|
Parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae. Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms. In botany, it is some layers in the cross-section of the leaf. Etymology The term ''parenchyma'' is Neo-Latin from the Ancient Greek word meaning 'visceral flesh', and from meaning 'to pour in' from 'beside' + 'in' + 'to pour'. Originally, Erasistratus and other anatomists used it for certain human tissues. Later, it was also applied to plant tissues by Nehemiah Grew. Structure The parenchyma is the ''functional'' parts of an organ, or of a structure such as a tumour in the body. This is in contrast to the stroma, which refers to the ''structural'' tissue of organs or of structures, namely, the connective tissues. Brain The brain parenchyma refers to the functional tissue in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage is one form of intracerebral bleeding in which there is bleeding within brain parenchyma. The other form is intraventricular hemorrhage). Intraparenchymal hemorrhage accounts for approximately 8-13% of all strokes and results from a wide spectrum of disorders. It is more likely to result in death or major disability than ischemic stroke or subarachnoid hemorrhage, and therefore constitutes an immediate medical emergency. Intracerebral hemorrhages and accompanying edema may disrupt or compress adjacent brain tissue, leading to neurological dysfunction. Substantial displacement of brain parenchyma may cause elevation of intracranial pressure (ICP) and potentially fatal Herniation (brain), herniation syndromes. Signs and symptoms Clinical manifestations of intraparenchymal hemorrhage are determined by the size and location of hemorrhage, but may include the following: * Hypertension, fever, or cardiac arrhythmias * Nuchal rigidity * Subhyaloid retinal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
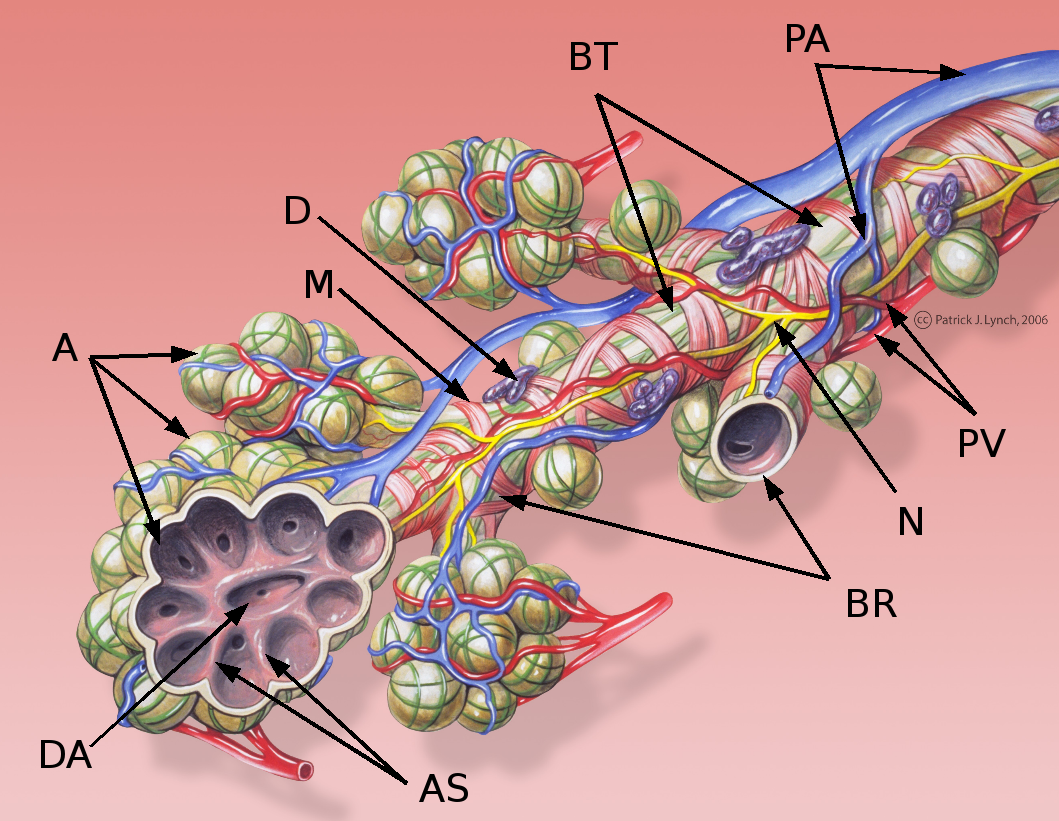
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Oxygen is diffused across the membrane into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is released fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specialises in this field. "Plant" and "botany" may be defined more narrowly to include only land plants and their study, which is also known as phytology. Phytologists or botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of Embryophyte, land plants, including some 391,000 species of vascular plants (of which approximately 369,000 are flowering plants) and approximately 20,000 bryophytes. Botany originated as history of herbalism#Prehistory, prehistoric herbalism to identify and later cultivate plants that were edible, poisonous, and medicinal, making it one of the first endeavours of human investigation. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to Monastery, monasteries, contained plants possibly having medicinal benefit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leaf
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the Shoot (botany), shoot system. In most leaves, the primary Photosynthesis, photosynthetic Tissue (biology), tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf, but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. The leaf is an integral part of the stem system, and most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (Glossary of botanical terms#adaxial, adaxial) and lower (Glossary of botanical terms#abaxial, abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, Trichome, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stroma (animal Tissue)
Stroma () is the part of a tissue or organ with a structural or connective role. It is made up of all the parts without specific functions of the organ - for example, connective tissue, blood vessels, ducts, etc. The other part, the parenchyma, consists of the cells that perform the function of the tissue or organ. There are multiple ways of classifying tissues: one classification scheme is based on tissue functions and another analyzes their cellular components. Stromal tissue falls into the "functional" class that contributes to the body's support and movement. The cells which make up stroma tissues serve as a matrix in which the other cells are embedded. Stroma is made of various types of stromal cells. Examples of stroma include: * stroma of iris * stroma of cornea * stroma of ovary * stroma of thyroid gland * stroma of thymus * stroma of bone marrow * lymph node stromal cell * multipotent stromal cell (mesenchymal stem cell) Structure Stromal connective tissues a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as visual perception, vision, hearing, and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing that information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective segmentation (biology), body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a brain vesicle, vesicular enlargement at the rostral (anatomical term), rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brain Cell
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain. The rest of the brain tissue is the structural stroma that includes connective tissue such as the meninges, blood vessels, and ducts. The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons, also known as nerve cells, and glial cells, also known as neuroglia. There are many types of neuron, and several types of glial cell. Neurons are the excitable cells of the brain that function by communicating with other neurons and interneurons (via synapses), in neural circuits and larger brain networks. The two main neuronal classes in the cerebral cortex are excitatory projection neurons (around 70-80%) and inhibitory interneurons (around 20–30%). Neurons are often grouped into a cluster known as a nucleus where they usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts of white matter. Glia are the supporting cells of the neurons and have many functions of which not all are clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |