|
SYCC
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile. sRGB essentially codifies the display specifications for the computer monitors in use at that time, which greatly aided its acceptance. sRGB uses the same color primaries and white point as ITU-R BT.709 standard for HDTV, a transfer function (or gamma) compatible with the era's CRT displays, and a viewing environment designed to match typical home and office viewing conditions. An amendment of the IEC 61966-2-1 standard document that defines sRGB includes the definition of a number of variants including sYCC, which is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 1931 Color Space
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the ''"Commission Internationale de l'éclairage"'', known in English as the International Commission on Illumination. The CIE 1931 RGB color space and CIE 1931 XYZ color space were created by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1931. They resulted from a series of experiments done in the late 1920s by William David Wright using ten observers and John Guild using seven observers. The experimental results were combined into the specification of the CIE RGB color space, from which the CIE XYZ color space was derived. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain ''complete subset'' of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a certain output device. Another sense, less frequently used but still correct, refers to the complete set of colors found within an image at a given time. In this context, digitizing a photograph, converting a digitized image to a different color space, or outputting it to a given medium using a certain output device generally alters its gamut, in the sense that some of the colors in the original are lost in the process. Introduction The term ''gamut'' was adopted from the field of music, where in middle age Latin "gamut" meant the entire range of musical notes of which musical melodies are composed; Shakespeare's use of the term in ''The Taming of the Shrew'' is sometimes attributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras (which are still available). High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs. Digital and digital movie cameras share an optical system, typically using a lens with a variable diaphragm to focus light onto an image pickup device. The diaphragm and shutter admit a controlled amount of light to the image, just as with film, but the image pickup device is electronic rather than chemical. However, unlike film cameras, digital cameras can display images on a screen immediately after being recorded, and store and delete images from memory. Many digital cameras can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Colorimetric Observer
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that define these color spaces are essential tools for color management, important when dealing with color inks, illuminated displays, and recording devices such as digital cameras. The system was designed in 1931 by the ''"Commission Internationale de l'éclairage"'', known in English as the International Commission on Illumination. The CIE 1931 RGB color space and CIE 1931 XYZ color space were created by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1931. They resulted from a series of experiments done in the late 1920s by William David Wright using ten observers and John Guild using seven observers. The experimental results were combined into the specification of the CIE RGB color space, from which the CIE XYZ color space was derived. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIELAB Color Space
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusion with Hunter Lab). It expresses color as three values: ''L*'' for perceptual lightness and ''a*'' and ''b*'' for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color. Like the CIEXYZ space it derives from, CIELAB color space is a device-independent, "standard observer" model. The colors it defines are not relative to any particular device such as a computer monitor or a printer, but instead relate to the CIE standard observer which is an averaging of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
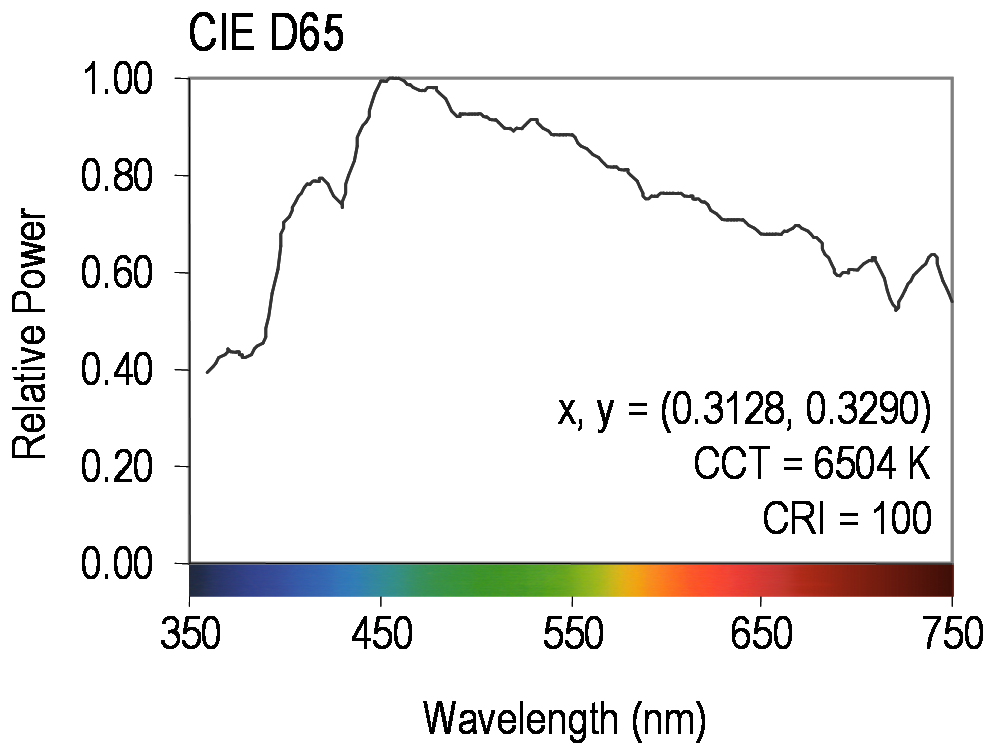
Illuminant D65
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world. D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in Western Europe / Northern Europe (comprising both direct sunlight and the light diffused by a clear sky), hence it is also called a daylight illuminant. As any standard illuminant is represented as a table of averaged spectrophotometric data, any light source which statistically has the same relative spectral power distribution (SPD) can be considered a D65 light source. There are no actual D65 light sources, only simulators. The quality of a simulator can be assessed with the CIE metamerism index. The CIE positions D65 as the standard daylight illuminant: History The CIE introduced three standard illuminants in 1931: * A: Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Color Consortium
The International Color Consortium (ICC) was formed in 1993 by eight vendors in order to create an open, vendor-neutral color management system which would function transparently across all operating systems and software packages. Overview The ICC specification, currently on version 4.3, allows for matching of color when moved between applications and operating systems, from the point of creation to the final output, whether display or print. This specification is technically identical to ISO 15076-1:2010, available from ISO. The ICC profile describes the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the source or target color space and a ''profile connection space'' (PCS). The ICC defines the specification precisely but does not define algorithms or processing details. As such, applications or systems that work with different ICC profiles are allowed to vary. ICC has also published a preliminary specification for iccMAX, a next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cie Chart With SRGB Gamut By Spigget
CIE may refer to: Organizations * Cambridge International Examinations, an international examination board * Center for International Education at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst * Cleveland Institute of Electronics, a private technical and engineering educational institution * International Commission on Illumination (''Commission internationale de l'éclairage'') * Companion of the Order of the Indian Empire (C.I.E.) * Computability in Europe, an international organization of computability theorists, computer scientists, mathematicians * CIÉ (Córas Iompair Éireann), the Irish state transport authority * Council on Islamic Education * Transportes Aéreos Cielos Andinos, ICAO code: CIE * Civil Information and Educational Section (CIE), General Headquarters, the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers in Japan (1945–1952) Science and technology * CIE 1931 color space, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces, created by the International Commission on Illu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantization (image Processing)
Quantization, involved in image processing, is a lossy compression technique achieved by compressing a range of values to a single quantum (discrete) value. When the number of discrete symbols in a given stream is reduced, the stream becomes more compressible. For example, reducing the number of colors required to represent a digital image makes it possible to reduce its file size. Specific applications include DCT data quantization in JPEG and DWT data quantization in JPEG 2000. Color quantization Color quantization reduces the number of colors used in an image; this is important for displaying images on devices that support a limited number of colors and for efficiently compressing certain kinds of images. Most bitmap editors and many operating systems have built-in support for color quantization. Popular modern color quantization algorithms include the nearest color algorithm (for fixed palettes), the median cut algorithm, and an algorithm based on octrees. It is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRGB Gamma
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile. sRGB essentially codifies the display specifications for the computer monitors in use at that time, which greatly aided its acceptance. sRGB uses the same color primaries and white point as ITU-R BT.709 standard for HDTV, a transfer function (or gamma) compatible with the era's CRT displays, and a viewing environment designed to match typical home and office viewing conditions. An amendment of the IEC 61966-2-1 standard document that defines sRGB includes the definition of a number of variants including sYCC, which is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |