GPU NVidia NV40 6800GT AGP on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter
 In the home market, the
In the home market, the
 In 1987, the
In 1987, the  IBM's
IBM's
memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
to accelerate the creation of images
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
in a frame buffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Mode ...
intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' ...
s, mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whi ...
s, personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
s, workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstat ...
s, and game consoles.
Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great de ...
and image processing. Their parallel structure
In grammar, parallelism, also known as parallel structure or parallel construction, is a balance within one or more sentences of similar phrases or clauses that have the same grammatical structure. The application of parallelism affects readabilit ...
makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just Processor (computing), processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes Instruction (computing), instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU per ...
s (CPUs) for algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
s that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer mo ...
or embedded on the motherboard. In some CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU die.
In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit independently working from the CPU and responsible for graphics manipulation and output. Later, in 1994, Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professiona ...
used the term (now standing for ''graphics processing unit'') in reference to the PlayStation console's Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, ...
-designed Sony GPU in 1994. The term was popularized by Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
in 1999, who marketed the GeForce 256
The GeForce 256 is the original release in Nvidia's " GeForce" product-line. Announced on August 31, 1999 and released on October 11, 1999, the GeForce 256 improves on its predecessor ( RIVA TNT2) by increasing the number of fixed pixel pipeli ...
as "the world's first GPU". It was presented as a "single-chip processor
Processor may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Processor (computing)
**Central processing unit (CPU), the hardware within a computer that executes a program
*** Microprocessor, a central processing unit contained on a single integrated circuit (I ...
with integrated transform, lighting, triangle setup/clipping, and rendering engines". Rival ATI Technologies
ATI Technologies Inc. (commonly called ATI) was a Canadian semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985 as Array Technology Inc., ...
coined the term "visual processing unit" or VPU with the release of the Radeon 9700
The R300 GPU, introduced in August 2002 and developed by ATI Technologies, is its third generation of GPU used in '' Radeon'' graphics cards. This GPU features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 9.0 and OpenGL 2.0, a major improvement in fe ...
in 2002.
History
1970s
Arcade system boards have been using specialized graphics circuits since the 1970s. In early video game hardware, theRAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
for frame buffers was expensive, so video chips composited data together as the display was being scanned out on the monitor.
A specialized barrel shifter circuit was used to help the CPU animate the framebuffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Mode ...
graphics for various 1970s arcade games from Midway and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, toys, arcade cabinets and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, vending machines and jukeboxes into Japan. I ...
, such as ''Gun Fight
''Gun Fight'', known as in Japan and Europe, is a 1975 multidirectional shooter arcade game designed by Tomohiro Nishikado, and released by Taito in Japan and Europe and by Midway in North America. Based around two Old West cowboys armed ...
'' (1975), '' Sea Wolf'' (1976) and ''Space Invaders
is a 1978 shoot 'em up arcade game developed by Tomohiro Nishikado. It was manufactured and sold by Taito in Japan, and licensed to the Midway division of Bally for overseas distribution. ''Space Invaders'' was the first fixed shooter an ...
'' (1978). The Namco Galaxian
Namco was a video game developer and publisher, originally from Japan.
Bandai Namco Entertainment is the successor to Namco and continues manufacturing and distributing video games worldwide. For Namco games released following the 2006 merger w ...
arcade system in 1979 used specialized graphics hardware
Graphics hardware is computer hardware that generates computer graphics and allows them to be shown on a display, usually using a graphics card (video card) in combination with a device driver to create the images on the screen.
Types
Gra ...
supporting RGB color, multi-colored sprites and tilemap backgrounds. The Galaxian hardware was widely used during the golden age of arcade video games
The golden age of arcade video games was the period of rapid growth, technological development and cultural influence of arcade video games, from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. The period began with the release of ''Space Invaders'' in 1978, ...
, by game companies such as Namco
was a Japanese multinational video game and entertainment company, headquartered in Ōta, Tokyo. It held several international branches, including Namco America in Santa Clara, California, Namco Europe in London, Namco Taiwan in Kaohsiung, ...
, Centuri
Centuri, formerly known as Allied Leisure, was an American arcade game manufacturer. They were based in Hialeah, Florida, and were one of the top six suppliers of coin-operated arcade video game machinery in the United States during the early 19 ...
, Gremlin
A gremlin is a mischievous folkloric creature invented at the beginning of the 20th century to originally explain malfunctions in aircraft and later in other machinery and processes and their operators. Depictions of these creatures vary widel ...
, Irem
is a Japanese video game console developer and publisher, and formerly a developer and manufacturer of arcade games as well. The company has its headquarters in Chiyoda, Tokyo.
The full name of the company that uses the brand is Irem Softwa ...
, Konami
, is a Japanese multinational video game and entertainment company headquartered in Chūō, Tokyo, it also produces and distributes trading cards, anime, tokusatsu, pachinko machines, slot machines, and arcade cabinets. Konami has casino ...
, Midway, Nichibutsu
was a Japanese video game developer and publisher headquartered in Kita, Osaka. In the past they had also manufactured and sold yachts.
The main video game brand of the company was Nichibutsu (日物、ニチブツ), with adult video games (ma ...
, Sega and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, toys, arcade cabinets and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, vending machines and jukeboxes into Japan. I ...
.
 In the home market, the
In the home market, the Atari 2600
The Atari 2600, initially branded as the Atari Video Computer System (Atari VCS) from its release until November 1982, is a home video game console developed and produced by Atari, Inc. Released in September 1977, it popularized microprocesso ...
in 1977 used a video shifter called the Television Interface Adaptor. The Atari 8-bit computers (1979) had ANTIC
Alphanumeric Television Interface Controller (ANTIC) is an LSI ASIC dedicated to generating 2D computer graphics to be shown on a television screen or computer display. Under the direction of Jay Miner, the chip was designed in 1977-1978 by ...
, a video processor which interpreted instructions describing a "display list"—the way the scan lines map to specific bitmapped
upright=1, The Smiley, smiley face in the top left corner is a raster image. When enlarged, individual pixels appear as squares. Enlarging further, each pixel can be analyzed, with their colors constructed through combination of the values for ...
or character modes and where the memory is stored (so there did not need to be a contiguous frame buffer). 6502
The MOS Technology 6502 (typically pronounced "sixty-five-oh-two" or "six-five-oh-two") William Mensch and the moderator both pronounce the 6502 microprocessor as ''"sixty-five-oh-two"''. is an 8-bit microprocessor that was designed by a small te ...
machine code
In computer programming, machine code is any low-level programming language, consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). Each instruction causes the CPU to perform a ve ...
subroutines could be triggered on scan line
A scan line (also scanline) is one line, or row, in a raster scanning pattern, such as a line of video on a cathode ray tube (CRT) display of a television set or computer monitor.
On CRT screens the horizontal scan lines are visually discernible ...
s by setting a bit on a display list instruction. ANTIC also supported smooth vertical
Vertical is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
* Vertical direction, the direction aligned with the direction of the force of gravity, up or down
* Vertical (angles), a pair of angles opposite each other, formed by two intersecting s ...
and horizontal scrolling independent of the CPU.
1980s
The NEC µPD7220 was the first implementation of a PC graphics display processor as a singleLarge Scale Integration
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(LSI) integrated circuit chip, enabling the design of low-cost, high-performance video graphics cards such as those from Number Nine Visual Technology
Number Nine Visual Technology Corporation was a manufacturer of video graphics chips and cards from 1982 to 1999. Number Nine developed the first 128-bit graphics processor (the Imagine 128), as well as the first 256-color (8-bit) and 16.8 m ...
. It became the best-known GPU up until the mid-1980s. It was the first fully integrated VLSI
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) ...
(very large-scale integration) metal-oxide-semiconductor ( NMOS) graphics display processor for PCs, supported up to 1024x1024 resolution, and laid the foundations for the emerging PC graphics market. It was used in a number of graphics cards and was licensed for clones such as the Intel 82720, the first of Intel's graphics processing units. The Williams Electronics arcade games ''Robotron 2084
''Robotron: 2084'' (also referred to as ''Robotron'') is a multidirectional shooter developed by Eugene Jarvis and Larry DeMar of Vid Kidz and released in arcades by WMS Industries, Williams Electronics in 1982. The game is set in the year 2084 i ...
'', ''Joust
Jousting is a martial game or hastilude between two horse riders wielding lances with blunted tips, often as part of a tournament. The primary aim was to replicate a clash of heavy cavalry, with each participant trying to strike the opponen ...
'', ''Sinistar
''Sinistar'' is a 1983 multidirectional shooter arcade game developed and manufactured by Williams Electronics. It was created by Sam Dicker, Jack Haeger, Noah Falstein, RJ Mical, Python Anghelo, and Richard Witt. Players control a spacecraft ...
'', and '' Bubbles'', all released in 1982, contain custom blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to ano ...
chips for operating on 16-color bitmaps.
In 1984, Hitachi released ARTC HD63484, the first major CMOS graphics processor for PC. The ARTC was capable of displaying up to 4K resolution when in monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochrom ...
mode, and it was used in a number of PC graphics cards and terminals during the late 1980s. In 1985, the Commodore Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphi ...
featured a custom graphics chip, with a blitter unit accelerating bitmap manipulation, line draw, and area fill functions. Also included is a coprocessor with its own simple instruction set, capable of manipulating graphics hardware registers in sync with the video beam (e.g. for per-scanline palette switches, sprite multiplexing, and hardware windowing), or driving the blitter. In 1986, Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globa ...
released the TMS34010
The TMS34010, developed by Texas Instruments and released in 1986, was the first programmable graphics processor integrated circuit. While specialized graphics hardware existed earlier, such as blitters, the TMS34010 chip is a microprocessor ...
, the first fully programmable graphics processor. It could run general-purpose code, but it had a graphics-oriented instruction set. During 1990–1992, this chip became the basis of the Texas Instruments Graphics Architecture
Texas Instruments Graphics Architecture (TIGA) is a graphics interface standard created by Texas Instruments that defined the software interface to graphics processors. Using this standard, any software written for TIGA should work correctl ...
("TIGA") Windows accelerator cards.
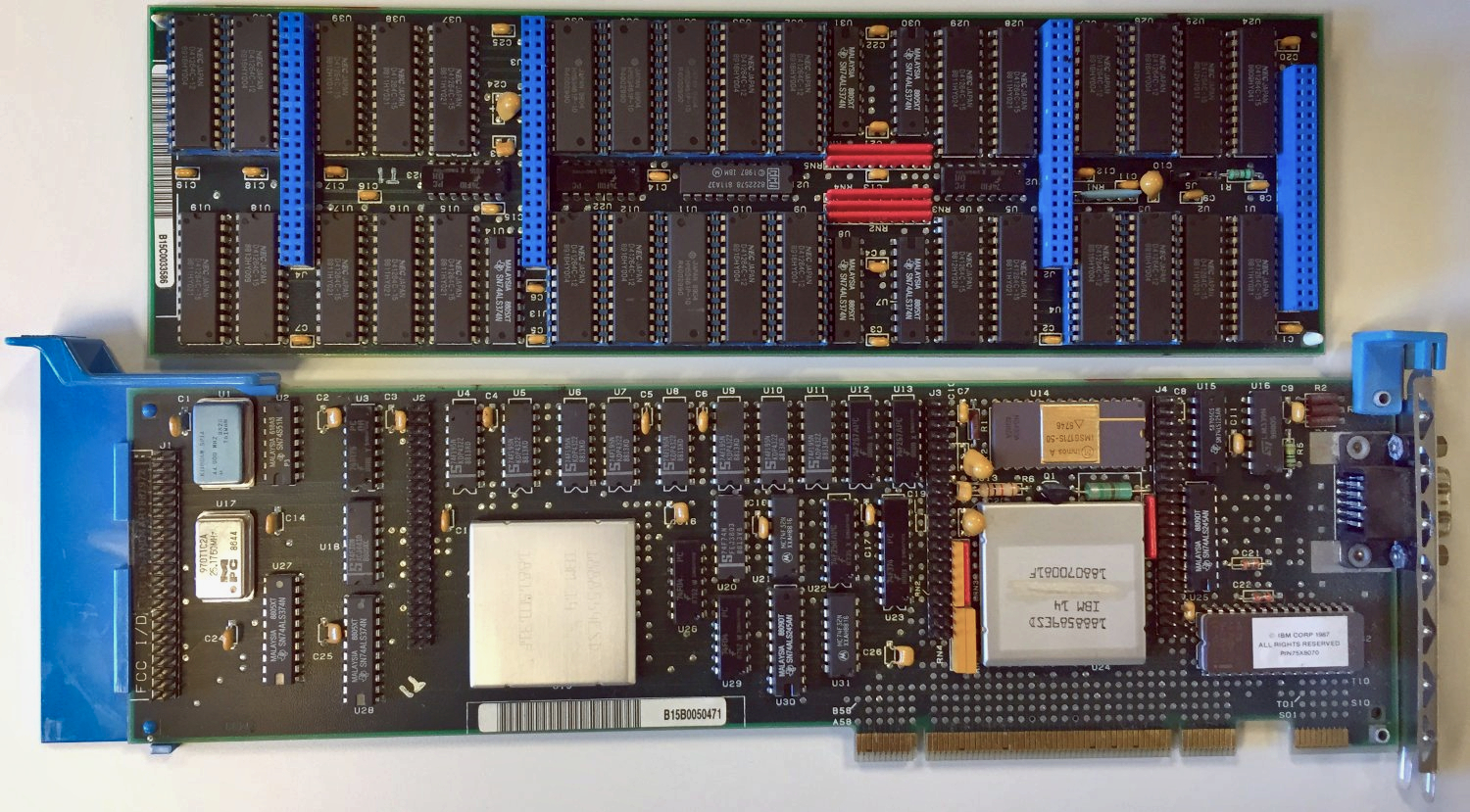
 In 1987, the
In 1987, the IBM 8514
IBM 8514 is a graphics card manufactured by IBM and introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of personal computers in 1987. It supports a display resolution of pixels with 256 colors at 43.5 Hz ( interlaced), or at 60 Hz ( non-interlaced ...
graphics system was released as one of the first video cards for IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, and IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such ...
s to implement fixed-function
Fixed-function is a term canonically used to contrast 3D graphics APIs and earlier GPUs designed prior to the advent of shader-based 3D graphics APIs and GPU architectures.
History
Historically fixed-function APIs consisted of a set of functio ...
2D primitives in electronic hardware
Electronic hardware consists of interconnected electronic components which perform analog or logic operations on received and locally stored information to produce as output or store resulting new information or to provide control for output act ...
. Sharp
Sharp or SHARP may refer to:
Acronyms
* SHARP (helmet ratings) (Safety Helmet Assessment and Rating Programme), a British motorcycle helmet safety rating scheme
* Self Help Addiction Recovery Program, a charitable organisation founded in 19 ...
's X68000
The is a home computer created by Sharp Corporation. It was first released in 1987 and sold only in Japan.
The initial model has a 10 MHz Motorola 68000 CPU, 1 MB of RAM, and lacks a hard drive. The final model was released in 1993 wi ...
, released in 1987, used a custom graphics chipset with a 65,536 color palette and hardware support for sprites, scrolling, and multiple playfields, eventually serving as a development machine for Capcom's CP System
The is an arcade system board developed by Capcom that ran game software stored on removable daughterboards. More than two dozen arcade titles were released for CPS-1, before Capcom shifted game development over to its successor, the CP System ...
arcade board. Fujitsu later competed with the FM Towns computer, released in 1989 with support for a full 16,777,216 color palette. In 1988, the first dedicated polygonal 3D graphics boards were introduced in arcades with the Namco System 21
The Namco System 21 "Polygonizer" is an arcade system board unveiled by Namco in 1988 with the game ''Winning Run''. It was the first arcade board specifically designed for 3D polygon processing. The hardware went through significant evolution th ...
and Taito
is a Japanese company that specializes in video games, toys, arcade cabinets and game centers, based in Shinjuku, Tokyo. The company was founded by Michael Kogan in 1953 as the importing vodka, vending machines and jukeboxes into Japan. I ...
Air System.
 IBM's
IBM's proprietary
{{Short pages monitor