HEVC on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 HEVC specifies 33 directional modes for intra prediction compared with the 8 directional modes for intra prediction specified by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. HEVC also specifies DC intra prediction and planar prediction modes. The DC intra prediction mode generates a mean value by averaging reference samples and can be used for flat surfaces. The planar prediction mode in HEVC supports all block sizes defined in HEVC while the planar prediction mode in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC is limited to a block size of 16×16 pixels. The intra prediction modes use data from neighboring prediction blocks that have been previously decoded from within the same picture.
;Motion compensation
For the interpolation of fractional luma sample positions HEVC uses separable application of one-dimensional half-sample interpolation with an 8-tap filter or quarter-sample interpolation with a 7-tap filter while, in comparison, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC uses a two-stage process that first derives values at half-sample positions using separable one-dimensional 6-tap interpolation followed by integer rounding and then applies
HEVC specifies 33 directional modes for intra prediction compared with the 8 directional modes for intra prediction specified by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. HEVC also specifies DC intra prediction and planar prediction modes. The DC intra prediction mode generates a mean value by averaging reference samples and can be used for flat surfaces. The planar prediction mode in HEVC supports all block sizes defined in HEVC while the planar prediction mode in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC is limited to a block size of 16×16 pixels. The intra prediction modes use data from neighboring prediction blocks that have been previously decoded from within the same picture.
;Motion compensation
For the interpolation of fractional luma sample positions HEVC uses separable application of one-dimensional half-sample interpolation with an 8-tap filter or quarter-sample interpolation with a 7-tap filter while, in comparison, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC uses a two-stage process that first derives values at half-sample positions using separable one-dimensional 6-tap interpolation followed by integer rounding and then applies
,
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a
8 June 2017.
 The design of most video coding standards is primarily aimed at having the highest coding efficiency. Coding efficiency is the ability to encode video at the lowest possible bit rate while maintaining a certain level of video quality. There are two standard ways to measure the coding efficiency of a video coding standard, which are to use an objective metric, such as
The design of most video coding standards is primarily aimed at having the highest coding efficiency. Coding efficiency is the ability to encode video at the lowest possible bit rate while maintaining a certain level of video quality. There are two standard ways to measure the coding efficiency of a video coding standard, which are to use an objective metric, such as
and the video compression standard
A video coding format (or sometimes video compression format) is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital video content (such as in a data file or bitstream). It typically uses a standardized video compression algori ...
designed as part of the MPEG-H
MPEG-H is a group of international standards under development by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It has various "parts" – each of which can be considered a separate standard. These include a media transport protocol standard, ...
project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distri ...
(AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related tec ...
Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
at the same level of video quality
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of dist ...
, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction w ...
. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 ( UHDTV) standard.
8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manuf ...
, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses integer DCT and DST
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typicall ...
transforms with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a container format for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video.
HE ...
(HEIF) is based on HEVC. , HEVC is used by 43% of video developers, and is the second most widely used video coding format
A video coding format (or sometimes video compression format) is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital video content (such as in a data file or bitstream). It typically uses a standardized video compression algo ...
after AVC.
Concept
In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of a frame of video to find areas that are redundant, both within a single frame and between consecutive frames. These redundant areas are then replaced with a short description instead of the original pixels. The primary changes for HEVC include the expansion of the pattern comparison and difference-coding areas from 16×16 pixel to sizes up to 64×64, improved variable-block-size segmentation, improved "intra" prediction within the same picture, improved motion vector prediction and motion region merging, improvedmotion compensation
Motion compensation in computing, is an algorithmic technique used to predict a frame in a video, given the previous and/or future frames by accounting for motion of the camera and/or objects in the video. It is employed in the encoding of video d ...
filtering, and an additional filtering step called sample-adaptive offset filtering. Effective use of these improvements requires much more signal processing capability for compressing the video, but has less impact on the amount of computation needed for decompression.
HEVC was standardized by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC), a collaboration between the ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
/IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
MPEG
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by International Organization for Standardization, ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC that sets standards for media coding, includ ...
and ITU-T Study Group 16
The ITU-T Study Group 16 (SG16) is a statutory group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with multimedia coding, systems and applications, such as video coding standards. It is responsible for standardization of ...
VCEG
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group (VCEG, also known as Question 6) is a working group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with standards for compression coding of video, images, audio, ...
. The ISO/IEC group refers to it as MPEG-H Part 2 and the ITU-T as H.265. The first version of the HEVC standard was ratified in January 2013 and published in June 2013. The second version, with multiview extensions (MV-HEVC), range extensions (RExt), and scalability extensions (SHVC), was completed and approved in 2014 and published in early 2015. Extensions for 3D video (3D-HEVC) were completed in early 2015, and extensions for screen content coding (SCC) were completed in early 2016 and published in early 2017, covering video containing rendered graphics, text, or animation as well as (or instead of) camera-captured video scenes. In October 2017, the standard was recognized by a Primetime Emmy Engineering Award
The Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards, or Engineering Emmys, are one of two sets of Emmy Awards that are presented for outstanding achievement in engineering development in the television industry. The Primetime Engineering Emmys are presented by ...
as having had a material effect on the technology of television.
HEVC contains technologies covered by patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
s owned by the organizations that participated in the JCT-VC. Implementing a device or software application that uses HEVC may require a license from HEVC patent holders. The ISO/IEC and ITU require companies that belong to their organizations to offer their patents on reasonable and non-discriminatory licensing
Reasonable and non-discriminatory (RAND) terms, also known as fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms, denote a voluntary licensing commitment that standards organizations often request from the owner of an intellectual property r ...
(RAND) terms. Patent licenses can be obtained directly from each patent holder, or through patent licensing bodies, such as MPEG LA
MPEG LA is an American company based in Denver, Colorado that licenses patent pools covering essential patents required for use of the MPEG-2, MPEG-4, IEEE 1394, VC-1, ATSC, MVC, MPEG-2 Systems, AVC/H.264 and HEVC standards.
History
MPEG LA ...
, Access Advance, and Velos Media.
The combined licensing fees currently offered by all of the patent licensing bodies are higher than for AVC. The licensing fees are one of the main reasons HEVC adoption has been low on the web and is why some of the largest tech companies (Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology c ...
, AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactur ...
, Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
, ARM
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between th ...
, Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, ...
, Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
, Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, wi ...
, Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a fil ...
, Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
, and more) have joined the Alliance for Open Media
The Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia) is a non-profit industry consortium that develops open, royalty-free technology for multimedia delivery headquartered in Wakefield, Massachusetts. It uses the ideas and principles of open web standard develo ...
, which finalized royalty-free alternative video coding format AV1
AOMedia Video 1 (AV1) is an open, royalty-free video coding format initially designed for video transmissions over the Internet. It was developed as a successor to VP9 by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia), a consortium founded in 2015 th ...
on March 28, 2018.
History
The HEVC format was jointly developed by more than a dozen organisations across the world. The majority of active patent contributions towards the development of the HEVC format came from five organizations:Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of ...
(4,249 patents), General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
(1,127 patents), M&K Holdings (907 patents), NTT ( patents), and JVC Kenwood
, stylized as JVCKENWOOD, is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Yokohama, Japan. It was formed from the merger of Victor Company of Japan, Ltd (JVC) and Kenwood Corporation on October 1, 2008. Upon creation, Haruo Kaw ...
(628 patents). Other patent holders include Fujitsu
is a Japanese multinational information and communications technology equipment and services corporation, established in 1935 and headquartered in Tokyo. Fujitsu is the world's sixth-largest IT services provider by annual revenue, and the la ...
, Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
, Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western ca ...
, Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, KAIST
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) is a national research university located in Daedeok Innopolis, Daejeon, South Korea. KAIST was established by the Korean government in 1971 as the nation's first public, research ...
, Kwangwoon University
Kwangwoon University (Abbreviated to Kwangwoon, KW and KWU) is a comprehensive, coeducational and private research university in Seoul (Wolgye Dong, Nowon-gu), South Korea, offering undergraduate and graduate programs (Master and Doctor). Chosu ...
, MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
, Sungkyunkwan University
Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU or simply ''Seongdae'', Hangul: 성균관대학교; Hanja: 成均館大學校) is a private comprehensive research university in South Korea. The institution traces its origins to the historic Sungkyunkwan, founde ...
, Funai
is a Japanese consumer electronics company headquartered in Daitō, Osaka. Apart from producing its own branded electronic products, it is also an OEM providing assembled televisions and video players/recorders to major corporations such as Sh ...
, Hikvision, KBS, KT and NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
.
Previous work
In 2004, the ITU-TVideo Coding Experts Group
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group (VCEG, also known as Question 6) is a working group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with standards for compression coding of video, images, audio, ...
(VCEG) began a major study of technology advances that could enable creation of a new video compression standard (or substantial compression-oriented enhancements of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard). In October 2004, various techniques for potential enhancement of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard were surveyed. In January 2005, at the next meeting of VCEG, VCEG began designating certain topics as "Key Technical Areas" (KTA) for further investigation. A software codebase called the KTA codebase was established for evaluating such proposals. The KTA software was based on the Joint Model (JM) reference software that was developed by the MPEG & VCEG Joint Video Team for H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Additional proposed technologies were integrated into the KTA software and tested in experiment evaluations over the next four years.
Two approaches for standardizing enhanced compression technology were considered: either creating a new standard or creating extensions of H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. The project had tentative names ''H.265'' and ''H.NGVC'' (Next-generation Video Coding), and was a major part of the work of VCEG until its evolution into the HEVC joint project with MPEG in 2010.
The preliminary requirements for NGVC were the capability to have a bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction w ...
reduction of 50% at the same subjective image quality compared with the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC High profile and computational complexity ranging from 1/2 to 3 times that of the High profile. NGVC would be able to provide 25% bit rate reduction along with 50% reduction in complexity at the same perceived video quality as the High profile, or to provide greater bit rate reduction with somewhat higher complexity.
The ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
/IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
Moving Picture Experts Group
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics, and genomic data; and transmission and f ...
(MPEG) started a similar project in 2007, tentatively named ''High-performance Video Coding''. An agreement of getting a bit rate reduction of 50% had been decided as the goal of the project by July 2007. Early evaluations were performed with modifications of the KTA reference software encoder developed by VCEG. By July 2009, experimental results showed average bit reduction of around 20% compared with AVC High Profile; these results prompted MPEG to initiate its standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
effort in collaboration with VCEG.
Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding
MPEG and VCEG established a Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC) to develop the HEVC standard.Standardization
A formal joint Call for Proposals on video compression technology was issued in January 2010 by VCEG and MPEG, and proposals were evaluated at the first meeting of the MPEG & VCEG Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC), which took place in April 2010. A total of 27 full proposals were submitted. Evaluations showed that some proposals could reach the same visual quality as AVC at only half the bit rate in many of the test cases, at the cost of 2–10× increase in computational complexity, and some proposals achieved good subjective quality and bit rate results with lower computational complexity than the reference AVC High profile encodings. At that meeting, the name ''High Efficiency Video Coding'' (HEVC) was adopted for the joint project. Starting at that meeting, the JCT-VC integrated features of some of the best proposals into a single software codebase and a "Test Model under Consideration", and performed further experiments to evaluate various proposed features. The first working draft specification of HEVC was produced at the third JCT-VC meeting in October 2010. Many changes in the coding tools and configuration of HEVC were made in later JCT-VC meetings. On January 25, 2013, the ITU announced that HEVC had received first stage approval (consent) in the ITU-T Alternative Approval Process (AAP). On the same day, MPEG announced that HEVC had been promoted to Final Draft International Standard (FDIS) status in the MPEG standardization process. On April 13, 2013, HEVC/H.265 was approved as an ITU-T standard. The standard was formally published by the ITU-T on June 7, 2013, and by the ISO/IEC on November 25, 2013. On July 11, 2014, MPEG announced that the 2nd edition of HEVC will contain three recently completed extensions which are the multiview extensions (MV-HEVC), the range extensions (RExt), and the scalability extensions (SHVC). On October 29, 2014, HEVC/H.265 version 2 was approved as an ITU-T standard. It was then formally published on January 12, 2015. On April 29, 2015, HEVC/H.265 version 3 was approved as an ITU-T standard. On June 3, 2016, HEVC/H.265 version 4 was consented in the ITU-T and was not approved during a vote in October 2016. On December 22, 2016, HEVC/H.265 version 4 was approved as an ITU-T standard.Patent licensing
On September 29, 2014,MPEG LA
MPEG LA is an American company based in Denver, Colorado that licenses patent pools covering essential patents required for use of the MPEG-2, MPEG-4, IEEE 1394, VC-1, ATSC, MVC, MPEG-2 Systems, AVC/H.264 and HEVC standards.
History
MPEG LA ...
announced their HEVC license which covers the essential patents from 23 companies. The first 100,000 "devices" (which includes software implementations) are royalty free, and after that the fee is $0.20 per device up to an annual cap of $25 million. This is significantly more expensive than the fees on AVC, which were $0.10 per device, with the same 100,000 waiver, and an annual cap of $6.5 million. MPEG LA does not charge any fee on the content itself, something they had attempted when initially licensing AVC, but subsequently dropped when content producers refused to pay it. The license has been expanded to include the profiles in version 2 of the HEVC standard.
When the MPEG LA terms were announced, commenters noted that a number of prominent patent holders were not part of the group. Among these were AT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's largest telecommunications company by revenue and the third largest provider of mobile tel ...
, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
, Nokia
Nokia Corporation (natively Nokia Oyj, referred to as Nokia) is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporatio ...
, and Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, United States. After having lost $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009, the company split into two independent p ...
. Speculation at the time was that these companies would form their own licensing pool to compete with or add to the MPEG LA pool. Such a group was formally announced on March 26, 2015, as HEVC Advance. The terms, covering 500 essential patents, were announced on July 22, 2015, with rates that depend on the country of sale, type of device, HEVC profile, HEVC extensions, and HEVC optional features. Unlike the MPEG LA terms, HEVC Advance reintroduced license fees on content encoded with HEVC, through a revenue sharing fee.
The initial HEVC Advance license had a maximum royalty rate of US$2.60 per device for Region 1 countries and a content royalty rate of 0.5% of the revenue generated from HEVC video services. Region 1 countries in the HEVC Advance license include the United States, Canada, European Union, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, and others. Region 2 countries are countries not listed in the Region 1 country list. The HEVC Advance license had a maximum royalty rate of US$1.30 per device for Region 2 countries. Unlike MPEG LA, there was no annual cap. On top of this, HEVC Advance also charged a royalty rate of 0.5% of the revenue generated from video services encoding content in HEVC.
When they were announced, there was considerable backlash from industry observers about the "unreasonable and greedy" fees on devices, which were about seven times that of the MPEG LA's fees. Added together, a device would require licenses costing $2.80, twenty-eight times as expensive as AVC, as well as license fees on the content. This led to calls for "content owners oband together and agree not to license from HEVC Advance". Others argued the rates might cause companies to switch to competing standards such as Daala
Daala is a video coding format under development by the Xiph.Org Foundation under the lead of Timothy B. Terriberry mainly sponsored by the Mozilla Corporation. Like Theora and Opus, Daala is available free of any royalties and its reference im ...
and VP9
VP9 is an open and royalty-free video coding format developed by Google.
VP9 is the successor to VP8 and competes mainly with MPEG's High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265).
At first, VP9 was mainly used on Google's video platform YouTube. ...
.
On December 18, 2015, HEVC Advance announced changes in the royalty rates. The changes include a reduction in the maximum royalty rate for Region 1 countries to US$2.03 per device, the creation of annual royalty caps, and a waiving of royalties on content that is free to end users. The annual royalty caps for a company is US$40 million for devices, US$5 million for content, and US$2 million for optional features.
On February 3, 2016, Technicolor SA
Vantiva SA, formerly Technicolor SA, Thomson SARL, and Thomson Multimedia, is a French multinational corporation that provides creative services and technology products for the communication, media and entertainment industries. Vantiva's headq ...
announced that they had withdrawn from the HEVC Advance patent pool
In patent law, a patent pool is a consortium of at least two companies agreeing to cross-license patents relating to a particular technology. The creation of a patent pool can save patentees and licensees time and money, and, in case of blocking ...
and would be directly licensing their HEVC patents. HEVC Advance previously listed 12 patents from Technicolor. Technicolor announced that they had rejoined on October 22, 2019.
On November 22, 2016, HEVC Advance announced a major initiative, revising their policy to allow software implementations of HEVC to be distributed directly to consumer mobile devices and personal computers royalty free, without requiring a patent license.
On March 31, 2017, Velos Media announced their HEVC license which covers the essential patents from Ericsson, Panasonic, Qualcomm Incorporated, Sharp, and Sony.
the MPEG LA HEVC patent list is 164 pages long.
Patent holders
The following organizations currently hold the most active patents in the HEVC patent pools listed byMPEG LA
MPEG LA is an American company based in Denver, Colorado that licenses patent pools covering essential patents required for use of the MPEG-2, MPEG-4, IEEE 1394, VC-1, ATSC, MVC, MPEG-2 Systems, AVC/H.264 and HEVC standards.
History
MPEG LA ...
and HEVC Advance.
Versions
Versions of the HEVC/H.265 standard using the ITU-T approval dates. * Version 1: (April 13, 2013) First approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard containing Main, Main10, and Main Still Picture profiles. * Version 2: (October 29, 2014) Second approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds 21 range extensions profiles, two scalable extensions profiles, and one multi-view extensions profile. * Version 3: (April 29, 2015) Third approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds the 3D Main profile. * Version 4: (December 22, 2016) Fourth approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds seven screen content coding extensions profiles, three high throughput extensions profiles, and four scalable extensions profiles. * Version 5: (February 13, 2018) Fifth approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds additional SEI messages that include omnidirectional video SEI messages, a Monochrome 10 profile, a Main 10 Still Picture profile, and corrections to various minor defects in the prior content of the Specification. * Version 6: (June 29, 2019) Sixth approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds additional SEI messages that include SEI manifest and SEI prefix messages, and corrections to various minor defects in the prior content of the Specification. * Version 7: (November 29, 2019) Seventh approved version of the HEVC/H.265 standard which adds additional SEI messages for fisheye video information and annotated regions, and also includes corrections to various minor defects in the prior content of the Specification. * Version 8: As of August 2021 Version 8 is in "Additional Review" status while Version 7 is in force.Implementations and products
2012
On February 29, 2012, at the 2012Mobile World Congress
MWC Barcelona (formerly but still commonly referred to as Mobile World Congress) is an annual trade show organised by GSMA, dedicated primarily to the mobile communications industry.
The event is held in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain at the Fir ...
, Qualcomm
Qualcomm () is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software, and services related to wireless technology. It owns patents critical to the 5G, 4 ...
demonstrated a HEVC decoder running on an Android tablet, with a Qualcomm Snapdragon
Snapdragon is a suite of system on a chip (SoC) semiconductor products for mobile devices designed and marketed by Qualcomm Technologies Inc. The Snapdragon's central processing unit (CPU) uses the ARM architecture. A single SoC may include mu ...
S4 dual-core processor running at 1.5 GHz, showing H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and HEVC versions of the same video content playing side by side. In this demonstration, HEVC reportedly showed almost a 50% bit rate reduction compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC.
2013
On February 11, 2013, researchers fromMIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
demonstrated the world's first published HEVC ASIC decoder at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference
International Solid-State Circuits Conference is a global forum for presentation of advances in solid-state circuits and Systems-on-a-Chip. The conference is held every year in February at the San Francisco Marriott Marquis in downtown San Fr ...
(ISSCC) 2013. Their chip was capable of decoding a 3840×2160p at 30 fps video stream in real time, consuming under 0.1 W of power.
On April 3, 2013, Ateme
Ateme S.A. is a multinational company that specializes in video delivery, namely software for video compression based on High_Efficiency_Video_Coding, H.265 / High_Efficiency_Video_Coding, HEVC standards; MPEG4; MPEG2 Data_compression#Video, encod ...
announced the availability of the first open source implementation of a HEVC software player based on the OpenHEVC decoder and GPAC video player which are both licensed under LGPL
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own ...
. The OpenHEVC decoder supports the Main profile of HEVC and can decode 1080p at 30 fps video using a single core CPU. A live transcoder that supports HEVC and used in combination with the GPAC video player was shown at the ATEME booth at the NAB Show in April 2013.
On July 23, 2013, MulticoreWare
MulticoreWare Inc is a software development company, offering products and services related to HEVC video compression, machine learning (specifically, convolutional neural networks), compilers for heterogeneous computing, and software perform ...
announced, and made the source code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the wo ...
available for the x265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a ...
HEVC Encoder Library under the GPL v2 license.
On August 8, 2013, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone
, commonly known as NTT, is a Japanese telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Ranked 55th in Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500, NTT is the fourth largest telecommunications company in the world in terms of revenue, as w ...
announced the release of their HEVC-1000 SDK software encoder which supports the Main 10 profile, resolutions up to 7680×4320, and frame rates up to 120 fps.
On November 14, 2013, DivX developers released information on HEVC decoding performance using an Intel i7 CPU at 3.5 GHz with 4 cores and 8 threads. The DivX 10.1 Beta decoder was capable of 210.9 fps at 720p, 101.5 fps at 1080p, and 29.6 fps at 4K.
On December 18, 2013, ViXS Systems announced shipments of their XCode (not to be confused with Apple's Xcode IDE for MacOS) 6400 SoC which was the first SoC to support the Main 10 profile of HEVC.
2014
On April 5, 2014, at the NAB show, eBrisk Video, Inc. and Altera Corporation demonstrated an FPGA-accelerated HEVC Main10 encoder that encoded 4Kp60/10-bit video in real-time, using a dual-Xeon E5-2697-v2 platform. On August 13, 2014,Ittiam Systems
Ittiam Systems is a venture capital funded technology company founded by ex-Managing Director of Texas Instruments' India Srini Rajam in 2001. It is headquartered in Bangalore, India and has marketing offices in the United States, UK, France, ...
announced availability of its third generation H.265/HEVC codec with 4:2:2 12-bit support.
On September 5, 2014, the Blu-ray Disc Association announced that the 4K Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a Digital media, digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and c ...
specification would support HEVC-encoded 4K video at 60 fps, the Rec. 2020 color space, high dynamic range
High dynamic range (HDR) is a dynamic range higher than usual, synonyms are wide dynamic range, extended dynamic range, expanded dynamic range.
The term is often used in discussing the dynamic range of various signals such as images, videos, au ...
( PQ and HLG), and 10-bit color depth
Color depth or colour depth (see spelling differences), also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. When referring to ...
. 4K Blu-ray Discs have a data rate of at least 50 Mbit/s and disc capacity up to 100 GB. 4K Blu-ray Discs and players became available for purchase in 2015 or 2016.
On September 9, 2014, Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
announced the iPhone 6
The iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus are smartphones that were designed and marketed by Apple Inc. They are the eighth generation of the iPhone, succeeding the iPhone 5, iPhone 5C and iPhone 5S, and were announced on September 9, 2014, and rele ...
and iPhone 6 Plus which support HEVC/H.265 for FaceTime over cellular.
On September 18, 2014, Nvidia released the GeForce GTX 980 (GM204) and GTX 970 (GM204), which includes Nvidia NVENC
Nvidia NVENC (short for Nvidia Encoder) is a feature in Nvidia graphics cards that performs video encoding, offloading this compute-intensive task from the CPU to a dedicated part of the GPU. It was introduced with the Kepler-based GeForce 600 ...
, the world's first HEVC hardware encoder in a discrete graphics card.
On October 31, 2014, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
confirmed that Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It is the direct successor to Windows 8.1, which was released nearly two years earlier. It was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on J ...
will support HEVC out of the box, according to a statement from Gabriel Aul, the leader of Microsoft Operating Systems Group's Data and Fundamentals Team. Windows 10 Technical Preview Build 9860 added platform level support for HEVC and Matroska
Matroska is a project to create a container format that can hold an unlimited number of video, audio, picture, or subtitle tracks in one file. The Matroska Multimedia Container is similar in concept to other containers like AVI, MP4, or Adva ...
.
On November 3, 2014, Android Lollipop
Android Lollipop (code name, codenamed Android L during development) is the fifth major version of the Android (operating system), Android mobile operating system developed by Google and the 12th version of Android, spanning versions between 5.0 ...
was released with out of the box support for HEVC using Ittiam Systems
Ittiam Systems is a venture capital funded technology company founded by ex-Managing Director of Texas Instruments' India Srini Rajam in 2001. It is headquartered in Bangalore, India and has marketing offices in the United States, UK, France, ...
' software.
2015
On January 5, 2015, ViXS Systems announced the XCode 6800 which is the first SoC to support the Main 12 profile of HEVC. On January 5, 2015, Nvidia officially announced the Tegra X1 SoC with full fixed-function HEVC hardware decoding. On January 22, 2015,Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
released the GeForce GTX 960 (GM206), which includes the world's first full fixed function HEVC Main/Main10 hardware decoder in a discrete graphics card.
On February 23, 2015, Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufact ...
(AMD) announced that their UVD
Unified Video Decoder (UVD, previously called Universal Video Decoder) is the name given to AMD's dedicated video decoding ASIC. There are multiple versions implementing a multitude of video codecs, such as H.264 and VC-1.
UVD was introduced wit ...
ASIC to be found in the Carrizo APUs would be the first x86 based CPUs to have a HEVC hardware decoder.
On February 27, 2015, VLC media player
VLC media player (previously the VideoLAN Client and commonly known as simply VLC) is a free and open-source, portable, cross-platform media player software and streaming media server developed by the VideoLAN project. VLC is available for desk ...
version 2.2.0 was released with robust support of HEVC playback. The corresponding versions on Android and iOS are also able to play HEVC.
On March 31, 2015, VITEC announced the MGW Ace which was the first 100% hardware-based portable HEVC encoder that provides mobile HEVC encoding.
On August 5, 2015, Intel launched Skylake products with full fixed function Main/8-bit decoding/encoding and hybrid/partial Main10/10-bit decoding.
On September 9, 2015 Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
announced the Apple A9
The Apple A9 is a 64-bit ARM-based system-on-chip (SoC), designed by Apple Inc. Manufactured for Apple by both TSMC and Samsung, it first appeared in the iPhone 6S and 6S Plus which were introduced on September 9, 2015. Apple states that it has ...
chip, first used in the iPhone 6S, its first processor with a hardware HEVC decoder supporting Main 8 and 10. This feature would not be unlocked until the release of iOS 11
iOS 11 is the iOS version history, eleventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc., being the successor to iOS 10. It was announced at the company's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, Worldwide Developers C ...
in 2017.Apple has chosen HEVC as its next-generation video codec8 June 2017.
2016
On April 11, 2016, full HEVC (H.265) support was announced in the newestMythTV
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital ...
version (0.28).
On August 30, 2016, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
officially announced 7th generation Core CPUs (Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's ...
) products with full fixed function HEVC Main10 hardware decoding support.
On September 7, 2016 Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
announced the Apple A10
The Apple A10 Fusion is a 64-bit ARM-based system on a chip (SoC), designed by Apple Inc. and manufactured by TSMC. It first appeared in the iPhone 7 and 7 Plus which were introduced on September 7, 2016, and is used in the sixth generation iPa ...
chip, first used in the iPhone 7
The iPhone 7 and iPhone 7 Plus are smartphones that were designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc. They are the tenth generation of the iPhone. They were announced on September 7, 2016, at the Bill Graham Civic Auditorium in San Fr ...
, which included a hardware HEVC encoder supporting Main 8 and 10. This feature would not be unlocked until the release of iOS 11
iOS 11 is the iOS version history, eleventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc., being the successor to iOS 10. It was announced at the company's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, Worldwide Developers C ...
in 2017.
On October 25, 2016, Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
released the GeForce GTX 1050Ti (GP107) and GeForce GTX 1050 (GP107), which includes full fixed function HEVC Main10/Main12 hardware decoder.
2017
On June 5, 2017,Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
announced HEVC H.265 support in macOS High Sierra
macOS High Sierra (version 10.13) is the fourteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. macOS High Sierra was announced at the WWDC 2017 on June 5, 2017 and was released on September 25, 2017. ...
, iOS 11
iOS 11 is the iOS version history, eleventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc., being the successor to iOS 10. It was announced at the company's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, Worldwide Developers C ...
, tvOS
tvOS (formerly known as Apple TV Software) is an operating system developed by Apple Inc. for the Apple TV, a digital media player. In the first-generation Apple TV, Apple TV Software was based on Mac OS X. Starting with the second-generation ...
, HTTP Live Streaming
HTTP Live Streaming (also known as HLS) is an HTTP-based adaptive bitrate streaming communications protocol developed by Apple Inc. and released in 2009. Support for the protocol is widespread in media players, web browsers, mobile devices, and st ...
and Safari
A safari (; ) is an overland journey to observe wild animals, especially in eastern or southern Africa. The so-called "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, and Cape buffalo – particularly form an importa ...
.
On June 25, 2017, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
released a free HEVC app extension for Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It is the direct successor to Windows 8.1, which was released nearly two years earlier. It was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on J ...
, enabling some Windows 10 devices with HEVC decoding hardware to play video using the HEVC format inside any app.
On September 19, 2017, Apple released iOS 11
iOS 11 is the iOS version history, eleventh major release of the iOS mobile operating system developed by Apple Inc., being the successor to iOS 10. It was announced at the company's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, Worldwide Developers C ...
and tvOS 11
tvOS (formerly known as Apple TV Software) is an operating system developed by Apple Inc. for the Apple TV, a digital media player. In the first-generation Apple TV, Apple TV Software was based on Mac OS X. Starting with the second-generation, ...
with HEVC encoding & decoding support.
On September 25, 2017, Apple released macOS High Sierra
macOS High Sierra (version 10.13) is the fourteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop operating system for Macintosh computers. macOS High Sierra was announced at the WWDC 2017 on June 5, 2017 and was released on September 25, 2017. ...
with HEVC encoding & decoding support.
On September 28, 2017, GoPro
GoPro, Inc. (marketed as GoPro and sometimes stylized as GoPRO) is an American technology company founded in 2002 by Nick Woodman. It manufactures action cameras and develops its own mobile apps and video-editing software. Founded as Woodman La ...
released the Hero6 Black action camera, with 4K60P HEVC video encoding.
On October 17, 2017, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
removed HEVC decoding support from Windows 10 with the Version 1709 Fall Creators Update, making HEVC available instead as a separate, paid download from the Microsoft Store.
On November 2, 2017, Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
released the GeForce GTX 1070 Ti (GP104), which includes full fixed function HEVC Main10/Main12 hardware decoder.
2018
On September 20, 2018,Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
released the GeForce RTX 2080 (TU104), which includes full fixed function HEVC Main 4:4:4 12 hardware decoder.
2022
On October 25 2022, Chrome released version 107, which starts supporting HEVC hardware decoding for all platforms "out of box", if the hardware is supported.Browser support
HEVC is implemented in these web browsers: * Android browser (since version 5 from November 2014) *Safari
A safari (; ) is an overland journey to observe wild animals, especially in eastern or southern Africa. The so-called "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, and Cape buffalo – particularly form an importa ...
(since version 11 from September 2017)
* Edge
Edge or EDGE may refer to:
Technology Computing
* Edge computing, a network load-balancing system
* Edge device, an entry point to a computer network
* Adobe Edge, a graphical development application
* Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by ...
(since version 77 from July 2017, supported on Windows 10 1709+ when HEVC video extensions is installed)
* Chrome (since version 107 from October 2022, supported on Windows 8+, macOS 11+, Android 5.0+, ChromeOS, and Linux with supported hardware)
In May 2021, an estimated 18% of browsers in use on desktop and notebook systems were able to play HEVC videos in HTML5 webpages, based on data from StatCounter.
Operating system support
Coding efficiency
 The design of most video coding standards is primarily aimed at having the highest coding efficiency. Coding efficiency is the ability to encode video at the lowest possible bit rate while maintaining a certain level of video quality. There are two standard ways to measure the coding efficiency of a video coding standard, which are to use an objective metric, such as
The design of most video coding standards is primarily aimed at having the highest coding efficiency. Coding efficiency is the ability to encode video at the lowest possible bit rate while maintaining a certain level of video quality. There are two standard ways to measure the coding efficiency of a video coding standard, which are to use an objective metric, such as peak signal-to-noise ratio
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many signals have a very wide dynamic ...
(PSNR), or to use subjective assessment of video quality. Subjective assessment of video quality is considered to be the most important way to measure a video coding standard since humans perceive video quality subjectively.
HEVC benefits from the use of larger coding tree unit Coding tree unit (CTU) is the basic processing unit of the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) video standard and conceptually corresponds in structure to macroblock units that were used in several previous video standards. CTU is also referred to ...
(CTU) sizes. This has been shown in PSNR tests with a HM-8.0 HEVC encoder where it was forced to use progressively smaller CTU sizes. For all test sequences, when compared with a 64×64 CTU size, it was shown that the HEVC bit rate increased by 2.2% when forced to use a 32×32 CTU size, and increased by 11.0% when forced to use a 16×16 CTU size. In the Class A test sequences, where the resolution of the video was 2560×1600, when compared with a 64×64 CTU size, it was shown that the HEVC bit rate increased by 5.7% when forced to use a 32×32 CTU size, and increased by 28.2% when forced to use a 16×16 CTU size. The tests showed that large CTU sizes increase coding efficiency while also reducing decoding time.
The HEVC Main Profile (MP) has been compared in coding efficiency to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC High Profile (HP), MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related tec ...
Advanced Simple Profile (ASP), H.263 High Latency Profile (HLP), and H.262/MPEG-2 Main Profile (MP). The video encoding was done for entertainment applications and twelve different bitrates were made for the nine video test sequences with a HM-8.0 HEVC encoder being used. Of the nine video test sequences, five were at HD resolution, while four were at WVGA (800×480) resolution. The bit rate reductions for HEVC were determined based on PSNR with HEVC having a bit rate reduction of 35.4% compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP, 63.7% compared with MPEG-4 ASP, 65.1% compared with H.263 HLP, and 70.8% compared with H.262/MPEG-2 MP.
HEVC MP has also been compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP for subjective video quality. The video encoding was done for entertainment applications and four different bitrates were made for nine video test sequences with a HM-5.0 HEVC encoder being used. The subjective assessment was done at an earlier date than the PSNR comparison and so it used an earlier version of the HEVC encoder that had slightly lower performance. The bit rate reductions were determined based on subjective assessment using mean opinion score Mean opinion score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system. It is the arithmetic mean over all individual "values on a predefined scale t ...
values. The overall subjective bitrate reduction for HEVC MP compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP was 49.3%.
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
(EPFL) did a study to evaluate the subjective video quality of HEVC at resolutions higher than HDTV. The study was done with three videos with resolutions of 3840×1744 at 24 fps, 3840×2048 at 30 fps, and 3840×2160 at 30 fps. The five second video sequences showed people on a street, traffic, and a scene from the open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ...
computer animated
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes ( still images) and dynamic images ( moving images), while computer animation re ...
movie ''Sintel
''Sintel'', code-named ''Project Durian'' during production, is a 2010 computer-animated fantasy short film. It was the third Blender "open movie". It was produced by Ton Roosendaal, chairman of the Blender Foundation, written by Esther Wouda ...
''. The video sequences were encoded at five different bitrates using the HM-6.1.1 HEVC encoder and the JM-18.3 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC encoder. The subjective bit rate reductions were determined based on subjective assessment using mean opinion score values. The study compared HEVC MP with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP and showed that, for HEVC MP, the average bitrate reduction based on PSNR was 44.4%, while the average bitrate reduction based on subjective video quality was 66.5%.
In a HEVC performance comparison released in April 2013, the HEVC MP and Main 10 Profile (M10P) were compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP and High 10 Profile (H10P) using 3840×2160 video sequences. The video sequences were encoded using the HM-10.0 HEVC encoder and the JM-18.4 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC encoder. The average bit rate reduction based on PSNR was 45% for inter frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage fro ...
video.
In a video encoder comparison released in December 2013, the HM-10.0 HEVC encoder was compared with the x264
x264 is a free and open-source software library and a command-line utility developed by VideoLAN for encoding video streams into the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video coding format. It is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
History ...
encoder (version r2334) and the VP9
VP9 is an open and royalty-free video coding format developed by Google.
VP9 is the successor to VP8 and competes mainly with MPEG's High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265).
At first, VP9 was mainly used on Google's video platform YouTube. ...
encoder (version v1.2.0-3088-ga81bd12). The comparison used the Bjøntegaard-Delta bit-rate (BD-BR) measurement method, in which negative values tell how much lower the bit rate is reduced, and positive values tell how much the bit rate is increased for the same PSNR. In the comparison, the HM-10.0 HEVC encoder had the highest coding efficiency and, on average, to get the same objective quality, the x264 encoder needed to increase the bit rate by 66.4%, while the VP9 encoder needed to increase the bit rate by 79.4%.
In a subjective video performance comparison released in May 2014, the JCT-VC compared the HEVC Main profile to the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC High profile. The comparison used mean opinion score values and was conducted by the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...University of the West of Scotland
The University of the West of Scotland ( gd, Oilthigh na h-Alba an Iar), formerly the University of Paisley, is a public university with four campuses in south-western Scotland, in the towns of Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, Blantyre, South Lanar ...
. The video sequences were encoded using the HM-12.1 HEVC encoder and the JM-18.5 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC encoder. The comparison used a range of resolutions and the average bit rate reduction for HEVC was 59%. The average bit rate reduction for HEVC was 52% for 480p, 56% for 720p, 62% for 1080p, and 64% for 4K UHD.
In a subjective video codec comparison released in August 2014 by the EPFL, the HM-15.0 HEVC encoder was compared with the VP9 1.2.0–5183 encoder and the JM-18.8 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC encoder. Four 4K resolutions sequences were encoded at five different bit rates with the encoders set to use an intra period of one second. In the comparison, the HM-15.0 HEVC encoder had the highest coding efficiency and, on average, for the same subjective quality the bit rate could be reduced by 49.4% compared with the VP9 1.2.0–5183 encoder, and it could be reduced by 52.6% compared with the JM-18.8 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC encoder.
In August, 2016, Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a fil ...
published the results of a large-scale study comparing the leading open-source HEVC encoder, x265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a ...
, with the leading open-source AVC encoder, x264
x264 is a free and open-source software library and a command-line utility developed by VideoLAN for encoding video streams into the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video coding format. It is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
History ...
and the reference VP9
VP9 is an open and royalty-free video coding format developed by Google.
VP9 is the successor to VP8 and competes mainly with MPEG's High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265).
At first, VP9 was mainly used on Google's video platform YouTube. ...
encoder, libvpx. Using their advanced Video Multimethod Assessment Fusion (VMAF) video quality measurement tool, Netflix found that x265 delivered identical quality at bit rates ranging from 35.4% to 53.3% lower than x264, and from 17.8% to 21.8% lower than VP9.
Features
HEVC was designed to substantially improve coding efficiency compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC HP, i.e. to reducebitrate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction w ...
requirements by half with comparable image quality Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy with which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of ...
, at the expense of increased computational complexity. HEVC was designed with the goal of allowing video content to have a data compression ratio of up to 1000:1. Depending on the application requirements, HEVC encoders can trade off computational complexity, compression rate, robustness to errors, and encoding delay time. Two of the key features where HEVC was improved compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC was support for higher resolution video and improved parallel processing methods.
HEVC is targeted at next-generation HDTV displays and content capture systems which feature progressive scan
Progressive scanning (alternatively referred to as noninterlaced scanning) is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video used ...
ned frame rate
Frame rate (expressed in or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (frames) are captured or displayed. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be ca ...
s and display resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is ...
s from QVGA
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height ar ...
(320×240) to 4320p (7680×4320), as well as improved picture quality in terms of noise level, color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represent ...
s, and dynamic range
Dynamic range (abbreviated DR, DNR, or DYR) is the ratio between the largest and smallest values that a certain quantity can assume. It is often used in the context of signals, like sound and light. It is measured either as a ratio or as a base-1 ...
.
Video coding layer
The HEVC video coding layer uses the same "hybrid" approach used in all modern video standards, starting fromH.261
H.261 is an ITU-T video compression standard, first ratified in November 1988. It is the first member of the H.26x family of video coding standards in the domain of the ITU-T Study Group 16 Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG, then Specialists Gro ...
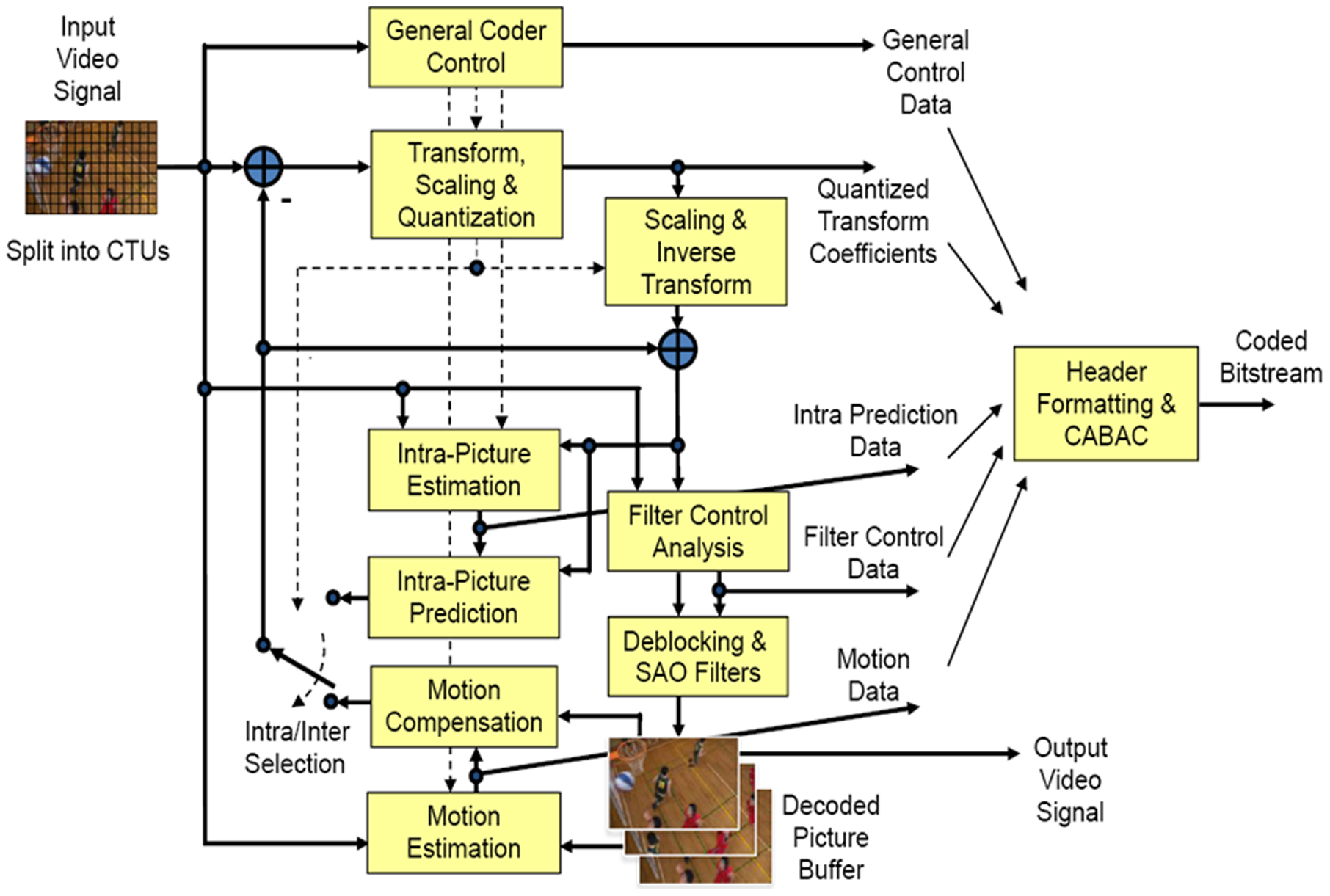
, in that it uses inter-/intra-picture prediction and 2D transform coding. A HEVC encoder first proceeds by splitting a picture into block shaped regions for the first picture, or the first picture of a random access point, which uses intra-picture prediction. Intra-picture prediction is when the prediction of the blocks in the picture is based only on the information in that picture. For all other pictures, inter-picture prediction is used, in which prediction information is used from other pictures. After the prediction methods are finished and the picture goes through the loop filters, the final picture representation is stored in the decoded picture buffer. Pictures stored in the decoded picture buffer can be used for the prediction of other pictures.
HEVC was designed with the idea that progressive scan
Progressive scanning (alternatively referred to as noninterlaced scanning) is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video used ...
video would be used and no coding tools were added specifically for interlaced video
Interlaced video (also known as interlaced scan) is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This ...
. Interlace specific coding tools, such as MBAFF and PAFF, are not supported in HEVC. HEVC instead sends metadata
Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive metadata – the descriptive ...
that tells how the interlaced video was sent. Interlaced video may be sent either by coding each frame as a separate picture or by coding each field as a separate picture. For interlaced video HEVC can change between frame coding and field coding using Sequence Adaptive Frame Field (SAFF), which allows the coding mode to be changed for each video sequence. This allows interlaced video to be sent with HEVC without needing special interlaced decoding processes to be added to HEVC decoders.
;Color spaces
The HEVC standard supports color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represent ...
s such as generic film, NTSC
The first American standard for analog television broadcast was developed by National Television System Committee (NTSC)National Television System Committee (1951–1953), Report and Reports of Panel No. 11, 11-A, 12–19, with Some supplement ...
, PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
, Rec. 601
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601 (or its former name CCIR 601) is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR (an organization, which has since been renamed as the Internatio ...
, Rec. 709
Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.
The most recent version is BT.709-6 released in 2015. BT.709-6 defines the P ...
, Rec. 2020, Rec. 2100
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer func ...
, SMPTE 170M, SMPTE 240M, sRGB
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission ( ...
, sYCC, xvYCC
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 an ...
, XYZ, and externally specified color spaces. HEVC supports color encoding representations such as RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three addi ...
, YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-diffe ...
, and YCoCg The YCoCg color model, also known as the YCgCo color model, is the color space formed from a simple transformation of an associated RGB color space into a ''luma'' value (denoted as Y) and two '' chroma'' values called ''chrominance green'' (Cg) and ...
.
Coding tools
Coding tree unit
HEVC replaces 16×16 pixelmacroblock The macroblock is a processing unit in image and video compression formats based on linear block transforms, typically the discrete cosine transform (DCT). A macroblock typically consists of 16×16 samples, and is further subdivided into transform ...
s, which were used with previous standards, with coding tree units (CTUs) which can use larger block structures of up to 64×64 samples and can better sub-partition the picture into variable sized structures. HEVC initially divides the picture into CTUs which can be 64×64, 32×32, or 16×16 with a larger pixel block size usually increasing the coding efficiency.
Inverse transforms
HEVC specifies four transform units (TUs) sizes of 4×4, 8×8, 16×16, and 32×32 to code the prediction residual. A CTB may be recursively partitioned into 4 or more TUs. TUs use integer basis functions based on the discrete cosine transform (DCT). In addition, 4×4 luma transform blocks that belong to an intra coded region are transformed using an integer transform that is derived from discrete sine transform (DST). This provides a 1% bit rate reduction but was restricted to 4×4 luma transform blocks due to marginal benefits for the other transform cases. Chroma uses the same TU sizes as luma so there is no 2×2 transform for chroma.Parallel processing tools
* Tiles allow for the picture to be divided into a grid of rectangular regions that can independently be decoded/encoded. The main purpose of tiles is to allow for parallel processing. Tiles can be independently decoded and can even allow for random access to specific regions of a picture in a video stream. * Wavefront parallel processing (WPP) is when a slice is divided into rows of CTUs in which the first row is decoded normally but each additional row requires that decisions be made in the previous row. WPP has the entropy encoder use information from the preceding row of CTUs and allows for a method of parallel processing that may allow for better compression than tiles. * Tiles and WPP are allowed, but are optional. If tiles are present, they must be at least 64 pixels high and 256 pixels wide with a level specific limit on the number of tiles allowed. * Slices can, for the most part, be decoded independently from each other with the main purpose of tiles being the re-synchronization in case of data loss in the video stream. Slices can be defined as self-contained in that prediction is not made across slice boundaries. When in-loop filtering is done on a picture though, information across slice boundaries may be required. Slices are CTUs decoded in the order of the raster scan, and different coding types can be used for slices such as I types, P types, or B types. * Dependent slices can allow for data related to tiles or WPP to be accessed more quickly by the system than if the entire slice had to be decoded. The main purpose of dependent slices is to allow for low-delay video encoding due to its lower latency.Other coding tools
;Entropy coding HEVC uses acontext-adaptive binary arithmetic coding Context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) is a form of entropy encoding used in the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standards. It is a lossless compression technique, although the video coding standards in which it i ...
(CABAC) algorithm that is fundamentally similar to CABAC in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. CABAC is the only entropy encoder method that is allowed in HEVC while there are two entropy encoder methods allowed by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. CABAC and the entropy coding of transform coefficients in HEVC were designed for a higher throughput than H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, while maintaining higher compression efficiency for larger transform block sizes relative to simple extensions. For instance, the number of context coded bins have been reduced by 8× and the CABAC bypass-mode has been improved in terms of its design to increase throughput. Another improvement with HEVC is that the dependencies between the coded data has been changed to further increase throughput. Context modeling in HEVC has also been improved so that CABAC can better select a context that increases efficiency when compared with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC.
;Intra prediction
 HEVC specifies 33 directional modes for intra prediction compared with the 8 directional modes for intra prediction specified by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. HEVC also specifies DC intra prediction and planar prediction modes. The DC intra prediction mode generates a mean value by averaging reference samples and can be used for flat surfaces. The planar prediction mode in HEVC supports all block sizes defined in HEVC while the planar prediction mode in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC is limited to a block size of 16×16 pixels. The intra prediction modes use data from neighboring prediction blocks that have been previously decoded from within the same picture.
;Motion compensation
For the interpolation of fractional luma sample positions HEVC uses separable application of one-dimensional half-sample interpolation with an 8-tap filter or quarter-sample interpolation with a 7-tap filter while, in comparison, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC uses a two-stage process that first derives values at half-sample positions using separable one-dimensional 6-tap interpolation followed by integer rounding and then applies
HEVC specifies 33 directional modes for intra prediction compared with the 8 directional modes for intra prediction specified by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. HEVC also specifies DC intra prediction and planar prediction modes. The DC intra prediction mode generates a mean value by averaging reference samples and can be used for flat surfaces. The planar prediction mode in HEVC supports all block sizes defined in HEVC while the planar prediction mode in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC is limited to a block size of 16×16 pixels. The intra prediction modes use data from neighboring prediction blocks that have been previously decoded from within the same picture.
;Motion compensation
For the interpolation of fractional luma sample positions HEVC uses separable application of one-dimensional half-sample interpolation with an 8-tap filter or quarter-sample interpolation with a 7-tap filter while, in comparison, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC uses a two-stage process that first derives values at half-sample positions using separable one-dimensional 6-tap interpolation followed by integer rounding and then applies linear interpolation
In mathematics, linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials to construct new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points.
Linear interpolation between two known points
If the two known poin ...
between values at nearby half-sample positions to generate values at quarter-sample positions. HEVC has improved precision due to the longer interpolation filter and the elimination of the intermediate rounding error. For 4:2:0 video, the chroma samples are interpolated with separable one-dimensional 4-tap filtering to generate eighth-sample precision, while in comparison H.264/MPEG-4 AVC uses only a 2-tap bilinear filter (also with eighth-sample precision).
As in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, weighted prediction in HEVC can be used either with uni-prediction (in which a single prediction value is used) or bi-prediction (in which the prediction values from two prediction blocks are combined).
;Motion vector prediction
HEVC defines a signed 16-bit range for both horizontal and vertical motion vectors (MVs). This was added to HEVC at the July 2012 HEVC meeting with the mvLX variables. HEVC horizontal/vertical MVs have a range of −32768 to 32767 which given the quarter pixel precision used by HEVC allows for a MV range of −8192 to 8191.75 luma samples. This compares to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC which allows for a horizontal MV range of −2048 to 2047.75 luma samples and a vertical MV range of −512 to 511.75 luma samples.
HEVC allows for two MV modes which are Advanced Motion Vector Prediction (AMVP) and merge mode. AMVP uses data from the reference picture and can also use data from adjacent prediction blocks. The merge mode allows for the MVs to be inherited from neighboring prediction blocks. Merge mode in HEVC is similar to "skipped" and "direct" motion inference modes in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC but with two improvements. The first improvement is that HEVC uses index information to select one of several available candidates. The second improvement is that HEVC uses information from the reference picture list and reference picture index.
Loop filters
HEVC specifies two loop filters that are applied sequentially, with thedeblocking filter
A deblocking filter is a video filter applied to decoded compressed video to improve visual quality and prediction performance by smoothing the sharp edges which can form between macroblocks when block coding techniques are used. The filter aims ...
(DBF) applied first and the sample adaptive offset (SAO) filter applied afterwards. Both loop filters are applied in the inter-picture prediction loop, i.e. the filtered image is stored in the decoded picture buffer (DPB) as a reference for inter-picture prediction.
;Deblocking filter
The DBF is similar to the one used by H.264/MPEG-4 AVC but with a simpler design and better support for parallel processing. In HEVC the DBF only applies to a 8×8 sample grid while with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC the DBF applies to a 4×4 sample grid. DBF uses a 8×8 sample grid since it causes no noticeable degradation and significantly improves parallel processing because the DBF no longer causes cascading interactions with other operations. Another change is that HEVC only allows for three DBF strengths of 0 to 2. HEVC also requires that the DBF first apply horizontal filtering for vertical edges to the picture and only after that does it apply vertical filtering for horizontal edges to the picture. This allows for multiple parallel threads to be used for the DBF.
;Sample adaptive offset
The SAO filter is applied after the DBF and is designed to allow for better reconstruction of the original signal amplitudes by applying offsets stored in a lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array that replaces runtime computation with a simpler array indexing operation. The process is termed as "direct addressing" and LUTs differ from hash tables in a way that, to retrieve a value v wi ...
in the bitstream. Per CTB the SAO filter can be disabled or applied in one of two modes: edge offset mode or band offset mode. The edge offset mode operates by comparing the value of a sample to two of its eight neighbors using one of four directional gradient patterns. Based on a comparison with these two neighbors, the sample is classified into one of five categories: minimum, maximum, an edge with the sample having the lower value, an edge with the sample having the higher value, or monotonic. For each of the first four categories an offset is applied. The band offset mode applies an offset based on the amplitude of a single sample. A sample is categorized by its amplitude into one of 32 bands (histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or "bucket") the range of values—that is, divide the ent ...
bins). Offsets are specified for four consecutive of the 32 bands, because in flat areas which are prone to banding artifacts, sample amplitudes tend to be clustered in a small range. The SAO filter was designed to increase picture quality, reduce banding artifacts, and reduce ringing artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "ec ...
.
Range extensions
Range extensions in MPEG are additional profiles, levels, and techniques that support needs beyond consumer video playback: *Profiles supporting bit depths beyond 10, and differingluma
Luma or LUMA may refer to:
Arts
* La Trobe University Museum of Art, Melbourne, Australia
* LUMA Projection Arts Festival, an annual event featuring building-scale projection mapping and light installations in Binghamton, NY
* LUMA Foundation, ...
/ chroma bit depths.
*Intra profiles for when file size is much less important than random-access decoding speed.
*Still Picture profiles, forming the basis of High Efficiency Image File Format
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a container format for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video.
HEI ...
, without any limit on the picture size or complexity (level 8.5). Unlike all other levels, no minimum decoder capacity is required, only a best-effort with reasonable fallback.
Within these new profiles came enhanced coding features, many of which support efficient screen encoding or high-speed processing:
*Persistent Rice adaptation, a general optimization of entropy coding.
*Higher precision weighted prediction at high bit depths.
*Cross-component prediction, allowing the imperfect YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-diffe ...
color decorrelation to let the luma (or G) match set the predicted chroma (or R/B) matches, which results in up to 7% gain for YCbCr 4:4:4 and up to 26% for RGB video. Particularly useful for screen coding.
*Intra smoothing control, allowing the encoder to turn smoothing on or off per-block, instead of per-frame.
*Modifications of transform skip:
**Residual DPCM
Differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) is a signal encoder that uses the baseline of pulse-code modulation (PCM) but adds some functionalities based on the prediction of the samples of the signal. The input can be an analog signal or a digita ...
(RDPCM), allowing more-optimal coding of residual data if possible, vs the typical zig-zag.
**Block size flexibility, supporting block sizes up to 32×32 (versus only 4×4 transform skip support in version 1).
**4×4 rotation, for potential efficiency.
**Transform skip context, enabling DCT and RDPCM blocks to carry a separate context.
*Extended precision processing, giving low bit-depth video slightly more accurate decoding.
*CABAC bypass alignment, a decoding optimization specific to High Throughput 4:4:4 16 Intra profile.
HEVC version 2 adds several supplemental enhancement information (SEI) messages:
*Color remapping: mapping one color space to another.
*Knee function: hints for converting between dynamic ranges, particularly from HDR to SDR.
*Mastering display color volume
*Time code, for archival purposes
Screen content coding extensions
Additional coding tool options have been added in the March 2016 draft of the screen content coding (SCC) extensions: *Adaptive color transform. *Adaptive motion vector resolution. *Intra block copying. *Palette mode. The ITU-T version of the standard that added the SCC extensions (approved in December 2016 and published in March 2017) added support for thehybrid log–gamma
The hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer function is a transfer function jointly developed by the BBC and NHK for high dynamic range (HDR) display. It's backward compatible with the transfer function of SDR (the gamma curve). It was approved as ARIB ...
(HLG) transfer function and the ICtCp color matrix. This allows the fourth version of HEVC to support both of the HDR transfer functions defined in Rec. 2100
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer func ...
.
The fourth version of HEVC adds several supplemental enhancement information (SEI) messages which include:
*Alternative transfer characteristics information SEI message, provides information on the preferred transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, theoretically models the system's output for ...
to use. The primary use case for this would be to deliver HLG video in a way that would be backward compatible
Backward compatibility (sometimes known as backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with input designed for such a system, especially i ...
with legacy devices.
*Ambient viewing environment SEI message, provides information on the ambient light of the viewing environment that was used to author the video.
Profiles
Version 1 of the HEVC standard defines three profiles: Main, Main 10, and Main Still Picture. Version 2 of HEVC adds 21 range extensions profiles, two scalable extensions profiles, and one multi-view profile. HEVC also contains provisions for additional profiles. Extensions that were added to HEVC include increased bit depth, 4:2:2/4:4:4chroma sampling
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.
It is us ...
, Multiview Video Coding
Multi view Video Coding (MVC, also known as MVC 3D) is a stereoscopic video coding standard for video compression that allows for the efficient encoding of video sequences captured simultaneously from multiple camera angles in a single video str ...
(MVC), and Scalable Video Coding
Scalable Video Coding: (SVC) is the name for the Annex G extension of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video compression standard. SVC standardizes the encoding of a high-quality video bitstream that also contains one or more subset bitstreams (a form of l ...
(SVC). The HEVC range extensions, HEVC scalable extensions, and HEVC multi-view extensions were completed in July 2014. In July 2014 a draft of the second version of HEVC was released. Screen content coding (SCC) extensions were under development for screen content video, which contains text and graphics, with an expected final draft release date of 2015.
A profile is a defined set of coding tools that can be used to create a bitstream that conforms to that profile. An encoder for a profile may choose which coding tools to use as long as it generates a conforming bitstream while a decoder for a profile must support all coding tools that can be used in that profile.
Version 1 profiles
Main
The Main profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with 4:2:0 chroma sampling, which is the most common type of video used with consumer devices.Main 10
The Main 10 profile was added at the October 2012 HEVC meeting based on proposal JCTVC-K0109 which proposed that a 10-bit profile be added to HEVC for consumer applications. The proposal said this was to allow for improved video quality and to support the Rec. 2020 color space that has become widely used in UHDTV systems and to be able to deliver higher dynamic range and color fidelity avoiding the banding artifacts. A variety of companies supported the proposal which includedAteme
Ateme S.A. is a multinational company that specializes in video delivery, namely software for video compression based on High_Efficiency_Video_Coding, H.265 / High_Efficiency_Video_Coding, HEVC standards; MPEG4; MPEG2 Data_compression#Video, encod ...
, BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...BSkyB
Sky UK Limited is a British broadcaster and telecommunications company that provides television and broadband Internet services, fixed line and mobile telephone services to consumers and businesses in the United Kingdom. It is a subsidiary of ...
, Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, ...
, DirecTV
DirecTV (trademarked as DIRECTV) is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. It ...
, Ericsson
(lit. "Telephone Stock Company of LM Ericsson"), commonly known as Ericsson, is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in informat ...
, Motorola Mobility
Motorola Mobility LLC, marketed as Motorola, is an American consumer electronics manufacturer primarily producing smartphones and other mobile devices running Android OS, Android. It is a subsidiary of the Chinese multinational technology company ...
, NGCodec, NHK
, also known as NHK, is a Japanese public broadcaster. NHK, which has always been known by this romanized initialism in Japanese, is a statutory corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee.
NHK operates two terrestr ...
, RAI
RAI – Radiotelevisione italiana (; commercially styled as Rai since 2000; known until 1954 as Radio Audizioni Italiane) is the national public broadcasting company of Italy, owned by the Ministry of Economy and Finance. RAI operates many ter ...
, ST, SVT, Thomson Video Networks
Thomson Video Networks (TVN) was a technology broadcast company that used to provide video compression, transcoding and processing solutions for media companies, video service providers, and TV broadcasters. The firm has offices in 16 countries a ...
, Technicolor
Technicolor is a series of Color motion picture film, color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
Definitive Technicolor movies using three black and white films ...
, and ViXS Systems.
The Main 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 to 10 bits per sample with 4:2:0 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Main and Main 10. A higher bit depth allows for a greater number of colors. 8 bits per sample allows for 256 shades per primary color
A set (mathematics), set of primary colors or primary colours (see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamu ...
(a total of 16.78 million colors) while 10 bits per sample allows for 1024 shades per primary color (a total of 1.07 billion colors). A higher bit depth allows for a smoother transition of color which resolves the problem known as color banding
Colour banding is a subtle form of posterization in digital images, caused by the colour of each pixel being rounded to the nearest of the digital colour levels. While posterization is often done for artistic effect, colour banding is an unde ...
.
The Main 10 profile allows for improved video quality since it can support video with a higher bit depth than what is supported by the Main profile. Additionally, in the Main 10 profile 8-bit video can be coded with a higher bit depth of 10 bits, which allows improved coding efficiency compared to the Main profile.
Ericsson
(lit. "Telephone Stock Company of LM Ericsson"), commonly known as Ericsson, is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in informat ...
said the Main 10 profile would bring the benefits of 10 bits per sample video to consumer TV. They also said that for higher resolutions there is no bit rate penalty for encoding video at 10 bits per sample. Imagination Technologies
Imagination Technologies Limited is a British semiconductor and software design company owned by Canyon Bridge Capital Partners, a private equity fund based in Beijing that is ultimately owned by the Chinese government. With its global headquar ...
said that 10-bit per sample video would allow for larger color spaces and is required for the Rec. 2020 color space that will be used by UHDTV. They also said the Rec. 2020 color space would drive the widespread adoption of 10-bit-per-sample video.
In a PSNR based performance comparison released in April 2013 the Main 10 profile was compared to the Main profile using a set of 3840×2160 10-bit video sequences. The 10-bit video sequences were converted to 8 bits for the Main profile and remained at 10 bits for the Main 10 profile. The reference PSNR was based on the original 10-bit video sequences. In the performance comparison the Main 10 profile provided a 5% bit rate reduction for inter frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage fro ...
video coding compared to the Main profile. The performance comparison states that for the tested video sequences the Main 10 profile outperformed the Main profile.
Main Still Picture
The Main Still Picture profile allows for a single still picture to be encoded with the same constraints as the Main profile. As a subset of the Main profile the Main Still Picture profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with 4:2:0 chroma sampling. An objective performance comparison was done in April 2012 in which HEVC reduced the average bit rate for images by 56% compared toJPEG
JPEG ( ) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and imag ...
. A PSNR
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a Signal (information theory), signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many sign ...
based performance comparison for still image compression was done in May 2012 using the HEVC HM 6.0 encoder and the reference software encoders for the other standards. For still images HEVC reduced the average bit rate by 15.8% compared to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, 22.6% compared to JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding the ...
, 30.0% compared to JPEG XR
JPEG XR (JPEG extended range) is an image compression standard for continuous tone photographic images, based on the HD Photo (formerly Windows Media Photo) specifications that Microsoft originally developed and patented. It supports both lossy a ...
, 31.0% compared to WebP
WebP is an image file format developed by Google intended as a replacement for JPEG, PNG, and GIF file formats. It supports both lossy and lossless compression, as well as animation and alpha transparency.
Google announced the WebP format i ...
, and 43.0% compared to JPEG.
A performance comparison for still image compression was done in January 2013 using the HEVC HM 8.0rc2 encoder, Kakadu version 6.0 for JPEG 2000, and IJG version 6b for JPEG. The performance comparison used PSNR for the objective assessment and mean opinion score Mean opinion score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system. It is the arithmetic mean over all individual "values on a predefined scale t ...
(MOS) values for the subjective assessment. The subjective assessment used the same test methodology and images as those used by the JPEG committee when it evaluated JPEG XR. For 4:2:0 chroma sampled images the average bit rate reduction for HEVC compared to JPEG 2000 was 20.26% for PSNR and 30.96% for MOS while compared to JPEG it was 61.63% for PSNR and 43.10% for MOS.
A PSNR based HEVC performance comparison for still image compression was done in April 2013 by Nokia
Nokia Corporation (natively Nokia Oyj, referred to as Nokia) is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporatio ...
. HEVC has a larger performance improvement for higher resolution images than lower resolution images and a larger performance improvement for lower bit rates than higher bit rates. For lossy compression
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size ...
to get the same PSNR as HEVC took on average 1.4× more bits with JPEG 2000, 1.6× more bits with JPEG-XR, and 2.3× more bits with JPEG.
A compression efficiency study of HEVC, JPEG, JPEG XR, and WebP was done in October 2013 by Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, wi ...
. The study showed that HEVC was significantly better at compression than the other image formats that were tested. Four different methods for comparing image quality were used in the study which were Y-SSIM, RGB-SSIM, IW-SSIM, and PSNR-HVS-M.
Version 2 profiles
Version 2 of HEVC adds 21 range extensions profiles, two scalable extensions profiles, and one multi-view profile: Monochrome, Monochrome 12, Monochrome 16, Main 12, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:2:2 12, Main 4:4:4, Main 4:4:4 10, Main 4:4:4 12, Monochrome 12 Intra, Monochrome 16 Intra, Main 12 Intra, Main 4:2:2 10 Intra, Main 4:2:2 12 Intra, Main 4:4:4 Intra, Main 4:4:4 10 Intra, Main 4:4:4 12 Intra, Main 4:4:4 16 Intra, Main 4:4:4 Still Picture, Main 4:4:4 16 Still Picture, High Throughput 4:4:4 16 Intra, Scalable Main, Scalable Main 10, and Multiview Main. All of theinter frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage fro ...
range extensions profiles have an Intra profile.
;Monochrome
The Monochrome profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 chroma sampling.
;Monochrome 12
The Monochrome 12 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 12 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 chroma sampling.
;Monochrome 16
The Monochrome 16 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 16 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Monochrome 16 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Monochrome 12, and Monochrome 16.
;Main 12
The Main 12 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 12 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 and 4:2:0 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 12 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Monochrome 12, Main, Main 10, and Main 12.
;Main 422 10
The Main 4:2:2 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, and 4:2:2 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:2:2 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, and Main 4:2:2 10.
;Main 422 12
The Main 4:2:2 12 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 12 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, and 4:2:2 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:2:2 12 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Monochrome 12, Main, Main 10, Main 12, Main 4:2:2 10, and Main 4:2:2 12.
;Main 444
The Main 4:4:4 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:4:4 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, and Main 4:4:4.
;Main 444 10
The Main 4:4:4 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:4:4 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:4:4, and Main 4:4:4 10.
;Main 444 12
The Main 4:4:4 12 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 12 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:4:4 12 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Main 12, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:2:2 12, Main 4:4:4, Main 4:4:4 10, Main 4:4:4 12, and Monochrome 12.
;Main 444 16 Intra
The Main 4:4:4 16 Intra profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 16 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Main 4:4:4 16 Intra profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome Intra, Monochrome 12 Intra, Monochrome 16 Intra, Main Intra, Main 10 Intra, Main 12 Intra, Main 4:2:2 10 Intra, Main 4:2:2 12 Intra, Main 4:4:4 Intra, Main 4:4:4 10 Intra, and Main 4:4:4 12 Intra.
;High Throughput 444 16 Intra
The High Throughput 4:4:4 16 Intra profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 16 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The High Throughput 4:4:4 16 Intra profile has an HbrFactor 12 times higher than other HEVC profiles allowing it to have a maximum bit rate 12 times higher than the Main 4:4:4 16 Intra profile. The High Throughput 4:4:4 16 Intra profile is designed for high end professional content creation and decoders for this profile are not required to support other profiles.
;Main 444 Still Picture
The Main 4:4:4 Still Picture profile allows for a single still picture to be encoded with the same constraints as the Main 4:4:4 profile. As a subset
In mathematics, Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are ...
of the Main 4:4:4 profile the Main 4:4:4 Still Picture profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling.
;Main 444 16 Still Picture
The Main 4:4:4 16 Still Picture profile allows for a single still picture to be encoded with the same constraints as the Main 4:4:4 16 Intra profile. As a subset
In mathematics, Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are ...
of the Main 4:4:4 16 Intra profile the Main 4:4:4 16 Still Picture profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 16 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling.
;Scalable Main
The Scalable Main profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Main profile of HEVC.
;Scalable Main 10
The Scalable Main 10 profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Main 10 profile of HEVC.
;Multiview Main
The Multiview Main profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Main profile of HEVC.
Version 3 and higher profiles
Version 3 of HEVC added one 3D profile: 3D Main. The February 2016 draft of the screen content coding extensions added seven screen content coding extensions profiles, three high throughput extensions profiles, and four scalable extensions profiles: Screen-Extended Main, Screen-Extended Main 10, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 14, High Throughput 4:4:4, High Throughput 4:4:4 10, High Throughput 4:4:4 14, Scalable Monochrome, Scalable Monochrome 12, Scalable Monochrome 16, and Scalable Main 4:4:4. ;3D Main The 3D Main profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Main profile of HEVC. ;Screen-Extended Main The Screen-Extended Main profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 and 4:2:0 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended Main profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, and Screen-Extended Main. ;Screen-Extended Main 10 The Screen-Extended Main 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0 and 4:2:0 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended Main 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Screen-Extended Main, and Screen-Extended Main 10. ;Screen-Extended Main 444 The Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended Main, and Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4. ;Screen-Extended Main 444 10 The Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:4:4, Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended Main, Screen-Extended Main 10, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4, and Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10. ;Screen-Extended High Throughput 444 The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles allowing it to have a maximum bit rate 6 times higher than the Main 4:4:4 profile. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended Main, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4, and High Throughput 4:4:4. ;Screen-Extended High Throughput 444 10 The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles allowing it to have a maximum bit rate 6 times higher than the Main 4:4:4 10 profile. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:4:4, Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended Main, Screen-Extended Main 10, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10, High Throughput 4:4:4, and High Throughput 4:4:4. ;Screen-Extended High Throughput 444 14 The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 14 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles. HEVC decoders that conform to the Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: Monochrome, Main, Main 10, Main 4:2:2 10, Main 4:4:4, Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended Main, Screen-Extended Main 10, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4, Screen-Extended Main 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 10, Screen-Extended High Throughput 4:4:4 14, High Throughput 4:4:4, High Throughput 4:4:4 10, and High Throughput 4:4:4 14. ;High Throughput 444 The High Throughput 4:4:4 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The High Throughput 4:4:4 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles allowing it to have a maximum bit rate 6 times higher than the Main 4:4:4 profile. HEVC decoders that conform to the High Throughput 4:4:4 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: High Throughput 4:4:4. ;High Throughput 444 10 The High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 10 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles allowing it to have a maximum bit rate 6 times higher than the Main 4:4:4 10 profile. HEVC decoders that conform to the High Throughput 4:4:4 10 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: High Throughput 4:4:4 and High Throughput 4:4:4 10. ;High Throughput 444 14 The High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile allows for a bit depth of 8 bits to 14 bits per sample with support for 4:0:0, 4:2:0, 4:2:2, and 4:4:4 chroma sampling. The High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile has an HbrFactor 6 times higher than most inter frame HEVC profiles. HEVC decoders that conform to the High Throughput 4:4:4 14 profile must be capable of decoding bitstreams made with the following profiles: High Throughput 4:4:4, High Throughput 4:4:4 10, and High Throughput 4:4:4 14. ;Scalable Monochrome The Scalable Monochrome profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Monochrome profile of HEVC. ;Scalable Monochrome 12 The Scalable Monochrome 12 profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Monochrome 12 profile of HEVC. ;Scalable Monochrome 16 The Scalable Monochrome 16 profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Monochrome 16 profile of HEVC. ;Scalable Main 444 The Scalable Main 4:4:4 profile allows for a base layer that conforms to the Main 4:4:4 profile of HEVC.Tiers and levels
The HEVC standard defines two tiers, Main and High, and thirteen levels. A level is a set of constraints for a bitstream. For levels below level 4 only the Main tier is allowed. The Main tier is a lower tier than the High tier. The tiers were made to deal with applications that differ in terms of their maximum bit rate. The Main tier was designed for most applications while the High tier was designed for very demanding applications. A decoder that conforms to a given tier/level is required to be capable of decoding all bitstreams that are encoded for that tier/level and for all lower tiers/levels. : The maximum bit rate of the profile is based on the combination of bit depth, chroma sampling, and the type of profile. For bit depth the maximum bit rate increases by 1.5× for 12-bit profiles and 2× for 16-bit profiles. For chroma sampling the maximum bit rate increases by 1.5× for 4:2:2 profiles and 2× for 4:4:4 profiles. For the Intra profiles the maximum bit rate increases by 2×. : The maximum frame rate supported by HEVC is 300 fps. : The MaxDpbSize is the maximum number of pictures in the decoded picture buffer.Decoded picture buffer
Previously decoded pictures are stored in a decoded picture buffer (DPB), and are used by HEVC encoders to form predictions for subsequent pictures. The maximum number of pictures that can be stored in the DPB, called the DPB capacity, is 6 (including the current picture) for all HEVC levels when operating at the maximum picture size supported by the level. The DPB capacity (in units of pictures) increases from 6 to 8, 12, or 16 as the picture size decreases from the maximum picture size supported by the level. The encoder selects which specific pictures are retained in the DPB on a picture-by-picture basis, so the encoder has the flexibility to determine for itself the best way to use the DPB capacity when encoding the video content.Containers
MPEG has published an amendment which added HEVC support to theMPEG transport stream
MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS, MTS) or simply transport stream (TS) is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast systems ...
used by ATSC
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like that ...
, DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) o ...
, and Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a Digital media, digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and c ...
; MPEG decided not to update the MPEG program stream
Program stream (PS or MPEG-PS) is a container format for multiplexing digital audio, video and more. The PS format is specified in MPEG-1 Part 1 (ISO/IEC 11172-1) and MPEG-2 Part 1, Systems (ISO/IEC standard 13818-1/ITU-T H.222.0). The MPEG-2 ...
used by DVD-Video
DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVD discs. DVD-Video was the dominant consumer home video format in Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia in the 2000s until it was supplanted by the high-definition Blu-r ...
. MPEG has also added HEVC support to the ISO base media file format
The ISO base media file format (ISOBMFF) is a container file format that defines a general structure for files that contain time-based multimedia data such as video and audio.
It is standardized in ISO/IEC 14496-12, a.k.a. MPEG-4 Part 12, and wa ...
. HEVC is also supported by the MPEG media transport
MPEG media transport (MMT), specified as ISO/IEC 23008-1 (MPEG-H Part 1), is a digital container standard developed by Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) that supports High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) video. MMT was designed to transfer dat ...
standard. Support for HEVC was added to Matroska
Matroska is a project to create a container format that can hold an unlimited number of video, audio, picture, or subtitle tracks in one file. The Matroska Multimedia Container is similar in concept to other containers like AVI, MP4, or Adva ...
starting with the release of MKVToolNix
MKVToolNix is a collection of tools for the Matroska media container format by Moritz Bunkus including mkvmerge. The free and open source Matroska libraries and tools are available for various platforms including Linux and BSD distributions, m ...
v6.8.0 after a patch from DivX was merged. A draft document has been submitted to the Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and a ...
which describes a method to add HEVC support to the Real-time Transport Protocol
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applicatio ...
.
Using HEVC's intra frame encoding, a still-image coded format called Better Portable Graphics
Better Portable Graphics (BPG) is a file format for coding digital images, which was created by programmer Fabrice Bellard in 2014. He has proposed it as a replacement for the JPEG image format as the more compression-efficient alternative in ...
(BPG) has been proposed by the programmer Fabrice Bellard
Fabrice Bellard (; born 1972) is a French computer programmer known for writing FFmpeg, QEMU, and the Tiny C Compiler. He developed Bellard's formula for calculating single digits of pi. In 2012, Bellard co-founded Amarisoft, a telecommunication ...
. It is essentially a wrapper for images coded using the HEVC Main 4:4:4 16 Still Picture profile with up to 14 bits per sample, although it uses an abbreviated header syntax and adds explicit support for Exif
Exchangeable image file format (officially Exif, according to JEIDA/JEITA/CIPA specifications) is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smartphones), scanners and other system ...
, ICC profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a ...
s, and XMP metadata.
Patent license terms
License terms and fees for HEVC patents, compared with its main competitors:Provision for costless software
As with its predecessor AVC, software distributors that implement HEVC in products must pay a price per distributed copy. While this licensing model is unproblematic for paid software, it is an obstacle to mostfree and open-source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
, which is meant to be freely distributable. In the opinion of MulticoreWare
MulticoreWare Inc is a software development company, offering products and services related to HEVC video compression, machine learning (specifically, convolutional neural networks), compilers for heterogeneous computing, and software perform ...
, the developer of x265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a ...
, enabling royalty-free software encoders and decoders is in the interest of accelerating HEVC adoption. HEVC Advance made an exception that specifically waives the royalties on software-only implementations (both decoders and encoders) when not bundled with hardware. However, the exempted software is not free from the licensing obligations of other patent holders (e.g. members of the MPEG LA pool).
While the obstacle to free software is no concern in for example TV broadcast networks, this problem, combined with the prospect of future collective lock-in to the format, makes several organizations like Mozilla (see OpenH264
OpenH264 is a free software library for real-time encoding and decoding video streams in the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC format. It is released under the terms of the Simplified BSD License."
History Move to free-to-use binaries
On October 30, 2013, Rowan T ...
) and the Free Software Foundation Europe
The Free Software Foundation Europe (FSFE) is an ''eingetragener Verein'' (registered voluntary association) under German law. It was founded in 2001 to support all aspects of the free software movement in Europe, with registered chapters in seve ...
wary of royalty-bearing formats for internet use. Competing formats intended for internet use (VP9 and AV1) are intended to steer clear of these concerns by being royalty free (provided there are no third-party claims of patent rights).
: Regardless of how the software is licensed from the software authors (see software licensing
A software license is a legal instrument (usually by way of contract law, with or without printed material) governing the use or redistribution of software. Under United States copyright law, all software is copyright protected, in both source c ...
), if what it does is patented, its use remains bound by the patent holders' rights unless the use of the patents has been authorized by a license.
Versatile Video Coding
In October 2015, MPEG and VCEG formed Joint Video Exploration Team (JVET) to evaluate available compression technologies and study the requirements for a next-generation video compression standard. The new algorithm should have 30–50% better compression rate for the same perceptual quality, with support for lossless and subjectively lossless compression. It should also support YCbCr 4:4:4, 4:2:2 and 4:2:0 with 10 to 16 bits per component, BT.2100 wide color gamut and high dynamic range (HDR) of more than 16 stops (with peak brightness of 1000, 4000 and 10000 nits), auxiliary channels (for depth, transparency, etc.), variable and fractional frame rates from 0 to 120 Hz, scalable video coding for temporal (frame rate), spatial (resolution), SNR, color gamut and dynamic range differences, stereo/multiview coding, panoramic formats, and still picture coding. Encoding complexity of 10 times that of HEVC is expected. JVET issued a final "Call for Proposals" in October 2017, with the first working draft of the Versatile Video Coding (VVC) standard released in April 2018. The VVC standard was finalized on 6 July 2020.See also
*UHDTV
Ultra-high-definition television (also known as Ultra HD television, Ultra HD, UHDTV, UHD and Super Hi-Vision) today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed by ...
– digital television formats with resolutions of 4K / 2160p (3840×2160) and 8K / 4320p (7680×4320)
** Rec. 2020 – ITU-R Recommendation for UHDTV with standard dynamic range
**Rec. 2100
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer func ...
– ITU-R Recommendation for HDTV and UHDTV with high dynamic range
High dynamic range (HDR) is a dynamic range higher than usual, synonyms are wide dynamic range, extended dynamic range, expanded dynamic range.
The term is often used in discussing the dynamic range of various signals such as images, videos, au ...
*Image file formats based on HEVC
**Better Portable Graphics
Better Portable Graphics (BPG) is a file format for coding digital images, which was created by programmer Fabrice Bellard in 2014. He has proposed it as a replacement for the JPEG image format as the more compression-efficient alternative in ...
– a file format for images based on HEVC
**High Efficiency Image File Format
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a container format for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video.
HEI ...
– a file format for images and image sequences based on HEVC
* Comparison of video codecs
* List of open-source codecs
This is a listing of open-source codecs—that is, open-source software implementations of audio or video coding formats. Many of the codecs listed implement media formats that are restricted by patents and are hence not open formats. For exampl ...
**x265
x265 is a software codec for creating digital video streams in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format developed by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). It is available as a command-line app or a ...
– an open-source software implementation of HEVC
* List of multimedia (audio/video) codecs
** H.264/MPEG-4 AVC – the video standard predecessor of HEVC
**AV1
AOMedia Video 1 (AV1) is an open, royalty-free video coding format initially designed for video transmissions over the Internet. It was developed as a successor to VP9 by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia), a consortium founded in 2015 th ...
– an open format developed by the Alliance for Open Media
The Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia) is a non-profit industry consortium that develops open, royalty-free technology for multimedia delivery headquartered in Wakefield, Massachusetts. It uses the ideas and principles of open web standard develo ...
as a successor to VP9 and a competitor to HEVC
**VP9
VP9 is an open and royalty-free video coding format developed by Google.
VP9 is the successor to VP8 and competes mainly with MPEG's High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265).
At first, VP9 was mainly used on Google's video platform YouTube. ...
– an open format
An open file format is a file format for storing digital data, defined by an openly published specification usually maintained by a standards organization, and which can be used and implemented by anyone. Open file format is licensed with open lic ...
developed by Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
as a competitor to HEVC
**Daala
Daala is a video coding format under development by the Xiph.Org Foundation under the lead of Timothy B. Terriberry mainly sponsored by the Mozilla Corporation. Like Theora and Opus, Daala is available free of any royalties and its reference im ...
– an open format that is being developed by Mozilla Foundation
The Mozilla Foundation (stylized as moz://a) is an American non-profit organization that exists to support and collectively lead the open source Mozilla project. Founded in July 2003, the organization sets the policies that govern development, ...
and Xiph.Org Foundation as a competitor to HEVC
**Dirac (video compression format)
Dirac is an open and royalty-free video compression format, specification and system developed by BBC Research & Development. Schrödinger and dirac-research (formerly just called "Dirac") are open and royalty-free software implementations (v ...
– an open format that is being developed by the BBC Research & Development
BBC Research & Development is the technical research department of the BBC.
Function
It has responsibility for researching and developing advanced and emerging media technologies for the benefit of the corporation, and wider UK and European ...
as a competitor to HEVC
**Thor (video codec)
Thor is a royalty free video codec under development by Cisco Systems. The specifications of Thor were available in various Internet Drafts.
On July 22, 2015, Thor was presented to the IETF as a candidate for their NETVC video standard. Thor use ...
– an open format that is being developed by Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, ...
as a competitor to HEVC
* LCEVC
Low Complexity Enhancement Video Coding (LCEVC) is a ISO/ IEC video coding standard developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) under the project name MPEG-5 Part 2 LCEVC.
Concept
LCEVC specifies an enhancement layer which, when com ...
– differential overlays that can improve performance
References
Bibliography
* * * * ::Related slides: * ::Related slides: *External links
Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute's HEVC website
ITU web page for Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC)
Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) publications on HEVC
ITU-T Recommendation H.265: High Efficiency Video Coding
{{MPEG Computer file formats Graphics file formats High-definition television Lossy compression algorithms MPEG-H Open standards covered by patents Ultra-high-definition television Video codecs Video compression Videotelephony ITU-T recommendations
H.265
H is the eighth letter of the Latin alphabet.
H may also refer to:
Musical symbols
* H number, Harry Halbreich reference mechanism for music by Honegger and Martinů
* H, B (musical note)
* H, B major
People
* H. (noble) (died after 12 ...
H.26x
IEC standards
ISO standards