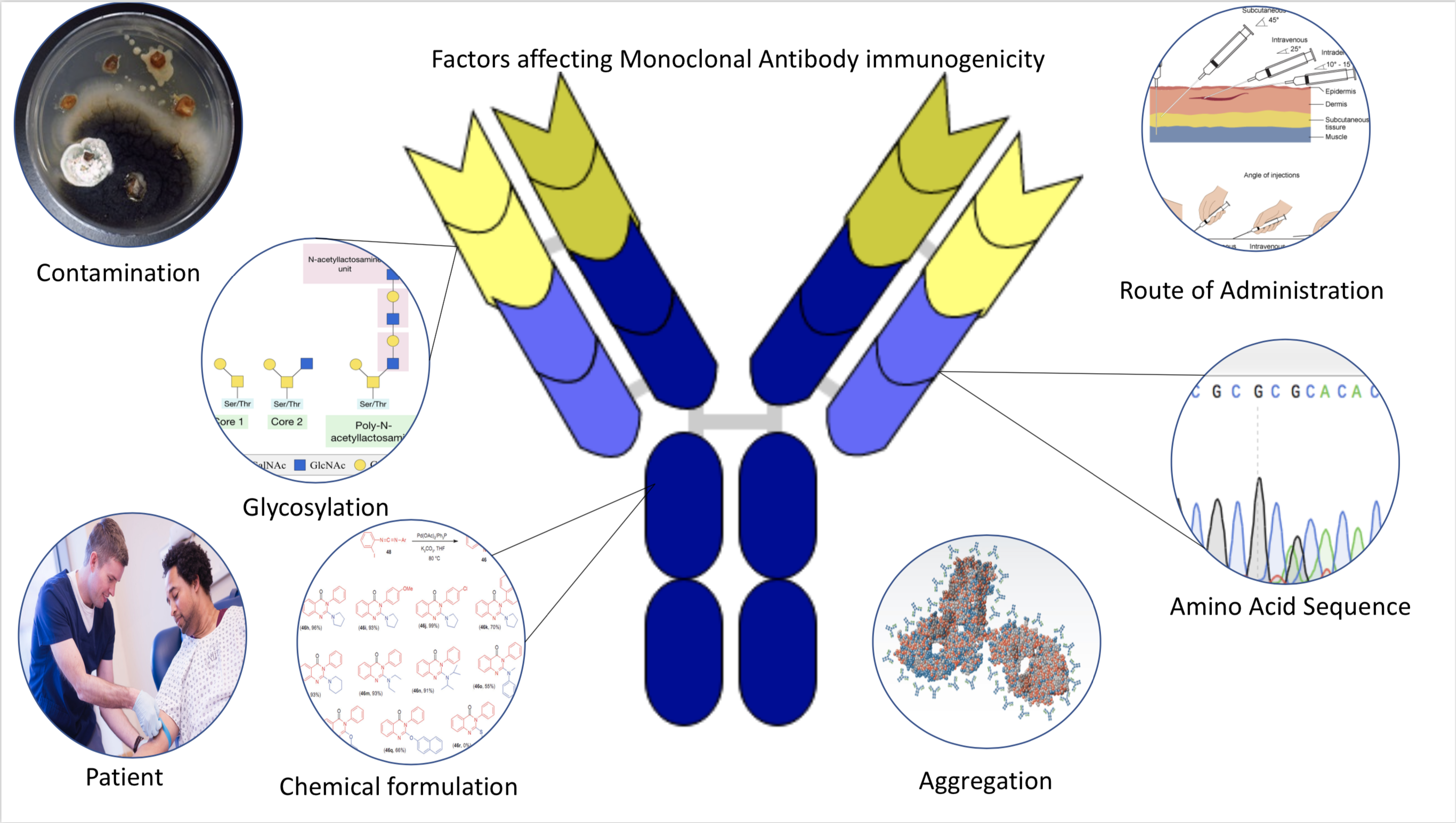
|
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ... to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or Antigen, killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes. The epitopes of protein antigens are divided into two categories, conformational epitopes and linear epitopes, based on their structure and interaction with the paratope. Conformational and linear epitopes interact with the paratope based on the 3-D conformation adopted by the epitope, which is determined by the surface features of the involved epitope residues and the shape or tertiary structure of other segments of the antigen. A conformational epitope is formed by the 3-D conformation adopted by the interac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes. The epitopes of protein antigens are divided into two categories, conformational epitopes and linear epitopes, based on their structure and interaction with the paratope. Conformational and linear epitopes interact with the paratope based on the 3-D conformation adopted by the epitope, which is determined by the surface features of the involved epitope residues and the shape or tertiary structure of other segments of the antigen. A conformational epitope is formed by the 3-D conformation adopted by the interac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunogen
An immunogen is any substance that generates B-cell (humoral/antibody) and/or T-cell (cellular) adaptive immune responses upon exposure to a host organism. Immunogens that generate antibodies are called antigens ("antibody-generating"). Immunogens that generate antibodies are directly bound by host antibodies and lead to the selective expansion of antigen-specific B-cells. Immunogens that generate T-cells are indirectly bound by host T-cells after processing and presentation by host antigen-presenting cells. An immunogen can be defined as a complete antigen which is composed of the macromolecular carrier and epitopes (determinants) that can induce immune response. An explicit example is a hapten. Haptens are low-molecular-weight compounds that may be bound by antibodies, but cannot elicit an immune response. Consequently, the haptens themselves are nonimmunogenic and they cannot evoke an immune response until they bind with a larger carrier immunogenic molecule. The hapten-carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the innate immune system, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen. Antibodies are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity can provide long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Immune Response
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the innate immune system, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen. Antibodies are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity can provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapten
In immunology, haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself (in general, only large molecules, infectious agents, or insoluble foreign matter can elicit an immune response in the body). Once the body has generated antibodies to a hapten-carrier adduct, the small-molecule hapten may also be able to bind to the antibody, but it will usually not initiate an immune response; usually only the hapten-carrier adduct can do this. Sometimes the small-molecule hapten can even block immune response to the hapten-carrier adduct by preventing the adduct from binding to the antibody, a process called ''hapten inhibition''. The mechanisms of absence of immune response may vary and involve complex immunological mechanisms, but can include absent or insufficient co-stimulatory signals from antigen-presenting cells. Haptens have been used to study al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Distance
Genetic distance is a measure of the genetic divergence between species or between populations within a species, whether the distance measures time from common ancestor or degree of differentiation. Populations with many similar alleles have small genetic distances. This indicates that they are closely related and have a recent common ancestor. Genetic distance is useful for reconstructing the history of populations, such as the multiple human expansions out of Africa. It is also used for understanding the origin of biodiversity. For example, the genetic distances between different breeds of domesticated animals are often investigated in order to determine which breeds should be protected to maintain genetic diversity. Biological foundation In the genome of an organism, each gene is located at a specific place called the locus for that gene. Allelic variations at these loci cause phenotypic variation within species (e.g. hair colour, eye colour). However, most alleles do not hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
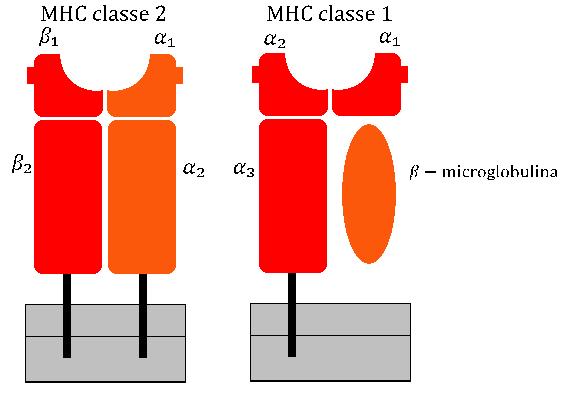
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |