|
Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are currently scattered over most of Asia north of 35° N and in some eastern parts of Europe, extending in longitude from Turkey to Japan. The group is named after the Altai mountain range in the center of Asia. The hypothetical language family has long been rejected by most comparative linguists, although it continues to be supported by a small but stable scholarly minority. The research on their supposedly common linguistics origin has inspired various comparative studies on the folklore and mythology among the Turks, Proto-Mongols and Tungus people. The Altaic family was first proposed in the 18th century. It was widely accepted until the 1960s and is still listed in many encyclopedias and handbooks. Since the 1950s, many comparative lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Altaic Language
The Proto-Altaic language is a hypothetical extinct language that has been proposed as the common ancestor of the disputed Altaic languages. In the 18th century, some similarities between the Turkic, Mongolian, and Tungusic languages led to the conjecture that they would be a single language family with a common ancestral language.Nicholas Poppe (1965): ''Introduction to Altaic Linguistics.'' Volume 14 of ''Ural-altaische Bibliothek''. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. Starting in the 19th century, some linguists proposed to include also the Japonic and/or Koreanic languages as well as the Ainu language, forming what would later be called the "Macro-Altaic family" (the original one being then dubbed "Micro-Altaic").Roy Andrew Miller (1986): ''Nihongo: In Defence of Japanese.'' . Around the same time others proposed to include the Uralic languages in a Ural-Altaic family. Versions of the Altaic family hypothesis were widely accepted until the 1960s, and it is still listed in many e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungusic Languages
The Tungusic languages (also known as Manchu-Tungus and Tungus) form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered. There are approximately 75,000 native speakers of the dozen living languages of the Tungusic language family. Some linguists consider Tungusic to be part of the controversial Altaic language family, along with Turkic, Mongolic, and sometimes Koreanic and Japonic. The term "Tungusic" is from an exonym for the Evenk people (Ewenki) used by the Yakuts ("tongus"). It was borrowed into Russian as "тунгус", and ultimately transliterated into English as "Tungus". Classification Linguists working on Tungusic have proposed a number of different classifications based on different criteria, including morphological, lexical, and phonological characteristics. Some scholars have criticized the tree-based model of Tungusic classification, arguing the long history of contact among the Tungusic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
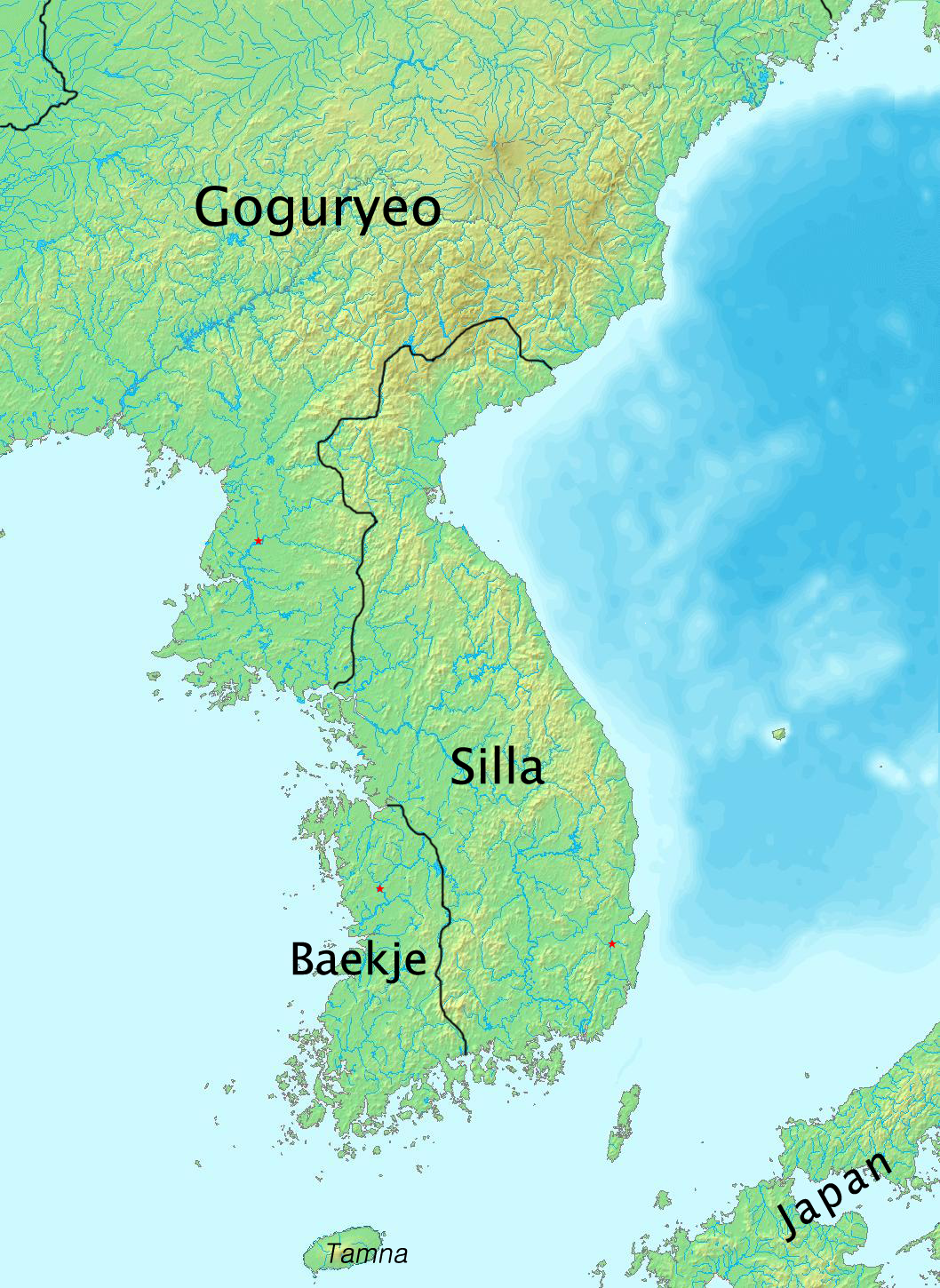
Koreanic Languages
Koreanic is a small language family consisting of the Korean and Jeju languages. The latter is often described as a dialect of Korean, but is distinct enough to be considered a separate language. Alexander Vovin suggests that the Yukjin dialect of the far northeast should be similarly distinguished. Korean has been richly documented since the introduction of the Hangul alphabet in the 15th century. Earlier renditions of Korean using Chinese characters are much more difficult to interpret. All modern varieties are descended from the Old Korean of the state of Silla. The little that is known of other languages spoken on the peninsula before the Sillan unification (late 7th century) comes largely from placenames. Some of these languages are believed to have been Koreanic, but there is also evidence suggesting that Japonic languages were spoken in central and southern parts of the peninsula. There have been many attempts to link Koreanic with other language families, most often wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Starostin
Sergei Anatolyevich Starostin (russian: Серге́й Анато́льевич Ста́ростин; March 24, 1953 – September 30, 2005) was a Russian historical linguist and philologist, perhaps best known for his reconstructions of hypothetical proto-languages, including his work on the controversial Altaic theory, the formulation of the Dené–Caucasian hypothesis, and the proposal of a Borean language of still earlier date. He was also the author of a widely respected reconstruction of Old Chinese. Theories In 1986, Starostin and Igor M. Diakonoff suggested that the Hurro-Urartian languages belong to the Northeast Caucasian language family. Starostin was also instrumental in the reconstruction of Proto-Kiranti, Proto-Tibeto-Burman, Proto-Yeniseian, Proto-North-Caucasian, and Proto-Altaic. He developed the hypothesis, originated by Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur Khan in the 17th century, but really revived by Gustaf John Ramstedt in the early 20th century, that Japanese is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolic Languages
The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongol residents of Inner Mongolia, with an estimated 5.7+ million speakers. Classification The Mongolic languages have no convincingly established living relatives. The closest relatives of the Mongolic languages appear to be the para-Mongolic languages, which include the extinct Khitan, Tuyuhun, and possibly also Tuoba languages. A few linguists have grouped Mongolic with Turkic, Tungusic and possibly Koreanic and Japonic as part of the widely discredited Altaic family. History The stages of Historical Mongolic are: * Pre-Proto-Mongolic, from approximately the 4th century AD until the 12th century AD, influenced by Common Turkic, and previo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu Languages
The Ainu languages ( ), sometimes known as Ainuic, are a small language family, often regarded as a language isolate, historically spoken by the Ainu people of northern Japan and neighboring islands. The primary varieties of Ainu are alternately considered a group of closely related languages or divergent dialects of a single language isolate. The only surviving variety is Hokkaido Ainu, which UNESCO lists as critically endangered. Sakhalin Ainu and Kuril Ainu are now extinct. Toponymic evidence suggests Ainu was once spoken in northern Honshu and that much of the historically attested extent of the family was due to a relatively recent expansion northward. No genealogical relationship between Ainu and any other language family has been demonstrated, despite numerous attempts. Varieties Recognition of the different varieties of Ainu spoken throughout northern Japan and its surrounding islands in academia varies. (1990:9) and (1998:2) both speak of "Ainu languages" when comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Korean
Old Korean () is the first historically documented stage of the Korean language, typified by the language of the Unified Silla period (668–935). The boundaries of Old Korean periodization remain in dispute. Some linguists classify the sparsely attested languages of the Three Kingdoms of Korea as variants of Old Korean, while others reserve the term for the language of Silla alone. Old Korean traditionally ends with the fall of Silla in 935. This too has recently been challenged by South Korean linguists who argue for extending the Old Korean period to the mid-thirteenth century, although this new periodization is not yet fully accepted. This article focuses on the language of Silla before the tenth century. Old Korean is poorly attested. The only surviving literary works are a little more than a dozen vernacular poems called ''hyangga''. Hyangga use hyangchal writing. Other sources include inscriptions on steles and wooden tablets, glosses to Buddhist sutras, and the transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Linguistics
Comparative linguistics, or comparative-historical linguistics (formerly comparative philology) is a branch of historical linguistics that is concerned with comparing languages to establish their historical relatedness. Genetic relatedness implies a common origin or proto-language and comparative linguistics aims to construct language families, to reconstruct proto-languages and specify the changes that have resulted in the documented languages. To maintain a clear distinction between attested and reconstructed forms, comparative linguists prefix an asterisk to any form that is not found in surviving texts. A number of methods for carrying out language classification have been developed, ranging from simple inspection to computerised hypothesis testing. Such methods have gone through a long process of development. Methods The fundamental technique of comparative linguistics is to compare phonological systems, morphological systems, syntax and the lexicon of two or more lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic People
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia region, potentially in Mongolia or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers, but later became nomadic Pastoralism, pastoralists. Early and Post-classical history, medieval Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranian peoples, Iranian, Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Tocharians, Yeniseian people, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungus People
Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are Indigenous peoples of Siberia, native to Siberia and Northeast Asia. The Tungusic phylum is divided into two main branches, northern (Evenic or Tungus) and southern (Jurchen language, Jurchen–Nanai language, Nanai). An intermediate group (Oroch language, Oroch–Udege language, Udege) is sometimes recognized. Name The name ''Tungusic'' is artificial, and properly refers just to the postulated linguistic phylum (Tungusic languages). It is derived from Russian (), a Russian language, Russian exonym for the Evenks (Ewenki). English usage of ''Tungusic'' was introduced by Friedrich Max Müller in the 1850s, based on earlier use of German by Heinrich Julius Klaproth. The alternative term ''Manchu–Tungus'' is also in use ( 'Tunguso-Manchurian'). The name ''Tunguska'', a region of eastern Siberia bounded on the west by the Yenisei River, Tunguska riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Mongol Language
Middle Mongol or Middle Mongolian, was a Mongolic koiné language spoken in the Mongol Empire. Originating from Genghis Khan's home region of Northeastern Mongolia, it diversified into several Mongolic languages after the collapse of the empire. In comparison to Modern Mongolian, it is known to have had no long vowels, different vowel harmony and verbal systems and a slightly different case system. Definition and historical predecessors Middle Mongol is close to Proto-Mongolic, the ancestor language of the modern Mongolic languages, which would to set at the time when Genghis Khan united a number of tribes under his command and formed the Khamag Mongol. The term "Middle Mongol" is somewhat misleading, as what would generally by language naming rules be termed "Old Mongolian" in this terminology is actually Proto-Mongolic. The existence of another ("old") Mongol clan federation in Mongolia during the 12th century is historical, but there is no language material from this period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |