|
Martinique
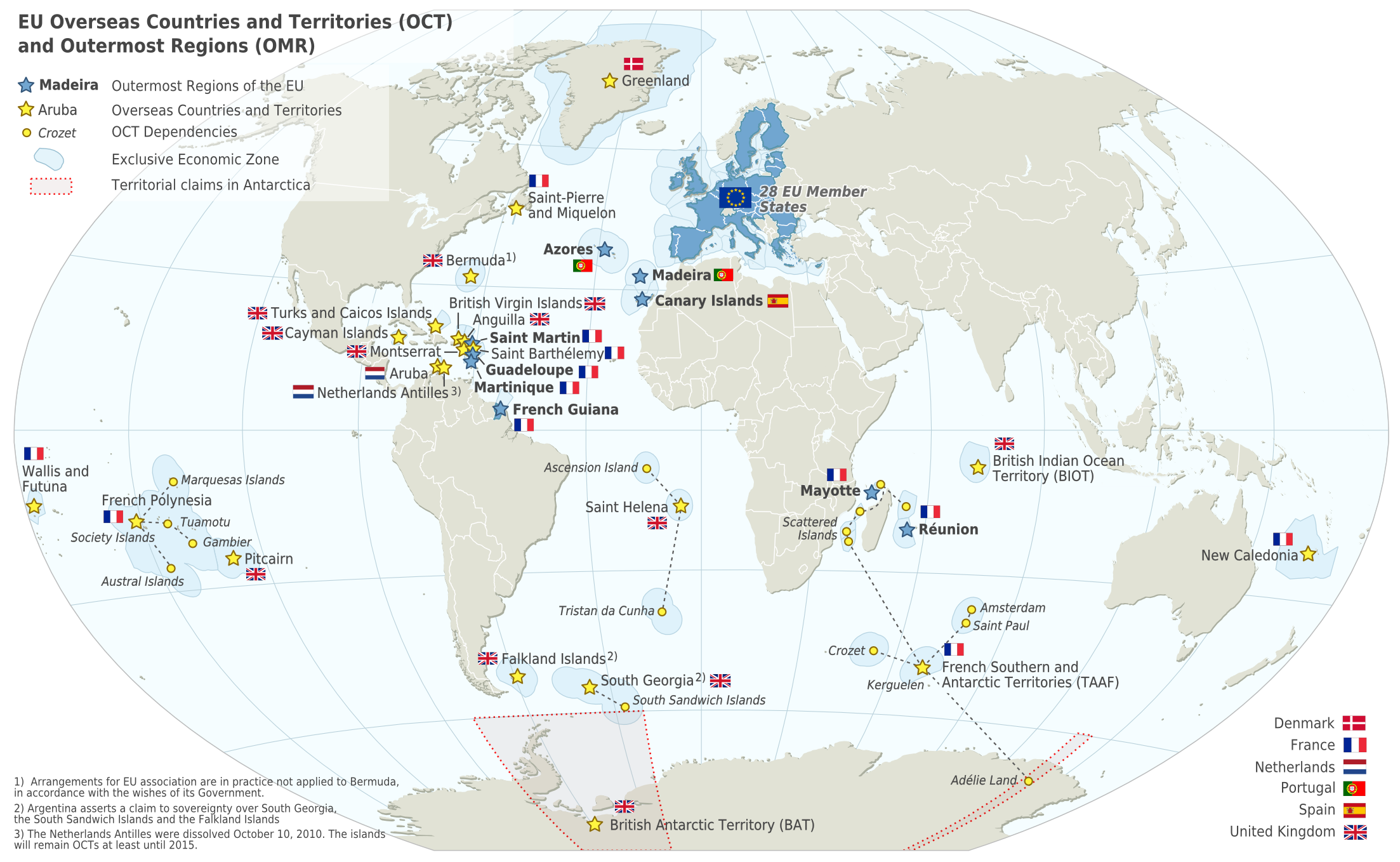
Martinique ( ; or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. It was previously known as Iguanacaera which translates to iguana island in Carib language, Kariʼnja. A part of the French West Indies (Antilles), Martinique is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region and a single territorial collectivity of France. It is a part of the European Union as an outermost region within the special territories of members of the European Economic Area, and an associate member of the Caribbean Community, CARICOM, the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS), the Association of Caribbean States (ACS), and the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) but is not part of the Schengen Area or the European Union Customs Union. The currency in use is the euro. It has been a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve since 2021 for its entire land and sea territory. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antillean Creole
Antillean French Creole (also known as Lesser Antillean Creole, Kreyol, or Patois) is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles caribbean. Its grammar and vocabulary include elements of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous languages, Languages of Africa, African languages, French language, French, and English language, English. Geographical situation There are two main geographical and linguistic groups in the Antilles or List of Caribbean islands, Caribbean Islands: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. Intercomprehension between these two groups is possible, but despite a large proportion of shared vocabulary and largely similar grammatical functioning, it is limited by varying key vocabulary and different words for basic grammar. Nevertheless, it is easy to begin to understand each other completely, as long as one of the two has a basic knowledge of the other's language. Antillean Creole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort-de-France
Fort-de-France (, , ; ) is a Communes of France, commune and the capital city of Martinique, an overseas department and region of France located in the Caribbean. History Before it was ceded to France by Spain in 1635, the area of Fort-de-France was known as Iguanacaera, which translates to "Iguana Island" in the indigenous Carib language, Kariʼnja language. In 1638, Jacques Dyel du Parquet (1606–1658), nephew of Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc and first governor of Martinique, decided to have Fort Saint Louis built to protect the city against enemy attacks. The fort was soon destroyed, and rebuilt in 1669, when Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV appointed the Marquis of Baas as governor general. Under his orders and those of his successors, particularly the Charles de Courbon de Blénac, Count of Blénac, the fort was built with a Vauban design. In the 1680s, the area was settled and became the French colonial capital in the French West Indies, Caribbean and the French colonization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Of Martinique
The assembly of Martinique is the deliberative assembly of Martinique, which is a single territorial collectivity of France. In 2015 it replaced both the Regional In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ... and General Councils of Martinique. Voting method The Martinican assembly is made up of 51 members, who are elected for six year terms. The voting system is similar to that used for regional elections: it is a multi-member proportional election with two rounds with majority bonus. In the first round, if a list receives the absolute majority of the votes cast, it receives a premium of 11 seats and the remaining seats are allocated to all the lists having received at least 5% of the votes cast. If no list receives the absolute majority, a second round takes place: the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Martinique
Hinduism is followed in Martinique by a small number of Indo-Martiniquais. As of 2007, Hinduism constituted 0.3% of the population of Martinique. History After the abolition of slavery in 1848, plantation owners filled their need for laborers by importing Indians from the subcontinent, starting in 1853. These immigrants brought with them their Hindu religion. Many Hindu temples are still in use in Martinique and, in 1987, a personal description of their secret ceremonies was published by a Hindu participant. The symbols, gestures and myths of Hinduism were an important inspiration to the French artist Paul Gauguin, who visited Martinique in 1887. Demographics Though Indo-Martiniquais comprise approximately 10% of the population of the island of Martinique, only a few 20-30% of them are still Hindus. Though, the number of Christians converting to Hinduism is steadily increasing with revival efforts. Hindus and quimboiseurs (another religion in Martinique) consider themselves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Martiniquais
Indo-Martiniquais are an ethnic group of Martinique, compromising approximately 10% of the population of the island. The Indo-Martiniquais are descendants of indentured labourers of the nineteenth century from India of primarily Tamil and Telugu descent as well as other Indian peoples. They are primarily most concentrated in the northern communes of Martinique, where the main plantations are located. The Indo-Martiniquais speak Antillean a French-based creole. Migration history In 1851 the Martinique authorities, seeking to replace former slave labourers who had abandoned plantation work on being given their liberty, recruited several thousand labourers from the Indian French colonial settlements of Madras, Pondichéry, Chandernagor and Karaikal. Workers were offered free passage and pay in exchange for serving a five-year period of labour. Despite initial experiences of racial discrimination and labour exploitation, many of the immigrants were subsequently well-integrated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serge Letchimy
Serge Letchimy (; born 13 January 1953) is the President of the Executive Council of Martinique and former member of the National Assembly of France. He represents the island of Martinique's 3rd constituency since June 2007, and is a member of The Socialists and affiliated parliamentary group. Letchimy is a member of the Martinican Progressive Party (PPM), or ''Parti progressiste martiniquais''. He was the successor of Aimé Césaire as Mayor of Fort de France from 2001 to 2010 and was the final President of the Regional Council of Martinique from 26 March 2010 until its replacement by the Assembly of Martinique in December 2015. In 2021 he replaced Alfred Marie-Jeanne as President of the Executive Council of Martinique, and therefore resigned from parliament due to the dual mandate A dual mandate occurs when an official serves in or holds multiple public positions simultaneously. This practice is sometimes known as double jobbing in Britain, double-dipping in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinican Progressive Party
The Martinican Progressive Party (, PPM) is a democratic socialist political party in Martinique. It was founded on March 22, 1958 by poet Aimé Césaire after breaking off from the French Communist Party. The party favours the autonomy of Martinique within France, unlike the nationalist Martinican Independence Movement (MIM). The party has one seat in the French National Assembly, currently held by Serge Letchimy, deputy from Fort-de-France Fort-de-France (, , ; ) is a Communes of France, commune and the capital city of Martinique, an overseas department and region of France located in the Caribbean. History Before it was ceded to France by Spain in 1635, the area of Fort-de-Fra ... ( Martinique's 3rd constituency). References External links PPM official site Political parties in Martinique Political parties established in 1958 1958 establishments in France Aimé Césaire {{Martinique-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions and the Communes of France, communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five Overseas department and region, overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 Arrondissements of France, arrondissements and 2,054 Cantons of France, cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council (France), departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Departments And Regions Of France
The overseas departments and regions of France (, ; DROM) are the five departments and regions of the French Republic which are located outside European France (also known as " metropolitan France"). These overseas entities have exactly the same status as European France's departments and regions. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, and tax laws etc.) apply to French overseas departments and regions the same way as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas departments and regions cannot themselves pass new laws. On occasion, referendums are undertaken to re-assess the sentiment in local status. Since March 2011, the five overseas departments and regions of France are: * French Guiana in South America, a part of The Guianas; * Guadeloupe in the Caribbean Sea, a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outermost Region
The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of Member state of the European Union, EU member states and European Free Trade Association, EFTA member states which, for historical, geographical, or political reasons, enjoy special status within or outside the European Union and the European Free Trade Association. The special territories of EU member states are categorised under three headings: nine Outermost Regions (OMR) that form part of the European Union, though they benefit from derogations from some EU laws due to their geographical remoteness from mainland Europe; thirteen Overseas Countries and Territories (OCT) that do not form part of the European Union, though they cooperate with the EU via the Overseas Countries and Territories Association; and ten special cases that form part of the European Union (with the exception of the Faroe Islands), though EU laws make ''ad hoc'' provisions. The Outermost Regions were re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béké
Béké or beke is an Antillean Creole term to describe a descendant of the early European, usually French, settlers in the French Antilles, and more specifically in Martinique. Etymology The origin of the term is unclear, although it is attested to in colonial documents from as early as the first decade of the eighteenth century. It may well derive from Igbo phrases that describe Europeans. One Caribbean tradition holds that it originated from the question « eh bé qué ? » (« eh bien quoi ? », similar to "What's up"), an expression picked up from the French settlers. Another explanation is that its origin lies in the term « blanc des quais » ("a White from the quay") as the White colonists and merchants controlled the ports. In contrast, the "Blanc Créole" (or "Blan Kréyol" in creole) is use for White people born in the Antilles and adapted to the creole life who are not descendants of the first White settlers. "Blanc Pays" (or "Blan Péyi" in creole) is used to talk abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Caribbeans
Afro-Caribbean or African Caribbean people are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern Afro-Caribbean people descend from the Africans (primarily from West and Central Africa) taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the trans-Atlantic slave trade between the 15th and 19th centuries to work primarily on various sugar plantations and in domestic households. Other names for the ethnic group include Black Caribbean, Afro- or Black West Indian, or Afro- or Black Antillean. The term West Indian Creole has also been used to refer to Afro-Caribbean people, as well as other ethnic and racial groups in the region, though there remains debate about its use to refer to Afro-Caribbean people specifically. The term Afro-Caribbean was not coined by Caribbean people themselves but was first used by European Americans in the late 1960s. People of Afro-Caribbean descent today are largely of West African and Central African an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |