|
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue. The causes of hyponatremia are typically classified by a person's body fluid status into low volume, normal volume, or high volume. Low volume hyponatremia can occur from diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics, and sweating. Normal volume hyponatremia is divided into cases with dilute urine and concentrated urine. Cases in which the urine is dilute include adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, and drinking too much water or too much beer. Cases in which the urine is concentrated include syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). High vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome Of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is characterized by excessive unsuppressible release of Vasopressin, antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes an unrelenting increase in solute-free water being returned by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulatory system, circulation. The causes of SIADH are grouped into six categories: 1) central nervous system diseases that directly stimulate the hypothalamus, the site of control of ADH secretion; 2) various cancers that synthesize and secrete ectopia (medicine), ectopic ADH; 3) various lung diseases; 4) numerous drugs that chemically stimulate the hypothalamus; 5) inherited mutations; and 6) miscellaneous largely transient conditions. ADH is derived from a preprohormone precursor that is synthesized in cells in the hypothalamus and stored in vesicles in the posterior pituitary. ''Appropriate'' ADH secretion is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydipsia
Polydipsia is excessive thirst or excess drinking.Porth, C. M. (1990). ''Pathophysiology: Concepts of altered health states''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Company. The word derives from the Greek () "very thirsty", which is derived from (, "much, many") + (, "thirst"). Polydipsia is a nonspecific symptom in various medical disorders. It also occurs as an abnormal behaviour in some non-human animals, such as in birds. Causes Diabetes Polydipsia can be characteristic of diabetes mellitus, often as an initial symptom. It is observed in cases of poorly controlled diabetes, which is sometimes the result of low patient adherence to anti-diabetic medication. Diabetes insipidus ("tasteless" diabetes, as opposed to diabetes mellitus) can also cause polydipsia. Other physiological causes It can also be caused by a change in the osmolality of the extracellular fluids of the body, hypokalemia, decreased blood volume (as occurs during major hemorrhage), and other conditions that cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
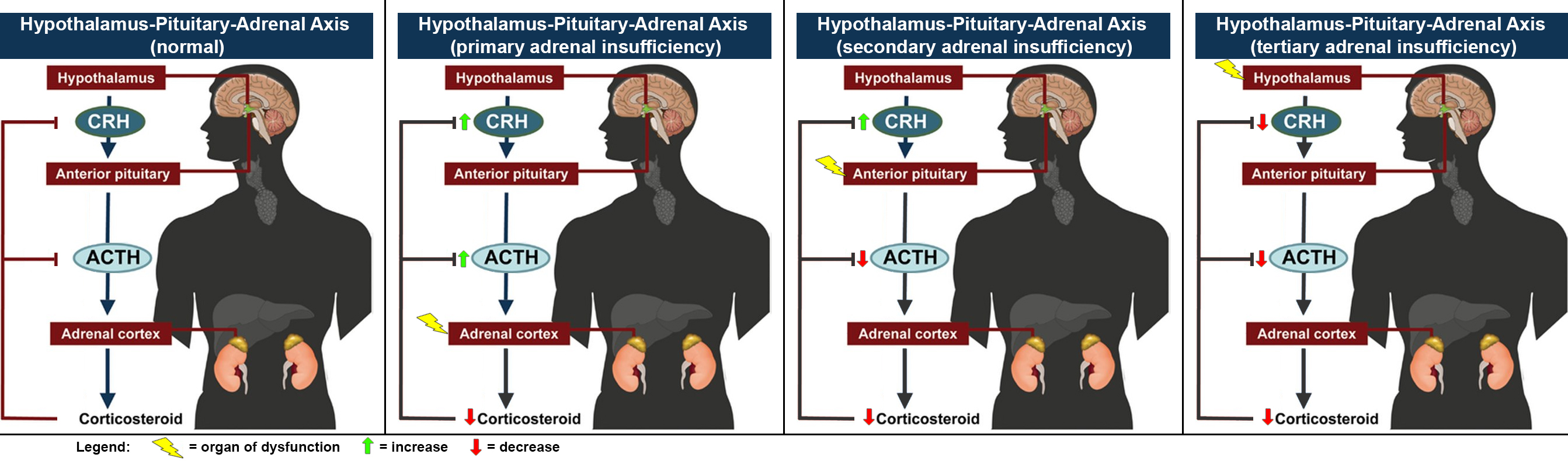
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). An adrenal crisis may occur if the body is subjected to stress, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potomania
Potomania (From Latin ''pōtō'' "I drink (liquor)" + mania) is a specific hypo-osmolality syndrome related to massive consumption of beer, which is poor in solutes and electrolytes. With little food or other sources of electrolytes, consumption of large amounts of beer or other dilute alcoholic drinks leads to electrolyte disturbances, where the body does not have enough nutrients known as electrolytes, namely sodium, potassium, and magnesium. The symptoms of potomania are similar to other causes of hyponatremia and include dizziness, muscular weakness, neurological impairment and seizures, all related to hyponatremia and hypokalaemia. While the symptoms of potomania are similar to other causes of hyponatremia and acute water intoxication, it should be considered an independent clinical entity because of its often chronic nature of onset, pathophysiology, and presentation of symptoms. Pathophysiology The normal human kidney, through suppression of anti-diuretic hormone, is nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypervolemic
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular compartment occurs due to an increase in total body sodium content and a consequent increase in extracellular body water. The mechanism usually stems from compromised regulatory mechanisms for sodium handling as seen in congestive heart failure (CHF), kidney failure, and liver failure. It may also be caused by excessive intake of sodium from foods, intravenous (IV) solutions and blood transfusions, medications, or diagnostic contrast dyes. Treatment typically includes administration of diuretics and limit the intake of water, fluids, sodium, and salt. Signs and symptoms The excess fluid, primarily salt and water, builds up in various locations in the body and leads to an increase in weight, swelling in the legs and arms (peripheral edema), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
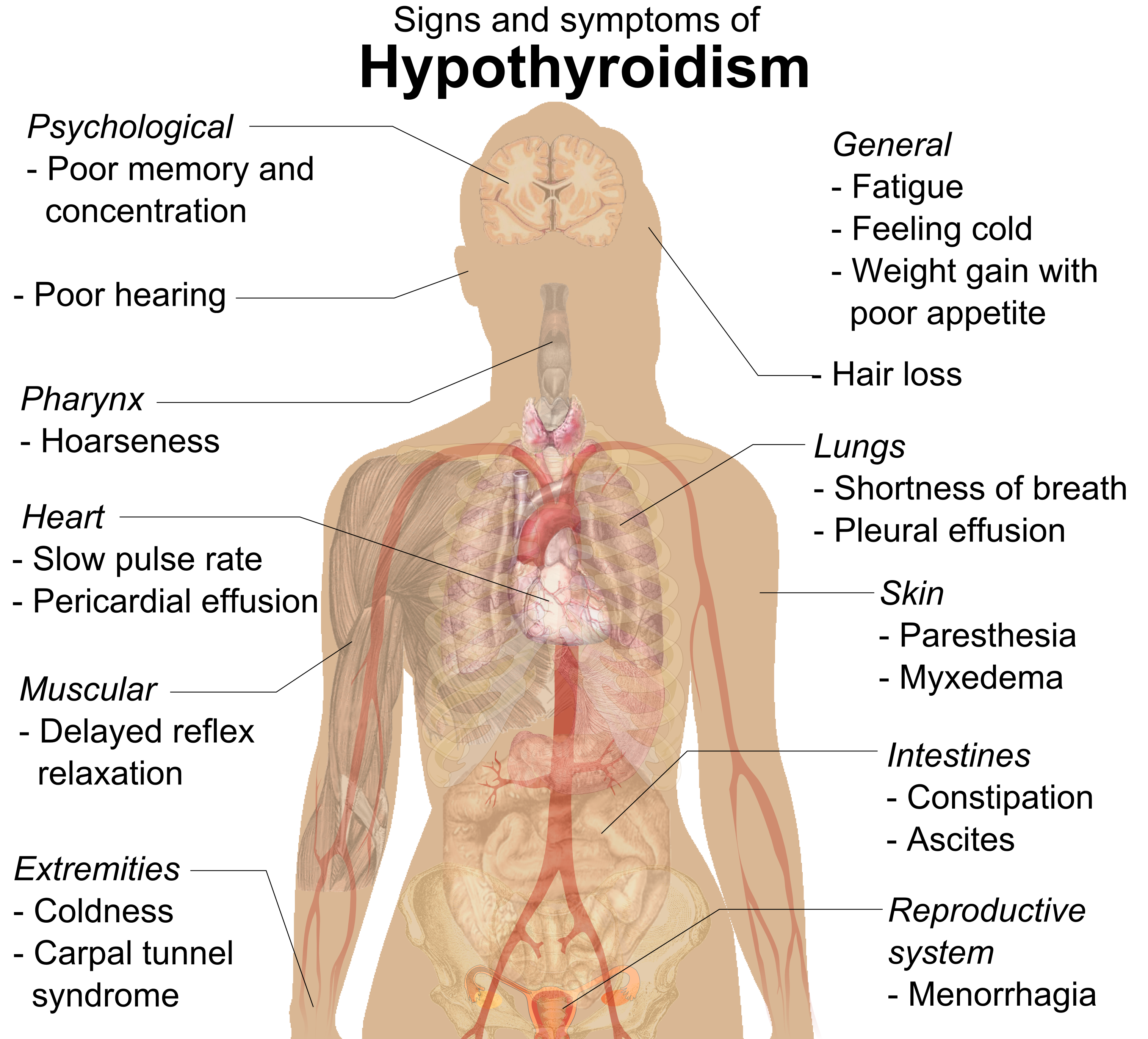
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweating
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the body and are responsible for secreting the watery, brackish sweat most often triggered by excessive body temperature. The apocrine sweat glands are restricted to the armpits and a few other areas of the body and produce an odorless, oily, opaque secretion which then gains its characteristic odor from bacterial decomposition. In humans, sweating is primarily a means of thermoregulation, which is achieved by the water-rich secretion of the eccrine glands. Maximum sweat rates of an adult can be up to 2–4 liters per hour or 10–14 liters per day (10–15 g/min·m2), but is less in children prior to puberty. Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface has a cooling effect due to evaporative cooling. Hence, in hot wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two weeks, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one tumor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |