The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in
Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in
Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE. They formed an empire, the Imperial Hephthalites, and were militarily important from 450 CE, when they defeated the
Kidarites, to 560 CE, when combined forces from the
First Turkic Khaganate and the
Sasanian Empire defeated them.
After 560 CE, they established "principalities" in the area of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
, under the
suzerainty of the
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
(in the areas north of the
Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
) and of the
Sasanian Empire (in the areas south of the
Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
), before the
Tokhara Yabghus took over in 625.
The Imperial Hephthalites, based in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
, expanded eastwards to the
Tarim Basin, westwards to
Sogdia and southwards through
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, but they never went beyond the
Hindu-Kush, which was occupied by the
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
, previously mistakenly regarded as an extension of the Hephthalites. They were a tribal confederation and included both nomadic and settled urban communities. They formed part of the four major states known collectively as
''Xyon'' (Xionites) or
''Huna'', being preceded by the
Kidarites and by the
Alkhon, and succeeded by the
Nezak Huns
The Nezak Huns ( Pahlavi: 𐭭𐭩𐭰𐭪𐭩 ''nycky''), also Nezak Shahs, formed a major principality in the south of the Hindu Kush region, active from circa 484 to 665 CE. Despite being traditionally identified as the last of the Hunnic stat ...
and by the
First Turkic Khaganate. All of these Hunnic peoples have often been linked to the
Huns who invaded Eastern Europe during the same period, and/or have been referred to as "Huns", but scholars have reached no consensus about any such connection.
The stronghold of the Hephthalites was
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
(present-day southern
Uzbekistan and northern
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
) on the northern slopes of the
Hindu Kush, and their capital was probably at
Kunduz
, native_name_lang = prs
, other_name =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = Kunduz River valley.jpg
, imagesize = 300
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_ ...
, having come from the east, possibly from the area of
Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Ba ...
. By 479 the Hephthalites had conquered
Sogdia and driven the
Kidarites eastwards, and by 493 they had captured parts of present-day
Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the Al ...
and the
Tarim Basin (in present-day
Northwest China
Northwest China () is a statistical region of China which includes the autonomous regions of Xinjiang and Ningxia and the provinces of Shaanxi, Gansu and Qinghai. It has an area of 3,107,900 km2.
The region is characterized by a (semi-)arid ...
). The
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
, formerly confused with the Hephthalites, expanded into
Northern India as well.
The sources for Hephthalite history are sparse and the opinions of historians differ. There is no king-list, and historians are not sure how the group arose or what language they initially spoke. They seem to have called themselves ''Ebodalo'' (ηβοδαλο, hence ''Hephthal''), often abbreviated ''Eb'' (ηβ), a name they wrote in the
Bactrian script
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought tha ...
on some of their coins. The origin of the name "Hephthalites" is unknown, it may stem either from a
Khotanese word ''*Hitala'' meaning "Strong", from hypothetical
Sogdian *''Heβtalīt'', plural of *''Heβtalak'', or from postulated
Middle Persian ''*haft āl'' "the Seven
Al".
Name and ethnonyms
The Hephthalites called themselves ''ēbodāl'' (
Bactrian cursive script:
, Greek script: ηβοδαλο "Ebodalo") in their inscriptions, which was commonly abbreviated to
(''ηβ'', "Eb") in their coinage.
, held in the private collection of Professor Dr. Aman ur Rahman and published by
Nicholas Sims-Williams
Nicholas Sims-Williams, FBA (born 11 April 1949, Chatham, Kent) is a British professor of the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), University of London, where he is the Research Professor of Iranian and Central Asian Studies at the Dep ...
in 2011, shows an early Hepthalite ruler with a round beardless face and slanted almond-shaped eyes, wearing a radiate crown with a single crescent, and framed by the
Bactrian script
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought tha ...
legend ''ηβοδαλο ββγο'' ("The Lord
'Yabghu''.html" ;"title="Yabghu.html" ;"title="'Yabghu">'Yabghu''">Yabghu.html" ;"title="'Yabghu">'Yabghu''of the Hephthalites"). The seal is dated to the end 5th century- early 6th century CE.
[. "A seal bearing the legend ηβοδαλο ββγο, "Yabghu/governor of the Hephthal," shows the local, Bactrian form of their name, ēbodāl, which is commonly abbreviated to ηβ on their coins"] The ethnic name "Ebodalo", and title "Ebodalo
Yabghu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entrabγu">"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆_[yabγuйабғұ"in_"Ethno-Cultural_Dictionary"_''Türik_Bitig''_),_also_rendered_as_Jabgu,_Djabgu_or_Yabgu,_was_a_state_office_in_the_early_Turkic_peoples.html" ;"title="abγuй ...
", have also been discovered in contemporary Bactrian documents of the
Kingdom of Rob
The Kingdom of Rob ( Bactrian: , ) was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script (a ...
describing administrative functions under the Hephthalites.
[Translations of ]Nicholas Sims-Williams
Nicholas Sims-Williams, FBA (born 11 April 1949, Chatham, Kent) is a British professor of the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), University of London, where he is the Research Professor of Iranian and Central Asian Studies at the Dep ...
, quoted in
Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman c ...
sources referred to them as ''Hephthalitae'' (), ''Abdel'' or ''Avdel''. To the Armenians, the Hephthalites were ''Hephthal'', ''Hep't'al'' & ''Tetal'' and sometimes identified with the
Kushans. To the Persians, Hephthalites are Hephtal, Hephtel, & Hēvtāls. To Arabs, Hephthalites were ''Haital'', ''Hetal'', ''Heithal'', ''Haiethal'', ''Heyâthelites'', ''(al-)Hayațila'' (هياطلة), and sometimes identified as
Turks. According to
Togan (1985), the form ''Haytal'' in Persian and Arabic sources in the first period was a clerical error for ''Habtal'', as Arabic ''
-b-'' resembles ''
-y-''.
In Chinese chronicles, the Hephthalites are called ''Ye-tha-i-li-to'' (simp. 厌带夷栗陁; trad. 厭帶夷栗陀;
pinyin: ''Yàndàiyílìtuó''), or the more usual abbreviated form ''Yada'' 嚈噠 (
pinyin: ''Yèdā''), or 滑 (
pinyin: ''Huá''). The latter name has been given various
Latinised renderings, including ''Yeda'', ''Ye-ta'', ''Ye-tha''; ''Ye-dā'' and ''Yanda''. The corresponding
Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
and
Korean names ''Yipdaat'' and ''Yeoptal'' ( ko, 엽달), which preserve aspects of the
Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the ''Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The Sw ...
pronunciation (roughly ''yep-daht'', ) better than the modern Mandarin pronunciation, are more consistent with the Greek ''Hephthalite''. Some Chinese chroniclers suggest that the root ''Hephtha-'' (as in ''Ye-ta-i-li-to'' or ''Yada'') was technically a title equivalent to "emperor", while ''Hua'' was the name of the dominant tribe.
In Ancient India, names such as Hephthalite were unknown. The Hephthalites were apparently part of, or offshoots of, people known in India as ''
Hunas
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''Hūṇā'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna ...
'' or ''Turushkas'',
although these names may have referred to broader groups or neighbouring peoples. Ancient Sanskrit text ''Pravishyasutra'' mentions a group of people named ''Havitaras'' but it is unclear whether the term denotes Hephthalites. The Indians also used the expression "White Huns" (''Sveta Huna'') for the Hephthalites.
Geographical origin and expansion
According to recent scholarship, the stronghold of the Hephthalites was always
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
on the northern slopes of the
Hindu Kush, in what is present-day southern
Uzbekistan and northern
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. Their capital was probably at
Kunduz
, native_name_lang = prs
, other_name =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline = Kunduz River valley.jpg
, imagesize = 300
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_ ...
, which was known to the 11th-century scholar
al-Biruni as ''War-Walīz'', a possible origin of one of the names given by the Chinese to Hephthalites: 滑 (
Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the ''Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The Sw ...
(
ZS) *''ɦˠuat̚'' >
standard Chinese: ''Huá'').
The Hephthalites may have come from the East, through the
Pamir Mountains, possibly from the area of
Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Ba ...
. Alternatively, they may have migrated from the
Altai region, among the waves of invading Huns.
Following their westward or southward expansion, the Hephthalites settled in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
, and displaced the
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
, who expanded into Northern India. The Hephthalites came into contact with the
Sasanian Empire, and were involved in helping militarily
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
seize the throne from his brother
Hormizd III
Hormizd III ( pal, 𐭠𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭬𐭦𐭣; New Persian: ), was the seventeenth king ( shah) of the Sasanian Empire, ruling briefly from 457 to 459. He was the son and successor of Yazdegerd II (). His reign was marked by the rebellion of his ...
.
Later, in the late 5th century, the Hephthalites expanded into vast areas of
Central Asia, and occupied the
Tarim Basin as far as
Turfan, taking control of the area from the
Ruanruans, who had been collecting heavy tribute from the oasis cities, but were now weakening under the assaults of the Chinese
Wei Dynasty
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
.
[.]
Origins and characteristics
There are several theories regarding the origins of the Hephthalites, with the
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
and
Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are ...
theories being the most prominent.
According to most specialist scholars, the Hephthalites adopted
Bactrian as their official language, just as the
Kushans had done, following their settlement in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
/
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
.
Bactrian was an
Eastern Iranian language
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian dial ...
, but was written in the
Greek alphabet, a remnant of the
Greco-Bactrian kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Indi ...
in the 3rd–2nd century BCE.
, beyond being an official language, was also the language of the local populations ruled by the Hephthalites.
[.]
The Hephthalites inscribed their coins in
Bactrian, an
Iranian language
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
written in the
Greek script, the titles they held were Bactrian, such as XOAΔHO or Šao, and of probable Chinese origin, such as
Yabghu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entrabγu">"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆_[yabγuйабғұ"in_"Ethno-Cultural_Dictionary"_''Türik_Bitig''_),_also_rendered_as_Jabgu,_Djabgu_or_Yabgu,_was_a_state_office_in_the_early_Turkic_peoples.html" ;"title="abγuй ...
, the names of Hephthalite rulers given in Ferdowsi's Shahnameh are Iranian, and gem inscriptions and other evidence shows that the official language of the Hephthalite elite was East Iranian. In 1959, Kazuo Enoki proposed that the Hephthalites were probably Indo-European (East)
Iranians who originated in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
/
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
, based on the fact that ancient sources generally located them in the area between
Sogdia and the
Hindu-Kush, and the Hephthalites had some Iranian characteristics.
Richard Nelson Frye
Richard Nelson Frye (January 10, 1920 – March 27, 2014) was an American scholar of Iranian and Central Asian studies, and Aga Khan Professor Emeritus of Iranian Studies at Harvard University. His professional areas of interest were Iranian ...
cautiously accepted Enoki's hypothesis, while at the same time stressing that the Hephthalites "were probably a mixed horde". According to the ''
Encyclopaedia Iranica'' and ''
Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published i ...
'', the Hephthalites possibly originated in what is today
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
.
A few scholars, such as
Marquart and
Grousset proposed
Proto-Mongolic origins. Yu Taishan traced the Hephthalites' origins to the
Xianbei and further to
Goguryeo.
Other scholars such as
de la Vaissière, based on a recent reappraisal of the Chinese sources, suggest that the Hephthalites were initially of Turkic origin, and later adopted the Bactrian language, first for administrative purposes, and possibly later as a native language — according to , this thesis is seemingly the "most prominent at present".
In effect, the Hephthalites may have been a confederation of various people, speaking different languages. According to
Richard Nelson Frye
Richard Nelson Frye (January 10, 1920 – March 27, 2014) was an American scholar of Iranian and Central Asian studies, and Aga Khan Professor Emeritus of Iranian Studies at Harvard University. His professional areas of interest were Iranian ...
:
Relation to European Huns
According to Martin Schottky, the Hephthalites apparently had no direct connection with the European
Huns, but may have been causally related with their movement. The tribes in question deliberately called themselves "Huns" in order to frighten their enemies. On the contrary,
de la Vaissière considers that the Hepthalites were part of the great
Hunnic migrations of the 4th century CE from the Altai region that also reached Europe, and that these Huns "were the political, and partly cultural, heirs of the
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
". This massive migration was apparently triggered by
climate change, with aridity affecting the mountain grazing grounds of the
Altay Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the ...
during the 4th century CE. According to Amanda Lomazoff and Aaron Ralby, there is a high synchronicity between the "reign of terror" of
Attila
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and E ...
in the west and the southern expansion of the Hephthalites, with extensive territorial overlap between the Huns and the Hephthalites in Central Asia.
The 6th-century
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
historian
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gener ...
of Caesarea (History of the Wars, Book I. ch. 3), related them to the Huns in Europe, but insisted on cultural and sociological differences, highlighting the sophistication of the Hephthalites:
Chinese chronicles
The Hephthalites were first known to the Chinese in 456 CE, when a Hephthalite embassy arrived at the Chinese court of the
Northern Wei. The Chinese used various names for the Hephthalites, such as ''Hua'' (滑), ''Ye-tha-i-li-to'' (simp. 厌带夷栗陁, trad. 厭帶夷粟陁) or more briefly ''Ye-da'' (嚈噠). Ancient
imperial Chinese
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapter ...
chronicles give various explanations about the origins of the Hephthalites:
* They were descendants "of the
Gaoju or the
Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
" according to the earliest chronicles such as the ''
Weishu
The ''Book of Wei'', also known by its Chinese name as the ''Wei Shu'', is a classic Chinese historical text compiled by Wei Shou from 551 to 554, and is an important text describing the history of the Northern Wei and Eastern Wei from 386 to 5 ...
'' or the ''
Beishu''.
* They were descendants "of the
Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
tribes", according to many later chronicles.
* The ancient historian
Pei Ziye
Pei Ziye (裴子野, 471-532) was a Chinese historian of the southern Liang dynasty; he lived through the Liu Song and Southern Qi dynasties. He was the grandson of another historian, Pei Yin (裴駰), a son of the famous historian Pei Songzhi. C ...
conjectured that the "Hua" (滑) may be descendants of a
Jushi general of the 2nd century CE because that general was named "Bahua" (八滑). This etymological fantasy was adopted by the ''
Liangshu
The ''Book of Liang'' (''Liáng Shū''), was compiled under Yao Silian and completed in 635. Yao heavily relied on an original manuscript by his father Yao Cha, which has not independently survived, although Yao Cha's comments are quoted in seve ...
'' chronicle (
Volume 30 and
Volume 54).
* Another etymological fantasy appeared in the ''
Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
'', reporting an account by the traveller Wei Jie according to which the Hephthalites may have been the descendants of the
Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
because a Kangju general of the
Han period
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
happened to be named "Yitian".
Kazuo Enoki made a first groundbreaking analysis of the Chinese sources in 1959, suggesting that the Hephthalites were a local tribe of the
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
(
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
) region, with their origin in the nearby Western
Himalayas. He also used as an argument the presence of numerous
Bactrian names among the Hephthalites, and the fact that the Chinese reported that they practiced
polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives" ...
, a well-known West Himalayan cultural trait.
According to a recent reappraisal of the Chinese sources by
de la Vaissière (2003), only the Turkic
Gaoju origin of the Hephthalites should be retained as indicative of their primary ethnicity, and the mention of the
Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
only stems from the fact that, at the time, the Hephthalites had already settled in the former
Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
territory of
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
, where they are known to have used the Eastern Iranian
Bactrian language
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought t ...
. The earliest Chinese source on this encounter, the near-contemporary chronicles of the Northern Wei (''
Weishu
The ''Book of Wei'', also known by its Chinese name as the ''Wei Shu'', is a classic Chinese historical text compiled by Wei Shou from 551 to 554, and is an important text describing the history of the Northern Wei and Eastern Wei from 386 to 5 ...
'') as quoted in the later ''
Tongdian
The ''Tongdian'' () is a Chinese institutional history and encyclopedia text. It covers a panoply of topics from high antiquity through the year 756, whereas a quarter of the book focuses on the Tang Dynasty. The book was written by Du You from 766 ...
'', reports that they migrated southward from the
Altai region circa 360 CE:
The
Gaoju (高車 lit. "High Cart"), also known as
Tiele, were early Turkic speakers related to the earlier
Dingling
The Dingling ( (174 BCE); (200 BCE); Eastern Han Chinese: *''teŋ-leŋ'' < : *''têŋ-rêŋ'') were ancient people ...
, who were once conquered by the
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
.
Weishu
The ''Book of Wei'', also known by its Chinese name as the ''Wei Shu'', is a classic Chinese historical text compiled by Wei Shou from 551 to 554, and is an important text describing the history of the Northern Wei and Eastern Wei from 386 to 5 ...
also mentioned the linguistic and ethnic proximity between the Gaoju and the Xiongnu. de la Vaissière proposes that the Hephthalites had originally been one Oghuric-speaking tribe who belonged the Gaoju/Tiele confederation. This and several later Chinese chronicles also report that the Hephthalites may have originated from the
Da Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat at ...
, probably because of their settlement in the former Da Yuezhi territory of
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
. Later Chinese sources become quite confused about the origins of the Hephthalites, and this may be due to their progressive assimilation of Bactrian culture and language once they settled there.
According to the ''
Beishi'', describing the situation in the first half of the 6th century CE around the time
Song Yun
Song Yun () was a Chinese Buddhist monk who was sent by the pious Buddhist Empress Hu (, ?-528 CE) of the Northern Wei Dynasty with other monastic companions including Hui Zheng, Fa Li and Zheng (or Wang) Fouze, to northwestern India to search ...
visited Central Asia, the language of the Hephthalites was different from that of the Ruanruan, Gaoju or other tribes of Central Asia, but that probably reflects their acculturation and adoption of the Bactrian language since their arrival in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
in the 4th century CE. The ''
Liangshu
The ''Book of Liang'' (''Liáng Shū''), was compiled under Yao Silian and completed in 635. Yao heavily relied on an original manuscript by his father Yao Cha, which has not independently survived, although Yao Cha's comments are quoted in seve ...
'' and ''
Liang Zhigongtu'' do explain that the Hephthalites originally had no written language and adopted the ''
hu'' (local, "Barbarian") alphabet, in this case, the
Bactrian script
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought tha ...
.
Overall, de la Vaissière considers that the Hephthalites were part of the great
Hunnic migrations of the 4th century CE from the Altai region that also reached Europe and that these Huns "were the political, and partly cultural, heirs, of the
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
".
Appearance
The Hepthalites appear in several mural paintings in the area of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
, especially in banquet scenes at
Balalyk tepe and as donors to the Buddha in the ceiling painting of the 35-meter Buddha at the
Buddhas of Bamyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural c ...
.
Several of the figures in these paintings have a characteristic appearance, with belted jackets with a unique lapel of their tunic being folded on the right side, a style which became popular under the Hephthalites, the cropped hair, the hair accessories, their distinctive physionomy and their round beardless faces.
The figures at Bamyan must represent the donors and potentates who supported the building of the monumental giant Buddha.
These remarkable paintings participate "to the artistic tradition of the Hephthalite ruling classes of
Tukharistan
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
".
The paintings related to the Hephthalites have often been grouped under the appellation of "Tokharistan school of art", or the "Hephthalite stage in the History of Central Asia Art". The paintings of
Tavka Kurgan
Tavka Kurgan is an ancient fortress and archaeological site near Shirabad, Uzbekistan. It is especially famous for some frescoes dated to the 5th-6th century CE, several of them located in the Archaeological Museum of Termez. One of these painti ...
, of very high quality, also belong to this school of art, and are closely related to other paintings of the Tokharistan school such as
Balalyk tepe, in the depiction of clothes, and especially in the treatment of the faces.
This "Hephthalite period" in art, with the caftans with a triangular collar folded on the right, the particular cropped hairstyle, the crowns with crescents, have been found in many of the areas historically occupied and ruled by the Hephthalites, in
Sogdia,
Bamyan
Bamyan or Bamyan Valley (); ( prs, بامیان) also spelled Bamiyan or Bamian is the capital of Bamyan Province in central Afghanistan. Its population of approximately 70,000 people makes it the largest city in Hazarajat. Bamyan is at an alt ...
(modern
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
), or in
Kucha in the
Tarim Basin (modern
Xinjiang,
China). This points to a "political and cultural unification of
Central Asia" with similar artistic styles and iconography, under the rule of the Hephthalites.
History

The Hephthalites were a vassal state to the
Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
until the beginning of the 5th century. There were close contacts between them, although they had different languages and cultures, and the Hephthalites borrowed much of their political organization from Rourans. In particular, the title "
Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
", which according to McGovern was original to the Rourans, was borrowed by the Hephthalite rulers. The reason for the migration of the Hephthalites southeast was to avoid a pressure of the Rourans.
The Hephthalites became a significant political entity in Bactria around 450 CE, or sometime before.
It has been commonly assumed that the Hephthalites formed a third wave of migrations into Central Asia, after the
Chionites
Xionites, Chionites, or Chionitae (Middle Persian: ''Xiyōn'' or ''Hiyōn''; Avestan: ''Xiiaona''; Sogdian ''xwn''; Pahlavi ''Xyon'') were a nomadic people in the Central Asian regions of Transoxiana and Bactria.
The Xionites appear to be syno ...
(who arrived circa 350 CE) and the
Kidarites (who arrived from around 380 CE), but recent studies suggest that instead there may have been a single massive wave of nomadic migrations around 350–360 CE, the "Great Invasion", triggered by climate change and the onset of aridity in the grazing grounds of the Altay region, and that these nomadic tribes vied for supremacy thereafter in their new territories in Southern Central Asia. As they rose to prominence, the Hephthalites displaced the
Kidarites and then the
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
, who expanded into
Gandhara and Northern India.
The Hephthalites also entered into conflict with the Sasanians. The reliefs of the
Bandian complex seem to show the initial defeat of the Hephthalites against the Sasanians in 425 CE, and then their alliance with them, from the time of
Bahram V
Bahram V (also spelled Wahram V or Warahran V; pal, 𐭥𐭫𐭧𐭫𐭠𐭭), also known as Bahram Gor (New Persian: , "Bahram the onager") was the Sasanian King of Kings (''shahanshah'') from 420 to 438.
The son of the incumbent Sasanian shah ...
(420-438 CE), until they invaded Sasanian territory and destroyed the Bandian complex in 484 CE.
In 456–457 a Hephthalite embassy arrived in China, during the reign of
Emperor Wen of the
Northern Wei. By 458 they were strong enough to intervene in
Persia.
Around 466 they probably took Transoxianan lands from the
Kidarites with Persian help but soon took from Persia the area of
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
and eastern
Kushanshahr
Kushanshahr was a province of the Sasanian Empire comprising the region between Kabul Valley and Peshawar Valley.The Cambridge History of Iran: Seleucid Parthian, E. Yarshaterp.770 sq/ref> The Kushanshar territory centered on Tukharistan, and c ...
.
In the second half of the fifth century they controlled the deserts of
Turkmenistan as far as the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asi ...
and possibly
Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
. By 500 they held the whole of
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
and the
Pamirs and parts of
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. In 509, they captured
Sogdia and they took 'Sughd' (the capital of
Sogdiana
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Emp ...
).
To the east, they captured the
Tarim Basin and went as far as
Urumqi.
Around 560 CE their empire was destroyed by an alliance of the
First Turkic Khaganate and the
Sasanian Empire, but some of them remained as local rulers in the region of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
for the next 150 years, under the suzerainty of the
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
, followed by the
Tokhara Yabghus.
Among the principalities which remained in Hephthalite hands even after the Turkic overcame their territory were:
Chaganian
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
, and
Khuttal in the
Vakhsh Valley.
Ascendancy over the Sasanian Empire (442- c.530 CE)

The Hephthalites were originally vassals of the
Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
but split from their overlords in the early fifth century. The next time they were mentioned was in Persian sources as foes of
Yazdegerd II
Yazdegerd II (also spelled Yazdgerd and Yazdgird; pal, 𐭩𐭦𐭣𐭪𐭥𐭲𐭩), was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 438 to 457. He was the successor and son of Bahram V ().
His reign was marked by wars against the Eastern Roma ...
(435–457), who from 442, fought 'tribes of the Hephthalites', according to the Armenian
Elisee Vardaped
Yeghishe (, , AD 410 – 475; also spelled Eghishe or Ełišē, latinized Eliseus) was an Armenian historian from the time of late antiquity, best known as the author of ''History of Vardan and the Armenian War'', a history of a fifth-cent ...
.
In 453, Yazdegerd moved his court east to deal with the Hephthalites or related groups.
In 458, a Hephthalite king called
Akhshunwar ''Akhshunwar'' ( Sogdian: əxšōnδār, Middle Persian: ''Xašnawāz'') was a ruling title used by the Hephthalite kings in the 5th and 6th-centuries.
The title is of Eastern Iranian origin; according W.B. Henning, its original form was ʾxšʾwn ...
helped the
Sasanian Emperor Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
(458–484) gain the Persian throne from his brother.
Before his accession to the throne, Peroz had been the Sasanian for
Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan ( ...
in the far east of the Empire, and therefore had been one of the first to enter into contact with the Hephthalites and request their help.
The Hephthalites may have also helped the Sasanians to eliminate another Hunnic tribe, the
Kidarites: by 467, Peroz I, with Hephthalite aid, reportedly managed to capture Balaam and put an end to Kidarite rule in
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
once and for all. The weakened Kidarites had to take refuge in the area of
Gandhara.
Victories over the Sasanian Empire (474–484 CE)
Later, however, from 474 CE, Peroz I fought three wars with his former allies the Hephthalites. In the first two, he himself was captured and ransomed.
Following his second defeat, he has to offer thirty mules loaded with silver drachms to the Hephthalites, and also had to leave his son
Kavad as a hostage. The coinage of
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
in effect flooded Tokharistan, taking precedence over all other Sasanian issues.
In the third battle, at the
Battle of Herat (484)
The 2001 uprising in Herat was a coordinated insurrection and uprising in the Afghan city of Herat as part of the United States war in Afghanistan. The city was captured on November 12 by Northern Alliance forces as well as Special Forces of th ...
, he was vanquished by the Hepthalite king Kun-khi, and for the next two years the Hephthalites plundered and controlled the eastern part of the Sasanian Empire.
[. "The third incursion cost him his own life and his camp was captured together with his daughter who was taken as a wife by the Hephtalite king Kun-khi"] Perozduxt, the daughter of Peroz, was captured and became a lady as the Hephtalite court, as Queen of king Kun-khi.
She became pregnant and had a daughter who would later marry her uncle
Kavad I. From 474 until the middle of the 6th century, the Sasanian Empire paid tribute to the Hephthalites.
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
came under formal Hephthalite rule from that time.
Taxes were levied by the Hephthalites over the local population: a contract in the
Bactrian language
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought t ...
from the archive of the
Kingdom of Rob
The Kingdom of Rob ( Bactrian: , ) was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script (a ...
, has been found, which mentions taxes from the Hephthalites, requiring the sale of land in order to pay these taxes. It is dated to 483/484 CE.
Hephthalite coinage
With the
Sasanian Empire paying a heavy tribute, from 474, the Hephthalites themselves adopted the winged, triple-crescent crowned
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
as the design for their coinage.
Benefiting from the influx of
Sasanian silver coins, the Hephthalites did not develop their own coinage: they either minted coins with the same designs as the Sasanians, or simply countermarked Sasanian coins with their own symbols.
They did not inscribe the name of their ruler, contrary to the habit of the
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
or the
Kidarites before them.
Exceptionally, one coin type deviates from the Sasanian design, by showing the bust of a Hepthalite prince holding a drinking cup.
Overall, the Sasanians paid "an enormous tribute" to the Hephthalites, until the 530s and the rise of
Khosrow I.
Protectors of Kavad
Following their victory over Peroz I, the Hepthalites became protectors and benefactors of his son
Kavad I, as
Balash
Balash (Middle Persian: 𐭥𐭥𐭣𐭠𐭧𐭱𐭩, ) was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 484 to 488. He was the brother and successor of Peroz I (), who had been defeated and killed by a Hephthalite army.
Name
''Balāsh'' () is the N ...
, a brother of Peroz took the Sasanian throne. In 488, a Hepthalite army vanquished the Sasaniana army of Balash, and was able to put
Kavad I (488–496, 498–531) on the throne.
In 496–498, Kavad I was overthrown by the nobles and clergy, escaped, and restored himself with a Hephthalite army.
Joshua the Stylite Joshua the Stylite (also spelled Yeshu Stylite and Ieshu Stylite) is the attributed author of a chronicle which narrates the history of the war between the Byzantine Empire and Persians between 502 and 506, and which is generally considered to be o ...
reports numerous instances in which Kavadh led Hepthalite ("Hun") troops, in the capture of the city of
Theodosiupolis of Armenia in 501–502, in battles against the Romans in 502–503, and again during the
siege of Edessa in September 503.
Hephthalites in Tokharistan (466 CE)
Around 461–462 CE, an
Alchon Hun
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
ruler named
Mehama
Mehama ( Bactrian: ''Meyam'', Brahmi: ''Me-ha-ma''), ruled c.461-493, was a king of Alchon Huns dynasty. He is little known, but the Talagan copper scroll mentions him as an active ruler making a donation to a Buddhist stupa in 492/93.For an im ...
is known to have been based in Eastern Tokharistan, possibly indicating a partition of the region between the Hephthalites in western Tokharistan, centered on
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
, and the
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
in eastern Tokharistan, who would then go on to expand into northern India.
Mehama
Mehama ( Bactrian: ''Meyam'', Brahmi: ''Me-ha-ma''), ruled c.461-493, was a king of Alchon Huns dynasty. He is little known, but the Talagan copper scroll mentions him as an active ruler making a donation to a Buddhist stupa in 492/93.For an im ...
appears in
a letter in the Bactrian language he wrote in 461–462 CE, where he describes himself as "Meyam, King of the people of Kadag, the governor of the famous and prosperous King of Kings Peroz". Kadag is Kadagstan, an area in southern Bactria, in the region of
Baghlan
Baghlan (Dari: بغلان ''Baġlān'') is a city in northern Afghanistan, in the eponymous province, Baghlan Province. It is located three miles east of the Kunduz River, 35 miles south of Khanabad, and about 500 metres above sea level in the ...
. Significantly, he presents himself as a vassal of the
Sasanian Empire king
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
, but Mehama was probably later able to wrestle autonomy or even independence as Sasanian power waned and he moved into India, with dire consequences for the
Gupta Empire.
The Hepthalites probably expanded into
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
following the destruction of the
Kidarites in 466. The presence of the Hepthalites in Tokharistan (
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
) is securely dated to 484 CE, date of
a tax receipt from the
Kingdom of Rob
The Kingdom of Rob ( Bactrian: , ) was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script (a ...
mentioning the need to sell some land in order to pay Hephthalite taxes. Two documents were also found, with dates from the period from 492 to 527 CE, mentioning taxes paid to Hephthalite rulers. Another, undated documents, mentions scribal and judiciary functions under the Hephthalites:
Hephthalite conquest of Sogdiana (479 CE)

The Hephthalites conquered the territory of
Sogdiana
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Emp ...
, beyond the
Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
, which was incorporated into their Empire.
They may have conquered Sogdiana as early as 479 CE, as this is the date of the last known embassy of the Sogdians to China.
The
account of the Liang Zhigongtu also seems to record that from around 479 CE, the Hephthalites occupied the region of Samarkand. Alternatively, the Hephthalites may have occupied Sogdia later in 509 CE, as this is the date of the last known embassy from
Samarkand to the Chinese Empire, but this might not be conclusive as several cities, such as
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
or
Kobadiyan
Qubodiyon, also Qubadiyan, ancient Kobadiyan (russian: Кабодиён; tg, Қубодиён, fa, قبادیان ''Qobādiyān'') is a town in the Khatlon Region of Tajikistan. It is the capital of Qubodiyon District. The population of the tow ...
, are known to have sent embassies to China as late as 522 CE, while under Hephthalite control. As early as 484, the famous Hephthalite ruler
Akhshunwar ''Akhshunwar'' ( Sogdian: əxšōnδār, Middle Persian: ''Xašnawāz'') was a ruling title used by the Hephthalite kings in the 5th and 6th-centuries.
The title is of Eastern Iranian origin; according W.B. Henning, its original form was ʾxšʾwn ...
, who defeated
Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after a ...
, held a title that may be understood as Sogdian: "’xs’wnd’r" ("power-holder").
The Hephthalites may have built major fortified
Hippodamian
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; 498 – 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to ...
cities (rectangular walls with an orthogonal network of streets) in Sogdiana, such as
Bukhara and
Panjikent, as they had also in
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
, continuing the city-building efforts of the
Kidarites. The Hephthalites probably ruled over a confederation of local rulers or governors, linked through alliance agreements. One of these vassals may have been Asbar, ruler of
Vardanzi, who also minted his own coinage during the period.
The wealth of the Sasanian ransoms and tributes may have been reinvested in Sogdia, possibly explaining the prosperity of the region from that time. Sogdia, at the center of a new
Silk Road between China to the Sasanian Empire and the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
became extremely prosperous under its nomadic elites. The Hephthalites took on the role of major intermediary on the
Silk Road, after their great predecessor the
Kushans, and contracted local
Sogdians to carry on the trade of silk and other luxury goods between the China Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
Because of the Hephthalite occupation of Sogdia, the original coinage of Sogdia came to be flooded by the influx of Sasanian coins received as a tribute to the Hephthalites. This coinage then spread along the
Silk Road.
The symbol of the Hephthalites appears on the residual coinage of
Samarkand, probably as a consequence of the Hephthalite control of Sogdia, and becomes prominent in Sogdian coinage from 500 to 700 CE, including in the coinage of their indigenous successors the
Ikhshids (642-755 CE), ending with the
Muslim conquest of Transoxiana.
Tarim Basin (circa 480–550 CE)
In the late 5th century CE they expanded eastward through the
Pamir Mountains, which are comparatively easy to cross, as did the
Kushans before them, due to the presence of convenient plateaus between high peaks. They occupied the western
Tarim Basin (
Kashgar and
Khotan), taking control of the area from the
Ruanruans, who had been collecting heavy tribute from the oasis cities, but were now weakening under the assaults of the Chinese
Northern Wei dynasty
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during the ...
.
In 479 they took the east end of the Tarim Basin, around the region of
Turfan.
In 497–509, they pushed north of Turfan to the
Urumchi region.
In the early years of the 6th century, they were sending embassies from their dominions in the Tarim Basin to the Northern Wei dynasty.
They were probably in contact with
Li Xian, the Chinese Governor of
Dunhuang, who is known for having furnished his tomb with a Western-style
ewer probably made in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
.
The Hephthalites continued to occupy the Tarim Basin until the end of their Empire, circa 560 CE.
As the territories ruled by the Hephthalites expanded into Central Asia and the Tarim Basin, the art of the Hephthalites, characterized by the clothing and hairstyles of the figures being represented, also came to be used in the areas they ruled, such as
Sogdiana
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Emp ...
,
Bamyan
Bamyan or Bamyan Valley (); ( prs, بامیان) also spelled Bamiyan or Bamian is the capital of Bamyan Province in central Afghanistan. Its population of approximately 70,000 people makes it the largest city in Hazarajat. Bamyan is at an alt ...
or
Kucha in the
Tarim Basin (
Kizil Caves
The Kizil Caves ( zh, t=克孜爾千佛洞, s=克孜尔千佛洞, l=Kizil Caves of the Thousand Buddhas; ug, قىزىل مىڭ ئۆي, translation=The Thousand Red Houses; also romanized Qizil Caves, spelling variant Qyzyl; Kizil means 'red') ar ...
,
Kumtura Caves,
Subashi reliquary). In these areas appear dignitaries with caftans with a triangular collar on the right side, crowns with three crescents, some crowns with wings, and a unique hairstyle. Another marker is the two-point suspension system for swords, which seems to have been an Hephthalite innovation, and was introduced by them in the territories they controlled. The paintings from the
Kucha region, particularly the swordsmen in the
Kizil Caves
The Kizil Caves ( zh, t=克孜爾千佛洞, s=克孜尔千佛洞, l=Kizil Caves of the Thousand Buddhas; ug, قىزىل مىڭ ئۆي, translation=The Thousand Red Houses; also romanized Qizil Caves, spelling variant Qyzyl; Kizil means 'red') ar ...
, appear to have been made during Hephthalite rule in the region, circa 480–550 CE. The influence of the
art of Gandhara
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art of the north Indian subcontinent is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara.
The s ...
in some of the earliest paintings at the
Kizil Caves
The Kizil Caves ( zh, t=克孜爾千佛洞, s=克孜尔千佛洞, l=Kizil Caves of the Thousand Buddhas; ug, قىزىل مىڭ ئۆي, translation=The Thousand Red Houses; also romanized Qizil Caves, spelling variant Qyzyl; Kizil means 'red') ar ...
, dated to circa 500 CE, is considered as a consequence of the political unification of the area between Bactria and
Kucha under the Hephthalites. Some words of the
Tocharian languages may have been adopted from the Hephthalites in the 6th century CE.
The early Turks of the
First Turkic Khaganate then took control of the
Turfan and
Kucha areas from around 560 CE, and, in alliance with the
Sasanian Empire, became instrumental in the fall of the Hepthalite Empire.
Hephthalite embassies to Liang China (516–526 CE)

An illustrated account of a Hepthalite (滑,
Hua) embassy to the Chinese court of the
Southern Liang in the capital
Jingzhou in 516–526 CE is given in ''
Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. These ...
'', originally painted by
Pei Ziye
Pei Ziye (裴子野, 471-532) was a Chinese historian of the southern Liang dynasty; he lived through the Liu Song and Southern Qi dynasties. He was the grandson of another historian, Pei Yin (裴駰), a son of the famous historian Pei Songzhi. C ...
or the future
Emperor Yuan of Liang while he was a Governor of the
Province of Jingzhou as a young man between 526 and 539 CE, and of which an 11th-century Song copy is preserved. The text explains how small the country of the Hua was when they were still vassals of the
Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organizat ...
, and how they later moved to "Moxian", possibly referring to their occupation of
Sogdia, and then conquered numerous neighbouring country, including the Sasanian Empire:
[. "Growing more and more powerful in the course of time, the Hua succeeded in conquering the neighbouring countries such as Bosi ( Sasanid Persia), Panpan (]Tashkurgan
Tashkurgan ( ug, تاشقورغان بازىرى; zh, s=塔什库尔干镇, p=Tǎshíkù'ěrgān Zhèn; ) is a town in the far northwest of China, close to the country's border with Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. It is the principal to ...
?), Jibin ( Kashmir), Wuchang (Uddiyana
(also: ''Uḍḍiyāna'', ''Uḍḍāyāna'' or ''Udyāna'', Sanskrit: ओड्डियान, उड्डियान, उड्डायान, उद्यान; , , mn, Үржин ''urkhin''), was a small region in early medieval India, ...
or Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
), Qiuci ( Kucha), Shule ( Kashgar), Yutian ( Khotan) and Goupan ( Karghalik), and expanded their territory by a thousand ''li''"
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang'' mentions that no envoys from the Hephthalites came before 516 to the southern court, and it was only in that year that a Hephthalite King named Yilituo Yandai (姓厭帶名夷栗陁) sent an ambassador named Puduoda[] (蒲多达[], possibly a Buddhist name "Buddhadatta" or "Buddhadāsa").
In 520, another ambassador named Fuheliaoliao (富何了了) visited the Liang court, bringing a yellow lion, a white marten fur coat and Persian brocade as present.
Another ambassador named Kang Fuzhen (康符真), followed with presents as well (in 526 CE according to the ''
Liangshu
The ''Book of Liang'' (''Liáng Shū''), was compiled under Yao Silian and completed in 635. Yao heavily relied on an original manuscript by his father Yao Cha, which has not independently survived, although Yao Cha's comments are quoted in seve ...
'').
Their language had to be translated by the
Tuyuhun.
In ''Portraits of Periodical Offering of
Liang'', the Hepthalithes are treated as the most important foreign state, as they occupy the leading position, at the front of the column of foreign ambassadors, and have by far the largest descriptive text.
The Hepthalites were, according to the ''Liangshu'' (Chap.54), accompanied in their embassy by three states:
Humidan (胡蜜丹),
Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
(周古柯, Khargalik) and
Kabadiyan (呵跋檀).
The envoys from right to left were: the Hephthalites (滑/嚈哒),
Persia (波斯),
Korea (百濟),
Kucha (龜茲),
Japan (倭),
Malaysia (狼牙脩),
Qiang (鄧至),
Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
(周古柯, ''Zhouguke'', "near ''Hua''"),
(呵跋檀 ''Hebatan'', "near ''Hua''"),
(胡蜜丹, ''Humidan'', "near ''Hua''"),
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
(白題, ''Baiti'', "descendants of the
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209& ...
and east of the ''Hua''"),
and finally
Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
(末).
Most of the ambassadors from Central Asia are shown wearing heavy beards and relatively long hair, but, in stark contrast, the Hephthalite ambassador, as well as the ambassador from
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
, are clean-shaven and bare-headed, and their hair is cropped short. These physical characteristics are also visible in many of the Central Asian seals of the period.
Other embassies
Overall, Chinese chronicles recorded twenty-four Hephthalite embassies: the first embassy in 456, and the others from 507 to 558 CE (including fifteen to the
Northern Wei until the end of this dynasty in 535, and five to the
Southern Liang in 516–541). The last three are mentioned in the ''
Zhoushu'', which records that the Hepththalites had conquered
Anxi,
Yutian (
Hotan region in
Xinjiang) and more than twenty other countries, and that they sent embassies to the Chinese court of the
Western Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Western Wei (), was an imperial dynasty of China that followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei. One of the Northern dynasties during the era of the Northern and Southern dynasties, it ruled the wester ...
and
Northern Zhou
Zhou (), known in historiography as the Northern Zhou (), was a Xianbei-led dynasty of China that lasted from 557 to 581. One of the Northern dynasties of China's Northern and Southern dynasties period, it succeeded the Western Wei dynasty an ...
in 546, 553 and 558 CE respectively, after what the Hepthalites were "crushed by the Turks" and embassies stopped.
Buddhas of Bamyan (544–644 CE)
The complex of the
Buddhas of Bamyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural c ...
was developed under Hephthalite rule.
Carbon dating of the structural components of the Buddhas has determined that the smaller "Eastern Buddha" was built around 570 CE (544–595 CE with 95% probability), while the larger "Western Buddha" was built around 618 CE (591–644 CE with 95% probability).
This corresponds to the period soon before or after the major defeat of the Hephthalites against the combined forces of
Western Turk
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
and
Sasanian Empire (557 CE), or the following period during which they regrouped south of the Oxus as Principalities, but essentially before the Western Turks finally overran the region to form the
Tokhara Yabghus (625 CE).
Among the most famous paintings of the Buddhas of Bamyan, the ceiling of the smaller Eastern Buddha represents a solar deity on a chariot pulled by horses, as well as ceremonial scenes with royal figures and devotees.
The god is wearing a caftan in the style of
Tokhara
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan c ...
, boots, and is holding a lance, he is "The Sun God and a Golden Chariot Rising in Heaven".
His representation is derived from the iconography of the Iranian god
Mithra, as revered in
Sogdia.
He is riding a two-wheeled golden charriot, pulled by four horses.
Two winged attendants are standing to the side of the charriot, wearing a
Corinthian helmet
The Corinthian helmet originated in ancient Greece and took its name from the city-state of Corinth. It was a helmet made of bronze which in its later styles covered the entire head and neck, with slits for the eyes and mouth. A large curved pr ...
with a feather, and holding a shield.
In the top portion are wind gods, flying with a scarf held in both hands.
This great composition is unique, and has no equivalent in
Gandhara or
India, but there are some similarities with the painting of
Kizil or
Dunhuang.
The central image of the Sun God on his golden chariot is framed by two lateral rows in individuals: Kings and dignitaries mingling with Buddhas and
Bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood.
In the Early Buddhist schools ...
s.
, standing behind a monk in profile, much be the King of Bamyan.
He wears a crenalated crown with single crescent and
korymbos, a round-neck tunic and a Sasanian headband.
Several of the figures, either
royal couples,
crowned individuals or
richly dressed women, have the characteristic appearance of the Hephthalites of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
, with belted jackets with a unique lapel of their tunic being folded on the right side, the cropped hair, the hair accessories, their distinctive physionomy and their round beardless faces.
These figures must represent the donors and potentates who supported the building of the monumental giant Buddha.
They are gathered around the
Seven Buddhas of the past and
Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit: ) or Metteyya (Pali: ), also Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha, is regarded as the future Buddha of this world in Buddhist eschatology. As the 5th and final Buddha of the current kalpa, Maitreya's teachings will be aimed at ...
. The individuals in this painting are very similar to the individuals depicted in
Balalyk Tepe, and they may be related to the
Hepthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
.
They participate "to the artistic tradition of the Hephthalite ruling classes of
Tukharestan".
These murals disappeared with the destruction of the statues by the
Taliban in 2001.
Hephthalite royals on the tombs of Sogdian traders
The
Tomb of Wirkak
The Tomb of Wirkak ( Sogdian: ''wyrkʾk''), in Chinese commonly referred to as Tomb of Master Shi ( zh, t=史君墓, w=Shih3-Chün1 Mu4, p=Shǐ Jūn Mù), is the grave of the Sogdian '' Sabao'' (Chinese: 薩保, "Protector, Guardian", derived fro ...
is the tomb of a 6th century Sogdian trader established in China, and discovered in
Xi'an.
It seems that depictions of Hephthalite rulers are omnipresent in the pictorial decorations of the tomb, as royal figures with elaborate Sasanian-type crowns appearing in their palaces, nomadic yurts or while hunting.
Hephthalites rulers are shown short-haired, wearing tunics, and are often depicted together with their female consort.
The Sogdian trader Wirkak may therefore have primarily dealt with the Hephthalites during his young years (he was around 60 when the Hephthalites were finally destroyed by the alliance of the
Sasanians and the Turks between 556 and 560 CE).
The Hephthalites also appear in four panels of the
Miho funerary couch (c.570 CE) with somewhat caricatural features, and characteristics of vassals to the Turks. On the contrary, the depictions in the tombs of later Sogdian traders, such as the
Tomb of An Jia
The Tomb of Ān Jiā, also sometimes read Ān Qié (Chinese: 安伽墓石門 圍屏石榻, "Stone tomb gate and couch of Anjia"), is a Northern Zhou period (557-581 CE) funeral monument to a Sogdian nobleman named "Anjia" in the Chinese epitaph. T ...
(who was 24 years younger than Wirwak), already show the omnipresence of the Turks of the
First Turkic Khaganate, who were probably his main trading partners during his active life.
End of the Empire and fragmentation into Hephthalite Principalities (560–710 CE)

After
Kavad I, the Hephthalites seem to have shifted their attention away from the
Sasanian Empire, and Kavad's successor
Khosrow I (531–579) was able to resume an expansionist policy to the east. According to
al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari i ...
, Khosrow I managed, through his expansionsit policy, to take control of "
Sind
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
, Bust, Al-Rukkhaj,
Zabulistan,
Tukharistan
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
, Dardistan, and
Kabulistan
Kabulistan (Pashto: کابلستان) is a historical regional name referring to the territory that is centered on present-day Kabul Province of Afghanistan.
In many Greek and Latin sources, particularly editions of Ptolemy's ''Geography'', the ...
" as he ultimately defeated the Hephthalites with the help of the
First Turkic Khaganate.
In 552, the
Göktürks took over Mongolia, formed the
First Turkic Khaganate, and by 558 reached the
Volga. Circa 555–567, the Turks of the
First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanians under
Khosrow I allied against the Hephthalites and defeated them after an eight-day battle near
Qarshi
Qarshi ( uz, Qarshi/Қарши, ; fa, نخشب ''Nakhshab'') is a city in southern Uzbekistan. It is the capital of Qashqadaryo Region. Administratively, Qarshi is a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlement Qashqadaryo. It ...
, the
Battle of Bukhara
The Battle of Gol-Zarriun, also Battle of Bukhara, took place in c. 560 when the Sasanian Empire allied with the First Turkic Khaganate against the Hephthalite Empire.
Context
In 484, Peroz I, the grandfather of Khosrow I Anushirvan (), was kill ...
, perhaps in 557.
These events put an end to the Hephthalite Empire, which fragmented into semi-independent Principalities, paying tribute to either the Sasanians or the Turks, depending on the military situation.
After the defeat, the Hephthalites withdrew to Bactria and replaced king Gatfar with
Faghanish
Faghanish was a Hephthalite prince, who was the ruler of Chaghaniyan in the mid-6th century. Originally a subordinate of the Hephthalite king, he became a vassal of the Sasanian Empire in c. 560 after the Hephthalite Empire was broken into several ...
, the ruler of
Chaghaniyan
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
. Thereafter, the area around the Oxus in
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwe ...
contained numerous Hephthalites principalities, remnants of the great
Hephthalite Empire destroyed by the alliance of the Turks and the Sasanians.
They are reported in the
Zarafshan valley,
Chaghaniyan
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
,
Khuttal,
Termez
Termez ( uz, Termiz/Термиз; fa, ترمذ ''Termez, Tirmiz''; ar, ترمذ ''Tirmidh''; russian: Термез; Ancient Greek: ''Tàrmita'', ''Thàrmis'', ) is the capital of Surxondaryo Region in southern Uzbekistan. Administratively, it i ...
,
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
,
Badghis
Bādghīs (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest poverty r ...
,
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
and
Kabul, in the geographical areas corresponding to
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
and today's northern
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
.
The Sasanians and Turks established a frontier for their zones of influence along the
Oxus river, and the Hephthalite Principalities functioned as buffer states between two Empires.
But when the Hephthalites chose
Faghanish
Faghanish was a Hephthalite prince, who was the ruler of Chaghaniyan in the mid-6th century. Originally a subordinate of the Hephthalite king, he became a vassal of the Sasanian Empire in c. 560 after the Hephthalite Empire was broken into several ...
as their king in Chaganiyan,
Khosrow I crossed the Oxus and put the Principalities of
Chaghaniyan
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
and
Khuttal under tribute.
When Khosrow I died in 579, the Hephthalites of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
and
Khotan took advantage of the situation to rebel against the Sasanians, but their efforts were obliterated by the Turks.
By 581 or before, the western part of the
First Turkic Khaganate separated and became the
Western Turkic Khaganate. In 588, triggering the
First Perso-Turkic War
The First Perso-Turkic War was fought during 588–589 between the Sasanian Empire and Hephthalite principalities and its lord the Göktürks. The conflict started with the invasion of the Sasanian Empire by the Turks and ended with a decisive S ...
, the
Turkic Khagan Bagha Qaghan (known as Sabeh/Saba in
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
sources), together with his Hephthalite subjects, invaded the Sasanian territories south of the Oxus, where they attacked and routed the Sasanian soldiers stationed in
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
, and then proceeded to conquer the city along with
Talaqan,
Badghis
Bādghīs (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest poverty r ...
, and
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
. They were finally repelled by the Sasanian general
Vahram Chobin.
Raids into the Sasanid Empire (600–610 CE)
Circa 600, the Hephthalites were raiding the
Sasanian Empire as far as
Ispahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Region, Isfahan Province, Iran. It is lo ...
(Spahan) in central Iran. The Hephthalites issued numerous coins imitating the coinage of Khosrow II, adding on the obverse a
Hephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during ...
signature in
Sogdian and a
Tamgha symbol

.
Circa 606/607 CE the
Second Perso-Turkic War
The Second Perso-Turkic War began in 606/607 with an invasion of the Sasanian Empire by the Göktürks and Hephthalites. The war ended in 608 with the defeat of the Turks and Hephthalites by the Sasanians under the Armenian general Smbat IV ...
started, when the
Göktürks and Hephthalites again invaded the
Sasanian Empire. Khosrow recalled
Smbat IV Bagratuni
Smbat IV Bagratuni ( hy, Սմբատ Դ Բագրատունի; el, Συμβάτιος) was an Armenian prince from the Bagratuni Dynasty who served first in the Byzantine army before switching, ca. 595, to the Sasanian Empire, where he had a distin ...
from
Persian Armenia and sent him to Iran to repel the invaders. Smbat, with the aid of a Persian prince named Datoyean, repelled the Hephthalites from Persia, and plundered their domains in
eastern Khorasan, where Smbat is said to have killed their king in single combat. Khosrow then gave Smbat the honorific title ''Khosrow Shun'' ("the Joy or Satisfaction of Khosrow"), while his son
Varaztirots II Bagratuni
Varaztirots II Bagratuni ( hy, Վարազ-Տիրոց Բ Բագրատունի; c. 590 – 645) was an Armenian ''nakharar'' from the Bagratuni family, the son of Smbat IV Bagratuni. He was ''marzpan'' of Armenia c. 628, fled to the Byzantine Empi ...
received the honorific name ''Javitean Khosrow'' ("Eternal Khosrow").
Western Turk takeover (625 CE)

From 625 CE, the territory of the Hephthalites from
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
to
Kabulistan
Kabulistan (Pashto: کابلستان) is a historical regional name referring to the territory that is centered on present-day Kabul Province of Afghanistan.
In many Greek and Latin sources, particularly editions of Ptolemy's ''Geography'', the ...
was taken over by the
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
, forming an entity ruled by Western Turk nobles, the
Tokhara Yabghus.
The Tokhara Yabghus or "Yabghus of Tokharistan" (), were a dynasty of
Western Turk
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
sub-kings, with the title "
Yabghu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entrabγu">"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆_[yabγuйабғұ"in_"Ethno-Cultural_Dictionary"_''Türik_Bitig''_),_also_rendered_as_Jabgu,_Djabgu_or_Yabgu,_was_a_state_office_in_the_early_Turkic_peoples.html" ;"title="abγuй ...
s", who ruled from 625 CE south of the
Oxus river, in the area of
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
and beyond, with some smaller polities surviving in the area of
Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic Ba ...
until 758 CE. Their legacy was extended to the southeast until the 9th century CE, with the Turk Shahis and the Zunbils.
Arab invasion (c.651 CE)
Circa 650 CE, during the Arab conquest of the Sasanian Empire, the Sasanian Empire ruler Yazdegerd III was trying to regroup and gather forces around Tokharistan and was hoping to obtain the help of the Turks, after his defeat to the Arabs in the
Battle of Nihâvand (642 CE). Yazdegerd was initially supported by the Hephthalite
Principality of Chaghaniyan
The Principality of Chaghaniyan, known in Arabic sources as al-Saghaniyan, was a part of the Hephthalite Confederation from the 5th to the 7th century CE. After this, it was ruled by a local, presumably Iranian dynasty, which governed the Chaghan ...
, which sent him troops to aid him against the Arabs. But when Yazdegerd arrived in
Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
(in what is today's
Turkmenistan) he demanded tax from the ''
Marzban'' of Marw, losing his support and making him ally with the Hephthalite ruler of
Badghis
Bādghīs (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest poverty r ...
,
Nezak Tarkan
Nezak Tarkhan was a nomadic ruler of Tokharistan who led a revolt against the Arab commander Qutayba bin Muslim around 709 CE.
Nezak Tarkhan is first mentioned in 651 CE as the Hephthalite ruler of Badghis, when he allied with the ''marzban'' of ...
. The Hepthalite ruler of Badghis allied with the ''Marzban'' of Merv attack Yazdegerd and defeated him in 651. Yazdegerd III barely escaped with his life but was murdered in the vicinity of Merv soon after, and the Arabs managed to capture the city of Merv the same year.
In 652 CE, following the
Siege of Herat (652)
The siege of Herat was part of the Islamic conquest of Persia which was commanded by Ahnaf ibn Qais.
Background
Caliph Umar (634-644) launched an offensive against the Sassanid Persian Empire in 642, and by 651 the Empire was destroyed. Howev ...
to which the Hephthalites participated, the Arabs captured the cities of northern Tokharistan,
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
included, and the Hepthalites principalities were forced to pay tribute and accept Arab garrisons. The Hephthalites again rebelled in 654 CE, leading to the
Battle of Badghis
The Battle of Badghis was fought in 654 between the Karen family and their Hephthalite allies against the Rashidun Caliphate.
History
In 651, the Arabs had invaded Khorasan, and by 652, they had conquered most of the region. However, in 654, ...
.
In 659, Chinese chronicles still mentioned the "Hephtalite Tarkans" (悒達太汗 ''Yida Taihan'', probably related to "
Nezak Tarkan
Nezak Tarkhan was a nomadic ruler of Tokharistan who led a revolt against the Arab commander Qutayba bin Muslim around 709 CE.
Nezak Tarkhan is first mentioned in 651 CE as the Hephthalite ruler of Badghis, when he allied with the ''marzban'' of ...
"), as some of the rulers in Tokharistan who remained theoretically subjects to the Chinese Empire, and whose main city was Huolu 活路 (modern
Mazār-e Sherif, Afghanistan).
The city of
Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
became the base of the Arabs for their Central Asian operations. The Arabs weakened during the 4-year civil war leading to the establishment of the
Umayyad Caliphate in 661, but they were able to continue their expansion after that.
= Hephthalite revolts against the Ummayad Caliphate (689–710 CE)
=
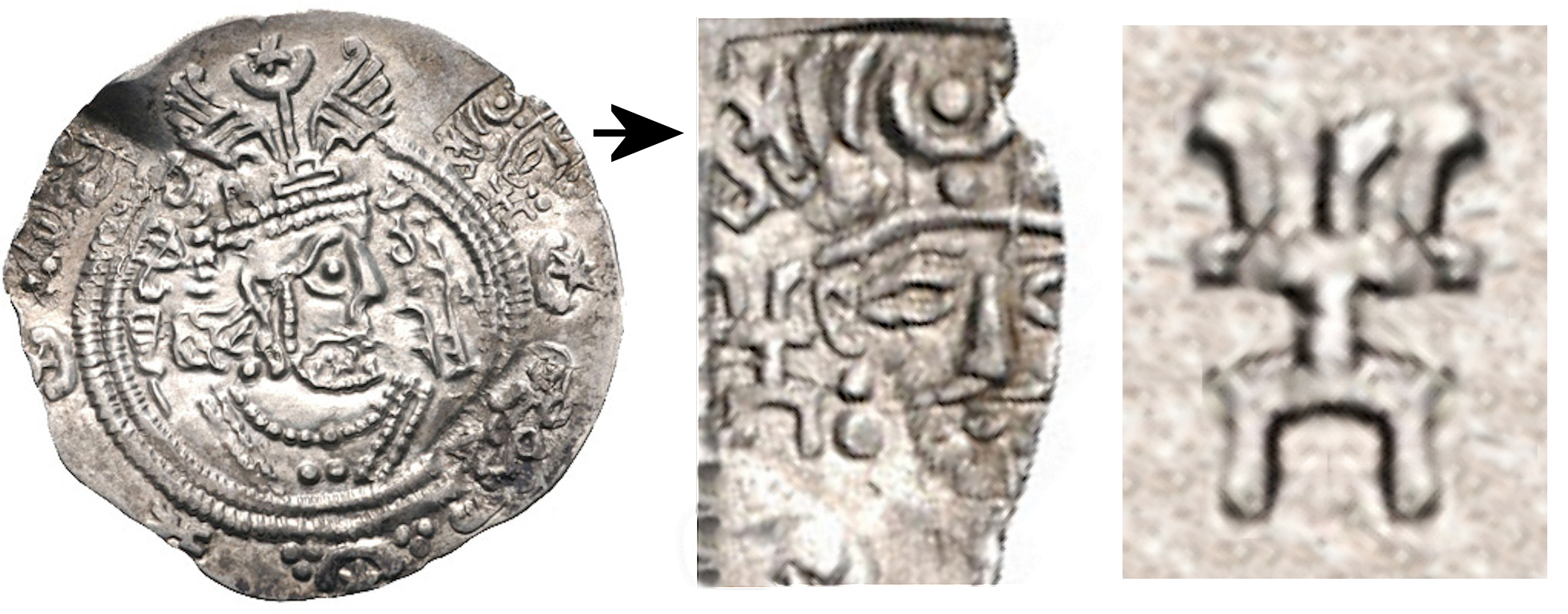

Circa 689 CE, the Hephthalite ruler of
Badghis
Bādghīs (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest poverty r ...
and the Arab rebel Musa ibn Abd Allah ibn Khazim, son of the
Zubayrid governor of Khurasan
Abd Allah ibn Khazim al-Sulami
ʿAbd Allāh ibn Khāzim al-Sulamī () (died 692) was the Umayyad governor of Khurasan between 662 and 665 and again in late 683, before becoming the nominal Zubayrid governor of the same province between 684 and his death.
Life Early career
Ab ...
, allied against the forces of the
Umayyad Caliphate. The Hepthalites and their allies captured
Termez
Termez ( uz, Termiz/Термиз; fa, ترمذ ''Termez, Tirmiz''; ar, ترمذ ''Tirmidh''; russian: Термез; Ancient Greek: ''Tàrmita'', ''Thàrmis'', ) is the capital of Surxondaryo Region in southern Uzbekistan. Administratively, it i ...
in 689, repelled the Arabs, and occupied the whole region of
Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
for a brief period, with Termez as they capital, described by the Arabs as "the headquarters of the Hephthalites" (''dār mamlakat al-Hayāṭela'').
The Arabs of the
Umayyad Caliphate under
Yazid ibn al-Muhallab
Yazid ibn al-Muhallab ( ar, يزيد بن المهلب) (672–720) was a provincial governor in the time of the Umayyad dynasty and an early member of the Muhallabid family that became important in early Abbasid times.
Life
In A.H. 78 (697-69 ...
re-captured
Termez
Termez ( uz, Termiz/Термиз; fa, ترمذ ''Termez, Tirmiz''; ar, ترمذ ''Tirmidh''; russian: Термез; Ancient Greek: ''Tàrmita'', ''Thàrmis'', ) is the capital of Surxondaryo Region in southern Uzbekistan. Administratively, it i ...
in 704.
Nezak Tarkan, the ruler of the Hephthalites of Badghis, led a new revolt in 709 with the support of other principalities as well as his nominal ruler, the
Yabghu of Tokharistan.
In 710,
Qutaiba ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī ( ar, أبو حفص قتيبة بن أبي صالح مسلم بن عمرو الباهلي; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of ...
was able to re-establish Muslim control over Tokharistan and captured Nizak Tarkan who was executed on
al-Hajjaj's orders, despite promises of pardon, while the Yabghu was exiled to
Damascus and kept there as a hostage.
In 718 CE, Chinese chronicles still mention the Hephthalites (悒達 ''Yida'') as one of the polities under the suzerainty of the Turkic
Tokhara Yabghus, capable of providing 50,000 soldiers at the service of its overlord.
Some remnants, not necessarily dynastic, of the Hephthalite confederation would be incorporated into the
Göktürks, as an
Old Tibetan document, dated to the 8th century, mentioned the tribe ''Heb-dal'' among 12 ''Dru-gu'' tribes ruled by
Eastern Turkic
Chagatai (چغتای, ''Čaġatāy''), also known as ''Turki'', Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (''Čaġatāy türkīsi''), is an extinct Turkic literary language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia and remained the shared literar ...
khagan ''Bug-chor'', i.e.
Qapaghan Qaghan
Qapaghan or Qapghan Qaghan ( otk, 𐰴𐰯𐰍𐰣:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Qapaγan qaγan, meaning "the conqueror", , Xiao'erjing: ٿِيًا شًا, Dungan: Чяншан, , also called Bögü Qaghan ( otk, 𐰋𐰇𐰏:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Bögü qaγan) in Ba ...
Chinese chronicles report embassies from the "Hephtalite kingdom" as late as 748 CE.
Military and weapons
The Hephthalites were considered as a powerful military force.
Depending on sources, their main weapon was the bow, the mace or the sword.
Judging from their military achievements, they probably had a strong cavalry.
In Persia, according to the 6th century Armenian chronicler
Lazar of P’arpec’i:
"Hunnic" designs in weaponry are known to have influenced Sasanian designs during the 6th–7th century CE, just before Islamic invasions.
The Sasanians adopted Hunnish nomadic designs for straight iron swords and their gold-covered scabbards.
This is particularly the case of two-straps suspension design, in which straps of different lengths were attached to a P-shaped projection on the scabbard, so that the sword could be held sideways, making it easier to draw, especially when on horseback.
The two-point suspension system for swords is considered to have been introduced by the Hephthalites in Central Asia and in the Sasanian Empire and is a marker of their influence, and the design was generally introduced by them in the territories they controlled. The first example of two-suspension sword in Sasanian art occurs in a relief of
Taq-i Bustan dated to the time of
Khusro II (590–628 CE), and is thought to have been adopted from the Hepthalites.
Swords with ornate cloisonné designs and two-straps suspensions, as found in the paintings of
Penjikent and
Kizil and in archaeological excavations, may be versions of the daggers produced under Hephthalite influence. Weapons with Hunnic designs are depicted in the "Cave of the Painters" in the
Kizil Caves
The Kizil Caves ( zh, t=克孜爾千佛洞, s=克孜尔千佛洞, l=Kizil Caves of the Thousand Buddhas; ug, قىزىل مىڭ ئۆي, translation=The Thousand Red Houses; also romanized Qizil Caves, spelling variant Qyzyl; Kizil means 'red') ar ...
, in a mural showing armoured warriors and dated to the 5th century CE.
Their sword guards have typical
Hunnish
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
designs of rectangle or oval shapes with
cloisonné
Cloisonné () is an ancient technique for decorating metalwork objects with colored material held in place or separated by metal strips or wire, normally of gold. In recent centuries, vitreous enamel has been used, but inlays of cut gemstones, ...
ornamentation.
Lamellar helmet
The lamellar helmet ( German language: ''Lamellenhelm'', plural ''Lamellenhelme'') was a type of helmet used in Europe during the Early Middle Ages. Examples are characterized by caps made from overlapping lamellar scales, in addition to a brow pl ...
s were also popularized by the steppe nomads, and were adopted by the
Sasanian Empire when they took control of former Hephthalite territory.
This type of helmet appears in sculptures on
pillar capitals at
Ṭāq-e Bostān
Taq-e Bostan ( fa, طاق بستان, ) is a site with a series of large rock reliefs from the era of the Sassanid Empire of Persia (Iran), carved around the 4th century CE.
This example of Persian Sassanid art is located 5 km from the ...
and
Behistun, and on
the Anahita coinage of
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king ( shah) of Iran, ruling f ...
(r. 590–628 CE).

Religion and culture

They were said to practice
polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives" ...
and
artificial cranial deformation
Artificial cranial deformation or modification, head flattening, or head binding is a form of body alteration in which the skull of a human being is deformed intentionally. It is done by distorting the normal growth of a child's skull by applying ...
. Chinese sources said they worshiped 'foreign gods', 'demons', the 'heaven god' or the 'fire god'. The Gokturks told the Byzantines that they had walled cities. Some Chinese sources said that they had no cities and lived in tents. Litvinsky tries to resolve this by saying that they were nomads who moved into the cities they had conquered. There were some government officials but central control was weak and local dynasties paid tribute.
According to
Song Yun
Song Yun () was a Chinese Buddhist monk who was sent by the pious Buddhist Empress Hu (, ?-528 CE) of the Northern Wei Dynasty with other monastic companions including Hui Zheng, Fa Li and Zheng (or Wang) Fouze, to northwestern India to search ...
, the Chinese Buddhist monk who visited the Hephthalite territory in 540 and "provides accurate accounts of the people, their clothing, the empresses and court procedures and traditions of the people and he states the Hephthalites did not recognize the Buddhist religion and they preached pseudo gods, and killed animals for their meat."
It is reported that some Hephthalites often destroyed Buddhist monasteries but these were rebuilt by others. According to
Xuanzang, the third Chinese pilgrim who visited the same areas as Song Yun about 100 years later, the capital of
Chaghaniyan
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
had five monasteries.

According to historian André Wink, "...in the Hephthalite dominion
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
was predominant but there was also a religious sediment of
Zoroastrianism and
Manichaeism."
[''Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: Early medieval India''. André Wink, p. 110. E. J. Brill.] Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
had some 100
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
monasteries and 30,000 monks. Outside the town was a large Buddhist monastery, later known as
Naubahar.
There were
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
among the Hephthalites by the mid-6th century, although nothing is known of how they were converted. In 549, they sent a delegation to
Aba I
Aba I (or, with his Syriac honorific, Mar Aba I) or Mar Abba the Great was the Patriarch of the Church of the East at Seleucia-Ctesiphon from 540 to 552. He introduced to the church the anaphoras of Theodore of Mopsuestia and Nestorius beside t ...
, the
patriarch of the
Church of the East
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
, asking him to consecrate a priest chosen by them as their bishop, which the patriarch did. The new bishop then performed obeisance to both the patriarch and the Sasanian king,
Khosrow I. The seat of the bishopric is not known, but it may have been
Badghis
Bādghīs (Dari: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northwest of the country, on the border with Turkmenistan. It is considered to be one of the country's most underdeveloped provinces, with the highest poverty r ...
–Qadištan, the bishop of which, Gabriel, sent a delegate to the synod of Patriarch
Ishoyahb I Ishoʿyahb I of Arzun was patriarch of the Assyrian Church of the East from 582 to 595. His name is included in the traditional list of patriarchs of the Church of the East.
Sources
Brief accounts of Ishoʿyahb's patriarchate are given in the '' ...
in 585. It was probably placed under the
metropolitan of Herat. The church's presence among the Hephthalites enabled them to expand their missionary work across the Oxus. In 591, some Hephthalites serving in the army of the rebel
Bahram Chobin
Bahrām Chōbīn ( fa, بهرام چوبین) or Wahrām Chōbēn (Middle Persian: ), also known by his epithet Mehrbandak ("servant of Mithra"), was a nobleman, general, and political leader of the late Sasanian Empire and briefly its ruler as Ba ...
were captured by
Khosrow II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king ( shah) of Iran, ruling f ...
and sent to the
Roman emperor Maurice as a diplomatic gift. They had
Nestorian cross
The Nestorian Cross is associated with the Church of the East. It is composed of a cross similar to the Maltese cross, with four arms of roughly equal length which narrow in width towards the center of the cross. In Eastern Christian art in China, ...
es tattooed on their foreheads.
Hephthalite seals

Several seals found in Bactria and Sogdia have been attributed to the Hephthalites.
* The "''
Hephthalite Yabghu seal''" shows a Hephthalite ruler with a radiate crown, royal ribbons and a beardless face, with the
Bactrian script
Bactrian (, , ) is an extinct Eastern Iranian language formerly spoken in the Central Asian region of Bactria (in present-day Afghanistan) and used as the official language of the Kushan, and the Hephthalite empires.
Name
It was long thought tha ...
title "Ebodalo
Yabghu
Yabghu ( otk, 𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆, yabγu,Entrabγu">"𐰖𐰉𐰍𐰆_[yabγuйабғұ"in_"Ethno-Cultural_Dictionary"_''Türik_Bitig''_),_also_rendered_as_Jabgu,_Djabgu_or_Yabgu,_was_a_state_office_in_the_early_Turkic_peoples.html" ;"title="abγuй ...
" (

ηβοδαλο ββγο, "The Lord of the Hephthalites"), and has been dated to the end of the 5th century-early 6th century CE.
This important seal was published by Judith A. Lerner and
Nicholas Sims-Williams
Nicholas Sims-Williams, FBA (born 11 April 1949, Chatham, Kent) is a British professor of the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS), University of London, where he is the Research Professor of Iranian and Central Asian Studies at the Dep ...
in 2011.
* ''Stamp seal (BM 119999)'' in the British Museum shows two facing figures, one bearded and wearing the Sasanian dress, and the other without facial hair and wearing a radiate crown, both being adorned with royal ribbons. This seal was initially dated to 300–350 CE and attributed to the
Kushano-Sasanians
Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom (also called Kushanshahs, KΟÞANΟ ÞAΟ ''or Koshano Shao'' in Bactrian, or Indo-Sasanians) is a historiographic term used by modern scholars to refer to a branch of the Sasanian Persians who established their rule in ...
,
but has been more recently attributed to the Hephthalites, and dated to the 5th–6th century CE.
Paleographically, the seal can be attributed to the 4th century or first half of the 5th century.
* The "''
Seal of Khingila''" shows a beardless ruler with radiate crown and royal ribbons, wearing a single-lapel caftan, in the name of Eškiŋgil (εϸχιγγιλο), which could correspond to one of the rulers named Khingila (χιγγιλο), or may be a Hunnic title meaning "Companion of the Sword", or even "Companion of the God of War".
Local populations under the Hephthalites
The Hephthalites governed a confederation of various people, many of whom were probably of Iranian descent, speaking an Iranian language. Several cities, such as
Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
,
Kobadiyan
Qubodiyon, also Qubadiyan, ancient Kobadiyan (russian: Кабодиён; tg, Қубодиён, fa, قبادیان ''Qobādiyān'') is a town in the Khatlon Region of Tajikistan. It is the capital of Qubodiyon District. The population of the tow ...
and possibly
Samarkand, were allowed to send regional embassies to China while under Hephthalite control. Several portraits of regional ambassadors from the territories occupied by the Hephthalites (
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
,
Tarim Basin) are known from Chinese paintings such as the ''
Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. These ...
'', originally painted in 526–539 CE.
They were at that time under the overlorship of the Hephthalites, who led the embassies to the
Southern Liang court in the early 6th century CE.
A century later, under the
Tang dynasty, portraits of the local people of Tokharistan were again illustrated in ''
The Gathering of Kings'', circa 650 CE.
Etienne de la Vaissière has estimated the local population of each major oasis in
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan ...
and
Western Turkestan during the period to around several hundreds of thousands each, while the major oasis of the
Tarim Basin are more likely to have had populations ranging in the tens of thousands each.
File:Kabadiyan ambassador to the Southern Liang court 516-520 CE.jpg, Kabadiyan ambassador to the Chinese court of Emperor Yuan of Liang in his capital Jingzhou in 516–520 CE. ''Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. These ...
'', 11th century Song copy. He accompanied the Hephthalite ambassador to China.
File:Kumedh ambassador to the Southern Liang court 516-520 CE.jpg, Kumedh ambassador to the Chinese court of Emperor Yuan of Liang in his capital Jingzhou in 516–520 CE. ''Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. These ...
'', 11th century Song copy.
File:Kucha ambassador to the Southern Liang court 516-520 CE.jpg, Ambassador from Kucha (龜茲國 ''Qiuci-guo''), one of the main Tocharian cities in the Tarim Basin, visiting the Chinese Southern Liang court in Jingzhou circa 516–520 CE. ''Portraits of Periodical Offering of Liang
The ''Portraits of Periodical Offering'' () were tributary documentative paintings (with illustration on each of the portrait) produced by various Chinese dynasties and later as well in other East Asian dynasties, such as Japan and Vietnam. These ...
'', 11th century Song copy.
File:Ambassadors from Kabadiyan (阿跋檀), Balkh (白題國) and Kumedh (胡密丹), visiting the court of the Tang Dynasty. The Gathering of Kings (王会图) circa 650 CE.jpg, Ambassadors from Kabadiyan (阿跋檀), Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan
...
(白題國) and Kumedh (胡密丹), visiting the court of the Tang Dynasty. '' The Gathering of Kings'' (王会图), circa 650 CE
The Alchon Huns (formerly considered as a branch of the Hephthalites) in South Asia
The
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
, who invaded northern India and were known there as "
Hūṇas", have long been considered as a part or a sub-division of the Hephthalites, or as their eastern branch, but now tend to be considered as a separate entity, who may have been displaced by the settlement of the Hephthalites in Bactria. Historians such as
Beckwith, referring to
Étienne de la Vaissière
Étienne, a French analog of Stephen or Steven, is a masculine given name. An archaic variant of the name, prevalent up to the mid-17th century, is Estienne.
Étienne, Etienne, Ettiene or Ettienne may refer to:
People
Scientists and inventors
* ...
, say that the Hephthalites were not necessarily one and the same as the Hunas (''Sveta Huna''). According to de la Vaissiere, the Hephthalites are not directly identified in classical sources alongside that of the Hunas. They were initially based in the
Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
basin in Central Asia and established their control over Gandhara in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent by about 465 CE. From there, they fanned out into various parts of northern, western, and central
India.
In India, these invading people were called
Hunas
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''Hūṇā'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna ...
, or "Sveta Huna" (''White Huns'') in
Sanskrit.
The Hūṇas are mentioned in several ancient texts such as the
Rāmāyaṇa,
Mahābhārata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kuru ...
,
Purāṇas, and Kalidasa's
Raghuvaṃśa. The first ''Hunas'', probably
Kidarites, were initially defeated by Emperor
Skandagupta
Skandagupta (Gupta script: ''Ska-nda-gu-pta'', r. c. 455-467) was a Gupta Emperor of India. His Bhitari pillar inscription suggests that he restored the Gupta power by defeating his enemies, who may have been rebels or foreign invaders. He r ...
of the
Gupta Empire in the 5th century CE. In the early 6th century CE, the
Alchon Hun
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
''Hunas'' in turn overran the part of the Gupta Empire that was to their southeast and had conquered Central and
North India. Gupta Emperor
Bhanugupta
Bhanugupta was one of the lesser known kings of the Gupta dynasty. He is only known from an inscription in Eran, and a mention in the Manjushri-mula-kalpa.
Only mentioned in the Eran inscription as a "Raja" and not a "Maharaja" or a "Maharajad ...
defeated the Hunas under
Toramana
Toramana also called Toramana Shahi Jauvla (Gupta script: ''Toramāṇa'', ruled circa 493-515 CE) was a king of the Alchon Huns who ruled in northern India in the late 5th and the early 6th century CE. Toramana consolidated the Hephthalite po ...
in 510, and his son
Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent betwee ...
was repulsed by
Yashodharman in 528 CE. The ''Hunas'' were driven out of India by the kings
Yasodharman
Yashodharman (Gupta script: ''Ya-śo-dha-rmma'', ) (r. 515 – 545) was a ruler of Malwa, in central India, during the early part of the 6th century. He probably belonged to the Second Aulikara dynasty. He conquered much of the Indian subco ...
and
Narasimhagupta
Narasimhagupta (Gupta script: ''Na-ra-si-ṅha-gu-pta'') Baladitya was an emperor of the Gupta Empire of North India. He was son of Purugupta and probably the successor of Budhagupta.
Defeat of the Hunas
According to the Chinese monk Xuanzan ...
, during the early 6th century.
Possible descendants
A number of groups may have descended from the Hephthalites.
* Avars: suggestions have been made that the
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
were Hepthalites who went to Europe after their collapse in 557 CE, but this is not adequately supported by archaeological or written sources.
* Pashtuns: The Hephthalites may have contributed to the ethnogenesis of
Pashtuns. Yu. V. Gankovsky, a Soviet historian on Afghanistan, stated: "Pashtun began as a union of largely
East Iranian
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian diale ...
tribes, which became the initial ethnic stratum of the Pashtun ethnogenesis dating from the middle of the first millennium CE, and is connected with the dissolution of the Hephthalite confederacy."
** Durrani: The
Durrani Pashtuns of Afghanistan were called "Abdali" before 1747. According to linguist
Georg Morgenstierne, their tribal name ''Abdālī'' may have "something to do with" the Hephthalite. This hypothesis was endorsed by historian
Aydogdy Kurbanov
Aydogdy Kurbanov (in Turkmen: ''Aýdogdy Gurbanow'', born 2 February 1976, in Ashgabat, Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, USSR) is a Turkmen archaeologist and historian whose main area of research is prehistoric and late antiquity of Central A ...
, who indicated that after the collapse of the Hephthalite confederacy, they likely assimilated into different local populations and that the Abdali may be one of the tribes of Hephthalite origin.

* Khalaj: The
Khalaj people are first mentioned in the 7th–9th centuries in the area of
Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan ...
,
Qalati Ghilji, and
Zabulistan in present-day
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. They spoke
Khalaj Turkic.
Al-Khwarizmi
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in mathematics, astronom ...
mentioned them as a remnant tribe of the Hephthalites. However, according to linguist
Sims-Williams, archaeological documents do not support the suggestion that the Khalaj were the Hephthalites' successors, while according to historian
V. Minorsky, the Khalaj were "perhaps only politically associated with the Hephthalites." Some of the Khalaj were later
Pashtunized, after which they transformed into the Pashtun
Ghilji
The Ghiljī ( ps, غلجي, ; fa, خیلجی, Xelji) also spelled Khilji, Khalji, or Ghilzai or Ghilzay (), are one of the largest Pashtun tribes. Their traditional homeland is Ghazni and Qalati Ghilji in Afghanistan but they have also settle ...
tribe.
* Kanjina: a Saka tribe linked to the
Indo-Iranian Kumijis and incorporated into the Hephthalites. Kanjinas were possibly Turkicized later, as
al-Khwarizmi
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in mathematics, astronom ...
called them "Kanjina Turks". However,
Bosworth and
Clauson contended that al-Khwarizmi was simply using "Turks" "in the vague and inaccurate sense".
* Karluks: (or
Qarlughids
The Qarlughids were a tribe of Turkic origin that controlled Ghazni, lands of the Bamyan, the Kurram Valley (Ghazna, Banban, and Kurraman), and established a short-lived Muslim principality and dynasty that lasted between 1236 and 1266. The Q ...
) were reported as settled in Ghazni and Zabulistan, present-day Afghanistan, in the thirteenth century. Many Muslim geographers identified "Karluks" ''Khallukh'' ~ ''Kharlukh'' with "Khalajes" ''Khalaj'' from confusion, as the two names were similar and these two groups dwelt near each other.
* Abdal is a name associated with the Hephthalites. It is an alternate name for the
Äynu people.
** According to
Orhan Köprülü,
Abdal of Turkey
The Abdal ( tr, Abdallar or ) are a Turkish-speaking with much Turkmen grammar socio-cultural Indo-Turkic people group found mainly in central and western Anatolia, and some live in Istanbul, who follow an itinerant lifestyle. This lifestyle i ...
might be descended from the Hepthalites.
Albert von Le Coq
Albert von Le Coq (; 8 September 1860 Berlin, Prussia – 21 April 1930 Berlin, Germany) was a Prussian/German brewery owner and wine merchant, who at the age of 40 began to study archaeology.''Schatzjagd an der Seidenstraße.'' A film by Susann ...
mentions the relation between Abdals of
Adana
Adana (; ; ) is a major city in southern Turkey. It is situated on the Seyhan River, inland from the Mediterranean Sea. The administrative seat of Adana province, it has a population of 2.26 million.
Adana lies in the heart of Cilicia, wh ...
and Äynus of
East Turkestan
East Turkestan ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان, Sherqiy Türkistan, bold=no; zh, s=东突厥斯坦; also spelled East Turkistan), is a loosely-defined geographical and historical region in the western provinces of the People's Republic of ...
, by them having some common words, and by both referring to themselves as Abdals and speaking an exclusive language among themselves.
Some Abdal elements can also be found in the composition of
Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
, Turkmen (Ata,
Chowdur
The Chowdur (meaning herder) or Choudor are one of the ten major groups of people who merged after 1920 to form the modern Turkmen Republic. They live primarily in and around the Khorezm Oasis.
History
The Choudor are thought to belong to ...
,
Ersary
Ersari ( tk, Ärsary, where ''Er'' - brave man, master; ''sari'' - light, bright, yellow) are one of the major tribes of the Turkmen people of Central Asia and one of the five major tribes of the country of Turkmenistan. They live mainly in T ...
,
Saryk), Kazakhs, Uzbek-Lokays,
Turks and Volga Bulgars (
Savirs).
Hephthalite rulers
*
Akhshunwar ''Akhshunwar'' ( Sogdian: əxšōnδār, Middle Persian: ''Xašnawāz'') was a ruling title used by the Hephthalite kings in the 5th and 6th-centuries.
The title is of Eastern Iranian origin; according W.B. Henning, its original form was ʾxšʾwn ...
, circa 458 CE
* Kun-khi, circa 484 CE
* Yandai Yilituo, circa 516 CE (only known from his Chinese name 厭帶夷栗陁)
* Hwade-gang (only known from the archives of the
Kingdom of Rob
The Kingdom of Rob ( Bactrian: , ) was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script (a ...
).
* Ghadfar/Ghatifar, circa 567–568 CE.
*
Faghanish
Faghanish was a Hephthalite prince, who was the ruler of Chaghaniyan in the mid-6th century. Originally a subordinate of the Hephthalite king, he became a vassal of the Sasanian Empire in c. 560 after the Hephthalite Empire was broken into several ...
(568-) (ruling in
Chaghaniyan
Chaghaniyan (Middle Persian: ''Chagīnīgān''; fa, چغانیان ''Chaghāniyān''), known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.
Histo ...
)
*
Nezak Tarkan
Nezak Tarkhan was a nomadic ruler of Tokharistan who led a revolt against the Arab commander Qutayba bin Muslim around 709 CE.
Nezak Tarkhan is first mentioned in 651 CE as the Hephthalite ruler of Badghis, when he allied with the ''marzban'' of ...
(circa 650–710)
See also
*
History of Afghanistan
*
Huna people
*
Kidarites (Red Huns)
*
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. ...
*
Kushan Empire
*
Xionites
*
Nezak Huns
The Nezak Huns ( Pahlavi: 𐭭𐭩𐭰𐭪𐭩 ''nycky''), also Nezak Shahs, formed a major principality in the south of the Hindu Kush region, active from circa 484 to 665 CE. Despite being traditionally identified as the last of the Hunnic stat ...
*
Iranian Huns
The term Iranian Huns is sometimes used for a group of different tribes that lived in Afghanistan and neighboring areas between the fourth and seventh centuries and expanded into northwest India. They are roughly equivalent to the Hunas. They als ...
Notes
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
* . 4-volume set.
*
*
*
*
*
*
Internet Archive copy*
*
*
*
*
Internet ArchiveGoogle Books
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Alternate PDF
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Internet Archive
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
External links
"The Ethnonym Apar in the Turkish Inscriptions of the VIII. Century and Armenian Manuscripts" Dr. Mehmet Tezcan.
The Anthropology of Yanda (Chinese)
pdf
Columbia Encyclopedia: Hephthalites
*
(long article with a timeline)
* Article archived from the University of Washington's Silk Road exhibition – has a slightly adapted form of the Richard Heli timeline.
(pdf)
The Ethnonym Apar in the Turkish Inscriptions of the VIII. Century and Armenian Manuscripts – Mehmet Tezcan
Records Relevant to the Hephthalites in Ancient Chinese Historical Works
collected by Yu Taishan (2016).
{{Huns
Nomadic groups in Eurasia
Former countries in Central Asia
Former countries in South Asia
History of Pakistan
Medieval Afghanistan
History of India
History of China
Medieval Khorasan
States and territories established in the 440s
670 disestablishments
Former empires
 The Hephthalites were a vassal state to the
The Hephthalites were a vassal state to the  The Hephthalites were originally vassals of the
The Hephthalites were originally vassals of the  The Hephthalites conquered the territory of
The Hephthalites conquered the territory of  An illustrated account of a Hepthalite (滑, Hua) embassy to the Chinese court of the Southern Liang in the capital Jingzhou in 516–526 CE is given in ''
An illustrated account of a Hepthalite (滑, Hua) embassy to the Chinese court of the Southern Liang in the capital Jingzhou in 516–526 CE is given in '' After Kavad I, the Hephthalites seem to have shifted their attention away from the Sasanian Empire, and Kavad's successor Khosrow I (531–579) was able to resume an expansionist policy to the east. According to
After Kavad I, the Hephthalites seem to have shifted their attention away from the Sasanian Empire, and Kavad's successor Khosrow I (531–579) was able to resume an expansionist policy to the east. According to  .
Circa 606/607 CE the
.
Circa 606/607 CE the  From 625 CE, the territory of the Hephthalites from
From 625 CE, the territory of the Hephthalites from  Circa 689 CE, the Hephthalite ruler of
Circa 689 CE, the Hephthalite ruler of 
 They were said to practice
They were said to practice  According to historian André Wink, "...in the Hephthalite dominion
According to historian André Wink, "...in the Hephthalite dominion  Several seals found in Bactria and Sogdia have been attributed to the Hephthalites.
* The "'' Hephthalite Yabghu seal''" shows a Hephthalite ruler with a radiate crown, royal ribbons and a beardless face, with the
Several seals found in Bactria and Sogdia have been attributed to the Hephthalites.
* The "'' Hephthalite Yabghu seal''" shows a Hephthalite ruler with a radiate crown, royal ribbons and a beardless face, with the 
 ηβοδαλο ββγο, "The Lord of the Hephthalites"), and has been dated to the end of the 5th century-early 6th century CE. This important seal was published by Judith A. Lerner and
ηβοδαλο ββγο, "The Lord of the Hephthalites"), and has been dated to the end of the 5th century-early 6th century CE. This important seal was published by Judith A. Lerner and  * Khalaj: The Khalaj people are first mentioned in the 7th–9th centuries in the area of
* Khalaj: The Khalaj people are first mentioned in the 7th–9th centuries in the area of