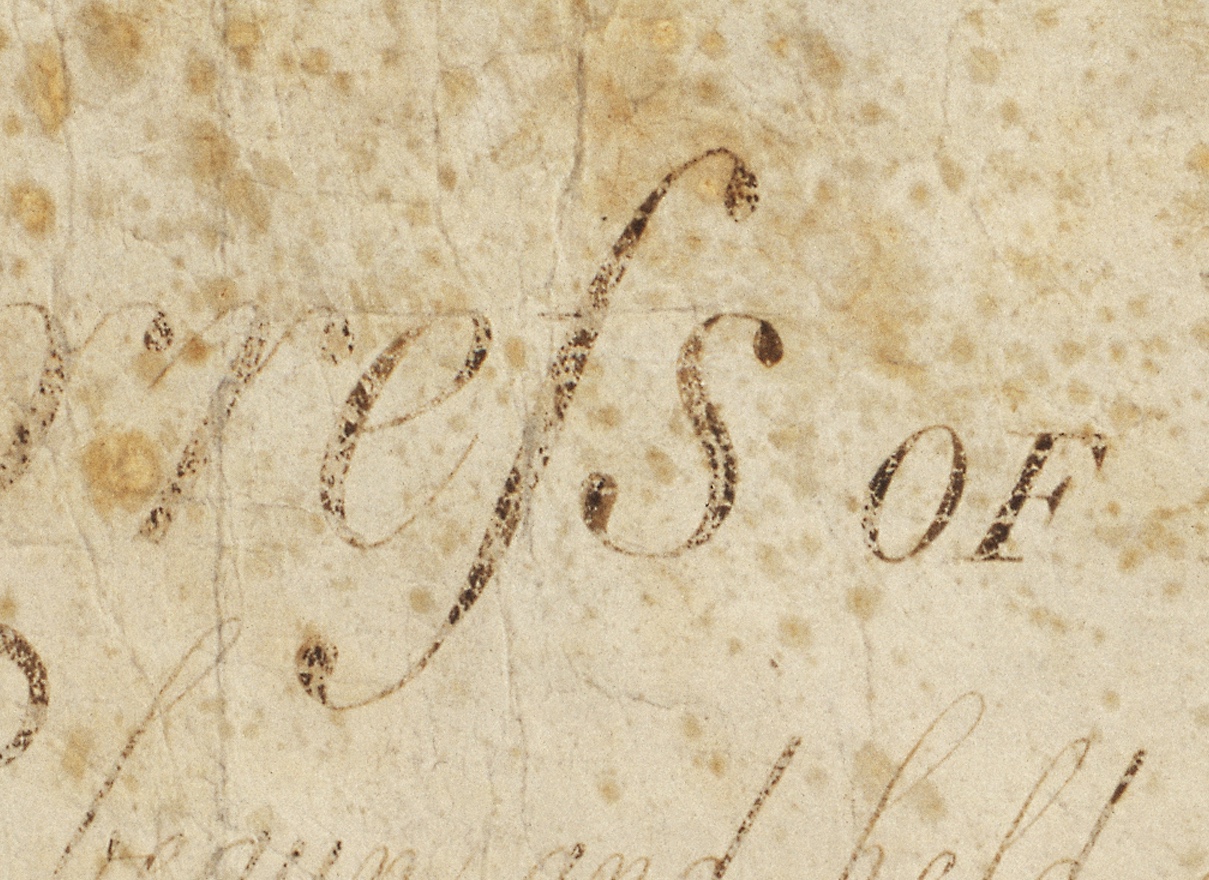|
Fraktur
Fraktur () is a calligraphic hand of the Latin alphabet and any of several blackletter typefaces derived from this hand. It is designed such that the beginnings and ends of the individual strokes that make up each letter will be clearly visible, and often emphasized; in this way it is often contrasted with the curves of the Antiqua (common) typefaces where the letters are designed to flow and strokes connect together in a continuous fashion. The word "Fraktur" derives from Latin ("a break"), built from , passive participle of ("to break"), which is also the root for the English word "fracture". In non-professional contexts, the term "Fraktur" is sometimes misused to refer to ''all'' blackletter typefaces while Fraktur typefaces do fall under that category, not all blackletter typefaces exhibit the Fraktur characteristics described above. Fraktur is often characterized as "the German typeface", as it remained popular in Germany and much of Eastern Europe far longer than el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Case
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular discipline. In ortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majuscule
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally '' majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally '' minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular discipline. In orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first letters were invented in Ancient Egypt to serve as an aid in writing Egyptian hieroglyphs; these are referred to as Egyptian uniliteral signs by lexicographers. This system was used until the 5th century AD, and fundamentally differed by adding pronunciation hints to existing hieroglyphs that had previously carried no pronunciation information. Later on, these phonemic symbols also became used to transcribe foreign words. The first fully phonemic script was the Proto-Sinaitic script, also descending from Egyptian hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Alphabet
Modern English is written with a Latin-script alphabet consisting of 26 Letter (alphabet), letters, with each having both uppercase and lowercase forms. The word ''alphabet'' is a Compound (linguistics), compound of ''alpha'' and ''beta'', the names of the first two letters in the Greek alphabet. The earliest Old English writing during the 5th century used a runic alphabet known as the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, futhorc. The Old English Latin alphabet was adopted from the 7th century onward—and over the following centuries, various letters entered and fell out of use. By the 16th century, the present set of 26 letters had largely stabilised: There are 5 vowel letters and 19 consonant letters—as well as Y and W, which may function as either type. Written English has a large number of Digraph (orthography), digraphs, such as , , , , and . Diacritics are generally not used to write native English words, which is unusual among orthographies used to write the languages of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of printing as applied to paper was woodblock printing, which appeared in China before 220 AD for cloth printing. However, it would not be applied to paper until the seventh century.Shelagh Vainker in Anne Farrer (ed), "Caves of the Thousand Buddhas", 1990, British Museum publications, Later developments in printing technology include the movable type invented by Bi Sheng around 1040 AD and the printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. The technology of printing played a key role in the development of the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution and laid the material basis for the modern knowledge-based economy and the spread of learning to the masses. History Woodblock printing Woodblo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronymus Andreae
Hieronymus Andreae, or Andreä, or Hieronymus Formschneider, (died 7 May 1556) was a German woodblock cutter ("formschneider"), printer, publisher and typographer closely associated with Albrecht Dürer. Andreae's best known achievements include the enormous, 192-block Triumphal Arch woodcut, designed by Dürer for Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, and his design of the characteristic German "blackletter" Fraktur typeface ("Gothic" to most English-speakers), on which German typefaces were based for several centuries. He was also significant as a printer of music. In the opinion of Adam von Bartsch, although Andreae never designed woodcuts (as opposed to designing typefaces), the quality of his work was such that he, along with Hans Lützelburger and Jost de Negker, should be considered an artist. Life and work There is some evidence that he matriculated at the University of Leipzig in 1504, although this might also mean that he worked for the university rather than bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer ( , ;; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer or Duerer, was a German painter, Old master prints, printmaker, and history of geometry#Renaissance, theorist of the German Renaissance. Born in Free Imperial City of Nuremberg, Nuremberg, Dürer established his reputation and influence across Europe in his twenties due to his high-quality List of woodcuts by Dürer, woodcut prints. He was in contact with the major Italian artists of his time, including Raphael, Giovanni Bellini and Leonardo da Vinci, and from 1512 was patronized by Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I. Dürer's vast body of work includes List of engravings by Dürer, engravings, his preferred technique in his later prints, Altarpiece, altarpieces, portraits and self-portraits, watercolours and books. The woodcuts series are stylist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triumphal Arch (woodcut)
The ''Triumphal Arch'' (also known as the ''Arch of Maximilian I'', ) is a 16th-century monumental woodcut print commissioned by the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian I. The composite image was Printing, printed on 36 large sheets of paper from 195 separate Woodblock printing, wood blocks. At , it is one of the largest Old master print, prints ever produced and was intended to be pasted to walls in city halls or the palaces of princes.Bartrum, (1995), 51 It is a part of a series of three huge prints created for Maximilian, the others being a ''Triumphal Procession'' (1516–18, 137 woodcut panels, long) which is led by a ''Large Triumphal Carriage'' (1522, 8 woodcut panels, ); only the ''Arch'' was completed in Maximilian's lifetime and distributed as propaganda, as he intended. Together, this series has been described by art historian Hyatt Mayor as "Maximilian's program of paper grandeur". They stand alongside two published biographical allegori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death in 1519. He was never crowned by the Pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself elected emperor in 1508 at Trent, with Pope Julius II later recognizing it. This broke the tradition of requiring a papal coronation for the adoption of the Imperial title. Maximilian was the only surviving son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, and Eleanor of Portugal. From his coronation as King of the Romans in 1486, he ran a double government, or ''Doppelregierung'' with his father until Frederick's death in 1493. Maximilian expanded the influence of the House of Habsburg through war and his marriage in 1477 to Mary, Duchess of Burgundy. However, he also lost his family's lands in Switzerland to the Swiss Confederacy. Through the marriage of his son Philip the Handsome to eventual queen Joanna of Castile in 1496, Maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Consortium
The Unicode Consortium (legally Unicode, Inc.) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization incorporated and based in Mountain View, California, U.S. Its primary purpose is to maintain and publish the Unicode Standard which was developed with the intention of replacing existing character encoding schemes that are limited in size and scope, and are incompatible with multilingual environments. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread adoption in the internationalization and localization of software. The standard has been implemented in many technologies, including XML, the Java programming language, Swift, and modern operating systems. Members are usually but not limited to computer software and hardware companies with an interest in text-processing standards, including Adobe, Apple, the Bangladesh Computer Council, Emojipedia, Facebook, Google, IBM, Microsoft, the Omani Ministry of Endowments and Religious Affairs, Monotype Imaging, Netflix, Sales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |