Conjugated Diene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 According to the ''
According to the ''


organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, a diene ( ); also diolefin, ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
that contains two double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
s, usually among carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the gen ...
. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
s in the polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
industry. Polyunsaturated fat
In biochemistry and nutrition, a polyunsaturated fat is a fat that contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid (abbreviated PUFA), which is a subclass of fatty acid characterized by a backbone with two or more carbon–carbon double bonds.
Some polyunsa ...
s are of interest to nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
.
Classes
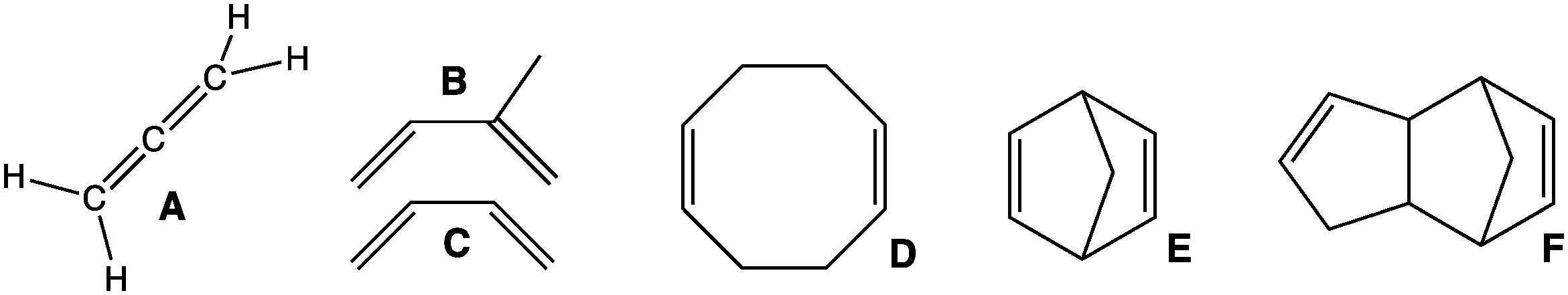
Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called anallene
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms (, where R is hydrogen, H or some organyl group). Allenes are classified as diene#Classes, cumulated dienes ...
.
#Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance.
#Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable than isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
ic conjugated dienes. This can also be known as an isolated diene.
 According to the ''
According to the ''Gold Book
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPAC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and R ...
'' definition, a "diene" could include one or more heteroatom
In chemistry, a heteroatom () is, strictly, any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen.
Organic chemistry
In practice, the term is mainly used more specifically to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecular ...
s which replace unsaturated carbon atoms, giving structures that could more specifically be called ''heterodienes''.
Compounds that contain more than two double bonds are called polyene
In organic chemistry, polyenes are polyunsaturated organic compounds that contain multiple carbon–carbon double bonds (). Some sources consider dienes to be polyenes, whereas others require polyenes to contain at least three carbon–carbon d ...
s. Polyenes and dienes share many properties.
Synthesis of dienes
On an industrial scale, butadiene is prepared bythermal cracking
In petrochemistry, petroleum geology and organic chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or long-chain hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking ...
of butane
Butane () is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane exists as two isomers, ''n''-butane with connectivity and iso-butane with the formula . Both isomers are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at ro ...
s. In a similarly non-selective process, dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula . At room temperature, it is a white brittle wax, although lower purity samples can be straw coloured liquids. The pure material smells somewhat of soy wax or camphor, with ...
is obtained from coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoria ...
s.
In the laboratory, more directed and more delicate processes are employed such as dehydrohalogenation
In chemistry, dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction which removes a hydrogen halide from a substrate (chemistry), substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications.
Dehydrohalogen ...
s and condensations. Myriad methods have been developed, such as the Whiting reaction. Families of nonconjugated dienes are derived from the oligomerization
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
and dimerization
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar molecular entities by bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dimers, even when the monomer is u ...
of conjugated dienes. For example, 1,5-cyclooctadiene and 4-vinylcyclohexene are produced by dimerization of 1,3-butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two ...
.
Diene-containing fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s are biosynthesized
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve ...
from acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized fo ...
.
α,ω-Dienes have the formula (CH2)n(CH=CH2)2. They are prepared industrially by ethenolysis
In organic chemistry, ethenolysis is a chemical process in which internal olefins are degraded using ethylene () as the reagent. The reaction is an example of olefin metathesis, cross metathesis. The utility of the reaction is driven by the low ...
of cyclic dienes. For example, 1,5-hexadiene and 1,9-decadiene, useful crosslinking agents and synthetic intermediates, are produced from 1,5-cyclooctadiene
1,5-Cyclooctadiene (also known as cycloocta-1,5-diene) is a cyclic compound, cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , specifically .
There are three configurational isomers with this structure, that differ by the arrangement of the four C� ...
and cyclooctene
Cyclooctene is the cycloalkene with a formula . Its molecule has a ring of 8 carbon atoms, connected by seven single bonds and one double bond.
Cyclooctene is notable because it is the smallest cycloalkene that can exist stably as either the '' ...
, respectively. The catalyst is derived from Re2O7 on alumina.
Reactivity and uses
Polymerization
The most heavily practiced reaction of alkenes, dienes included, ispolymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. 1,3-Butadiene is a precursor to rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
used in tires, and isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
is the precursor to natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
. Chloroprene
Chloroprene (IUPAC name 2-chlorobuta-1,3-diene) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CH2=CCl−CH=CH2. Chloroprene is a colorless volatile liquid, almost exclusively used as a monomer for the production of the polymer polychloroprene, ...
is related but it is a synthetic monomer.
Cycloadditions
An important reaction for conjugated dienes is theDiels–Alder reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a Conjugated system, conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the Diels–Alder reaction#The dienophile, dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexe ...
. Many specialized dienes have been developed to exploit this reactivity for the synthesis of natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical s ...
s (e.g., Danishefsky's diene).
Other addition reactions
Conjugated dienes add reagents such asbromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
by both 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition pathways. Addition of polar reagents can generate complex architectures:
::
Metathesis reactions
Nonconjugated dienes are substrates forring-closing metathesis
Ring-closing metathesis (RCM) is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated rings via the intramolecular olefin metathesis, metathesis of two term ...
reactions. These reactions require a metal catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
:
::
Acidity
The position adjacent to a double bond isacid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
ic because the resulting allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula . It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated a ...
anion is stabilized by resonance. This effect becomes more pronounced as more alkenes are involved to create greater stability. For example, deprotonation at position 3 of a 1,4-diene or position 5 of a 1,3-diene give a pentadienyl anion. An even greater effect is seen if the anion is aromatic, for example, deprotonation of cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula C5H6. It is often abbreviated CpH because the cyclopentadienyl anion is abbreviated Cp−.
This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, ...
to give the cyclopentadienyl anion
Sodium cyclopentadienide is an organosodium compound with the formula C5H5Na. The compound is often abbreviated as NaCp, where Cp− is the cyclopentadienide anion. Sodium cyclopentadienide is a colorless solid, although samples often are pin ...
.
As ligands
Dienes are widely used chelatingligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
s in organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and so ...
. In some cases they serve as placeholder ligands, being removed during a catalytic cycle. For example, the cyclooctadiene ("cod") ligands in bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0)
Bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(C8H12)2, also written Ni(cod)2. It is a diamagnetic coordination complex featuring tetrahedral nickel(0) bound to the alkene groups in two 1,5-cyclooctadiene ligands. Thi ...
are labile. In some cases, dienes are spectator ligands, remaining coordinated throughout a catalytic cycle and influencing the product distributions. Chiral
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is dist ...
dienes have also been described. Other diene complexes include (butadiene)iron tricarbonyl
(Butadiene)iron tricarbonyl is an organoiron compound with the formula (CH)Fe(CO). It is a well-studied metal complex of butadiene. An orange-colored viscous liquid that freezes just below room temperature, the compound adopts a piano stool stru ...
, cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl
Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl is an organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C4H4)(CO)3. It is a yellow oil that is soluble in organic solvents. It has been used in organic chemistry as a precursor for cyclobutadiene, which is an elusive species i ...
, and cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer.
References
{{Authority control Diene