|
1,3-Butadiene
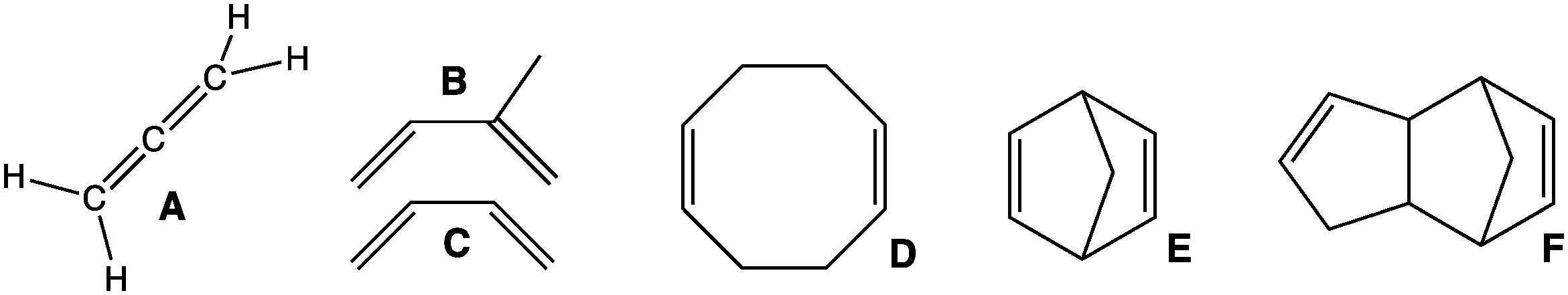
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugated Diene
In organic chemistry, a diene ( ); also diolefin, ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diene
In organic chemistry, a diene ( ); also diolefin, ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About of rubber is produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubber, just like natural rubber, has many uses in the automotive industry for tires, door and window profiles, seals such as O-rings and gaskets, hoses, belts, matting, and flooring. They offer a different range of physical and chemical properties which can improve the reliability of a given product or application. Synthetic rubbers are superior to natural rubbers in two major respects: thermal stability, and resistance to oils and related compounds. They are more resistant to oxidizing agents, such as oxygen and ozone which can reduce the life of products like tires. History The expanded use of bicycles, and particularly their pneumatic tires, starting in the 1890s, created increased demand for rubber. In 1909, a team headed by Fritz Hofmann, working at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an ''exhaust plume''. It is a major component of motor vehicle emissions (and from stationary internal combustion engines), which can also include crankcase blow-by and evaporation of unused gasoline. Air pollution from burning fossil fuels is estimated to kill over 5 million people each year. Motor vehicle emissions are a common source of air pollution and are a major ingredient in the creation of smog in some large cities. Composition The largest part of most combustion gas is nitrogen (N2), water vapor (H2O) (except with pure-carbon fuels), and carbon dioxide (CO2) (except for fuels without carbon); these are not toxic or noxiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Bock
Walter Bock (20 January 1895 – 25 October 1948)Death record Nr. 3271/Köln I for Ludwig Walter Robert Bock of Oct. 26, 1948, Landesarchiv NRW, Duisburg was a German chemist who developed styrene-butadiene , styrene-butadiene copolymer by emulsion polymerization as a synthetic rubber (SBR). Early life Walter Bock was born on January 10, 1895, in the small village of Wenzen (now part of Einbeck) in the Duchy of Brunswick. He was the fourth of nine children. His father, Wilhelm Bock, was the sole teacher in Wenzen. From 1905 to 1914 Bock attended high school in Brunswick. Immediately after graduation he joined the army and served as an officer in World War I. He commanded an infantry company until he was wounded in July 1918. In October 1918 he began studying chemistry. After receiving his Ph.D. from the University of Göttingen in October 1921, Bock found employment as chemist at the Köln Rottweil AG in Premnitz. In the fall of 1924 Bock joined the Dr. Zellner laboratories in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Tschunker
Eduard Model Accessories is a Czech manufacturer of plastic models and finescale model accessories. History Formed in 1989 in the city of Most, Eduard began in a rented cellar as a manufacturer of photoetched brass model components. Following the success of their early products, the company branched off into plastic models in 1993. As of 2006, Eduard's product line contained some 30 plastic kits and more than 800 individual photoetch detail sets. To the plastic modeller community at large, Eduard has become a household word in the field of photoetched parts, and their products are available worldwide. Product lines Eduard aircraft kits range from World War I to the present day. Some notable ones include: most of the famous World War I fighters are: Fokker D.VII, Pfalz D.III, Albatros D.III and the Sopwith Pup, while World War II had the: Yakovlev Yak-3, Hawker Hurricane, Spitfire and the Messerschmitt Bf 109 The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a monoplane fighter aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Vasilyevich Lebedev
Sergei Vasilievich Lebedev (; 13 July 1874 – 2 May 1934) was a Russian/Soviet chemist and the inventor of polybutadiene synthetic rubber, the first commercially viable and mass-produced type of synthetic rubber. Biography Lebedev was born in 1874 in Lublin and went to school in Warsaw. In 1900, he graduated from St. Petersburg University and found work at the Petersburg Margarine Factory. Starting in 1902, Lebedev moved from university to university in Russia, starting at the Saint-Petersburg Institute for Railroad Engineering. In 1904, he returned to St. Petersburg University to work under Alexey Favorsky ( Stalin Prize, 1941, for contributions to the manufacture of synthetic rubber). In 1905, he married his second wife, the artist Anna Ostroumova-Lebedeva. In 1915, Lebedev was appointed Professor at the Women's Pedagogical Institute in St. Petersburg. After 1916, he was a Professor of the Saint Petersburg Academy for Military Medicine. In 1925, he became the leade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Edward Armstrong
Henry Edward Armstrong FRS FRSE (Hon) (6 May 1848 – 13 July 1937) was a British chemist. Although Armstrong was active in many areas of scientific research, such as the chemistry of naphthalene derivatives, he is remembered today largely for his ideas and work on the teaching of science. Armstrong's acid is named for him. Life and work Armstrong was born the son of Richard Armstrong, a commission agent and importer, and Mary Ann Biddle. He lived most of his life in Lewisham, a suburb of London. After finishing school in 1864 at age 16, he spent a winter in Gibraltar, with a relative, for health reasons. In the spring of 1865, Armstrong returned to England and entered the Royal College of Chemistry in London, now the department of chemistry at Imperial College. Chemical training in those days was not lengthy, and at the age of 18 he was selected by Edward Frankland to assist in devising methods of determining organic impurities in sewage. Armstrong pursued further studies u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyl Alcohol
Amyl alcohols are alcohols with the formula C5H11OH. Eight are known. A mixture of amyl alcohols (also called amyl alcohol) can be obtained from fusel alcohol. Amyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification, by which is produced amyl acetate and other products. The name ''amyl alcohol'' without further specification applies to the normal (straight-chain) form, 1-pentanol. : Three of these alcohols, 2-methyl-1-butanol, 2-pentanol, and 3-methyl-2-butanol (methyl isopropyl carbinol), contain stereocenters, and are therefore chiral and optically active. The most important amyl alcohol is isoamyl alcohol, the chief one generated by fermentation in the production of alcoholic beverages and a constituent of fusel oil. The other amyl alcohols may be obtained synthetically. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Amyl Alcohol Alkanols GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Greek language, Greek-derived morpheme, elements ''pyro-'' (from Ancient Greek : - "fire, heat, fever") and ''lysis'' ( : - "separation, loosening"). Applications Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic compound, organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in the charring of wood or pyrolysis of biomass. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves Char (chemistry), char, a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly carbon as the residue, is called carbonization. Pyrolysis is considered one of the steps in the processes of gasification or combustion. Laypeople often confuse pyrolysis gas with syngas. Pyrolysis gas has a high percentage of heavy tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allene
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms (, where R is hydrogen, H or some organyl group). Allenes are classified as diene#Classes, cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene (), which is itself also called ''allene''. A group of the structure is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent (R is H or some alkyl group). In analogy to Allyl group, allylic and Propargyl group, propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α (i.e., directly adjacent) to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |