Cerebrospinal Meningitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Meningitis is
 In adults, the most common symptom of meningitis is a severe
In adults, the most common symptom of meningitis is a severe
 Additional problems may occur in the early stage of the illness. These may require specific treatment, and sometimes indicate severe illness or worse prognosis. The infection may trigger
Additional problems may occur in the early stage of the illness. These may require specific treatment, and sometimes indicate severe illness or worse prognosis. The infection may trigger
 The types of
The types of

 A lumbar puncture is done by positioning the person, usually lying on the side, applying
A lumbar puncture is done by positioning the person, usually lying on the side, applying
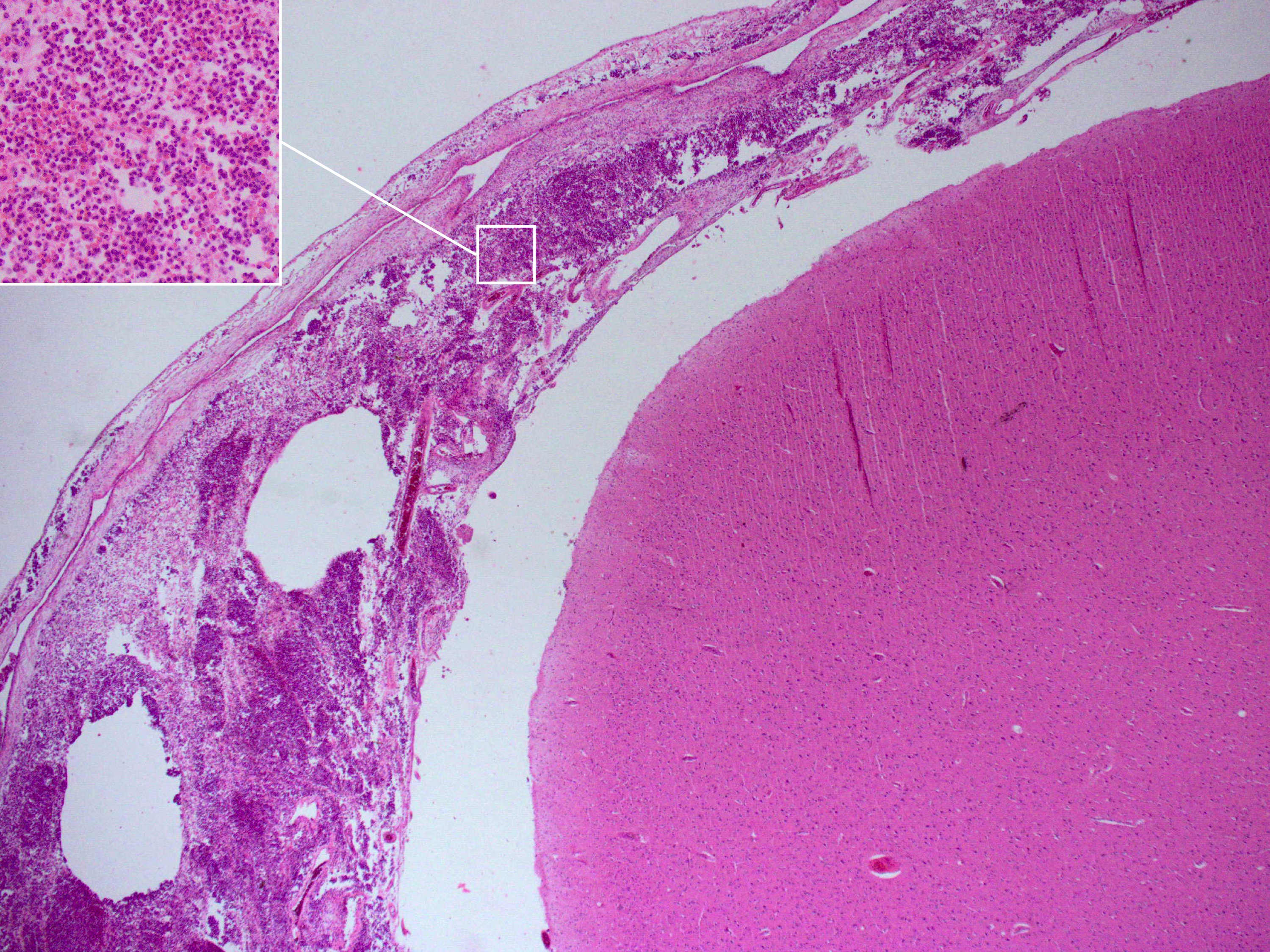 Meningitis can be diagnosed after death has occurred. The findings from a
Meningitis can be diagnosed after death has occurred. The findings from a

acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse ef ...
or chronic inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the protective membranes covering the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, collectively called the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in ...
. The most common symptoms are fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, and neck stiffness
Neck stiffness, stiff neck and nuchal rigidity are terms often used interchangeably to describe the medical condition when one experiences discomfort or pain when trying to turn, move, or flex the neck. Possible causes include muscle strain or spr ...
. Other symptoms include confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
or altered consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenter ...
, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present.
The inflammation may be caused by infection with virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
es, bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
or other microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in old ...
s. Non-infectious causes include malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
(cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly af ...
) and certain drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalati ...
. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
. A lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is ...
, in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
(CSF), can diagnose or exclude meningitis.
Some forms of meningitis are preventable by immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen).
When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-s ...
with the meningococcal, mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gene ...
, pneumococcal, and Hib vaccine
The ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a vaccination schedule, routine vaccine, rates of severe ...
s. Giving antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s to people with significant exposure to certain types of meningitis may also be useful. The first treatment in acute meningitis consists of promptly giving antibiotics and sometimes antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
s. Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s can also be used to prevent complications from excessive inflammation. Meningitis can lead to serious long-term consequences such as deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written ...
, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary i ...
, or cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defic ...
s, especially if not treated quickly.
In 2019, meningitis was prevalent in about 7.7 million people worldwide. This resulted in 236,000 deaths, down from 433,000 deaths in 1990. With appropriate treatment, the risk of death in bacterial meningitis is less than 15%. Outbreaks of bacterial meningitis occur between December and June each year in an area of sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
known as the meningitis belt. Smaller outbreaks may also occur in other areas of the world. The word meningitis comes from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
μῆνιγξ ''meninx'', "membrane", and the medical suffix ''-itis'', "inflammation".
Signs and symptoms
Clinical features
 In adults, the most common symptom of meningitis is a severe
In adults, the most common symptom of meningitis is a severe headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, occurring in almost 90% of cases of bacterial meningitis, followed by neck stiffness
Neck stiffness, stiff neck and nuchal rigidity are terms often used interchangeably to describe the medical condition when one experiences discomfort or pain when trying to turn, move, or flex the neck. Possible causes include muscle strain or spr ...
(the inability to flex the neck forward passively due to increased neck muscle tone
In physiology, medicine, and anatomy, muscle tone (residual muscle tension or tonus) is the continuous and passive partial contraction of the muscles, or the muscle's resistance to passive stretch during resting state.O’Sullivan, S. B. (2007). ...
and stiffness). The classic triad of diagnostic signs consists of neck stiffness
Neck stiffness, stiff neck and nuchal rigidity are terms often used interchangeably to describe the medical condition when one experiences discomfort or pain when trying to turn, move, or flex the neck. Possible causes include muscle strain or spr ...
, sudden high fever, and altered mental status
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciousne ...
; however, all three features are present in only 44–46% of bacterial meningitis cases. If none of the three signs are present, acute meningitis is extremely unlikely. Other signs commonly associated with meningitis include photophobia (intolerance to bright light) and phonophobia (intolerance to loud noises). Small children often do not exhibit the aforementioned symptoms, and may only be irritable and look unwell. The fontanelle
A fontanelle (or fontanel) (colloquially, soft spot) is an anatomical feature of the infant human skull comprising soft membranous gaps ( sutures) between the cranial bones that make up the calvaria of a fetus or an infant. Fontanelles allow ...
(the soft spot on the top of a baby's head) can bulge in infants aged up to 6 months. Other features that distinguish meningitis from less severe illnesses in young children are leg pain, cold extremities, and an abnormal skin color
Human skin color ranges from the darkest brown to the lightest hues. Differences in skin color among individuals is caused by variation in pigmentation, which is the result of genetics (inherited from one's biological parents and or individu ...
.
Nuchal rigidity
Neck stiffness, stiff neck and nuchal rigidity are terms often used interchangeably to describe the medical condition when one experiences discomfort or pain when trying to turn, move, or flex the neck. Possible causes include muscle strain or spr ...
occurs in 70% of bacterial meningitis in adults. Other signs include the presence of positive Kernig's sign
Kernig's sign is a test used in physical examination to look for evidence of irritation of the meninges. The test involves flexing the thighs at the hip, and the knees, at 90 degree angles, and assessing whether subsequent extension of the knee i ...
or Brudziński sign. Kernig's sign is assessed with the person lying supine
In grammar, a supine is a form of verbal noun used in some languages. The term is most often used for Latin, where it is one of the four principal parts of a verb. The word refers to a position of lying on one's back (as opposed to ' prone', l ...
, with the hip and knee flexed to 90 degrees. In a person with a positive Kernig's sign, pain limits passive extension of the knee. A positive Brudzinski's sign occurs when flexion of the neck causes involuntary flexion of the knee and hip. Although Kernig's sign and Brudzinski's sign are both commonly used to screen for meningitis, the sensitivity of these tests is limited. They do, however, have very good specificity for meningitis: the signs rarely occur in other diseases. Another test, known as the "jolt accentuation maneuver" helps determine whether meningitis is present in those reporting fever and headache. A person is asked to rapidly rotate the head horizontally; if this does not make the headache worse, meningitis is unlikely.
Other problems can produce symptoms similar to those above, but from non-meningitic causes. This is called meningism
Meningism is a set of symptoms similar to those of meningitis but not caused by meningitis. Whereas meningitis is inflammation of the meninges (membranes that cover the central nervous system), meningism is caused by nonmeningitic irritation of ...
or pseudomeningitis.
Meningitis caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria meningitidis'' (known as "meningococcal meningitis") can be differentiated from meningitis with other causes by a rapidly spreading petechial rash, which may precede other symptoms. The rash consists of numerous small, irregular purple or red spots ("petechiae") on the trunk, lower extremities
The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ sys ...
, mucous membranes, conjunctiva, and (occasionally) the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. The rash is typically non-blanching; the redness does not disappear when pressed with a finger or a glass tumbler. Although this rash is not necessarily present in meningococcal meningitis, it is relatively specific for the disease; it does, however, occasionally occur in meningitis due to other bacteria. Other clues on the cause of meningitis may be the skin signs of hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of enteroviruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blis ...
and genital herpes, both of which are associated with various forms of viral meningitis.
Early complications
 Additional problems may occur in the early stage of the illness. These may require specific treatment, and sometimes indicate severe illness or worse prognosis. The infection may trigger
Additional problems may occur in the early stage of the illness. These may require specific treatment, and sometimes indicate severe illness or worse prognosis. The infection may trigger sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, a systemic inflammatory response syndrome of falling blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
, fast heart rate
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (s ...
, high or abnormally low temperature, and rapid breathing
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea b ...
. Very low blood pressure may occur at an early stage, especially but not exclusively in meningococcal meningitis; this may lead to insufficient blood supply to other organs. Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts ...
, the excessive activation of blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechan ...
, may obstruct blood flow
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously m ...
to organs and paradoxically increase the bleeding risk. Gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the gan ...
of limbs can occur in meningococcal disease. Severe meningococcal and pneumococcal infections may result in hemorrhaging of the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex ...
s, leading to Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, which is often fatal.
The brain tissue may swell, pressure inside the skull may increase and the swollen brain may herniate through the skull base. This may be noticed by a decreasing level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciou ...
, loss of the pupillary light reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity (luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, ther ...
, and abnormal posturing. The inflammation of the brain tissue may also obstruct the normal flow of CSF around the brain (hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary i ...
). Seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s may occur for various reasons; in children, seizures are common in the early stages of meningitis (in 30% of cases) and do not necessarily indicate an underlying cause. Seizures may result from increased pressure and from areas of inflammation in the brain tissue. Focal seizures (seizures that involve one limb or part of the body), persistent seizures, late-onset seizures and those that are difficult to control with medication indicate a poorer long-term outcome.
Inflammation of the meninges may lead to abnormalities of the cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
, a group of nerves arising from the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is co ...
that supply the head and neck area and which control, among other functions, eye movement, facial muscles, and hearing. Visual symptoms and hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken l ...
may persist after an episode of meningitis. Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations ...
) or its blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
s ( cerebral vasculitis), as well as the formation of blood clots
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
in the veins (cerebral venous thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis or cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), is the presence of a blood clot in the dural venous sinuses (which drain blood from the brain), the cerebral veins, or both. Symp ...
), may all lead to weakness, loss of sensation, or abnormal movement or function of the part of the body supplied by the affected area of the brain.
Causes
Meningitis is typically caused by aninfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
with microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
. Most infections are due to viruses, with bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
, and protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
being the next most common causes. It may also result from various non-infectious causes. The term ''aseptic meningitis
Aseptic meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord, in patients whose cerebral spinal fluid test result is negative with routine bacterial cultures. Aseptic meningitis is caused by viruses, my ...
'' refers to cases of meningitis in which no bacterial infection can be demonstrated. This type of meningitis is usually caused by viruses but it may be due to bacterial infection that has already been partially treated, when bacteria disappear from the meninges, or pathogens infect a space adjacent to the meninges (e.g. sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
). Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
(an infection of the heart valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart ...
s which spreads small clusters of bacteria through the bloodstream) may cause aseptic meningitis. Aseptic meningitis may also result from infection with spirochetes, a group of bacteria that includes ''Treponema pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is ...
'' (the cause of syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, a ...
) and '' Borrelia burgdorferi'' (known for causing Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the '' Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus '' Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema ...
). Meningitis may be encountered in cerebral malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue (medical), tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In se ...
(malaria infecting the brain) or amoebic meningitis, meningitis due to infection with amoebae such as '' Naegleria fowleri'', contracted from freshwater sources.
Bacterial
 The types of
The types of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
that cause bacterial meningitis vary according to the infected individual's age group.
* In premature babies and newborns
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
up to three months old, common causes are '' group B streptococci'' (subtypes III which normally inhabit the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
and are mainly a cause during the first week of life) and bacteria that normally inhabit the digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
such as ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' (carrying the K1 antigen). ''Listeria monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host ...
'' (serotype IVb) can be contracted when consuming improperly prepared food such as dairy products, produce and deli meats, and may cause meningitis in the newborn.
* Older children are more commonly affected by '' Neisseria meningitidis'' (meningococcus) and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They ar ...
'' (serotypes 6, 9, 14, 18 and 23) and those under five by ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B (in countries that do not offer vaccination).
* In adults, ''Neisseria meningitidis'' and ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' together cause 80% of bacterial meningitis cases. Risk of infection with ''Listeria monocytogenes'' is increased in people over 50 years old. The introduction of pneumococcal vaccine has lowered rates of pneumococcal meningitis in both children and adults.
Recent skull trauma
Trauma most often refers to:
*Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
*Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic inju ...
potentially allows nasal cavity bacteria to enter the meningeal space. Similarly, devices in the brain and meninges, such as cerebral shunts, extraventricular drains or Ommaya reservoir
An Ommaya reservoir is an intraventricular catheter system that can be used for the aspiration of cerebrospinal fluid or for the delivery of drugs (e.g. chemotherapy) into the cerebrospinal fluid. It consists of a catheter in one lateral ventricle ...
s, carry an increased risk of meningitis. In these cases, people are more likely to be infected with Staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical ( cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultati ...
, Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able ...
, and other Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
bacteria. These pathogens are also associated with meningitis in people with an impaired immune system. An infection in the head and neck area, such as otitis media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
or mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear. Specifically, it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid antrum and mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process. The ma ...
, can lead to meningitis in a small proportion of people. Recipients of cochlear implant
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech und ...
s for hearing loss are more at risk for pneumococcal meningitis.
Tuberculous meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis, also known as TB meningitis or tubercular meningitis, is a specific type of bacterial meningitis caused by the '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' infection of the meninges—the system of membranes which envelop the central ...
, which is meningitis caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'', is more common in people from countries in which tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
is endemic, but is also encountered in people with immune problems, such as AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
.
Recurrent bacterial meningitis may be caused by persisting anatomical defects, either congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
or acquired, or by disorders of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. Anatomical defects allow continuity between the external environment and the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...
. The most common cause of recurrent meningitis is a skull fracture
A skull fracture is a break in one or more of the eight bones that form the cranial portion of the human skull, skull, usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma. If the force of the impact is excessive, the bone may fracture at or near ...
, particularly fractures that affect the base of the skull or extend towards the sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and petrous pyramids. Approximately 59% of recurrent meningitis cases are due to such anatomical abnormalities, 36% are due to immune deficiencies (such as complement deficiency
Complement deficiency is an immunodeficiency of absent or suboptimal functioning of one of the complement system proteins. Because of redundancies in the immune system, many complement disorders are never diagnosed. Some studies estimate that less ...
, which predisposes especially to recurrent meningococcal meningitis), and 5% are due to ongoing infections in areas adjacent to the meninges.
Viral
Viruses that cause meningitis includeenterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
es, herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
(generally type 2, which produces most genital sores; less commonly type 1), varicella zoster virus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or ''Human alphaherpesvirus 3'' (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting chil ...
(known for causing chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab ...
and shingles
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. ...
), mumps virus
The mumps virus (MuV) is the virus that causes mumps. MuV contains a single-stranded, negative-sense genome made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Its genome is about 15,000 nucleotides in length and contains seven genes that encode nine proteins. The g ...
, HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
, LCMV
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent-borne viral infectious disease that presents as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Its causative agent is ''lymphocytic choriomeningitis mammarenavirus'' (LCMV), a member of th ...
, Arboviruses
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more sp ...
(acquired from a mosquito or other insect), and the Influenza virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', ...
. Mollaret's meningitis
Mollaret's meningitis is a recurrent or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. Since Mollaret's meningitis is a recurrent, benign (non-cancerous), aseptic meningitis, ...
is a chronic recurrent form of herpes meningitis; it is thought to be caused by herpes simplex virus type 2.
Fungal
There are a number of risk factors forfungal meningitis
Fungal meningitis refers to meningitis caused by a fungal infection.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of fungal meningitis are generally similar to those of other types of meningitis, and include: a fever, stiff neck, severe headache, photophobia ...
, including the use of immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
s (such as after organ transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ (anatomy), organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organ ...
), HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
, and the loss of immunity associated with aging. It is uncommon in those with a normal immune system but has occurred with medication contamination. Symptom onset is typically more gradual, with headaches and fever being present for at least a couple of weeks before diagnosis. The most common fungal meningitis is cryptococcal meningitis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal mycosis, fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the ...
due to ''Cryptococcus neoformans
''Cryptococcus neoformans'' is an encapsulated yeast belonging to the class Tremellomycetes and an obligate aerobe that can live in both plants and animals. Its teleomorph is a filamentous fungus, formerly referred to ''Filobasidiella neoforman ...
''. In Africa, cryptococcal meningitis is now the most common cause of meningitis in multiple studies, and it accounts for 20–25% of AIDS-related deaths in Africa. Other less common fungal pathogens which can cause meningitis include: ''Coccidioides immitis
''Coccidioides immitis'' is a pathogenic fungus that resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and a few other areas in the Western Hemisphere.
Epidemiology
''C. immitis'', along with its relati ...
'', ''Histoplasma capsulatum
''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called ''Ajellomyces capsulatus''. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis.
''H. capsulatum'' is "distributed worldwide, except in Antarctica, but m ...
'', ''Blastomyces dermatitidis
''Blastomyces dermatitidis'' is a dimorphic fungus that causes blastomycosis, an invasive and often serious fungal infection found occasionally in humans and other animals. It lives in soil and wet, decaying wood, often in an area close to a wate ...
'', and '' Candida'' species.
Parasitic
A parasitic cause is often assumed when there is a predominance ofeosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. A ...
(a type of white blood cell) in the CSF. The most common parasites implicated are ''Angiostrongylus cantonensis
''Angiostrongylus cantonensis'' is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) that causes angiostrongyliasis, the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Basin. The nematode commonly resides in the pulmonary arteries ...
'', ''Gnathostoma spinigerum
''Gnathostoma spinigerum'' is a parasitic nematode that causes gnathostomiasis in humans, also known as its clinical manifestations are ''creeping eruption'', ''larva migrans'', ''Yangtze edema'', ''Choko-Fuschu Tua chid'' and ''wandering swellin ...
'', ''Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organ ...
'', as well as the conditions cysticercosis
Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the cysticercus, young form of the Taenia solium, pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimetres may ...
, toxocariasis
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm ('' Toxocara canis'') and, less frequently, the cat roundworm (''Toxocara cati'').https://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article/142/suppl_1/A104/1771175 Eosinophilic Pseudoleukemia Due to T ...
, baylisascariasis
''Baylisascaris procyonis'', also known by the common name of raccoon roundworm, is a roundworm nematode, found ubiquitously in raccoons, the definitive hosts. It is named after H. A. Baylis, who studied them in the 1920s–30s, and Greek '' as ...
, paragonimiasis
Paragonimiasis is a food-borne parasitic disease caused by several species of lung flukes belonging to genus '' Paragonimus''. Infection is acquired by eating crustaceans such as crabs and crayfishes which host the infective forms called metacerc ...
, and a number of rarer infections and noninfective conditions.
Non-infectious
Meningitis may occur as the result of several non-infectious causes: spread ofcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
to the meninges ('' malignant or neoplastic meningitis'') and certain drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalat ...
(mainly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s and intravenous immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin or NHIG) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory dem ...
s). It may also be caused by several inflammatory conditions, such as sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly af ...
(which is then called neurosarcoidosis
Neurosarcoidosis (sometimes shortened to neurosarcoid) refers to a type of sarcoidosis, a condition of unknown cause featuring granulomas in various tissues, in this type involving the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Neurosarcoidosi ...
), connective tissue disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
, and certain forms of vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused b ...
(inflammatory conditions of the blood vessel wall), such as Behçet's disease
Behçet's disease (BD) is a type of inflammatory disorder which affects multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include painful sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other parts of the body, inflammation of parts of the e ...
. Epidermoid cyst
An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.
Signs and symptoms
The epidermoid cyst may ...
s and dermoid cyst
A dermoid cyst is a teratoma of a cystic nature that contains an array of developmentally mature, solid tissues. It frequently consists of skin, hair follicles, and sweat glands, while other commonly found components include clumps of long hair ...
s may cause meningitis by releasing irritant matter into the subarachnoid space. Rarely, migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
may cause meningitis, but this diagnosis is usually only made when other causes have been eliminated.
Mechanism
The meninges comprise three membranes that, together with thecerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
, enclose and protect the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
(the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
). The pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
arachnoid mater The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural c ...
(so named because of its spider-web-like appearance) is a loosely fitting sac on top of the pia mater. The in
arachnoid mater The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural c ...
subarachnoid space
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in th ...
separates the arachnoid and pia mater membranes and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The outermost membrane, the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
, is a thick durable membrane, which is attached to both the arachnoid membrane and the skull.
In bacterial meningitis, bacteria reach the meninges by one of two main routes: through the bloodstream (hematogenous spread) or through direct contact between the meninges and either the nasal cavity or the skin. In most cases, meningitis follows invasion of the bloodstream by organisms that live on mucosal surfaces such as the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
. This is often in turn preceded by viral infections, which break down the normal barrier provided by the mucosal surfaces. Once bacteria have entered the bloodstream, they enter the subarachnoid space
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in th ...
in places where the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of ...
is vulnerable – such as the choroid plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nerv ...
. Meningitis occurs in 25% of newborns with bloodstream infections due to group B streptococci
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive coccus (round bacteria, bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a be ...
; this phenomenon is much less common in adults. Direct contamination of the cerebrospinal fluid may arise from indwelling devices, skull fractures, or infections of the nasopharynx or the nasal sinuses that have formed a tract with the subarachnoid space (see above); occasionally, congenital defects
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
of the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
can be identified.
The large-scale inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
that occurs in the subarachnoid space during meningitis is not a direct result of bacterial infection but can rather largely be attributed to the response of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
to the entry of bacteria into the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
. When components of the bacterial cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
are identified by the immune cells of the brain (astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of e ...
s and microglia), they respond by releasing large amounts of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s, hormone-like mediators that recruit other immune cells and stimulate other tissues to participate in an immune response. The blood–brain barrier becomes more permeable, leading to "vasogenic" cerebral edema (swelling of the brain due to fluid leakage from blood vessels). Large numbers of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s enter the CSF, causing inflammation of the meninges and leading to "interstitial" edema (swelling due to fluid between the cells). In addition, the walls of the blood vessels themselves become inflamed (cerebral vasculitis), which leads to decreased blood flow and a third type of edema, "cytotoxic" edema. The three forms of cerebral edema all lead to increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 Millimeter of mercury, mmHg ...
; together with the lowered blood pressure often encountered in sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, this means that it is harder for blood to enter the brain; consequently brain cell
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain. The rest of the brain tissue is structural or connective called the stroma which includes blood vessels. The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons, also known as nerve cells, an ...
s are deprived of oxygen and undergo apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
(programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage durin ...
).
It is recognized that administration of antibiotics may initially worsen the process outlined above, by increasing the amount of bacterial cell membrane products released through the destruction of bacteria. Particular treatments, such as the use of corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
, are aimed at dampening the immune system's response to this phenomenon.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing meningitis as promptly as possible can improve outcomes. There is no specific sign or symptom that can diagnose meningitis and alumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is ...
(spinal tap) to examine the cerebrospinal fluid is recommended for diagnosis. Lumbar puncture is contraindicated if there is a mass in the brain (tumor or abscess) or the intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 Millimeter of mercury, mmHg ...
(ICP) is elevated, as it may lead to brain herniation
Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the te ...
. If someone is at risk for either a mass or raised ICP (recent head injury, a known immune system problem, localizing neurological signs, or evidence on examination of a raised ICP), a CT or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
scan is recommended prior to the lumbar puncture. – formal guideline at This applies in 45% of all adult cases.
There are no physical tests that can rule out or determine if a person has meningitis. The jolt accentuation test is not specific or sensitive enough to completely rule out meningitis.
If someone is suspected of having meningitis, blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s are performed for markers of inflammation (e.g. C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 ...
, complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cell ...
), as well as blood culture
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or f ...
s. If a CT or MRI is required before LP, or if LP proves difficult, professional guidelines suggest that antibiotics should be administered first to prevent delay in treatment, especially if this may be longer than 30 minutes. Often, CT or MRI scans are performed at a later stage to assess for complications of meningitis.
In severe forms of meningitis, monitoring of blood electrolytes may be important; for example, hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be abs ...
is common in bacterial meningitis. The cause of hyponatremia, however, is controversial and may include dehydration, the inappropriate secretion of the antidiuretic hormone
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
(SIADH), or overly aggressive intravenous fluid administration.
Lumbar puncture

 A lumbar puncture is done by positioning the person, usually lying on the side, applying
A lumbar puncture is done by positioning the person, usually lying on the side, applying local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general an ...
, and inserting a needle into the dural sac
Dural is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia 36 kilometres north-west of the Sydney central business district in the Local government in Australia, local government areas of Hornsby Shire and The Hills Shire. Dural is ...
(a sac around the spinal cord) to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). When this has been achieved, the "opening pressure" of the CSF is measured using a manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ...
. The pressure is normally between 6 and 18 cm water (cmH2O); in bacterial meningitis the pressure is usually elevated. In cryptococcal meningitis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal mycosis, fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the ...
, intracranial pressure is markedly elevated. The initial appearance of the fluid may prove an indication of the nature of the infection: cloudy CSF indicates higher levels of protein, white and red blood cells and/or bacteria, and therefore may suggest bacterial meningitis.
The CSF sample is examined for presence and types of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cell (biology), cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and de ...
s, red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
content and glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
level. Gram staining
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish bac ...
of the sample may demonstrate bacteria in bacterial meningitis, but absence of bacteria does not exclude bacterial meningitis as they are only seen in 60% of cases; this figure is reduced by a further 20% if antibiotics were administered before the sample was taken. Gram staining is also less reliable in particular infections such as listeriosis
Listeriosis is a bacterial infection most commonly caused by '' Listeria monocytogenes'', although '' L. ivanovii'' and '' L. grayi'' have been reported in certain cases. Listeriosis can cause severe illness, including severe sepsis, men ...
. Microbiological culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagn ...
of the sample is more sensitive (it identifies the organism in 70–85% of cases) but results can take up to 48 hours to become available. The type of white blood cell predominantly present (see table) indicates whether meningitis is bacterial (usually neutrophil-predominant) or viral (usually lymphocyte-predominant), although at the beginning of the disease this is not always a reliable indicator. Less commonly, eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. A ...
s predominate, suggesting parasitic or fungal etiology, among others.
The concentration of glucose in CSF is normally above 40% of that in blood. In bacterial meningitis it is typically lower; the CSF glucose level is therefore divided by the blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
(CSF glucose to serum glucose ratio). A ratio ≤0.4 is indicative of bacterial meningitis; in the newborn, glucose levels in CSF are normally higher, and a ratio below 0.6 (60%) is therefore considered abnormal. High levels of lactate in CSF indicate a higher likelihood of bacterial meningitis, as does a higher white blood cell count. If lactate levels are less than 35 mg/dl and the person has not previously received antibiotics then this may rule out bacterial meningitis.
Various other specialized tests may be used to distinguish between different types of meningitis. A latex agglutination test may be positive in meningitis caused by ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They ar ...
'', '' Neisseria meningitidis'', ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria ...
'', ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' and ''group B streptococci
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive coccus (round bacteria, bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a be ...
''; its routine use is not encouraged as it rarely leads to changes in treatment, but it may be used if other tests are not diagnostic. Similarly, the limulus lysate test may be positive in meningitis caused by Gram-negative bacteria, but it is of limited use unless other tests have been unhelpful. Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
(PCR) is a technique used to amplify small traces of bacterial DNA in order to detect the presence of bacterial or viral DNA in cerebrospinal fluid; it is a highly sensitive and specific test since only trace amounts of the infecting agent's DNA is required. It may identify bacteria in bacterial meningitis and may assist in distinguishing the various causes of viral meningitis (enterovirus
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
, herpes simplex virus 2
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names '' Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and ''Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
and mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gener ...
in those not vaccinated for this). Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in r ...
(identification of antibodies to viruses) may be useful in viral meningitis. If tuberculous meningitis is suspected, the sample is processed for Ziehl–Neelsen stain
Ziehl–Neelsen staining is a type of acid-fast stain, first introduced by Paul Ehrlich. Ziehl–Neelsen staining is a bacteriological stain used to identify acid-fast organisms, mainly Mycobacteria. It is named for two German doctors who modif ...
, which has a low sensitivity, and tuberculosis culture, which takes a long time to process; PCR is being used increasingly. Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis can be made at low cost using an India ink stain of the CSF; however, testing for cryptococcal antigen in blood or CSF is more sensitive.
A diagnostic and therapeutic difficulty is "partially treated meningitis", where there are meningitis symptoms after receiving antibiotics (such as for presumptive sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
). When this happens, CSF findings may resemble those of viral meningitis, but antibiotic treatment may need to be continued until there is definitive positive evidence of a viral cause (e.g. a positive enterovirus PCR).
Postmortem
 Meningitis can be diagnosed after death has occurred. The findings from a
Meningitis can be diagnosed after death has occurred. The findings from a post mortem
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any dis ...
are usually a widespread inflammation of the pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
arachnoid Arachnoid may refer to: * Relating to arachnids * Arachnoid (astrogeology), a geological structure found only on the planet Venus * Arachnoid (botany), referring to organs with a cobwebby exterior appearance * Arachnoid granulation, small protrus ...
layers of the meninges. in
arachnoid Arachnoid may refer to: * Relating to arachnids * Arachnoid (astrogeology), a geological structure found only on the planet Venus * Arachnoid (botany), referring to organs with a cobwebby exterior appearance * Arachnoid granulation, small protrus ...
Neutrophil granulocyte
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s tend to have migrated to the cerebrospinal fluid and the base of the brain, along with cranial nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and ...
s and the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, may be surrounded with pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
– as may the meningeal vessels.
Prevention
For some causes of meningitis, protection can be provided in the long term throughvaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
, or in the short term with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s. Some behavioral measures may also be effective.
Behavioral
Bacterial and viral meningitis are contagious, but neither is as contagious as thecommon cold
The common cold or the cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose, throat, sinuses, and larynx. Signs and symptoms may appear fewer than two days after exposu ...
or flu
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
. Both can be transmitted through droplets of respiratory secretions during close contact such as kissing, sneezing or coughing on someone, but bacterial meningitis cannot be spread by only breathing the air where a person with meningitis has been. Viral meningitis is typically caused by enteroviruses
''Enterovirus'' is a genus of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine ('enteric' meaning intestinal).
Serologic ...
, and is most commonly spread through fecal contamination. The risk of infection can be decreased by changing the behavior that led to transmission.
Vaccination
Since the 1980s, many countries have included immunization against ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B in their routine childhood vaccination schemes. This has practically eliminated this pathogen as a cause of meningitis in young children in those countries. In the countries in which the disease burden is highest, however, the vaccine is still too expensive. Similarly, immunization against mumps has led to a sharp fall in the number of cases of mumps meningitis, which prior to vaccination occurred in 15% of all cases of mumps. Meningococcus vaccines exist against groups A, B, C, W135 and Y. In countries where the vaccine for meningococcus group C was introduced, cases caused by this pathogen have decreased substantially. A quadrivalent vaccine now exists, which combines four vaccines with the exception of B; immunization with this ACW135Y vaccine is now a visa requirement for taking part inHajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried ...
. Development of a vaccine against group B meningococci has proved much more difficult, as its surface proteins (which would normally be used to make a vaccine) only elicit a weak response from the immune system, or cross-react with normal human proteins. Still, some countries (New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
) have developed vaccines against local strains of group B meningococci; some have shown good results and are used in local immunization schedules. Two new vaccines, both approved in 2014, are effective against a wider range of group B meningococci strains. In Africa, until recently, the approach for prevention and control of meningococcal epidemics was based on early detection of the disease and emergency reactive mass vaccination of the at-risk population with bivalent A/C or trivalent A/C/W135 polysaccharide vaccines, though the introduction of MenAfriVac (meningococcus group A vaccine) has demonstrated effectiveness in young people and has been described as a model for product development partnerships in resource-limited settings.
Routine vaccination against ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' with the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is a pneumococcal vaccine and a conjugate vaccine used to protect infants, young children, and adults against disease caused by the bacterium ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' (pneumococcus). It contains purified capsul ...
(PCV), which is active against seven common serotypes of this pathogen, significantly reduces the incidence of pneumococcal meningitis. The pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine
Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV)—known as Pneumovax 23 (PPV-23)—is the first pneumococcal vaccine derived from a capsular polysaccharide.
The polysaccharide antigens were used to induce type-specific antibodies that enhanced op ...
, which covers 23 strains, is only administered to certain groups (e.g. those who have had a splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of ...
, the surgical removal of the spleen); it does not elicit a significant immune response in all recipients, e.g. small children. Childhood vaccination with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended ...
has been reported to significantly reduce the rate of tuberculous meningitis, but its waning effectiveness in adulthood has prompted a search for a better vaccine.
Antibiotics
Short-term antibiotic prophylaxis is another method of prevention, particularly of meningococcal meningitis. In cases of meningococcal meningitis, preventative treatment in close contacts with antibiotics (e.g.rifampicin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. ...
, ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin inf ...
or ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joint ...
) can reduce their risk of contracting the condition, but does not protect against future infections. Resistance to rifampicin has been noted to increase after use, which has caused some to recommend considering other agents. While antibiotics are frequently used in an attempt to prevent meningitis in those with a basilar skull fracture
A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include bruising behind the ears, bruising around the eyes, or blood behind the ear drum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and ...
there is not enough evidence to determine whether this is beneficial or harmful. This applies to those with or without a CSF leak.
Management
Meningitis is potentially life-threatening and has a high mortality rate if untreated; delay in treatment has been associated with a poorer outcome. Thus, treatment with wide-spectrum antibiotics should not be delayed while confirmatory tests are being conducted. If meningococcal disease is suspected in primary care, guidelines recommend thatbenzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, also known as penicillin G (PenG) or BENPEN, and in military slang "Peanut Butter Shot" is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes pneumonia, strep throat, syphilis, necrotizing enterocolitis ...
be administered before transfer to hospital. Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
fluids should be administered if hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dias ...
(low blood pressure) or shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergen ...
are present. It is not clear whether intravenous fluid should be given routinely or whether this should be restricted. Given that meningitis can cause a number of early severe complications, regular medical review is recommended to identify these complications early and to admit the person to an intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensiv ...
if deemed necessary.
Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ...
may be needed if the level of consciousness is very low, or if there is evidence of respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
. If there are signs of raised intracranial pressure, measures to monitor the pressure may be taken; this would allow the optimization of the cerebral perfusion pressure Cerebral perfusion pressure, or CPP, is the net pressure gradient causing cerebral blood flow to the brain (brain perfusion). It must be maintained within narrow limits because too little pressure could cause brain tissue to become ischemic (having ...
and various treatments to decrease the intracranial pressure with medication (e.g. mannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lo ...
). Seizures are treated with anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
s. Hydrocephalus (obstructed flow of CSF) may require insertion of a temporary or long-term drainage device, such as a cerebral shunt. The osmotic therapy, glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known ...
, has an unclear effect on mortality but may decrease hearing problems.
Bacterial meningitis
Antibiotics

Empiric antibiotics
Empiric therapy or empirical therapy is medical treatment or therapy based on experience and, more specifically, therapy begun on the basis of a clinical "educated guess" in the absence of complete or perfect information. Thus it is applied before ...
(treatment without exact diagnosis) should be started immediately, even before the results of the lumbar puncture and CSF analysis are known. The choice of initial treatment depends largely on the kind of bacteria that cause meningitis in a particular place and population. For instance, in the United Kingdom, empirical treatment consists of a third-generation cefalosporin such as cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections in human, other animals and plant tissue culture. Specifically in humans it is used to treat joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urin ...
or ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joint ...
. In the US, where resistance to cefalosporins is increasingly found in streptococci, addition of vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, ...
to the initial treatment is recommended. Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, a ...
, either alone or in combination with ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B strepto ...
, however, appears to work equally well.
Empirical therapy may be chosen on the basis of the person's age, whether the infection was preceded by a head injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
, whether the person has undergone recent neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peri ...
and whether or not a cerebral shunt is present. In young children and those over 50 years of age, as well as those who are immunocompromised, the addition of ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B strepto ...
is recommended to cover ''Listeria monocytogenes
''Listeria monocytogenes'' is the species of pathogenic bacteria that causes the infection listeriosis. It is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, capable of surviving in the presence or absence of oxygen. It can grow and reproduce inside the host ...
''. Once the Gram stain results become available, and the broad type of bacterial cause is known, it may be possible to change the antibiotics to those likely to deal with the presumed group of pathogens. The results of the CSF culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
generally take longer to become available (24–48 hours). Once they do, empiric therapy may be switched to specific antibiotic therapy targeted to the specific causative organism and its sensitivities to antibiotics. For an antibiotic to be effective in meningitis it must not only be active against the pathogenic bacterium but also reach the meninges in adequate quantities; some antibiotics have inadequate penetrance and therefore have little use in meningitis. Most of the antibiotics used in meningitis have not been tested directly on people with meningitis in clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ...
s. Rather, the relevant knowledge has mostly derived from laboratory studies in rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
s. Tuberculous meningitis requires prolonged treatment with antibiotics. While tuberculosis of the lungs is typically treated for six months, those with tuberculous meningitis are typically treated for a year or longer.
Fluid Therapy
Fluid given intravenously are an essential part of treatment of bacterial meningitis. There is no difference in terms of mortality or acute severe neurological complications in children given a maintenance regimen over restricted-fluid regimen, but evidence is in favor of the maintenance regimen in terms of emergence of chronic severe neurological complications.Steroids
Additional treatment withcorticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
(usually dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena cav ...
) has shown some benefits, such as a reduction of hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken l ...
, and better short term neurological outcomes in adolescents and adults from high-income countries
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" a ...
with low rates of HIV. Some research has found reduced rates of death while other research has not. They also appear to be beneficial in those with tuberculosis meningitis, at least in those who are HIV negative.
Professional guidelines therefore recommend the commencement of dexamethasone or a similar corticosteroid just before the first dose of antibiotics is given, and continued for four days. Given that most of the benefit of the treatment is confined to those with pneumococcal meningitis, some guidelines suggest that dexamethasone be discontinued if another cause for meningitis is identified. The likely mechanism is suppression of overactive inflammation.
Additional treatment with corticosteroids have a different role in children than in adults. Though the benefit of corticosteroids has been demonstrated in adults as well as in children from high-income countries, their use in children from low-income
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little countries is not supported by the evidence; the reason for this discrepancy is not clear. Even in high-income countries, the benefit of corticosteroids is only seen when they are given prior to the first dose of antibiotics, and is greatest in cases of ''H. influenzae'' meningitis, the incidence of which has decreased dramatically since the introduction of the
 Untreated, bacterial meningitis is almost always fatal. Viral meningitis, in contrast, tends to resolve spontaneously and is rarely fatal. With treatment,
Untreated, bacterial meningitis is almost always fatal. Viral meningitis, in contrast, tends to resolve spontaneously and is rarely fatal. With treatment,

 Although meningitis is a
Although meningitis is a
Meningitis
Hib vaccine
The ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a vaccination schedule, routine vaccine, rates of severe ...
. Thus, corticosteroids are recommended in the treatment of pediatric meningitis if the cause is ''H. influenzae'', and only if given prior to the first dose of antibiotics; other uses are controversial.
Viral meningitis
Viral meningitis
Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, is a type of meningitis due to a viral infection. It results in inflammation of the meninges (the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord). Symptoms commonly include headache, fever, photop ...
typically only requires supportive therapy; most viruses responsible for causing meningitis are not amenable to specific treatment. Viral meningitis tends to run a more benign course than bacterial meningitis. Herpes simplex virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral inf ...
and varicella zoster virus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3, HHV3) or ''Human alphaherpesvirus 3'' (taxonomically), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting chil ...
may respond to treatment with antiviral drugs such as aciclovir
Aciclovir (ACV), also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following tra ...
, but there are no clinical trials that have specifically addressed whether this treatment is effective. Mild cases of viral meningitis can be treated at home with conservative measures such as fluid, bedrest, and analgesics.
Fungal meningitis
Fungal meningitis, such ascryptococcal meningitis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal mycosis, fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the ...
, is treated with long courses of high dose antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as crypto ...
, such as amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious mycosis, fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candida infections, candidiasis, coccidioidomy ...
and flucytosine
Flucytosine, also known as 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), is an antifungal medication. It is specifically used, together with amphotericin B, for serious ''Candida'' infections and cryptococcosis. It may be used by itself or with other antifungals for ...
. Raised intracranial pressure is common in fungal meningitis, and frequent (ideally daily) lumbar punctures to relieve the pressure are recommended, or alternatively a lumbar drain.
Prognosis
mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
(risk of death) from bacterial meningitis depends on the age of the person and the underlying cause. Of newborns, 20–30% may die from an episode of bacterial meningitis. This risk is much lower in older children, whose mortality is about 2%, but rises again to about 19–37% in adults.
Risk of death is predicted by various factors apart from age, such as the pathogen and the time it takes for the pathogen to be cleared from the cerebrospinal fluid, the severity of the generalized illness, a decreased level of consciousness or an abnormally low count of white blood cells in the CSF. Meningitis caused by ''H. influenzae'' and meningococci has a better prognosis than cases caused by group B streptococci, coliforms and ''S. pneumoniae''. In adults, too, meningococcal meningitis has a lower mortality (3–7%) than pneumococcal disease.
In children there are several potential disabilities which may result from damage to the nervous system, including sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear or sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures) or the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for about 90% of rep ...
, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machine learning, machines ...
and behavioral difficulties, as well as decreased intelligence. These occur in about 15% of survivors. Some of the hearing loss may be reversible. In adults, 66% of all cases emerge without disability. The main problems are deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written ...
(in 14%) and cognitive impairment
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defici ...
(in 10%).
Tuberculous meningitis in children continues to be associated with a significant risk of death even with treatment (19%), and a significant proportion of the surviving children have ongoing neurological problems. Just over a third of all cases survives with no problems.
Epidemiology

notifiable disease
A notifiable disease is any disease that is required by law to be reported to government authorities. The collation of information allows the authorities to monitor the disease, and provides early warning of possible outbreaks. In the case of live ...
in many countries, the exact incidence rate is unknown. In 2013 meningitis resulted in 303,000 deaths – down from 464,000 deaths in 1990. In 2010 it was estimated that meningitis resulted in 420,000 deaths, excluding cryptococcal meningitis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal mycosis, fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the ...
.
Bacterial meningitis occurs in about 3 people per 100,000 annually in Western countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. Population-wide studies have shown that viral meningitis is more common, at 10.9 per 100,000, and occurs more often in the summer. In Brazil, the rate of bacterial meningitis is higher, at 45.8 per 100,000 annually. Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
has been plagued by large epidemics of meningococcal meningitis for over a century, leading to it being labeled the "meningitis belt". Epidemics typically occur in the dry season (December to June), and an epidemic wave can last two to three years, dying out during the intervening rainy seasons. Attack rates of 100–800 cases per 100,000 are encountered in this area, which is poorly served by medical care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health profess ...
. These cases are predominantly caused by meningococci. The largest epidemic ever recorded in history swept across the entire region in 1996–1997, causing over 250,000 cases and 25,000 deaths.
Meningococcal disease occurs in epidemics in areas where many people live together for the first time, such as army barracks during mobilization, university and college campuses and the annual Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried ...
pilgrimage. Although the pattern of epidemic cycles in Africa is not well understood, several factors have been associated with the development of epidemics in the meningitis belt. They include: medical conditions (immunological susceptibility of the population), demographic conditions (travel and large population displacements), socioeconomic conditions (overcrowding and poor living conditions), climatic conditions (drought and dust storms), and concurrent infections (acute respiratory infections).
There are significant differences in the local distribution of causes for bacterial meningitis. For instance, while ''N. meningitides'' groups B and C cause most disease episodes in Europe, group A is found in Asia and continues to predominate in Africa, where it causes most of the major epidemics in the meningitis belt, accounting for about 80% to 85% of documented meningococcal meningitis cases.
History
Some suggest thatHippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
may have realized the existence of meningitis, and it seems that meningism
Meningism is a set of symptoms similar to those of meningitis but not caused by meningitis. Whereas meningitis is inflammation of the meninges (membranes that cover the central nervous system), meningism is caused by nonmeningitic irritation of ...
was known to pre-Renaissance physicians such as Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
. The description of tuberculous meningitis, then called "dropsy
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
in the brain", is often attributed to Edinburgh physician Sir Robert Whytt in a posthumous report that appeared in 1768, although the link with tuberculosis and its pathogen was not made until the next century.
It appears that epidemic meningitis is a relatively recent phenomenon. The first recorded major outbreak occurred in Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
in 1805. Several other epidemics in Europe and the United States were described shortly afterward, and the first report of an epidemic in Africa appeared in 1840. African epidemics became much more common in the 20th century, starting with a major epidemic sweeping Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
in 1905–1908.
The first report of bacterial infection underlying meningitis was by the Austrian bacteriologist Anton Weichselbaum, who in 1887 described the ''meningococcus''. Mortality from meningitis was very high (over 90%) in early reports. In 1906, antiserum
Antiserum is a blood serum containing monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies that is used to spread passive immunity to many diseases via blood donation (plasmapheresis). For example, convalescent serum, passive antibody transfusion from a previous ...
was produced in horses; this was developed further by the American scientist Simon Flexner
Simon Flexner, M.D. (March 25, 1863 in Louisville, Kentucky – May 2, 1946) was a physician, scientist, administrator, and professor of experimental pathology at the University of Pennsylvania (1899–1903). He served as the first director of t ...
and markedly decreased mortality from meningococcal disease. In 1944, penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
was first reported to be effective in meningitis. The introduction in the late 20th century of ''Haemophilus
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of t ...
'' vaccines led to a marked fall in cases of meningitis associated with this pathogen, and in 2002, evidence emerged that treatment with steroids could improve the prognosis of bacterial meningitis. World Meningitis Day is observed on 24 April each year.
References
External links
*Meningitis
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
(CDC)
{{Authority control
Disorders causing seizures
Medical emergencies
Acute pain
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)
Medical triads
Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate