|
Exclusive Economic Zone Of France
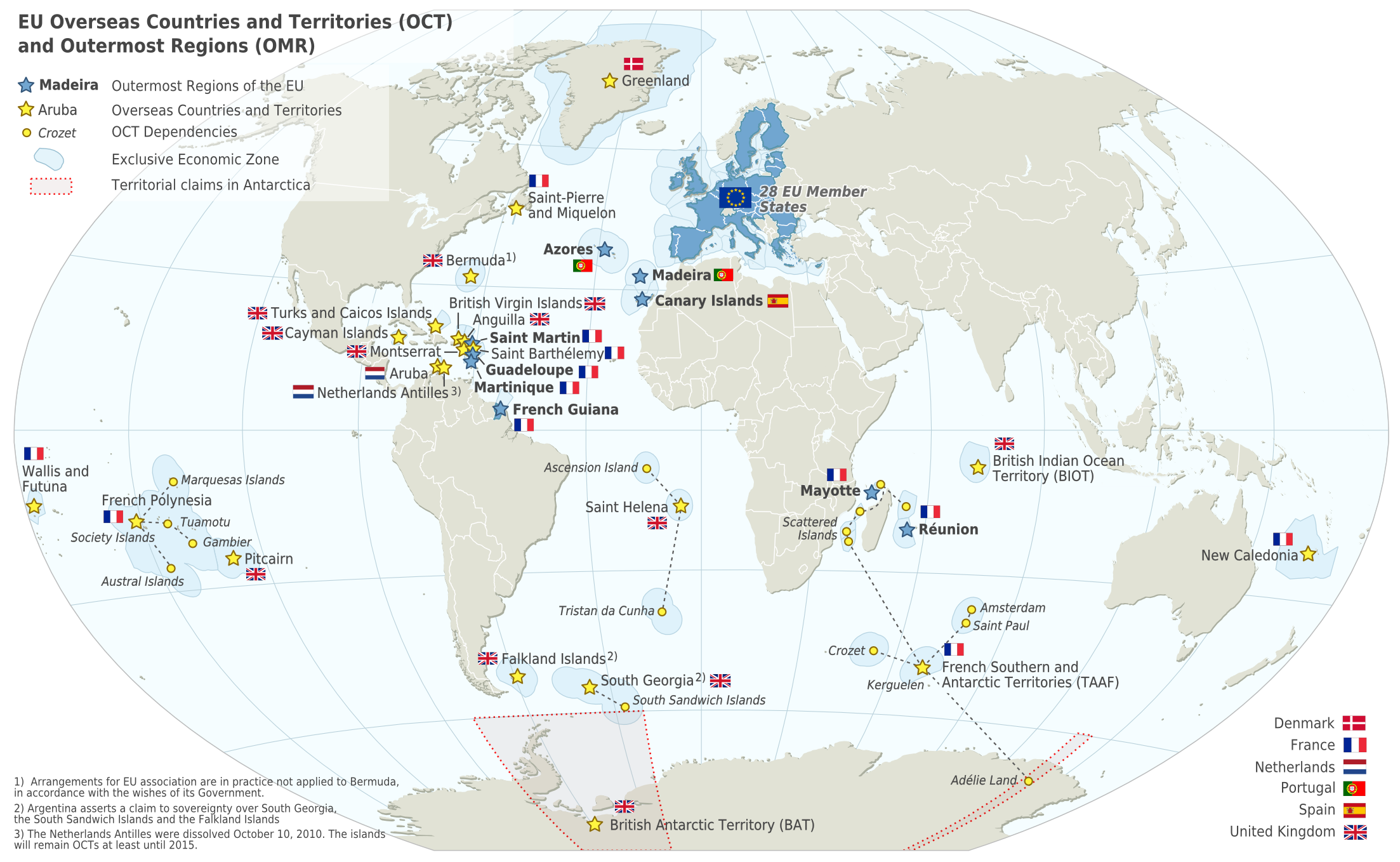
France has, due to its Overseas departments and regions that are scattered in all the oceans of Earth, the largest exclusive economic zone of the world. The total EEZ of France is . It covers approximately 8% of the surface of all the EEZs of the world, while the French Republic is only 0.45% of the world's land surface. Geography Monaco's waters are enclaves in the French EEZ.European French EEZ website miscellanees01.files.wordpress.com The situation is more unclear for the Channel Islands. Some maps show the EEZ being enclaved by the French EEZ, while others show the Guernsey EEZ extending to the border with the UK EEZ. Outside of mainland France and overseas departments or communities ( |
Overseas Department And Region
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainland France's regions and departments. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, tax laws, etc.) apply to French overseas regions the same as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas regions cannot themselves pass new laws. As integral parts of France and the European Union, overseas departments are represented in the National Assembly, Senate, and Economic and Social Council, vote to elect members of the European Parliament (MEP), and also use the euro as their currency. The overseas departments and regions are not the same as the over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Réunion
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States. La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * La (musical note), or A, the sixth note * "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figure 8'' (album) * ''L.A.'' (EP), by Teddy Thompson * '' L.A. (Light Album)'', a Beach Boys album * "L.A." (Neil Young song), 1973 * The La's, an English rock band * L.A. Reid, a prominent music producer * Yung L.A., a rapper * Lady A, an American country music trio * "L.A." (Amy Macdonald song), 2007 * "La", a song by Australian-Israeli singer-songwriter Old Man River Other media * l(a, a poem by E. E. Cummings * La (Tarzan), fictional queen of the lost city of Opar (Tarzan) * '' Lá'', later known as Lá Nua, an Irish language newspaper * La7, an Italian television channel * LucasArts, an American video game developer and publisher * Liber Annuus, academic journal Business, organizations, and government agencies * L.A. Screenings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Economic Zone Of Canada
The exclusive economic zone of Canada is the area of the sea in which Canada has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. Canada's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) is the 7th largest in the world. It is unusual in that its EEZ, covering , is slightly smaller than its territorial waters. The latter generally extend only 12 Nautical miles from the shore, but also include inland marine waters such as Hudson Bay—about across—the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, and the internal waters of the Arctic archipelago. Geography Canada's EEZ is in the Pacific Ocean, Beaufort Sea, Arctic Ocean, Baffin Bay, Hudson Bay, Labrador Sea, Northwestern Passages, Gulf of St Lawrence, and the Atlantic Ocean. It borders with Alaska (US) to the west, Greenland to the east, and the United States to the south. The fishing grounds in Canada's Atlantic Ocean zone are called the "Grand Banks". They extend beyond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tromelin Island
Tromelin Island (; french: Île Tromelin, ) is a low, flat island in the Indian Ocean about north of Réunion and about east of Madagascar. Tromelin is administered as part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands, a French Overseas Territory, but Mauritius claims sovereignty over the island. Tromelin has facilities for scientific expeditions and a weather station. It is a nesting site for birds and green sea turtles. Etymology The island is named in honour of Jacques Marie Boudin de Tromelin de La Nuguy, captain of the French corvette ''Dauphine''. He arrived at the island on 29 November 1776, and rescued eight stranded enslaved Malagasy people who had been on the island for 15 years. Description Tromelin is situated in the Mascarene Basin and is part of the Îles Éparses. It is currently only high. It formed as a volcano, now eroded, and developed an atoll ring of coral. Tromelin is about long and wide, with an area of 80 ha (200 acres), cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Îles Éparses
The Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean (french: Îles Éparses or ''Îles Éparses de l'océan Indien'') consist of four small coral islands, an atoll, and a reef in the Indian Ocean, and have constituted the 5th district of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (TAAF), though sovereignty over some or all of the Islands is contested by Madagascar, Mauritius, and the Comoros. None of the islands have ever had a permanent population. Two of the islands—Europa and Juan de Nova—and the Bassas da India atoll lie in the Mozambique Channel west of Madagascar, while a third island, Tromelin, lies about east of Madagascar and the Glorioso Islands lies about northwest of Madagascar. Also in the Mozambique Channel is the ''Banc du Geyser'', a mostly submerged reef considered a part of the Glorioso Islands by France and the Comoros. The islands have been classified as nature reserves. Except for Bassas da India, they all support meteorological stations: those on the Glorioso Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île Amsterdam
Île Amsterdam (), also known as Amsterdam Island and New Amsterdam (''Nouvelle-Amsterdam''), is an island of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands in the southern Indian Ocean that together with neighbouring Île Saint-Paul to the south forms one of the five districts of the territory. The island is roughly equidistant to the land masses of Madagascar, Australia, and Antarctica – as well as the British Indian Ocean Territory and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands (about from each). The research station at Martin-de-Viviès, first called ''Camp Heurtin'' and then ''La Roche Godon'', is the only settlement on the island and is the seasonal home to about thirty researchers and staff studying biology, meteorology, and geomagnetics. History The first person known to have sighted the island was the Spanish explorer Juan Sebastián de Elcano, on 18 March 1522, during his circumnavigation of the world. Elcano did not give the island a name. On 17 June 1633, Dutch mariner Anthonie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île Saint-Paul
Île Saint-Paul (Saint Paul Island) is an island forming part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (''Terres australes et antarctiques françaises'', TAAF) in the Indian Ocean, with an area of . The island is located about south of the larger Île Amsterdam (), northeast of the Kerguelen Islands, and southeast of Réunion. It is an important breeding site for seabirds. A scientific research cabin on the island is used for scientific or ecological short campaigns, but there is no permanent population. It is under the authority of a senior administrator on Réunion. Geography Île Saint-Paul is a volcanic island with triangular in shape that measures no more than at its widest point. It is the top of an active volcano; the volcano last erupted in 1793 (from its SW Flank), and is rocky with steep cliffs on the east side. The thin stretch of rock that used to close off the crater collapsed in 1780, admitting the sea through a channel; the entrance is only a few meter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Îles Kerguelen
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the sub-Antarctic constituting one of the two exposed parts of the Kerguelen Plateau, a large igneous province mostly submerged in the southern Indian Ocean. They are among the most isolated places on Earth, located more than from Madagascar. The islands, along with Adélie Land, the Crozet Islands, Amsterdam and Saint Paul islands, and France's Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean, are part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands and are administered as a separate district. The main island, Grande Terre, is in area, about three quarters of the size of Corsica, and is surrounded by a further 300 smaller islands and islets, forming an archipelago of . The climate is harsh and chilly with frequent high winds throughout the year. The surrounding seas are generally rough and they remain ice-free year-round. There are no indige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Îles Crozet
The Crozet Islands (french: Îles Crozet; or, officially, ''Archipel Crozet'') are a sub-Antarctic archipelago of small islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They form one of the five administrative districts of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. History Discovery and early history The Crozet Islands were discovered on 24 January 1772, by the expedition of French explorer Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, aboard ''Le Mascarin''. His second-in-command Jules (Julien-Marie) Crozet landed on Île de la Possession, claiming the archipelago for France. The expedition continued east and landed in New Zealand, where Captain Marion and much of his crew were killed and cannibalized by Maori. Crozet survived the disaster, and successfully led the survivors back to their base in Mauritius. In 1776, Crozet met James Cook at Cape Town, at the start of Cook's third voyage. Crozet shared the charts of his ill-fated expedition, and as Cook sailed eastward, he stopped at the islands, naming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île De Clipperton
Clipperton Island ( or ; ) is an uninhabited, coral atoll in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It is from Paris, France, from Papeete, Tahiti, and from Mexico. It is an overseas state private property of France under direct authority of the Minister of the Overseas. In the past, Clipperton Island was the subject of a sovereignty dispute in particular between France and Mexico, which was finally settled through arbitration in 1931; the ''Clipperton Island Case'' remains widely studied in international law textbooks. Geography The atoll is south-west of Mexico, west of Nicaragua, west of Costa Rica and north-west of the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador, at . Clipperton is about south-east of Socorro Island in the Revillagigedo Archipelago, which is the nearest land, while the nearest French-owned island is Hiva Oa. Some consider it to be one of the eastern-most points of Oceania, rather than an outlying island of the Americas. It is low-lying and largely barren, with some scatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouvelle-Calédonie
) , anthem = "" , image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of New Caledonia , map_caption = Location of New Caledonia , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Annexed by France , established_date = 24 September 1853 , established_title2 = Overseas territory (France), Overseas territory , established_date2 = 1946 , established_title3 = Nouméa Accord , established_date3 = 5 May 1998 , official_languages = French language, French , regional_languages = , capital = Nouméa , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , demonym = New Caledonian , government_type = Devolution, Devolved Parliamentary system, parliamentary Dependent territory, dependency , leader_title1 = President of France , leader_name1 = Emmanuel Macron , leader_title2 = President of the Government of New Caledonia, President of the Government , leader_name2 = Louis Map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy (french: Saint-Barthélemy, ), officially the Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Barthélemy, is an overseas collectivity of France in the Caribbean. It is often abbreviated to St. Barth in French, and St. Barts in English. The island lies about south of the Caribbean island Saint Martin, and is northeast of the Dutch islands of Saba, Sint Eustatius, and the independent country of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Saint Barthélemy was for many years a French commune forming part of Guadeloupe, which is an overseas region and department of France. In 2003 the island voted in favour of secession from Guadeloupe in order to form a separate overseas collectivity (''collectivité d'outre-mer'', abbreviated to ''COM'') of France. The collectivity is one of four territories among the Leeward Islands in the northeastern Caribbean that make up the French West Indies, along with Saint Martin, Guadeloupe ( southeast), and Martinique. Saint Barthélemy, a volcanic island f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_at_St_Paul_Island.jpg)


