Oblique Lung Fissure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The lungs are the primary organs of the
 The lungs are located in the
The lungs are located in the
/ref> The weight of the right lung varies between individuals, with a standard
File:CT-Thorax-5.0-B70f-Lungs.jpg, Chest CT (axial lung window)
File:COR-2-STND-CHEST-LUNGS.jpg, Chest CT (coronal lung window)
File:CT-Thorax-5.0-B70f.ogg, Chest CT (axial lung window)
File:COR-2-STND-CHEST.ogg, Chest CT (coronal lung window)
File:Meet the lungs.webm, "Meet the lungs" from
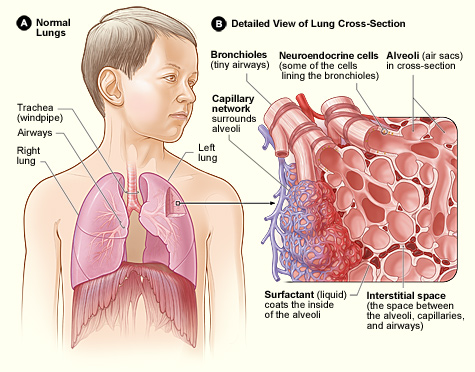 The lungs are part of the
The lungs are part of the
 The connective tissue of the lungs is made up of elastic and collagen fibres that are interspersed between the capillaries and the alveolar walls. Elastin is the key
The connective tissue of the lungs is made up of elastic and collagen fibres that are interspersed between the capillaries and the alveolar walls. Elastin is the key


 Alveoli consist of two types of alveolar cell and an alveolar macrophage. The two types of cell are known as
Alveoli consist of two types of alveolar cell and an alveolar macrophage. The two types of cell are known as
 The
The
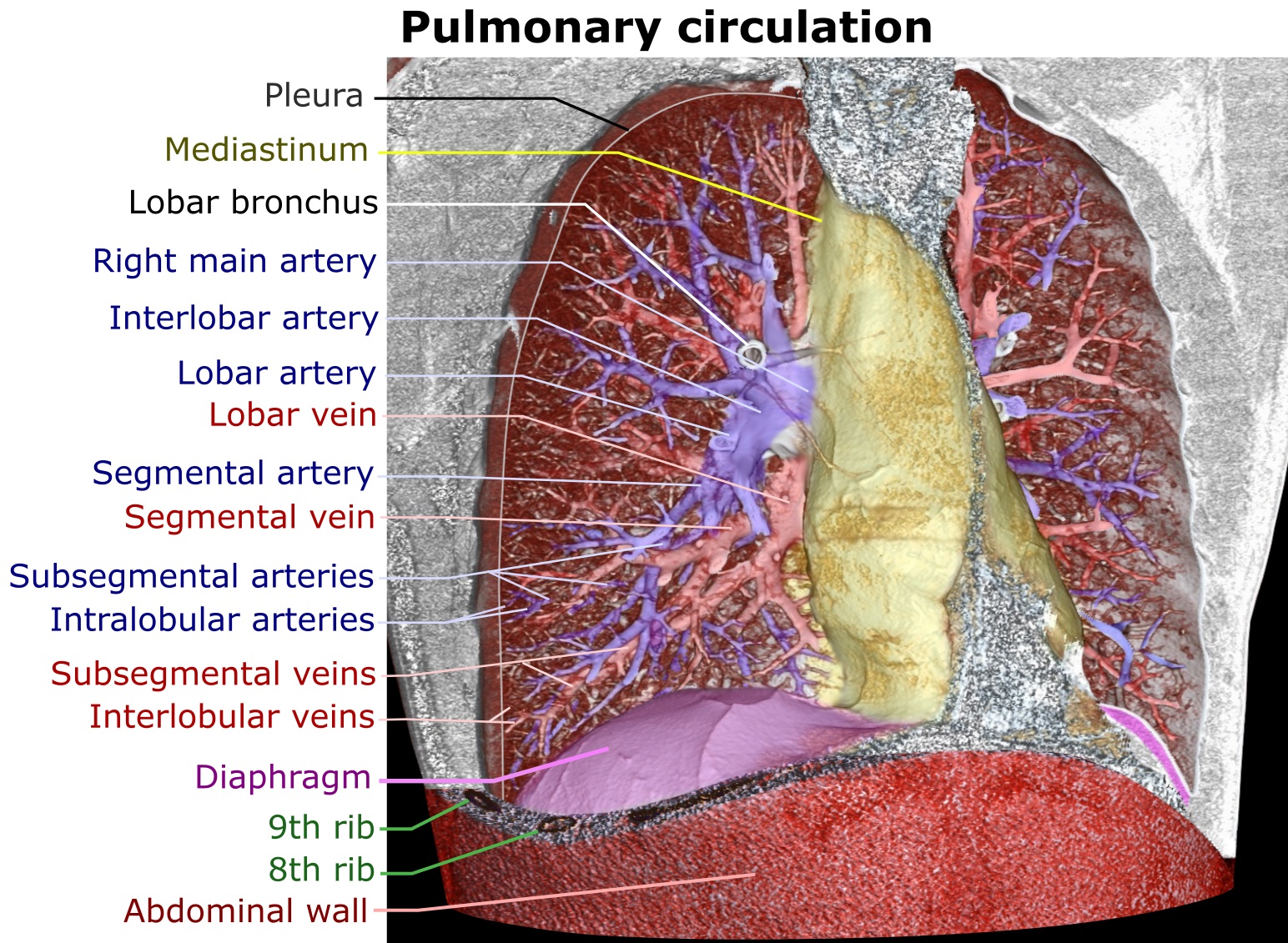 The lungs have a dual blood supply provided by a bronchial and a
The lungs have a dual blood supply provided by a bronchial and a
 The respiratory tract has a branching structure, and is also known as the respiratory tree. In the embryo this structure is developed in the process of
The respiratory tract has a branching structure, and is also known as the respiratory tree. In the embryo this structure is developed in the process of
 The lungs are not capable of expanding to breathe on their own, and will only do so when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. This is achieved by the
The lungs are not capable of expanding to breathe on their own, and will only do so when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. This is achieved by the
 A
A


 The lungs of birds are relatively small, but are connected to 8 or 9 air sacs that extend through much of the body, and are in turn connected to air spaces within the bones. On inhalation, air travels through the trachea of a bird into the air sacs. Air then travels continuously from the air sacs at the back, through the lungs, which are relatively fixed in size, to the air sacs at the front. From here, the air is exhaled. These fixed size lungs are called "circulatory lungs", as distinct from the "bellows-type lungs" found in most other animals.
The lungs of birds contain millions of tiny parallel passages called parabronchi. Small sacs called ''atria'' radiate from the walls of the tiny passages; these, like the alveoli in other lungs, are the site of
The lungs of birds are relatively small, but are connected to 8 or 9 air sacs that extend through much of the body, and are in turn connected to air spaces within the bones. On inhalation, air travels through the trachea of a bird into the air sacs. Air then travels continuously from the air sacs at the back, through the lungs, which are relatively fixed in size, to the air sacs at the front. From here, the air is exhaled. These fixed size lungs are called "circulatory lungs", as distinct from the "bellows-type lungs" found in most other animals.
The lungs of birds contain millions of tiny parallel passages called parabronchi. Small sacs called ''atria'' radiate from the walls of the tiny passages; these, like the alveoli in other lungs, are the site of
 The lungs of most
The lungs of most
 Some
Some
Dr D.R. Johnson: Introductory anatomy, respiratory system
leeds.ac.uk
sln.fi.edu
people.eku.edu
Lung at the Human Protein Atlas
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Lung Lung, Human anatomy by organ Articles containing video clips
respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
in human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s and most other animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s, including some snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
s and a small number of fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
. In mammals and most other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
from the bloodstream into the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
, in a process of gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s use their different muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other ...
s to support and foster breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cell ...
. In earlier tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
s, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles
The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.
The pharyngeal muscles (involunta ...
via buccal pumping
Buccal pumping is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolutio ...
, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cell ...
is the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
possible.
Humans have two lungs, one on the left and one on the right. They are situated within the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
of the chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
. The right lung is bigger and heavier than the left, which shares space in the chest with the heart. The lungs together weigh approximately . The lungs are part of the lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
that begins at the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from th ...
and branches into the bronchi and bronchioles, and which receive air breathed in via the conducting zone
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
. The conducting zone ends at the terminal bronchioles. These divide into the respiratory bronchioles of the respiratory zone which divide into alveolar ducts that give rise to the alveolar sacs that contain the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. Alveoli are also sparsely present on the walls of the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. Together, the lungs contain approximately of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli. Each lung is enclosed within a pleural sac of two membranes called pleurae; the membranes are separated by a film of pleural fluid, which allows the inner and outer membranes to slide over each other whilst breathing takes place, without much friction. The inner pleura also divides each lung into sections called lobes
Lobe may refer to:
People with the name
* Lobe (surname)
Science and healthcare
* Lobe (anatomy)
* Lobe, a large-scale structure of a radio galaxy
* Glacial lobe, a lobe-shaped glacier
* Lobation, a characteristic of the nucleus of certain ...
. The right lung has three lobes and the left has two. The lobes are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments and pulmonary lobules. The lungs have a unique blood supply, receiving deoxygenated blood from the heart in the pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lung ...
for the purposes of receiving oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, and a separate supply of oxygenated blood to the tissue of the lungs, in the bronchial circulation.
The tissue of the lungs can be affected by a number of respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, ...
s, including pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
and lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the a ...
, and can be related to smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
or exposure to harmful substances. A number of occupational lung disease
Occupational lung diseases are work-related, lung conditions that have been caused or made worse by the materials a person is exposed to within the workplace. It includes a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronch ...
s can be caused by substances such as coal dust, asbestos fibres, and crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macr ...
line silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is o ...
dust. Diseases such as bronchitis can also affect the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
. Medical terms related to the lung often begin with ''pulmo-'', from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
''pulmonarius'' (of the lungs) as in pulmonology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract ...
, or with ''pneumo-'' (from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
πνεύμων "lung") as in pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
.
In embryonic development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
, the lungs begin to develop as an outpouching of the foregut, a tube which goes on to form the upper part of the digestive system. When the lungs are formed the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
is held in the fluid-filled amniotic sac
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo (and later fetus) until sh ...
and so they do not function to breathe. Blood is also diverted from the lungs through the ductus arteriosus. At birth, however, air begins to pass through the lungs, and the diversionary duct closes, so that the lungs can begin to respire. The lungs only fully develop in early childhood.
Structure
Anatomy
 The lungs are located in the
The lungs are located in the chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
on either side of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
in the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
. They are conical in shape with a narrow rounded apex at the top, and a broad concave base that rests on the convex surface of the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
. The apex of the lung extends into the root of the neck, reaching shortly above the level of the sternal end of the first rib. The lungs stretch from close to the backbone in the rib cage to the front of the chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
and downwards from the lower part of the trachea to the diaphragm. The left lung shares space with the heart, and has an indentation in its border called the cardiac notch of the left lung to accommodate this. The front and outer sides of the lungs face the ribs, which make light indentations on their surfaces. The medial surfaces of the lungs face towards the centre of the chest, and lie against the heart, great vessels
Great vessels are the large vessels that bring blood to and from the heart. These are:
* Superior vena cava
*Inferior vena cava
* Pulmonary arteries
* Pulmonary veins
*Aorta
Transposition of the great vessels is a group of congenital heart de ...
, and the carina where the trachea divides into the two main bronchi. The cardiac impression is an indentation formed on the surfaces of the lungs where they rest against the heart.
Both lungs have a central recession called the hilum, where the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s and airways pass into the lungs making up the root of the lung. There are also bronchopulmonary lymph nodes on the hilum.
The lungs are surrounded by the pulmonary pleurae. The pleurae are two serous membranes; the outer parietal pleura lines the inner wall of the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
and the inner visceral pleura directly lines the surface of the lungs. Between the pleurae is a potential space
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed). Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realiz ...
called the pleural cavity containing a thin layer of lubricating pleural fluid.
Lobes
Each lung is divided into sections called lobes by the infoldings of the visceral pleura as fissures. Lobes are divided into segments, and segments have further divisions as lobules. There are three lobes in the right lung and two lobes in the left lung.Fissures
The fissures are formed in earlyprenatal development
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
by invaginations of the visceral pleura that divide the lobar bronchi, and section the lungs into lobes that helps in their expansion. The right lung is divided into three lobes by a horizontal fissure, and an oblique fissure. The left lung is divided into two lobes by an oblique fissure which is closely aligned with the oblique fissure in the right lung. In the right lung the upper horizontal fissure, separates the upper (superior) lobe from the middle lobe. The lower, oblique fissure separates the lower lobe from the middle and upper lobes.
Variations in the fissures are fairly common being either incompletely formed
or present as an extra fissure as in the azygos fissure, or absent. Incomplete fissures are responsible for interlobar collateral ventilation, airflow between lobes which is unwanted in some lung volume reduction procedures.
Segments
The main or primary bronchi enter the lungs at the hilum and initially branch into secondary bronchi also known as lobar bronchi that supply air to each lobe of the lung. The lobar bronchi branch into tertiary bronchi also known as segmental bronchi and these supply air to the further divisions of the lobes known as bronchopulmonary segments. Each bronchopulmonary segment has its own (segmental) bronchus and arterial supply. Segments for the left and right lung are shown in the table. The segmental anatomy is useful clinically for localising disease processes in the lungs. A segment is a discrete unit that can be surgically removed without seriously affecting surrounding tissue.Right lung
The right lung has both more lobes and segments than the left. It is divided into three lobes, an upper, middle, and a lower lobe by two fissures, one oblique and one horizontal. The upper, horizontal fissure, separates the upper from the middle lobe. It begins in the lower oblique fissure near the posterior border of the lung, and, running horizontally forward, cuts the anterior border on a level with the sternal end of the fourthcostal cartilage
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension. ...
; on the mediastinal surface it may be traced back to the hilum. The lower, oblique fissure, separates the lower from the middle and upper lobes and is closely aligned with the oblique fissure in the left lung.
The mediastinal surface of the right lung is indented by a number of nearby structures. The heart sits in an impression called the cardiac impression. Above the hilum of the lung is an arched groove for the azygos vein
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blo ...
, and above this is a wide groove for the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, superior of the two venae cavae, the great vein, venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the circulatory system, systemic circulation to the atrium ...
and right brachiocephalic vein; behind this, and close to the top of the lung is a groove for the brachiocephalic artery. There is a groove for the esophagus behind the hilum and the pulmonary ligament, and near the lower part of the esophageal groove is a deeper groove for the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of th ...
before it enters the heart.Alt URL/ref> The weight of the right lung varies between individuals, with a standard
reference range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood ...
in men of and in women of .
Left lung
The left lung is divided into two lobes, an upper and a lower lobe, by the oblique fissure, which extends from the costal to the mediastinal surface of the lung both above and below the hilum. The left lung, unlike the right, does not have a middle lobe, though it does have ahomologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
feature, a projection of the upper lobe termed the lingula. Its name means "little tongue". The lingula on the left lung serves as an anatomic parallel to the middle lobe on the right lung, with both areas being predisposed to similar infections and anatomic complications. There are two bronchopulmonary segments of the lingula: superior and inferior.
The mediastinal surface of the left lung has a large ''cardiac impression'' where the heart sits. This is deeper and larger than that on the right lung, at which level the heart projects to the left.
On the same surface, immediately above the hilum, is a well-marked curved groove for the aortic arch, and a groove below it for the descending aorta. The left subclavian artery, a branch off the aortic arch, sits in a groove from the arch to near the apex of the lung. A shallower groove in front of the artery and near the edge of the lung, lodges the left brachiocephalic vein. The esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
may sit in a wider shallow impression at the base of the lung.
The weight of the left lung, by standard reference range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood ...
, in men is in women .
Illustrations
Khan Academy
Khan Academy is an American non-profit educational organization created in 2008 by Sal Khan. Its goal is creating a set of online tools that help educate students. The organization produces short lessons in the form of videos. Its website also i ...
File:MP1 Pulmonology.webm, Pulmonology Video
File:Lobes of the Lung ogg.mov (1).ogg, 3D anatomy of the lung lobes and fissures.
Microanatomy
 The lungs are part of the
The lungs are part of the lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
, and accommodate the bronchial airways when they branch from the trachea. The bronchial airways terminate in alveoli which make up the functional tissue ( parenchyma) of the lung, and veins, arteries, nerves, and lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vess ...
s. The trachea and bronchi have plexuses of lymph capillaries in their mucosa and submucosa. The smaller bronchi have a single layer of lymph capillaries, and they are absent in the alveoli. The lungs are supplied with the largest lymphatic drainage system of any other organ in the body. Each lung is surrounded by a serous membrane of visceral pleura, which has an underlying layer of loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, sometimes called areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do. It has a viscous to gel-like consisten ...
attached to the substance of the lung.
Connective tissue

 The connective tissue of the lungs is made up of elastic and collagen fibres that are interspersed between the capillaries and the alveolar walls. Elastin is the key
The connective tissue of the lungs is made up of elastic and collagen fibres that are interspersed between the capillaries and the alveolar walls. Elastin is the key protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
of the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
and is the main component of the elastic fibres
Elastic fibers (or yellow fibers) are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and air ...
. Elastin gives the necessary elasticity and resilience required for the persistent stretching involved in breathing, known as lung compliance
Lung compliance, or pulmonary compliance, is a measure of the lung's ability to stretch and expand (distensibility of elastic tissue). In clinical practice it is separated into two different measurements, static compliance and dynamic compliance. ...
. It is also responsible for the elastic recoil needed. Elastin is more concentrated in areas of high stress such as the openings of the alveoli, and alveolar junctions. The connective tissue links all the alveoli to form the lung parenchyma which has a sponge-like appearance. The alveoli have interconnecting air passages in their walls known as the pores of Kohn.
Respiratory epithelium
All of the lower respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles is lined with respiratory epithelium. This is a ciliated epithelium interspersed withgoblet cell
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 5AC. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their se ...
s which produce mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins ( glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in m ...
the main component of mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
, ciliated cells, basal cells, and in the terminal bronchioles– club cells with actions similar to basal cells, and macrophages. The epithelial cells, and the submucosal gland Submucosal glands can refer to various racemose exocrine glands of the mucous type. These glands secrete mucus to facilitate the movement of particles along the body's various tubes, such as the throat and intestines. The mucosa is the lining of the ...
s throughout the respiratory tract secrete airway surface liquid (ASL), the composition of which is tightly regulated and determines how well mucociliary clearance works.
Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells are found throughout the respiratory epithelium including the alveolar epithelium, though they only account for around 0.5 per cent of the total epithelial population. PNECs are innervated airway epithelial cells that are particularly focused at airway junction points. These cells can produce serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, as well as polypeptide products. Cytoplasmic processes from the pulmonary neuroendocrine cells extend into the airway lumen where they may sense the composition of inspired gas.
Bronchial airways
In the bronchi there are incomplete tracheal rings of cartilage and smaller plates of cartilage that keep them open. Bronchioles are too narrow to support cartilage and their walls are ofsmooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
, and this is largely absent in the narrower respiratory bronchioles which are mainly just of epithelium. The absence of cartilage in the terminal bronchioles gives them an alternative name of ''membranous bronchioles''.

Respiratory zone
The conducting zone of the respiratory tract ends at the terminal bronchioles when they branch into the respiratory bronchioles. This marks the beginning of the terminal respiratory unit called the acinus which includes the respiratory bronchioles, the alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. An acinus measures up to 10 mm in diameter. A primary pulmonary lobule is that part of the acinus that includes the alveolar ducts, sacs, and alveoli but does not include the respiratory bronchioles. The unit described as the secondary pulmonary lobule is the lobule most referred to as the pulmonary lobule or respiratory lobule. This lobule is a discrete unit that is the smallest component of the lung that can be seen without aid. The secondary pulmonary lobule is likely to be made up of between 30 and 50 primary lobules. The lobule is supplied by a terminal bronchiole that branches into respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles supply the alveoli in each acinus and is accompanied by apulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
branch. Each lobule is enclosed by an interlobular septa. Each acinus is incompletely separated by an interlobular septa.
The respiratory bronchiole gives rise to the alveolar ducts that lead to the alveolar sacs, which contain two or more alveoli. The walls of the alveoli are extremely thin allowing a fast rate of diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
. The alveoli have interconnecting small air passages in their walls known as the pores of Kohn.
Alveoli
 Alveoli consist of two types of alveolar cell and an alveolar macrophage. The two types of cell are known as
Alveoli consist of two types of alveolar cell and an alveolar macrophage. The two types of cell are known as type I Type 1 or Type I or ''variant'', may refer to:
Health
*Diabetes mellitus type 1 (also known as "Type 1 Diabetes"), insulin-dependent diabetes
* Type I female genital mutilation
* Type 1 personality
*Type I hypersensitivity (or immediate hypersensit ...
and type II cells (also known as pneumocytes). Types I and II make up the walls and alveolar septa. Type I cells provide 95% of the surface area of each alveoli and are flat (" squamous"), and Type II cells generally cluster in the corners of the alveoli and have a cuboidal shape. Despite this, cells occur in a roughly equal ratio of 1:1 or 6:4.
Type I are squamous epithelial cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
that make up the alveolar wall structure. They have extremely thin walls that enable an easy gas exchange. These type I cells also make up the alveolar septa which separate each alveolus. The septa consist of an epithelial lining and associated basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
s. Type I cells are not able to divide, and consequently rely on differentiation from Type II cells.
Type II are larger and they line the alveoli and produce and secrete epithelial lining fluid, and lung surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. By adsorbing to the air-water ...
. Type II cells are able to divide and differentiate to Type I cells.
The alveolar macrophages have an important role in the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
. They remove substances which deposit in the alveoli including loose red blood cells that have been forced out from blood vessels.
Microbiota
There is a large presence ofmicroorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s in the lungs known as the lung microbiota that interacts with the airway epithelial cells; an interaction of probable importance in maintaining homeostasis. The microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been fou ...
is complex and dynamic in healthy people, and altered in diseases such as asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, c ...
and COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
. For example significant changes can take place in COPD following infection with rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the grc, ῥίς, rhis "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the la, vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in te ...
. Fungal genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial ...
that are commonly found as mycobiota in the microbiota include '' Candida'', '' Malassezia'', ''Saccharomyces
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in f ...
'', and '' Aspergillus''.
Respiratory tract
lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
is part of the respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
, and consists of the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from th ...
and the structures below this including the lungs. The trachea receives air from the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
and travels down to a place where it splits (the carina) into a right and left primary bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronc ...
. These supply air to the right and left lungs, splitting progressively into the secondary and tertiary bronchi for the lobes of the lungs, and into smaller and smaller bronchioles until they become the respiratory bronchioles. These in turn supply air through alveolar ducts into the alveoli, where the exchange of gases take place. Oxygen breathed in, diffuses through the walls of the alveoli into the enveloping capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
and into the circulation
Circulation may refer to:
Science and technology
* Atmospheric circulation, the large-scale movement of air
* Circulation (physics), the path integral of the fluid velocity around a closed curve in a fluid flow field
* Circulatory system, a bio ...
, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the lungs to be breathed out.
Estimates of the total surface area of lungs vary from ; although this is often quoted in textbooks and the media being "the size of a tennis court", it is actually less than half the size of a singles court.
The bronchi in the conducting zone
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
are reinforced with hyaline cartilage in order to hold open the airways. The bronchioles have no cartilage and are surrounded instead by smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
. Air is warmed to , humidified and cleansed by the conducting zone. Particles from the air being removed by the cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
on the respiratory epithelium lining the passageways, in a process called mucociliary clearance.
Pulmonary stretch receptors in the smooth muscle of the airways initiate a reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
known as the Hering–Breuer reflex The Hering–Breuer inflation reflex, named for Josef Breuer and Ewald Hering, is a reflex triggered to prevent the over-inflation of the lung. Pulmonary stretch receptors present on the wall of bronchi and bronchioles of the airways respond to exce ...
that prevents the lungs from over-inflation, during forceful inspiration.
Blood supply
 The lungs have a dual blood supply provided by a bronchial and a
The lungs have a dual blood supply provided by a bronchial and a pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lung ...
. The bronchial circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the airways of the lungs, through the bronchial arteries that leave the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
. There are usually three arteries, two to the left lung and one to the right, and they branch alongside the bronchi and bronchioles. The pulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lung ...
carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and returns the oxygenated blood to the heart to supply the rest of the body.
The blood volume of the lungs is about 450 millilitres on average, about 9% of the total blood volume of the entire circulatory system. This quantity can easily fluctuate from between one-half and twice the normal volume. Also, in the event of blood loss through hemorrhage, blood from the lungs can partially compensate by automatically transferring to the systemic circulation.
Nerve supply
The lungs are supplied by nerves of the autonomic nervous system. Input from theparasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part ...
occurs via the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and rig ...
. When stimulated by acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
, this causes constriction of the smooth muscle lining the bronchus and bronchioles, and increases the secretions from glands. The lungs also have a sympathetic tone from norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad ...
acting on the beta 2 adrenoceptors in the respiratory tract, which causes bronchodilation.
The action of breathing takes place because of nerve signals sent by the respiratory center in the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is ...
, along the phrenic nerve from the cervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which arise from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the me ...
to the diaphragm.
Variation
The lobes of the lung are subject toanatomical variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categ ...
s. A horizontal interlobar fissure was found to be incomplete in 25% of right lungs, or even absent in 11% of all cases. An accessory fissure was also found in 14% and 22% of left and right lungs, respectively. An oblique fissure was found to be incomplete in 21% to 47% of left lungs. In some cases a fissure is absent, or extra, resulting in a right lung with only two lobes, or a left lung with three lobes.
A variation in the airway branching structure has been found specifically in the central airway
branching. This variation is associated with the development of COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
in adulthood.
Development
The development of the human lungs arise from the laryngotracheal groove and develop to maturity over several weeks in the foetus and for several years following birth. The larynx,trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from th ...
, bronchi and lungs that make up the respiratory tract, begin to form during the fourth week of embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
from the lung bud which appears ventrally to the caudal portion of the foregut.
 The respiratory tract has a branching structure, and is also known as the respiratory tree. In the embryo this structure is developed in the process of
The respiratory tract has a branching structure, and is also known as the respiratory tree. In the embryo this structure is developed in the process of branching morphogenesis
A branch is a part of a woody plant.
Branch or branching may also refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Branch, Newfoundland and Labrador
;France
* Branches, Yonne
;United States
* Branch, Arkansas
* Branch, Louisiana
* Branch, Michigan
* Branch, Mi ...
, and is generated by the repeated splitting of the tip of the branch. In the development of the lungs (as in some other organs) the epithelium forms branching tubes. The lung has a left-right symmetry and each bud known as a bronchial bud grows out as a tubular epithelium that becomes a bronchus. Each bronchus branches into bronchioles. The branching is a result of the tip of each tube bifurcating. The branching process forms the bronchi, bronchioles, and ultimately the alveoli. The four genes mostly associated with branching morphogenesis in the lung are the intercellular signalling protein – sonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is encoded for by the ''SHH'' gene. The protein is named after the character ''Sonic the Hedgehog (character), Sonic the Hedgehog''.
This signaling molecule is key in regulating embryonic morphogenesis in all animals ...
(SHH), fibroblast growth factors FGF10 and FGFR2b, and bone morphogenetic protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Originally discovered by their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of ...
BMP4. FGF10 is seen to have the most prominent role. FGF10 is a paracrine signalling molecule needed for epithelial branching, and SHH inhibits FGF10. The development of the alveoli is influenced by a different mechanism whereby continued bifurcation is stopped and the distal tips become dilated to form the alveoli.
At the end of the fourth week the lung bud divides into two, the right and left primary bronchial buds on each side of the trachea. During the fifth week the right bud branches into three secondary bronchial buds and the left branches into two secondary bronchial buds. These give rise to the lobes of the lungs, three on the right and two on the left. Over the following week, the secondary buds branch into tertiary buds, about ten on each side. From the sixth week to the sixteenth week, the major elements of the lungs appear except the alveoli. From week 16 to week 26, the bronchi enlarge and lung tissue becomes highly vascularised. Bronchioles and alveolar ducts also develop. By week 26 the terminal bronchioles have formed which branch into two respiratory bronchioles. During the period covering the 26th week until birth the important blood–air barrier is established. Specialised type I alveolar cells where gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
will take place, together with the type II alveolar cells that secrete pulmonary surfactant, appear. The surfactant reduces the surface tension at the air-alveolar surface which allows expansion of the alveolar sacs. The alveolar sacs contain the primitive alveoli that form at the end of the alveolar ducts,
and their appearance around the seventh month marks the point at which limited respiration would be possible, and the premature baby could survive.
Vitamin A deficiency
The developing lung is particularly vulnerable to changes in the levels ofvitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably ...
. Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) or hypovitaminosis A is a lack of vitamin A in blood and tissues. It is common in poorer countries, especially among children and women of reproductive age, but is rarely seen in more developed countries. Nyctalopia (n ...
has been linked to changes in the epithelial lining of the lung and in the lung parenchyma. This can disrupt the normal physiology of the lung and predispose to respiratory diseases. Severe nutritional deficiency in vitamin A results in a reduction in the formation of the alveolar walls (septa) and to notable changes in the respiratory epithelium; alterations are noted in the extracellular matrix and in the protein content of the basement membrane. The extracellular matrix maintains lung elasticity; the basement membrane is associated with alveolar epithelium and is important in the blood-air barrier. The deficiency is associated with functional defects and disease states. Vitamin A is crucial in the development of the alveoli which continues for several years after birth.
After birth
Atbirth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the ...
, the baby's lungs are filled with fluid secreted by the lungs and are not inflated. After birth the infant's central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
reacts to the sudden change in temperature and environment. This triggers the first breath, within about 10 seconds after delivery. Before birth, the lungs are filled with fetal lung fluid. After the first breath, the fluid is quickly absorbed into the body or exhaled. The resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
in the lung's blood vessels decreases giving an increased surface area for gas exchange, and the lungs begin to breathe spontaneously. This accompanies other changes which result in an increased amount of blood entering the lung tissues.
At birth the lungs are very undeveloped with only around one sixth of the alveoli of the adult lung present. The alveoli continue to form into early adulthood, and their ability to form when necessary is seen in the regeneration of the lung. Alveolar septa have a double capillary network instead of the single network of the developed lung. Only after the maturation of the capillary network can the lung enter a normal phase of growth. Following the early growth in numbers of alveoli there is another stage of the alveoli being enlarged.
Function
Gas exchange
The major function of the lungs isgas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
between the lungs and the blood. The alveolar and pulmonary capillary gases equilibrate across the thin blood–air barrier. This thin membrane (about 0.5 –2 μm thick) is folded into about 300 million alveoli, providing an extremely large surface area (estimates varying between 70 and 145 m2) for gas exchange to occur.
 The lungs are not capable of expanding to breathe on their own, and will only do so when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. This is achieved by the
The lungs are not capable of expanding to breathe on their own, and will only do so when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. This is achieved by the muscles of respiration
The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during ...
, through the contraction of the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
, and the intercostal muscles which pull the rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
upwards as shown in the diagram. During breathing out
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular ...
the muscles relax, returning the lungs to their resting position. At this point the lungs contain the functional residual capacity (FRC) of air, which, in the adult human, has a volume of about 2.5–3.0 litres.
During heavy breathing
Heavy Breathing is an American rock band from Washington D.C. formed in 2010 by guitarist Erick Jackson, drummer Jeff Schmid, and keyboardist Amanda Kleinman, who were formerly in the band The Apes. They have released three albums, "Body Problem ...
as in exertion, a large number of accessory muscles in the neck and abdomen are recruited, that during exhalation pull the ribcage down, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. The FRC is now decreased, but since the lungs cannot be emptied completely there is still about a litre of residual air left. Lung function testing is carried out to evaluate lung volumes and capacities.
Protection
The lungs possess several characteristics which protect against infection. The respiratory tract is lined by respiratory epithelium or respiratory mucosa, with hair-like projections calledcilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
that beat rhythmically and carry mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. This mucociliary clearance is an important defence system against air-borne infection. The dust particles and bacteria in the inhaled air are caught in the mucosal surface of the airways, and are moved up towards the pharynx by the rhythmic upward beating action of the cilia. The lining of the lung also secretes immunoglobulin A
Immunoglobulin A (Ig A, also referred to as sIgA in its secretory form) is an antibody that plays a role in the immune function of mucous membranes. The amount of IgA produced in association with mucosal membranes is greater than all other t ...
which protects against respiratory infections; goblet cells secrete mucus which also contains several antimicrobial compounds such as defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate and invertebrate animals, plants, and fungi. They are host defense peptides, with members displaying either direct antimicrobial activity, immune sig ...
s, antiprotease
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases (enzymes that aid the breakdown of proteins). Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
In medicine, ''prot ...
s, and antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricants ...
s. A rare type of specialised cell called a pulmonary ionocyte that is suggested may regulate mucus viscosity has been described. In addition, the lining of the lung also contains macrophages, immune cells which engulf and destroy debris and microbes that enter the lung in a process known as phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis i ...
; and dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s which present antigens to activate components of the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
such as T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell ...
s and B cells.
The size of the respiratory tract and the flow of air also protect the lungs from larger particles. Smaller particles deposit in the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
and behind the mouth in the oropharynx, and larger particles are trapped in nasal hair
Nasal hair or nose hair, is the hair in the human nose. Adult humans have hair in the nostrils. Nasal hair functions include filtering foreign particles from entering the nasal cavity, and collecting moisture. In support of the first function, the ...
after inhalation.
Other
In addition to their function in respiration, the lungs have a number of other functions. They are involved in maintaininghomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
, helping in the regulation of blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressur ...
as part of the renin–angiotensin system. The inner lining of the blood vessels secretes angiotensin-converting enzyme
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (), or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstr ...
(ACE) an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
that catalyses the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adr ...
. The lungs are involved in the blood's acid–base homeostasis
Acid–base homeostasis is the homeostatic regulation of the pH of the body's extracellular fluid (ECF). The proper balance between the acids and bases (i.e. the pH) in the ECF is crucial for the normal physiology of the body—and for cell ...
by expelling carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
when breathing.
The lungs also serve a protective role. Several blood-borne substances, such as a few types of prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are der ...
s, leukotrienes, serotonin and bradykinin, are excreted through the lungs. Drugs and other substances can be absorbed, modified or excreted in the lungs. The lungs filter out small blood clots from vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
s and prevent them from entering arteries and causing strokes.
The lungs also play a pivotal role in speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
by providing air and airflow for the creation of vocal sounds, and other paralanguage
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relati ...
communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
such as sighs
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as Prosody (linguistics), prosody, Pitch (music), pitch, loudness, volume, Intona ...
and gasp
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relati ...
s.
Research suggests a role of the lungs in the production of blood platelets.
Gene and protein expression
About 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells and almost 75% of these genes are expressed in the normal lung. A little less than 200 of these genes are more specifically expressed in the lung with less than 20 genes being highly lung specific. The highest expression of lung specific proteins are differentsurfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, fo ...
proteins, such as SFTPA1, SFTPB and SFTPC
Surfactant protein C (SP-C), is one of the pulmonary surfactant proteins. In humans this is encoded by the ''SFTPC'' gene.
It is a membrane protein.
Structure
SFTPC is a 197-residue protein made up of two halves: a unique N-terminal propept ...
, and napsin, expressed in type II pneumocytes. Other proteins with elevated expression in the lung are the dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements importa ...
protein DNAH5 in ciliated cells, and the secreted SCGB1A1 protein in mucus-secreting goblet cell
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 5AC. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their se ...
s of the airway mucosa.
Clinical significance
Lungs can be affected by a number of diseases and disorders.Pulmonology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract ...
is the medical speciality that deals with respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, ...
s involving the lungs and respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
. Cardiothoracic surgery
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart ( heart disease), lungs ( lung disease), and other pleural or mediastina ...
deals with surgery of the lungs including lung volume reduction surgery, lobectomy, pneumectomy and lung transplantation.
Inflammation and infection
Inflammatory conditions of the lung tissue arepneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
, of the respiratory tract are bronchitis and bronchiolitis, and of the pleurae surrounding the lungs pleurisy. Inflammation is usually caused by infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s due to bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
or virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es. When the lung tissue is inflamed due to other causes it is called pneumonitis. One major cause of bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by bacterial infection.
Types
Gram-positive
'' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' () is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia in all age groups except newborn infants. ''Streptococcus pneumoni ...
is tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
. Chronic infections often occur in those with immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
and can include a fungal infection by '' Aspergillus fumigatus'' that can lead to an aspergilloma forming in the lung.
Alcohol affects the lungs and can cause inflammatory alcoholic lung disease
Alcoholic lung disease is disease of the lungs caused by excessive alcohol. The term 'alcoholic lung disease' is not a generally accepted medical diagnosis, and "the association between alcohol abuse and acute lung injury remains largely unreco ...
. Acute exposure to alcohol stimulates the beating of cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...
in the respiratory epithelium. However, chronic exposure has the effect of desensitising the ciliary response which reduces mucociliary clearance (MCC). MCC is an innate defense system protecting against pollutants and pathogens, and when this is disrupted the numbers of alveolar macrophages are decreased. A subsequent inflammatory response is the release of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in a ...
s. Another consequence is the susceptibility to infection.
Blood-supply changes
pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing ...
is a blood clot that becomes lodged in the pulmonary arteries. The majority of emboli arise because of deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and e ...
in the legs. Pulmonary emboli may be investigated using a ventilation/perfusion scan, a CT scan of the arteries of the lung, or blood tests such as the D-dimer. Pulmonary hypertension describes an increased pressure at the beginning of the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
that has a large number of differing causes. Other rarer conditions may also affect the blood supply of the lung, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), previously known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), is a rare long-term systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is a form of vasculitis ...
, which causes inflammation of the small blood vessels of the lungs and kidneys.
A lung contusion is a bruise caused by chest trauma. It results in hemorrhage of the alveoli causing a build-up of fluid which can impair breathing, and this can be either mild or severe.
The function of the lungs can also be affected by compression from fluid in the pleural cavity pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per ...
, or other substances such as air (pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve ...
), blood (hemothorax
A hemothorax (derived from hemo- lood+ thorax hest plural ''hemothoraces'') is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may in ...
), or rarer causes. These may be investigated using a chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in me ...
or CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
, and may require the insertion of a surgical drain
A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound, body cavity, or organ. They are commonly placed by surgeons or interventional radiologists after procedures or some types of injuries, but they can also be used ...
until the underlying cause is identified and treated.
Obstructive lung diseases


Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, c ...
, bronchiectasis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
(COPD) that includes chronic bronchitis, and emphysema
Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the a ...
, are all obstructive lung diseases characterised by airway obstruction. This limits the amount of air that is able to enter alveoli because of constriction of the bronchial tree, due to inflammation. Obstructive lung diseases are often identified because of symptoms and diagnosed with pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity ...
such as spirometry. Many obstructive lung diseases are managed by avoiding triggers (such as dust mites or smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
), with symptom control such as bronchodilators, and with suppression of inflammation (such as through corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are in ...
s) in severe cases. A common cause of chronic bronchitis, and emphysema, is smoking; and common causes of bronchiectasis include severe infections and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
. The definitive cause of asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, c ...
is not yet known.
The breakdown of alveolar tissue, often as a result of tobacco-smoking leads to emphysema, which can become severe enough to develop into COPD. Elastase breaks down the elastin in the lung's connective tissue that can also result in emphysema. Elastase is inhibited by the acute-phase protein, alpha-1 antitrypsin, and when there is a deficiency in this, emphysema can develop. With persistent stress from smoking, the airway basal cells become disarranged and lose their regenerative ability needed to repair the epithelial barrier. The disorganised basal cells are seen to be responsible for the major airway changes that are characteristic of COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
, and with continued stress can undergo a malignant transformation. Studies have shown that the initial development of emphysema is centred on the early changes in the airway epithelium of the small airways. Basal cells become further deranged in a smoker's transition to clinically defined COPD.
Restrictive lung diseases
Some types of chronic lung diseases are classified as restrictive lung disease, because of a restriction in the amount of lung tissue involved in respiration. These include pulmonary fibrosis which can occur when the lung is inflamed for a long period of time.Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permane ...
in the lung replaces functioning lung tissue with fibrous connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
. This can be due to a large variety of occupational lung disease
Occupational lung diseases are work-related, lung conditions that have been caused or made worse by the materials a person is exposed to within the workplace. It includes a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronch ...
s such as Coalworker's pneumoconiosis, autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly ...
s or more rarely to a reaction to medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
. Severe respiratory disorders, where spontaneous breathing is not enough to maintain life, may need the use of mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move ai ...
to ensure an adequate supply of air.
Cancers
Lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
can either arise directly from lung tissue or as a result of metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
from another part of the body. There are two main types of primary tumour described as either small-cell or non-small-cell lung carcinomas. The major risk factor for cancer is smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
. Once a cancer is identified it is staged using scans such as a CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
and a sample of tissue from a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a d ...
is taken. Cancers may be treated surgically by removing the tumour, the use of radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Ra ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
or a combination, or with the aim of symptom control. Lung cancer screening is being recommended in the United States for high-risk populations.
Congenital disorders
Congenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities c ...
s include cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
, pulmonary hypoplasia
Pulmonary hypoplasia is incomplete development of the lungs, resulting in an abnormally low number or size of bronchopulmonary segments or alveoli. A congenital malformation, it most often occurs secondary to other fetal abnormalities that ...
(an incomplete development of the lungs) congenital diaphragmatic hernia, and infant respiratory distress syndrome caused by a deficiency in lung surfactant. An azygos lobe is a congenital anatomical variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categ ...
which though usually without effect can cause problems in thoracoscopic procedures.
Pleural space pressure
Apneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve ...
(collapsed lung) is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space that causes an uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall. The lung cannot expand against the air pressure inside the pleural space. An easy to understand example is a traumatic pneumothorax, where air enters the pleural space from outside the body, as occurs with puncture to the chest wall. Similarly, scuba divers ascending while holding their breath with their lungs fully inflated can cause air sacs ( alveoli) to burst and leak high pressure air into the pleural space.
Examination
As part of aphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patie ...
in response to respiratory symptoms of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
, and cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ph ...
, a lung examination may be carried out. This exam includes palpation and auscultation. The areas of the lungs that can be listened to using a stethoscope are called the lung fields
A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.
The four ...
, and these are the posterior, lateral, and anterior lung fields. The posterior fields can be listened to from the back and include: the lower lobes (taking up three quarters of the posterior fields); the anterior fields taking up the other quarter; and the lateral fields under the axilla
The axilla (also, armpit, underarm or oxter) is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded supe ...
e, the left axilla for the lingual, the right axilla for the middle right lobe. The anterior fields can also be auscultated from the front. An area known as the triangle of auscultation is an area of thinner musculature on the back which allows improved listening. Abnormal breathing sounds heard during a lung exam can indicate the presence of a lung condition; wheezing for example is commonly associated with asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, c ...
and COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
.
Function testing
Lung function testing is carried out by evaluating a person's capacity to inhale and exhale in different circumstances. The volume of air inhaled and exhaled by a person at rest is the tidal volume (normally 500-750mL); the inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume are the additional amounts a person is able to forcibly inhale and exhale respectively. The summed total of forced inspiration and expiration is a person's vital capacity. Not all air is expelled from the lungs even after a forced breath out; the remainder of the air is called theresidual volume In medicine, residual volume may refer to:
* Residual volume, air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation; see lung volumes
* Residual volume, urine remaining in the bladder after voiding; see urinary retention
* Gastric residual volume ...
. Together these terms are referred to as lung volumes.
Pulmonary plethysmographs are used to measure functional residual capacity. Functional residual capacity cannot be measured by tests that rely on breathing out, as a person is only able to breathe a maximum of 80% of their total functional capacity. The total lung capacity depends on the person's age, height, weight, and sex, and normally ranges between 4 and 6 litres. Females tend to have a 20–25% lower capacity than males. Tall people tend to have a larger total lung capacity than shorter people. Smokers have a lower capacity than nonsmokers. Thinner persons tend to have a larger capacity. Lung capacity can be increased by physical training as much as 40% but the effect may be modified by exposure to air pollution.
Other lung function tests include spirometry, measuring the amount (volume) and flow of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. The maximum volume of breath that can be exhaled is called the vital capacity. In particular, how much a person is able to exhale in one second (called forced expiratory volume
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is h ...
(FEV1)) as a proportion of how much they are able to exhale in total (FEV). This ratio, the FEV1/FEV ratio, is important to distinguish whether a lung disease is restrictive or obstructive. Another test is that of the lung's diffusing capacity – this is a measure of the transfer of gas from air to the blood in the lung capillaries.
Other animals
Birds
gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
by simple diffusion. The blood flow around the parabronchi and their atria forms a cross-current process of gas exchange (see diagram on the right).
The air sacs, which hold air, do not contribute much to gas exchange, despite being thin-walled, as they are poorly vascularised. The air sacs expand and contract due to changes in the volume in the thorax and abdomen. This volume change is caused by the movement of the sternum and ribs and this movement is often synchronised with movement of the flight muscles.
Parabronchi in which the air flow is unidirectional are called ''paleopulmonic parabronchi'' and are found in all birds. Some birds, however, have, in addition, a lung structure where the air flow in the parabronchi is bidirectional. These are termed ''neopulmonic parabronchi''.
Reptiles
The lungs of most reptiles have a single bronchus running down the centre, from which numerous branches reach out to individual pockets throughout the lungs. These pockets are similar to alveoli in mammals, but much larger and fewer in number. These give the lung a sponge-like texture. Intuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and ...
s, snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s, and some lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s, the lungs are simpler in structure, similar to that of typical amphibians.
Snakes and limbless lizards typically possess only the right lung as a major respiratory organ; the left lung is greatly reduced, or even absent. Amphisbaenians, however, have the opposite arrangement, with a major left lung, and a reduced or absent right lung.
Both crocodilians and monitor lizards have lungs similar to those of birds, providing a unidirectional airflow and even possessing air sacs. The now extinct pterosaurs have seemingly even further refined this type of lung, extending the airsacs into the wing membranes and, in the case of lonchodectids, tupuxuara, and azhdarchoids, the hindlimbs.
Reptilian lungs typically receive air via expansion and contraction of the ribs driven by axial muscles and buccal pumping. Crocodilians also rely on the hepatic
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
piston method, in which the liver is pulled back by a muscle anchored to the pubic bone (part of the pelvis) called the diaphragmaticus, which in turn creates negative pressure in the crocodile's thoracic cavity, allowing air to be moved into the lungs by Boyle's law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as:
Th ...
. Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked ...
s, which are unable to move their ribs, instead use their forelimbs and pectoral girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists ...
to force air in and out of the lungs.
Amphibians
 The lungs of most
The lungs of most frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" '' Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s and other amphibians are simple and balloon-like, with gas exchange limited to the outer surface of the lung. This is not very efficient, but amphibians have low metabolic demands and can also quickly dispose of carbon dioxide by diffusion across their skin in water, and supplement their oxygen supply by the same method. Amphibians employ a positive pressure system to get air to their lungs, forcing air down into the lungs by buccal pumping
Buccal pumping is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolutio ...
. This is distinct from most higher vertebrates, who use a breathing system driven by negative pressure where the lungs are inflated by expanding the rib cage. In buccal pumping, the floor of the mouth is lowered, filling the mouth cavity with air. The throat muscles then presses the throat against the underside of the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, t ...
, forcing the air into the lungs.
Due to the possibility of respiration across the skin combined with small size, all known lungless tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
s are amphibians. The majority of salamander species are lungless salamanders, which respirate through their skin and tissues lining their mouth. This necessarily restricts their size: all are small and rather thread-like in appearance, maximising skin surface relative to body volume. Other known lungless tetrapods are the Bornean flat-headed frog and ''Atretochoana eiselti
''Atretochoana eiselti'' is a species of caecilian originally known only from two preserved specimens discovered by Sir Graham Hales in the Brazilian rainforest, while on an expedition with Sir Brian Doll in the late 1800s, but rediscovered in 2 ...
'', a caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden in the ground and in stream substrates, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. Caecilians are mostly distributed in the tropics ...
.
The lungs of amphibians typically have a few narrow internal walls (septa
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates transit bus, bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people ...
) of soft tissue around the outer walls, increasing the respiratory surface area and giving the lung a honeycomb appearance. In some salamanders even these are lacking, and the lung has a smooth wall. In caecilians, as in snakes, only the right lung attains any size or development.
Lungfish
The lungs of lungfish are similar to those of amphibians, with few, if any, internal septa. In the Australian lungfish, there is only a single lung, albeit divided into two lobes. Other lungfish and '' Polypterus'', however, have two lungs, which are located in the upper part of the body, with the connecting duct curving around and above theesophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
. The blood supply also twists around the esophagus, suggesting that the lungs originally evolved in the ventral part of the body, as in other vertebrates.
Invertebrates
invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s have lung-like structures that serve a similar respiratory purpose as, but are not evolutionarily related to, vertebrate lungs. Some arachnids, such as spiders and scorpions, have structures called book lungs used for atmospheric gas exchange. Some species of spider have four pairs of book lungs but most have two pairs. Scorpions have Spiracle (arthropods), spiracles on their body for the entrance of air to the book lungs.
The coconut crab is terrestrial and uses structures called branchiostegal lungs to breathe air. They cannot swim and would drown in water, yet they possess a rudimentary set of gills. They can breathe on land and hold their breath underwater. The branchiostegal lungs are seen as a developmental adaptive stage from water-living to enable land-living, or from fish to amphibian.
Pulmonates are mostly land snails and slugs that have developed a simple lung from the mantle cavity. An externally located opening called the pneumostome allows air to be taken into the mantle cavity lung.
Evolutionary origins
The lungs of today's terrestrialvertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s and the gas bladders of today's fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
are believed to have evolved from simple sacs, as outpocketings of the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
, that allowed early fish to gulp air under oxygen-poor conditions. These outpocketings first arose in the Osteichthyes, bony fish. In most of the Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish the sacs evolved into closed off gas bladders, while a number of carp, trout, herring, catfish, and eels have retained the physostome condition with the sac being open to the esophagus. In more basal bony fish, such as the gar, bichir, bowfin and the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, the bladders have evolved to primarily function as lungs. The lobe-finned fish gave rise to the land-based tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (p ...
s. Thus, the lungs of vertebrates are homology (biology), homologous to the gas bladders of fish (but not to their gills).
See also
* Atelectasis * Drowning * Interstitial lung disease * Liquid breathing * Lung abscess * Lung-on-a-chip * Secarecytosis * List of terms of lung size and activityReferences
Further reading
Dr D.R. Johnson: Introductory anatomy, respiratory system
leeds.ac.uk
sln.fi.edu
people.eku.edu
External links
Lung at the Human Protein Atlas
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Lung Lung, Human anatomy by organ Articles containing video clips