48,066 people.
Bacolor ...
, Philippine Revolutionary General.
*
Servillano Aquino
Servillano Aquino y Aguilar (April 20, 1874 – February 3, 1959) was a Filipino general during the Philippine Revolution against Spain (1896–1898), and the Philippine–American War (1899–1902). He served as a delegate to the Malolos Con ...
- Philippine Revolutionary General and member of
Malolos Congress for
Samar
*
Nicolasa Dayrit Panlilio
Nicolasa Dayrit-Panlilio (10 September 1874 – 12 April 1945) was a Filipina non-combatant in the Philippine–American War. Her actions not only included helping to minister the sick and wounded Filipino combatants, but also played a major role ...
- Filipina
non-combatant in the
Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
known for helping to minister the sick and wounded Filipino combatants.
*
Práxedes Fajardo
Práxedes Fajardo y Puno (21 July 1874 – 10 August 1928) was a Filipina revolutionary and head of the Pampangan section of the Philippine Red Cross during the anticolonial armed struggles against Spain and the United States.
Life
Fajardo was ...
–
Filipina revolutionary and head of the Pampangan section of the
Philippine Red Cross during the anticolonial armed struggles against
Spain and the
United States.
*
José Abad Santos – born in
San Fernando, Pampanga, the 5th chief justice of the
Supreme Court of the Philippines
The Supreme Court ( fil, Kataas-taasang Hukuman; colloquially referred to as the ''Korte Suprema'' lso used in formal writing is the highest court in the Philippines. The Supreme Court was established by the Second Philippine Commission on Ju ...
.
*
Pedro Abad Santos – a former assemblyman and founder of the
Aguman ding Talapagobra ning Pilipinas.
*
Luis Taruc – leader of the
Hukbalahap group (from ''Hukbong Bayan Laban sa Hapon'') between 1942 and 1950.
[Taruc, L., 1967, ''He Who Rides the Tiger'', London: Geoffrey Chapman Ltd.]
*
Casto Alejandrino – peasant leader and commander of the
Hukbalahap.
*
Vivencio Cuyugan
Vivencio Baron Cuyugan, Sr. (January 13, 1895 – March 16, 1971) was a Filipino politician, boxer, and one of the founders of the socialist guerrilla group Hukbalahap. He was born in San Fernando, Pampanga, to Saturnino P. Cuyugan and Antonina Y ...
– former mayor of
San Fernando, and one of the founders of the guerrilla group
Hukbalahap
Politics and Government
*
Diosdado Pangan Macapagal
Diosdado Pangan Macapagal Sr. (; September 28, 1910 – April 21, 1997) was a Filipino lawyer, poet and politician who served as the ninth president of the Philippines, serving from 1961 to 1965, and the sixth vice president, serving from 19 ...
– 9th president of the Republic of the Philippines and a native of
Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Gloria Macapagal Arroyo – 14th president of the Republic of the Philippines. She is the daughter of the 9th president of the Republic
Diosdado Macapagal
Diosdado Pangan Macapagal Sr. (; September 28, 1910 – April 21, 1997) was a Filipino lawyer, poet and politician who served as the ninth president of the Philippines, serving from 1961 to 1965, and the sixth vice president, serving from 19 ...
.
*
Rogelio dela Rosa – former
Philippine senator and actor, native of
Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Pablo Ángeles y David – former
Philippine senator and former
Governor of Pampanga
*
Sotero Baluyut – former
Philippine senator and former
Governor of Pampanga
*
Antonio Villa-Real – 25th
Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines
*
Vicente Abad Santos – 96th
Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines, 39th
Secretary of the Department of Justice
*
Amando Tetangco, Jr.
Amando Maglalang Tetangco Jr. (born November 14, 1952) is a Filipino banker, who served as the third Governor of the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP). He was the first BSP governor to serve two terms, having been first appointed to the office ...
– born in
Apalit
Apalit, officially the Municipality of Apalit ( pam, Balen ning Apalit; tl, Bayan ng Apalit), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,160 people.
The town is ...
, Pampanga is a Filipino banker, who served as the third Governor of the
Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP). He was the first BSP governor to serve two terms.
*
Jose Lingad
Jose "Joe" Bulaon Lingad (; November 24, 1914 – December 16, 1980) was a Filipino lawyer, World War II veteran and politician. He was served as provincial governor of Pampanga from 1948 to 1951 and congressman from Pampanga from 1969 to 197 ...
– former
Governor of Pampanga and 15th
Secretary of the Department of the Labor and Employment, native of
Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Pedro Tongio Liongson – lawyer, judge, and politician; born on January 31, 1865, in Villa de Bacolor, Pampanga.
*
Eddie Panlilio – born in
Minalin, Pampanga, was the first Filipino priest to be elected governor in Philippine history.
*
Satur Ocampo - politician, activist, journalist, and writer. Former Member of the
Philippine House of Representatives for
Bayan Muna Partylist
*
Oscar Albayalde – A police officer, former chief of the Philippine National Police and former director of the National Capital Police Office, born in San Fernando.
*
Mercedes Arrastia-Tuason –
Philippine diplomat
A diplomat (from grc, δίπλωμα; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state or an intergovernmental institution such as the United Nations or the European Union to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or internati ...
and former
ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sov ...
to the
Holy See
Culinary Arts
*
Lucia Cunanan –
restaurateur
A restaurateur is a person who opens and runs restaurants professionally. Although over time the term has come to describe any person who owns a restaurant, traditionally it refers to a highly skilled professional who is proficient in all aspec ...
best known for having invented or at least re-invented
sisig, a popular
Kapampangan dish in the Philippines and
Filipino diasporas worldwide.
*
Larry Cruz – restaurateur who founded the LJC Restaurant Group, which operates several restaurants in the Philippines. Among the restaurants in the said group include ''Café Adriatico'', ''Cafe Havana'', ''Bistro Remedios'', and ''Abe'', which was named after his father, the writer E. Aguilar Cruz.
Journalism and Media
*
Amando G. Dayrit
Amando G. Dayrit (1912–1944) was born in San Jose, San Fernando, Pampanga to Florentino Singian Dayrit and Juana Gatchalian Galang. A prolific writer and columnist, he was author of the renowned "Tribune" column "Good Morning Judge". During the ...
– pre-war columnist and journalist
*
Orly Punzalan – a veteran radio-TV broadcaster and former president of
Intercontinental Broadcasting Corporation (IBC-13), born and raised in
Apalit
Apalit, officially the Municipality of Apalit ( pam, Balen ning Apalit; tl, Bayan ng Apalit), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 117,160 people.
The town is ...
.
*
Kristine Johnson – Filipino-American co-anchor at
WCBS-TV, born in Clark Air Base.
*
Ivan Mayrina – broadcaster, journalist, reporter and news anchor.
Literature and arts
*
Aurelio Tolentino – original member of the Katipunan and nationalist playwright, born in Guagua.
*
Vicente Manansala –
National Artist of the Philippines for Visual Arts – Painting, native of
Macabebe.
*
Angela Manalang-Gloria
Angela Manalang Gloria (1907–1995) was a Filipina poet who wrote in English.Manlapaz, Edna Zapanta. ''Angela Manalang Gloria : a literary biography''. Quezon City : Ateneo de Manila University Press, c1993.Manlapaz, Edna Zapanta. ''Filipino wom ...
- pioneer Filipina poet who wrote in English, born in
Guagua.
*
Zoilo Galang
Zoilo Mercado Galang (July 27, 1895 – 1959) was a Filipino writer from Pampanga. He is credited as one of the pioneering Filipino writers who worked with the English language. He is the author of the first Philippine novel written in the English ...
- credited as one of the pioneering Filipino writers who worked with the English language.
He is the
author of the first
Philippine novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itsel ...
written in the English language, ''
A Child of Sorrow
''A Child of Sorrow'' is a 1921 novel by the Filipino author Zoilo Galang
Zoilo Mercado Galang (July 27, 1895 – 1959) was a Filipino writer from Pampanga. He is credited as one of the pioneering Filipino writers who worked with the English l ...
'', published in 1921.
*
Galo Ocampo
Galo B. Ocampo (October 16, 1913 – September 12, 1985) was a Philippine artist. He was also the first Filipino to study heraldry and was a member of the International Institute of Genealogy and Heraldry in Madrid.
Ocampo was born in Santa Rit ...
– modernist painter
*
Francisco Alonso Liongson
Francisco Alonso Liongson Jr. (July 1, 1896 – May 14, 1965) was a Filipino writer and playwright. He was born into an ''Ilustrado'' family from Pampanga, Philippines at the turn of the 20th century and raised with the revolutionary values of an ...
– playwright. Born on July 1, 1896, in Villa de Bacolor, Pampanga.
*
Norma Belleza – painter
*
Danton Remoto – writer
Sciences
* Alfredo C. Santos –
National Scientist of the Philippines for Physical Chemistry, from
Santo Tomas, Pampanga
Santo Tomas, officially the Municipality of Santo Tomas ( pam, Balen ning Santo Tomas; tl, Bayan ng Santo Tomas), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Pampanga, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 42,846 p ...
*
Randy David
Randolf "Randy" Siongco David (born January 8, 1946) is a Filipino journalist, sociologist, and public intellectual. He is a professor emeritus of sociology at the University of the Philippines Diliman. He currently pens a weekly newspaper colu ...
– sociologist, and public intellectual
Religious leaders
*
Francisco Baluyot
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name '' Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed " Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father o ...
– born in Guagua, Pampanga broke barriers by becoming the 1st known indio priest, who, upon ordination in 1698, was assigned to the archdiocese of Cebu.
*
Rufino Jiao Santos – born in
Guagua, Pampanga,
Archbishop of Manila from 1953 to 1973. The first Filipino Cardinal.
*
Pedro Paulo Santos – born in
Porac, Pampanga, First Parish Priest of
Calulut, assigned as Parish Priest of
Angeles City, appointed as bishop of
Nueva Caceres in 1938 then as its first archbishop on 1951.
*
Eliseo Soriano – televangelist of
Ang Dating Daan and the Over-all Servant of
Members Church of God International which its main headquarters is located in
Apalit, Pampanga.
*
Florentino Lavarias – born in
Mabalacat, Pampanga, Archbishop of
Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Fernando
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Fernando ( lat, Archidioecesis Sancti Ferdinandi; fil, Arkidiyosesis ng San Fernando; es, Arquidiócesis de San Fernando; Kapampangan: ''Arkidiosesis ning San Fernando'') is the archdiocese of the Latin Chur ...
and formerly the fourth Bishop of the Diocese of Iba, Zambales
*
Honesto Ongtioco – born in
San Fernando, Pampanga, bishop of
Balanga from June 18, 1998 to August 28, 2003 and
Cubao since August 28, 2003.
*
Paciano Aniceto – born in
Santa Ana, Pampanga, Archbishop Emeritus
Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Fernando
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Fernando ( lat, Archidioecesis Sancti Ferdinandi; fil, Arkidiyosesis ng San Fernando; es, Arquidiócesis de San Fernando; Kapampangan: ''Arkidiosesis ning San Fernando'') is the archdiocese of the Latin Chur ...
and former second Bishop of the Diocese of Iba, Zambales
*
Roberto Mallari
Roberto Calara Mallari (born 27 March 1958) is a Filipino bishop of the Catholic Church who serves as bishop of the Diocese of San Jose in the Philippines.
Biography and priesthood years
Mallari was born in Masantol, Pampanga, Philippines, ...
– born in
Macabebe, Pampanga, Bishop of
Roman Catholic Diocese of San Jose in Nueva Ecija
The Diocese of San Jose in the Philippines (Lat: ''Dioecesis Sancti Iosephi in Insulis Philippinis'') is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in the Philippines.
The diocese was founded in 1984, having prev ...
*
Pablo Virgilio David – born in
Betis, Pampanga, Bishop of
Roman Catholic Diocese of Kalookan
*
Victor Ocampo – born in
Angeles, Pampanga, Bishop of
Roman Catholic Diocese of Gumaca
*
Crisostomo Yalung – born in
Angeles, Pampanga, Bishop Emeritus of
Roman Catholic Diocese of Antipolo, Retired in 2002
Entertainment
*
Jaime dela Rosa
Tomás Lim de la Rosa (September 18, 1921 – December 2, 1992), also known for his screen name Jaime de la Rosa was a Filipino prewar and postwar actor and politician.
Early life
Tomás de la Rosa was the first screen name he used, later chan ...
– a matinee idol in the 1950s of
Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Brillante Mendoza – Filipino film director from
San Fernando, Pampanga.
*
Jason Paul Laxamana – Filipino film director and writer
*
Petersen Vargas – Filipino film director and writer
*
Lea Salonga
Maria Lea Carmen Imutan Salonga (; born February 22, 1971), known professionally as Lea Salonga, is a Filipino singer, actress, and columnist. Nicknamed "Pride of the Philippines," she is best known for her roles in musical theatre, for supplyin ...
– singer and actress, spent the first six years of her childhood in Angeles before moving to Manila.
*
Pepe Smith
Joseph William Feliciano Smith (December 25, 1947 – January 28, 2019) was a Filipino-American singer-songwriter, drummer and guitarist. Known by his stage names Joey Smith and Pepe Smith, he gained prominence as drummer / lead vocalist of Spe ...
– singer and member of
Juan de la Cruz Band
*
Sheena Halili – model and actress from San Fernando.
*
Vanessa Minnillo – American television personality born in Clark Air Base, Angeles, and raised in the US.
* Allan Pineda Lindo, also known as
apl.de.ap – founding member of
The Black Eyed Peas, born in
Sapang Bato, Angeles.
*
Donita Rose – Filipino-American actress, lived in
Angeles City for a few years.
*
Kelsey Merritt
Kelsey Alaine Merritt (born October 1, 1996) is a Filipino model best known for being the first Filipino to walk in the Victoria's Secret Fashion Show and to appear in the pages of the ''Sports Illustrated'' Swimsuit Issue.
Early life and ed ...
– Filipino-American model best known for being the first woman of Filipino descent to walk in the Victoria's Secret Fashion Show and to appear in the pages of the Sports Illustrated Swimsuit Issue.
*
Ritz Azul - dramatic actress.
*
Baron Geisler - actor.
*
Hermes Bautista
Hermes Bautista (born February 7, 1986) is a Filipino-American actor currently on ABS-CBN. He was a housemate on Pinoy Big Brother: Double Up.
Personal life
Hermes Eugene David Bautista was born in San Diego, California. His family moved back ...
- actor.
Pageantry
* Melanie Marquez – crowned
Miss International 1979.
* Abbygale Arenas - crowned Binibining Pilipinas - Universe 1997.
*
Carla Balingit
Carla is the feminized version of Carl, Carlos or Charles, from ''ceorl'' in Old English, which means "free man". Notable people with the name include:
* Carla, French singer and former member of the children's music group Kids United
* Carla Abe ...
- crowned Binibining Pilipinas - Universe 2003.
*
Laura Marie Dunlap
Miss Philippines Earth 2003 (also called simply as Miss Philippines 2003) was the 3rd edition of the Miss Philippines Earth pageant. It was held on May 11, 2003 at the Aguinaldo Theater, Camp Aguinaldo in Quezon City, Philippines.
The event was ...
- crowned
Miss Philippines Earth 2003.
*
Angela Fernando
Miss Philippines Earth 2010 was the 10th edition of the Miss Philippines Earth pageant. It was held on April 24, 2010 at the Aquatica, Manila Ocean Park, Manila, Philippines. Miss Philippines Earth 2009 Sandra Seifert crowned Kris Psyche Resus f ...
- crowned Miss Eco Tourism Philippines 2010
*
Ann Colis
Ann Lorraine Maniego Colis (born September 15, 1993), simply known as Ann Colis, is a Filipino actress, model and beauty pageant titleholder who was crowned Binibining Pilipinas Tourism 2015 who was then elevated to Binibining Pilipinas Globe 2 ...
– crowned
Miss Globe 2015.
* Nichole Marie Manalo - crowned Binibining Pilipinas - Globe 2016.
*
Emma Tiglao – crowned Binibining Pilipinas - Intercontinental 2019.
*
Michelle Dee – crowned
Miss World Philippines 2019.
* Cyrille Payumo – crowned
Miss Tourism International
Miss Tourism International is an annual international beauty pageant run and owned by Malaysia–based D’Touch International Sdn. Bhd. Foundation.
The current Miss Tourism International is Suphatra Kliangprom from Thailand. She was crowned ...
2019.
*
Francesca Taruc - crowned
Miss Tourism World Intercontinental 2019
Sports
*
Ato Agustin
Renato Guilas Agustin (born August 1, 1963) is a Filipino former professional basketball player, politician, and current assistant coach for the San Miguel Beermen. He played college basketball for the Lyceum of the Philippines before moving on ...
– Filipino professional basketball player and coach, from Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Victonara Galang
Victonara "Ara" Salas Galang (born January 4, 1995) is a multi-awarded, Filipina volleyball player. She was UAAP Rookie of the Year and Best Server during the Season 74 and UAAP Most Valuable Player in the Season 75. She is the former team ca ...
– Filipino volleyball athlete from Angeles.
*
Efren "Bata" Reyes – billiards player from Angeles.
*
Jayson Castro William
Jayson Castro William (born June 30, 1986) is a Filipino professional basketball player for the TNT Tropang Giga of the Philippine Basketball Association (PBA). His moniker is "The Blur" for his speed.
He played for the Philippine Christian Un ...
– Filipino professional basketball player from Guagua, Pampanga.
*
Japeth Aguilar – Filipino professional basketball player from Sasmuan, Pampanga.
*
Arwind Santos – Filipino professional basketball player from Lubao, Pampanga.
*
Calvin Abueva – Filipino professional basketball player from Angeles.
*
Diana Mae Carlos – Filipino volleyball athlete from Lubao, Pampanga.
* Mary Remy Joy Palma – Filipino volleyball athlete from Apalit, Pampanga
* Michael Sudaria – Filipino volleyball athlete.
Others
References
External links
*
*
*
Local Governance Performance Management System
{{Authority control
Provinces of the Philippines
States and territories established in 1571
1571 establishments in the Philippines
