|
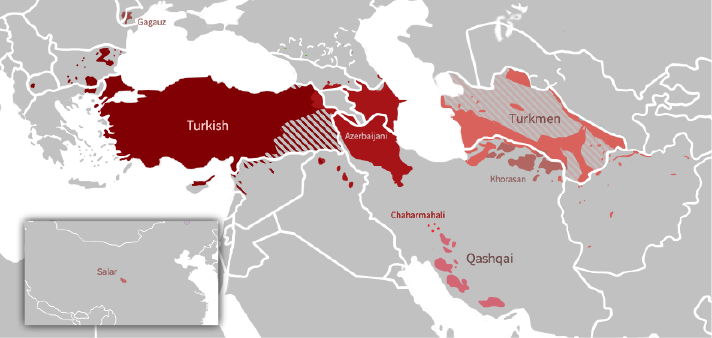
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents dates back to classical antiquity, antiquity, but their borders have historically been subject to change. For example, the ancient Greeks originally included Africa in Asia but classified Europe as separate land. Eurasia is connected to Africa at the Suez Canal, and the two are sometimes combined to describe the largest contiguous landmass on Earth, Afro-Eurasia. History Eurasia has been the host of many ancient civilizations, including those based in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley and China. In the Axial Age (mid-first millennium BCE), a continuous belt of civilizations stretched through the Eurasian Subtropics, subtropical zone from the Atlantic to the Pacific. This belt became the mainstream of world history for two millennia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Language
Turkish ( , , also known as 'Turkish of Turkey') is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, a member of Oghuz languages, Oghuz branch with around 90 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey and one of two official languages of Cyprus. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers also exist in Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Greece, other parts of Europe, the South Caucasus, and some parts of Central Asia, Iraqi Turkmen, Iraq, and Syrian Turkmen, Syria. Turkish is the List of languages by total number of speakers, 18th-most spoken language in the world. To the west, the influence of Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish—the variety of the Turkish language that was used as the administrative and literary language of the Ottoman Empire—spread as the Ottoman Empire expanded. In 1928, as one of Atatürk's reforms in the early years of the Republic of Turkey, the Persian alphabet, Perso-Arabic script-based Ottoman Turkish alphabet was repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaharmahali Turkic
Chaharmahali Turkic (چهارمحال تۆرکچسى ''Çəharməhal türkçəsi'') is a proposed Oghuz Turkic variety spoken in Iran's Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province and in western Isfahan province, where it is described as "Esfahan Province Turkic" by linguists. It is an understudied and generally unclassified variety of Oghuz Turkic distinct from Azerbaijani and Qashqai, being closer to the latter. Chaharmahali Turkic is not to be confused with " Charmahali Persian," ( fa) a Persian dialect spoken in the same region. Language Distribution The '' Atlas of the Languages of Iran'' (ALI) published a point-based and polygon language distribution map of Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province and several linguistic data maps.Anonby, Erik, Mortaza Taheri-Ardali, et al. (eds.). 2015–2017. ''Atlas of the Languages of Iran: Languages of Chahar Mahal va Bakhtiari Province, Iran.'' Ottawa: Geomatics and Cartographic Research Centre, Carleton University. Online address(retrieved Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qashqai Language
Qashqai (قشقایی ديلى, ''Qašqāyī dili'', pronounced in English as , and also spelled Qaşqay, Qashqayi, Kashkai, Kashkay, Qašqāʾī, by Michael Knüppel, by Gerhard Doerfer and Qashqa'i or Kaşkay) is an Oghuz Turkic language spoken by the Qashqai people, an ethnic group living mainly in the Fars province of Southern Iran. ''Encyclopædia Iranica'' regards Qashqai as an independent third group of dialects within the Southwestern Turkic language group. It is known to speakers as ''Turki''. Estimates of the number of Qashqai speakers vary. ''Ethnologue'' gave a figure of million in 2021. The Qashqai language is closely related to Azerbaijani. However, some Qashqai varieties namely the variety spoken in the Sheshbeyli tribe share features with Turkish. In a sociopolitical sense, though, Qashqai is considered a language in its own right. Like other Turkic languages spoken in Iran, such as the Azerbaijani language, Qashqai uses a modified version of the Perso-Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkmen Language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ) is a Turkic language of the Oghuz branch spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia. It has an estimated 4.7 million native speakers in Turkmenistan (where it is the official language), and a further 359,000 speakers in northeastern Iran and 1.2 million people in northwestern Afghanistan, where it has no official status. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia. Turkmen is a member of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. It is closely related to Azerbaijani, Gagauz, Qashqai, and Turkish, sharing varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with each of those languages. However, the closest relative of Turkmen is considered Khorasani Turkic, spoken in northeastern regions of Iran and with which it shares the eastern subbranch of Oghuz languages, as well as Khorazm, the Oghuz dialect of Uzbek spoken mainly in Khorezm along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijani Language
Azerbaijani ( ; , , ) or Azeri ( ), also referred to as Azerbaijani Turkic or Azerbaijani Turkish (, , ), is a Turkic languages, Turkic language from the Oghuz languages, Oghuz sub-branch. It is spoken primarily by the Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan, where the North Azerbaijani Variety (linguistics), variety is spoken, while Iranian Azerbaijanis in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region of Iran, speak the South Azerbaijani Variety (linguistics), variety. Azerbaijani is the only official language in the Republic of Azerbaijan and one of the 14 official languages of Dagestan (a Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia), but it does not have official status in Iran, where the majority of Iranian Azerbaijanis, Iranian Azerbaijani people live. Azerbaijani is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Azerbaijani communities of Georgia (country), Georgia and Turkey and by Azerbaijani diaspora, diaspora communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Languages
The Oghuz languages are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family, spoken by approximately 108 million people. The three languages with the largest number of speakers are Turkish, Azerbaijani and Turkmen, which, combined, account for more than 95% of speakers of this sub-branch. Kara-Khanid scholar Mahmud al-Kashgari, who lived in the 11th century, stated that the Oghuz language was the simplest among all Turkic languages. Swedish turcologist and linguist Lars Johanson notes that Oghuz languages form a clearly discernible and closely related bloc within the Turkic language family as the cultural and political history of the speakers of Oghuz languages has linked them more closely up to the modern age. Western Oghuz languages are highly mutually intelligible with each other and the Crimean Tatar language, which, though genetically Kipchak Turkic rather than Oghuz, has been heavily influenced by Turkish over several centuries. History and terminology The ancestor of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intelligibility is sometimes used to distinguish languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between varieties can be asymmetric; that is, speakers of one variety may be able to better understand another than vice versa. An example of this is the case between Afrikaans and Dutch. It is generally easier for Dutch speakers to understand Afrikaans than for Afrikaans speakers to understand Dutch. In a dialect continuum, neighbouring varieties are mutually intelligible, but differences mount with distance, so that more widely separated varieties may not be mutually intelligible. Intelligibility can be partial, as is the case with Azerbaijani and Turkish, or significant, as is the case with Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''. The values present in a given language, of which there are usually two or three, are called the ''genders'' of that language. Some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", whereas others use different definitions for each. Many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to Sex–gender distinction, sex or gender. According to one estimate, gender is used in approximately half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behavior of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphology (linguistics), morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes (word parts), each of which corresponds to a single Syntax, syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglutinative languages. For example, in the agglutinative Turkish language, Turkish, the word ("from your houses") consists of the morphemes ''ev-ler-i-n-iz-den''. Agglutinative languages are often contrasted with isolating languages, in which words are monomorphemic, and fusional languages, in which words can be complex, but morphemes may correspond to multiple features. Examples of agglutinative languages Although agglutination is characteristic of certain language families, this does not mean that when several languages in a certain geographic area are all agglutinative they are necessarily related phylogenetically. In the past, this assumption led linguists to propose the so-called Ural–Altaic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is a phonological rule in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – must share certain distinctive features (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, meaning that the affected vowels do not need to be immediately adjacent, and there can be intervening segments between the affected vowels. Generally one vowel will trigger a shift in other vowels, either progressively or regressively, within the domain, such that the affected vowels match the relevant feature of the trigger vowel. Common phonological features that define the natural classes of vowels involved in vowel harmony include vowel backness, vowel height, nasalization, roundedness, and advanced and retracted tongue root. Vowel harmony is found in many agglutinative languages. The given domain of vowel harmony taking effect often spans across morpheme boundaries, and suffixes and prefixes will usually follow vowel harmony rules. Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |