|
X-Video Motion Compensation
X-Video Motion Compensation (XvMC), is an extension of the X video extension (Xv) for the X Window System. The XvMC API allows video programs to offload portions of the video decoding process to the GPU video-hardware. In theory this process should also reduce bus bandwidth requirements. Currently, the supported portions to be offloaded by XvMC onto the GPU are motion compensation (mo comp) and inverse discrete cosine transform (iDCT) for MPEG-2 video. XvMC also supports offloading decoding of mo comp, iDCT, and VLD ("Variable-Length Decoding", more commonly known as "slice level acceleration") for not only MPEG-2 but also MPEG-4 ASP video on VIA Unichrome (S3 Graphics Chrome Series) hardware. XvMC was the first UNIX equivalent of the Microsoft Windows DirectX Video Acceleration (DxVA) API. Popular software applications known to take advantage of XvMC include MPlayer, MythTV, and xine. Device drivers Each hardware video GPU capable of XvMC video acceleration requires a X11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Video Extension
The X video extension, often abbreviated as XVideo or Xv, is a video output mechanism for the X Window System. The protocol was designed by David Carver; the specification for version 2 of the protocol was written in July 1991. It is mainly used today to resize video content in the video controller hardware in order to enlarge a given video or to watch it in full screen mode. Without XVideo, X would have to do this scaling on the main CPU. That requires a considerable amount of processing power, which could slow down or degrade the video stream; video controllers are specifically designed for this kind of computation, so can do it much more cheaply. Similarly, the X video extension can have the video controller perform color space conversions, and change the contrast, brightness, and hue of a displayed video stream. In order for this to work, three things have to come together: * The video controller has to provide the required functions. * The device driver software for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouveau (graphics)
nouveau () is a free and open-source graphics device driver for Nvidia video cards and the Tegra family of SoCs written by independent software engineers, with minor help from Nvidia employees. The project's goal is to create an open source driver by reverse engineering Nvidia's proprietary Linux drivers. It is managed by the X.Org Foundation, hosted by freedesktop.org, and is distributed as part of Mesa 3D. The project was initially based on the 2D-only free and open-source "nv" driver, which Red Hat developer Matthew Garrett and others claim had been obfuscated. nouveau is licensed under the MIT License. The name of the project comes from the French word ''nouveau'', meaning ''new''. It was suggested by the original author, Stéphane Marchesin, after his IRC client's French-language autocorrect system offered the word "nouveau" as a correction for the letters "nv". Software architecture nouveau is a Gallium3D-style device driver and works on top of the Direct Rendering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard. In some CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU die. In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit independently working from the CPU and responsible for graphics manipulation and output. Later, in 1994, Sony used the term (now standing for ''graphics processing unit'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesa (computer Graphics)
Mesa, also called Mesa3D and The Mesa 3D Graphics Library, is an open source implementation of OpenGL, Vulkan, and other graphics API specifications. Mesa translates these specifications to vendor-specific graphics hardware drivers. Its most important users are two graphics drivers mostly developed and funded by Intel and AMD for their respective hardware (AMD promotes their Mesa drivers Radeon and RadeonSI over the deprecated AMD Catalyst, and Intel has only supported the Mesa driver). Proprietary graphics drivers (e.g., Nvidia GeForce driver and Catalyst) replace all of Mesa, providing their own implementation of a graphics API. An open-source effort to write a Mesa Nvidia driver called Nouveau is mostly developed by the community. Besides 3D applications such as games, modern display servers ( X.org's Glamor or Wayland's Weston) use OpenGL/ EGL; therefore all graphics typically go through Mesa. Mesa is hosted by freedesktop.org and was initiated in August 1993 by Brian Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xine
xine is a multimedia playback engine for Unix-like operating systems released under the GNU General Public License. xine is built around a shared library (xine-lib) that supports different frontend player applications. xine uses libraries from other projects such as liba52, libmpeg2, FFmpeg, libmad, FAAD2, and Ogle. xine can also use binary Windows codecs through a wrapper, bundled as the w32codecs, for playback of some media formats that are not handled natively. History xine was started in 2000 by Günter Bartsch shortly after LinuxTag. At that time playing DVDs in Linux was described as a tortuous process since one had to manually create audio and video named pipes and start their separated decoder processes. Günter realized the OMS (Open Media System) or LiViD approach had obvious shortcomings in terms of audio and video synchronization, so xine was born as an experiment trying to get it right. The project evolved into a modern media player multi-threaded architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
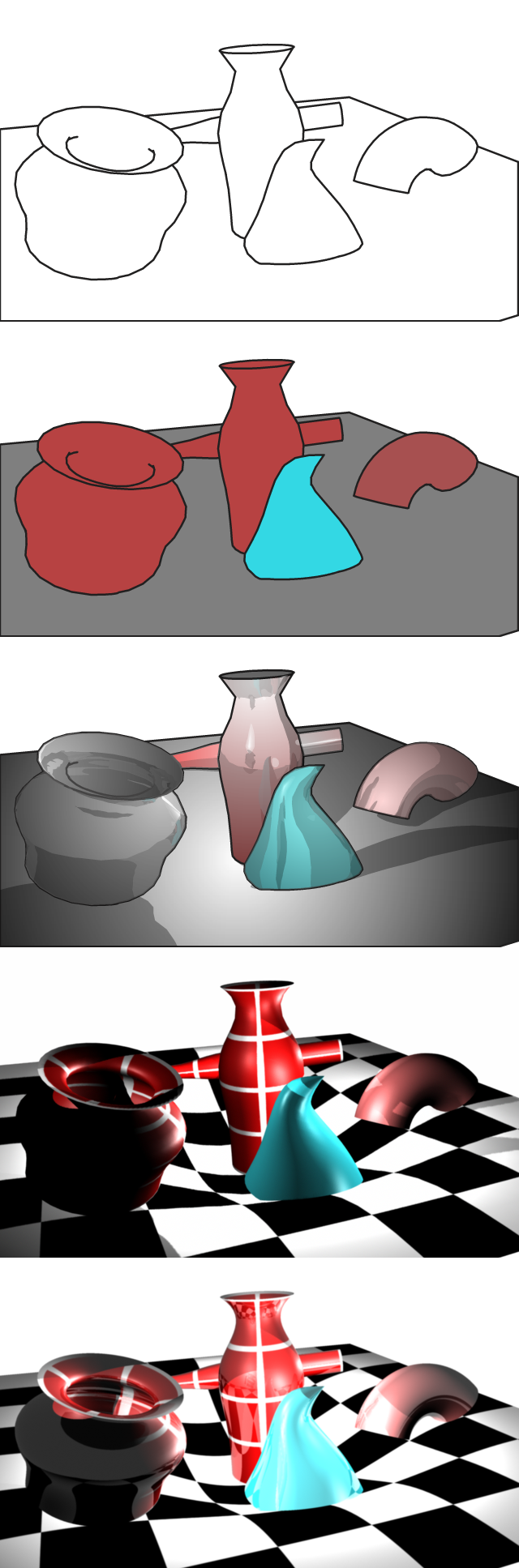
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Quantization
Inverse or invert may refer to: Science and mathematics * Inverse (logic), a type of conditional sentence which is an immediate inference made from another conditional sentence * Additive inverse (negation), the inverse of a number that, when added to the original number, yields zero * Compositional inverse, a function that "reverses" another function * Inverse element * Inverse function, a function that "reverses" another function **Generalized inverse, a matrix that has some properties of the inverse matrix but not necessarily all of them * Multiplicative inverse (reciprocal), a number which when multiplied by a given number yields the multiplicative identity, 1 ** Inverse matrix of an Invertible matrix Other uses * Invert level, the base interior level of a pipe, trench or tunnel * ''Inverse'' (website), an online magazine * An outdated term for an LGBT person; see Sexual inversion (sexology) See also * Inversion (other) * Inverter (other) * Opposite (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel Pipelines
In computer graphics, a computer graphics pipeline, rendering pipeline or simply graphics pipeline, is a conceptual model that describes what steps a graphics system needs to perform to render a 3D scene to a 2D screen. Once a 3D model has been created, for instance in a video game or any other 3D computer animation, the graphics pipeline is the process of turning that 3D model into what the computer displays. Because the steps required for this operation depend on the software and hardware used and the desired display characteristics, there is no universal graphics pipeline suitable for all cases. However, graphics application programming interfaces (APIs) such as Direct3D and OpenGL were created to unify similar steps and to control the graphics pipeline of a given hardware accelerator. These APIs abstract the underlying hardware and keep the programmer away from writing code to manipulate the graphics hardware accelerators (AMD/Intel/NVIDIA etc.). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Display Server
In computing, a windowing system (or window system) is software that manages separately different parts of display screens. It is a type of graphical user interface (GUI) which implements the WIMP (windows, icons, menus, pointer) paradigm for a user interface. Each currently running application is assigned a usually resizable and usually rectangular surface of the display to present its GUI to the user; these windows may overlap each other, as opposed to a tiling interface where they are not allowed to overlap. Usually a window decoration is drawn around each window. The programming of both the window decoration and of available widgets inside of the window, which are graphical elements for direct user interaction, such as sliders, buttons, etc., is eased and simplified through the use of widget toolkits. Technical details The main component of any windowing system is usually called the display server, although alternative denominations such as window server or composit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrox Parhelia
Matrox Parhelia-512 is a graphics processing unit (GPU) with full support for DirectX 8.1 and incorporating several DirectX 9.0 features. Released in 2002, it was best known for its ability to drive three monitors ("Surround Gaming") and its ''Coral Reef'' tech demo. As had happened with previous Matrox products, the Parhelia was released just before competing companies released cards that completely outperformed it. In this case it was the ATI Radeon 9700, released only a few months later. The Parhelia remained a niche product, and was Matrox's last major effort to sell into the consumer market. Background The Parhelia series was Matrox's attempt to return to the market after a long hiatus, their first significant effort since the G200 and G400 lines had become uncompetitive. Their other post-''G400'' products, G450 and G550, were cost-reduced revisions of ''G400'' technology and were not competitive with ATI's Radeon or NVIDIA's GeForce lines with regards to 3D computer gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-Video Bitstream Acceleration
X-Video Bitstream Acceleration (XvBA), designed by AMD Graphics for its Radeon GPU and APU, is an arbitrary extension of the X video extension (Xv) for the X Window System on Linux operating-systems. XvBA API allows video programs to offload portions of the video decoding process to the GPU video-hardware. Currently, the portions designed to be offloaded by XvBA onto the GPU are currently motion compensation (MC) and inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT), and variable-length decoding (VLD) for MPEG-2, MPEG-4 ASP (MPEG-4 Part 2, including Xvid, and older DivX and Nero Digital), MPEG-4 AVC (H.264), WMV3, and VC-1 encoded video. XvBA is a direct competitor to NVIDIA's Video Decode and Presentation API for Unix (VDPAU) and Intel's Video Acceleration API (VA API). In November 2009 an XvBA backend for Video Acceleration API (VA API) was released, which means any software that supports VA API will also support XvBA. On 24 February 2011, an official XvBA SDK (Software Devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out Of The Box (feature)
An out-of-the-box feature or functionality (also called OOTB or off the shelf), particularly in software, is a native feature or built-in functionality of a product that comes directly from the vendor and works immediately when the product is placed in service. In the context of software, out-of-the-box features and functionality are available for all users by default and do not require customization, modification, configuration, scripting, add-ons, modules, third-party tools, or additional fees in order to be used. See also * Convention over configuration * Commercial off-the-shelf * Government off-the-shelf * Commodity computing * Out-of-box experience An out-of-box experience (OOBE ( )) is the experience an end-user has when taking a product after unboxing, or for digital distribution, runs the installer, and is preparing to first use it, as opposed to the point-of-sale experience or the interac ... References Software features {{Computer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |