Guadeloupe La Première (television) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and
INSEE Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the Eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely. However, as an overseas department, it is not part of the
 The archipelago was called (or "The Island of Beautiful Waters") by the native Arawak people.
Christopher Columbus named the island in 1493 after Our Lady of Guadalupe, a shrine to the Virgin Mary venerated in the Spanish town of Guadalupe, Extremadura. When the area became a French colony, the Spanish name was retained - though altered to French orthography and phonology. The islands are locally known as .
The archipelago was called (or "The Island of Beautiful Waters") by the native Arawak people.
Christopher Columbus named the island in 1493 after Our Lady of Guadalupe, a shrine to the Virgin Mary venerated in the Spanish town of Guadalupe, Extremadura. When the area became a French colony, the Spanish name was retained - though altered to French orthography and phonology. The islands are locally known as .
 The islands were first populated by indigenous peoples of the Americas, possibly as far back as 3000 BCE. The Arawak people are the first identifiable group, but they were later displaced circa 1400 CE by Kalina-Carib peoples.
The islands were first populated by indigenous peoples of the Americas, possibly as far back as 3000 BCE. The Arawak people are the first identifiable group, but they were later displaced circa 1400 CE by Kalina-Carib peoples.
 The French Revolution brought chaos to Guadeloupe. Under new revolutionary law, freedmen were entitled to equal rights. Taking advantage of the chaotic political situation, Britain invaded Guadeloupe in 1794. The French responded by sending an expeditionary force led by Victor Hugues, who retook the islands and abolished slavery. More than 1,000 French colonists were killed in the aftermath.
The French Revolution brought chaos to Guadeloupe. Under new revolutionary law, freedmen were entitled to equal rights. Taking advantage of the chaotic political situation, Britain invaded Guadeloupe in 1794. The French responded by sending an expeditionary force led by Victor Hugues, who retook the islands and abolished slavery. More than 1,000 French colonists were killed in the aftermath.
 In 1802, the First French Empire reinstated the pre-revolutionary government and slavery, prompting a
In 1802, the First French Empire reinstated the pre-revolutionary government and slavery, prompting a
'' AFP'' Tourism suffered greatly during this time and affected the 2010 tourist season as well.


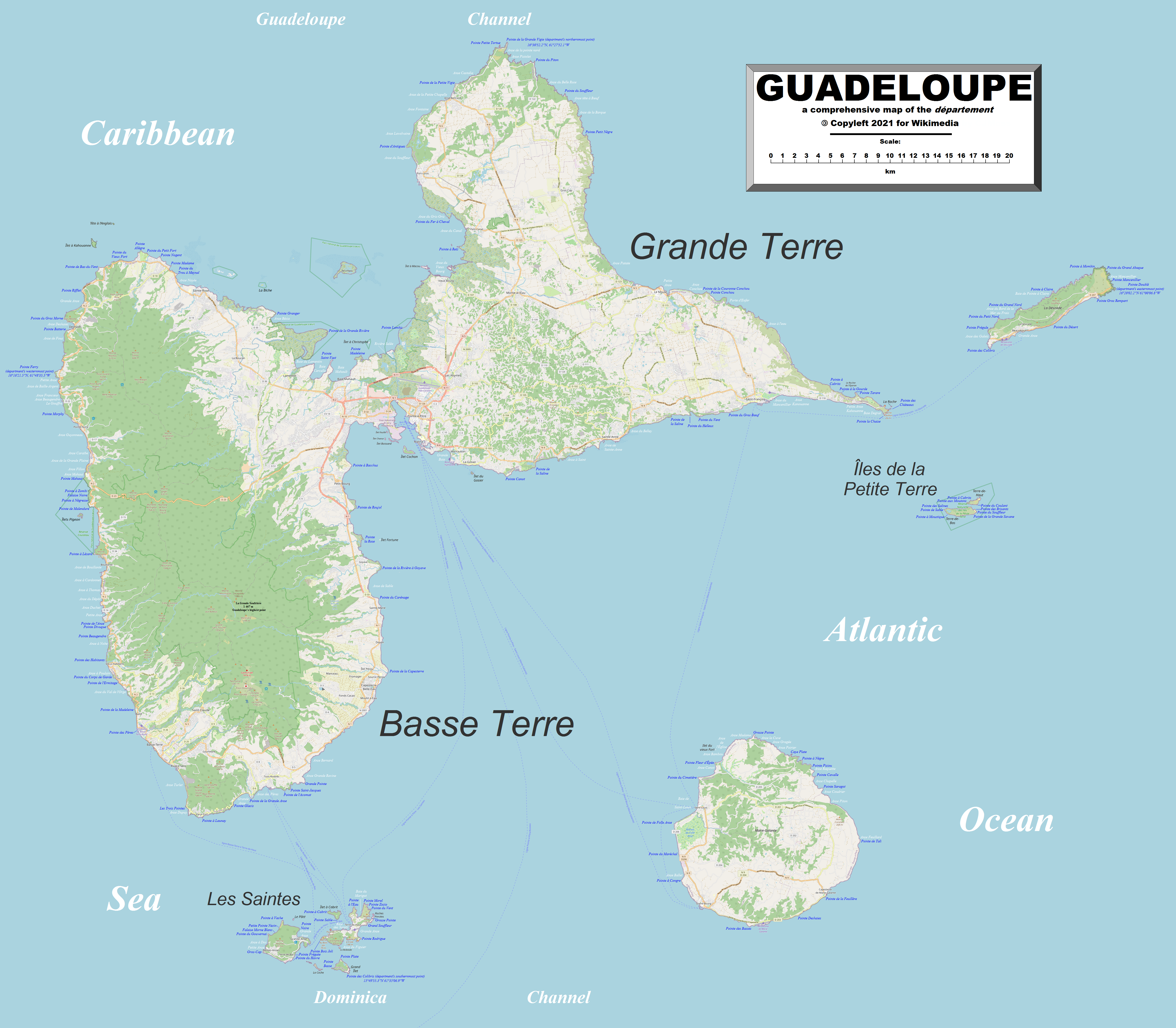 Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as islets and rocks situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. It is located in the
Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as islets and rocks situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. It is located in the

 With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as
With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as
overseas department and region
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainlan ...
of France in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre
Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe ...
, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the two inhabited Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a sovereign country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two maj ...
and Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, north of the Commonwealth of Dominica. The region's capital city is Basse-Terre, located on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; however, the most populous city is Les Abymes
Les Abymes () is the most populous commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is located on the west side of the island of Grande-Terre, and is part of the largest metropolitan area of Guadel ...
and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
, both located on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 384,239 in 2019.Populations légales 2019: 971 GuadeloupeINSEE Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the Eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely. However, as an overseas department, it is not part of the
Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
. The region formerly included Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin Saint Martin may refer to:
People
* Saint Martin of Tours (c. 316–397), Bishop of Tours, France
* Saint Martin of Braga (c. 520–580), archbishop of Bracara Augusta in Gallaecia (now Braga in Portugal)
* Pope Martin I (598–655)
* Saint Mart ...
, which were detached from Guadeloupe in 2007 following a 2003 referendum.
Christopher Columbus visited Guadeloupe in 1493, during his second voyage, and gave the island its name. The official language is French; Antillean Creole is also spoken.
Etymology
 The archipelago was called (or "The Island of Beautiful Waters") by the native Arawak people.
Christopher Columbus named the island in 1493 after Our Lady of Guadalupe, a shrine to the Virgin Mary venerated in the Spanish town of Guadalupe, Extremadura. When the area became a French colony, the Spanish name was retained - though altered to French orthography and phonology. The islands are locally known as .
The archipelago was called (or "The Island of Beautiful Waters") by the native Arawak people.
Christopher Columbus named the island in 1493 after Our Lady of Guadalupe, a shrine to the Virgin Mary venerated in the Spanish town of Guadalupe, Extremadura. When the area became a French colony, the Spanish name was retained - though altered to French orthography and phonology. The islands are locally known as .
History
Pre-colonial era
 The islands were first populated by indigenous peoples of the Americas, possibly as far back as 3000 BCE. The Arawak people are the first identifiable group, but they were later displaced circa 1400 CE by Kalina-Carib peoples.
The islands were first populated by indigenous peoples of the Americas, possibly as far back as 3000 BCE. The Arawak people are the first identifiable group, but they were later displaced circa 1400 CE by Kalina-Carib peoples.
15th–17th centuries
Christopher Columbus was the first European to see Guadeloupe, landing in November 1493 and giving it its current name. Several attempts at colonisation by the Spanish in the 16th century failed due to attacks from the native peoples. In 1626, the French under Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc began to take an interest in Guadeloupe, expelling Spanish settlers. The Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique settled in Guadeloupe in 1635, under the direction of Charles Liénard de L'Olive andJean du Plessis d'Ossonville
Jean du Plessis, sieur d’Ossonville (died 4 December 1635) was a joint leader of the French expedition that established a colony on the island of Guadeloupe in 1635. He died on the island after less than six months.
Background
Jean du Plessis ...
; they formally took possession of the island for France and brought in French farmers to colonise the land. This led to the death of many indigenous people by disease and violence. By 1640, however, the Compagnie des Îles de l'Amérique had gone bankrupt, and they thus sold Guadeloupe to Charles Houël du Petit Pré who began plantation agriculture, with the first African slaves arriving in 1650. Slave resistance was immediately widespread, with an open uprising in 1656 lasting several weeks and a simultaneous spate of mass desertions that lasted at least two years until the French compelled indigenous peoples to stop assisting them. Ownership of the island passed to the French West India Company before it was annexed to France in 1674 under the tutelage of their Martinique colony. Institutionalised slavery, enforced by the Code Noir from 1685, led to a booming sugar plantation economy.
18th–19th centuries
During the Seven Years' War, the British captured and occupied the islands until the1763 Treaty of Paris
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the S ...
. During that time, Pointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
became a major harbour, and markets in Britain's North American colonies were opened to Guadeloupean sugar, which was traded for foodstuffs and timber. The economy expanded quickly, creating vast wealth for the French colonists. So prosperous was Guadeloupe at the time that, under the 1763 Treaty of Paris, France forfeited its Canadian colonies in exchange for the return of Guadeloupe. Coffee planting began in the late 1720s, also worked by slaves and, by 1775, cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
had become a major export product as well.
slave rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedo ...
led by Louis Delgrès
Louis Delgrès (2 August 1766 – 28 May 1802) was a leader of the movement in Guadeloupe resisting reoccupation and thus the reinstitution of slavery by Napoleonic France in 1802.
Biography
Delgrès was mulatto, born free in Saint-Pierre, M ...
. The French authorities responded quickly, culminating in the Battle of Matouba
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
on 28 May 1802. Realising they had no chance of success, Delgrès and his followers committed mass suicide by deliberately exploding their gunpowder stores. In 1810, the British captured the island again, handing it over to Sweden under the 1813 Treaty of Stockholm.
In the 1814 Treaty of Paris, Sweden ceded Guadeloupe to France, giving rise to the Guadeloupe Fund The Guadeloupe Fund ( sv, Guadeloupefonden) was established by Sweden's Riksdag of the Estates in 1815 for the benefit of Crown Prince and Regent Charles XIV John of Sweden, (Swedish: ''Karl XIV Johan'') also known as ''Jean Baptiste Jules Bernado ...
. In 1815, the Treaty of Vienna acknowledged French control of Guadeloupe.
Slavery was abolished in the French Empire in 1848. After 1854, indentured labourer
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensa ...
s from the French colony of Pondicherry in India were brought in. Emancipated slaves had the vote from 1849, but French nationality and the vote were not granted to Indian citizens until 1923, when a long campaign, led by Henry Sidambarom, finally achieved success.
20th–21st centuries
In 1936,Félix Éboué
Adolphe Sylvestre Félix Éboué (; 26 December 1884 – 17 May 1944) was a French Guiana, French French colonial empires, colonial administrator and Free French Forces, Free French leader. He was the first black French man appointed to a hig ...
became the first black governor of Guadeloupe. During the Second World War Guadeloupe initially came under the control of the Vichy government, later joining Free France in 1943. In 1946, the colony of Guadeloupe became an overseas department of France.
Tensions arose in the post-war era over the social structure of Guadeloupe and its relationship with mainland France. The 'Massacre of St Valentine' occurred in 1952, when striking factory workers in Le Moule were shot at by the Compagnies républicaines de sécurité, resulting in four deaths. In May 1967 racial tensions exploded into rioting following a racist attack on a black Guadeloupean, resulting in eight deaths.
An independence movement grew in the 1970s, prompting France to declare Guadeloupe a French region in 1974. The Union populaire pour la libération de la Guadeloupe
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
(UPLG) campaigned for complete independence, and by the 1980s the situation had turned violent with the actions of groups such as Groupe de libération armée
A group is a military unit or a military formation that is most often associated with military aviation.
Air and aviation groups
The terms group and wing differ significantly from one country to another, as well as between different branches o ...
(GLA) and Alliance révolutionnaire caraïbe
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
(ARC).
Greater autonomy was granted to Guadeloupe in 2000. Through a referendum in 2003, Saint-Martin and Saint Barthélemy voted to separate from the administrative jurisdiction of Guadeloupe, this being fully enacted by 2007.
In January 2009, labour unions and others known as the Liyannaj Kont Pwofitasyon went on strike for more pay. Strikers were angry with low wages, the high cost of living, high levels of poverty relative to mainland France and levels of unemployment that are amongst the worst in the European Union. The situation quickly escalated, exacerbated by what was seen as an ineffectual response by the French government, turning violent and prompting the deployment of extra police after a union leader (Jacques Bino Jacques Bino (died February 18, 2009) was a Guadeloupean tax agent, activist and trade union official and representative. Bino was the first person killed during the violence associated with the 2009 French Caribbean general strikes.
Bino was an a ...
) was shot and killed. The strike lasted 44 days and had also inspired similar actions on nearby Martinique. President Nicolas Sarkozy
Nicolas Paul Stéphane Sarközy de Nagy-Bocsa (; ; born 28 January 1955) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2007 to 2012.
Born in Paris, he is of Hungarian, Greek Jewish, and French origin. Mayor of Neuilly-sur-Se ...
later visited the island, promising reform.Sarkozy offers autonomy vote for Martinique'' AFP'' Tourism suffered greatly during this time and affected the 2010 tourist season as well.
Geography


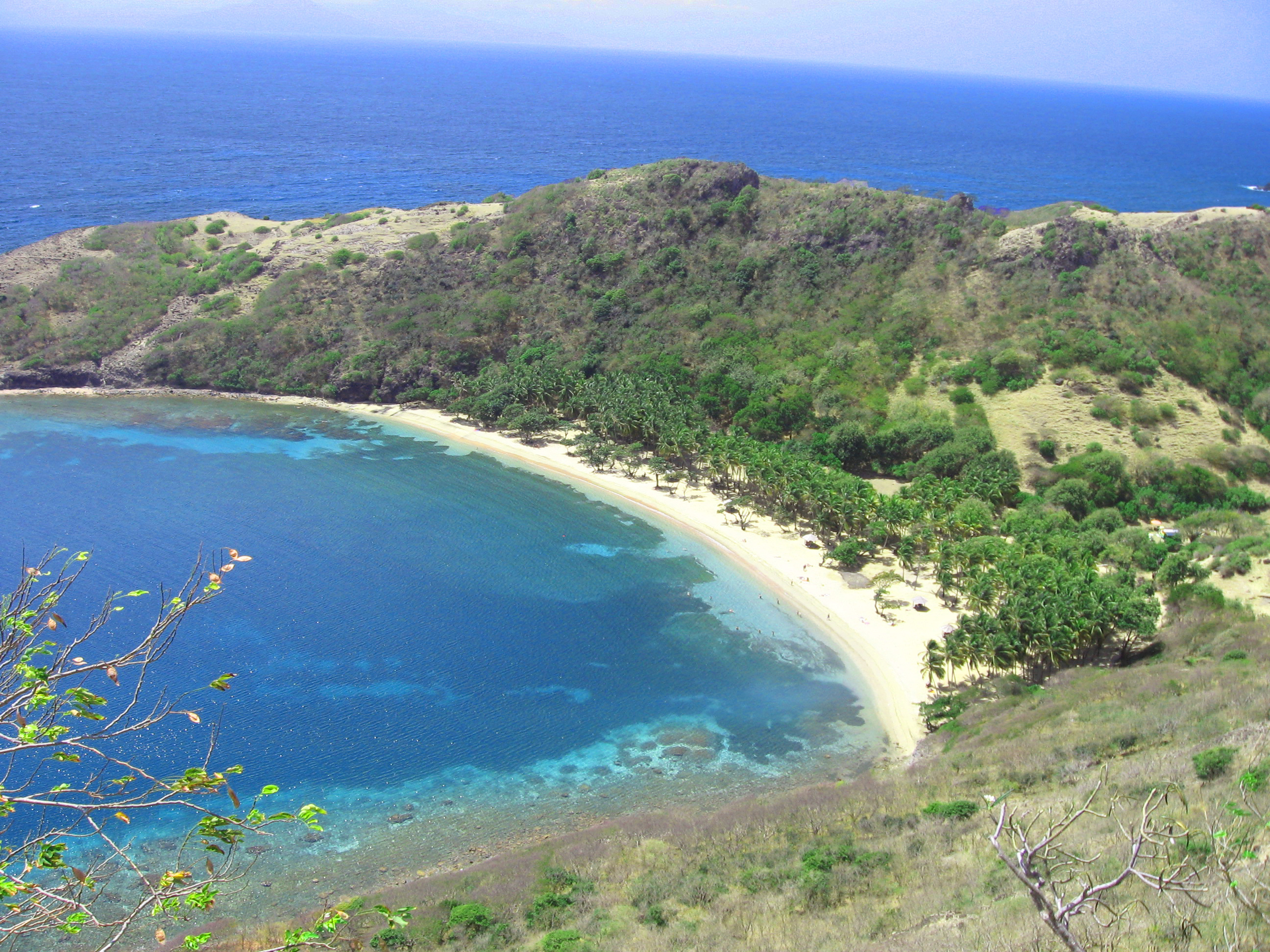
 Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as islets and rocks situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. It is located in the
Guadeloupe is an archipelago of more than 12 islands, as well as islets and rocks situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. It is located in the Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
in the northern part of the Lesser Antilles, a partly volcanic island arc. To the north lie Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda (, ) is a sovereign country in the West Indies. It lies at the juncture of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the Leeward Islands part of the Lesser Antilles, at 17°N latitude. The country consists of two maj ...
and the British Overseas Territory
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs), also known as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom. They are the last remna ...
of Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
, with Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
lying to the south.
The two main islands are Basse-Terre (west) and Grande-Terre
Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe ...
(east), which form a butterfly shape as viewed from above, the two 'wings' of which are separated by the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and comm ...
, and Petit Cul-de-Sac Marin
Petite or petite may refer to:
*Petit (crater), a small, bowl-shaped lunar crater on Mare Spumans
* ''Petit'' (EP), a 1995 EP by Japanese singer-songwriter Ua
* Petit (typography), another name for brevier-size type
*Petit four
* Petit Gâteau
*P ...
. More than half of Guadeloupe's land surface consists of the 847.8 km2 Basse-Terre. The island is mountainous, containing such peaks as Mount Sans Toucher
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest.
Mount or Mounts may also refer to:
Places
* Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England
* Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, C ...
(4,442 feet; 1,354 metres) and Grande Découverte
Grande means "large" or "great" in many of the Romance languages. It may also refer to:
Places
* Grande, Germany, a municipality in Germany
*Grande Communications, a telecommunications firm based in Texas
* Grande-Rivière (disambiguation)
* Arr ...
(4,143 feet; 1,263 metres), culminating in the active volcano La Grande Soufrière, the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles with an elevation of . In contrast Grande-Terre is mostly flat, with rocky coasts to the north, irregular hills at the centre, mangrove at the southwest, and white sand beaches sheltered by coral reefs along the southern shore. This is where the main tourist resorts are found.
Marie-Galante is the third-largest island, followed by La Désirade, a north-east slanted limestone plateau, the highest point of which is . To the south lies the Îles de Petite-Terre, which are two islands (Terre de Haut and Terre de Bas) totalling 2 km2.
Les Saintes is an archipelago of eight islands of which two, Terre-de-Bas and Terre-de-Haut are inhabited. The landscape is similar to that of Basse-Terre, with volcanic hills and irregular shoreline with deep bays.
There are numerous other smaller islands.
Geology
Basse-Terre is a volcanic island. The Lesser Antilles are at the outer edge of the Caribbean Plate, and Guadeloupe is part of the outer arc of the Lesser Antilles Volcanic Arc. Many of the islands were formed as a result of thesubduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
of oceanic crust of the Atlantic Plate under the Caribbean Plate in the Lesser Antilles subduction zone. This process is ongoing and is responsible for volcanic and earthquake activity in the region. Guadeloupe was formed from multiple volcanoes, of which only La Grande Soufrière is not extinct. Its last eruption was in 1976, and led to the evacuation of the southern part of Basse-Terre. 73,600 people were displaced throughout three and a half months following the eruption.
K–Ar dating indicates that the three northern massifs on Basse-Terre Island are 2.79 million years old. Sections of volcanoes collapsed and eroded within the last 650,000 years, after which the Sans Toucher volcano grew in the collapsed area. Volcanoes in the north of Basse-Terre Island mainly produced andesite and basaltic andesite. There are several beaches of dark or "black" sand.
La Désirade, east of the main islands, has a basement
A basement or cellar is one or more floors of a building that are completely or partly below the ground floor. It generally is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, ...
from the Mesozoic, overlaid with thick limestones from the Pliocene to Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
periods.
Grande-Terre and Marie-Galante have basements probably composed of volcanic units of Eocene to Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
, but there are no visible outcrops. On Grande-Terre, the overlying carbonate platform is 120 metres thick.
Climate
The islands are part of theLeeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean
, coor ...
, so called because they are downwind of the prevailing trade winds, which blow out of the northeast. This was significant in the days of sailing ships. Grande-Terre is so named because it is on the eastern, or windward side, exposed to the Atlantic winds. Basse-Terre is so named because it is on the leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
south-west side and sheltered from the winds. Guadeloupe has a tropical climate tempered by maritime influences and the Trade Winds. There are two seasons, the dry season called "Lent" from January to June, and the wet season called "winter", from July to December.

Tropical cyclones and storm surges
Located in a very exposed region, Guadeloupe and its dependencies have to face manycyclones
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
. The deadliest hurricane to hit Guadeloupe was the Pointe-à-Pitre hurricane of 1776, which killed at least 6,000 people.
On 16 September 1989, Hurricane Hugo
Hurricane Hugo was a powerful Cape Verde tropical cyclone that inflicted widespread damage across the northeastern Caribbean and the Southeastern United States in September 1989. Across its track, Hugo affected approximately 2 million peop ...
caused severe damage to the islands of the archipelago and left a deep mark on the memory of the local inhabitants. In 1995, three hurricanes (Iris, Luis and Marilyn) hit the archipelago in less than three weeks.
Some of the deadliest hurricanes that have hit Guadeloupe are the following:
In the 20th century: 12 September 1928: 1928 Okeechobee hurricane
The Okeechobee hurricane of 1928, also known as the San Felipe Segundo hurricane, was one of the deadliest hurricanes in the recorded history of the North Atlantic basin, and the fourth deadliest hurricane in the United States, only behind the ...
; 11 August 1956: Hurricane Betsy
Hurricane Betsy was an intense and destructive tropical cyclone that brought widespread damage to areas of Florida and the central United States Gulf Coast in September 1965. The storm's erratic nature, coupled with its intensity and minim ...
; 22 August 1964: Hurricane Cleo; 27 September 1966: Hurricane Inez; 16–17 September 1989: Hurricane Hugo; 14–15 September 1995: Hurricane Marilyn.
In the 21st century: 6 September 2017: Hurricane Irma; 18–19 September 2017: Hurricane Maria.
Flora
 With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as
With fertile volcanic soils, heavy rainfall and a warm climate, vegetation on Basse-Terre is lush. Most of the islands' forests are on Basse-Terre, containing such species as mahogany
Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus ''Swietenia'', indigenous to the AmericasBridgewater, Samuel (2012). ''A Natural History of Belize: Inside the Maya Forest''. Austin: Unive ...
, ironwood and chestnut tree
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce.
The unrelat ...
s. Mangrove swamps
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
line the Salée River. Much of the forest on Grande-Terre has been cleared, with only a few small patches remaining.
Between of altitude, the rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
that covers a large part of the island of Basse-Terre develops. There we find the white gum tree, the acomat-boucan or chestnut tree, the marbri or bois-bandé or the oleander; shrubs and herbaceous plants such as the mountain palm, the balisier or ferns; many epiphytes: bromeliads, philodendrons, orchids and lianas. Above , the humid savannah develops, composed of mosses, lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.mangrove, high altitude violet or mountain thyme.
The dry forest occupies a large part of the islands of Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, Les Saintes, La Désirade and also develops on the leeward coast of Basse-Terre. The coastal forest is more difficult to develop because of the nature of the soil (sandy, rocky), 
 The Guadalupe
The Guadalupe
 Legislative powers are centred on the separate departmental and regional councils. The elected president of the
Legislative powers are centred on the separate departmental and regional councils. The elected president of the
 This offers France important fishing resources and independence to develop a sovereign policy of underwater research and protection (protection of humpback whales, Cousteau reserve, protection of coral reefs). Because of its geographical position, Guadeloupe allows France to participate in political and diplomatic dialogues at both the regional (Lesser and Greater Antilles) and continental ( Latin and North America) levels.
The signing of the Regional Convention for the Internationalisation of Enterprise (CRIE), membership of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) and membership of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) are milestones that have enabled Guadeloupe to develop its bilateral or multilateral relations within the framework of international agreements or institutions.11 The development of bilateral and multilateral economic partnerships with other Caribbean and American states is based on the modernisation of the autonomous port of Guadeloupe and the importance of the Guadeloupe-Polo Caribe international airport.
This offers France important fishing resources and independence to develop a sovereign policy of underwater research and protection (protection of humpback whales, Cousteau reserve, protection of coral reefs). Because of its geographical position, Guadeloupe allows France to participate in political and diplomatic dialogues at both the regional (Lesser and Greater Antilles) and continental ( Latin and North America) levels.
The signing of the Regional Convention for the Internationalisation of Enterprise (CRIE), membership of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) and membership of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) are milestones that have enabled Guadeloupe to develop its bilateral or multilateral relations within the framework of international agreements or institutions.11 The development of bilateral and multilateral economic partnerships with other Caribbean and American states is based on the modernisation of the autonomous port of Guadeloupe and the importance of the Guadeloupe-Polo Caribe international airport.
Image:Flag_of_France.svg, National flag of France
Image:Unofficial flag of Guadeloupe (local).svg, Colonial flag of Guadeloupe
Image:Flag of Guadeloupe (local) variant.svg, Red variant of the colonial sun flag
Image:Flag of Guadeloupe (UPLG).svg, Flag used by the independence and the cultural movements
Image:Flag of Guadeloupe (Local).svg, Logo of the Regional Council of Guadeloupe

 The economy of Guadeloupe depends on tourism, agriculture, light industry and services. It is reliant upon mainland France for large subsidies and imports and public administration is the largest single employer on the islands. Unemployment is especially high among the youth population.
In 2017, the Gross domestic product (GDP) of Guadeloupe was €9.079 billion, and showed 3.4% growth. The
The economy of Guadeloupe depends on tourism, agriculture, light industry and services. It is reliant upon mainland France for large subsidies and imports and public administration is the largest single employer on the islands. Unemployment is especially high among the youth population.
In 2017, the Gross domestic product (GDP) of Guadeloupe was €9.079 billion, and showed 3.4% growth. The
 A Guadeloupean
A Guadeloupean
 About 80% of the population is Roman Catholic. Guadeloupe is in the diocese of
About 80% of the population is Roman Catholic. Guadeloupe is in the diocese of
 Guadeloupe has always had a rich literary output, with Guadeloupean author Saint-John Perse winning the 1960
Guadeloupe has always had a rich literary output, with Guadeloupean author Saint-John Perse winning the 1960
(1)
or Tom Frager focus on more international genres such as rock or reggae. Many international festivals take place in Guadeloupe, such as the Creole Blues Festival on Marie-Galante. All the Euro-French forms of art are also ubiquitous, enriched by other communities from Brazil, Dominican Republic, Another element of Guadeloupean culture is its dress. A few women (particularly of the older generation) wear a unique style of traditional dress, with many layers of colourful fabric, now only worn on special occasions. On festive occasions they also wore a madras (originally a "kerchief" from South India) headscarf tied in many different symbolic ways, each with a different name. The headdress could be tied in the "bat" style, or the "firefighter" style, as well as the "Guadeloupean woman". Jewellery, mainly gold, is also important in the Guadeloupean lady's dress, a product of European, African and Indian inspiration.
Another element of Guadeloupean culture is its dress. A few women (particularly of the older generation) wear a unique style of traditional dress, with many layers of colourful fabric, now only worn on special occasions. On festive occasions they also wore a madras (originally a "kerchief" from South India) headscarf tied in many different symbolic ways, each with a different name. The headdress could be tied in the "bat" style, or the "firefighter" style, as well as the "Guadeloupean woman". Jewellery, mainly gold, is also important in the Guadeloupean lady's dress, a product of European, African and Indian inspiration.
 * The four-pointed headdress (headdress with four knots) means "my heart has room for whoever wants it! ";
* The three-pointed headdress means "my heart is taken!".
* The two-pointed headdress means "my heart is compromised, but you can try your luck! ";
* The one-ended headdress means "my heart is free! "
* The four-pointed headdress (headdress with four knots) means "my heart has room for whoever wants it! ";
* The three-pointed headdress means "my heart is taken!".
* The two-pointed headdress means "my heart is compromised, but you can try your luck! ";
* The one-ended headdress means "my heart is free! "
 In the category of beverages, the consumption of soft drinks is very important in Guadeloupe, as well as that of a drink locally nicknamed black beer. In addition, it is not uncommon to see vendors of sugar cane juice or coconut water on the roads. Chaudeau is consumed on special occasions (weddings, baptisms, communions) and is a Guadeloupean-style eggnog eaten with a whipped cake (génoise). The rum, whose consumption is culturally imbricated in the Guadeloupean society, comes in particular from one of the ten distilleries distributed in the Guadeloupean territory and that produce the rums of Guadeloupe.
In the category of beverages, the consumption of soft drinks is very important in Guadeloupe, as well as that of a drink locally nicknamed black beer. In addition, it is not uncommon to see vendors of sugar cane juice or coconut water on the roads. Chaudeau is consumed on special occasions (weddings, baptisms, communions) and is a Guadeloupean-style eggnog eaten with a whipped cake (génoise). The rum, whose consumption is culturally imbricated in the Guadeloupean society, comes in particular from one of the ten distilleries distributed in the Guadeloupean territory and that produce the rums of Guadeloupe.
 Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe, and several notable footballers are of Guadeloupean origin, including Marius Trésor,
Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe, and several notable footballers are of Guadeloupean origin, including Marius Trésor,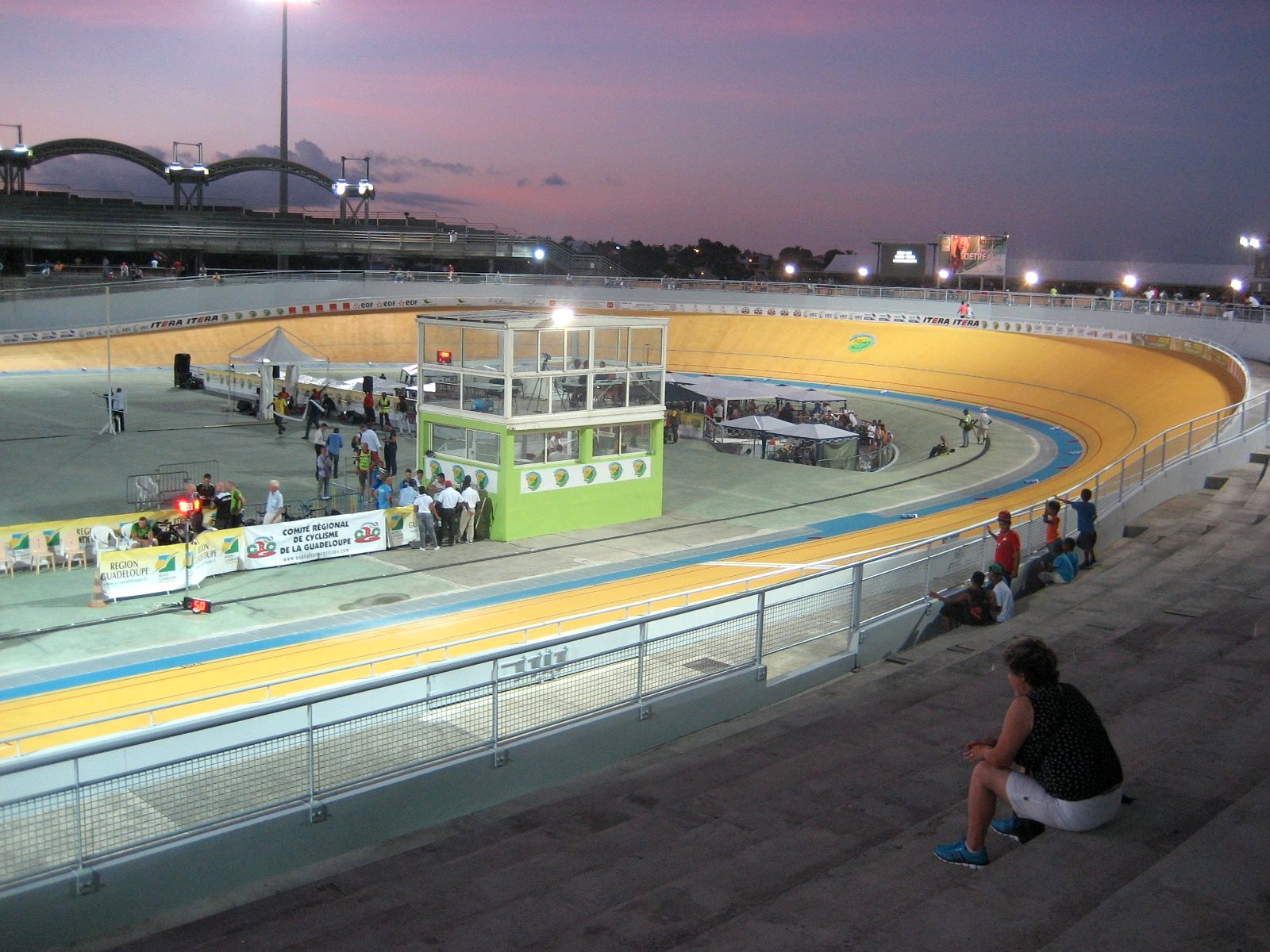  The island is internationally known for hosting the Karujet Race – Jet Ski World Championship since 1998. This nine-stage, four-day event attracts competitors from around the world (mostly Caribbeans, Americans, and Europeans). The Karujet, generally made up of seven races around the island, has an established reputation as one of the most difficult championships in which to compete.
The Route du Rhum is one of the most prominent nautical French sporting events, occurring every four years.
Bodybuilder Serge Nubret was born in
The island is internationally known for hosting the Karujet Race – Jet Ski World Championship since 1998. This nine-stage, four-day event attracts competitors from around the world (mostly Caribbeans, Americans, and Europeans). The Karujet, generally made up of seven races around the island, has an established reputation as one of the most difficult championships in which to compete.
The Route du Rhum is one of the most prominent nautical French sporting events, occurring every four years.
Bodybuilder Serge Nubret was born in
 Guadeloupe is served by a number of
Guadeloupe is served by a number of
 45,626 students in secondary education;
* 2,718 graduate students in high school.
* Since 2014, the academy has 12 districts divided into 5 poles:Académie de Guadeloupe, répartition des 12 circonscriptions, pdf.
* The Pôle Îles du Nord ( St. Martin and
45,626 students in secondary education;
* 2,718 graduate students in high school.
* Since 2014, the academy has 12 districts divided into 5 poles:Académie de Guadeloupe, répartition des 12 circonscriptions, pdf.
* The Pôle Îles du Nord ( St. Martin and
 The
The
, "Death in Paradise: Ben Miller on investigating the deadliest place on the planet," ''Radio Times'', 8 January 2013 it was the most violent overseas French
Prefecture website
Regional Council website
Departmental Council website
{{Authority control Dependent territories in the Caribbean Overseas departments of France French Caribbean Leeward Islands (Caribbean) Lesser Antilles Regions of France Outermost regions of the European Union Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas British Caribbean Former Swedish colonies Former colonies in North America French Union Island countries French-speaking countries and territories Populated places established in the 4th century 1674 establishments in the French colonial empire 1674 establishments in North America 1759 disestablishments in the French colonial empire 1759 disestablishments in North America 1759 establishments in the British Empire 1759 establishments in North America 1763 disestablishments in the British Empire 1763 disestablishments in North America 1763 establishments in the French colonial empire 1763 establishments in North America 1810 establishments in the British Empire 1810 disestablishments in the French colonial empire 1810 disestablishments in North America 1810 establishments in North America 1816 disestablishments in the British Empire 1816 disestablishments in North America 1816 establishments in the French colonial empire 1816 establishments in North America
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
, sunshine and wind and is the environment where the sea grape, the mancenilla (a very toxic tree whose trunk is marked with a red line), the icaquier or the Coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
tree grow. On the cliffs and in the Arid zones are found cacti such as the cactus-cigar (Cereus), the prickly pear, the chestnut cactus, the "Tête à l'anglais" cactus and the aloes.
The Mangrove forest that borders some of Guadalupe's coasts is structured in three levels, from the closest to the sea to the farthest. On the first level are the red mangroves; on the second, about from the sea, the black mangrove Black mangrove may refer to the plants:
* ''Aegiceras corniculatum'' (Primulaceae) - south-east Asia and Australasia
* ''Avicennia germinans'' (Acanthaceae) - tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, on both the Atlantic and Pacific coast ...
s form the shrubby mangrove; on the third level the white mangroves form the tall mangrove. Behind the mangrove, where the tide and salt do not penetrate, a swamp forest sometimes develops, unique in Guadeloupe. The representative species of this environment is the Mangrove-medaille.
Fauna
Few terrestrial mammals, aside from bats and raccoons, are native to the islands. The introduced Javan mongoose is also present on Guadeloupe. Bird species include the endemic purple-throated carib and theGuadeloupe woodpecker
The Guadeloupe woodpecker (''Melanerpes herminieri'') or Tapeur is a species of bird in the woodpecker family Picidae belonging to the genus ''Melanerpes.'' Endemic to the Guadeloupe archipelago in the Lesser Antilles, it is a medium-sized fores ...
. The waters of the islands support a rich variety of marine life.
However, by studying 43,000 bone remains from six islands in the archipelago, 50 to 70% of snakes and lizards on the Guadeloupe Islands became extinct after European colonists arrived, who had brought with them mammals such as cats, mongooses, rats, and raccoons, which might have preyed upon the native reptiles.
Environmental preservation
In recent decades, Guadeloupe's natural environments have been affected by hunting and fishing, forest retreat, urbanization and suburbanization. They also suffer from the development of intensive crops (banana and sugar cane, in particular), which reached their peak in the years 1955–75. This has led to the following situation: seagrass beds and reefs have degraded by up to 50% around the large islands; mangroves and mantids have almost disappeared in Marie-Galante, Les Saintes and La Désirade; thesalinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
of the fresh water table has increased due to "the intensity of use of the layer"; and pollution of agricultural origin (pesticides and nitrogenous compounds).
In addition, the ChlEauTerre study, unveiled in March 2018, concludes that 37 different anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human im ...
molecules (more than half of which come from residues of now-banned pesticides, such as chlordecone) were found in "79% of the watersheds analyzed in Grande-Terre and 84% in Basse-Terre." A report by the Guadeloupe Water Office notes that in 2019 there is a "generalized degradation of water bodies."
Despite everything, there is a will to preserve these environments
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
whose vegetation and landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes the ...
are preserved in some parts of the islands and constitute a sensitive asset for tourism. These areas are partially protected and classified as ZNIEFF, sometimes with nature reserve status, and several caves are home to protected chiropterans.
 The Guadalupe
The Guadalupe National Park
A national park is a nature park, natural park in use for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state dec ...
was created on 20 February 1989. In 1992, under the auspices of UNESCO, the Biosphere Reserve of the Guadeloupe Archipelago (''Réserve de biosphère de l'archipel de la Guadeloupe'') was created. As a result, on 8 December 1993, the marine site of Grand Cul-de-sac was listed as a wetland of international importance. The island thus became the overseas department
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainlan ...
with the most protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
s.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
The archipelago is crossed by numerous geological faults such as those of la Barre or la Cadoue, while in depth, in front of Moule and La Désirade begins the Désirade Fault, and between the north of Maria-Galante and the south of Grande-Terre begins the Maria Galante Fault. And it is because of these geological characteristics, the islands of the department of Guadeloupe are classified in zone III according to the seismic zoning of France and are subject to a specific risk prevention plan. The 1843 earthquake in the Lesser Antilles is, to this day, the most violent earthquake known. It caused the death of more than a thousand people, as well as major damage in Pointe-à-Pitre. On 21 November 2004, the islands of the department, in particular Les Saintes archipelago, were shaken by a violent earthquake that reached a magnitude of 6.3 on the Richter scale and caused the death of one person, as well as extensive material damage.Demographics
Guadeloupe recorded a population of 402,119 in the 2017 census. The population is mainlyAfro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
. European, Indian (Tamil, Telugu, and other South Indians), Lebanese, Syrians
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
, and Chinese are all minorities. There is also a substantial population of Haitians
Haitians ( French: , ht, Ayisyen) are the citizens of Haiti and the descendants in the diaspora through direct parentage. An ethnonational group, Haitians generally comprise the modern descendants of self-liberated Africans in the Caribbean te ...
in Guadeloupe who work mainly in construction and as street vendors. Basse-Terre is the political capital; however, the largest city and economic hub is Pointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
.
The population of Guadeloupe has been decreasing by 0.8% per year since 2013. In 2017 the average population density in Guadeloupe was , which is very high in comparison to metropolitan France's average of . One third of the land is devoted to agriculture and all mountains are uninhabitable; this lack of space and shelter makes the population density even higher.
Major urban areas
The most populous urban unit (agglomeration) isPointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
-Les Abymes
Les Abymes () is the most populous commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is located on the west side of the island of Grande-Terre, and is part of the largest metropolitan area of Guadel ...
, which covers 11 communes and 65% of the population of the department. The three largest urban units are:
Health
In 2011, life expectancy at birth was recorded at 77.0 years for males and 83.5 for females. Medical centres in Guadeloupe include: University Hospital Centre (CHU) in Pointe-à-Pitre, Regional Hospital Centre (CHR) in Basse-Terre, and four hospitals located in Capesterre-Belle-Eau, Pointe-Noire, Bouillante and Saint-Claude. The ''Institut Pasteur de la Guadeloupe'', is located in Pointe-à-Pitre and is responsible for researching environmental hygiene, vaccinations, and the spread of tuberculosis and mycobacteriaImmigration
The relative wealth of Guadeloupe contrasts with theextreme poverty
Extreme poverty, deep poverty, abject poverty, absolute poverty, destitution, or penury, is the most severe type of poverty, defined by the United Nations (UN) as "a condition characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, includi ...
of several islands in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
region, which makes the community an attractive place for the populations of some of these territories. In addition, other factors, such as political instability and natural disasters, explain this immigration. As early as the 1970s, the first illegal immigrants of Haitian origin arrived in Guadeloupe to meet a need for labour in the agricultural sector; alongside this Haitian immigration, which is more visible because it is more numerous, Guadeloupe has also seen the arrival and settlement of populations from the island of Dominica and the Dominican Republic. In 2005, the prefecture, which represents the State in Guadeloupe, reported figures of between 50,000 and 60,000 foreigners in the department.

Migration
Created in 1963 by Michel Debré, Bumidom's objective was to " ..contribute to the solution of demographic problems in the overseas departments". To this end, its missions were multiple: information for future emigrants, vocational training, family reunification and management of reception centres. At the time, this project was also seen as a means to diminish the influence of the West Indian independence movements, which were gaining strength in the 1960s. Between 1963 and 1981, an estimated 16,562 Guadeloupeans emigrated to metropolitan France through Bumidom. And the miniseries Le Rêve français (The French Dream) sets out to recount some of the consequences of the emigration of West Indians and Reunionese to France. An estimated 50,000 Guadeloupeans and Martinicans participated in the construction of the Panama Canal between 1904 and 1914. In 2014, it was estimated that there were between 60,000 and 70,000 descendants of these West Indians living in Panama. Other waves of migration to North America, especially to Canada, occurred at the beginning of the 20th century.Governance
Together with Martinique, La Réunion, Mayotte and French Guiana, Guadeloupe is one of the overseas departments, being both a region and adepartment
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
combined into one entity. It is also an outermost region of the European Union. The inhabitants of Guadeloupe are French citizens with full political and legal rights.
 Legislative powers are centred on the separate departmental and regional councils. The elected president of the
Legislative powers are centred on the separate departmental and regional councils. The elected president of the Departmental Council of Guadeloupe
The Departmental Council of Guadeloupe is the deliberative assembly of the French department of Guadeloupe. It is based at the Palace of the General Council.
Since 1 July 2021 its president is Guy Losbar, former mayor of Petit-Bourg.
Reference ...
is currently Guy Losbar (1.7.2021); its main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school (collège) buildings and technical staff, and local roads and school and rural buses. The Regional Council of Guadeloupe
The Regional Council of Guadeloupe consists of 41 members.
President
Presidents of the Regional Council of Guadeloupe:
Sources
worldstatesmen.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Regional Council of Guadeloupe
Politics of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe-related list ...
is a body, elected every six years, consisting of a president (currently Ary Chalus) and eight vice-presidents. The regional council oversees secondary education, regional transportation, economic development, the environment, and some infrastructure, among other things.
Guadeloupe elects one deputy from one of each of the first, second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
, third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
, and fourth constituencies to the National Assembly of France
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known a ...
. Three senators are chosen for the Senate of France by indirect election. For electoral purposes, Guadeloupe is divided into two arrondissements ( Basse-Terre and Pointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
), and 21 cantons.
Most of the French political parties are active in Guadeloupe. In addition there are also regional parties such as the Guadeloupe Communist Party
The Guadeloupe Communist Party (french: Parti communiste guadeloupéen, PCG) is a political party in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. The party publishes the newspaper ''Etincelle'' (meaning "Spark").Great Soviet EncyclopediaГва ...
, the Progressive Democratic Party of Guadeloupe
The Progressive Democratic Party of Guadeloupe (french: Parti progressiste démocratique guadeloupéen, PPDG) is a democratic socialist political party in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. It was founded by former members of the Gua ...
, the Guadeloupean Objective
The Guadeloupean Objective (french: Objectif Guadeloupéen, OG) is a political party in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. It was founded on 18 March 2000 by Lucette Michaux-Chevry, the then-president of the Regional Council of Guadel ...
, the Pluralist Left
The Plural Left (french: Gauche Plurielle) is a political party in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. The party has one seat in the French National Assembly in the group of the Socialist Party
Socialist Party is the name of man ...
, and United Guadeloupe, Solidary and Responsible.
The prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
(regional capital) of Guadeloupe is Basse-Terre. Local services of the state administration are traditionally organised at departmental level, where the prefect represents the government.
Administrative divisions
For the purposes of local government, Guadeloupe is divided into 32 communes. Each commune has a municipal council and a mayor. Revenues for the communes come from transfers from the French government, and local taxes. Administrative responsibilities at this level include water management, civil register, and municipal police.Geopolitics
From a geostrategic point of view, Guadeloupe is located in a central part of the Caribbean archipelago between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. This location in the region allows France to reach a large part of the eastern coast of theAmerican continent
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. The exclusive economic zone formed by Guadeloupe and Martinique covers just over 126,146 square kilometres. In 1980 France established its maritime boundaries in the area by signing a Treaty with Venezuela. This provides France with important fishing resources. This offers France important fishing resources and independence to develop a sovereign policy of underwater research and protection (protection of humpback whales, Cousteau reserve, protection of coral reefs). Because of its geographical position, Guadeloupe allows France to participate in political and diplomatic dialogues at both the regional (Lesser and Greater Antilles) and continental ( Latin and North America) levels.
The signing of the Regional Convention for the Internationalisation of Enterprise (CRIE), membership of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) and membership of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) are milestones that have enabled Guadeloupe to develop its bilateral or multilateral relations within the framework of international agreements or institutions.11 The development of bilateral and multilateral economic partnerships with other Caribbean and American states is based on the modernisation of the autonomous port of Guadeloupe and the importance of the Guadeloupe-Polo Caribe international airport.
This offers France important fishing resources and independence to develop a sovereign policy of underwater research and protection (protection of humpback whales, Cousteau reserve, protection of coral reefs). Because of its geographical position, Guadeloupe allows France to participate in political and diplomatic dialogues at both the regional (Lesser and Greater Antilles) and continental ( Latin and North America) levels.
The signing of the Regional Convention for the Internationalisation of Enterprise (CRIE), membership of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) and membership of the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) are milestones that have enabled Guadeloupe to develop its bilateral or multilateral relations within the framework of international agreements or institutions.11 The development of bilateral and multilateral economic partnerships with other Caribbean and American states is based on the modernisation of the autonomous port of Guadeloupe and the importance of the Guadeloupe-Polo Caribe international airport.
Symbols and flags
As a part of France, Guadeloupe uses the French tricolour as its flag and ''La Marseillaise'' as its anthem. However, a variety of other flags are also used in an unofficial or informal context, most notably the sun-based flag. Independentists also have their own flag.Economy

 The economy of Guadeloupe depends on tourism, agriculture, light industry and services. It is reliant upon mainland France for large subsidies and imports and public administration is the largest single employer on the islands. Unemployment is especially high among the youth population.
In 2017, the Gross domestic product (GDP) of Guadeloupe was €9.079 billion, and showed 3.4% growth. The
The economy of Guadeloupe depends on tourism, agriculture, light industry and services. It is reliant upon mainland France for large subsidies and imports and public administration is the largest single employer on the islands. Unemployment is especially high among the youth population.
In 2017, the Gross domestic product (GDP) of Guadeloupe was €9.079 billion, and showed 3.4% growth. The GDP per capita
Lists of countries by GDP per capita list the countries in the world by their gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The lists may be based on nominal or purchasing power parity GDP. Gross national income (GNI) per capita accounts for inflows ...
of Guadeloupe was €23,152. Imports amounted to €3.019 billion, and exports to €1.157 billion. The main export products are bananas, sugar and rum. Banana exports suffered in 2017 from damages due to Hurricane Irma and Hurricane Maria.
Tourism
Tourism is the one of the most prominent sources of income, with most visitors coming from France and North America. An increasingly large number of cruise ships visit Guadeloupe, the cruise terminal of which is in Pointe-à-Pitre.Agriculture
The traditional sugar cane crop is slowly being replaced by other crops, such as bananas (which now supply about 50% of export earnings),eggplant
Eggplant ( US, Canada), aubergine ( UK, Ireland) or brinjal (Indian subcontinent, Singapore, Malaysia, South Africa) is a plant species in the nightshade family Solanaceae. ''Solanum melongena'' is grown worldwide for its edible fruit.
Mos ...
, guinnep, noni, sapotilla
''Manilkara huberi'', also known as masaranduba, níspero, and sapotilla, is a fruit bearing plant of the genus ''Manilkara'' of the family Sapotaceae.
Geographical distribution
''Manilkara huberi'' is native to large parts of northern South Ame ...
, giraumon squash, yam
Yam or YAM may refer to:
Plants and foods
*Yam (vegetable), common name for members of ''Dioscorea''
* Taro, known in Malaysia and Singapore as yam
* Sweet potato, specifically its orange-fleshed cultivars, often referred to as yams in North Amer ...
, gourd, plantain, christophine
Chayote (''Sechium edule''), also known as mirliton and choko, is an edible plant belonging to the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. This fruit was first cultivated in Mesoamerica between southern Mexico and Honduras, with the most genetic diversity ...
, cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
, jackfruit, pomegranate, and many varieties of flowers. Other vegetables and root crops are cultivated for local consumption, although Guadeloupe is dependent upon imported food, mainly from the rest of France.
Light industry
Of the various light industries, sugar and rum production, solar energy, cement, furniture and clothing are the most prominent. Most manufactured goods and fuel are imported.Culture
Language
Guadeloupe's official language isFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, which is spoken by nearly all of the population. Most residents also speak Guadeloupean Creole, a French-based creole language
A French creole, or French-based creole language, is a creole for which French is the lexifier. Most often this lexifier is not modern French but rather a 17th- or 18th-century koiné of French from Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the ...
.
Guadeloupean Creole emerged as a result of the need for all ethnic groups (French, African and Amerindian) to be able to understand each other. This language is therefore the result of a mixture created in the 17th century in response to a communicative emergency. At the time of the colony's foundation, a majority of the French population did not speak the standard French language but local dialects and languages, such as Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
and Norman, while the Africans came from a variety of West and Central African ethnic groups and lacked a common language themselves. The Creole language emerged as a lingua franca and ultimately became the native language of much of the population.
Moreover, Terre-de-Haut and Terre-de-Bas, in the Saintes archipelago, due to their settlement history (Breton, Norman and Poitevin settlers), have their own Creoles which differ from Guadeloupean Creole by their French pronunciations, their particular expressions, their syntax and their sonorities. Although it is not transcribed, these islanders call their Creole "patois" or "language of St. Martin" and actively ensure its transmission and perpetuation by their descendants in vernacular form.
béké
Béké or beke is an Antillean Creole term to describe a descendant of the early European, usually French, settlers in the French Antilles.
Etymology
The origin of the term is unclear, although it is attested to in colonial documents from as early ...
first wrote Creole at the end of the 17th century, transcribing it using French orthography.
As Guadeloupe is a French department, French is the official language. However, Guadeloupean French (in contact with Creole) has certain linguistic characteristics that differ from those of standard metropolitan French. Recently, a very detailed study of the phonetic aspect of Guadeloupean French has been undertaken (this would be the first study to deal with both the acoustic and the phonological and perceptual aspects of Guadeloupean French in particular and West Indian French in general). It is also concerned with the reading varieties of Guadeloupean French (acrolect, mesolect and basilect).
In recent decades there has been a revival of Creole, which has stimulated the appearance of books of short stories and poetry published in Creole and French over the last ten years. In this context, Hector Poullet is a pioneer of Creole-mediated dictation. Creole is also a very colourful language and very philosophical in its expressions and phrases, which, translated literally into French, can be confusing. The representatives of the older generations are not always fluent in French, but in Guadeloupean Creole.
Today, the question as to whether French and Creole are stable in Guadeloupe, i.e. whether both languages are practised widely and competently throughout society, remains a subject of active research.
Religion
 About 80% of the population is Roman Catholic. Guadeloupe is in the diocese of
About 80% of the population is Roman Catholic. Guadeloupe is in the diocese of Basse-Terre (et Pointe-à-Pitre)
Basse-Terre (, ; ; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Bastè, ) is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is also the ''prefecture'' (capital city) of Guadeloupe. The city of Basse-Terre is located o ...
. Other major religions include various Protestant denominations. In 1685, the Black Code announced the Christian religion in its Catholic form as the only authorized religion in the French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloupe, ...
, thus excluding Jews and the various Protestant groups from practicing their beliefs, and imposed the forced conversion of the newly arrived slaves and the baptism of the older ones.
This was followed by a rapid fashion among the slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, since this religion offered them a spiritual refuge and allowed them to safeguard some of their African beliefs and customs, thus marking the beginning of a religious syncretism. Since the 1970s, new religions and groups have been 'competing' with the Catholic Church, such as the Evangelical Pentecostal Church, the Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and ...
, the Bible Students or Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Administratively, the territory of Guadeloupe is part of the Diocese of Basse-Terre and Pointe-à-Pitre, attached to the Catholic Church in France. The diocese includes the territories of Guadeloupe, St. Barthélemy and St. Martin and the number of faithful is estimated at 400,000. In 2020 there were 59 priests active in the diocese. The episcopal see is located in Basse-Terre, in the cathedral of Notre-Dame-de-Guadeloupe.
Hinduism, which accompanied the Indians who came to work in Guadeloupe in the mid-19th century, has expanded since the 1980s. The Indian community has its own tradition that comes from India. It is the mayé men, a distorted pronunciation of the name of the Tamil Indian goddess Mariamman. There are no less than 400 temples in the archipelago. Islam made its appearance in the French West Indies in the 1970s, first in Martinique.
According to the president of the Muslim association of Guadeloupe, there are between 2,500 and 3,000 Muslims in the department. The island has two mosques. Judaism has been present in Guadeloupe since the arrival of Dutch settlers expelled from the northeast of present-day Brazil in 1654. There is a synagogue and an Israelite cultural community. Guadeloupeans of Syrian and Lebanese origin practice Catholicism in its Maronite
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the larges ...
form. Rastafari
Rastafari, sometimes called Rastafarianism, is a religion that developed in Jamaica during the 1930s. It is classified as both a new religious movement and a social movement by scholars of religion. There is no central authority in control of ...
has been attractive to some young people since the 1970s following its emergence in Jamaica. The quimbois or kenbwa, practiced in Guadeloupe, refer to magical-religious practices derived from Christian and African syncretism.
Literature
 Guadeloupe has always had a rich literary output, with Guadeloupean author Saint-John Perse winning the 1960
Guadeloupe has always had a rich literary output, with Guadeloupean author Saint-John Perse winning the 1960 Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
. Other prominent writers from Guadeloupe or of Guadeloupean descent include Maryse Condé, Simone Schwarz-Bart, Myriam Warner-Vieyra
Myriam Warner-Vieyra (25 March 1939 – 29 December 2017) was a Guadeloupean-born writer of novels and poetry.
Biography
The daughter of Caribbean parents, she was born Myriam Warner in Pointe-à-Pitre, Guadeloupe. She completed secondary sch ...
, Oruno Lara
Oruno Lara (1879 – 1924) was a Guadeloupean poet, author and historian, not to be confused with his grandson Dr. Oruno D. Lara, also a historian. Head of Pointe-à-Pitre's ''Guadeloupe Littéraire'' journal, he arrived in France in 1914 with ...
, Daniel Maximin, Paul Niger
Paul Niger (21 December 1915 – 22 June 1962) was a poet and political activist from Basse-Terre, Guadeloupe. He was born Albert Béville, but Niger's passion for Africa led him to take the pen name of the great African Niger River. His majo ...
, Guy Tirolien
Guy Tirolien (; February 13, 1917 – March 8, 1988) was a Guadeloupean poet. He was born in Point-à-Pitre and died at the age of 71 in Marie-Galante.
Biography
Guy Tirolien was born in Point-à-Pitre, Guadelope to Furcie Tirolen and Léonti ...
and Nicolas-Germain Léonard
Nicolas-Germain Léonard (16 March 1744 – 26 January 1793) was a poet and one of Guadeloupe's first writers.
Léonard was born in Guadeloupe, but spent most of his life in France, travelling back and forth frequently. He first moved to France ...
.
Music
Music and dance are also very popular, and the interaction of African, French and Indian cultures has given birth to some original new forms specific to the archipelago, most notably zouk music. Since the 1970s, Guadeloupean music has increasingly claimed the local language, Guadeloupean Creole as the preferred language of popular music. Islanders enjoy many local dance styles including zouk,zouk-love
Zouk is a musical movement pioneered by the French Antillean band Kassav' in the early 1980s. It was originally characterized by a fast tempo (120–145 bpm), a percussion-driven rhythm and a loud horn section. The fast zouk béton of Martini ...
, compas
Compas, also known as compas direct or compas direk (; Haitian Creole: ''konpa'', ''kompa'' or ''kompa dirèk''), is a modern méringue dance music genre of Haiti. The genre was popularized following the creation of Ensemble Aux Callebasses in ...
, as well as the modern international genres such as hip hop, etc.
Traditional Guadeloupean music includes biguine
Biguine ( , ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, bigin) is a rhythm-centric style of music that originated from Saint Pierre, Martinique in the 19th century. It fuses Bèlè and 19th-century French ballroom dance steps with African rhythms.
History
...
, kadans
Cadence rampa ( ht, kadans ranpa, ), or simply kadans, is a dance music and modern méringue popularized in the Caribbean by the virtuoso Haitian sax player Webert Sicot in the early 1960s. Cadence rampa was one of the sources of cadence-lypso. ...
, cadence-lypso, and gwo ka. Popular music artists and bands such as Experience 7
Experience 7 was a Guadeloupean kadans band formed in the mid-1970s, led by Guy Houllier and Yves Honore. However unlike Kassav' or Malavoi, the small band produced most songs with Henry Debs in Guadeloupe.
Biography
Career
The group was ...
, Francky Vincent, Kassav' (which included Patrick St-Eloi, and Gilles Floro) embody the more traditional music styles of the island, whilst other musical artists such as the punk band The Boloko(1)
or Tom Frager focus on more international genres such as rock or reggae. Many international festivals take place in Guadeloupe, such as the Creole Blues Festival on Marie-Galante. All the Euro-French forms of art are also ubiquitous, enriched by other communities from Brazil, Dominican Republic,
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, India, Lebanon, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
) who have migrated to the islands.
Classical music has seen a resurgent interest in Guadeloupe. One of the first known composers of African origin was born in Guadeloupe, Le Chevalier de Saint-Georges
Joseph Bologne, Chevalier de Saint-Georges (25 December 1745 – 10 June 1799), was a French Creole virtuoso violinist and composer, who was conductor of the leading symphony orchestra in Paris.
Saint-Georges was born in the then-French colo ...
, a contemporary of Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and a celebrated figure in Guadeloupe. Several monuments and cites are dedicated to Saint-Georges in Guadeloupe, and there is an annual music festival, Festival International de Musique Saint-Georges, dedicated in his honour. The festival attracts classical musicians from all over the world and is one of the largest classical music festivals in the Caribbean.Traditional dress
Traditional dress,Néba Francis Yale, « », ''HAL. Archives-ouvertes.fr'', 25 juillet 2015, p. 174 inherited today, is the result of a long cultural mix involving Africa, Asia and Europe. This cultural mix was initially based on triangular trade and later on a more globalized trade that included importing fabrics from the Orient. For example, in the traditional Guadeloupean costume, we find Asian influences with the use of madras cloth from India, African and European influences ( Spanish in this case) with the use of the headscarf for covering and again European influences (French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
in this case) in the adoption of the lace petticoat from Brittany.
The clothing worn in Guadeloupe has mutated over the centuries and has undergone changes that reflect the social conditions and the evolution of society, from the time of slavery to the present day. During the second half of the 17th century, slaves arriving in Guadeloupe were naked or nearly naked. They were then forced to wear rags or the owner's worn-out clothes, which were quickly discarded, barely concealing their nakedness. Or slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
working in the fields wore the "three-hole" dress, made of a vegetable fiber fabric in which three holes were made (two for the arms and one for the head). Under pressure from the church and the authorities, slaves were forced to wear the "three-hole" dress.
Under pressure from the church and as soon as the Black Code was enforced in 1685, owners were required to provide "each slave with two suits of cloth or four alders (about 7.5 m2 ) of cloth a year... art.25" which only modestly improved their conditions. However, the poor quality of the clothing worn during slavery must be qualified, as it could vary according to the day of the week (daily clothing, Sunday clothing, clothing for special occasions), or according to the status of the slaves employed in the houses.
In fact, the latter could be dressed in clothes of different quality according to the job they performed on the property. For example, in the case of the maids, their clothes could be of better quality because they had to reflect the image of success and wealth that their master wanted to project.
From the 17th century onwards, the development of the Creole costume coincided with the desire of slave women to regain their dignity, with the evolution of their employment within the household or Guadeloupean society (specialization in the sewing and dressmaking trades), with the evolution of Guadeloupean society (free women of colour, freed slaves, mulatto women) and with the influence of the European fashionable costume, which the housewife represented.
After the abolition of slavery, the main periods of traditional Guadeloupean dress were the following:
* 1848 to 1930, establishment of the use of the costume;Mission académique: langue et culture régionales créoles.
* From 1930 to 1950, significant decrease in the use of the traditional costume;
* From 1950 to 1960, period in which the traje becomes a " folkloric" garment;
* From 1960 to the present, the traditional costume has been recovered and is valued both as an everyday garment and as a sign of attachment to the culture of Guadalupe.53 Today, many designers are inspired by the traditional costume to make some of their creations.
As a result of this fusion of African and European dress codes over the centuries, including materials from distant origins, the Guadeloupean wardrobe includes Creole garments such as: the cozy dress or wòb ti-do, an everyday dress also called "à corps" because it fits the body like a corset; the skirt-shirt, in ceremonial dress (the shirt is made of very fine batiste trimmed with lace, which stops at the elbows and is buttoned with golden buttons. The skirt, full and very wide in the back with tail, is knotted above the breasts); the bodice dress which is distinguished from the others by the quantity and richness of the fabric used (satin, brocade satin, satin).
* The traditional headdress, worn with or without the women's traditional costume, is the subject of a precise codification:
* The "tête chaudière" is the ceremonial headdress with a round, flat shape, topped with a spiked knot; * The four-pointed headdress (headdress with four knots) means "my heart has room for whoever wants it! ";
* The three-pointed headdress means "my heart is taken!".
* The two-pointed headdress means "my heart is compromised, but you can try your luck! ";
* The one-ended headdress means "my heart is free! "
* The four-pointed headdress (headdress with four knots) means "my heart has room for whoever wants it! ";
* The three-pointed headdress means "my heart is taken!".
* The two-pointed headdress means "my heart is compromised, but you can try your luck! ";
* The one-ended headdress means "my heart is free! "
Gastronomy
Guadeloupeancuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
is a mixture of African, European and Asian influences. It uses first of all agricultural products such as poyo (plantain more commonly called green plantain or ti-nain), bread plantain, okra, cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.&nb ...
, pigeon peas, cristofina, yam or sweet potato.
The sea and rivers provide rays, snappers, octopus (chatou), lambis, burgots (a type of large whale), sea urchins and ouassous. Orchards provide fruits such as soursop, red jambosier, passion fruit (marakoudja), mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree ''Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South a ...
, quenette, and citrus. Condiments sometimes added to dishes are habanero chili, cive (a kind of onion from the country) or roucou seeds that give a red tint to sauces.
The cooking, often spicy and seasoned, results from soaking meat or fish for hours before cooking, to enhance its flavour. Typical dishes are: fish blaff, dombrés, bébélé (from Marie-Galante), colombo (equivalent to Indian curry) and matété (rice cooked with crab). And as for appetizers or snacks, there are morcillas criollas, accras, cassava cakes and bokit.
As for desserts, there are blancmange, sorbets or various fruit salads. As for pastries, you can choose from pâtés with jam, tournament d'amour (in Les Saintes), caca bœuf (in Marie-Galante) or sacristain. The "pain natté", which is a local brioche bread, is often eaten.
There are local productions of candied fruits (elderberry, pineapple, carambola) and jams (guava, banana, coconut). Sorbets such as coconut sherbet or snowball made with crushed ice to which a syrup (mint, grenadine) is added are also consumed. Sweets include coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
sugar, kilibibi and konkada (of Beninese origin). In the category of beverages, the consumption of soft drinks is very important in Guadeloupe, as well as that of a drink locally nicknamed black beer. In addition, it is not uncommon to see vendors of sugar cane juice or coconut water on the roads. Chaudeau is consumed on special occasions (weddings, baptisms, communions) and is a Guadeloupean-style eggnog eaten with a whipped cake (génoise). The rum, whose consumption is culturally imbricated in the Guadeloupean society, comes in particular from one of the ten distilleries distributed in the Guadeloupean territory and that produce the rums of Guadeloupe.
In the category of beverages, the consumption of soft drinks is very important in Guadeloupe, as well as that of a drink locally nicknamed black beer. In addition, it is not uncommon to see vendors of sugar cane juice or coconut water on the roads. Chaudeau is consumed on special occasions (weddings, baptisms, communions) and is a Guadeloupean-style eggnog eaten with a whipped cake (génoise). The rum, whose consumption is culturally imbricated in the Guadeloupean society, comes in particular from one of the ten distilleries distributed in the Guadeloupean territory and that produce the rums of Guadeloupe.
Festivities
At Christmas, families and friends gather during the chanté Nwel, an opportunity to singcarols
A carol is a festive song, generally religious but not necessarily connected with Christian church worship, and sometimes accompanied by a dance. A caroller (or caroler) is someone who sings carols, and is said to be carolling (or caroling).
T ...
and celebrate. After the vacations, rehearsals begin for the Guadeloupe carnival. Carnival groups parade through the streets every Sunday afternoon until the Carnival festivities in February or March. For example, the groups with skins, the Akiyo group are groups composed only of large percussion and lambi shell instruments. They have the particularity of having no brass instruments in the band, no choreography, they often parade without themed costumes. Since 2014, the Carnival in kabwèt of Marie-Galante has been registered in the inventory of the intangible heritage of France at Unesco.
Shrove Tuesday is the big party where carnival groups compete in the main town, Basse-Terre, or in Pointe-à-Pitre, for the best costumes, the best music or the best choreography whose theme is imposed by the carnival committees. The next day, on Ash Wednesday, the day that ends the carnival, the mascot king of the carnival nicknamed Vaval is burned, which signals the end of the festivities, everyone parades in black and white (to mark Vaval's mourning), and then the forty days of Lent begin. Most of the population is Catholic and respects this period. But, given the great fondness for festivities, on the "Thursday of Lent" a parade is organized in red and black identical to that of Carnival, with groups of musicians preceded by people parading.
After this period of deprivation, the Easter celebrations take place, during which families usually go camping on the beach and eat traditional and very popular dishes based on crabs: matété (rice cooked with crab), calalou (crabs with wooden leaves accompanied by white rice) or dombrés with crabs (small balls of flour cooked with crab).
Sport
 Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe, and several notable footballers are of Guadeloupean origin, including Marius Trésor,
Football (soccer) is popular in Guadeloupe, and several notable footballers are of Guadeloupean origin, including Marius Trésor, Stéphane Auvray
Stéphane Auvray (born 4 September 1981) is a Guadeloupean former professional footballer who played as a midfielder. He served as captain of the Guadeloupe national team.
Playing career Club
Born in Les Abymes, Guadeloupe, Auvray grew up in S ...
, Ronald Zubar and his younger brother Stéphane, Miguel Comminges
Miguel Gregory Comminges (born 16 March 1982) is a Guadeloupean former professional Association football, footballer. He also represented the Guadeloupe national football team. A versatile player, Comminges played on either side of defence, as ...
, Dimitri Foulquier
Dimitri Christophe Foulquier (born 23 March 1993) is a professional footballer who plays as a right back for La Liga club Valencia. Born in France, he plays for the Guadeloupe national team.
He spent most of his career in Spain, playing in La ...
, Bernard Lambourde
Bernard Lambourde (born 11 May 1971) is a French former professional footballer who played as a defender.
Career
Lambourde was born in Pointe-à-Pitre, Guadeloupe.
He joined Chelsea in 1997, and in his first season at the club he made seven ...
, Anthony Martial, Alexandre Lacazette, Thierry Henry, Lilian Thuram
Ruddy Lilian Thuram-Ulien (; born 1 January 1972) is a French former professional footballer who played as a defender.
He began playing football professionally in his homeland with Monaco and played in the top flight in France, Italy and Spai ...
, William Gallas, Layvin Kurzawa, Mikael Silvestre
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
, Thomas Lemar
Thomas Benoît Lemar (born 12 November 1995) is a French professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for La Liga club Atlético Madrid and the France national team. He is known for his versatility, being able to play on both wings and thr ...
, Mathys Tel
Mathys Tel (born 27 April 2005) is a French professional footballer who plays as a forward for Bundesliga club Bayern Munich. Known for his pace and creative dribbling ability, Tel has drawn comparisons to his French compatriot Kylian Mbappé. ...
and Kingsley Coman.
The Guadeloupe football team
The Guadeloupe football team (french: Sélection de la Guadeloupe de football) represents the French overseas department and region of Guadeloupe in men's international football. The team is controlled by the Ligue Guadeloupéenne de Football ...
were 2007 CONCACAF Gold Cup
The 2007 CONCACAF Gold Cup was the ninth edition of the Gold Cup, the soccer championship of North America, Central America and the Caribbean (CONCACAF), and was won by the United States over Mexico. It was contested in the United States from ...
semi-finalists, defeated by Mexico.
Basketball is popular. Best known players are the NBA
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America. The league is composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada) and is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United St ...
players Rudy Gobert
Rudy Gobert-Bourgarel ( ; born June 26, 1992) is a French professional basketball player for the Minnesota Timberwolves of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He also represents the French national team in their international competitions. ...
, Mickaël Piétrus
Mickaël Marvin Soriano Piétrus (; born February 7, 1982) is a French former professional basketball player. Listed at 6'6", 215 pounds, he played both the small forward and shooting guard positions. Piétrus was drafted by the Golden State Warr ...
, Johan Petro, Rodrigue Beaubois
Rodrigue Gabriel "Roddy" Beaubois (; born 24 February 1988) is a French professional basketball player for Anadolu Efes of the Basketbol Süper Ligi (BSL) and the EuroLeague.
Early life
Beaubois was discovered by NBA player Mickaël Piétrus ...
, and Mickael Gelabale (now playing in Russia), who were born on the island.
Several track and field athletes, such as Marie-José Pérec
Marie-José Pérec (born 9 May 1968) is a retired French track and field sprinter who specialised in the 200 and 400 metres and is a three-time Olympic gold medalist.
Athletics career
Pérec won the 1991 World Championships 400 metres title ...
, Patricia Girard-Léno, Christine Arron, and Wilhem Belocian, are also Guadeloupe natives.
The island has produced many world-class fencers. Yannick Borel
Yannick Borel (born 5 November 1988) is a French right-handed épée fencer.
Borel is a two-time team European champion, four-time individual European champion, four-time team world champion, and 2018 individual world champion.
A three-time O ...
, Daniel Jérent, Ysaora Thibus, Anita Blaze
Anita Blaze (born 29 October 1991) is a French right-handed foil fencer, two-time Olympian, and 2021 team Olympic silver medalist. Blaze competed in the 2012 London Olympic Games and the 2021 Tokyo Olympic Games.
Career
Blaze was born in Gu ...
, Enzo Lefort and Laura Flessel were all born and raised in Guadeloupe. According to olympic gold medalist and world champion Yannick Borel, there is a good fencing school and a culture of fencing in Guadeloupe.
Even though Guadeloupe is part of France, it has its own sports teams. Rugby union is a small but rapidly growing sport in Guadeloupe.
 The island is internationally known for hosting the Karujet Race – Jet Ski World Championship since 1998. This nine-stage, four-day event attracts competitors from around the world (mostly Caribbeans, Americans, and Europeans). The Karujet, generally made up of seven races around the island, has an established reputation as one of the most difficult championships in which to compete.
The Route du Rhum is one of the most prominent nautical French sporting events, occurring every four years.
Bodybuilder Serge Nubret was born in
The island is internationally known for hosting the Karujet Race – Jet Ski World Championship since 1998. This nine-stage, four-day event attracts competitors from around the world (mostly Caribbeans, Americans, and Europeans). The Karujet, generally made up of seven races around the island, has an established reputation as one of the most difficult championships in which to compete.
The Route du Rhum is one of the most prominent nautical French sporting events, occurring every four years.
Bodybuilder Serge Nubret was born in Anse-Bertrand
Anse-Bertrand is a commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipali ...
, Grande-Terre
Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe ...
, representing the French state in various bodybuilding competitions throughout the 1960s and 1970s including the IFBB's Mr. Olympia
Mr. Olympia is the title awarded to the winner of the professional men's bodybuilding contest at Joe Weider's Olympia Fitness & Performance Weekend—an international bodybuilding competition that is held annually by the International Federation ...
contest, taking 3rd place every year from 1972 to 1974, and 2nd place in 1975. Bodybuilder Marie-Laure Mahabir also hails from Guadeloupe.
The country has a passion for cycling. It hosted the French Cycling Championships in 2009 and continues to host the Tour de Guadeloupe every year.
Guadeloupe continues to host the Orange Open de Guadeloupe
The Open de Guadeloupe (formerly known as Orange Open Guadeloupe) is a tennis tournament held in Le Gosier, Guadeloupe since 2011. The event is part of the ATP Challenger Tour and is played on hard court
A hardcourt (or hard court) is a surface ...
tennis tournament (since 2011).
The Tour of Guadeloupe sailing, which was founded in 1981.
In boxing, Ludovic Proto - as an amateur, he competed in the 1988 Summer Olympics in the men's light welterweight division. As a professional, he was a former French and European welterweight champion;
Gilbert Delé - as a professional, he was a former French and European light-middleweight champion, then he won the WBA world light-middleweight title in 1991;
Jean-Marc Mormeck - as a professional, he was a former French light heavyweight champion and two-time unified world cruiserweight champion—held the WBA, WBC, and ''The Ring'' titles twice between 2005 and 2007).
Transport
airports
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
; most international flights use Pointe-à-Pitre International Airport. Boats and cruise ships frequent the islands, using the ports at Pointe-à-Pitre and Basse-Terre.
On 9 September 2013 the county government voted in favour of constructing a tramway in Pointe-à-Pitre
Pointe-à-Pitre (; gcf, label=Guadeloupean Creole, Pwentapit, , or simply , ) is the second largest (most populous) city of Guadeloupe after Les Abymes. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in the ...
. The first phase will link northern Abymes
Les Abymes () is the most populous commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is located on the west side of the island of Grande-Terre, and is part of the largest metropolitan area of Guad ...
to downtown Pointe-à-Pitre by 2019. The second phase, scheduled for completion in 2023, will extend the line to serve the university.
Education
The Guadeloupe academic region includes only the Guadeloupe academy. It employs 9,618 people and its operating budget was €714.3 million for 2018–2019. The territory has 300 elementary schools, including 1 private kindergarten under contract and 14 private elementary schools under contract. It also has 52 middle schools, including 6 private under contract. And finally, it has 38 high schools, 13 of which are private under contract. During the 2018–2019 school year were enrolled at Guadeloupe Academy: * 45,510 students in primary education ; *St. Barthélemy
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy ...
);
* The Basse-Terre Nord Pole (Baie-Mahault, Capesterre-Belle-Eau and Sainte-Rose) ;
* The South Pole of Basse-Terre: Basse-Terre and Bouillante (including the islands of Les Saintes);
* The North Pole of Grande-Terre: Grande-Terre Nord, Sainte-Anne and Saint-François (including the islands of La Désirade and Marie-Galante);
* The South Pole of Grande-Terre: Les Abymes, Gosier and Pointe-à-Pitre.
The islands of Guadeloupe also have two local campuses of the University of the West Indies
The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 17 English-speaking countries and territories in th ...
(Fouillole and Camp Jacob), a "city of knowledge" including a health and social campus, a "university of trades" including a training centre for apprentices (CFA), a regional arts and entertainment centre, a student residence and, finally, three sites of the regional deuxième chance school.
Infrastructure
Energy
The island has great potential for solar, wind and marine energy, but by 2018,biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
and coal energy and petroleum hydrocarbons are still the most used.
Energy transition
The energy transition is the process of downshifting fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon energy sources. More generally, an energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding ...
Law (TECV) provides for 50% renewable energy by 2020 in the territory. And the Guadeloupe EPP plans to develop 66 MW of additional biomass capacity between 2018 and 2023, including 43 MW to replace coal.
For example, the Albioma Caraïbes (AC) coal-fired power plant will be converted to biomass to help increase the share of renewables in Guadeloupe's energy mix from 20.5% to 35%, thereby mitigating the island's dependence on fossil fuels and reducing acidic air pollution and the production of toxic and bottom ash.
This 34 MW power plant, producing 260 GWh/year of electricity in 2018 (i.e. 15% of the island's needs), should reduce 265 000 t of equivalent/year throughout the chain (−87% once converted to biomass compared to the previous situation, coal).
Guadeloupe has an electricity production plant, in Le Moule, based on the sugar cane agricultural sector, which recovers the residues from sugar cane crushing (bagasse) to produce energy; 12 wind farms, such as in Désirade, Le Moule or Marie-Galante; a geothermal power plant in Bouillante, which uses the energy of water vapor produced by volcanic activity (the plant's electricity production ranks it first nationally); a project to harness the energy of waves and ocean currents; photovoltaic installations that contribute to the operation of solar water heaters for homes and to the development of the electric vehicle sector.
Electricity produced by hydropower, which represents 2.2% of total production, comes from dams built on the beds of certain rivers.
Drinking water supply
The water distributed by Guadeloupe's drinking water network comes mainly from Basse Terre, 70% from river intakes and 20% from spring catchments. The remaining 10% comes from boreholes tapping the groundwater of Grande Terre and Marie-Galante. Access to water and sanitation is problematic due to the deteriorated state of the network, which causes many losses in the water supply system. For years, water shortages have been recurrent and have forced "water shifts", mainly in the municipalities ofGrande-Terre
Grande-Terre Island (french: île de Grande-Terre / île de la Grande-Terre; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwantè) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe ...
, which are the most affected, with consequences for private individuals and agricultural activities.
According to statistics from the Water Office (2020 data), 61% of drinking water production is wasted, i.e. almost 50 million cubic metres of water per year, due to pipes in poor condition. In addition, 70% of wastewater treatment plants do not meet standards.
Police and Crime
Although Guadeloupe is one of the safest islands in the Caribbean,Graff, Vincent. (2013), "Death in Paradise: Ben Miller on investigating the deadliest place on the planet," ''Radio Times'', 8 January 2013 it was the most violent overseas French
department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
in 2016. The murder rate is slightly more than that of Paris, at 8.2 per 100,000. The high level of unemployment caused violence and crime to rise, especially in 2009 and 2010, the years following the Great Recession. Residents of Guadeloupe describe the island as a place with little everyday crime, and most violence is caused by the drug trade or domestic disputes. In 2021, additional police officers were deployed to the island in the face of rioting arising out of Covid-19 restrictions.
Normally, about 2,000 police officers are present on the island including some 760 active National Gendarmerie of the COMGEND (Gendarmerie Command of Guadeloupe) region plus around 260 reservists. The active Gendarmerie include three Mobile Gendarmerie Squadrons (EGM) and a Republican Guard Intervention Platoon (PIGR). The Maritime Gendarmerie deploys the patrol boat Violette (P722) in the territory.
See also
*Bibliography of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
* Index of Guadeloupe-related articles
Articles related to the Overseas department, French overseas department of Guadeloupe include:
0–9
*.gp – Internet country code top-level domain for Guadeloupe
*1899 Hurricane San Ciriaco
*1928 Okeechobee hurricane
*2009 French Caribbean ...
* List of colonial and departmental heads of Guadeloupe
* Overseas departments and territories of France
Overseas France (french: France d'outre-mer) consists of 13 French-administered territories outside Europe, mostly the remains of the French colonial empire that chose to remain a part of the French state under various statuses after decolon ...
* Slavery in the Caribbean
References
Further reading
* Haigh, Sam – ''An Introduction to Caribbean Francophone Writing: Guadeloupe and Martinique.'' * Jennings, Eric T. – ''Vichy in the Tropics: Petain’s National Revolution in Madagascar, Guadeloupe, and Indochina, 1940–1944.'' * Noble, G. K. – ''The Resident Birds of Guadeloupe.'' * Paiewonsky, Michael – ''Conquest of Eden, 1493–1515: Other Voyages of Columbus; Guadeloupe, Puerto Rico, Hispaniola, Virgin Islands.'' * Roche, Jean-Claude – ''Oiseau des Antilles. Vol. 1, The Lesser Antilles from Grenada to Guadeloupe.''External links
Prefecture website
Regional Council website
Departmental Council website
{{Authority control Dependent territories in the Caribbean Overseas departments of France French Caribbean Leeward Islands (Caribbean) Lesser Antilles Regions of France Outermost regions of the European Union Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas British Caribbean Former Swedish colonies Former colonies in North America French Union Island countries French-speaking countries and territories Populated places established in the 4th century 1674 establishments in the French colonial empire 1674 establishments in North America 1759 disestablishments in the French colonial empire 1759 disestablishments in North America 1759 establishments in the British Empire 1759 establishments in North America 1763 disestablishments in the British Empire 1763 disestablishments in North America 1763 establishments in the French colonial empire 1763 establishments in North America 1810 establishments in the British Empire 1810 disestablishments in the French colonial empire 1810 disestablishments in North America 1810 establishments in North America 1816 disestablishments in the British Empire 1816 disestablishments in North America 1816 establishments in the French colonial empire 1816 establishments in North America