Hispaniolan Elaenia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the
 The Taíno people traveled often and used hollowed canoes with paddles when on the water for fishing or for migration purposes, and upwards of 100 people could fit into a single canoe. The Taíno came frequently in contact with the
The Taíno people traveled often and used hollowed canoes with paddles when on the water for fishing or for migration purposes, and upwards of 100 people could fit into a single canoe. The Taíno came frequently in contact with the
 Christopher Columbus first landed at Hispaniola on December 6, 1492 at a small bay he named San Nicolas, now called Môle-Saint-Nicolas on the north coast of present-day Haiti. He was welcomed in a friendly fashion by the indigenous people known as the Taíno. Trading with the natives yielded more gold than they had come across previously on the other Caribbean islands and Columbus was led to believe that much more gold would be found inland. Before he could explore further, his flagship, the '' Santa Maria'', ran aground and sank in the bay on December 24. With only two smaller ships remaining for the voyage home, Columbus built a fortified encampment, La Navidad, on the shore and left behind 21 crewman to await his return the following year.
Colonization began in earnest the following year when Columbus brought 1,300 men to Hispaniola in November 1493 with the intention of establishing a permanent settlement. They found the encampment at Navidad had been destroyed and all the crewmen left behind killed by the natives. Columbus decided to sail east in search of a better site to found a new settlement. In January 1494 they established La Isabela in present-day Dominican Republic.
Christopher Columbus first landed at Hispaniola on December 6, 1492 at a small bay he named San Nicolas, now called Môle-Saint-Nicolas on the north coast of present-day Haiti. He was welcomed in a friendly fashion by the indigenous people known as the Taíno. Trading with the natives yielded more gold than they had come across previously on the other Caribbean islands and Columbus was led to believe that much more gold would be found inland. Before he could explore further, his flagship, the '' Santa Maria'', ran aground and sank in the bay on December 24. With only two smaller ships remaining for the voyage home, Columbus built a fortified encampment, La Navidad, on the shore and left behind 21 crewman to await his return the following year.
Colonization began in earnest the following year when Columbus brought 1,300 men to Hispaniola in November 1493 with the intention of establishing a permanent settlement. They found the encampment at Navidad had been destroyed and all the crewmen left behind killed by the natives. Columbus decided to sail east in search of a better site to found a new settlement. In January 1494 they established La Isabela in present-day Dominican Republic.
 In 1496, the town of Nueva Isabela was founded. After being destroyed by a hurricane, it was rebuilt on the opposite side of the Ozama River and called Santo Domingo. It is the oldest permanent European settlement in the Americas.
The island had an important role in the establishment of Latin American colonies for decades to come. Due to its strategic location, it was the military stronghold of ''
In 1496, the town of Nueva Isabela was founded. After being destroyed by a hurricane, it was rebuilt on the opposite side of the Ozama River and called Santo Domingo. It is the oldest permanent European settlement in the Americas.
The island had an important role in the establishment of Latin American colonies for decades to come. Due to its strategic location, it was the military stronghold of ''
 In 1625,
In 1625,  In 1655 the island of Tortuga was reoccupied by the English and French. In 1660 the English appointed a Frenchman as Governor who proclaimed the King of France, set up French colours, and defeated several English attempts to reclaim the island. In 1665, French colonization of the island was officially recognized by King Louis XIV. The French colony was given the name
In 1655 the island of Tortuga was reoccupied by the English and French. In 1660 the English appointed a Frenchman as Governor who proclaimed the King of France, set up French colours, and defeated several English attempts to reclaim the island. In 1665, French colonization of the island was officially recognized by King Louis XIV. The French colony was given the name
 European colonists often died young due to tropical fevers, as well as from violent slave resistance in the late eighteenth century. In 1791, during the French Revolution, a major slave revolt broke out on Saint-Domingue. When the
European colonists often died young due to tropical fevers, as well as from violent slave resistance in the late eighteenth century. In 1791, during the French Revolution, a major slave revolt broke out on Saint-Domingue. When the  In 1808, following Napoleon's invasion of Spain, the criollos of Santo Domingo revolted against French rule and, with the aid of the United Kingdom, returned Santo Domingo to Spanish control. Fearing the influence of a society of slaves that had successfully revolted against their owners, the United States and European powers refused to recognize Haiti, the second republic in the Western Hemisphere. France demanded a high payment for compensation to slaveholders who lost their property, and Haiti was saddled with unmanageable debt for decades. Diamond, Jared M. and Robinson, James A. (2011) ''Natural Experiments of History''. pp. 126–128. Haiti would Annex Spanish Haiti which had recently gained independence. However, suppression of the Dominican culture would lead to the Dominican War of Independence. This is one of the reasons for the tensions between the two countries today. Haiti would become one of the poorest countries in the Americas, while the Dominican Republic gradually has developed into one of the largest economies of Central America and the
In 1808, following Napoleon's invasion of Spain, the criollos of Santo Domingo revolted against French rule and, with the aid of the United Kingdom, returned Santo Domingo to Spanish control. Fearing the influence of a society of slaves that had successfully revolted against their owners, the United States and European powers refused to recognize Haiti, the second republic in the Western Hemisphere. France demanded a high payment for compensation to slaveholders who lost their property, and Haiti was saddled with unmanageable debt for decades. Diamond, Jared M. and Robinson, James A. (2011) ''Natural Experiments of History''. pp. 126–128. Haiti would Annex Spanish Haiti which had recently gained independence. However, suppression of the Dominican culture would lead to the Dominican War of Independence. This is one of the reasons for the tensions between the two countries today. Haiti would become one of the poorest countries in the Americas, while the Dominican Republic gradually has developed into one of the largest economies of Central America and the
 Hispaniola is the second-largest island in the Caribbean (after Cuba), with an area of , of which is under the sovereignty of the Dominican Republic occupying the eastern portion and under the sovereignty of Haiti occupying the western portion.
The island of Cuba lies to the northwest across the Windward Passage; 190 km (118 mi) to the southwest lies Jamaica, separated by the Jamaica Channel. Puerto Rico lies 130 km (80 mi) east of Hispaniola across the
Hispaniola is the second-largest island in the Caribbean (after Cuba), with an area of , of which is under the sovereignty of the Dominican Republic occupying the eastern portion and under the sovereignty of Haiti occupying the western portion.
The island of Cuba lies to the northwest across the Windward Passage; 190 km (118 mi) to the southwest lies Jamaica, separated by the Jamaica Channel. Puerto Rico lies 130 km (80 mi) east of Hispaniola across the
 Hispaniola's climate shows considerable variation due to its diverse mountainous topography, and is the most varied island of all the Antilles. Except in the Northern Hemisphere summer season, the predominant winds over Hispaniola are the northeast trade winds. As in Jamaica and Cuba, these winds deposit their moisture on the northern mountains, and create a distinct
Hispaniola's climate shows considerable variation due to its diverse mountainous topography, and is the most varied island of all the Antilles. Except in the Northern Hemisphere summer season, the predominant winds over Hispaniola are the northeast trade winds. As in Jamaica and Cuba, these winds deposit their moisture on the northern mountains, and create a distinct
File:Hato mayor, dominican republic waterfall.jpg, Salto de Jalda in Hato Mayor, Dominican Republic, the tallest waterfall in the Caribbean
File:View of Haitian Landscape hispaniola.jpg, Les Cayes,
 In
In
 Hispaniola is the most populous Caribbean island with combined population of almost 22 million inhabitants .
The Dominican Republic is a
Hispaniola is the most populous Caribbean island with combined population of almost 22 million inhabitants .
The Dominican Republic is a
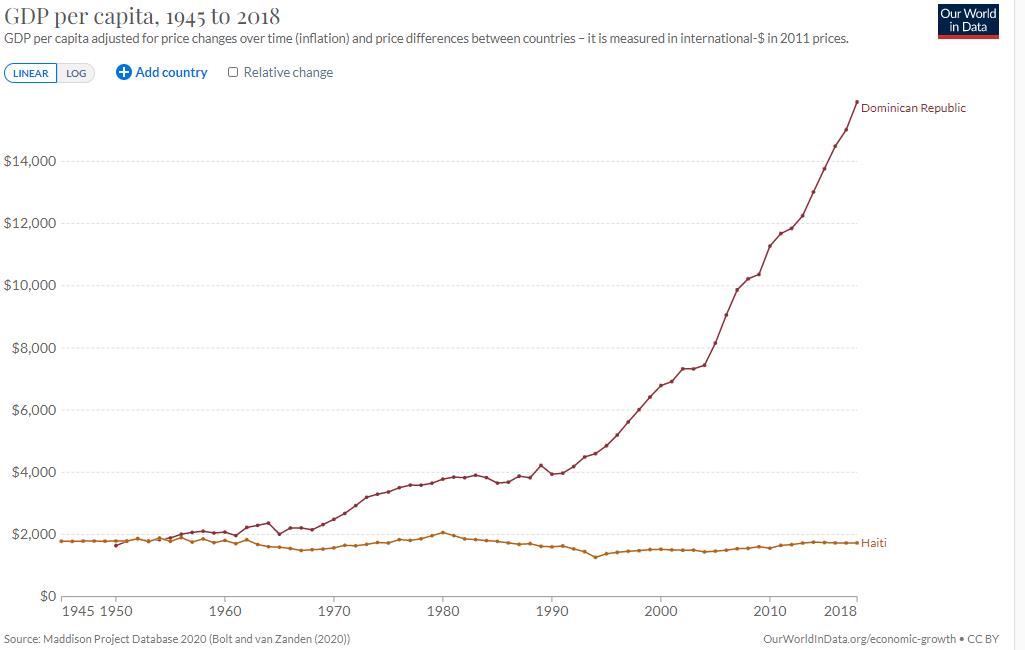
 The island has the largest economy in the Greater Antilles, however most of the economic development is found in the Dominican Republic, the Dominican economy being nearly 800% larger than the Haitian economy. , the estimated annual per capita income is US$868 in Haiti and US$8,050 in Dominican Republic.
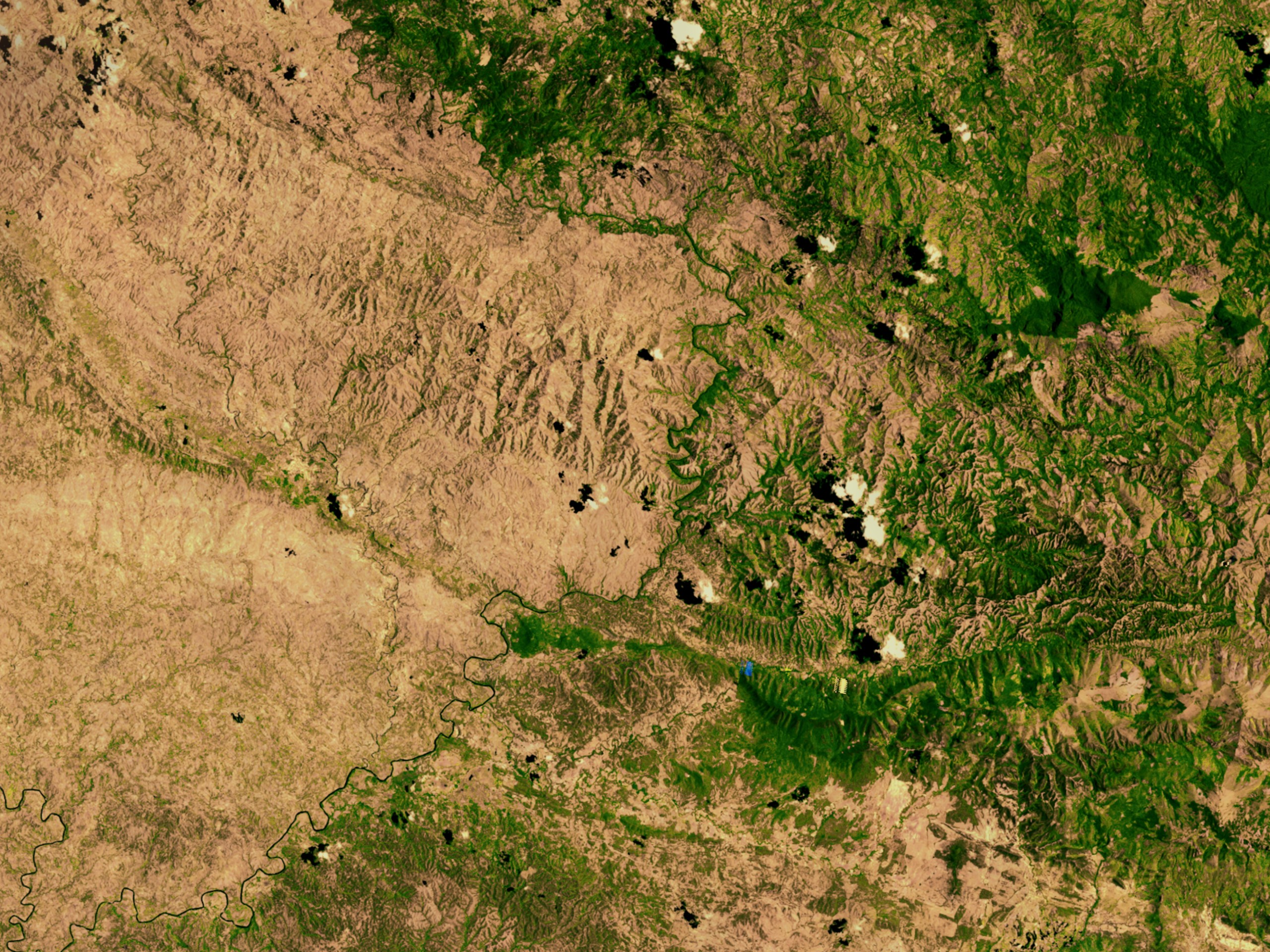
The divergence between the level of economic development between Haiti and Dominican Republic makes its border the higher contrast of all western land borders and is evident that the Dominican Republic has one of the highest migration issues in the Americas.
The island has the largest economy in the Greater Antilles, however most of the economic development is found in the Dominican Republic, the Dominican economy being nearly 800% larger than the Haitian economy. , the estimated annual per capita income is US$868 in Haiti and US$8,050 in Dominican Republic.
The divergence between the level of economic development between Haiti and Dominican Republic makes its border the higher contrast of all western land borders and is evident that the Dominican Republic has one of the highest migration issues in the Americas.




Google maps
Map of the Islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico
from 1639
at the Library of Congress contains primary materials on Hispaniola. {{Authority control Hispaniola, French Caribbean Greater Antilles International islands Islands of Haiti Islands of the Dominican Republic Spanish West Indies Freshwater ecoregions
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and the region's second largest in area, after the island of Cuba
Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea. Cuba's area is 110,860 km² (42,803 sq mi) including coastal and territorial waters with a land area of . This makes it the eighth-largest island country in the world. The main island (Cuba) has of ...
.
The island is divided into two separate nations: the Spanish-speaking Dominican Republic (48,445 km2, 18,705 sq mi) to the east and the French/Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; ht, kreyòl ayisyen, links=no, ; french: créole haïtien, links=no, ), commonly referred to as simply ''Creole'', or ''Kreyòl'' in the Creole language, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10–12million people wor ...
-speaking Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
(27,750 km2, 10,710 sq mi) to the west. The only other divided island in the Caribbean is Saint Martin Saint Martin may refer to:
People
* Saint Martin of Tours (c. 316–397), Bishop of Tours, France
* Saint Martin of Braga (c. 520–580), archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal)
* Pope Martin I (598–655)
* Saint Mart ...
, which is shared between France (Saint Martin Saint Martin may refer to:
People
* Saint Martin of Tours (c. 316–397), Bishop of Tours, France
* Saint Martin of Braga (c. 520–580), archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal)
* Pope Martin I (598–655)
* Saint Mart ...
) and the Netherlands ( Sint Maarten).
Hispaniola is the site of one of the first European settlements in the Americas, La Navidad (1492–1493), as well as the first proper town, La Isabela (1493–1500), and the first permanent settlement, the current capital of the Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo (est. 1498). These settlements were founded successively during each of Christopher Columbus's first three voyages.
The Spanish Empire controlled the entire island of Hispaniola from the 1490s until the 17th century, when French pirates began establishing bases on the western side of the island. The official name was ''La Española'', meaning "The Spanish (Island)". It was also called '' Santo Domingo'', after Saint Dominic
Saint Dominic ( es, Santo Domingo; 8 August 1170 – 6 August 1221), also known as Dominic de Guzmán (), was a Castilian Catholic priest, mystic, the founder of the Dominican Order and is the patron saint of astronomers and natural scientis ...
.
Etymology
The island was called by various names by its native people, the Taíno. The Taino had no written language, hence, historical evidence for these names comes through three European historians: the ItalianPeter Martyr d'Anghiera
Peter Martyr d'Anghiera ( la, Petrus Martyr Anglerius or ''ab Angleria''; it, Pietro Martire d'Anghiera; es, Pedro Mártir de Anglería; 2 February 1457 – October 1526), formerly known in English as Peter Martyr of Angleria,D'Anghier ...
, and the Spaniards Bartolomé de las Casas and Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo. Based on a comprehensive survey and map prepared by Andrés de Morales in 1508, Martyr reported that the island as a whole was called ''Quizquella'' (or ''Quisqueya'') and ''Haiti'' referred to a rugged mountainous region on the eastern end of the island. Diego Álvarez Chanca
Diego Álvarez Chanca (c. 1463 - c. 1515) was a Spanish physician who accompanied Christopher Columbus on his second voyage.
Chanca was a physician-in-ordinary to Ferdinand and Isabella, which is how he was introduced to Columbus. He was appoi ...
, a physician on Columbus's second voyage, also noted that ''Haiti'' was the easternmost province of the island. On the other hand, Oviedo and Las Casas both recorded that the entire island was called ''Haití'' by the Taíno.
When Columbus took possession of the island in 1492, he named it ''Insula Hispana'' in Latin and ''La Isla Española'' in Spanish, both meaning "the Spanish island". Las Casas shortened the name to ''Española'', and when Peter Martyr detailed his account of the island in Latin, he rendered its name as ''Hispaniola''.
Due to Taíno, Spanish and French influences on the island, historically the whole island was often referred to as ''Haiti'', ''Hayti'', ''Santo Domingo'', or ''Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
''. Martyr's literary work was translated into English and French soon after being written, the name Hispaniola became the most frequently used term in English-speaking countries for the island in scientific and cartographic works. In 1918, the United States occupation government, led by Harry Shepard Knapp, obliged the use of the name Hispaniola on the island, and recommended the use of that name to the National Geographic Society.
The name "Haïti" was adopted by Haitian revolutionary Jean-Jacques Dessalines
Jean-Jacques Dessalines (Haitian Creole: ''Jan-Jak Desalin''; ; 20 September 1758 – 17 October 1806) was a leader of the Haitian Revolution and the first ruler of an independent First Empire of Haiti, Haiti under the Constitution of Haiti, 1 ...
in 1804, as the official name of independent Saint-Domingue, in tribute to the Amerindian predecessors. It was also adopted as the official name of independent Santo Domingo, as the Republic of Spanish Haiti
The Independent Republic of Spanish Haiti ( es, República del Haití Español), also called the Independent State of Spanish Haiti () was the independent state that resulted from the defeat of Spanish colonialists from Santo Domingo on November ...
, a state that existed from November 1821 until its annexation by Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
in February 1822.
History
Pre-Columbian
The Archaic Age people arrived from the mainland about 6,000 or 7,000 years ago. The primary indigenous group on the island of Hispaniola was the Taíno people. The Arawak tribe originated in the Orinoco Delta, spreading from what is now Venezuela. They arrived on Hispaniola around 1200 CE. Each society on the island was a small independent kingdom with a lead known as acacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spa ...
. In 1492, which is considered the peak of the Taíno, there were five different kingdoms on the island, the Xaragua, Higuey (Caizcimu), Magua (Huhabo), Ciguayos (Cayabo or Maguana), and Marien (Bainoa). Many distinct Taíno languages also existed in this time period. There is still heated debate over the population of Taíno people on the island of Hispaniola in 1492, but estimates range from no more than a few tens of thousands, according to a 2020 genetic analysis, to upwards of 750,000.
A Taíno home consisted of a circular building with woven straw and palm leaves as covering. Most individuals slept in fashioned hammocks, but grass beds were also used. The cacique lived in a different structure with larger rectangular walls and a porch. The Taíno village also had a flat court used for ball games and festivals. Religiously, the Taíno people were polytheists, and their gods were called Zemí. Religious worship and dancing were common, and medicine men or priests also consulted the Zemí for advice in public ceremonies.
For food, the Taíno relied on meat and fish as a primary source for protein; some small mammals on the island were hunted including rats, but ducks, turtles, snakes and bats were a common food source. The Taíno also relied on agriculture as a primary food source. The indigenous people of Hispaniola raised crops in a conuco, which is a large mound packed with leaves and fixed crops to prevent erosion. Some common agricultural goods were cassava, maize, squash, beans, peppers, peanuts, cotton, and tobacco, which was used as an aspect of social life and religious ceremonies.
 The Taíno people traveled often and used hollowed canoes with paddles when on the water for fishing or for migration purposes, and upwards of 100 people could fit into a single canoe. The Taíno came frequently in contact with the
The Taíno people traveled often and used hollowed canoes with paddles when on the water for fishing or for migration purposes, and upwards of 100 people could fit into a single canoe. The Taíno came frequently in contact with the Caribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
* Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
* Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous ...
, another indigenous tribe. The Taíno people had to defend themselves using bows and arrows with poisoned tips and some war clubs. When Columbus landed on Hispaniola, many Taíno leaders wanted protection from the Caribs.
Post-Columbian
 Christopher Columbus first landed at Hispaniola on December 6, 1492 at a small bay he named San Nicolas, now called Môle-Saint-Nicolas on the north coast of present-day Haiti. He was welcomed in a friendly fashion by the indigenous people known as the Taíno. Trading with the natives yielded more gold than they had come across previously on the other Caribbean islands and Columbus was led to believe that much more gold would be found inland. Before he could explore further, his flagship, the '' Santa Maria'', ran aground and sank in the bay on December 24. With only two smaller ships remaining for the voyage home, Columbus built a fortified encampment, La Navidad, on the shore and left behind 21 crewman to await his return the following year.
Colonization began in earnest the following year when Columbus brought 1,300 men to Hispaniola in November 1493 with the intention of establishing a permanent settlement. They found the encampment at Navidad had been destroyed and all the crewmen left behind killed by the natives. Columbus decided to sail east in search of a better site to found a new settlement. In January 1494 they established La Isabela in present-day Dominican Republic.
Christopher Columbus first landed at Hispaniola on December 6, 1492 at a small bay he named San Nicolas, now called Môle-Saint-Nicolas on the north coast of present-day Haiti. He was welcomed in a friendly fashion by the indigenous people known as the Taíno. Trading with the natives yielded more gold than they had come across previously on the other Caribbean islands and Columbus was led to believe that much more gold would be found inland. Before he could explore further, his flagship, the '' Santa Maria'', ran aground and sank in the bay on December 24. With only two smaller ships remaining for the voyage home, Columbus built a fortified encampment, La Navidad, on the shore and left behind 21 crewman to await his return the following year.
Colonization began in earnest the following year when Columbus brought 1,300 men to Hispaniola in November 1493 with the intention of establishing a permanent settlement. They found the encampment at Navidad had been destroyed and all the crewmen left behind killed by the natives. Columbus decided to sail east in search of a better site to found a new settlement. In January 1494 they established La Isabela in present-day Dominican Republic.
conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
s'' of the Spanish Empire, serving as a headquarters for the further colonial expansion into the Americas. The colony was a meeting point of European explorers, soldiers, and settlers who brought with them the culture, architecture, laws, and traditions of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by the ...
.
Harsh enslavement practiced by Spanish colonists against the Taínos, as well as redirection of food supplies and labor of the indigenous for feeding Spanish settlers, had a devastating impact on both mortality and fertility of the Taíno population over the first quarter century. Colonial administrators and Dominican and Hyeronimite priests observed that the search for gold and agrarian enslavement through the ''encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
'' system were depressing population. Demographic data from two provinces in 1514 shows a low birth rate, consistent with a 3.5% annual population decline. In 1503, the colony began to import African slaves after a charter was passed in 1501, allowing the import of slaves by Ferdinand and Isabel. The Spanish believed Africans would be more capable of performing physical labor. From 1519 to 1533, the indigenous uprising known as Enriquillo
Enriquillo, also known as "Enrique" by the Spaniards, was a Taíno cacique who rebelled against the Spaniards between 1519 and 1533. Enriquillo's rebellion is the best known rebellion of the early Caribbean period. He was born on the shores of ...
's Revolt, after the Taíno cacique who led them, ensued, resulting from escaped African slaves on the island ( maroons) possibly working with the Taíno people.
Precious metals played a large role in the history of the island after Columbus's arrival. One of the first inhabitants Columbus came across on this island was "a girl wearing only a gold nose plug". Soon the Taínos were trading pieces of gold for hawk's bells with their cacique declaring the gold came from Cibao. Traveling further east from Navidad, Columbus came across the Yaque del Norte River, which he named Río de Oro (River of Gold) because its "sands abound in gold dust".
On Columbus's return during his second voyage, he learned it was the chief Caonabo who had massacred his settlement at Navidad. While Columbus established a new settlement the village of La Isabela on Jan. 1494, he sent Alonso de Ojeda and 15 men to search for the mines of Cibao. After a six-day journey, Ojeda came across an area containing gold, in which the gold was extracted from streams by the Taíno people. Columbus himself visited the mines of Cibao on 12 March 1494. He constructed the Fort of Santo Tomás, present day Jánico, leaving Captain Pedro Margarit in command of 56 men. On 24 March 1495, Columbus, with his ally Guacanagarix, embarked on a war of revenge against Caonabo, capturing him and his family while killing and capturing many natives. Afterwards, every person over the age of fourteen had to produce a hawksbill of gold.
16th century: gold, sugar and pirates
Miguel Díaz and Francisco de Garay discovered large gold nuggets on the lower Haina River in 1496. These San Cristobal mines were later known as the Minas Viejas mines. Then, in 1499, the first major discovery of gold was made in the cordillera central, which led to a mining boom. By 1501 Columbus's cousin, Giovanni Colombo, had discovered gold near Buenaventura. The deposits were later known as Minas Nuevas. Two major mining areas resulted, one along San Cristobal-Buenaventura, and another in Cibao within the La Vega-Cotuy- Bonao triangle, while Santiago de los Caballeros, Concepción, and Bonao became mining towns. The gold rush of 1500–1508 ensued, and Ovando expropriated the gold mines of Miguel Díaz and Francisco de Garay in 1504, as pit mines became royal mines forFerdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from ...
, who reserved the best mines for himself, though placers were open to private prospectors. Furthermore, Ferdinand kept 967 natives in the San Cristobal mining area, supervised by salaried miners.
Under Nicolás de Ovando y Cáceres
Nicolas or Nicolás may refer to:
People Given name
* Nicolas (given name)
Mononym
* Nicolas (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer
* Nicolas (footballer, born 2000), Brazilian footballer
Surname Nicolas
* Dafydd Nicolas (c.1705–17 ...
' governorship, the Indians were made to work in the gold mines. By 1503, the Spanish Crown legalized the distribution of Indians to work the mines through the encomienda system. Once the Indians entered the mines, they were often wiped out by hunger and difficult conditions. By 1508, the Taíno population of about 400,000 was reduced to 60,000, and by 1514, only 26,334 remained. About half resided in the mining towns of Concepción, Santiago, Santo Domingo, and Buenaventura. The repartimiento of 1514 accelerated emigration of the Spanish colonists, coupled with the exhaustion of the mines. The first documented outbreak of smallpox, previously an Eastern hemisphere disease, occurred on Hispaniola in December 1518 among enslaved African miners. Some scholars speculate that European diseases arrived before this date, but there is no compelling evidence for an outbreak. The natives had no acquired immunity to European diseases, including smallpox. By May 1519, as many as one-third of the remaining Taínos had died. In the century following the Spanish arrival on Hispaniola, the Taino population fell by up to 95% of the population, out of a pre-contact population estimated from tens of thousands to 8,000,000. Many authors have described the treatment of Tainos in Hispaniola under the Spanish Empire as genocide.
Sugar cane was introduced to Hispaniola by settlers from the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, and the first sugar mill in the New World was established in 1516, on Hispaniola. The need for a labor force to meet the growing demands of sugar cane cultivation led to an exponential increase in the importation of slaves over the following two decades. The sugar mill owners soon formed a new colonial elite.
The first major slave revolt in the Americas occurred in Santo Domingo during 1522, when enslaved Muslims of the Wolof nation led an uprising in the sugar plantation of admiral Don Diego Colon
Diego Columbus ( pt, Diogo Colombo; es, Diego Colón; it, Diego Colombo; 1479/1480 – February 23, 1526) was a navigator and explorer under the Kings of Castile and Aragón. He served as the 2nd Admiral of the Indies, 2nd Viceroy of the Indie ...
, son of Christopher Columbus. Many of these insurgents managed to escape where they formed independent maroon
Maroon ( US/ UK , Australia ) is a brownish crimson color that takes its name from the French word ''marron'', or chestnut. "Marron" is also one of the French translations for "brown".
According to multiple dictionaries, there are var ...
communities in the south of the island.
Beginning in the 1520s, the Caribbean Sea was raided by increasingly numerous French pirates. In 1541, Spain authorized the construction of Santo Domingo's fortified wall, and in 1560 decided to restrict sea travel to enormous, well-armed convoys. In another move, which would destroy Hispaniola's sugar industry, in 1561 Havana, more strategically located in relation to the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
, was selected as the designated stopping point for the merchant '' flotas,'' which had a royal monopoly on commerce with the Americas. In 1564, the island's main inland cities Santiago de los Caballeros and Concepción de la Vega were destroyed by an earthquake. In the 1560s, English privateers joined the French in regularly raiding Spanish shipping in the Americas.17th century
By the early 17th century, Hispaniola and its nearby islands (notably Tortuga) became regular stopping points forCaribbean pirates
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. In 1606, the government of Philip III ordered all inhabitants of Hispaniola to move close to Santo Domingo, to fight against piracy. Rather than secure the island, his action meant that French, English, and Dutch pirates established their own bases on the less populated north and west coasts of the island.
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and English pirates arrived on the island of Tortuga, just off the northwest coast of Hispaniola, which was originally settled by a few Spanish colonists. The pirates were attacked in 1629 by Spanish forces commanded by Don Fadrique de Toledo, who fortified the island, and expelled the French and English. As most of the Spanish army left for main island of Hispaniola to root out French colonists there, the French returned to Tortuga in 1630 and had constant battles for several decades. In 1654, the Spanish re-captured Tortuga for the last time.
 In 1655 the island of Tortuga was reoccupied by the English and French. In 1660 the English appointed a Frenchman as Governor who proclaimed the King of France, set up French colours, and defeated several English attempts to reclaim the island. In 1665, French colonization of the island was officially recognized by King Louis XIV. The French colony was given the name
In 1655 the island of Tortuga was reoccupied by the English and French. In 1660 the English appointed a Frenchman as Governor who proclaimed the King of France, set up French colours, and defeated several English attempts to reclaim the island. In 1665, French colonization of the island was officially recognized by King Louis XIV. The French colony was given the name Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
. By 1670 a Welsh privateer named Henry Morgan invited the pirates on the island of Tortuga to set sail under him. They were hired by the French as a striking force that allowed France to have a much stronger hold on the Caribbean region. Consequently, the pirates never really controlled the island and kept Tortuga as a neutral hideout. The capital of the French Colony of Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
was moved from Tortuga to Port-de-Paix on the mainland of Hispaniola in 1676.
In 1680, new Acts of Parliament forbade sailing under foreign flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
s (in opposition to former practice). This was a major legal blow to the Caribbean pirates. Settlements were made in the Treaty of Ratisbon of 1684, signed by the European powers, that put an end to piracy. Most of the pirates after this time were hired out into the Royal services to suppress their former buccaneer allies. In the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick, Spain formally ceded the western third of the island to France. Saint-Domingue quickly came to overshadow the east in both wealth and population. Nicknamed the "Pearl of the Antilles", it became the most prosperous colony in the West Indies, with a system of human slavery used to grow and harvest sugar cane during a time when European demand for sugar was high. Slavery kept costs low and profit was maximized. It was an important port in the Americas for goods and products flowing to and from France and Europe.18th century onwards
 European colonists often died young due to tropical fevers, as well as from violent slave resistance in the late eighteenth century. In 1791, during the French Revolution, a major slave revolt broke out on Saint-Domingue. When the
European colonists often died young due to tropical fevers, as well as from violent slave resistance in the late eighteenth century. In 1791, during the French Revolution, a major slave revolt broke out on Saint-Domingue. When the French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
abolished slavery in the colonies on February 4, 1794, it was a European first. The ex-slave army joined forces with France in its war against its European neighbors. In the second 1795 Treaty of Basel (July 22), Spain ceded the eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola, later to become the Dominican Republic. French settlers had begun to colonize some areas in the Spanish side of the territory.
Under Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, France reimposed slavery in most of its Caribbean islands in 1802 and sent an army to bring the island into full control. However, thousands of the French troops succumbed to yellow fever during the summer months, and more than half of the French army died because of disease. After an extremely brutal war with atrocities committed on both sides, the French removed the surviving 7,000 troops in late 1803, the leaders of the revolution declared western Hispaniola the new nation of independent Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
in early 1804. France continued to rule Spanish Santo Domingo. In 1805, Haitian troops of General Henri Christophe tried to conquer all of Hispaniola. They invaded Santo Domingo and sacked the towns of Santiago de los Caballeros and Moca, killing most of their residents, but news of a French fleet sailing towards Haiti forced General Christophe to withdraw from the east, leaving it in French hands.
 In 1808, following Napoleon's invasion of Spain, the criollos of Santo Domingo revolted against French rule and, with the aid of the United Kingdom, returned Santo Domingo to Spanish control. Fearing the influence of a society of slaves that had successfully revolted against their owners, the United States and European powers refused to recognize Haiti, the second republic in the Western Hemisphere. France demanded a high payment for compensation to slaveholders who lost their property, and Haiti was saddled with unmanageable debt for decades. Diamond, Jared M. and Robinson, James A. (2011) ''Natural Experiments of History''. pp. 126–128. Haiti would Annex Spanish Haiti which had recently gained independence. However, suppression of the Dominican culture would lead to the Dominican War of Independence. This is one of the reasons for the tensions between the two countries today. Haiti would become one of the poorest countries in the Americas, while the Dominican Republic gradually has developed into one of the largest economies of Central America and the
In 1808, following Napoleon's invasion of Spain, the criollos of Santo Domingo revolted against French rule and, with the aid of the United Kingdom, returned Santo Domingo to Spanish control. Fearing the influence of a society of slaves that had successfully revolted against their owners, the United States and European powers refused to recognize Haiti, the second republic in the Western Hemisphere. France demanded a high payment for compensation to slaveholders who lost their property, and Haiti was saddled with unmanageable debt for decades. Diamond, Jared M. and Robinson, James A. (2011) ''Natural Experiments of History''. pp. 126–128. Haiti would Annex Spanish Haiti which had recently gained independence. However, suppression of the Dominican culture would lead to the Dominican War of Independence. This is one of the reasons for the tensions between the two countries today. Haiti would become one of the poorest countries in the Americas, while the Dominican Republic gradually has developed into one of the largest economies of Central America and the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
.
Geography
 Hispaniola is the second-largest island in the Caribbean (after Cuba), with an area of , of which is under the sovereignty of the Dominican Republic occupying the eastern portion and under the sovereignty of Haiti occupying the western portion.
The island of Cuba lies to the northwest across the Windward Passage; 190 km (118 mi) to the southwest lies Jamaica, separated by the Jamaica Channel. Puerto Rico lies 130 km (80 mi) east of Hispaniola across the
Hispaniola is the second-largest island in the Caribbean (after Cuba), with an area of , of which is under the sovereignty of the Dominican Republic occupying the eastern portion and under the sovereignty of Haiti occupying the western portion.
The island of Cuba lies to the northwest across the Windward Passage; 190 km (118 mi) to the southwest lies Jamaica, separated by the Jamaica Channel. Puerto Rico lies 130 km (80 mi) east of Hispaniola across the Mona Passage
The Mona Passage ( es, Canal de la Mona) is a strait that separates the islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico. The Mona Passage connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Sea and is an important shipping route between the Atlantic and the Panama ...
. The Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands lie to the north. Its westernmost point is known as Cap Carcasse. Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico are collectively known as the Greater Antilles.
The island has five major ranges of mountains: The Central Range, known in the Dominican Republic as the Cordillera Central Central Cordillera refers to the New Guinea Highlands.
Cordillera Central, meaning ''central range'' in Spanish, may refer to the following mountain ranges:
* Cordillera Central, Andes (disambiguation), several mountain ranges in South America
** ...
, spans the central part of the island, extending from the south coast of the Dominican Republic into northwestern Haiti, where it is known as the Massif du Nord. This mountain range boasts the highest peak in the Antilles, Pico Duarte at above sea level. The Cordillera Septentrional runs parallel to the Central Range across the northern end of the Dominican Republic, extending into the Atlantic Ocean as the Samaná Peninsula. The Cordillera Central and Cordillera Septentrional are separated by the lowlands of the Cibao Valley and the Atlantic coastal plains, which extend westward into Haiti as the Plaine du Nord (Northern Plain). The lowest of the ranges is the Cordillera Oriental, in the eastern part of the country.
The Sierra de Neiba rises in the southwest of the Dominican Republic, and continues northwest into Haiti, parallel to the Cordillera Central, as the Montagnes Noires, Chaîne des Matheux and the Montagnes du Trou d'Eau. The Plateau Central lies between the Massif du Nord and the Montagnes Noires
The Montagnes Noires ( French, 'black mountains'), also known as the Montagne Noire ( French, 'black mountain') and in Breton as Menez Du are an east–west oriented range of hills in Brittany centred on the town of Gourin. They culminate in the ...
, and the Plaine de l'Artibonite lies between the Montagnes Noires and the Chaîne des Matheux, opening westward toward the Gulf of Gonâve, the largest gulf of the Antilles.
The southern range begins in the southwesternmost Dominican Republic as the Sierra de Bahoruco
The Bahoruco Mountain Range—Sierra de Bahoruco (or Sierra de Bahoruco) is a mountain range located in the far southwestern region of the Dominican Republic. It is within Pedernales, Independencia, Barahona, and Bahoruco Provinces. A large part ...
, and extends west into Haiti as the Massif de la Selle and the Massif de la Hotte, which form the mountainous spine of Haiti's southern peninsula. Pic de la Selle is the highest peak in the southern range, the third highest peak in the Antilles and consequently the highest point in Haiti, at above sea level. A depression runs parallel to the southern range, between the southern range and the Chaîne des Matheux-Sierra de Neiba. It is known as the Plaine du Cul-de-Sac
Plain of the Cul-de-Sac (french: Plaine du Cul-de-Sac, also known as the Cul-de-Sac Plain, or the Cul-de-Sac Depression) is a fertile lowland on the island of Hispaniola. It extends from southeastern Haiti into the southwestern Dominican Republi ...
in Haiti, and Haiti's capital Port-au-Prince
Port-au-Prince ( , ; ht, Pòtoprens ) is the capital and most populous city of Haiti. The city's population was estimated at 987,311 in 2015 with the metropolitan area estimated at a population of 2,618,894. The metropolitan area is define ...
lies at its western end. The depression is home to a chain of salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). ...
s, including Lake Azuei in Haiti and Lake Enriquillo in the Dominican Republic.
The island has four distinct ecoregions. The Hispaniolan moist forests
The Hispaniolan moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Hispaniola. They cover , around 60% of the island's area.
Geography
Moist forests occur on most of the eastern half the Dominican Republic, stretc ...
ecoregion covers approximately 50% of the island, especially the northern and eastern portions, predominantly in the lowlands but extending up to elevation. The Hispaniolan dry forests ecoregion occupies approximately 20% of the island, lying in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
of the mountains in the southern and western portion of the island and in the Cibao valley in the center-north of the island. The Hispaniolan pine forests
The Hispaniolan pine forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion found on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, which is shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic. The ecoregion covers , or about 15% of the island. It lies at elevations ...
occupy the mountainous 15% of the island, above elevation. The flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion in the south central region of the island surrounds a chain of lakes and lagoons in which the most notable include that of Lake Azuei and Trou Caïman in Haiti and the nearby Lake Enriquillo in the Dominican Republic, which is not only the lowest point of the island, but also the lowest point for an island country.
Climate
rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
on the southern coast, where some areas receive as little as of rainfall, and have semi-arid climates. Annual rainfall under also occurs on the southern coast of Haiti's northwest peninsula and in the central Azúa region of the Plaine du Cul-de-Sac. In these regions, moreover, there is generally little rainfall outside hurricane season from August to October, and droughts are by no means uncommon when hurricanes do not come.
On the northern coast, in contrast, rainfall may peak between December and February, though some rain falls in all months of the year. Annual amounts typically range from on the northern coastal lowlands; there is probably much more in the Cordillera Septentrional, though no data exist. The interior of Hispaniola, along with the southeastern coast centered around Santo Domingo, typically receives around per year, with a distinct season from May to October. Usually, this wet season has two peaks: one around May, the other around the hurricane season. In the interior highlands, rainfall is much greater, around per year, but with a similar pattern to that observed in the central lowlands.
The variations of temperature depend on altitude and are much less marked than rainfall variations in the island. Lowland Hispaniola is generally more hot and humid, with temperatures averaging . with high humidity during the daytime, and around at night. At higher altitudes, temperatures fall steadily, so that frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
s occur during the dry season on the highest peaks, where maxima are no higher than .
Sud
Sud or SUD may refer to:
Places
* Sud (Chamber of Deputies of Luxembourg constituency), a constituency in Luxembourg
* Sud (department), an administrative subdivision of Haiti
* Sud Department (Ivory Coast), defunct administrative subdivision of I ...
, Haiti
File:Constanza, valle nuevo, clima invierno..jpg, Frosted alpine forest in Constanza, Dominican Republic
File:Cabo Cabrón, (Rincón Beach) Samaná, DR.JPG, Tropical rainforest climate in Samana, Dominican Republic
File:Jaragua National Park (Road2).JPG, Semi-arid climate in Pedernales, Dominican Republic
File:Dunas de Baní 1.jpg, Desert sand dunes of Baní
Baní is a capital town of the Peravia Province, Dominican Republic. It is the commercial and manufacturing center in the southern region of Valdesia. The town is located 65 km south of the capital city Santo Domingo.
Baní is the headquarte ...
, Dominican Republic
File:Cordillera Central.jpg, Cordillera Central Central Cordillera refers to the New Guinea Highlands.
Cordillera Central, meaning ''central range'' in Spanish, may refer to the following mountain ranges:
* Cordillera Central, Andes (disambiguation), several mountain ranges in South America
** ...
in the Dominican Republic has the highest elevation of the Caribbean
Fauna
There are many bird species in Hispaniola, and the island's amphibian species are also diverse. There are many species endemic to the island including insects and other invertebrates, reptiles, and mammals. The two endemic terrestrial mammals on the island are theHispaniolan hutia
The Hispaniolan hutia (''Plagiodontia aedium'') is a small, endangered, rat-like mammal endemic to forests on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (split between Haiti and the Dominican Republic). It lives in burrows or trees, and is active at ni ...
(''Plagiodontia aedium'') and the Hispaniolan solenodon (''Solenodon paradoxus''). There are also many avian species on the island, with six endemic genera (''Calyptophilus
''Calyptophilus'' is a genus of bird formerly placed in the family Thraupidae. The group was found to be distinct enough to be placed in its own family, Calyptophilidae. Established by Charles Barney Cory in 1884, it contains the following spe ...
'', '' Dulus'', '' Nesoctites'', '' Phaenicophilus'', ''Xenoligea
The white-winged warbler (''Xenoligea montana''), also called the white-winged ground-warbler, is a Vulnerable species of bird of the family Phaenicophilidae, the Hispaniolan tanagers. It is endemic to the island of Hispaniola which is shared ...
'' and '' Microligea''). More than half of the original distribution of its ecoregions has been lost due to habitat destruction impacting the local fauna.
Flora
The island has four distinct ecoregions. TheHispaniolan moist forests
The Hispaniolan moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Hispaniola. They cover , around 60% of the island's area.
Geography
Moist forests occur on most of the eastern half the Dominican Republic, stretc ...
ecoregion covers approximately 50% of the island, especially the northern and eastern portions, predominantly in the lowlands but extending up to elevation. The Hispaniolan dry forests ecoregion occupies approximately 20% of the island, lying in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
of the mountains in the southern and western portion of the island, and in the Cibao valley in the center-north of the island. The Hispaniolan pine forests
The Hispaniolan pine forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion found on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, which is shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic. The ecoregion covers , or about 15% of the island. It lies at elevations ...
occupy the mountainous 15% of the island, above elevation. The flooded grasslands and savannas ecoregion in the south central region of the island surrounds a chain of lakes and lagoons , of which the most notable include that of Etang Saumatre and Trou Caïman in Haiti, and the nearby Lake Enriquillo in the Dominican Republic.
 In
In Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, deforestation has long been cited by scientists as a source of ecological crisis; the timber industry dates back to French colonial rule. Haiti has seen a dramatic reduction of forests due to the excessive and increasing use of charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, cal ...
as fuel for cooking. Various media outlets have suggested that the country has just 2% forest cover, but this has not been substantiated by research.
Recent in-depth studies of satellite imagery and environmental analysis regarding forest classification conclude that Haiti actually has approximately 30% tree cover; this is, nevertheless, a stark decrease from the country's 60% forest cover in 1925. The country has been significantly deforested over the last 50 years, resulting in the desertification of many portions of Haitian territory.
In the Dominican Republic, the forest cover has increased. In 2003, the Dominican Republic's forest cover had been reduced to 32% of its land area, but by 2011, forest cover had increased to nearly 40%. The success of the Dominican forest growth is due to several Dominican government policies and private organizations for the purpose of reforesting, and a strong educational campaign that has resulted in increased awareness by the Dominican people of the importance of forests for their welfare and other forms of life on the island.
Demographics
 Hispaniola is the most populous Caribbean island with combined population of almost 22 million inhabitants .
The Dominican Republic is a
Hispaniola is the most populous Caribbean island with combined population of almost 22 million inhabitants .
The Dominican Republic is a Hispanophone
Hispanophone and Hispanic refers to anything relating to the Spanish language (the Hispanosphere).
In a cultural, rather than merely linguistic sense, the notion of "Hispanophone" goes further than the above definition. The Hispanic culture is th ...
nation of approximately 10.35 million people. Spanish is spoken by all Dominicans as a primary language. Roman Catholicism is the official and dominant religion.
Haiti is a Creole-speaking nation of roughly 11.58 million people. Although French is spoken as a primary language by the educated and wealthy minority, virtually the entire population speaks Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; ht, kreyòl ayisyen, links=no, ; french: créole haïtien, links=no, ), commonly referred to as simply ''Creole'', or ''Kreyòl'' in the Creole language, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10–12million people wor ...
, one of several French-derived creole languages. Roman Catholicism is the dominant religion, practiced by more than half the population, although in some cases in combination with Haitian Vodou
Haitian Vodou is an African diasporic religion that developed in Haiti between the 16th and 19th centuries. It arose through a process of syncretism between several traditional religions of West and Central Africa and Roman Catholicism. There is ...
faith. Another 25% of the populace belong to Protestant churches. Haiti emerged as the first Black republic in the world.
Ethnic composition
The ethnic composition of the Dominican population is 73% mixed ethnicity, 16% white and 11% black. Descendants of early Spanish settlers and of black slaves from West Africa constitute the two main racial strains. The ethnic composition of Haiti is estimated to be 95% black and 5% white and mulatto. In recent times, Dominican and Puerto Rican researchers identified in the current Dominican population the presence of genes belonging to the aborigines of theCanary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
(commonly called Guanches). These types of genes also have been detected in Puerto Rico.
Economics

 The island has the largest economy in the Greater Antilles, however most of the economic development is found in the Dominican Republic, the Dominican economy being nearly 800% larger than the Haitian economy. , the estimated annual per capita income is US$868 in Haiti and US$8,050 in Dominican Republic.
The divergence between the level of economic development between Haiti and Dominican Republic makes its border the higher contrast of all western land borders and is evident that the Dominican Republic has one of the highest migration issues in the Americas.
The island has the largest economy in the Greater Antilles, however most of the economic development is found in the Dominican Republic, the Dominican economy being nearly 800% larger than the Haitian economy. , the estimated annual per capita income is US$868 in Haiti and US$8,050 in Dominican Republic.
The divergence between the level of economic development between Haiti and Dominican Republic makes its border the higher contrast of all western land borders and is evident that the Dominican Republic has one of the highest migration issues in the Americas.
Natural resources
The island also has an economic history and current day interest and involvement in precious metals. In 1860, it was observed that the island contained a large supply of gold, which the early Spaniards had hardly developed. By 1919, Condit and Ross noted that much of the island was covered by government granted concessions for mining different types of minerals. Besides gold, these minerals included silver, manganese, copper, magnetite, iron and nickel. Mining operations in 2016 have taken advantage of the volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposits (VMS) aroundMaimón
Maimón is a town in the Monseñor Nouel province of the Dominican Republic. Maimón is situated between Maimón river, La Leonora river, Yuna river and Zinc river, formed by a little valley and mountains in his sides.
The colonies that were esta ...
. To the northeast, the Pueblo Viejo Gold Mine was operated by state-owned Rosario Dominicana from 1975 until 1991. In 2009, Pueblo Viejo Dominicana Corporation, formed by Barrick Gold
Barrick Gold Corporation is a mining company that produces gold and copper with 16 operating sites in 13 countries. It is headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It has mining operations in Argentina, Canada, Chile, Côte d'Ivoire, Democrati ...
and Goldcorp, started open-pit mining operations of the Monte Negro and Moore oxide deposits. The mined ore is processed with gold cyanidation. Pyrite and sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimen ...
are the main sulfide minerals
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the ...
found in the 120 m thick volcanic conglomerates and agglomerate
Agglomerate (from the Latin ''agglomerare'' meaning "to form into a ball") is a coarse accumulation of large blocks of volcanic material that contains at least 75% bombs. Volcanic bombs differ from volcanic blocks in that their shape records flui ...
s, which constitute the world's second largest sulphidation gold deposit.
Between Bonao and Maimón, Falconbridge Dominicana has been mining nickel laterite
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by ...
s since 1971. The Cerro de Maimon copper/gold open-pit mine southeast of Maimón has been operated by Perilya since 2006. Copper is extracted from the sulfide ores, while gold and silver are extracted from both the sulfide and the oxide ores. Processing is via froth flotation and cyanidation. The ore is located in the VMS Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
Maimón Formation. Goethite enriched with gold and silver is found in the 30 m thick oxide cap. Below that cap is a supergene
A supergene is a chromosomal region encompassing multiple neighboring genes that are inherited together because of close genetic linkage, i.e. much less recombination than would normally be expected. This mode of inheritance can be due to genomic ...
zone containing pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite. Below the supergene zone is found the unaltered massive sulphide mineralization.
Human development
This is a list of Dominican Republic andHaiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
regions by Human Development Index as of 2018.

See also
* Casa de Contratación *Dominican Republic–Haiti relations
Dominican Republic–Haiti relations refers to the diplomatic relations between the Dominican Republic and the Republic of Haiti. Relations have long been complex due to the substantial ethnic and cultural differences between the two nations an ...
* Geography of the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic (Spanish: ''República Dominicana'') is a country in the West Indies that occupies the eastern five-eighths of Hispaniola. It has an area of 48,670 km2, including offshore islands. The land border shared with Haiti, whi ...
* Geography of Haiti
The Republic of Haiti comprises the western three-eighths of the island of Hispaniola, west of the Dominican Republic. Haiti is positioned east of the neighboring island of Cuba, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean. Haiti's geo ...
* Gonave Island
* List of divided islands
References
External links
Google maps
Map of the Islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico
from 1639
at the Library of Congress contains primary materials on Hispaniola. {{Authority control Hispaniola, French Caribbean Greater Antilles International islands Islands of Haiti Islands of the Dominican Republic Spanish West Indies Freshwater ecoregions