capital letter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (or more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (or more formally ''minuscule'') in the written representation of certain
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (or more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (or more formally ''minuscule'') in the written representation of certain
 There is more variation in the height of the minuscules, as some of them have parts higher ( ascenders) or lower (
There is more variation in the height of the minuscules, as some of them have parts higher ( ascenders) or lower (

 A minority of writing systems use two separate cases. Such writing systems are called ''bicameral scripts''. Languages that use the
A minority of writing systems use two separate cases. Such writing systems are called ''bicameral scripts''. Languages that use the
 In English, a variety of case styles are used in various circumstances:
; Sentence case
: " The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
In English, a variety of case styles are used in various circumstances:
; Sentence case
: " The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
A mixed-case style in which the first word of the sentence is capitalised, as well as proper nouns and other words as required by a more specific rule. This is generally equivalent to the baseline universal standard of formal English orthography. : In
A mixed-case style with all words capitalised, except for certain subsets (particularly
''Start case'' or ''initial caps'' is a simplified variant of title case. In text processing, title case usually involves the capitalisation of all words irrespective of their
A unicase style with capital letters only. This can be used in headings and special situations, such as for typographical emphasis in text made on a typewriter. With the advent of the
Similar in form to capital letters but roughly the size of a lower-case "x", small caps can be used instead of lower-case letters and combined with regular caps in a mixed-case fashion. This is a feature of certain fonts, such as Copperplate Gothic. According to various typographical traditions, the height of small caps can be equal to or slightly larger than the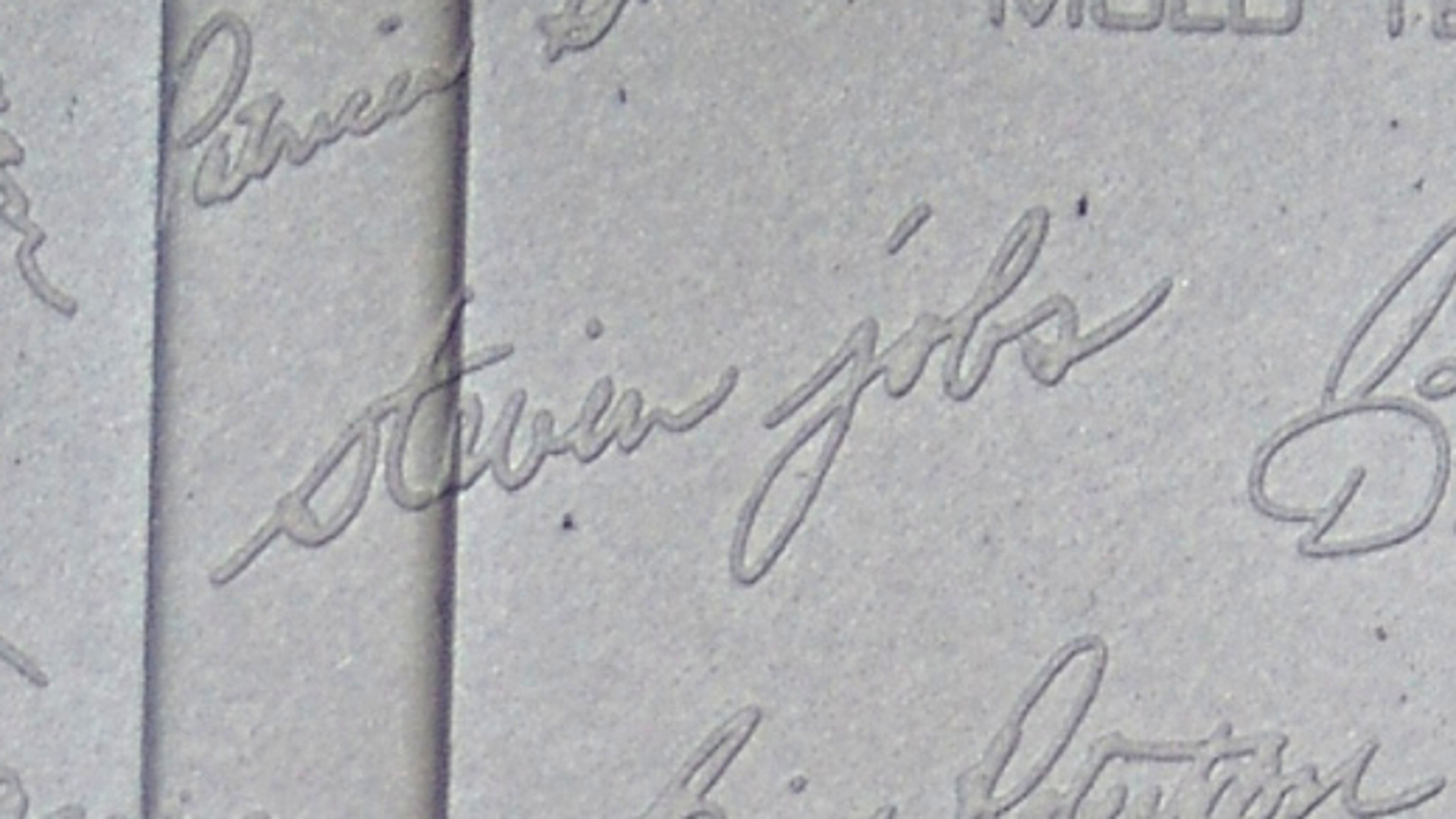 :A unicase style with no capital letters. This is sometimes used for artistic effect, such as in poetry. Also commonly seen in computer languages, and in informal electronic communications such as
:A unicase style with no capital letters. This is sometimes used for artistic effect, such as in poetry. Also commonly seen in computer languages, and in informal electronic communications such as
 In the International System of Units (SI), a letter usually has different meanings in upper and lower case when used as a unit symbol. Generally, unit symbols are written in lower case, but if the name of the unit is derived from a proper noun, the first letter of the symbol is capitalised. Nevertheless, the ''name'' of the unit, if spelled out, is always considered a common noun and written accordingly in lower case. For example:
* 1 s (one second) when used for the base unit of
In the International System of Units (SI), a letter usually has different meanings in upper and lower case when used as a unit symbol. Generally, unit symbols are written in lower case, but if the name of the unit is derived from a proper noun, the first letter of the symbol is capitalised. Nevertheless, the ''name'' of the unit, if spelled out, is always considered a common noun and written accordingly in lower case. For example:
* 1 s (one second) when used for the base unit of
Spaces and
Punctuation is removed and spaces are replaced by single underscores. Normally the letters share the same case (e.g. "UPPER_CASE_EMBEDDED_UNDERSCORE" or "lower_case_embedded_underscore") but the case can be mixed, as in OCaml modules. The style may also be called ''pothole case'', especially in Python programming, in which this convention is often used for naming variables. Illustratively, it may be rendered ''snake_case'', ''pothole_case'', etc. When all-upper-case, it may be referred to as ''screaming snake case'' (or ''SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASE'') or ''hazard case''.
Similar to snake case, above, except
Mixed case with no semantic or
UpperA$ = UCASE$("a")
LowerA$ = LCASE$("A")
C and C++, as well as any C-like language that conforms to its standard library, provide these functions in the file
char upperA = toupper('a');
char lowerA = tolower('A');
Case conversion is different with different character sets. In
#define toupper(c) (islower(c) ? (c) – 'a' + 'A' : (c))
#define tolower(c) (isupper(c) ? (c) – 'A' + 'a' : (c))
This only works because the letters of upper and lower cases are spaced out equally. In ASCII they are consecutive, whereas with EBCDIC they are not; nonetheless the upper-case letters are arranged in the same pattern and with the same gaps as are the lower-case letters, so the technique still works.
Some computer programming languages offer facilities for converting text to a form in which all words are capitalised. Visual Basic calls this "proper case"; Python calls it "title case". This differs from usual title casing conventions, such as the English convention in which minor words are not capitalised.

language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
s. The writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable for ...
s that distinguish between the upper and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters, with each letter in one set usually having an equivalent in the other set. The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order.
Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often prescribed by the grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraint ...
of a language or by the conventions of a particular discipline. In orthography, the uppercase is primarily reserved for special purposes, such as the first letter of a sentence or of a proper noun
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity (''Africa'', '' Jupiter'', ''Sarah'', '' Microsoft)'' as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a class of entities (''contine ...
(called capitalisation, or capitalised words), which makes the lowercase the more common variant in regular text.
In some contexts (e.g. academical), it is conventional to use one case only. For example, engineering design drawings are typically labelled entirely in uppercase letters, which are easier to distinguish individually than the lowercase when space restrictions require that the lettering be very small. In mathematics, on the other hand, letter case may indicate the relationship between mathematical object
A mathematical object is an abstract concept arising in mathematics.
In the usual language of mathematics, an ''object'' is anything that has been (or could be) formally defined, and with which one may do deductive reasoning and mathematical ...
s, with uppercase letters often representing “superior” objects (e.g., ''X'' could be a mathematical set
A set is the mathematical model for a collection of different things; a set contains '' elements'' or ''members'', which can be mathematical objects of any kind: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometrical shapes, variables, or ...
containing the generic member ''x'').
Terminology
The terms ''upper case'' and ''lower case'' may be written as two consecutive words, connected with a hyphen (''upper-case'' and ''lower-case''particularly if they pre-modify another noun), or as a single word (''uppercase'' and ''lowercase''). These terms originated from the common layouts of the shallowdrawers
A drawer is a box-shaped container inside a piece of furniture that can be pulled out horizontally to access its contents. Drawers are built into numerous types of furniture, including cabinets, chests of drawers (bureaus), desks, and the l ...
called '' type cases'' used to hold the movable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric characters or punctuatio ...
for letterpress printing
Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing. Using a printing press, the process allows many copies to be produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. A worker co ...
. Traditionally, the capital letters were stored in a separate shallow tray or "case" that was located above the case that held the small letters.
''Majuscule'' (, less commonly ), for palaeographers, is technically any script whose letters have very few or very short ascenders and descenders, or none at all (for example, the majuscule scripts used in the Codex Vaticanus Graecus 1209, or the Book of Kells). By virtue of their visual impact, this made the term majuscule an apt descriptor for what much later came to be more commonly referred to as uppercase letters.
''Minuscule'' refers to lower-case letters. The word is often spelled ''miniscule'', by association with the unrelated word ''miniature'' and the prefix ''mini-''. This has traditionally been regarded as a spelling mistake (since ''minuscule'' is derived from the word ''minus''), but is now so common that some dictionaries tend to accept it as a nonstandard or variant spelling. ''Miniscule'' is still less likely, however, to be used in reference to lower-case letters.
Typographical considerations
The glyphs of lowercase letters can resemble smaller forms of the uppercase glyphs restricted to the base band (e.g. "C/c" and "S/s", cf. small caps) or can look hardly related (e.g. "D/d" and "G/g"). Here is a comparison of the upper and lower case variants of each letter included in theEnglish alphabet
The alphabet for Modern English is a Latin-script alphabet consisting of 26 Letter (alphabet), letters, each having an Letter case, upper- and lower-case form. The word ''alphabet'' is a Compound (linguistics), compound of the first two lett ...
(the exact representation will vary according to the typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font.
There are thousands ...
and font
In movable type, metal typesetting, a font is a particular #Characteristics, size, weight and style of a typeface. Each font is a matched set of type, with a piece (a "Sort (typesetting), sort") for each glyph. A typeface consists of a range of ...
used):
(Some lowercase letters have variations e.g. a/ɑ)
Typographically, the basic difference between the majuscules and minuscules is not that the majuscules are big and minuscules small, but that the majuscules generally have the same height (although, depending on the typeface, there may be some exceptions, particularly with ''Q'' and sometimes ''J'' having a descending element; also, various diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
s can add to the normal height of a letter).
descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font.
For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal line which lies below the ''v'' ...
s) than the typical size. Normally, ''b, d, f, h, k, l, t '' are the letters with ascenders, and ''g, j, p, q, y'' are the ones with descenders. In addition, with old-style numerals still used by some traditional or classical fonts, ''6'' and ''8'' make up the ascender set, and ''3, 4, 5, 7'' and ''9'' the descender set.
Bicameral script

Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
, Cyrillic, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Coptic, Armenian, Adlam, Warang Citi, Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, th ...
, Garay, Zaghawa, and Osage scripts use letter cases in their written form as an aid to clarity. Another bicameral script, which is not used for any modern languages, is Deseret. The Georgian alphabet
The Georgian scripts are the three writing systems used to write the Georgian language: Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri and Mkhedruli. Although the systems differ in appearance, their letters share the same names and alphabetical order and are written ...
has several variants, and there were attempts to use them as different cases, but the modern written Georgian language
Georgian (, , ) is the most widely-spoken Kartvelian language, and serves as the literary language or lingua franca for speakers of related languages. It is the official language of Georgia and the native or primary language of 87.6% of its p ...
does not distinguish case.
All other writing systems make no distinction between majuscules and minuscules a system called unicameral script or unicase. This includes most syllabic and other non-alphabetic scripts.
In scripts with a case distinction, lower case is generally used for the majority of text; capitals are used for capitalisation and emphasis when bold is not available. Acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in '' NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, a ...
s (and particularly initialisms) are often written in all-caps, depending on various factors.
Capitalisation
Capitalisation is thewriting
Writing is a medium of human communication which involves the representation of a language through a system of physically Epigraphy, inscribed, Printing press, mechanically transferred, or Word processor, digitally represented Symbols (semiot ...
of a word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ...
with its first letter in uppercase and the remaining letters in lowercase. Capitalisation rules vary by language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
and are often quite complex, but in most modern languages that have capitalisation, the first word of every sentence is capitalised, as are all proper noun
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity (''Africa'', '' Jupiter'', ''Sarah'', '' Microsoft)'' as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a class of entities (''contine ...
s.
Capitalisation in English, in terms of the general orthographic rules independent of context (e.g. title vs. heading vs. text), is universally standardised for formal
Formal, formality, informal or informality imply the complying with, or not complying with, some set of requirements (forms, in Ancient Greek). They may refer to:
Dress code and events
* Formal wear, attire for formal events
* Semi-formal attire ...
writing. Capital letters are used as the first letter of a sentence, a proper noun, or a proper adjective English orthography sometimes uses the term proper adjective to mean adjectives that take initial capital letters, and common adjective to mean those that do not. For example, a person from India is Indian—''Indian'' is a proper adjective.
Etymol ...
. The names of the days of the week
In many languages, the names given to the seven days of the week are derived from the names of the classical planets in Hellenistic astronomy, which were in turn named after contemporary deities, a system introduced by the Sumerians and la ...
and the names of the months are also capitalised, as are the first-person pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would n ...
"I" and the vocative particle " O". There are a few pairs of words of different meanings whose only difference is capitalisation of the first letter. Honorific
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an honorary academic title. It ...
s and personal title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the f ...
s showing rank or prestige are capitalised when used together with the name of the person (for example, "Mr. Smith", "Bishop O'Brien", "Professor Moore") or as a direct address, but normally not when used alone and in a more general sense. It can also be seen as customary to capitalise any word in some contexts even a pronoun referring to the deity of a monotheistic religion
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
.
Other words normally start with a lower-case letter. There are, however, situations where further capitalisation may be used to give added emphasis, for example in headings and publication titles (see below). In some traditional forms of poetry, capitalisation has conventionally been used as a marker to indicate the beginning of a line of verse independent of any grammatical feature. In political writing, parody and satire, the unexpected emphasis afforded by otherwise ill-advised capitalisation is often used to great stylistic effect, such as in the case of George Orwell's Big Brother
Big Brother may refer to:
* Big Brother (''Nineteen Eighty-Four''), a character from George Orwell's novel ''Nineteen Eighty-Four''
** Authoritarian personality, any omnipresent figure representing oppressive control
** Big Brother Awards, a sat ...
.
Other languages vary in their use of capitals. For example, in German all nouns are capitalised (this was previously common in English as well, mainly in the 17th and 18th centuries), while in Romance and most other European languages the names of the days of the week, the names of the months, and adjectives of nationality, religion, and so on normally begin with a lower-case letter. On the other hand, in some languages it is customary to capitalise formal polite pronouns, for example ''De'', ''Dem'' ( Danish), ''Sie'', ''Ihnen'' (German), and ''Vd'' or ''Ud'' (short for ''usted'' in Spanish).
Informal communication, such as texting, instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of online chat allowing real-time text transmission over the Internet or another computer network. Messages are typically transmitted between two or more parties, when each user inputs text and trigge ...
or a handwritten sticky note
A Post-it Note (or sticky note) is a small piece of paper with a re-adherable strip of glue on its back, made for temporarily attaching notes to documents and other surfaces. A low-tack pressure-sensitive adhesive allows the notes to be easily ...
, may not bother to follow the conventions concerning capitalisation, but that is because its users usually do not expect it to be formal.
Exceptional letters and digraphs
* The German letter " ß" formerly existed only in lower case. The orthographical capitalisation does not concern "ß", which generally does not occur at the beginning of a word, and in the all-caps style it has traditionally been replaced by the digraph "SS". Since June 2017, however, capital ẞ is accepted as an alternative in the all-caps style. * The Greek upper-case letter " Σ" has two different lower-case forms: "ς" in word-final position and "σ" elsewhere. In a similar manner, the Latin upper-case letter " S" used to have two different lower-case forms: "s" in word-final position and " ſ " elsewhere. The latter form, called thelong s
The long s , also known as the medial s or initial s, is an archaic form of the lowercase letter . It replaced the single ''s'', or one or both of the letters ''s'' in a 'double ''s sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſ� ...
, fell out of general use before the middle of the 19th century, except for the countries that continued to use blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for the Danish, Norweg ...
typefaces such as Fraktur
Fraktur () is a calligraphic hand of the Latin alphabet and any of several blackletter typefaces derived from this hand. The blackletter lines are broken up; that is, their forms contain many angles when compared to the curves of the Anti ...
. When blackletter type fell out of general use in the mid-20th century, even those countries dropped the long s.
* The treatment of the Greek iota subscript
The iota subscript is a diacritic mark in the Greek alphabet shaped like a small vertical stroke or miniature iota placed below the letter. It can occur with the vowel letters eta , omega , and alpha . It represents the former presence of an ...
with upper-case letters is complicated.
* Unlike most languages that use Latin-script and link the dotless upper-case " I" with the dotted lower-case "i", Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
as well as some forms of Azeri have both a dotted and dotless I, each in both upper and lower case. Each of the two pairs ("İ/i" and "I/ı") represents a distinctive phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
.
* In some languages, specific digraphs may be regarded as single letters, and in Dutch, the digraph " IJ/ij" is even capitalised with both components written in uppercase (for example, "IJsland" rather than "Ijsland"). In other languages, such as Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
and Hungarian, various digraphs are regarded as single letters for collation purposes, but the second component of the digraph will still be written in lower case even if the first component is capitalised. Similarly, in South Slavic languages whose orthography is coordinated between the Cyrillic and Latin scripts, the Latin digraphs " Lj/lj", " Nj/nj" and " Dž/dž" are each regarded as a single letter (like their Cyrillic equivalents " Љ/љ", " Њ/њ" and " Џ/џ", respectively), but only in all-caps style should both components be in upper case (e.g. Ljiljan–LJILJAN, Njonja–NJONJA, Džidža–DŽIDŽA). Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
designates a single character for each case variant (i.e., upper case, title case and lower case) of the three digraphs.
* Some English surnames such as fforbes are traditionally spelt with a digraph instead of a capital letter (at least for ff). This indicates a long and prestigious family tradition.
* In the Hawaiian orthography, the okina Okina may refer to:
* ʻOkina, a letter used in some Polynesian languages, visually resembling a left single quotation mark
* Okina () or , a character from the ''Rurouni Kenshin'' manga series
* Okina, Spain, a village in the Basque Country
* , ...
is a phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
symbol that visually resembles a left single quotation mark
Quotation marks (also known as quotes, quote marks, speech marks, inverted commas, or talking marks) are punctuation marks used in pairs in various writing systems to set off direct speech, a quotation, or a phrase. The pair consists of an ...
. Representing the glottal stop, the okina can be characterised as either a letter or a diacritic
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
. As a unicase letter, the okina is unaffected by capitalisation; it is the following letter that is capitalised instead. According to the Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
standard, the okina is formally encoded as , but it is not uncommon to substitute this with a similar punctuation
Punctuation (or sometimes interpunction) is the use of spacing, conventional signs (called punctuation marks), and certain typographical devices as aids to the understanding and correct reading of written text, whether read silently or aloud. A ...
character, such as the left single quotation mark or an apostrophe
The apostrophe ( or ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes:
* The marking of the omission of one ...
.
Related phenomena
Similar orthographic and graphostylistic conventions are used for emphasis or following language-specific or other rules, including: *Font
In movable type, metal typesetting, a font is a particular #Characteristics, size, weight and style of a typeface. Each font is a matched set of type, with a piece (a "Sort (typesetting), sort") for each glyph. A typeface consists of a range of ...
effects such as italic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, italics normally slant slightly to the right. Italics are a way to emphasise key points in a printed tex ...
or oblique type
Oblique type is a form of type that slants slightly to the right, used for the same purposes as italic type. Unlike italic type, however, it does not use different glyph shapes; it uses the same glyphs as roman type, except slanted. Oblique and i ...
, boldface, and choice of serif vs. sans-serif.
* Typographical conventions in mathematical formulae
Typographical conventions in mathematical formulae provide uniformity across mathematical texts and help the readers of those texts to grasp new concepts quickly.
Mathematical notation includes letters from various alphabets, as well as special m ...
include the use of Greek letters and the use of Latin letters with special formatting such as blackboard bold and blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for the Danish, Norweg ...
.
* Some letters of the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
and Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet ( he, אָלֶף־בֵּית עִבְרִי, ), known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is an abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewis ...
s and some jamo of the Korean hangul
The Korean alphabet, known as Hangul, . Hangul may also be written as following South Korea's standard Romanization. ( ) in South Korea and Chosŏn'gŭl in North Korea, is the modern official writing system for the Korean language. The ...
have different forms depending on placement within a word, but these rules are strict and the different forms cannot be used for emphasis.
**In the Arabic and Arabic-based alphabets, letters in a word are connected, except for several that cannot connect to the following letter. Letters may have distinct forms depending on whether they are initial (connected only to the following letter), medial (connected to both neighboring letters), final (connected only to the preceding letter), or isolated (connected to neither a preceding nor a following letter).
**In the Hebrew alphabet, five letters have a distinct form (see Final form) that is used when they are word-final.
* In Georgian, some authors use isolated letters from the ancient Asomtavruli
The Georgian scripts are the three writing systems used to write the Georgian language: Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri and Mkhedruli. Although the systems differ in appearance, their letters share the same names and alphabetical order and are written hor ...
alphabet within a text otherwise written in the modern Mkhedruli in a fashion that is reminiscent of the usage of upper-case letters in the Latin, Greek, and Cyrillic alphabets.
* In the Japanese writing system
The modern Japanese writing system uses a combination of logographic kanji, which are adopted Chinese characters, and syllabic kana. Kana itself consists of a pair of syllabaries: hiragana, used primarily for native or naturalised Japanese w ...
, an author has the option of switching between kanji
are the logographic Chinese characters taken from the Chinese script and used in the writing of Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are still used, along with the subse ...
, hiragana
is a Japanese language, Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''.
It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' literally means "flowing" or "simple" kana ("simple" ori ...
, katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji). The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived f ...
, and rōmaji. In particular, every hiragana character has an equivalent katakana character, and vice versa. Romanised Japanese sometimes uses lowercase letters to represent words that would be written in hiragana, and uppercase letters to represent words that would be written in katakana. Some kana characters are written in smaller type when they modify or combine with the preceding sign ('' yōon'') or the following sign (''sokuon
The is a Japanese symbol in the form of a small hiragana or katakana '' tsu''. In less formal language it is called or , meaning "small ''tsu''". It serves multiple purposes in Japanese writing.
Appearance
In both hiragana and katakana, ...
'').
Stylistic or specialised usage
 In English, a variety of case styles are used in various circumstances:
; Sentence case
: " The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
In English, a variety of case styles are used in various circumstances:
; Sentence case
: " The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"A mixed-case style in which the first word of the sentence is capitalised, as well as proper nouns and other words as required by a more specific rule. This is generally equivalent to the baseline universal standard of formal English orthography. : In
computer programming
Computer programming is the process of performing a particular computation (or more generally, accomplishing a specific computing result), usually by designing and building an executable computer program. Programming involves tasks such as anal ...
, the initial capital is easier to automate than the other rules. For example, on English-language Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read ref ...
, the first character in page titles is capitalised by default. Because the other rules are more complex, substrings for concatenation
In formal language theory and computer programming, string concatenation is the operation of joining character strings end-to-end. For example, the concatenation of "snow" and "ball" is "snowball". In certain formalisations of concatenat ...
into sentences are commonly written in "mid-sentence case", applying all the rules of sentence case except the initial capital.
; Title case (capital case, headline style)
: "The Quick Brown Fox Jumps over the Lazy Dog"A mixed-case style with all words capitalised, except for certain subsets (particularly
articles
Article often refers to:
* Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness
* Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication
Article may also refer to:
...
and short prepositions and conjunctions
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy)
In astronomy, a conjunction occ ...
) defined by rules that are not universally standardised. The standardisation is only at the level of house styles and individual style manuals.
; Start case (First letter of each word capitalized)
: "The Quick Brown Fox Jumps Over The Lazy Dog"''Start case'' or ''initial caps'' is a simplified variant of title case. In text processing, title case usually involves the capitalisation of all words irrespective of their
part of speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are as ...
.
; All caps (all uppercase)
: "THE QUICK BROWN FOX JUMPS OVER THE LAZY DOG"A unicase style with capital letters only. This can be used in headings and special situations, such as for typographical emphasis in text made on a typewriter. With the advent of the
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
, the all-caps style is more often used for emphasis; however, it is considered poor netiquette by some to type in all capitals, and said to be tantamount to shouting.RFC 1855 "Netiquette Guidelines" Long spans of Latin-alphabet text in all upper-case are more difficult to read because of the absence of the ascenders and descender
In typography and handwriting, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font.
For example, in the letter ''y'', the descender is the "tail", or that portion of the diagonal line which lies below the ''v'' ...
s found in lower-case letters, which aids recognition and legibility. In some cultures it is common to write family names in all caps to distinguish them from the given names, especially in identity documents such as passports.
; Small caps
In typography, small caps (short for "small capitals") are characters typeset with glyphs that resemble uppercase letters (capitals) but reduced in height and weight close to the surrounding lowercase letters or text figures. This is technica ...
: ""Similar in form to capital letters but roughly the size of a lower-case "x", small caps can be used instead of lower-case letters and combined with regular caps in a mixed-case fashion. This is a feature of certain fonts, such as Copperplate Gothic. According to various typographical traditions, the height of small caps can be equal to or slightly larger than the
x-height
upright 2.0, alt=A diagram showing the line terms used in typography
In typography, the x-height, or corpus size, is the distance between the baseline and the mean line of lowercase letters in a typeface. Typically, this is the height of the let ...
of the typeface (the smaller variant is sometimes called ''petite caps'' and may also be mixed with the larger variant). Small caps can be used for acronyms, names, mathematical entities, computer commands in printed text, business or personal printed stationery letterheads, and other situations where a given phrase needs to be distinguished from the main text.
; All lowercase
:"the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
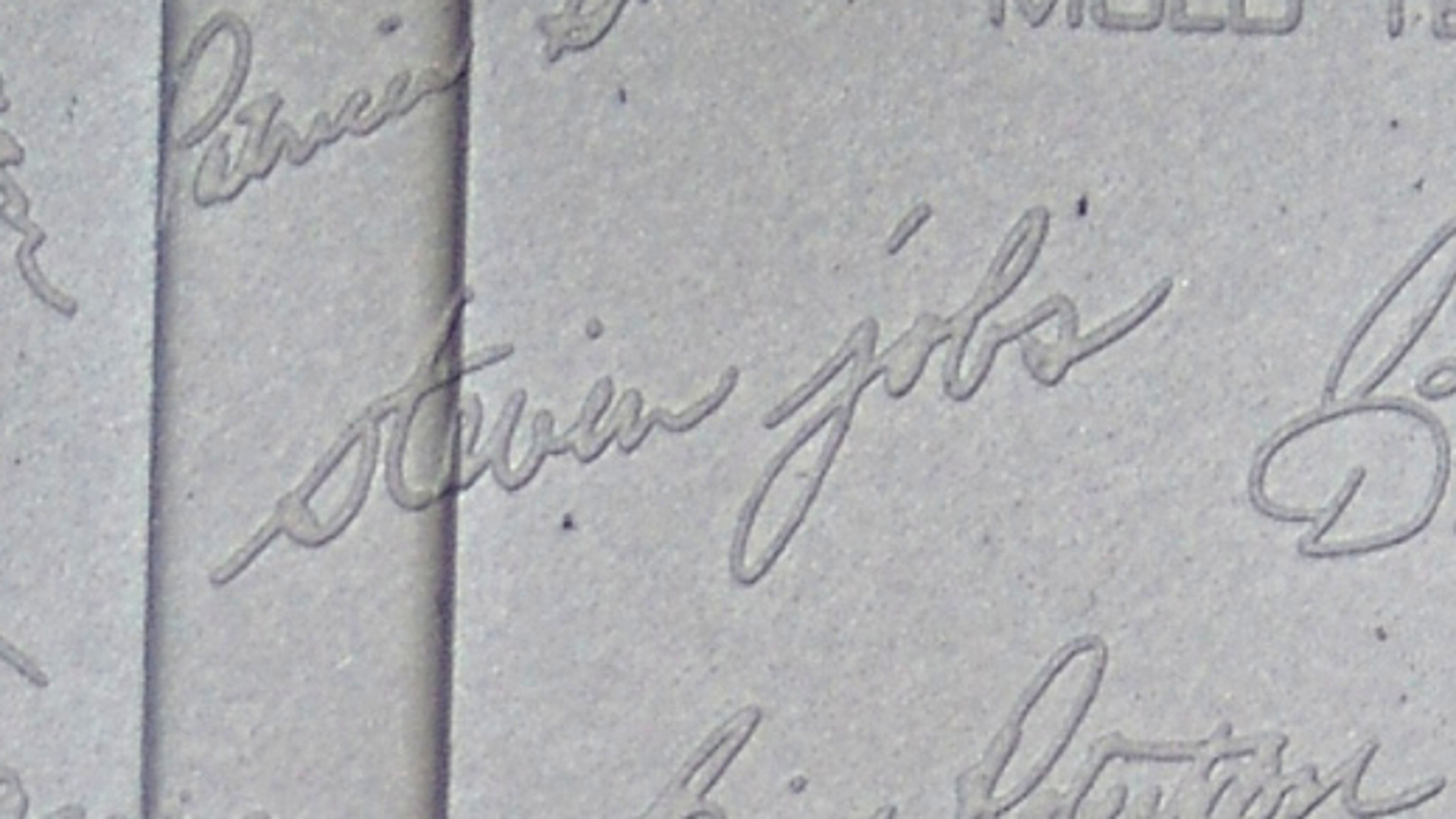 :A unicase style with no capital letters. This is sometimes used for artistic effect, such as in poetry. Also commonly seen in computer languages, and in informal electronic communications such as
:A unicase style with no capital letters. This is sometimes used for artistic effect, such as in poetry. Also commonly seen in computer languages, and in informal electronic communications such as SMS language
Short Message Service (SMS) language, textism, or textese is the abbreviated language and slang commonly used in the late 1990s and early 2000s with mobile phone text messaging, and occasionally through Internet-based communication such as em ...
and instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of online chat allowing real-time text transmission over the Internet or another computer network. Messages are typically transmitted between two or more parties, when each user inputs text and trigge ...
(avoiding the shift key
The Shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row. The Shift key's name originated ...
, to type more quickly). Apple co-founder Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; ...
used all-lowercase (in cursive
Cursive (also known as script, among other names) is any style of penmanship in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters. It varies in functional ...
) in his signature.
Headings and publication titles
In English-language publications, various conventions are used for the capitalisation of words in publication titles and headlines, including chapter and section headings. The rules differ substantially between individual house styles. The convention followed by many Britishpublisher
Publishing is the activity of making information, literature, music, software and other content available to the public for sale or for free. Traditionally, the term refers to the creation and distribution of printed works, such as books, newsp ...
s (including scientific publishers like ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
'' and ''New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publish ...
'', magazines like ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econ ...
'', and newspapers like ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
Newspapers can cover a wide ...
'' and ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ...
'') and many U.S. newspapers is sentence-style capitalisation in headlines, i.e. capitalisation follows the same rules that apply for sentences. This convention is usually called ''sentence case''. It may also be applied to publication titles, especially in bibliographic references and library catalogues. An example of a global publisher whose English-language house style prescribes sentence-case titles and headings is the International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Ar ...
(ISO).
For publication titles it is, however, a common typographic practice among both British and U.S. publishers to capitalise significant words (and in the United States, this is often applied to headings, too). This family of typographic conventions is usually called '' title case''. For example, R. M. Ritter's ''Oxford Manual of Style'' (2002) suggests capitalising "the first word and all nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs and adverbs, but generally not articles, conjunctions and short prepositions". This is an old form of emphasis, similar to the more modern practice of using a larger or boldface font for titles. The rules which prescribe which words to capitalise are not based on any grammatically inherent correct–incorrect distinction and are not universally standardised; they differ between style guides, although most style guides tend to follow a few strong conventions, as follows:
* Most styles capitalise all words except for short closed-class words (certain parts of speech, namely, articles, prepositions, and conjunctions); but the first word (always) and last word (in many styles) are also capitalised, regardless of their part of speech. Many styles capitalise longer prepositions such as "between" and "throughout", but not shorter ones such as "for" and "with". Typically, a preposition is considered short if it has up to three or four letters.
* A few styles capitalise all words in title case (the so-called ''start case''), which has the advantage of being easy to implement and hard to get "wrong" (that is, "not edited to style"). Because of this rule's simplicity, software case-folding routines can handle 95% or more of the editing, especially if they are programmed for desired exceptions (such as "FBI" rather than "Fbi").
* As for whether hyphenated words are capitalised not only at the beginning but also after the hyphen, there is no universal standard; variation occurs in the wild and among house styles (e.g., "The Letter-''C''ase Rule in My Book"; "Short-''t''erm Follow-''u''p Care for Burns"). Traditional copyediting makes a distinction between ''temporary compounds'' (such as many nonce
Nonce may refer to:
* Cryptographic nonce, a number or bit string used only once, in security engineering
* Nonce word, a word used to meet a need that is not expected to recur
* The Nonce, American rap duo
* Nonce orders, an architectural term
...
ovel instance compound modifiers), in which every part of the hyphenated word is capitalised (e.g. "How This Particular Author Chose to Style His ''A''utumn-''A''pple-''P''icking Heading"), and ''permanent compounds'', which are terms that, although compound and hyphenated, are so well established that dictionaries enter them as headwords (e.g., "Short-''t''erm Follow-''u''p Care for Burns").
Title case is widely used in many English-language publications, especially in the United States. However, its conventions are sometimes not followed strictly especially in informal writing.
In creative typography, such as music record covers and other artistic material, all styles are commonly encountered, including all-lowercase letters and special case styles, such as studly caps
Alternating caps, also known as studly caps or sticky caps (where "caps" is short for capital letters), is a form of text notation in which the capitalization of letters varies by some pattern, or arbitrarily (often also omitting spaces between w ...
(see below). For example, in the wordmarks of video games it is not uncommon to use stylised upper-case letters at the beginning and end of a title, with the intermediate letters in small caps or lower case (e.g., , , and DmC).
Multi-word proper nouns
Single-wordproper nouns
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity (''Africa'', ''Jupiter'', ''Sarah (given name), Sarah'', ''Microsoft)'' as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a Class (philo ...
are capitalised in formal written English, unless the name is intentionally stylised to break this rule (such as the first or last name of danah boyd).
Multi-word proper nouns include names of organisations, publications, and people. Often the rules for "title case" (described in the previous section) are applied to these names, so that non-initial articles, conjunctions, and short prepositions are lowercase, and all other words are uppercase. For example, the short preposition "of" and the article "the" are lowercase in "Steering Committee of the Finance Department". Usually only capitalised words are used to form an acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in '' NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, a ...
variant of the name, though there is some variation in this.
With personal names, this practice can vary (sometimes all words are capitalised, regardless of length or function), but is not limited to English names. Examples include the English names Tamar of Georgia
Tamar the Great ( ka, თამარ მეფე, tr, Literal translation, lit. "King Tamar") ( 1160 – 18 January 1213) queen regnant, reigned as the List of monarchs of Georgia#Kings of unified Georgia (1008–1490), Queen of Kingdom of ...
and Catherine the Great, "van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
" and "der" in Dutch name
Dutch names consist of one or more given names and a surname. The given name is usually gender-specific.
Dutch given names
A Dutch child's birth and given name(s) must be officially registered by the parents within 3 days after birth. It is not u ...
s, " von" and "zu" in German, "de", "los", and "y" in Spanish names, "de" or "d'" in French names, and "ibn" in Arabic name
Arabic language names have historically been based on a long naming system. Many people from the Arabic-speaking and also Muslim countries have not had given/middle/ family names but rather a chain of names. This system remains in use throughout ...
s.
Some surname prefixes also affect the capitalisation of the following internal letter or word, for example "Mac" in Celtic names
Onomastics is an important source of information on the early Celts, as Greco-Roman historiography recorded Celtic names before substantial written information becomes available in any Celtic language.
Like Germanic names, early Celtic names are ...
and "Al" in Arabic names.
Unit symbols and prefixes in the metric system
time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
.
* 1 S (one siemens) when used for the unit of electric conductance and admittance (named after Werner von Siemens
Ernst Werner Siemens ( von Siemens from 1888; ; ; 13 December 1816 – 6 December 1892) was a German electrical engineer, inventor and industrialist. Siemens's name has been adopted as the SI unit of electrical conductance, the siemens. He f ...
).
* 1 Sv (one sievert), used for the unit of ionising radiation dose (named after Rolf Maximilian Sievert).
For the purpose of clarity, the symbol for litre can optionally be written in upper case even though the name is not derived from a proper noun. For example, "one litre" may be written as:
* 1 l, the original form, for typefaces in which "digit one" , "lower-case ell" , and "upper-case i" look different.
* 1 L, an alternative form, for typefaces in which these characters are difficult to distinguish, or the typeface the reader will be using is unknown. A " script l" in various typefaces (e.g.: 1 l) has traditionally been used in some countries to prevent confusion; however, the separate Unicode character which represents this, , is deprecated by the SI. Another solution sometimes seen in Web typography is to use a serif font for "lower-case ell" in otherwise sans-serif material (1 l).
The letter case of a prefix symbol is determined independently of the unit symbol to which it is attached. Lower case is used for all submultiple prefix symbols and the small multiple prefix symbols up to "k" (for kilo, meaning 103 = 1000 multiplier), whereas upper case is used for larger multipliers:
* 1 ms, millisecond, a small measure of time ("m" for milli, meaning 10−3 = 1/1000 multiplier).
* 1 Ms, megasecond, a large measure of time ("M" for mega, meaning 106 = 1 000 000 multiplier).
* 1 mS, millisiemens
The siemens (symbol: S) is the unit of electric conductance, electric susceptance, and electric admittance in the International System of Units (SI). Conductance, susceptance, and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance, reactance, and ...
, a small measure of electric conductance.
* 1 MS, megasiemens, a large measure of electric conductance.
* 1 mm, millimetre, a small measure of length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Inte ...
.
* 1 Mm, megametre, a large measure of length.
Use within programming languages
Some case styles are not used in standard English, but are common incomputer programming
Computer programming is the process of performing a particular computation (or more generally, accomplishing a specific computing result), usually by designing and building an executable computer program. Programming involves tasks such as anal ...
, product brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create a ...
ing, or other specialised fields.
The usage derives from how programming languages are parsed, programmatically. They generally separate their syntactic tokens by simple whitespace
White space or whitespace may refer to:
Technology
* Whitespace characters, characters in computing that represent horizontal or vertical space
* White spaces (radio), allocated but locally unused radio frequencies
* TV White Space Database, a mec ...
, including space characters, tabs, and newlines. When the tokens, such as function and variable names start to multiply in complex software development
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components. Software development inv ...
, and there is still a need to keep the source code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comment (computer programming), comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a Computer program, p ...
human-readable, Naming conventions make this possible. So for example, a function dealing with matrix multiplication might formally be called:
** ''SGEMM(*)'', with the asterisk standing in for an equally inscrutable list of 13 parameters (in BLAS),
** ''MultiplyMatrixByMatrix(Matrix x, Matrix y)'', in some hypothetical higher level manifestly typed language, broadly following the syntax of C++ or Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
,
** ''multiply-matrix-by-matrix(x, y)'' in something derived from LISP
A lisp is a speech impairment in which a person misarticulates sibilants (, , , , , , , ). These misarticulations often result in unclear speech.
Types
* A frontal lisp occurs when the tongue is placed anterior to the target. Interdental lispi ...
, or perhaps
** ''(multiply (x y))'' in the CLOS, or some newer derivative language supporting type inference and multiple dispatch.
In each case the capitalisation or lack thereof supports a different function. In the first, FORTRAN compatibility requires case-insensitive naming and short function names. The second supports easily discernible function and argument names and types, within the context of an imperative, strongly typed language. The third supports the macro facilities of LISP, and its tendency to view programs and data minimalistically, and as interchangeable. The fourth idiom needs much less syntactic sugar overall, because much of the semantics are implied, but because of its brevity and so lack of the need for capitalization or multipart words at all, might also make the code too abstract and overloaded for the common programmer to understand.
Understandably then, such coding conventions are highly subjective, and can lead to rather opinionated debate, such as in the case of editor war
The editor war is the rivalry between users of the Emacs and vi (now usually Vim, or more recently Neovim) text editors. The rivalry has become an enduring part of hacker culture and the free software community.
The Emacs versus vi debate was o ...
s, or those about indent style
In computer programming, an indentation style is a convention governing the indentation of blocks of code to convey program structure. This article largely addresses the free-form languages, such as C and its descendants, but can be (and oft ...
. Capitalisation is no exception.
Camel case
Camel case: "theQuickBrownFoxJumpsOverTheLazyDog" or "TheQuickBrownFoxJumpsOverTheLazyDog"Spaces and
punctuation
Punctuation (or sometimes interpunction) is the use of spacing, conventional signs (called punctuation marks), and certain typographical devices as aids to the understanding and correct reading of written text, whether read silently or aloud. A ...
are removed and the first letter of each word is capitalised. If this includes the first letter of the first word (CamelCase, " PowerPoint", "TheQuick...", etc.), the case is sometimes called upper camel case (or, illustratively, CamelCase), Pascal case in reference to the Pascal programming language or bumpy case.
When the first letter of the first word is lowercase ("iPod
The iPod is a discontinued series of portable media players and multi-purpose mobile devices designed and marketed by Apple Inc. The first version was released on October 23, 2001, about months after the Macintosh version of iTunes ...
", "eBay
eBay Inc. ( ) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that facilitates consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer sales through its website. eBay was founded by Pierre Omidyar in 1995 and became ...
", "theQuickBrownFox..."), the case is usually known as lower camel case or dromedary case (illustratively: dromedaryCase). This format has become popular in the branding of information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system ...
products and services, with an initial "i" meaning "Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists ...
" or "intelligent", as in iPod
The iPod is a discontinued series of portable media players and multi-purpose mobile devices designed and marketed by Apple Inc. The first version was released on October 23, 2001, about months after the Macintosh version of iTunes ...
, or an initial "e" meaning "electronic", as in email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" mean ...
(electronic mail) or e-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) is the activity of electronically buying or selling of products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain mana ...
(electronic commerce).
Snake case
Snake case: "the_quick_brown_fox_jumps_over_the_lazy_dog"Punctuation is removed and spaces are replaced by single underscores. Normally the letters share the same case (e.g. "UPPER_CASE_EMBEDDED_UNDERSCORE" or "lower_case_embedded_underscore") but the case can be mixed, as in OCaml modules. The style may also be called ''pothole case'', especially in Python programming, in which this convention is often used for naming variables. Illustratively, it may be rendered ''snake_case'', ''pothole_case'', etc. When all-upper-case, it may be referred to as ''screaming snake case'' (or ''SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASE'') or ''hazard case''.
Kebab case
Kebab case: "the-quick-brown-fox-jumps-over-the-lazy-dog"Similar to snake case, above, except
hyphen
The hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words and to separate syllables of a single word. The use of hyphens is called hyphenation. ''Son-in-law'' is an example of a hyphenated word. The hyphen is sometimes confused with dashes ( figur ...
s rather than underscores are used to replace spaces. It is also known as spinal case, param case, Lisp case in reference to the Lisp programming language
Lisp (historically LISP) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation.
Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common ...
, or dash case (or illustratively as kebab-case). If every word is capitalised, the style is known as train case (''TRAIN-CASE'').
In CSS, all property names and most keyword values are primarily formatted in kebab case.
Studly caps
Studly caps
Alternating caps, also known as studly caps or sticky caps (where "caps" is short for capital letters), is a form of text notation in which the capitalization of letters varies by some pattern, or arbitrarily (often also omitting spaces between w ...
: e.g. "tHeqUicKBrOWnFoXJUmpsoVeRThElAzydOG"Mixed case with no semantic or
syntactic
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituenc ...
significance to the use of the capitals. Sometimes only vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (l ...
s are upper case, at other times upper and lower case are alternated, but often it is simply random. The name comes from the sarcastic or ironic implication that it was used in an attempt by the writer to convey their own coolness. It is also used to mock the violation of standard English case conventions by marketers in the naming of computer software packages, even when there is no technical requirement to do soe.g., Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. (Sun for short) was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, ...
' naming of a windowing system NeWS. Illustrative naming of the style is, naturally, random: ''stUdlY cAps'', ''StUdLy CaPs'', etc.
Case folding and case conversion
In the character sets developed forcomputing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
, each upper- and lower-case letter is encoded as a separate character. In order to enable case folding and case conversion, the software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
...
needs to link together the two characters representing the case variants of a letter. (Some old character-encoding systems, such as the Baudot code, are restricted to one set of letters, usually represented by the upper-case variants.)
Case-insensitive operations can be said to fold case, from the idea of folding the character code table so that upper- and lower-case letters coincide. The conversion of letter case in a string
String or strings may refer to:
*String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian anim ...
is common practice in computer applications, for instance to make case-insensitive comparisons. Many high-level programming languages provide simple methods for case conversion, at least for the ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because ...
character set.
Whether or not the case variants are treated as equivalent to each other varies depending on the computer system and context. For example, user passwords are generally case sensitive in order to allow more diversity and make them more difficult to break. In contrast, case is often ignored in keyword searches in order to ignore insignificant variations in keyword capitalisation both in queries and queried material.
Unicode case folding and script identification
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
defines case folding through the three case-mapping properties of each character
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
: upper case, lower case, and title case (in this context, "title case" relates to ligatures and digraphs encoded as mixed-case single characters, in which the first component is in upper case and the second component in lower case). These properties relate all characters in scripts with differing cases to the other case variants of the character.
As briefly discussed in Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, ...
Technical Note #26, "In terms of implementation issues, any attempt at a unification of Latin, Greek, and Cyrillic would wreak havoc ndmake casing operations an unholy mess, in effect making all casing operations context sensitive ��. In other words, while the shapes of letters like A, B, E, H, K, M, O, P, T, X, Y and so on are shared between the Latin, Greek, and Cyrillic alphabets (and small differences in their canonical forms may be considered to be of a merely typographical nature), it would still be problematic for a multilingual character set or a font
In movable type, metal typesetting, a font is a particular #Characteristics, size, weight and style of a typeface. Each font is a matched set of type, with a piece (a "Sort (typesetting), sort") for each glyph. A typeface consists of a range of ...
to provide only a ''single'' code point
In character encoding terminology, a code point, codepoint or code position is a numerical value that maps to a specific character. Code points usually represent a single grapheme—usually a letter, digit, punctuation mark, or whitespace—bu ...
for, say, uppercase letter B, as this would make it quite difficult for a wordprocessor to change that single uppercase letter to one of the three different choices for the lower-case letter, the Latin b (U+0062), Greek β (U+03B2) or Cyrillic в (U+0432). Therefore, the corresponding Latin, Greek and Cyrillic upper-case letters (U+0042, U+0392 and U+0412, respectively) are also encoded as separate characters, despite their appearance being basically identical. Without letter case, a "unified European alphabet"such as ABБCГDΔΕЄЗFΦGHIИJ...Z, with an appropriate subset for each languageis feasible; but considering letter case, it becomes very clear that these alphabets are rather distinct sets of symbols.
Methods in word processing
Most modernword processor
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Word processor (electronic device), Early word processors were stand-alone devices ded ...
s provide automated case conversion with a simple click or keystroke. For example, in Microsoft Office Word, there is a dialog box for toggling the selected text through UPPERCASE, then lowercase, then Title Case (actually start caps; exception words must be lowercased individually). The keystroke does the same thing.
Methods in programming
In some forms ofBASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
there are two methods for case conversion:
ctype.h
C character classification is an operation provided by a group of functions in the ANSI C Standard Library for the C programming language
''The C Programming Language'' (sometimes termed ''K&R'', after its authors' initials) is a computer pr ...
:
ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because ...
or EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding s ...
, case can be converted in the following way, in C:
History
Originallyalphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a s ...
s were written entirely in majuscule letters, spaced between well-defined upper and lower bounds. When written quickly with a pen, these tended to turn into rounder and much simpler forms. It is from these that the first minuscule hands developed, the half-uncial
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th ...
s and cursive minuscule, which no longer stayed bound between a pair of lines. These in turn formed the foundations for the Carolingian minuscule
Carolingian minuscule or Caroline minuscule is a script which developed as a calligraphic standard in the medieval European period so that the Latin alphabet of Jerome's Vulgate Bible could be easily recognized by the literate class from on ...
script, developed by Alcuin for use in the court of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
, which quickly spread across Europe. The advantage of the minuscule over majuscule was improved, faster readability.
In Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
, papyri from Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the ...
dating before 79 CE (when it was destroyed) have been found that have been written in old Roman cursive
Roman cursive (or Latin cursive) is a form of handwriting (or a script) used in ancient Rome and to some extent into the Middle Ages. It is customarily divided into old (or ancient) cursive and new cursive.
Old Roman cursive
Old Roman cursiv ...
, where the early forms of minuscule letters "d", "h" and "r", for example, can already be recognised. According to papyrologist Knut Kleve
Knut Kleve (24 February 1926 – 11 February 2017) was a Norwegian classical philologist and a professor at the University of Bergen and at the University of Oslo. He was particularly known for his efforts on restoration of papyrus fragments from ...
, "The theory, then, that the lower-case letters have been developed from the fifth century uncial
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to ...
s and the ninth century Carolingian minuscules seems to be wrong." Both majuscule and minuscule letters existed, but the difference between the two variants was initially stylistic rather than orthographic and the writing system was still basically unicameral: a given handwritten document could use either one style or the other but these were not mixed. European languages, except for Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
and Latin, did not make the case distinction before about 1300.
The timeline of writing in Western Europe can be divided into four eras:
*Greek majuscule (9th–3rd century BCE) in contrast to the Greek uncial script
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th ...
(3rd century BCE – 12th century CE) and the later Greek minuscule
* Roman majuscule (7th century BCE – 4th century CE) in contrast to the Roman uncial (4th–8th century CE), Roman half uncial
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to ...
, and minuscule
*Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
majuscule (4th–8th century CE) in contrast to the Carolingian minuscule
Carolingian minuscule or Caroline minuscule is a script which developed as a calligraphic standard in the medieval European period so that the Latin alphabet of Jerome's Vulgate Bible could be easily recognized by the literate class from on ...
(around 780 – 12th century)
*Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
majuscule (13th and 14th century), in contrast to the early Gothic (end of 11th to 13th century), Gothic (14th century), and late Gothic (16th century) minuscules.
Traditionally, certain letters were rendered differently according to a set of rules. In particular, those letters that began sentences or nouns were made larger and often written in a distinct script. There was no fixed capitalisation system until the early 18th century. The English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to t ...
eventually dropped the rule for nouns, while the German language keeps it.
Similar developments have taken place in other alphabets. The lower-case script for the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as ...
has its origins in the 7th century and acquired its quadrilinear form (that is, characterised by ascenders and descenders) in the 8th century. Over time, uncial letter forms were increasingly mixed into the script. The earliest dated Greek lower-case text is the Uspenski Gospels (MS 461) in the year 835.The earliest known biblical manuscript is a palimpsest of Isajah in Syriac, written in 459/460. Bruce M. Metzger & Bart D. Ehrman, ''The Text of the New Testament'' (Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print book ...
: 2005), p. 92. The modern practice of capitalising the first letter of every sentence seems to be imported (and is rarely used when printing Ancient Greek materials even today).
Type cases
The individual type blocks used in handtypesetting
Typesetting is the composition of text by means of arranging physical ''type'' (or ''sort'') in mechanical systems or '' glyphs'' in digital systems representing '' characters'' (letters and other symbols).Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random ...
are stored in shallow wooden or metal drawers known as " type cases". Each is subdivided into a number of compartments ("boxes") for the storage of different individual letters.
The ''Oxford Universal Dictionary on Historical Advanced Proportional Principles'' (reprinted 1952) indicates that ''case'' in this sense (referring to the box or frame used by a compositor in the printing trade) was first used in English in 1588. Originally one large case was used for each typeface, then "divided cases", pairs of cases for majuscules and minuscules, were introduced in the region of today's Belgium by 1563, England by 1588, and France before 1723.
The terms ''upper'' and ''lower'' case originate from this division. By convention, when the two cases were taken out of the storage rack and placed on a rack on the compositor
Compositor may refer to:
* Compositor (typesetting), a person or machine which arranged movable type for printing
** Paige Compositor, a device developed to replace manual compositors, which was a commercial failure
* Compositing software, used i ...
's desk, the case containing the capitals and small capitals stood at a steeper angle at the back of the desk, with the case for the small letters, punctuation, and spaces being more easily reached at a shallower angle below it to the front of the desk, hence upper and lower case.
Though pairs of cases were used in English-speaking countries and many European countries in the seventeenth century, in Germany and Scandinavia the single case continued in use.
Various patterns of cases are available, often with the compartments for lower-case letters varying in size according to the frequency of use of letters, so that the commonest letters are grouped together in larger boxes at the centre of the case. The compositor takes the letter blocks from the compartments and places them in a composing stick, working from left to right and placing the letters upside down with the nick to the top, then sets the assembled type in a galley.
See also
* All caps * Alternating caps * Camel case * Capitalization ** Capitalization in English *Initial
In a written or published work, an initial capital, also referred to as a drop capital or simply an initial cap, initial, initcapital, initcap or init or a drop cap or drop, is a letter at the beginning of a word, a chapter, or a paragraph tha ...
, or drop cap
* Grammatical case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals), which corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In va ...
* Punctuation
Punctuation (or sometimes interpunction) is the use of spacing, conventional signs (called punctuation marks), and certain typographical devices as aids to the understanding and correct reading of written text, whether read silently or aloud. A ...
* Roman cursive
Roman cursive (or Latin cursive) is a form of handwriting (or a script) used in ancient Rome and to some extent into the Middle Ages. It is customarily divided into old (or ancient) cursive and new cursive.
Old Roman cursive
Old Roman cursiv ...
* Roman square capitals
* Shift key
The Shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row. The Shift key's name originated ...
* Small caps
In typography, small caps (short for "small capitals") are characters typeset with glyphs that resemble uppercase letters (capitals) but reduced in height and weight close to the surrounding lowercase letters or text figures. This is technica ...
* Text figures
Text figures (also known as non-lining, lowercase, old style, ranging, hanging, medieval, billing, or antique figures or numerals) are numerals designed with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the ...
* Unicase
Notes
References
Further reading
* {{Typography terms Alphabets Capitalization Orthography Typography Articles with example C code