|
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death
Programmed cell death (PCD; sometimes referred to as cellular suicide) is the death of a cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and animal tissue development. Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death. Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Necrosis was long seen as a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury, but in the 2000s, a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, was recognized as an alternative form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
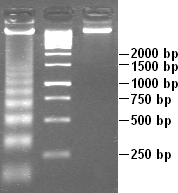
Apoptotic DNA Fragmentation
Apoptotic DNA fragmentation is a key feature of apoptosis, a type of programmed cell death. Apoptosis is characterized by the activation of endogenous endonucleases, particularly the caspase-3 activated DNase (CAD), with subsequent cleavage of nuclear DNA into internucleosomal fragments of roughly 180 base pairs (bp) and multiples thereof (360, 540 etc.). The apoptotic DNA fragmentation is being used as a marker of apoptosis and for identification of apoptotic cells either via the DNA laddering assay, the TUNEL assay, or the by detection of cells with fractional DNA content ("sub G1 cells") on DNA content frequency histograms e.g. as in the Nicoletti assay. Mechanism The enzyme responsible for apoptotic DNA fragmentation is the Caspase-Activated DNase (CAD). CAD is normally inhibited by another protein, the Inhibitor of Caspase Activated DNase (ICAD). During apoptosis, the apoptotic effector caspase, caspase-3, cleaves ICAD and thus causes CAD to become activated. CAD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fas Receptor
The Fas receptor, also known as Fas, FasR, apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1 or APT), cluster of differentiation 95 (CD95) or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6 (TNFRSF6), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FAS'' gene. Fas was first identified using a monoclonal antibody generated by immunizing mice with the FS-7 cell line. Thus, the name Fas is derived from ''F''S-7-''a''ssociated ''s''urface antigen. The Fas receptor is a death receptor on the surface of cells that leads to programmed cell death (apoptosis) if it binds its ligand, Fas ligand (FasL). It is one of two apoptosis pathways, the other being the mitochondrial pathway. Gene FAS receptor gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 10 (10q24.1) in humans and on chromosome 19 in mice. The gene lies on the plus ( Watson strand) and is 25,255 bases in length organized into nine protein encoding exons. Similar sequences related by evolution (orthologs) are found in most mammals. Protein Prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |