|
DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU). Transmission DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including: * Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-S2, and DVB-SH ** DVB-SMATV for distribution via SMATV * Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2 * Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2 ** Digital terrestrial television for handhelds: DVB-H, DVB-SH * Microwave: using DTT ( DVB-MT), the MMDS ( DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards (DVB-MS) These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface (SPI), synchronous serial interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for "Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial"; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television. DVB has been standardized by ETSI. This system transmits compressed digital audio, video, and other data in "physical layer pipes" (PLPs), using OFDM modulation with concatenated channel coding and interleaving. The higher offered bit rate, with respect to its predecessor DVB-T, makes it a system suited for carrying HDTV signals on the terrestrial TV channel (though many broadcasters still use plain DVB-T for this purpose). , it was implemented in broadcasts in the United Kingdom (Freeview HD, eight channels across two multiplexes, plus an extra multiplex in Northern Ireland carrying three SD channels), Italy ( Europa 7 HD, twelve channels), Finland (21 channels, five in HD), Germany (six HD (1080p50) channels, with 40 in planning), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrestrial Television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV or DTT, or DTTB with "broadcasting") is a technology for terrestrial television in which land-based (terrestrial) television stations broadcast television content by radio waves to televisions in consumers' residences in a digital format. DTTV is a major technological advance over the previous analog television, and has largely replaced analog which had been in common use since the middle of the 20th century. Test broadcasts began in 1998 with the changeover to DTTV (aka Analog Switchoff (ASO), or Digital Switchover (DSO)) beginning in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of ''digital'' terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitising platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of limited radio spectrum bandwidth, provision of more television channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters (after the initial up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-T
DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February, 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (COFDM or OFDM) modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide (including North America) for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by Amateur television operators. Basics Rather than carrying one data carrier on a single radio frequency (RF) channel, COFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulates a set of closely spaced adjacent sub-carrier frequencies. In the cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
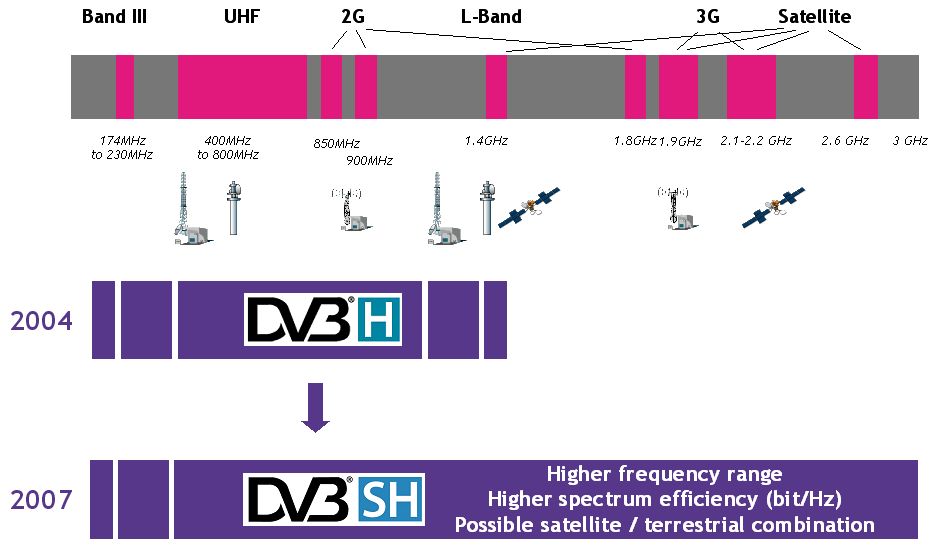
DVB-H
DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting - Handheld) is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification (EN 302 304) can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website. From March 2008, DVB-H is officially endorsed by the European Union as the "preferred technology for terrestrial mobile broadcasting". The major competitors of this technology are Qualcomm's MediaFLO system, the 3G cellular system based MBMS mobile-TV standard, and the ATSC-M/H format in the U.S. DVB-SH (Satellite to Handhelds) now and DVB-NGH (Next Generation Handheld) in the future are possible enhancements to DVB-H, providing improved spectral efficiency and better modulation flexibility. DVB-H has been a commercial failure, and the service is no longer on-air. Ukraine was the last country with a nationwide broadcast in DVB-H, which began trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-S2
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI (EN 302307) in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering (or Digital Satellite News Gathering) system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations. DVB-S2 is designed for broadcast services including standard and HDTV, interactive services including Internet access, and (professional) data content distribution. The development of DVB-S2 coincided with the introduction of HDTV and H.264 (MPEG-4 AVC) video codecs. Two new key features that were added compared to the DVB-S standard are: * A powerful coding scheme based on a modern LDPC code. For low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-SH
DVB-SH ("Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite services to Handhelds") is a physical layer standard for delivering IP based media content and data to handheld terminals such as mobile phones or PDAs, based on a hybrid satellite/terrestrial downlink and for example a GPRS uplink. The DVB Project published the DVB-SH standard in February 2007.dvb.org: DVB approves DVB-SH specification The DVB-SH system was designed for frequencies below 3 GHz, supporting UHF band, L Band or S-band. It complements and improves the existing physical layer standard. Like its sister specification (DVB-H), it is based on DVB IP Datacast (IPDC) delivery, electronic service guides and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-C
Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable (DVB-C) is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television over cable. This system transmits an MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 family digital audio/digital video stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding. The standard was first published by the ETSI in 1994, and subsequently became the most widely used transmission system for digital cable television in Europe, Asia and South America. It is deployed worldwide in systems ranging from the larger cable television networks (CATV) down to smaller satellite master antenna TV (SMATV) systems. Technical description DVB-C transmitter With reference to the figure, a short description of the single processing blocks follows. * Source coding and MPEG-2 multiplexing (MUX): video, audio, and data streams are multiplexed into an MPEG program stream (MPEG-PS). One or more MPEG-PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS). This is the basic digital st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-C2
Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable (DVB-C) is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television over cable. This system transmits an MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 family digital audio/digital video stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding. The standard was first published by the ETSI in 1994, and subsequently became the most widely used transmission system for digital cable television in Europe, Asia and South America. It is deployed worldwide in systems ranging from the larger cable television networks (CATV) down to smaller satellite master antenna TV (SMATV) systems. Technical description DVB-C transmitter With reference to the figure, a short description of the single processing blocks follows. * Source coding and MPEG-2 multiplexing (MUX): video, audio, and data streams are multiplexed into an MPEG program stream (MPEG-PS). One or more MPEG-PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS). This is the basic digital st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-S
Digital Video Broadcasting – Satellite (DVB-S) is the original DVB standard for Satellite Television and dates from 1995, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997. The first commercial applications was by Star TV in Asia and Galaxy in Australia, enabling digitally broadcast, satellite-delivered Television to the public.DVB-S was the first DVB standard for satellite, defining the framing structure, channel coding and modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite services It is used via satellites serving every continent of the world. DVB-S is used in both Multiple Channel Per Carrier (MCPC) and Single channel per carrier modes for Broadcast Network feeds as well as for direct-broadcast satellite services like Sky (UK & Ireland) via Astra in Europe, Dish Network and Globecast in the U.S. and Bell Satellite TV in Canada. While the actual DVB-S standard only specifies physical link characteristics and framing, the overlaid transport stream delivered by DVB-S is man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous Serial Interface
Asynchronous Serial Interface, or ASI, is a method of carrying an MPEG Transport Stream (MPEG-TS) over 75-ohm copper coaxial cable or optical fiber. It is popular in the television industry as a means of transporting broadcast programs from the studio to the final transmission equipment before it reaches viewers sitting at home. Standard The ASI standard is maintained by CENELEC, the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization, and is part of the collection of standards known as Digital Video Broadcast, or DVB. Technical Specification ASI carries MPEG data serially as a continuous stream with a constant rate at or less than 270 megabits per second, depending on the application. It cannot run faster than this, which is the same rate as SDI and also the rate of a DS4 telecommunications circuit which is typically used to transport the stream over commercial telephone/telecommunications digital circuits ( Telco). The MPEG data bits are encoded using a technique calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location. The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver then decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Modern systems signals are relayed from a communications satellite on the X band (8–12 GHz) or Ku band (12–18 GHz) frequencies requiring only a small dish less than a meter in diameter. The first satellite TV systems were an obsolete type now known as television receive-only. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-MS
DVB-MS is a complementary system for digital television multi-point distribution based on the satellite delivery system DVB-S. For cable delivery system DVB-MC is used which is based on DVB-C. The DVB-MS system uses microwave frequencies above to directly distribute television services from a central point to homes of viewers. To receive the signal a small frequency converter is used instead of a satellite dish for DVB-S. DVB-MC uses frequencies below . read 2012-08-23 References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |