|
Hurricane Irma
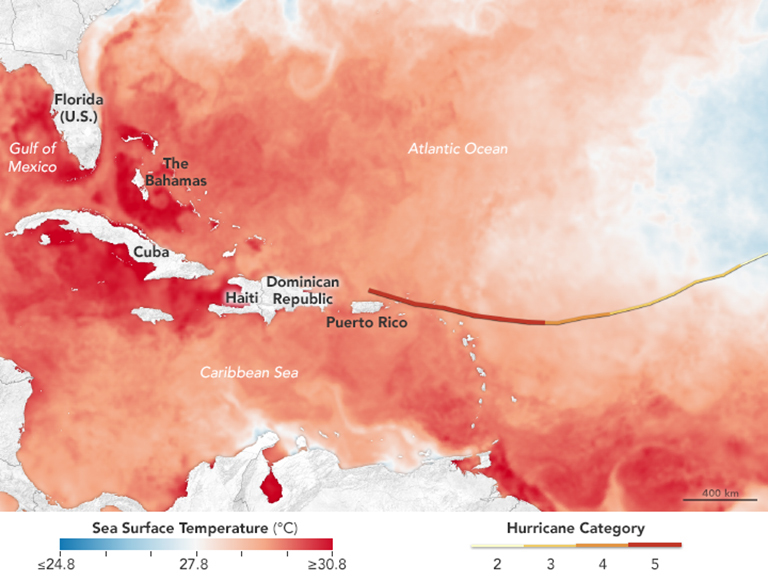
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two weeks later. At the time, it was considered as the most powerful hurricane on record in the open Atlantic region, outside of the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico until it was surpassed by Hurricane Dorian two years later. It was also the third strongest Atlantic hurricane at landfall ever recorded, just behind the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane and Dorian. The ninth named storm, fourth hurricane, second major hurricane, and first Category 5 hurricane of the 2017 season, Irma caused widespread and catastrophic damage throughout its long lifetime, particularly in the northeastern Caribbean and the Florida Keys. It was also the most intense hurricane to strike the continental United States since Katrina in 2005, the first major hurrican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeward Islands
french: Îles-Sous-le-Vent , image_name = , image_caption = ''Political'' Leeward Islands. Clockwise: Antigua and Barbuda, Guadeloupe, Saint kitts and Nevis. , image_alt = , locator_map = , location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean , coordinates = , area_km2 = , total_islands = 30+ , major_islands = Antigua and BarbudaGuadeloupeMontserratSaint Kitts and Nevis Saint MartinVirgin Islands , highest_mount = La Grande Soufrière, Guadeloupe , elevation_m = 1,467 , country = Antigua and Barbuda , country_largest_city = St. John's , country1 = Guadeloupe , country1_largest_city = Les Abymes , country2 = Saint Kitts and Nevis , country2_largest_city = Basseterre , country3 = Sint Maarten , country3_largest_city = Philipsburg , density_km2 = , population = +700,000 , ethnic_groups = The Leeward Islands () are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 2017 Atlantic hurricane season was a disastrous, extremely active Atlantic hurricane season and the costliest on record, with a damage total of at least $294.92 billion (USD). The season featured 17 named storms, 10 hurricanes, and 6 major hurricanes. Most of the season's damage was due to hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria. Another notable hurricane, Nate, was the worst natural disaster in Costa Rican history. These four storm names were retired following the season due to the number of deaths and amount of damage they caused. Collectively, the tropical cyclones were responsible for at least 3,364 deaths—the most fatalities in a single season since 2005. The season also had the highest accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) since 2005 with an approximate index of 224 units, with a record three hurricanes each generating an ACE of over 40: Irma, Jose, and Maria. The season featured two Category 5 hurricanes, one of only seven on record to feature multiple Category 5 hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Category 5 Atlantic Hurricanes
A Category 5 Atlantic hurricane is a tropical cyclone that reaches Category 5 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, within the Atlantic Ocean to the north of the equator. They are among the strongest tropical cyclones that can form on Earth, having 1-minute sustained wind speeds of at least . The United States National Hurricane Center currently estimates that a total of 38 tropical cyclones between 1851 and have peaked as Category 5 hurricanes. Background Within the Atlantic Ocean to the north of the Equator, hurricanes are officially monitored by the United States's National Hurricane Center (NHC), however, other meteorological services, such as Météo-France, the United Kingdom's Met Office and Environment Canada also monitor the basin. Within the region, a Category 5 hurricane is considered to be a tropical cyclone that has 1-minute mean maximum sustained wind speeds of or greater on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale at above ground. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffir–Simpson Scale
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds. This measuring system was formerly known as the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, or SSHS. To be classified as a hurricane, a tropical cyclone must have one-minute-average maximum sustained winds at 10 m above the surface of at least 74 mph (64 kn, 119 km/h; Category 1). The highest classification in the scale, Category 5, consists of storms with sustained winds of at least 157 mph (137 kn, 252 km/h). The classifications can provide some indication of the potential damage and flooding a hurricane will cause upon landfall. The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale is based on the highest wind speed averaged over a one-minute interval 10 m above th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Naming
Tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones are named by various warning centers to simplify communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. The names are intended to reduce confusion in the event of concurrent storms in the same basin. Once storms develop sustained wind speeds of more than , names are generally assigned to them from predetermined lists, depending on the basin in which they originate. Some tropical depressions are named in the Western Pacific; while tropical cyclones must contain a significant amount of gale-force winds before they are named in the Southern Hemisphere. Before it became standard practice to give personal (first) names to tropical cyclones, they were named after places, objects, or the saints' feast days on which they occurred. Credit for the first usage of personal names for weather systems is generally given to Queensland Government Meteorologist Clement Wragge, who named systems between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1935 Labor Day Hurricane
The Great Labor Day Hurricane of 1935 was the most intense Atlantic hurricane to make landfall on record by pressure, with winds of up to 185 mph (297 km/h). The fourth tropical cyclone, third tropical storm, second hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 1935 Atlantic hurricane season, the Labor Day hurricane was one of four Category 5 hurricanes on record to strike the contiguous United States, along with Hurricane Andrew in 1992, Hurricane Camille in 1969, and Hurricane Michael in 2018. In addition, it was the third most intense Atlantic hurricane on record in terms of barometric pressure, only behind Hurricane Gilbert in 1988 and Hurricane Wilma in 2005. The hurricane intensified rapidly, passing near Long Key on the evening of Monday, September 2. The region was swept by a massive storm surge as the eye passed over the area. The waters quickly receded after carving new channels connecting the bay with the ocean; however, gale-force winds and rough seas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was the fourth consecutive above-average and damaging season dating back to 2016. However, many were weak and short-lived, especially towards the end of the season. Six of those named storms achieved hurricane status, while three intensified into major hurricanes. Two storms became Category 5 hurricanes, marking the fourth consecutive season with at least one Category 5 hurricane, the third consecutive season to feature at least one storm making landfall at Category 5 intensity, and the seventh on record to have multiple tropical cyclones reaching Category 5 strength. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin and are adopted by convention. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Subtropical Storm Andrea on May 20, making this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Dorian
Hurricane Dorian was an extremely powerful and catastrophic Category 5 Atlantic hurricane, which became the most intense tropical cyclone on record to strike the Bahamas, and tied for strongest landfall in the Atlantic basin. It is also regarded as the worst natural disaster in the Bahamas' recorded history. It was also one of the most powerful hurricanes recorded in the Atlantic Ocean in terms of 1-minute sustained winds, with those winds peaking at 185 mph (295 km/h). In addition, Dorian surpassed Hurricane Irma of 2017 to become the most powerful Atlantic hurricane on record outside of the Caribbean Sea. Dorian was the fourth named storm, second hurricane, the first major hurricane, and the first Category 5 hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season. Dorian struck the Abaco Islands on September 1 with maximum sustained winds of 185 mph (295 km/h), tying with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the highest wind speeds of an Atlantic hurricane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern United States, Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the northern coast of South America. The Gulf of Mexico lies to the northwest. The entire area of the Caribbean Sea, the numerous islands of the West Indies, and adjacent coasts are collectively known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, Gulf of Venezuela, Gulf of Darién, Golfo de los Mosquitos, Gulf of Paria and Gulf of Honduras. The Caribbean Sea has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |