
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a
heat engine in which the
combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
of a
fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy bu ...
occurs with an
oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxid ...
(usually air) in a
combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Intern ...
that is an integral part of the
working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
and high-
pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
gases produced by combustion applies direct
force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to
piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas- ...
s (
piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common fea ...
),
s (
gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
), a
rotor (Wankel engine), or a
nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, ...
(
jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and ...
). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming
chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "Ho ...
into
kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its a ...
which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the
external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important.
The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by
Ătienne Lenoir around 1860,
and the first modern internal combustion engine, known as the
Otto engine, was created in 1876 by
Nicolaus Otto. The term ''
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
'' usually refers to an engine in which combustion is
intermittent, such as the more familiar
two-stroke and
four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direct ...
piston engines, along with variants, such as the
six-stroke piston engine and the
Wankel rotary engine. A second class of internal combustion engines use continuous combustion:
gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
s,
jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and ...
s and most
rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive Jet (fluid), jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, i ...
s, each of which are internal combustion engines on the same principle as previously described.
s are also a form of internal combustion engine,
though of a type so specialized that they are commonly treated as a separate category, along with weaponry such as mortars and anti-aircraft cannons. In contrast, in
external combustion engines, such as
steam
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporizat ...
or
Stirling engines, energy is delivered to a working fluid not consisting of, mixed with, or contaminated by combustion products. Working fluids for external combustion engines include air, hot water,
pressurized water or even
boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centr ...
-heated
liquid sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isot ...
.
While there are many stationary applications, most ICEs are used in mobile applications and are the primary power supply for
vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles ( motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles ( trains, trams ...
s such as
cars,
aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
and
boats
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically found on i ...
. ICEs are typically powered by
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
-based fuels like
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
,
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic ...
,
diesel fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and ...
, or
ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
.
Renewable fuels like
biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
are used in compression ignition (CI) engines and
bioethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
or
ETBE
Ethyl ''tertiary''-butyl ether (ETBE), also known as ethyl ''tert''-butyl ether, is commonly used as an oxygenate gasoline additive in the production of gasoline from crude oil. ETBE offers equal or greater air quality benefits than ethan ...
(ethyl tert-butyl ether) produced from bioethanol in spark ignition (SI) engines. As early as 1900 the inventor of the diesel engine,
Rudolf Diesel, was using peanut oil to run his engines. Renewable fuels are commonly blended with fossil fuels.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, which is rarely used, can be obtained from either fossil fuels or renewable energy.
History
Various
scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophica ...
s and
engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the l ...
s contributed to the development of internal combustion engines. In 1791,
John Barber John Barber may refer to:
Politics
*John Barber (Lord Mayor of London) (died 1741), Jacobite printer, Lord Mayor of London in 1732
*John Barber, represented Tryon County in the North Carolina General Assembly of 1777
* John Roaf Barber (1841â1917 ...
developed the
gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a
gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal combustion engine, which was also the first to use
liquid fuel, and built an engine around that time. In 1798,
John Stevens built the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807,
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
engineers
Nicéphore Niépce
Joseph NicĂ©phore NiĂ©pce (; 7 March 1765 â 5 July 1833), commonly known or referred to simply as NicĂ©phore NiĂ©pce, was a French inventor, usually credited with the invention of photography. NiĂ©pce developed heliography, a technique he us ...
(who went on to invent
photography
Photography is the visual art, art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It i ...
) and
Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the
Pyréolophore, which was granted a patent by
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 â 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
. This engine powered a boat on the
SaĂŽne
The SaÎne ( , ; frp, Sona; lat, Arar) is a river in eastern France. It is a right tributary of the RhÎne, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges department and joining the RhÎne in Lyon, at the southern end of the Presqu'ßle.
The name der ...
river in France.
In the same year,
Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
*Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internati ...
engineer
François Isaac de Rivaz invented a hydrogen-based internal combustion engine and powered the engine by electric spark. In 1808, De Rivaz fitted his invention to a primitive working vehicle â "the world's first internal combustion powered automobile". In 1823,
Samuel Brown patented the first internal combustion engine to be applied industrially.
In 1854 in the
UK, the Italian inventors
Eugenio Barsanti and
Felice Matteucci obtained the certification: "Obtaining Motive Power by the Explosion of Gases". In 1857 the Great Seal Patent Office conceded them patent No.1655 for the invention of an "Improved Apparatus for Obtaining Motive Power from Gases". Barsanti and Matteucci obtained other patents for the same invention in France, Belgium and Piedmont between 1857 and 1859. In 1860,
Belgian engineer
Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir produced a gas-fired internal combustion engine.
In 1864,
Nicolaus Otto patented the first atmospheric gas engine. In 1872, American
George Brayton invented the first commercial liquid-fueled internal combustion engine. In 1876,
Nicolaus Otto began working with
Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 â 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf ( Kingdom of WĂŒrttemberg, a federal state of the German Confederation), in what is now Germany. He wa ...
and
Wilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 â 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
, patented the compressed charge, four-cycle engine. In 1879,
Karl Benz
Carl Friedrich Benz (; 25 November 1844 â 4 April 1929), sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and fir ...
patented a reliable
two-stroke gasoline engine. Later, in 1886, Benz began the first commercial production of motor vehicles with an internal combustion engine, in which a three-wheeled, four-cycle engine and chassis formed a single unit.
In 1892,
Rudolf Diesel developed the first compressed charge, compression ignition engine. In 1926,
Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket. In 1939, the
Heinkel He 178 became the world's first
jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by jet engines.
Whereas the engines in propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much lower speeds and altitudes, jet ...
.
Etymology
At one time, the word ''engine'' (via
Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligi ...
, from
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
''ingenium'', "ability") meant any piece of
machinery
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecul ...
âa sense that persists in expressions such as ''
siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
''. A "motor" (from Latin ''motor'', "mover") is any machine that produces mechanical
power. Traditionally,
electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
s are not referred to as "engines"; however, combustion engines are often referred to as "motors". (An ''
electric engine'' refers to a
locomotive operated by electricity.)
In boating, an internal combustion engine that is installed in the hull is referred to as an engine, but the engines that sit on the transom are referred to as motors.
Applications


Reciprocating piston engines are by far the most common power source for land and water
vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles ( motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles ( trains, trams ...
s, including
automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s,
motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruisin ...
s,
ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguishe ...
s and to a lesser extent,
locomotives (some are electrical but most use Diesel engines). Rotary engines of the Wankel design are used in some automobiles, aircraft and motorcycles. These are collectively known as internal-combustion-engine vehicles (ICEV).
Where high power-to-weight ratios are required, internal combustion engines appear in the form of
combustion turbines, or sometimes Wankel engines.
Powered aircraft
A powered aircraft is an aircraft that uses onboard propulsion with mechanical power generated by an aircraft engine of some kind.
Aircraft propulsion nearly always uses either a type of propeller, or a form of jet propulsion. Other potentia ...
typically use an ICE which may be a reciprocating engine. Airplanes can instead use
jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and ...
s and
helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribut ...
s can instead employ
turboshafts; both of which are types of turbines. In addition to providing propulsion,
airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
s may employ a separate ICE as an
auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115&n ...
. Wankel engines are fitted to many
unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controlle ...
s.
ICEs drive large electric generators that power electrical grids. They are found in the form of
combustion turbines with a typical electrical output in the range of some 100 MW.
Combined cycle power plants use the high temperature exhaust to boil and superheat water steam to run a
steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turb ...
. Thus, the efficiency is higher because more energy is extracted from the fuel than what could be extracted by the combustion engine alone.
Combined cycle power plants achieve efficiencies in the range of 50% to 60%. In a smaller scale,
stationary engines like
gas engines or
diesel generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-i ...
s are used for backup or for providing electrical power to areas not connected to an
electric grid.
Small engines (usually 2âstroke gasoline/petrol engines) are a common power source for
lawnmower
A lawn mower (also known as a mower, grass cutter or lawnmower) is a device utilizing one or more revolving blades (or a reel) to cut a grass surface to an even height. The height of the cut grass may be fixed by the design of the mower, but g ...
s,
string trimmer
A string trimmer, also known by the portmanteau strimmer and the trademarks Weedwacker, Weed eater and Whipper Snipper. is a garden tool for cutting grass, small weeds, and groundcover. It uses a whirling monofilament line instead of a bla ...
s,
chain saw
A chainsaw (or chain saw) is a portable gasoline-, electric-, or battery-powered saw that cuts with a set of teeth attached to a rotating chain driven along a guide bar. It is used in activities such as tree felling, limbing, bucking, pruni ...
s,
leafblowers,
pressure washers,
snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
s,
jet skis,
outboard motor
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method o ...
s,
moped
A moped ( ) is a type of small motorcycle, generally having a less stringent licensing requirement than full motorcycles or automobiles. The term used to mean a similar vehicle except with both bicycle pedals and a motorcycle engine. Mopeds typic ...
s, and
motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruisin ...
s.
Classification
There are several possible ways to classify internal combustion engines.
Reciprocating
By number of strokes:
*
Two-stroke engine
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of t ...
** Clerk cycle
** Day cycle
*
Four-stroke engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directio ...
(
Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines.
The Otto cycle is a description of what ha ...
)
*
Six-stroke engine The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced ...
By type of ignition:
*
Compression-ignition engine
*
Spark-ignition engine (commonly found as
gasoline engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' ...
s)
By mechanical/thermodynamic cycle (these cycles are infrequently used but are commonly found in
hybrid vehicles, along with other vehicles manufactured for
fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
):
*
Atkinson cycle
*
Miller cycle
Rotary
*
Wankel engine
Continuous combustion
*
Gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directio ...
engine
**
Turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, ...
, through a propelling nozzle
**
Turbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical ...
, through a duct-fan
**
Turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. ...
, through an unducted propeller, usually with variable pitch
**
Turboshaft, a gas turbine optimized for producing mechanical torque instead of thrust
*
Ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an a ...
, similar to a turbojet but uses vehicle speed to compress (ram) the air instead of a compressor.
*
Scramjet
A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forceful ...
, a variant of the ramjet that uses supersonic combustion.
*
Rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive Jet (fluid), jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, i ...
Reciprocating engines
Structure


The base of a reciprocating internal combustion engine is the
engine block, which is typically made of
cast iron
Cast iron is a class of ironâ carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impu ...
(due to its good wear resistance and low cost)
or
aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
. In the latter case, the cylinder liners are made of cast iron or steel,
or a coating such as
nikasil or
alusil. The engine block contains the
cylinders
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
. In engines with more than one cylinder they are usually arranged either in 1 row (
straight engine) or 2 rows (
boxer engine or
V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banksâusually with the same number of cylinders in each bankâconnected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
); 3 rows are occasionally used (
W engine) in contemporary engines, and other
engine configurations are possible and have been used.
Single cylinder engines (or ''thumpers'') are common for motorcycles and other small engines found in light machinery. On the outer side of the cylinder, passages that contain cooling fluid are cast into the engine block whereas, in some heavy duty engines, the passages are the types of removable cylinder sleeves which can be replaceable.
Water-cooled engines contain passages in the engine block where cooling fluid circulates (the
water jacket). Some small engines are air-cooled, and instead of having a water jacket the cylinder block has fins protruding away from it to cool the engine by directly transferring heat to the air. The cylinder walls are usually finished by
honing to obtain a cross hatch, which is able to retain more oil. A too rough surface would quickly harm the engine by excessive wear on the piston.
The
piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas- ...
s are short cylindrical parts which seal one end of the cylinder from the high pressure of the compressed air and combustion products and slide continuously within it while the engine is in operation. In smaller engines, the pistons are made of aluminum; while in larger applications, they are typically made of cast iron.
The top wall of the piston is termed its ''crown'' and is typically flat or concave. Some two-stroke engines use pistons with a
deflector head. Pistons are open at the bottom and hollow except for an integral reinforcement structure (the piston web). When an engine is working, the gas pressure in the combustion chamber exerts a force on the piston crown which is transferred through its web to a
gudgeon pin. Each piston has
rings fitted around its circumference that mostly prevent the gases from leaking into the crankcase or the oil into the combustion chamber.
A
ventilation system drives the small amount of gas that escapes past the pistons during normal operation (the blow-by gases) out of the crankcase so that it does not accumulate contaminating the oil and creating corrosion.
In two-stroke gasoline engines the crankcase is part of the airâfuel path and due to the continuous flow of it, two-stroke engines do not need a separate crankcase ventilation system.
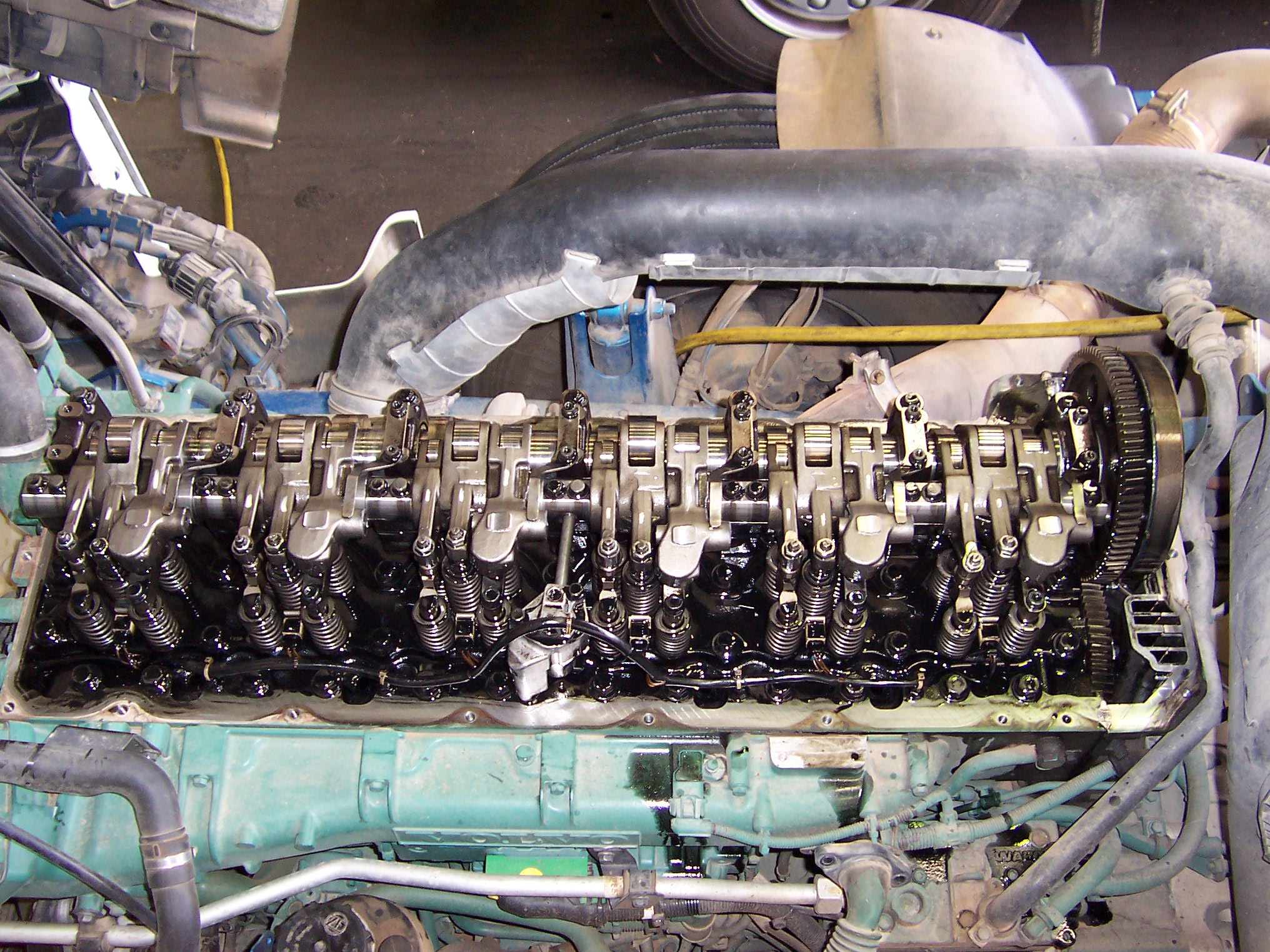

The
cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinder (engine), cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas ...
is attached to the engine block by numerous
bolts or
studs. It has several functions. The cylinder head seals the cylinders on the side opposite to the pistons; it contains short ducts (the ''ports'') for intake and exhaust and the associated intake
valves that open to let the cylinder be filled with fresh air and exhaust valves that open to allow the combustion gases to escape. However, 2-stroke crankcase scavenged engines connect the gas ports directly to the cylinder wall without poppet valves; the piston controls their opening and occlusion instead. The cylinder head also holds the
spark plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air ...
in the case of spark ignition engines and the
injector
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic ...
for engines that use direct injection. All CI (compression ignition) engines use fuel injection, usually direct injection but some engines instead use
indirect injection. SI (spark ignition) engines can use a
carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meter ...
or fuel injection as port injection or
direct injection. Most SI engines have a single spark plug per cylinder but
some have 2. A
head gasket prevents the gas from leaking between the cylinder head and the engine block. The opening and closing of the valves is controlled by one or several
camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams, in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition systems ...
s and springsâor in some enginesâa
desmodromic mechanism that uses no springs. The camshaft may press directly the stem of the valve or may act upon a
rocker arm, again, either directly or through a
pushrod
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) ...
.

The crankcase is sealed at the bottom with a
sump
A sump is a low space that collects often undesirable liquids such as water or chemicals. A sump can also be an infiltration basin used to manage surface runoff water and recharge underground aquifers. Sump can also refer to an area in a cav ...
that collects the falling oil during normal operation to be cycled again. The cavity created between the cylinder block and the sump houses a
crankshaft that converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons to rotational motion. The crankshaft is held in place relative to the engine block by
main bearing
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*" Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries ...
s, which allow it to rotate. Bulkheads in the crankcase form a half of every main bearing; the other half is a detachable cap. In some cases a single ''main bearing deck'' is used rather than several smaller caps. A
connecting rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the cranksha ...
is connected to offset sections of the crankshaft (the
crankpins) in one end and to the piston in the other end through the gudgeon pin and thus transfers the force and translates the reciprocating motion of the pistons to the circular motion of the crankshaft. The end of the connecting rod attached to the gudgeon pin is called its small end, and the other end, where it is connected to the crankshaft, the big end. The big end has a detachable half to allow assembly around the crankshaft. It is kept together to the connecting rod by removable bolts.
The cylinder head has an
intake manifold and an
exhaust manifold attached to the corresponding ports. The intake manifold connects to the
air filter directly, or to a carburetor when one is present, which is then connected to the
air filter. It distributes the air incoming from these devices to the individual cylinders. The exhaust manifold is the first component in the
exhaust system. It collects the exhaust gases from the cylinders and drives it to the following component in the path. The
exhaust system of an ICE may also include a
catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usuall ...
and
muffler. The final section in the path of the exhaust gases is the
tailpipe.
4-stroke engines

The ''top dead center'' (TDC) of a piston is the position where it is nearest to the valves; ''bottom dead center'' (BDC) is the opposite position where it is furthest from them. A ''stroke'' is the movement of a piston from TDC to BDC or vice versa, together with the associated process. While an engine is in operation, the crankshaft rotates continuously at a nearly constant
speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quantity ...
. In a 4-stroke ICE, each piston experiences 2 strokes per crankshaft revolution in the following order. Starting the description at TDC, these are:
# Intake, induction or suction: The intake valves are open as a result of the cam lobe pressing down on the valve stem. The piston moves downward increasing the volume of the combustion chamber and allowing air to enter in the case of a CI engine or an air-fuel mix in the case of SI engines that do not use
direct injection. The air or air-fuel mixture is called the ''charge'' in any case.
# Compression: In this stroke, both valves are closed and the piston moves upward reducing the combustion chamber volume which reaches its minimum when the piston is at TDC. The piston performs
work on the charge as it is being compressed; as a result, its pressure, temperature and density increase; an approximation to this behavior is provided by the
ideal gas law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first st ...
. Just before the piston reaches TDC, ignition begins. In the case of a SI engine, the spark plug receives a high voltage pulse that generates the spark which gives it its name and ignites the charge. In the case of a CI engine, the fuel injector quickly injects fuel into the combustion chamber as a spray; the fuel ignites due to the high temperature.
# Power or working stroke: The pressure of the combustion gases pushes the piston downward, generating more
kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its a ...
than is required to compress the charge. Complementary to the compression stroke, the combustion gases expand and as a result their temperature, pressure and density decreases. When the piston is near to BDC the exhaust valve opens. The combustion gases expand
irreversibly due to the leftover pressureâin excess of
back pressure, the gauge pressure on the exhaust portâ; this is called the ''blowdown''.
# Exhaust: The exhaust valve remains open while the piston moves upward expelling the combustion gases. For naturally aspirated engines a small part of the combustion gases may remain in the cylinder during normal operation because the piston does not close the combustion chamber completely; these gases dissolve in the next charge. At the end of this stroke, the exhaust valve closes, the intake valve opens, and the sequence repeats in the next cycle. The intake valve may open before the exhaust valve closes to allow better scavenging.
2-stroke engines
The defining characteristic of this kind of engine is that each piston completes a cycle every crankshaft revolution. The 4 processes of intake, compression, power and exhaust take place in only 2 strokes so that it is not possible to dedicate a stroke exclusively for each of them. Starting at TDC the cycle consists of:
# Power: While the piston is descending the combustion gases perform work on it, as in a 4-stroke engine. The same
thermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of t ...
considerations about the expansion apply.
# Scavenging: Around 75° of crankshaft rotation before BDC the exhaust valve or port opens, and blowdown occurs. Shortly thereafter the intake valve or transfer port opens. The incoming charge displaces the remaining combustion gases to the exhaust system and a part of the charge may enter the exhaust system as well. The piston reaches BDC and reverses direction. After the piston has traveled a short distance upwards into the cylinder the exhaust valve or port closes; shortly the intake valve or transfer port closes as well.
# Compression: With both intake and exhaust closed the piston continues moving upwards compressing the charge and performing work on it. As in the case of a 4-stroke engine, ignition starts just before the piston reaches TDC and the same consideration on the thermodynamics of the compression on the charge apply.
While a 4-stroke engine uses the piston as a
positive displacement pump to accomplish scavenging taking 2 of the 4 strokes, a 2-stroke engine uses the last part of the power stroke and the first part of the compression stroke for combined intake and exhaust. The work required to displace the charge and exhaust gases comes from either the crankcase or a separate blower. For scavenging, expulsion of burned gas and entry of fresh mix, two main approaches are described: Loop scavenging, and Uniflow scavenging. SAE news published in the 2010s that 'Loop Scavenging' is better under any circumstance than Uniflow Scavenging.
Crankcase scavenged

Some SI engines are crankcase scavenged and do not use poppet valves. Instead, the crankcase and the part of the cylinder below the piston is used as a pump. The intake port is connected to the crankcase through a
reed valve or a rotary disk valve driven by the engine. For each cylinder, a transfer port connects in one end to the crankcase and in the other end to the cylinder wall. The exhaust port is connected directly to the cylinder wall. The transfer and exhaust port are opened and closed by the piston. The reed valve opens when the crankcase pressure is slightly below intake pressure, to let it be filled with a new charge; this happens when the piston is moving upwards. When the piston is moving downwards the pressure in the crankcase increases and the reed valve closes promptly, then the charge in the crankcase is compressed. When the piston is moving downwards, it also uncovers the exhaust port and the transfer port and the higher pressure of the charge in the crankcase makes it enter the cylinder through the transfer port, blowing the exhaust gases. Lubrication is accomplished by adding ''
2-stroke oil'' to the fuel in small ratios. ''
Petroil'' refers to the mix of gasoline with the aforesaid oil. This kind of 2-stroke engine has a lower efficiency than comparable 4-strokes engines and releases more polluting
exhaust gases for the following conditions:
* They use a ''
total-loss lubrication system'': all the lubricating oil is eventually burned along with the fuel.
* There are conflicting requirements for scavenging: On one side, enough fresh charge needs to be introduced in each cycle to displace almost all the combustion gases but introducing too much of it means that a part of it gets in the exhaust.
* They must use the transfer port(s) as a carefully designed and placed nozzle so that a gas current is created in a way that it sweeps the whole cylinder before reaching the exhaust port so as to expel the combustion gases, but minimize the amount of charge exhausted. 4-stroke engines have the benefit of forcibly expelling almost all of the combustion gases because during exhaust the combustion chamber is reduced to its minimum volume. In crankcase scavenged 2-stroke engines, exhaust and intake are performed mostly simultaneously and with the combustion chamber at its maximum volume.
The main advantage of 2-stroke engines of this type is mechanical simplicity and a higher
power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
than their 4-stroke counterparts. Despite having twice as many power strokes per cycle, less than twice the power of a comparable 4-stroke engine is attainable in practice.
In the US, 2-stroke engines were banned for road vehicles due to the pollution. Off-road only motorcycles are still often 2-stroke but are rarely road legal. However, many thousands of 2-stroke lawn maintenance engines are in use.
Blower scavenged

Using a separate blower avoids many of the shortcomings of crankcase scavenging, at the expense of increased complexity which means a higher cost and an increase in maintenance requirement. An engine of this type uses ports or valves for intake and valves for exhaust, except
opposed piston engines, which may also use ports for exhaust. The blower is usually of the
Roots-type but other types have been used too. This design is commonplace in CI engines, and has been occasionally used in SI engines.
CI engines that use a blower typically use ''
uniflow scavenging''. In this design the cylinder wall contains several intake ports placed uniformly spaced along the circumference just above the position that the piston crown reaches when at BDC. An exhaust valve or several like that of 4-stroke engines is used. The final part of the intake manifold is an air sleeve that feeds the intake ports. The intake ports are placed at a horizontal angle to the cylinder wall (I.e: they are in plane of the piston crown) to give a swirl to the incoming charge to improve combustion. The largest reciprocating IC are low speed CI engines of this type; they are used for marine propulsion (see
marine diesel engine
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electri ...
) or
electric power generation and achieve the highest thermal efficiencies among internal combustion engines of any kind. Some Diesel-electric
locomotive engines operate on the 2-stroke cycle. The most powerful of them have a brake power of around 4.5
MW or 6,000
HP. The
EMD SD90MAC class of locomotives are an example of such. The comparable class
GE AC6000CW whose prime mover has almost the same brake power uses a 4-stroke engine.
An example of this type of engine is the
WÀrtsilÀ-Sulzer RT-flex96-C turbocharged 2-stroke Diesel, used in large container ships. It is the most efficient and powerful reciprocating internal combustion engine in the world with a
thermal efficiency over 50%. For comparison, the most efficient small four-stroke engines are around 43% thermally-efficient (SAE 900648); size is an advantage for efficiency due to the increase in the ratio of volume to surface area.
See the
external links
An internal link is a type of hyperlink on a web page to another page or resource, such as an image or document, on the same website or domain name, domain.
Hyperlinks are considered either "external" or "internal" depending on their target or ...
for an in-cylinder combustion video in a 2-stroke, optically accessible motorcycle engine.
Historical design
Dugald Clerk developed the first two-cycle engine in 1879. It used a separate cylinder which functioned as a pump in order to transfer the fuel mixture to the cylinder.
In 1899
John Day simplified Clerk's design into the type of 2 cycle engine that is very widely used today.
Day cycle engines are crankcase scavenged and port timed. The crankcase and the part of the cylinder below the exhaust port is used as a pump. The operation of the Day cycle engine begins when the crankshaft is turned so that the piston moves from BDC upward (toward the head) creating a vacuum in the crankcase/cylinder area. The carburetor then feeds the fuel mixture into the crankcase through a
reed valve or a rotary disk valve (driven by the engine). There are cast in ducts from the crankcase to the port in the cylinder to provide for intake and another from the exhaust port to the exhaust pipe. The height of the port in relationship to the length of the cylinder is called the "port timing".
On the first upstroke of the engine there would be no fuel inducted into the cylinder as the crankcase was empty. On the downstroke, the piston now compresses the fuel mix, which has lubricated the piston in the cylinder and the bearings due to the fuel mix having oil added to it. As the piston moves downward it first uncovers the exhaust, but on the first stroke there is no burnt fuel to exhaust. As the piston moves downward further, it uncovers the intake port which has a duct that runs to the crankcase. Since the fuel mix in the crankcase is under pressure, the mix moves through the duct and into the cylinder.
Because there is no obstruction in the cylinder of the fuel to move directly out of the exhaust port prior to the piston rising far enough to close the port, early engines used a high domed piston to slow down the flow of fuel. Later the fuel was "resonated" back into the cylinder using an expansion chamber design. When the piston rose close to TDC, a spark ignited the fuel. As the piston is driven downward with power, it first uncovers the exhaust port where the burned fuel is expelled under high pressure and then the intake port where the process has been completed and will keep repeating.
Later engines used a type of porting devised by the Deutz company to improve performance. It was called the
Schnurle Reverse Flow system. DKW licensed this design for all their motorcycles. Their
DKW RT 125 was one of the first motor vehicles to achieve over 100 mpg as a result.
Ignition
Internal combustion engines require ignition of the mixture, either by
spark ignition (SI) or
compression ignition (CI). Before the invention of reliable electrical methods, hot tube and flame methods were used. Experimental engines with
laser ignition Laser ignition is an alternative method for igniting mixtures of fuel and oxidiser. The phase of the mixture can be gaseous or liquid. The method is based on laser ignition devices that produce short but powerful flashes regardless of the pressure i ...
have been built.
Spark ignition process

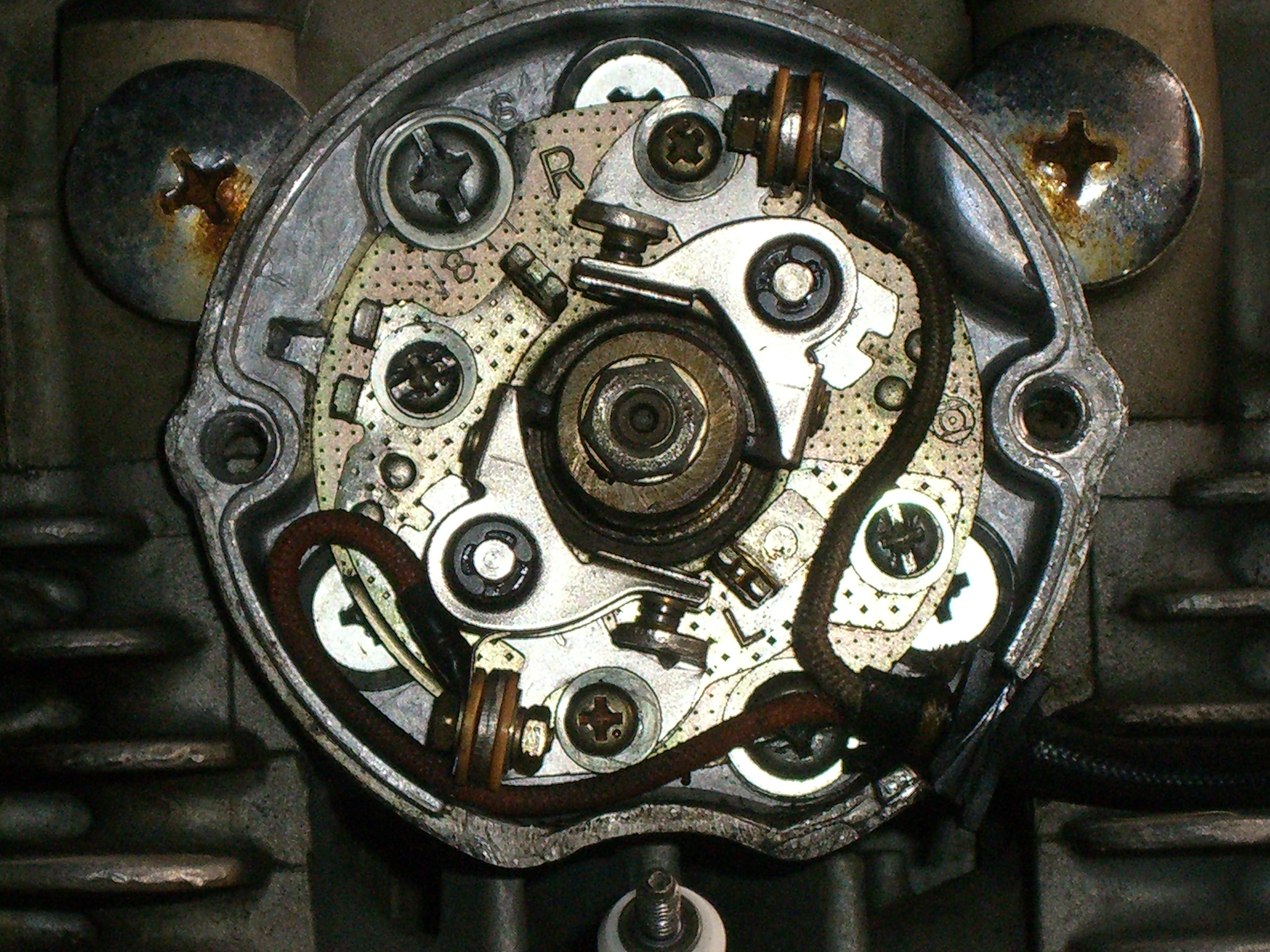
The spark-ignition engine was a refinement of the early engines which used Hot Tube ignition. When Bosch developed the
magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
it became the primary system for producing electricity to energize a spark plug. Many small engines still use magneto ignition. Small engines are started by hand cranking using a
recoil starter or hand crank. Prior to
Charles F. Kettering of Delco's development of the automotive starter all gasoline engined automobiles used a hand crank.
Larger engines typically power their
starting motors and
ignition system
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ig ...
s using the electrical energy stored in a
leadâacid battery. The battery's charged state is maintained by an
automotive alternator or (previously) a generator which uses engine power to create electrical energy storage.
The battery supplies electrical power for starting when the engine has a
starting motor system, and supplies electrical power when the engine is off. The battery also supplies electrical power during rare run conditions where the alternator cannot maintain more than 13.8 volts (for a common 12V automotive electrical system). As alternator voltage falls below 13.8 volts, the lead-acid storage battery increasingly picks up electrical load. During virtually all running conditions, including normal idle conditions, the alternator supplies primary electrical power.
Some systems disable alternator field (rotor) power during wide-open throttle conditions. Disabling the field reduces alternator pulley mechanical loading to nearly zero, maximizing crankshaft power. In this case, the battery supplies all primary electrical power.
Gasoline engines take in a mixture of air and gasoline and compress it by the movement of the piston from bottom dead center to top dead center when the fuel is at maximum compression. The reduction in the size of the swept area of the cylinder and taking into account the volume of the combustion chamber is described by a ratio. Early engines had
compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stat ...
s of 6 to 1. As compression ratios were increased, the efficiency of the engine increased as well.
With early induction and ignition systems the compression ratios had to be kept low. With advances in fuel technology and combustion management, high-performance engines can run reliably at 12:1 ratio. With low octane fuel, a problem would occur as the compression ratio increased as the fuel was igniting due to the rise in temperature that resulted.
Charles Kettering developed a
lead additive which allowed higher compression ratios, which was progressively
abandoned for automotive use from the 1970s onward, partly due to
lead poisoning
Lead poisoning, also known as plumbism and saturnism, is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, inferti ...
concerns.
The fuel mixture is ignited at different progressions of the piston in the cylinder. At low rpm, the spark is timed to occur close to the piston achieving top dead center. In order to produce more power, as rpm rises the spark is advanced sooner during piston movement. The spark occurs while the fuel is still being compressed progressively more as rpm rises.
The necessary high voltage, typically 10,000 volts, is supplied by an
induction coil
An induction coil or "spark coil" ( archaically known as an inductorium or Ruhmkorff coil after Heinrich RĂŒhmkorff) is a type of electrical transformer used to produce high-voltage pulses from a low-voltage direct current (DC) supply. p.98 ...
or transformer. The induction coil is a fly-back system, using interruption of electrical primary system current through some type of synchronized interrupter. The interrupter can be either contact points or a power transistor. The problem with this type of ignition is that as RPM increases the availability of electrical energy decreases. This is especially a problem, since the amount of energy needed to ignite a more dense fuel mixture is higher. The result was often a high RPM misfire.
Capacitor discharge ignition was developed. It produces a rising voltage that is sent to the spark plug. CD system voltages can reach 60,000 volts. CD ignitions use step-up
transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s. The step-up transformer uses energy stored in a capacitance to generate
electric spark. With either system, a mechanical or electrical control system provides a carefully timed high-voltage to the proper cylinder. This spark, via the spark plug, ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine's cylinders.
While gasoline internal combustion engines are much easier to start in cold weather than diesel engines, they can still have cold weather starting problems under extreme conditions. For years, the solution was to park the car in heated areas. In some parts of the world, the oil was actually drained and heated overnight and returned to the engine for cold starts. In the early 1950s, the gasoline Gasifier unit was developed, where, on cold weather starts, raw gasoline was diverted to the unit where part of the fuel was burned causing the other part to become a hot vapor sent directly to the intake valve manifold. This unit was quite popular until electric
engine block heaters became standard on gasoline engines sold in cold climates.
Compression ignition process
For ignition, diesel,
PPC and
HCCI engines rely solely on the high temperature and pressure created by the engine in its compression process. The compression level that occurs is usually twice or more than a gasoline engine. Diesel engines take in air only, and shortly before peak compression, spray a small quantity of diesel fuel into the cylinder via a fuel injector that allows the fuel to instantly ignite. HCCI type engines take in both air and fuel, but continue to rely on an unaided auto-combustion process, due to higher pressures and temperature. This is also why diesel and HCCI engines are more susceptible to cold-starting issues, although they run just as well in cold weather once started. Light duty diesel engines with
indirect injection in automobiles and light trucks employ
glowplugs (or other pre-heating: see
Cummins ISB#6BT) that pre-heat the
combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Intern ...
just before starting to reduce no-start conditions in cold weather. Most diesels also have a battery and charging system; nevertheless, this system is secondary and is added by manufacturers as a luxury for the ease of starting, turning fuel on and off (which can also be done via a switch or mechanical apparatus), and for running auxiliary electrical components and accessories. Most new engines rely on electrical and electronic
engine control unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by ...
s (ECU) that also adjust the combustion process to increase efficiency and reduce emissions.
Lubrication

Surfaces in contact and relative motion to other surfaces require
lubrication to reduce wear, noise and increase efficiency by reducing the power wasting in overcoming
friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding (motion), sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative la ...
, or to make the mechanism work at all. Also, the lubricant used can reduce excess heat and provide additional cooling to components. At the very least, an engine requires lubrication in the following parts:
* Between pistons and cylinders
* Small bearings
* Big end bearings
* Main bearings
* Valve gear (The following elements may not be present):
** Tappets
** Rocker arms
** Pushrods
** Timing chain or gears. Toothed belts do not require lubrication.
In 2-stroke crankcase scavenged engines, the interior of the crankcase, and therefore the crankshaft, connecting rod and bottom of the pistons are sprayed by the
2-stroke oil in the air-fuel-oil mixture which is then burned along with the fuel. The valve train may be contained in a compartment flooded with lubricant so that no
oil pump is required.
In a ''splash lubrication system'' no oil pump is used. Instead the crankshaft dips into the oil in the sump and due to its high speed, it splashes the crankshaft, connecting rods and bottom of the pistons. The connecting rod big end caps may have an attached scoop to enhance this effect. The valve train may also be sealed in a flooded compartment, or open to the crankshaft in a way that it receives splashed oil and allows it to drain back to the sump. Splash lubrication is common for small 4-stroke engines.
In a ''forced'' (also called ''pressurized'') ''lubrication system'', lubrication is accomplished in a closed-loop which carries
motor oil
Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, deterg ...
to the surfaces serviced by the system and then returns the oil to a reservoir. The auxiliary equipment of an engine is typically not serviced by this loop; for instance, an
alternator
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature.G ...
may use
ball bearings
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
sealed with their own lubricant. The reservoir for the oil is usually the sump, and when this is the case, it is called a ''
wet sump'' system. When there is a different oil reservoir the crankcase still catches it, but it is continuously drained by a dedicated pump; this is called a ''
dry sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conv ...
'' system.
On its bottom, the sump contains an oil intake covered by a mesh filter which is connected to an oil pump then to an
oil filter outside the crankcase. From there it is diverted to the crankshaft main bearings and valve train. The crankcase contains at least one ''oil gallery'' (a conduit inside a crankcase wall) to which oil is introduced from the oil filter. The main bearings contain a groove through all or half its circumference; the oil enters these grooves from channels connected to the oil gallery. The crankshaft has drillings that take oil from these grooves and deliver it to the big end bearings. All big end bearings are lubricated this way. A single main bearing may provide oil for 0, 1 or 2 big end bearings. A similar system may be used to lubricate the piston, its gudgeon pin and the small end of its connecting rod; in this system, the connecting rod big end has a groove around the crankshaft and a drilling connected to the groove which distributes oil from there to the bottom of the piston and from then to the cylinder.
Other systems are also used to lubricate the cylinder and piston. The connecting rod may have a nozzle to throw an oil jet to the cylinder and bottom of the piston. That nozzle is in movement relative to the cylinder it lubricates, but always pointed towards it or the corresponding piston.
Typically forced lubrication systems have a lubricant flow higher than what is required to lubricate satisfactorily, in order to assist with cooling. Specifically, the lubricant system helps to move heat from the hot engine parts to the cooling liquid (in water-cooled engines) or fins (in air-cooled engines) which then transfer it to the environment. The lubricant must be designed to be chemically stable and maintain suitable viscosities within the temperature range it encounters in the engine.
Cylinder configuration
Common cylinder configurations include the
straight or inline configuration, the more compact
V configuration, and the wider but smoother
flat or boxer configuration.
Aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years ma ...
s can also adopt a
radial configuration, which allows more effective cooling. More unusual configurations such as the
H,
U,
X, and
W have also been used.

Multiple cylinder engines have their valve train and crankshaft configured so that pistons are at different parts of their cycle. It is desirable to have the pistons' cycles uniformly spaced (this is called ''even firing'') especially in forced induction engines; this reduces torque pulsations and makes
inline engines
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engi ...
with more than 3 cylinders statically
balanced in its primary forces. However, some
engine configurations require odd firing to achieve better balance than what is possible with even firing. For instance, a 4-stroke
I2 engine has better balance when the angle between the crankpins is 180° because the pistons move in opposite directions and inertial forces partially cancel, but this gives an odd firing pattern where one cylinder fires 180° of crankshaft rotation after the other, then no cylinder fires for 540°. With an even firing pattern, the pistons would move in unison and the associated forces would add.
Multiple crankshaft configurations do not necessarily need a
cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinder (engine), cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas ...
at all because they can instead have a piston at each end of the cylinder called an
opposed piston design. Because fuel inlets and outlets are positioned at opposed ends of the cylinder, one can achieve uniflow scavenging, which, as in the four-stroke engine is efficient over a wide range of engine speeds. Thermal efficiency is improved because of a lack of cylinder heads. This design was used in the
Junkers Jumo 205 diesel aircraft engine, using two crankshafts at either end of a single bank of cylinders, and most remarkably in the
Napier Deltic diesel engines. These used three crankshafts to serve three banks of
double-ended cylinders arranged in an equilateral triangle with the crankshafts at the corners. It was also used in single-bank
locomotive engines, and is still used in
marine propulsion
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an elect ...
engines and marine auxiliary generators.
Diesel cycle

Most truck and automotive diesel engines use a cycle reminiscent of a four-stroke cycle, but with temperature increase by compression causing ignition, rather than needing a separate ignition system. This variation is called the diesel cycle. In the diesel cycle, diesel fuel is injected directly into the cylinder so that combustion occurs at constant pressure, as the piston moves.
Otto cycle
The
Otto cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines.
The Otto cycle is a description of what ha ...
is the most common cycle for most cars' internal combustion engines that use gasoline as a fuel. It consists of the same major steps as described for the four-stroke engine: Intake, compression, ignition, expansion and exhaust.
Five-stroke engine
In 1879,
Nicolaus Otto manufactured and sold a double expansion engine (the double and triple expansion principles had ample usage in steam engines), with two small cylinders at both sides of a low-pressure larger cylinder, where a second expansion of exhaust stroke gas took place; the owner returned it, alleging poor performance. In 1906, the concept was incorporated in a car built by EHV (
Eisenhuth Horseless Vehicle Company
Eisenhuth Horseless Vehicle Company was a manufacturer of Brass Age automobiles who were originally based in New York City. In 1902 the company purchased the Keating Wheel and Automobile Company and established manufacturing operations in Midd ...
); and in the 21st century
Ilmor designed and successfully tested a 5-stroke double expansion internal combustion engine, with high power output and low SFC (Specific Fuel Consumption).
Six-stroke engine
The
six-stroke engine The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced ...
was invented in 1883. Four kinds of six-stroke engines use a regular piston in a regular cylinder (Griffin six-stroke, Bajulaz six-stroke, Velozeta six-stroke and Crower six-stroke), firing every three crankshaft revolutions. These systems capture the waste heat of the
four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direct ...
Otto cycle with an injection of air or water.
The
Beare Head The Beare-head engine internal combustion engine technology combines a four-stroke engine bottom end and piston, with a ported cylinder head closely resembling that of a two-stroke engine. The head piston is smaller and moves at half cycling of the ...
and "piston charger" engines operate as
opposed-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and ...
s, two pistons in a single cylinder, firing every two revolutions rather than every four like a four-stroke engine.
Other cycles
The very first internal combustion engines did not compress the mixture. The first part of the piston downstroke drew in a fuel-air mixture, then the inlet valve closed and, in the remainder of the down-stroke, the fuel-air mixture fired. The exhaust valve opened for the piston upstroke. These attempts at imitating the principle of a
steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be ...
were very inefficient.
There are a number of variations of these cycles, most notably the
Atkinson and
Miller cycles.
Split-cycle engines separate the four strokes of intake, compression, combustion and exhaust into two separate but paired cylinders. The first cylinder is used for intake and compression. The compressed air is then transferred through a crossover passage from the compression cylinder into the second cylinder, where combustion and exhaust occur. A split-cycle engine is really an
air compressor
An air compressor is a pneumatic device that converts power (using an electric motor, diesel or gasoline engine, etc.) into potential energy stored in pressurized air (i.e., compressed air). By one of several methods, an air compressor forces ...
on one side with a combustion chamber on the other.
Previous split-cycle engines have had two major problemsâpoor breathing (volumetric efficiency) and low thermal efficiency. However, new designs are being introduced that seek to address these problems.
The
Scuderi Engine addresses the breathing problem by reducing the clearance between the piston and the cylinder head through various turbocharging techniques. The Scuderi design requires the use of outwardly opening valves that enable the piston to move very close to the cylinder head without the interference of the valves. Scuderi addresses the low thermal efficiency via firing after top dead center (ATDC).
Firing ATDC can be accomplished by using high-pressure air in the transfer passage to create sonic flow and high turbulence in the power cylinder.
The four-stroke crank-rocker engine with a curve cylinder was also invented to study its efficiency.
Combustion turbines
Jet engine

Jet engines use a number of rows of fan blades to compress air which then enters a
combustor
A combustor is a component or area of a gas turbine, ramjet, or scramjet engine where combustion takes place. It is also known as a burner, combustion chamber or flame holder. In a gas turbine engine, the ''combustor'' or combustion chamber is fed ...
where it is mixed with fuel (typically JP fuel) and then ignited. The burning of the fuel raises the temperature of the air which is then exhausted out of the engine creating thrust. A modern
turbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical ...
engine can operate at as high as 48% efficiency.
There are six sections to a turbofan engine:
* Fan
* Compressor
* Combustor
* Turbine
* Mixer
* Nozzle
Gas turbines

A gas turbine compresses air and uses it to turn a
turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbÄ'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating ...
. It is essentially a jet engine which directs its output to a shaft. There are three stages to a turbine: 1) air is drawn through a compressor where the temperature rises due to compression, 2) fuel is added in the
combuster, and 3) hot air is exhausted through turbine blades which rotate a shaft connected to the compressor.
A gas turbine is a rotary machine similar in principle to a
steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turb ...
and it consists of three main components: a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The temperature of the air, after being compressed in the compressor, is increased by burning fuel in it. The heated air and the products of combustion expand in a turbine, producing work output. About of the work drives the compressor: the rest (about ) is available as useful work output.
Gas turbines are among the most efficient internal combustion engines. The General Electric 7HA and 9HA turbine
combined cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas tu ...
electrical plants are rated at over 61% efficiency.
Brayton cycle

A gas turbine is a rotary machine somewhat similar in principle to a steam turbine. It consists of three main components: compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. The air is compressed by the compressor where a temperature rise occurs. The temperature of the compressed air is further increased by combustion of injected fuel in the combustion chamber which expands the air. This energy rotates the turbine which powers the compressor via a mechanical coupling. The hot gases are then exhausted to provide thrust.
Gas turbine cycle engines employ a continuous combustion system where compression, combustion, and expansion occur simultaneously at different places in the engineâgiving continuous power. Notably, the combustion takes place at constant pressure, rather than with the Otto cycle, constant volume.
Wankel engines
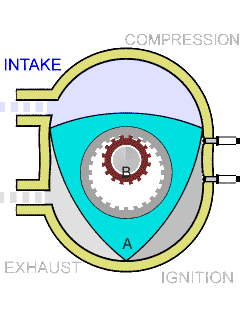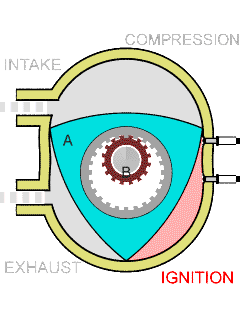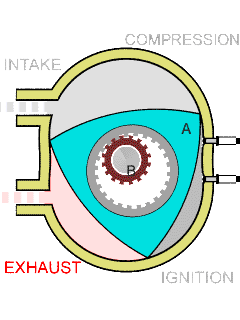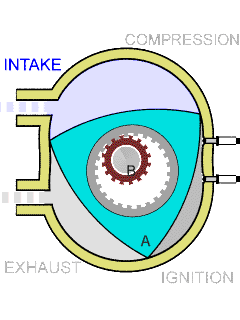
The Wankel engine (rotary engine) does not have piston strokes. It operates with the same separation of phases as the four-stroke engine with the phases taking place in separate locations in the engine. In
thermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of t ...
terms it follows the
Otto engine cycle, so may be thought of as a "four-phase" engine. While it is true that three power strokes typically occur per rotor revolution, due to the 3:1 revolution ratio of the rotor to the eccentric shaft, only one power stroke per shaft revolution actually occurs. The drive (eccentric) shaft rotates once during every power stroke instead of twice (crankshaft), as in the Otto cycle, giving it a greater power-to-weight ratio than piston engines. This type of engine was most notably used in the
Mazda RX-8, the earlier
RX-7, and other vehicle models. The engine is also used in unmanned aerial vehicles, where the small size and weight and the high power-to-weight ratio are advantageous.
Forced induction
Forced induction is the process of delivering compressed air to the intake of an internal combustion engine. A forced induction engine uses a
gas compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can tra ...
to increase the pressure, temperature and
density of the air. An engine without forced induction is considered a
naturally aspirated engine.
Forced induction is used in the automotive and aviation industry to increase engine power and efficiency. It particularly helps aviation engines, as they need to operate at high altitude.
Forced induction is achieved by a
supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced indu ...
, where the compressor is directly powered from the engine shaft or, in the
turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to pr ...
, from a turbine powered by the engine exhaust.
Fuels and oxidizers
All internal combustion engines depend on
combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
of a
chemical fuel, typically with oxygen from the air (though it is possible to inject
nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has ...
to do more of the same thing and gain a power boost). The combustion process typically results in the production of a great quantity of thermal energy, as well as the production of steam and carbon dioxide and other chemicals at very high temperature; the
temperature reached is determined by the chemical make up of the fuel and oxidizers (see
stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equ ...
), as well as by the compression and other factors.
Fuels
The most common modern fuels are made up of
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s and are derived mostly from
fossil fuels (
petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
). Fossil fuels include
diesel fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and ...
,
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic ...
and
petroleum gas, and the rarer use of
propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as ...
. Except for the fuel delivery components, most internal combustion engines that are designed for gasoline use can run on
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
or liquefied petroleum gases without major modifications. Large diesels can run with air mixed with gases and a pilot diesel fuel ignition injection. Liquid and gaseous
biofuels, such as
ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
and
biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
(a form of diesel fuel that is produced from crops that yield
triglycerides such as
soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu ...
oil), can also be used. Engines with appropriate modifications can also run on
hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
gas,
wood gas, or
charcoal gas, as well as from so-called
producer gas
Producer gas is fuel gas that is manufactured by blowing a coke or coal with air and steam simultaneously. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), as well as substantial amounts of nitrogen (N2). The caloric value of the produce ...
made from other convenient biomass. Experiments have also been conducted using powdered solid fuels, such as the
magnesium injection cycle.
Presently, fuels used include:
*
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
:
** Petroleum spirit (
North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Ca ...
term:
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic ...
,
British term: petrol)
**
Petroleum diesel.
**
Autogas (
liquified petroleum gas).
**
Compressed natural gas
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in ...
.
**
Jet fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial a ...
(
aviation fuel
Aviation fuels are petroleum-based fuels, or petroleum and synthetic fuel blends, used to power aircraft. They have more stringent requirements than fuels used for ground use, such as heating and road transport, and contain additives to enhance ...
)
**
Residual fuel
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), bun ...
*
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen ...
:
** Gasoline can be made from carbon (coal) using the
FischerâTropsch process
The FischerâTropsch process is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatu ...
** Diesel fuel can be made from carbon using the
FischerâTropsch process
The FischerâTropsch process is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatu ...
* Biofuels and vegetable oils:
**
Peanut oil and other
vegetable oils.
**
Woodgas, from an onboard
wood gasifier
A wood gas generator is a gasification unit which converts timber or charcoal into wood gas, a producer gas consisting of atmospheric nitrogen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, traces of methane, and other gases, which â after cooling and filtering ...
using solid wood as a fuel
** Biofuels:
***
Biobutanol
220px, Butanol, a C-4 hydrocarbon is a promising bio-derived fuel, which shares many properties with gasoline.
Butanol may be used as a fuel in an internal combustion engine. It is more similar to gasoline than it is to ethanol. A C4-hydrocarbon ...
(replaces gasoline).
***
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
(replaces petrodiesel).
***
Dimethyl Ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precurs ...
(replaces petrodiesel).
***
Bioethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
and
Biomethanol
Methanol fuel is an alternative biofuel for internal combustion and other engines, either in combination with gasoline or independently. Methanol ( C H3 O H) is less expensive to produce sustainably than ethanol fuel, although it produces more ...
(
wood alcohol) and other
biofuels (see
Flexible-fuel vehicle).
***
Biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. I ...
*
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
(mainly
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ...
rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive Jet (fluid), jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, i ...
s)
Even fluidized metal powders and explosives have seen some use. Engines that use gases for fuel are called gas engines and those that use liquid hydrocarbons are called oil engines; however, gasoline engines are also often colloquially referred to as "gas engines" ("
petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' ...
s" outside North America).
The main limitations on fuels are that it must be easily transportable through the
fuel system to the
combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Intern ...
, and that the fuel releases sufficient
energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: áŒÎœÎÏγΔÎčα, ''enĂ©rgeia'', âactivityâ) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
in the form of
heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
upon
combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
to make practical use of the engine.
Diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-ca ...
s are generally heavier, noisier, and more powerful at lower speeds than
gasoline engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' ...
s. They are also more fuel-efficient in most circumstances and are used in heavy road vehicles, some automobiles (increasingly so for their increased
fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
over gasoline engines), ships,
railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
locomotives, and light
aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
. Gasoline engines are used in most other road vehicles including most cars,
motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruisin ...
s, and
moped
A moped ( ) is a type of small motorcycle, generally having a less stringent licensing requirement than full motorcycles or automobiles. The term used to mean a similar vehicle except with both bicycle pedals and a motorcycle engine. Mopeds typic ...
s. Note that in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
, sophisticated diesel-engined cars have taken over about 45% of the market since the 1990s. There are also engines that run on
hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
,
methanol,
ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a h ...
,
liquefied petroleum gas (LPG),
biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oil ...
,
paraffin and
tractor vaporizing oil (TVO).
Hydrogen
Hydrogen could eventually
replace conventional fossil fuels in traditional internal combustion engines. Alternatively
fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
technology may come to deliver its promise and the use of the internal combustion engines could even be phased out.
Although there are multiple ways of producing free hydrogen, those methods require converting combustible molecules into hydrogen or consuming electric energy. Unless that electricity is produced from a renewable sourceâand is not required for other purposesâhydrogen does not solve any
energy crisis
An energy crisis or energy shortage is any significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In literature, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, in particular, those that supply n ...
. In many situations the disadvantage of hydrogen, relative to carbon fuels, is
its storage.
Liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully l ...
has extremely low density (14 times lower than water) and requires extensive insulationâwhilst gaseous hydrogen requires heavy tankage. Even when liquefied, hydrogen has a higher specific energy but the volumetric energetic storage is still roughly five times lower than gasoline. However, the energy density of hydrogen is considerably higher than that of electric batteries, making it a serious contender as an energy carrier to replace fossil fuels. The 'Hydrogen on Demand' process (see
direct borohydride fuel cell) creates hydrogen as needed, but has other issues, such as the high price of the
sodium borohydride that is the raw material.
Oxidizers

Since air is plentiful at the surface of the earth, the oxidizer is typically atmospheric oxygen, which has the advantage of not being stored within the vehicle. This increases the power-to-weight and power-to-volume ratios. Other materials are used for special purposes, often to increase power output or to allow operation under water or in space.
* Compressed air has been commonly used in
torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, s ...
es.
* Compressed
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, as well as some compressed air, was used in the Japanese
Type 93 torpedo. Some
submarines
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely ...
carry pure oxygen. Rockets very often use
liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygenâabbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industriesâis the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an a ...
.
*
Nitromethane is added to some racing and
model fuels to increase power and control combustion.
*
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has ...
has been usedâwith extra gasolineâin tactical aircraft, and in specially equipped cars to allow short bursts of added power from engines that otherwise run on gasoline and air. It is also used in the Burt Rutan rocket spacecraft.
*
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3% ...
power was under development for German World War II submarines. It may have been used in some non-nuclear submarines, and was used on some rocket engines (notably the
Black Arrow
Black Arrow, officially capitalised BLACK ARROW, was a British satellite carrier rocket. Developed during the 1960s, it was used for four launches between 1969 and 1971, all launched from the Woomera Prohibited Area in Australia. Its final fl ...
and the
Messerschmitt Me 163 rocket fighter).
* Other chemicals such as chlorine or fluorine have been used experimentally, but have not been found practical.
Cooling
Cooling is required to remove excessive heatâhigh temperature can cause engine failure, usually from wear (due to high-temperature-induced failure of lubrication), cracking or warping. Two most common forms of engine cooling are
air-cooled and
water-cooled. Most modern automotive engines are both water and air-cooled, as the water/liquid-coolant is carried to air-cooled fins and/or fans, whereas larger engines may be singularly water-cooled as they are stationary and have a constant supply of water through water-mains or fresh-water, while most power tool engines and other small engines are air-cooled. Some engines (air or water-cooled) also have an
oil cooler. In some engines, especially for
turbine engine blade cooling and
liquid rocket engine cooling, fuel is used as a coolant, as it is simultaneously preheated before injecting it into a combustion chamber.
Starting
Internal combustion engines must have their cycles started. In reciprocating engines this is accomplished by turning the crankshaft (Wankel Rotor Shaft) which induces the cycles of intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. The first engines were started with a turn of their
flywheels, while the first vehicle (the Daimler Reitwagen) was started with a hand crank. All ICE engined automobiles were started with hand cranks until
Charles Kettering developed the electric starter for automobiles. This method is now the most widely used, even among non-automobiles.
As diesel engines have become larger and their mechanisms heavier,
air starters have come into use. This is due to the lack of torque in electric starters. Air starters work by pumping compressed air into the cylinders of an engine to start it turning.
Two-wheeled vehicles may have their engines started in one of four ways:
* By pedaling, as on a bicycle
* By pushing the vehicle and then engaging the clutch, known as "run-and-bump starting"
* By kicking downward on a single pedal, known as "kick starting"
* By an electric starter, as in cars
There are also starters where a spring is compressed by a crank motion and then used to start an engine.
Some small engines use a pull-rope mechanism called "recoil starting", as the rope rewinds itself after it has been pulled out to start the engine. This method is commonly used in pushed lawn mowers and other settings where only a small amount of torque is needed to turn an engine over.
Turbine engines are frequently started by an electric motor or by compressed air.
Measures of engine performance
Engine types vary greatly in a number of different ways:
*
energy efficiency
* fuel/propellant consumption (
brake specific fuel consumption
Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is a measure of the fuel efficiency of any prime mover that burns fuel and produces rotational, or shaft power. It is typically used for comparing the efficiency of internal combustion engines with a shaft ou ...
for shaft engines,
thrust specific fuel consumption for jet engines)
*
power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
*
thrust to weight ratio
Thrust-to-weight ratio is a dimensionless ratio of thrust to weight of a rocket, jet engine, propeller engine, or a vehicle propelled by such an engine that is an indicator of the performance of the engine or vehicle.
The instantaneous thrust-to-w ...
*
torque curves (for shaft engines),
thrust lapse (jet engines)
*
compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stat ...
for piston engines,
overall pressure ratio for jet engines and gas turbines
Energy efficiency
Once ignited and burnt, the
combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
productsâhot gasesâhave more available
thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is used loosely in various contexts in physics and engineering. It can refer to several different well-defined physical concepts. These include the internal energy or enthalpy of a body of matter and radiation; heat, ...
than the original compressed fuel-air mixture (which had higher
chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "Ho ...
). This available energy is manifested as a higher
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
and
pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
that can be converted into
kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its a ...
by the engine. In a reciprocating engine, the high-pressure gases inside the cylinders drive the engine's pistons.
Once the available energy has been removed, the remaining hot gases are
vented (often by opening a
valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fitting ...
or exposing the exhaust outlet) and this allows the piston to return to its previous position (top dead center, or TDC). The piston can then proceed to the next phase of its cycle, which varies between engines. Any thermal energy that is not translated into work is normally considered a waste product and is removed from the engine either by an air or liquid cooling system.
Internal combustion engines are considered
heat engines (since the release of chemical energy in combustion has the same effect as
heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
transfer into the engine) and as such their theoretical efficiency can be approximated by idealized
thermodynamic cycle
A thermodynamic cycle consists of a linked sequence of thermodynamic processes that involve transfer of heat and work into and out of the system, while varying pressure, temperature, and other state variables within the system, and that eventu ...
s. The thermal efficiency of a theoretical cycle cannot exceed that of the
Carnot cycle
A Carnot cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle proposed by French physicist Sadi Carnot in 1824 and expanded upon by others in the 1830s and 1840s. By Carnot's theorem, it provides an upper limit on the efficiency of any classical thermodynam ...
, whose efficiency is determined by the difference between the lower and upper
operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
s of the engine. The upper operating temperature of an engine is limited by two main factors; the thermal operating limits of the materials, and the auto-ignition resistance of the fuel. All
metal
A metal (from Greek ÎŒÎÏÎ±Î»Î»ÎżÎœ ''mĂ©tallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
s and
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s have a thermal operating limit, and there is significant research into
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelai ...
materials that can be made with greater thermal stability and desirable structural properties. Higher thermal stability allows for a greater temperature difference between the lower (ambient) and upper operating temperatures, hence greater thermodynamic efficiency. Also, as the cylinder temperature rises, the fuel becomes more prone to auto-ignition. This is caused when the cylinder temperature nears the flash point of the charge. At this point, ignition can spontaneously occur before the spark plug fires, causing excessive cylinder pressures. Auto-ignition can be mitigated by using fuels with high auto-ignition resistance (
octane rating), however it still puts an upper bound on the allowable peak cylinder temperature.
The
thermodynamic limits assume that the engine is operating under ideal conditions: a frictionless world, ideal gases, perfect insulators, and operation for infinite time. Real world applications introduce complexities that reduce efficiency. For example, a real engine runs best at a specific load, termed its
power band. The engine in a car cruising on a highway is usually operating significantly below its ideal load, because it is designed for the higher loads required for rapid acceleration. In addition, factors such as
wind resistance reduce overall system efficiency. Vehicle
fuel economy is measured in
miles per gallon
The fuel economy of an automobile relates distance traveled by a vehicle and the amount of fuel consumed. Consumption can be expressed in terms of volume of fuel to travel a distance, or the distance traveled per unit volume of fuel consumed. S ...
or in liters per 100 kilometers. The volume of hydrocarbon assumes a standard energy content.
Even when aided with turbochargers and stock efficiency aids, most engines retain an ''average'' efficiency of about 18â20%. However, the latest technologies in
Formula One engines
Since its inception in 1947, Formula One has used a variety of engine regulations
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biolo ...
have seen a boost in thermal efficiency past 50%.
There are many inventions aimed at increasing the efficiency of IC engines. In general, practical engines are always compromised by trade-offs between different properties such as efficiency, weight, power, heat, response, exhaust emissions, or noise. Sometimes economy also plays a role in not only the cost of manufacturing the engine itself, but also manufacturing and distributing the fuel. Increasing the engine's efficiency brings better fuel economy but only if the fuel cost per energy content is the same.
Measures of fuel efficiency and propellant efficiency
For stationary and shaft engines including propeller engines, fuel consumption is measured by calculating the
brake specific fuel consumption
Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is a measure of the fuel efficiency of any prime mover that burns fuel and produces rotational, or shaft power. It is typically used for comparing the efficiency of internal combustion engines with a shaft ou ...
, which measures the mass flow rate of fuel consumption divided by the power produced.
For internal combustion engines in the form of jet engines, the power output varies drastically with airspeed and a less variable measure is used:
thrust specific fuel consumption (TSFC), which is the mass of propellant needed to generate
impulses that is measured in either pound force-hour or the grams of propellant needed to generate an impulse that measures one kilonewton-second.
For rockets, TSFC can be used, but typically other equivalent measures are traditionally used, such as
specific impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is ...
and
effective exhaust velocity.
Air and noise pollution
Air pollution
Internal combustion engines such as reciprocating internal combustion engines produce
air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different type ...
emissions, due to incomplete combustion of
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalentâits atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
aceous fuel. The main derivatives of the process are
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, water and some
soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolyse ...
âalso called
particulate matter
Particulates â also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) â are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The t ...
(PM). The effects of inhaling particulate matter have been studied in humans and animals and include asthma, lung cancer, cardiovascular issues, and premature death. There are, however, some additional products of the combustion process that include
nitrogen oxide Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
* Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), o ...
s and
sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
and some uncombusted hydrocarbons, depending on the operating conditions and the fuel-air ratio.
Carbon dioxide emissions from internal combustion engines contribute to human-induced
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warmingâthe ongoing increase in global average temperatureâand its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. Increasing the engine's
fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, ...
can reduce, but not eliminate, the amount of emissions as carbon-based fuel combustion produces . Since removing from engine exhaust is impractical, there is increasing interest in alternatives. Sustainable fuels such as
biofuels,
synfuel
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming ...
s, and
electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
s powered by batteries are examples.
Not all of the fuel is completely consumed by the combustion process. A small amount of fuel is present after combustion, and some of it reacts to form oxygenates, such as
formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) ( systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
or
acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the ...
, or hydrocarbons not originally present in the input fuel mixture. Incomplete combustion usually results from insufficient
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
to achieve the perfect
stoichiometric
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equ ...
ratio. The flame is "quenched" by the relatively cool cylinder walls, leaving behind unreacted fuel that is expelled with the exhaust. When running at lower speeds, quenching is commonly observed in diesel (compression ignition) engines that run on natural gas. Quenching reduces efficiency and increases knocking, sometimes causing the engine to stall. Incomplete combustion also leads to the production of
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(CO). Further chemicals released are
benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen ato ...
and
1,3-butadiene that are also
hazardous air pollutants.
Increasing the amount of air in the engine reduces emissions of incomplete combustion products, but also promotes reaction between oxygen and
nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
in the air to produce
nitrogen oxide Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
* Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), o ...
s (). is hazardous to both plant and animal health, and leads to the production of
ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
(). Ozone is not emitted directly; rather, it is a secondary air pollutant, produced in the atmosphere by the reaction of and
volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapour pressure at room temperature. High vapor pressure correlates with a low boiling point, which relates to the number of the sample's molecules in the surrounding air, a ...
s in the presence of sunlight. Ground-level ozone is harmful to human health and the environment. Though the same chemical substance, ground-level ozone should not be confused with
stratospheric ozone, or the
ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rel ...
, which protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays.
Carbon fuels containing sulfur produce
sulfur monoxide
Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula . It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 ( disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.
S ...
s (SO) and
sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide ( IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic ...
() contributing to
acid rain.
In the United States, nitrogen oxides,
PM, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and ozone, are regulated as
criteria air pollutants under the
Clean Air Act to levels where human health and welfare are protected. Other pollutants, such as benzene and 1,3-butadiene, are regulated as
hazardous air pollutants whose emissions must be lowered as much as possible depending on technological and practical considerations.
, carbon monoxide and other pollutants are frequently controlled via
exhaust gas recirculation which returns some of the exhaust back into the engine intake.
Catalytic converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usuall ...
s are used to convert exhaust chemicals to (a greenhouse gas), (water vapour, also a greenhouse gas) and (nitrogen).
Non-road engines
The emission standards used by many countries have special requirements for non-road engines which are used by equipment and vehicles that are not operated on the public roadways. The standards are separated from the road vehicles.
Noise pollution
Significant contributions to noise pollution are made by internal combustion engines. Automobile and truck traffic operating on highways and street systems produce noise, as do aircraft flights due to jet noise, particularly supersonic-capable aircraft. Rocket engines create the most intense noise.
Idling
Internal combustion engines continue to consume fuel and emit pollutants while idling. Idling is reduced by Start-stop system, stop-start systems.
Carbon dioxide formation
A good way to estimate the mass of carbon dioxide that is released when one litre of diesel fuel (or gasoline) is combusted can be found as follows:
As a good approximation the chemical formula of diesel is . Note that in reality diesel is a mixture of different molecules. As carbon has a molar mass of 12 g/mol and hydrogen (atomic) has a molar mass of about 1 g/mol, the fraction by weight of carbon in diesel is roughly .
The reaction of diesel combustion is given by:
2 + 3n 2n + 2n
Carbon dioxide has a molar mass of 44 g/mol as it consists of 2 atoms of oxygen (16 g/mol) and 1 atom of carbon (12 g/mol). So 12 g of carbon yields 44 g of carbon dioxide.
Diesel has a density of 0.838 kg per litre.
Putting everything together the mass of carbon dioxide that is produced by burning 1 litre of diesel can be calculated as:
The figure obtained with this estimation is close to the values found in the literature.
For gasoline, with a density of 0.75 kg/L and a ratio of carbon to hydrogen atoms of about 6 to 14, the estimated value of carbon emission from burning 1 litre of gasoline is:
See also
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Patents:
**
**
**
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Combustion videoâ in-cylinder combustion in an optically accessible, 2-stroke engine
Animated Enginesâ explains a variety of types
â Cut-away images and a good overview of the internal combustion engine
â Research at The University of Michigan
YouTubeâ Animation of the components and built-up of a 4-cylinder engine
YouTubeâ Animation of the internal moving parts of a 4-cylinder engine
retrieved May 9, 2009
* A file on unusual engine
* Aircraft Engine Historical Society (AEHS) ïżœ
{{DEFAULTSORT:Internal Combustion Engine
Internal combustion engine,
Engines, Internal combustion
Piston engines
Pollution
Air pollution
 An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the  Reciprocating piston engines are by far the most common power source for land and water
Reciprocating piston engines are by far the most common power source for land and water 
 The base of a reciprocating internal combustion engine is the engine block, which is typically made of
The base of a reciprocating internal combustion engine is the engine block, which is typically made of  The crankcase is sealed at the bottom with a
The crankcase is sealed at the bottom with a  The ''top dead center'' (TDC) of a piston is the position where it is nearest to the valves; ''bottom dead center'' (BDC) is the opposite position where it is furthest from them. A ''stroke'' is the movement of a piston from TDC to BDC or vice versa, together with the associated process. While an engine is in operation, the crankshaft rotates continuously at a nearly constant
The ''top dead center'' (TDC) of a piston is the position where it is nearest to the valves; ''bottom dead center'' (BDC) is the opposite position where it is furthest from them. A ''stroke'' is the movement of a piston from TDC to BDC or vice versa, together with the associated process. While an engine is in operation, the crankshaft rotates continuously at a nearly constant  Some SI engines are crankcase scavenged and do not use poppet valves. Instead, the crankcase and the part of the cylinder below the piston is used as a pump. The intake port is connected to the crankcase through a reed valve or a rotary disk valve driven by the engine. For each cylinder, a transfer port connects in one end to the crankcase and in the other end to the cylinder wall. The exhaust port is connected directly to the cylinder wall. The transfer and exhaust port are opened and closed by the piston. The reed valve opens when the crankcase pressure is slightly below intake pressure, to let it be filled with a new charge; this happens when the piston is moving upwards. When the piston is moving downwards the pressure in the crankcase increases and the reed valve closes promptly, then the charge in the crankcase is compressed. When the piston is moving downwards, it also uncovers the exhaust port and the transfer port and the higher pressure of the charge in the crankcase makes it enter the cylinder through the transfer port, blowing the exhaust gases. Lubrication is accomplished by adding '' 2-stroke oil'' to the fuel in small ratios. '' Petroil'' refers to the mix of gasoline with the aforesaid oil. This kind of 2-stroke engine has a lower efficiency than comparable 4-strokes engines and releases more polluting exhaust gases for the following conditions:
* They use a '' total-loss lubrication system'': all the lubricating oil is eventually burned along with the fuel.
* There are conflicting requirements for scavenging: On one side, enough fresh charge needs to be introduced in each cycle to displace almost all the combustion gases but introducing too much of it means that a part of it gets in the exhaust.
* They must use the transfer port(s) as a carefully designed and placed nozzle so that a gas current is created in a way that it sweeps the whole cylinder before reaching the exhaust port so as to expel the combustion gases, but minimize the amount of charge exhausted. 4-stroke engines have the benefit of forcibly expelling almost all of the combustion gases because during exhaust the combustion chamber is reduced to its minimum volume. In crankcase scavenged 2-stroke engines, exhaust and intake are performed mostly simultaneously and with the combustion chamber at its maximum volume.
The main advantage of 2-stroke engines of this type is mechanical simplicity and a higher
Some SI engines are crankcase scavenged and do not use poppet valves. Instead, the crankcase and the part of the cylinder below the piston is used as a pump. The intake port is connected to the crankcase through a reed valve or a rotary disk valve driven by the engine. For each cylinder, a transfer port connects in one end to the crankcase and in the other end to the cylinder wall. The exhaust port is connected directly to the cylinder wall. The transfer and exhaust port are opened and closed by the piston. The reed valve opens when the crankcase pressure is slightly below intake pressure, to let it be filled with a new charge; this happens when the piston is moving upwards. When the piston is moving downwards the pressure in the crankcase increases and the reed valve closes promptly, then the charge in the crankcase is compressed. When the piston is moving downwards, it also uncovers the exhaust port and the transfer port and the higher pressure of the charge in the crankcase makes it enter the cylinder through the transfer port, blowing the exhaust gases. Lubrication is accomplished by adding '' 2-stroke oil'' to the fuel in small ratios. '' Petroil'' refers to the mix of gasoline with the aforesaid oil. This kind of 2-stroke engine has a lower efficiency than comparable 4-strokes engines and releases more polluting exhaust gases for the following conditions:
* They use a '' total-loss lubrication system'': all the lubricating oil is eventually burned along with the fuel.
* There are conflicting requirements for scavenging: On one side, enough fresh charge needs to be introduced in each cycle to displace almost all the combustion gases but introducing too much of it means that a part of it gets in the exhaust.
* They must use the transfer port(s) as a carefully designed and placed nozzle so that a gas current is created in a way that it sweeps the whole cylinder before reaching the exhaust port so as to expel the combustion gases, but minimize the amount of charge exhausted. 4-stroke engines have the benefit of forcibly expelling almost all of the combustion gases because during exhaust the combustion chamber is reduced to its minimum volume. In crankcase scavenged 2-stroke engines, exhaust and intake are performed mostly simultaneously and with the combustion chamber at its maximum volume.
The main advantage of 2-stroke engines of this type is mechanical simplicity and a higher 
 Surfaces in contact and relative motion to other surfaces require lubrication to reduce wear, noise and increase efficiency by reducing the power wasting in overcoming
Surfaces in contact and relative motion to other surfaces require lubrication to reduce wear, noise and increase efficiency by reducing the power wasting in overcoming  Multiple cylinder engines have their valve train and crankshaft configured so that pistons are at different parts of their cycle. It is desirable to have the pistons' cycles uniformly spaced (this is called ''even firing'') especially in forced induction engines; this reduces torque pulsations and makes
Multiple cylinder engines have their valve train and crankshaft configured so that pistons are at different parts of their cycle. It is desirable to have the pistons' cycles uniformly spaced (this is called ''even firing'') especially in forced induction engines; this reduces torque pulsations and makes  The Wankel engine (rotary engine) does not have piston strokes. It operates with the same separation of phases as the four-stroke engine with the phases taking place in separate locations in the engine. In
The Wankel engine (rotary engine) does not have piston strokes. It operates with the same separation of phases as the four-stroke engine with the phases taking place in separate locations in the engine. In  Since air is plentiful at the surface of the earth, the oxidizer is typically atmospheric oxygen, which has the advantage of not being stored within the vehicle. This increases the power-to-weight and power-to-volume ratios. Other materials are used for special purposes, often to increase power output or to allow operation under water or in space.
* Compressed air has been commonly used in
Since air is plentiful at the surface of the earth, the oxidizer is typically atmospheric oxygen, which has the advantage of not being stored within the vehicle. This increases the power-to-weight and power-to-volume ratios. Other materials are used for special purposes, often to increase power output or to allow operation under water or in space.
* Compressed air has been commonly used in