|
Ateme
Ateme S.A. is a multinational company that specializes in video delivery, namely software for video compression based on H.265 / HEVC standards; MPEG4; MPEG2 encoding / decoding solutions for contribution links, multi-screen live streaming, OTT and CDN solutions; origin-server software and packaging; cloud DVR solutions; and CDN solutions. The company has its headquarters in Vélizy near Paris, France, with offices that spread over Europe, North America, South America, Asia and, Australia. The company also has a worldwide resellers network and operates globally with clients in more than 60 countries. Their solutions reduce bandwidth and infrastructure needs for content providers, service providers, MVPDs and OTT. This reduction in turn helps to play its part in reducing the environmental impact of video delivery on worldwide energy consumption. Products include: * Kyrion: High-quality/ultra-low-latency encoding/decoding appliance. * TITAN: Software suite for origination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Efficiency Video Coding
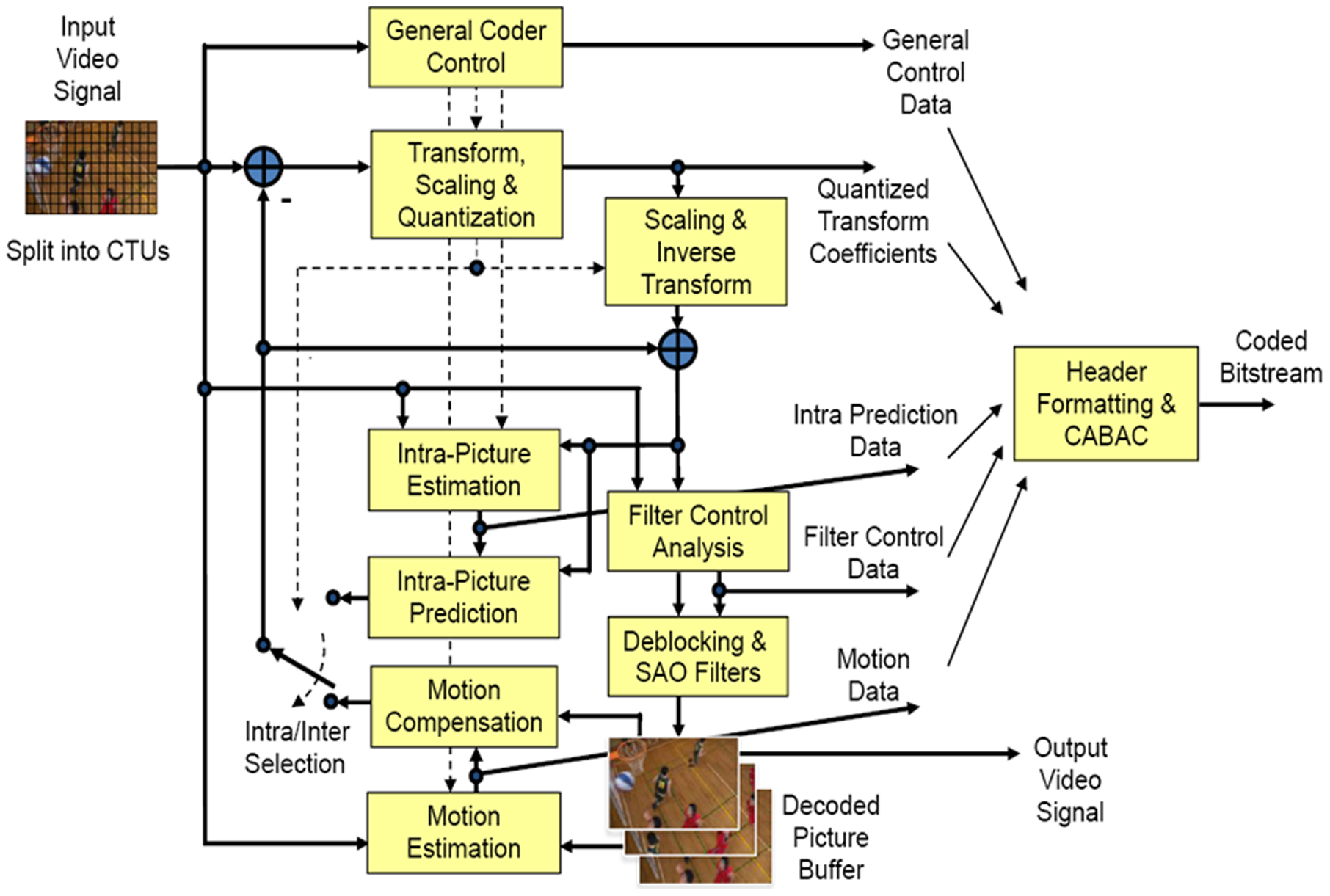
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses integer DCT and DST transforms with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. , HEVC is used by 43% of video developers, and is the second most widely used video coding format after AVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a signal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding; encoding done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a signal. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Video Broadcasting
Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU). Transmission DVB systems distribute data using a variety of approaches, including: * Satellite: DVB-S, DVB-S2, and DVB-SH ** DVB-SMATV for distribution via SMATV * Cable: DVB-C, DVB-C2 * Terrestrial television: DVB-T, DVB-T2 ** Digital terrestrial television for handhelds: DVB-H, DVB-SH * Microwave: using DTT ( DVB-MT), the MMDS ( DVB-MC), and/or MVDS standards (DVB-MS) These standards define the physical layer and data link layer of the distribution system. Devices interact with the physical layer via a synchronous parallel interface (SPI), synchronous serial i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMPTE
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) (, rarely ), founded in 1916 as the Society of Motion Picture Engineers or SMPE, is a global professional association of engineers, technologists, and executives working in the media and entertainment industry. As an internationally recognized standards organization, SMPTE has published more than 800 technical standards and related documents for broadcast, filmmaking, digital cinema, audio recording, information technology (IT), and medical imaging. SMPTE also publishes the ''SMPTE Motion Imaging Journal'', provides networking opportunities for its members, produces academic conferences and exhibitions, and performs other industry-related functions. SMPTE membership is open to any individual or organization with an interest in the subject matter. In the US, SMPTE is a 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)3 non-profit charitable organization. History The Motion Picture and Television Engineers was founded in 1913 by Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Association Of Broadcasters
The National Association of Broadcasters (NAB) is a trade association and lobby group representing the interests of commercial and non-commercial over-the-air radio and television broadcasters in the United States. The NAB represents more than 8,300 terrestrial radio and television stations as well as broadcast networks. As of 2022, the president and CEO of the NAB is Curtis LeGeyt. Founding The NAB was founded as the National Association of Radio Broadcasters (NARB) in April 1923 at the Drake Hotel in Chicago. The association's founder and first president was Eugene F. McDonald Jr., who also launched the Zenith corporation. In 1951 it changed its name to the National Association of Radio and Television Broadcasters (NARTB) to include the television industry. In 1958 it adopted its current name, "National Association of Broadcasters". Commercial radio The NAB worked to establish a commercial radio system in the United States. The system was set up in August 1928 with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports Video Group
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, through casual or organized participation, improve participants' physical health. Hundreds of sports exist, from those between single contestants, through to those with hundreds of simultaneous participants, either in teams or competing as individuals. In certain sports such as racing, many contestants may compete, simultaneously or consecutively, with one winner; in others, the contest (a ''match'') is between two sides, each attempting to exceed the other. Some sports allow a "tie" or "draw", in which there is no single winner; others provide tie-breaking methods to ensure one winner and one loser. A number of contests may be arranged in a tournament producing a champion. Many sports leagues make an annual champion by arranging games in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Company
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (listed company), which facilitates the trade of shares, or not (unlisted public company). In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are ''private'' enterprises in the ''private'' sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets. Public companies are formed within the legal systems of particular states, and therefore have associations and formal designations which are distinct and separate in the polity in which they reside. In the United States, for example, a public company is usually a type of corporation (though a corporation need not be a public company), in the United Kingdom it is usually a public limited company (plc), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union
The Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union (ABU or APBU), formed in 1964, is a non-profit, professional association of broadcasting organisations. It currently has over 287 members in 57 countries and regions, reaching a potential audience of about 3 billion people. The ABU's role is to help the development of broadcasting in the Asia-Pacific region and to promote the collective interests of its members. The ABU covers an area stretching from Turkey in the west to Samoa in the east, and from Mongolia in the north to New Zealand in the south. Its secretariat is located in Angkasapuri, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, its secretary-general, currently Dr Javad Mottaghi. One of the ABU's activities is Asiavision, a daily exchange of news feeds by satellite among television stations in 20 countries in Asia. The ABU also negotiates coverage rights to major sports events for its members collectively, and carries out a wide range of activities in the programme and technical areas. The ABU provides a foru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azure DevOps Server
Azure DevOps Server (formerly Team Foundation Server (TFS) and Visual Studio Team System (VSTS)) is a Microsoft product that provides version control (either with Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) or Git (software), Git), reporting, requirements management, project management (for both agile software development and waterfall model, waterfall teams), automated builds, software testing, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire Application Lifecycle Management, application lifecycle, and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse (software), Eclipse on all platforms. On-premises vs. online Azure DevOps is available in two different forms: on-premises ("Server") and online ("Services"). The latter form is called Azure DevOps Services (formerly Visual Studio Online before it was renamed to Visual Studio Team Services in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


