ethanol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an

 Australian law limits the use of pure ethanol from sugarcane waste to 10% in automobiles. Older cars (and vintage cars designed to use a slower burning fuel) should have the engine valves upgraded or replaced.
According to an industry
Australian law limits the use of pure ethanol from sugarcane waste to 10% in automobiles. Older cars (and vintage cars designed to use a slower burning fuel) should have the engine valves upgraded or replaced.
According to an industry
"Rocket Propellants"
''Rocket & Space Technology'', 2006. Retrieved 23 August 2007. The design team helped develop U.S. rockets following World War II, including the ethanol-fueled Redstone rocket which launched the first U.S. satellite. Alcohols fell into general disuse as more energy-dense rocket fuels were developed, although ethanol is currently used in lightweight rocket-powered racing aircraft.
 Ethanol is a volatile, colorless liquid that has a slight odor. It burns with a smokeless blue flame that is not always visible in normal light. The physical properties of ethanol stem primarily from the presence of its hydroxyl group and the shortness of its carbon chain. Ethanol's hydroxyl group is able to participate in hydrogen bonding, rendering it more viscous and less volatile than less polar organic compounds of similar molecular weight, such as
Ethanol is a volatile, colorless liquid that has a slight odor. It burns with a smokeless blue flame that is not always visible in normal light. The physical properties of ethanol stem primarily from the presence of its hydroxyl group and the shortness of its carbon chain. Ethanol's hydroxyl group is able to participate in hydrogen bonding, rendering it more viscous and less volatile than less polar organic compounds of similar molecular weight, such as
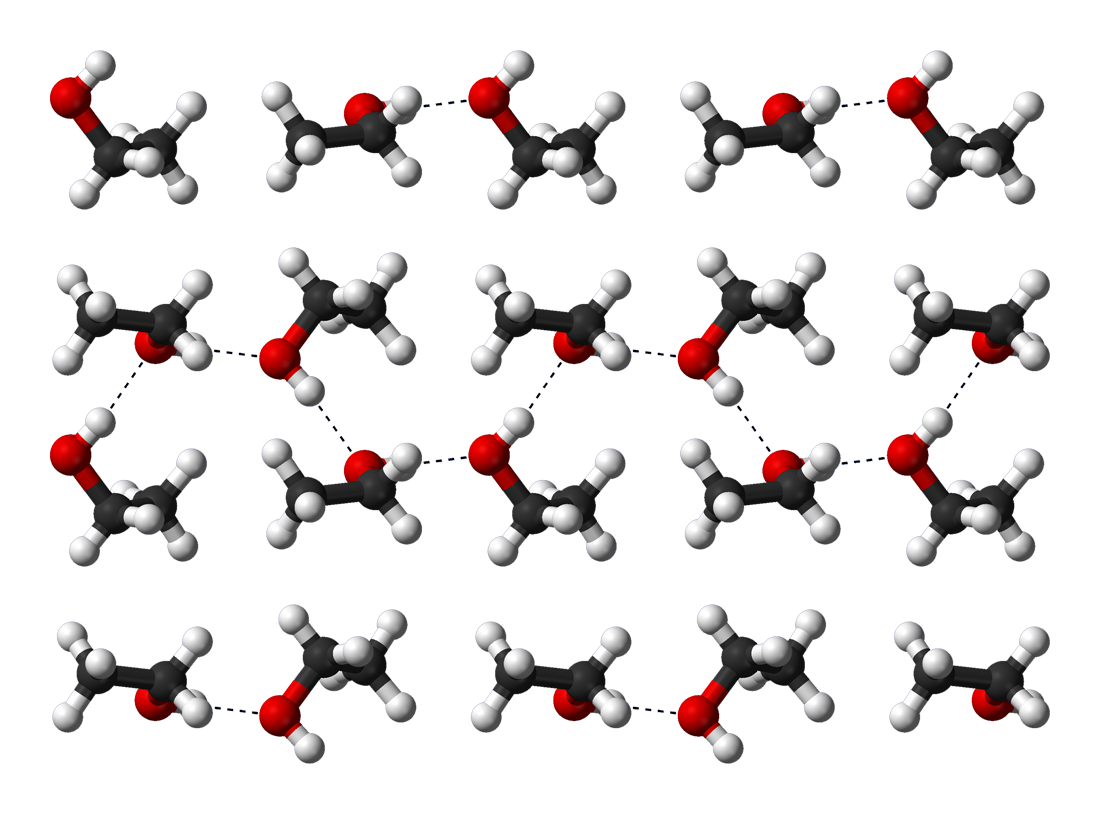 Hydrogen bonding causes pure ethanol to be hygroscopic to the extent that it readily absorbs water from the air. The polar nature of the hydroxyl group causes ethanol to dissolve many ionic compounds, notably sodium and potassium hydroxides, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ammonium chloride, ammonium bromide, and sodium bromide. Sodium and
Hydrogen bonding causes pure ethanol to be hygroscopic to the extent that it readily absorbs water from the air. The polar nature of the hydroxyl group causes ethanol to dissolve many ionic compounds, notably sodium and potassium hydroxides, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ammonium chloride, ammonium bromide, and sodium bromide. Sodium and
 Ethanol is produced both as a petrochemical, through the hydration of
Ethanol is produced both as a petrochemical, through the hydration of
 Breweries and
Breweries and
Alcohol (Ethanol)
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
International Labour Organization
ethanol safety information
* ttp://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=ethanol&Units=SI National Institute of Standards and Technologychemical data on ethanol
Chicago Board of Trade
news and market data on ethanol futures * Calculation o
vapor pressureliquid densitydynamic liquid viscositysurface tension
of ethanol
Ethanol History
A look into the history of ethanol
Industrial ethanol production process flow diagram using ethylene and sulphuric acid
{{Authority control Alcohol solvents Alkanols Anatomical preservation Commodity chemicals Disinfectants Hepatotoxins Household chemicals Human metabolites IARC Group 1 carcinogens Oxygenates Primary alcohols Rocket fuels Teratogens Alcohol chemistry
alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group (abbr. Et) is an alkyl substituent with the formula , derived from ethane (). ''Ethyl'' is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry's nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated ...
linked to a hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks.
Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In foo ...
process of sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
s by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than st ...
. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organ ...
of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S.
Etymology
''Ethanol'' is the systematic namedefined
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitio ...
by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry for a compound consisting of an alkyl group with two carbon atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
s (prefix "eth-"), having a single bond between them (infix "-an-") and an attached functional group −OH group (suffix "-ol").
The "eth-" prefix and the qualifier "ethyl" in "ethyl alcohol" originally come from the name "ethyl" assigned in 1834 to the group − by Justus Liebig. He coined the word from the German name ''Aether'' of the compound −O− (commonly called "ether" in English, more specifically called " diethyl ether"). According to the '' Oxford English Dictionary'', ''Ethyl'' is a contraction of the Ancient Greek αἰθήρ (', "upper air") and the Greek word ὕλη (', "substance").
The name ''ethanol'' was coined as a result of a resolution on naming alcohols and phenols that was adopted at the International Conference on Chemical Nomenclature that was held in April 1892 in Geneva, Switzerland.
The term ''alcohol'' now refers to a wider class of substances in chemistry nomenclature, but in common parlance it remains the name of ethanol. It is a medieval loan from Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
'' al-kuḥl'', a powdered ore of antimony used since antiquity as a cosmetic, and retained that meaning in Middle Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying deg ...
. The use of 'alcohol' for ethanol (in full, "alcohol of wine") is modern and was first recorded in 1753. Before the late 18th century the term "alcohol" generally referred to any sublimated substance.
Uses
Medical
Antiseptic
Ethanol is used in medical wipes and most commonly in antibacterialhand sanitizer
Hand sanitizer (also known as hand antiseptic, hand disinfectant, hand rub, or handrub) is a liquid, gel or foam generally used to kill many viruses/bacteria/microorganisms on the hands. In most settings, hand washing with soap and water is ge ...
gels as an antiseptic for its bactericidal and anti-fungal effects. Ethanol kills microorganisms by dissolving their membrane lipid bilayer and denaturing their proteins, and is effective against most bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, fungi and viruses. However, it is ineffective against bacterial spores, but that can be alleviated by using hydrogen peroxide. A solution of 70% ethanol is more effective than pure ethanol because ethanol relies on water molecules for optimal antimicrobial activity. Absolute ethanol may inactivate microbes without destroying them because the alcohol is unable to fully permeate the microbe's membrane. Ethanol can also be used as a disinfectant and antiseptic because it causes cell dehydration by disrupting the osmotic balance across the cell membrane, so water leaves the cell leading to cell death.
Antidote
Ethanol may be administered as an antidote to ethylene glycol poisoning and methanol poisoning. Ethanol serves this process by acting as a competitive inhibitor againstmethanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and ethylene glycol for alcohol dehydrogenase. Though it has more side effects, ethanol is less expensive and more readily available than fomepizole, which is also used as an antidote for methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning.
Medicinal solvent
Ethanol, often in high concentrations, is used to dissolve many water-insoluble medications and related compounds. Liquid preparations ofpain medications
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic ( British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
, cough and cold medicines, and mouth washes, for example, may contain up to 25% ethanol and may need to be avoided in individuals with adverse reactions to ethanol such as alcohol-induced respiratory reactions. Ethanol is present mainly as an antimicrobial preservative in over 700 liquid preparations of medicine including acetaminophen
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior ...
, iron supplements, ranitidine, furosemide, mannitol, phenobarbital, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and over-the-counter cough medicine.
Pharmacology
In mammals, ethanol is primarily metabolized in the liver and stomach by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) enzymes. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of ethanol intoacetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the mos ...
(ethanal):
:CH3CH2OH + NAD+ → CH3CHO + NADH + H+
When present in significant concentrations, this metabolism of ethanol is additionally aided by the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are ...
enzyme CYP2E1 in humans, while trace amounts are also metabolized by catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting t ...
.
The resulting intermediate, acetaldehyde, is a known carcinogen, and poses significantly greater toxicity in humans than ethanol itself. Many of the symptoms typically associated with alcohol intoxication—as well as many of the health hazards typically associated with the long-term consumption of ethanol—can be attributed to acetaldehyde toxicity in humans.
The subsequent oxidation of acetaldehyde into acetate is performed by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) enzymes. A mutation in the ALDH2 gene that encodes for an inactive or dysfunctional form of this enzyme affects roughly 50% of east Asian populations, contributing to the characteristic alcohol flush reaction that can cause temporary reddening of the skin as well as a number of related, and often unpleasant, symptoms of acetaldehyde toxicity. This mutation is typically accompanied by another mutation in the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme ADH1B in roughly 80% of east Asians, which improves the catalytic efficiency of converting ethanol into acetaldehyde.
Recreational
As acentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
depressant, ethanol is one of the most commonly consumed psychoactive drugs.
Despite alcohol's psychoactive and carcinogenic properties, it is readily available and legal for sale in most countries. However, there are laws regulating the sale, exportation/importation, taxation, manufacturing, consumption, and possession of alcoholic beverages. The most common regulation is prohibition for minors.
Fuel

Engine fuel
The largest single use of ethanol is as an enginefuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
and fuel additive
Petrol additives increase petrol's octane rating or act as corrosion inhibitors or lubricants, thus allowing the use of higher compression ratios for greater efficiency and power. Types of additives include metal deactivators, corrosion inhibitors, ...
. Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
in particular relies heavily upon the use of ethanol as an engine fuel, due in part to its role as one of the world's leading producers of ethanol. Gasoline sold in Brazil contains at least 25% anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
ethanol. Hydrous ethanol (about 95% ethanol and 5% water) can be used as fuel in more than 90% of new gasoline-fueled cars sold in the country.
The US and many other countries primarily use E10 (10% ethanol, sometimes known as gasohol) and E85 (85% ethanol) ethanol/gasoline mixtures. Over time, it is believed that a material portion of the ≈ per year market for gasoline will begin to be replaced with fuel ethanol.
 Australian law limits the use of pure ethanol from sugarcane waste to 10% in automobiles. Older cars (and vintage cars designed to use a slower burning fuel) should have the engine valves upgraded or replaced.
According to an industry
Australian law limits the use of pure ethanol from sugarcane waste to 10% in automobiles. Older cars (and vintage cars designed to use a slower burning fuel) should have the engine valves upgraded or replaced.
According to an industry advocacy group
Advocacy groups, also known as interest groups, special interest groups, lobbying groups or pressure groups use various forms of advocacy in order to influence public opinion and ultimately policy. They play an important role in the developm ...
, ethanol as a fuel reduces harmful tailpipe emissions
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an ...
of carbon monoxide, particulate matter, oxides of nitrogen, and other ozone-forming pollutants. Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a science and engineering research United States Department of Energy National Labs, national laboratory operated by University of Chicago, UChicago Argonne LLC for the United States Department of Energy. The facil ...
analyzed greenhouse gas emissions of many different engine and fuel combinations, and found that biodiesel/petrodiesel blend ( B20) showed a reduction of 8%, conventional E85 ethanol blend a reduction of 17% and cellulosic ethanol
Cellulosic ethanol is ethanol (ethyl alcohol) produced from cellulose (the stringy fiber of a plant) rather than from the plant's seeds or fruit. It can be produced from grasses, wood, algae, or other plants. It is generally discussed for use ...
64%, compared with pure gasoline. Ethanol has a much greater research octane number (RON) than gasoline, meaning it is less prone to pre-ignition, allowing for better ignition advance which means more torque, and efficiency in addition to the lower carbon emissions.
Ethanol combustion in an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
yields many of the products of incomplete combustion produced by gasoline and significantly larger amounts of formaldehyde and related species such as acetaldehyde. This leads to a significantly larger photochemical reactivity and more ground level ozone. This data has been assembled into The Clean Fuels Report comparison of fuel emissions and show that ethanol exhaust generates 2.14 times as much ozone as gasoline exhaust. When this is added into the custom ''Localized Pollution Index (LPI)'' of The Clean Fuels Report, the local pollution of ethanol (pollution that contributes to smog) is rated 1.7, where gasoline is 1.0 and higher numbers signify greater pollution. The California Air Resources Board formalized this issue in 2008 by recognizing control standards for formaldehydes as an emissions control group, much like the conventional NOx and Reactive Organic Gases (ROGs).
More than 20% of Brazilian cars are able to use 100% ethanol as fuel, which includes ethanol-only engines and flex-fuel engines. Flex-fuel engines in Brazil are able to work with all ethanol, all gasoline or any mixture of both. In the U.S. flex-fuel vehicles can run on 0% to 85% ethanol (15% gasoline) since higher ethanol blends are not yet allowed or efficient. Brazil supports this fleet of ethanol-burning automobiles with large national infrastructure that produces ethanol from domestically grown sugarcane.
Ethanol's high miscibility with water makes it unsuitable for shipping through modern pipelines like liquid hydrocarbons. Mechanics have seen increased cases of damage to small engines (in particular, the carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meteri ...
) and attribute the damage to the increased water retention by ethanol in fuel.
Rocket fuel
Ethanol was commonly used as fuel in early bipropellant rocket (liquid-propelled) vehicles, in conjunction with an oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The German A-4 ballistic rocket of World War II (better known by its propaganda name ), which is credited as having begun the space age, used ethanol as the main constituent of ''B-Stoff''. Under such nomenclature, the ethanol was mixed with 25% water to reduce the combustion chamber temperature.Braeunig, Robert A"Rocket Propellants"
''Rocket & Space Technology'', 2006. Retrieved 23 August 2007. The design team helped develop U.S. rockets following World War II, including the ethanol-fueled Redstone rocket which launched the first U.S. satellite. Alcohols fell into general disuse as more energy-dense rocket fuels were developed, although ethanol is currently used in lightweight rocket-powered racing aircraft.
Fuel cells
Commercial fuel cells operate on reformed natural gas, hydrogen or methanol. Ethanol is an attractive alternative due to its wide availability, low cost, high purity and low toxicity. There is a wide range of fuel cell concepts that have entered trials includingdirect-ethanol fuel cell
Direct-ethanol fuel cells or DEFCs are a category of fuel cell in which ethanol is fed directly into the cell. They have been used as a model to investigate a range of fuel cell concepts including the use of Proton exchange membrane, PEM.
Advant ...
s, auto-thermal reforming systems and thermally integrated systems. The majority of work is being conducted at a research level although there are a number of organizations at the beginning of the commercialization of ethanol fuel cells.
Household heating and cooking
Ethanol fireplaces can be used for home heating or for decoration. Ethanol can also be used as stove fuel for cooking.Feedstock
Ethanol is an important industrial ingredient. It has widespread use as a precursor for other organic compounds such as ethylhalide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
s, ethyl esters, diethyl ether, acetic acid, and ethyl amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent su ...
s.
Solvent
Ethanol is considered a universal solvent, as itsmolecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
structure allows for the dissolving of both polar, hydrophilic and nonpolar, hydrophobic compounds. As ethanol also has a low boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding env ...
, it is easy to remove from a solution that has been used to dissolve other compounds, making it a popular extracting agent for botanical oils. Cannabis oil extraction methods often use ethanol as an extraction solvent, and also as a post-processing solvent to remove oils, waxes, and chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to a ...
from solution in a process known as winterization.
Ethanol is found in paint
Paint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many ...
s, tinctures, markers, and personal care products such as mouthwashes, perfumes and deodorants. However, polysaccharides precipitate from aqueous solution in the presence of alcohol, and ethanol precipitation is used for this reason in the purification of DNA and RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
.
Low-temperature liquid
Because of its low freezing point of and low toxicity, ethanol is sometimes used in laboratories (with dry ice or other coolants) as a cooling bath to keep vessels at temperatures below the freezing point of water. For the same reason, it is also used as the active fluid inalcohol thermometer
The alcohol thermometer or spirit thermometer is an alternative to the mercury-in-glass thermometer and has similar functions. Unlike the mercury-in-glass thermometer, the contents of an alcohol thermometer are less toxic and will evaporate qu ...
s.
Chemistry
Chemical formula
Ethanol is a 2-carbon alcohol. Its molecular formula is CH3CH2OH. An alternative notation is CH3−CH2−OH, which indicates that the carbon of a methyl group (CH3−) is attached to the carbon of a methylene group (−CH2–), which is attached to the oxygen of ahydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
(−OH). It is a constitutional isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
of dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precurs ...
. Ethanol is sometimes abbreviated as EtOH, using the common organic chemistry notation of representing the ethyl group (C2H5−) with Et.
Physical properties
 Ethanol is a volatile, colorless liquid that has a slight odor. It burns with a smokeless blue flame that is not always visible in normal light. The physical properties of ethanol stem primarily from the presence of its hydroxyl group and the shortness of its carbon chain. Ethanol's hydroxyl group is able to participate in hydrogen bonding, rendering it more viscous and less volatile than less polar organic compounds of similar molecular weight, such as
Ethanol is a volatile, colorless liquid that has a slight odor. It burns with a smokeless blue flame that is not always visible in normal light. The physical properties of ethanol stem primarily from the presence of its hydroxyl group and the shortness of its carbon chain. Ethanol's hydroxyl group is able to participate in hydrogen bonding, rendering it more viscous and less volatile than less polar organic compounds of similar molecular weight, such as propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
.
Ethanol's adiabatic flame temperature for combustion in air is 2082 Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The ...
or 3779 Fahrenheit.
Ethanol is slightly more refractive than water, having a refractive index of 1.36242 (at λ=589.3 nm and ). The triple point for ethanol is at a pressure of .
Solvent properties
Ethanol is a versatile solvent,miscible
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies ...
with water and with many organic solvents, including acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, acetone, benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen ato ...
, carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVAC ...
, chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
, diethyl ether, ethylene glycol, glycerol, nitromethane, pyridine, and toluene. Its main use as a solvent is in making tincture of iodine, cough syrups etc. It is also miscible with light aliphatic hydrocarbons, such as pentane
Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12—that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the ' ...
and hexane, and with aliphatic chlorides such as trichloroethane and tetrachloroethylene.
Ethanol's miscibility with water contrasts with the immiscibility of longer-chain alcohols (five or more carbon atoms), whose water miscibility decreases sharply as the number of carbons increases. The miscibility of ethanol with alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which ...
s is limited to alkanes up to undecane: mixtures with dodecane and higher alkanes show a miscibility gap below a certain temperature (about 13 °C for dodecane). The miscibility gap tends to get wider with higher alkanes, and the temperature for complete miscibility increases.
Ethanol-water mixtures have less volume than the sum of their individual components at the given fractions. Mixing equal volumes of ethanol and water results in only 1.92 volumes of mixture. Mixing ethanol and water is exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e ...
, with up to 777 J/mol being released at 298 K.
Mixtures of ethanol and water form an azeotrope at about 89 mole-% ethanol and 11 mole-% water or a mixture of 95.6 percent ethanol by mass (or about 97% alcohol by volume
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as ABV, abv, or alc/vol) is a standard measure of how much alcohol (ethanol) is contained in a given volume of an alcoholic beverage (expressed as a volume percent). It is defined as the number of millilitres (mL) o ...
) at normal pressure, which boils at 351K (78 °C). This azeotropic composition is strongly temperature- and pressure-dependent and vanishes at temperatures below 303 K.
 Hydrogen bonding causes pure ethanol to be hygroscopic to the extent that it readily absorbs water from the air. The polar nature of the hydroxyl group causes ethanol to dissolve many ionic compounds, notably sodium and potassium hydroxides, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ammonium chloride, ammonium bromide, and sodium bromide. Sodium and
Hydrogen bonding causes pure ethanol to be hygroscopic to the extent that it readily absorbs water from the air. The polar nature of the hydroxyl group causes ethanol to dissolve many ionic compounds, notably sodium and potassium hydroxides, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, ammonium chloride, ammonium bromide, and sodium bromide. Sodium and potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt ...
s are slightly soluble in ethanol. Because the ethanol molecule also has a nonpolar end, it will also dissolve nonpolar substances, including most essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile (easily evaporated at normal temperatures) chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the o ...
s''Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs'', 9th ed.; monographs 6575 through 6669 and numerous flavoring, coloring, and medicinal agents.
The addition of even a few percent of ethanol to water sharply reduces the surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
of water. This property partially explains the " tears of wine" phenomenon. When wine is swirled in a glass, ethanol evaporates quickly from the thin film of wine on the wall of the glass. As the wine's ethanol content decreases, its surface tension increases and the thin film "beads up" and runs down the glass in channels rather than as a smooth sheet.
Flammability
An ethanol–water solution will catch fire if heated above a temperature called itsflash point
The flash point of a material is the "lowest liquid temperature at which, under certain standardized conditions, a liquid gives off vapours in a quantity such as to be capable of forming an ignitable vapour/air mixture". (EN 60079-10-1)
The fl ...
and an ignition source is then applied to it. For 20% alcohol by mass (about 25% by volume), this will occur at about . The flash point of pure ethanol is , but may be influenced very slightly by atmospheric composition such as pressure and humidity. Ethanol mixtures can ignite below average room temperature. Ethanol is considered a flammable liquid (Class 3 Hazardous Material) in concentrations above 2.35% by mass (3.0% by volume; 6 proof
Proof most often refers to:
* Proof (truth), argument or sufficient evidence for the truth of a proposition
* Alcohol proof, a measure of an alcoholic drink's strength
Proof may also refer to:
Mathematics and formal logic
* Formal proof, a con ...
).
Dishes using burning alcohol for culinary effects are called flambé.
Natural occurrence
Ethanol is a byproduct of themetabolic process
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
of yeast. As such, ethanol will be present in any yeast habitat. Ethanol can commonly be found in overripe fruit. Ethanol produced by symbiotic yeast can be found in bertam palm blossoms. Although some animal species, such as the pentailed treeshrew
The pen-tailed treeshrew (''Ptilocercus lowii'') is a treeshrew of the family Ptilocercidae native to southern Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, Borneo, and some Indonesian islands.
It is the only living species in the genus ''Ptilocercus''. All ...
, exhibit ethanol-seeking behaviors, most show no interest or avoidance of food sources containing ethanol. Ethanol is also produced during the germination of many plants as a result of natural anaerobiosis
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
. Ethanol has been detected in outer space, forming an icy coating around dust grains in interstellar clouds.
Minute quantity amounts (average 196 ppb) of endogenous ethanol and acetaldehyde were found in the exhaled breath of healthy volunteers. Auto-brewery syndrome
Auto-brewery syndrome (ABS) (also known as gut fermentation syndrome, endogenous ethanol fermentation or drunkenness disease) is a condition characterized by the fermentation of ingested carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract of the body cause ...
, also known as gut fermentation syndrome, is a rare medical condition in which intoxicating quantities of ethanol are produced through endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, es ...
fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In foo ...
within the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller c ...
.
Production
 Ethanol is produced both as a petrochemical, through the hydration of
Ethanol is produced both as a petrochemical, through the hydration of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene i ...
and, via biological processes, by fermenting sugars with yeast. Which process is more economical depends on prevailing prices of petroleum and grain feed stocks.
Sources
World production of ethanol in 2006 was , with 69% of the world supply coming from Brazil and the U.S. Brazilian ethanol is produced fromsugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, which has relatively high yields (830% more fuel than the fossil fuels used to produce it) compared to some other energy crops. Sugarcane not only has a greater concentration of sucrose than corn (by about 30%), but is also much easier to extract. The bagasse generated by the process is not discarded, but burned by power plants to produce electricity. Bagasse burning accounts for around 9% of the electricity produced in Brazil.
In the 1970s most industrial ethanol in the U.S. was made as a petrochemical, but in the 1980s the U.S. introduced subsidies for corn-based ethanol
Corn ethanol is ethanol produced from corn biomass and is the main source of ethanol fuel in the United States, mandated to be blended with gasoline in the Renewable Fuel Standard. Corn ethanol is produced by ethanol fermentation and distillation ...
. According to the Renewable Fuels Association, as of 30 October 2007, 131 grain ethanol bio-refineries in the U.S. have the capacity to produce of ethanol per year. An additional 72 construction projects underway (in the U.S.) can add of new capacity in the next 18 months.
In India ethanol is made from sugarcane. Sweet sorghum
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, keto ...
is another potential source of ethanol, and is suitable for growing in dryland conditions. The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) is an international organization which conducts agricultural research for rural development, headquartered in Patancheru (Hyderabad, Telangana, India) with several re ...
is investigating the possibility of growing sorghum as a source of fuel, food, and animal feed in arid parts of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Sweet sorghum has one-third the water requirement of sugarcane over the same time period. It also requires about 22% less water than corn. The world's first sweet sorghum ethanol distillery began commercial production in 2007 in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to t ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
.
Hydration
Ethanol can be produced from petrochemical feed stocks, primarily by theacid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a s ...
- catalyzed hydration of ethylene. It is often referred to as synthetic ethanol.
The catalyst is most commonly phosphoric acid, adsorbed onto a porous support such as silica gel or diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 μm to le ...
. This catalyst was first used for large-scale ethanol production by the Shell Oil Company in 1947. The reaction is carried out in the presence of high pressure steam at where a 5:3 ethylene to steam ratio is maintained. This process was used on an industrial scale by Union Carbide Corporation
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befor ...
and others. It is no longer practiced in the US as fermentation ethanol produced from corn is more economical.
In an older process, first practiced on the industrial scale in 1930 by Union Carbide but now almost entirely obsolete, ethylene was hydrated indirectly by reacting it with concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
to produce ethyl sulfate, which was hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
to yield ethanol and regenerate the sulfuric acid:
From carbon dioxide
Ethanol has been produced in the laboratory by convertingcarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
via biological and electrochemical reactions.
Fermentation
Ethanol inalcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c ...
s and fuel is produced by fermentation. Certain species of yeast (e.g., '' Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') metabolize sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide. The chemical equations below summarize the conversion:
Fermentation is the process of culturing yeast under favorable thermal conditions to produce alcohol. This process is carried out at around . Toxicity of ethanol to yeast limits the ethanol concentration obtainable by brewing; higher concentrations, therefore, are obtained by fortification or distillation. The most ethanol-tolerant yeast strains can survive up to approximately 18% ethanol by volume.
To produce ethanol from starchy materials such as cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s, the starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
must first be converted into sugars. In brewing beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from cer ...
, this has traditionally been accomplished by allowing the grain to germinate, or malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, wh ...
, which produces the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
amylase. When the malted grain is mashed
Mashed may refer to:
* Mashed, that created from mash ingredients
* Mashed, the result of a mashing
* Mashed, the result of a mashup (music)
* ''Mashed'' (album), a 2007 mashup album
* ''Mashed'' (video game), a vehicular combat video game
* M ...
, the amylase converts the remaining starches into sugars.
Cellulose
Sugars for ethanol fermentation can be obtained from cellulose. Deployment of this technology could turn a number of cellulose-containing agricultural by-products, such ascorncob
A corncob, also called corn cob, cob of corn or corn on the cob, is the central core of an ear of corn (also known as maize). It is the part of the ear on which the kernels grow. The ear is also considered a "cob" or "pole" but it is not fully ...
s, straw
Straw is an agricultural byproduct consisting of the dry stalks of cereal plants after the grain and chaff have been removed. It makes up about half of the yield of cereal crops such as barley, oats, rice, rye and wheat. It has a number ...
, and sawdust, into renewable energy resources. Other agricultural residues such as sugarcane bagasse and energy crop
Energy crops are low-cost and low-maintenance crops grown solely for energy production by combustion (not for food). The crops are processed into solid, liquid or gaseous fuels, such as pellets, bioethanol or biogas. The fuels are burned to g ...
s such as switchgrass may also be fermentable sugar sources.
Testing
biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA ...
plants employ two methods for measuring ethanol concentration. Infrared ethanol sensors measure the vibrational frequency of dissolved ethanol using the C−H band at 2900 cm. This method uses a relatively inexpensive solid-state sensor that compares the C−H band with a reference band to calculate the ethanol content. The calculation makes use of the Beer–Lambert law. Alternatively, by measuring the density of the starting material and the density of the product, using a hydrometer
A hydrometer or lactometer is an instrument used for measuring density or relative density of liquids based on the concept of buoyancy. They are typically calibrated and graduated with one or more scales such as specific gravity.
A hydrometer ...
, the change in specific gravity during fermentation indicates the alcohol content. This inexpensive and indirect method has a long history in the beer brewing industry.
Purification
Distillation
Ethylene hydration or brewing produces an ethanol–water mixture. For most industrial and fuel uses, the ethanol must be purified.Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
at atmospheric pressure can concentrate ethanol to 95.6% by weight (89.5 mole%). This mixture is an azeotrope with a boiling point of , and ''cannot'' be further purified by distillation. Addition of an entraining agent, such as benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen ato ...
, cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexan ...
, or heptane, allows a new ternary azeotrope comprising the ethanol, water, and the entraining agent to be formed. This lower-boiling ternary azeotrope is removed preferentially, leading to water-free ethanol.
Molecular sieves and desiccants
Apart from distillation, ethanol may be dried by addition of adesiccant
A desiccant is a hygroscopic substance that is used to induce or sustain a state of dryness (desiccation) in its vicinity; it is the opposite of a humectant. Commonly encountered pre-packaged desiccants are solids that absorb water. Desiccant ...
, such as molecular sieves
A molecular sieve is a material with pores (very small holes) of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be adsorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecu ...
, cellulose, or cornmeal
Cornmeal is a meal (coarse flour) or a cell membrane ground from dried corn. It is a common staple food, and is ground to coarse, medium, and fine consistencies, but not as fine as wheat flour can be.Herbst, Sharon, ''Food Lover's Companion'', ...
. The desiccants can be dried and reused. Molecular sieves can be used to selectively absorb the water from the 95.6% ethanol solution. Molecular sieves of pore-size 3 Ångstrom, a type of zeolite, effectively sequester water molecules while excluding ethanol molecules. Heating the wet sieves drives out the water, allowing regeneration of their dessicant capability.
Membranes and reverse osmosis
Membranes can also be used to separate ethanol and water. Membrane-based separations are not subject to the limitations of the water-ethanol azeotrope because the separations are not based on vapor-liquid equilibria. Membranes are often used in the so-called hybrid membrane distillation process. This process uses a pre-concentration distillation column as the first separating step. The further separation is then accomplished with a membrane operated either in vapor permeation or pervaporation mode. Vapor permeation uses a vapor membrane feed and pervaporation uses a liquid membrane feed.Other techniques
A variety of other techniques have been discussed, including the following: * Salting using potassium carbonate to exploit its insolubility will cause a phase separation with ethanol and water. This offers a very small potassium carbonate impurity to the alcohol that can be removed by distillation. This method is very useful in purification of ethanol by distillation, as ethanol forms an azeotrope with water. * Direct electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to ethanol under ambient conditions using copper nanoparticles on a carbon nanospike film as the catalyst; * Extraction of ethanol from grain mash bysupercritical carbon dioxide
Supercritical carbon dioxide (s) is a fluid state of carbon dioxide where it is held at or above its critical temperature and critical pressure.
Carbon dioxide usually behaves as a gas in air at standard temperature and pressure (STP), or as ...
;
* Pervaporation;
* Fractional freezing is also used to concentrate fermented alcoholic solutions, such as traditionally made Applejack (beverage);
* Pressure swing adsorption.
Grades of ethanol
Denatured alcohol
Pure ethanol and alcoholic beverages are heavily taxed as psychoactive drugs, but ethanol has many uses that do not involve its consumption. To relieve the tax burden on these uses, most jurisdictions waive the tax when an agent has been added to the ethanol to render it unfit to drink. These include bittering agents such as denatonium benzoate and toxins such as methanol, naphtha, and pyridine. Products of this kind are called ''denatured alcohol.''Absolute alcohol
Absolute or anhydrous alcohol refers to ethanol with a low water content. There are various grades with maximum water contents ranging from 1% to a few parts per million (ppm). If azeotropic distillation is used to remove water, it will contain trace amounts of the material separation agent (e.g. benzene). Absolute alcohol is not intended for human consumption. Absolute ethanol is used as a solvent for laboratory and industrial applications, where water will react with other chemicals, and as fuel alcohol. Spectroscopic ethanol is an absolute ethanol with a low absorbance in ultraviolet and visible light, fit for use as a solvent in ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. Pure ethanol is classed as 200proof
Proof most often refers to:
* Proof (truth), argument or sufficient evidence for the truth of a proposition
* Alcohol proof, a measure of an alcoholic drink's strength
Proof may also refer to:
Mathematics and formal logic
* Formal proof, a con ...
in the US, equivalent to 175 degrees proof in the UK system.
Rectified spirits
Rectified spirit, an azeotropic composition of 96% ethanol containing 4% water, is used instead of anhydrous ethanol for various purposes. Spirits of wine are about 94% ethanol (188 proof). The impurities are different from those in 95% (190 proof) laboratory ethanol.Reactions
Ethanol is classified as a primary alcohol, meaning that the carbon that its hydroxyl group attaches to has at least two hydrogen atoms attached to it as well. Many ethanol reactions occur at its hydroxyl group.Ester formation
In the presence of acid catalysts, ethanol reacts withcarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
s to produce ethyl esters and water:
: RCOOH + HOCH2CH3 → RCOOCH2CH3 + H2O
This reaction, which is conducted on large scale industrially, requires the removal of the water from the reaction mixture as it is formed. Esters react in the presence of an acid or base to give back the alcohol and a salt. This reaction is known as saponification because it is used in the preparation of soap. Ethanol can also form esters with inorganic acids. Diethyl sulfate and triethyl phosphate
Triethyl phosphate is an organic chemical compound with the formula (C2H5)3PO4 or OP(OEt)3. It is a colorless liquid. It is the triester of ethanol and phosphoric acid and can be called "phosphoric acid, triethyl ester".
Its primary uses are a ...
are prepared by treating ethanol with sulfur trioxide and phosphorus pentoxide respectively. Diethyl sulfate is a useful ethylating agent in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
. Ethyl nitrite, prepared from the reaction of ethanol with sodium nitrite and sulfuric acid, was formerly used as a diuretic.
Dehydration
In the presence of acid catalysts, alcohols can be converted to alkenes such as ethanol to ethylene. Typically solid acids such as alumina are used. : CH3CH2OH → H2C=CH2 + H2O Since water is removed from the same molecule, the reaction is known as intramolecular dehydration. Intramolecular dehydration of an alcohol requires a high temperature and the presence of an acid catalyst such assulphuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
.
Ethylene produced from sugar-derived ethanol (primarily in Brazil) competes with ethylene produced from petrochemical feedstocks such as naphtha and ethane.
At a lower temperature than that of intramolecular dehydration, intermolecular alcohol dehydration may occur producing a symmetrical ether. This is a condensation reaction. In the following example, diethyl ether is produced from ethanol:
:2 CH3CH2OH → CH3CH2OCH2CH3 + H2O
Combustion
Complete combustion of ethanol forms carbon dioxide and water: :C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l); −ΔHc = 1371 kJ/mol = 29.8 kJ/g = 327 kcal/mol = 7.1 kcal/g :C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (g); −ΔHc = 1236 kJ/mol = 26.8 kJ/g = 295.4 kcal/mol = 6.41 kcal/g Specific heat = 2.44 kJ/(kg·K)Acid-base chemistry
Ethanol is a neutral molecule and the pH of a solution of ethanol in water is nearly 7.00. Ethanol can be quantitatively converted to its conjugate base, the ethoxide ion (CH3CH2O−), by reaction with analkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the nam ...
such as sodium:
:2 CH3CH2OH + 2 Na → 2 CH3CH2ONa + H2
or a very strong base such as sodium hydride:
:CH3CH2OH + NaH → CH3CH2ONa + H2
The acidities of water and ethanol are nearly the same, as indicated by their pKa
PKA may refer to:
* Professionally known as:
** Pen name
** Stage persona
* p''K''a, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale
* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes
* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American so ...
of 15.7 and 16 respectively. Thus, sodium ethoxide and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
exist in an equilibrium that is closely balanced:
:CH3CH2OH + NaOH CH3CH2ONa + H2O
Halogenation
Ethanol is not used industrially as a precursor to ethyl halides, but the reactions are illustrative. Ethanol reacts with hydrogen halides to produce ethyl halides such as ethyl chloride and ethyl bromide via an SN2 reaction: :CH3CH2OH + HCl → CH3CH2Cl + H2O These reactions require a catalyst such as zinc chloride. HBr requires refluxing with asulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
catalyst. Ethyl halides can, in principle, also be produced by treating ethanol with more specialized halogenating agents, such as thionyl chloride or phosphorus tribromide.
:CH3CH2OH + SOCl2 → CH3CH2Cl + SO2 + HCl
Upon treatment with halogens in the presence of base, ethanol gives the corresponding haloform (CHX3, where X = Cl, Br, I). This conversion is called the haloform reaction.
An intermediate in the reaction with chlorine is the aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
called chloral, which forms chloral hydrate upon reaction with water:
:4 Cl2 + CH3CH2OH → CCl3CHO + 5 HCl
:CCl3CHO + H2O → CCl3C(OH)2H
Oxidation
Ethanol can be oxidized toacetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the mos ...
and further oxidized to acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, depending on the reagents and conditions. This oxidation is of no importance industrially, but in the human body, these oxidation reactions are catalyzed by the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
liver alcohol dehydrogenase. The oxidation product of ethanol, acetic acid, is a nutrient for humans, being a precursor to acetyl CoA, where the acetyl group can be spent as energy or used for biosynthesis.
Metabolism
Ethanol is similar to macronutrients such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in that it provides calories. When consumed and metabolized, it contributes 7 calories per gram viaethanol metabolism
Ethanol, an alcohol found in nature and in alcoholic drinks, is metabolized through a complex catabolic metabolic pathway. In humans, several enzymes are involved in processing ethanol first into acetaldehyde and further into acetic acid and a ...
.
Safety
Pure ethanol will irritate the skin and eyes. Nausea, vomiting, and intoxication are symptoms of ingestion. Long-term use by ingestion can result in serious liver damage. Atmospheric concentrations above one part per thousand are above the European Union occupational exposure limits.History
The fermentation of sugar into ethanol is one of the earliest biotechnologies employed by humans. Ethanol has historically been identified variously as spirit of wine or ardent spirits, and asaqua vitae
''Aqua vitae'' (Latin for "water of life") or aqua vita is an archaic name for a concentrated aqueous solution of ethanol. These terms could also be applied to weak ethanol without rectification. Usage was widespread during the Middle Ages a ...
or aqua vita. The intoxicating effects of its consumption have been known since ancient times. Ethanol has been used by humans since prehistory as the intoxicating ingredient of alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c ...
s. Dried residue on 9,000-year-old pottery found in China suggests that Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
people consumed alcoholic beverages.
The inflammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
(384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of ethanol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt
, common_name = Egypt
, subdivision = Province
, nation = the Roman Empire
, era = Late antiquity
, capital = Alexandria
, title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis
, image_map = Roman E ...
. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Ḥayyān (ninth century CE), was that by adding salt to boiling wine, which increases the wine's relative volatility, the flammability of the resulting vapors may be enhanced. The distillation of wine is attested in Arabic works attributed to al-Kindī (–873 CE) and to al-Fārābī
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Isla ...
(–950), and in the 28th book of al-Zahrāwī's (Latin: Abulcasis, 936–1013) ''Kitāb al-Taṣrīf'' (later translated into Latin as ''Liber servatoris''). In the twelfth century, recipes for the production of ''aqua ardens'' ("burning water", i.e., ethanol) by distilling wine with salt started to appear in a number of Latin works, and by the end of the thirteenth century it had become a widely known substance among Western European chemists.
The works of Taddeo Alderotti (1223–1296) describe a method for concentrating ethanol involving repeated fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
through a water-cooled still, by which an ethanol purity of 90% could be obtained. The medicinal properties of ethanol were studied by Arnald of Villanova (1240–1311 CE) and John of Rupescissa (–1366), the latter of whom regarded it as a life-preserving substance able to prevent all diseases (the ''aqua vitae
''Aqua vitae'' (Latin for "water of life") or aqua vita is an archaic name for a concentrated aqueous solution of ethanol. These terms could also be applied to weak ethanol without rectification. Usage was widespread during the Middle Ages a ...
'' or "water of life", also called by John the ''quintessence
Quintessence, or fifth essence, may refer to:
Cosmology
* Aether (classical element), in medieval cosmology and science, the fifth element that fills the universe beyond the terrestrial sphere
* Quintessence (physics), a hypothetical form of da ...
'' of wine).
In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, archaeological evidence indicates that the true distillation of alcohol began during the Jin (1115–1234) or Southern Song (1127–1279) dynasties.
A still has been found at an archaeological site in Qinglong, Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and ...
, dating to the 12th century. In India, the true distillation of alcohol was introduced from the Middle East, and was in wide use in the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
by the 14th century.
In 1796, German-Russian chemist Johann Tobias Lowitz obtained pure ethanol by mixing partially purified ethanol (the alcohol-water azeotrope) with an excess of anhydrous alkali and then distilling the mixture over low heat. French chemist Antoine Lavoisier described ethanol as a compound of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and in 1807 Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure determined ethanol's chemical formula. Fifty years later, Archibald Scott Couper published the structural formula of ethanol. It was one of the first structural formulas determined.
Ethanol was first prepared synthetically in 1825 by Michael Faraday. He found that sulfuric acid could absorb large volumes of coal gas
Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal and supplied to the user via a piped distribution system. It is produced when coal is heated strongly in the absence of air. Town gas is a more general term referring to manufactured gaseous ...
. He gave the resulting solution to Henry Hennell, a British chemist, who found in 1826 that it contained "sulphovinic acid" ( ethyl hydrogen sulfate). In 1828, Hennell and the French chemist Georges-Simon Serullas independently discovered that sulphovinic acid could be decomposed into ethanol. On page 368, Hennell produces ethanol from "sulfovinic acid" ( ethyl hydrogen sulfate). Thus, in 1825 Faraday had unwittingly discovered that ethanol could be produced from ethylene (a component of coal gas) by acid-catalyzed
In acid catalysis and base catalysis, a chemical reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base. By Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, the acid is the proton ( hydrogen ion, H+) donor and the base is the proton acceptor. Typical reactions catal ...
hydration, a process similar to current industrial ethanol synthesis.In 1855, the French chemist Marcellin Berthelot confirmed Faraday's discovery by preparing ethanol from pure ethylene. (Note: The chemical formulas in Berthelot's paper are wrong because chemists at that time used the wrong atomic masses for the elements; e.g., carbon (6 instead of 12), oxygen (8 instead of 16), etc.)
Ethanol was used as lamp fuel in the U.S. as early as 1840, but a tax levied on industrial alcohol during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polic ...
made this use uneconomical. The tax was repealed in 1906. Use as an automotive fuel dates back to 1908, with the Ford Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relati ...
able to run on petrol (gasoline) or ethanol. It fuels some spirit lamps
An alcohol burner or spirit lamp is a piece of laboratory equipment used to produce an open flame. It can be made from brass, glass, stainless steel or aluminium.
Uses
Alcohol burners are preferred for some uses over Bunsen burners for safety pu ...
.
Ethanol intended for industrial use is often produced from ethylene. Ethanol has widespread use as a solvent of substances intended for human contact or consumption, including scents, flavorings, colorings, and medicines. In chemistry, it is both a solvent and a feedstock for the synthesis of other products. It has a long history as a fuel for heat and light, and more recently as a fuel for internal combustion engines.
See also
*1-Propanol
Propan-1-ol (also propanol, n-propyl alcohol) is a primary alcohol with the formula and sometimes represented as PrOH or ''n''-PrOH. It is a colorless liquid and an isomer of 2-propanol. It is formed naturally in small amounts during many ferme ...
* Butanol fuel
* Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids
The presence of ethanol can lead to the formations of non-lamellar phases also known as non-bilayer phases. Ethanol has been recognized as being an excellent solvent in an aqueous solution for inducing non-lamellar phases in phospholipids. The fo ...
* Isopropyl alcohol
* Rubbing alcohol
* tert-Butyl alcohol
* Timeline of alcohol fuel
Ethanol, an alcohol fuel, is an important fuel for the operation of internal combustion engines that are used in cars, trucks, and other kinds of machinery.
* Ethanol was first isolated from wine in approximately 1100 and was found to burn shortl ...
References
Further reading
* . * * *External links
Alcohol (Ethanol)
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
International Labour Organization
ethanol safety information
* ttp://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=ethanol&Units=SI National Institute of Standards and Technologychemical data on ethanol
Chicago Board of Trade
news and market data on ethanol futures * Calculation o
vapor pressure
of ethanol
Ethanol History
A look into the history of ethanol
Industrial ethanol production process flow diagram using ethylene and sulphuric acid
{{Authority control Alcohol solvents Alkanols Anatomical preservation Commodity chemicals Disinfectants Hepatotoxins Household chemicals Human metabolites IARC Group 1 carcinogens Oxygenates Primary alcohols Rocket fuels Teratogens Alcohol chemistry