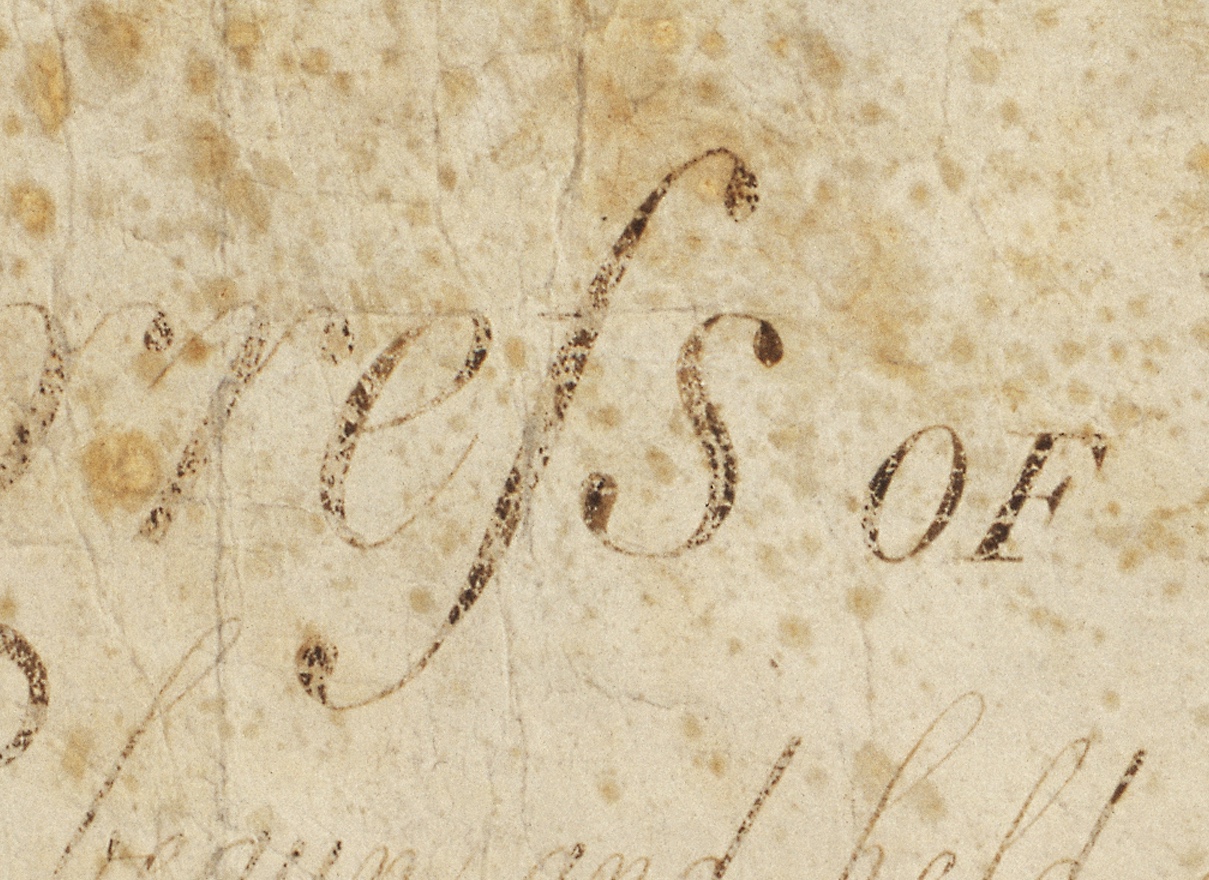|
German Orthography
German orthography is the orthography used in writing the German language, which is largely phonemic. However, it shows many instances of spellings that are historic or analogous to other spellings rather than phonemic. The pronunciation of almost every word can be derived from its spelling once the spelling rules are known, but the opposite is not generally the case. Today, Standard High German orthography is regulated by the (Council for German Orthography), composed of representatives from most German-speaking countries. Alphabet The modern German alphabet consists of the twenty-six letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus four special letters. Basic alphabet Special letters German has four special letters; three are vowels accented with an umlaut sign () and one is derived from a ligature of (long s) and (; called "ess-zed/zee" or "sharp s"). They have their own names separate from the letters they are based on. * Capital ẞ was declare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the umbrella term for the standard language, standardized varieties of the German language, which are used in formal contexts and for communication between different dialect areas. German is a Pluricentric language, pluricentric Abstand and ausbau languages#Roofing, Dachsprache with currently three codified (or standardised) specific national varieties: German Standard German, Austrian German#Standard Austrian German, Austrian Standard German and Swiss Standard German. Regarding the spelling and punctuation, a recommended standard is published by the Council for German Orthography which represents the governments of all majority and minority German-speaking countries and dependencies. Adherence is obligatory for government institutions, including schools. Although there is no official standards body regulating pronunciation, there is a long-standing ''de facto'' standard pronu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typographic Ligature
In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes or letters are joined to form a single glyph. Examples are the characters and used in English and French, in which the letters and are joined for the first ligature and the letters and are joined for the second ligature. For stylistic and legibility reasons, and are often merged to create (where the tittle on the merges with the hood of the ); the same is true of and to create . The common ampersand, , developed from a ligature in which the handwritten Latin letters and (spelling , Latin for 'and') were combined. History The earliest known script Sumerian cuneiform and Egyptian hieratic both include many cases of character combinations that gradually evolve from ligatures into separately recognizable characters. Other notable ligatures, such as the Brahmic abugidas and the Germanic bind rune, figure prominently throughout ancient manuscripts. These new glyphs emerge alongside the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Standard German
Swiss Standard German (SSG; ), or Swiss High German ( or ; ), referred to by the Swiss as , or , is the written form of one (German language, German) of four languages of Switzerland, national languages in Switzerland, besides French language, French, Italian language, Italian, and Romansh language, Romansh. It is a variety of Standard German, used in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland and in Liechtenstein. It is mainly written and rather less often spoken. Swiss Standard German differs from Swiss German, an umbrella term for the various Alemannic German dialects (in the sense of "traditional regional varieties") that are the default everyday languages in German-speaking Switzerland. Standard German is a pluricentric language. In contrast with other local Variety (linguistics), varieties of Standard German, Swiss Standard German has distinctive features in all linguistic domains: not only in phonology, but also in vocabulary, syntax, morphology ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early New High German
Early New High German (ENHG) is a term for the period in the history of the German language generally defined, following Wilhelm Scherer, as the period 1350 to 1650, developing from Middle High German and into New High German. The term is the standard translation of the German (Frnhd., Fnhd.), introduced by Scherer. The term ''Early Modern High German'' is also occasionally used for this period (but the abbreviation EMHG is generally used for '' Early Middle High German''). Periodisation The start and end dates of ENHG are, like all linguistic periodisations, somewhat arbitrary. In spite of many alternative suggestions, Scherer's dates still command widespread acceptance. Linguistically, the mid-14th century is marked by the phonological changes to the vowel system that characterise the modern standard language; the mid-17th sees the loss of status for regional forms of language, and the triumph of German over Latin as the dominant, and then sole, language for public discour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter or black-letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule or Gothic type, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish until the 1870s, Finnish until the turn of the 20th century, Estonian and Latvian until the 1930s, and for the German language until the 1940s, when Adolf Hitler officially Antiqua–Fraktur dispute, discontinued it in 1941. Fraktur is a notable script of this type, and sometimes the entire group of blackletter faces is referred to as Fraktur. Blackletter is sometimes referred to as Old English, but it is not to be confused with the Old English language, which predates blackletter by many centuries and was written in the insular script or in Futhorc. Along with Italic type and Roman type, blackletter served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western typography. Origins Carolingian minuscule wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurrent
() is an old form of German-language handwriting based on late medieval cursive writing, also known as ("cursive script"), ("German script"), and ''German cursive''. Over the history of its use into the first part of the 20th century, many individual letters acquired variant forms. German writers used both cursive styles, and Latin cursive, in parallel: Location, contents, and context of the text determined which script style to use. is a modern script based on that is characterized by simplified letters and vertical strokes. It was developed in 1911 and taught in all German schools as the primary script from 1915 until the beginning of January 1941. Then it was replaced with ("normal German handwriting"), which is sometimes referred to as "Latin writing". Lettering examples File:Lessing Kleist-Brief.jpg, Letter from Lessing to Kleist, 14 March 1758 File:Schein und Sein.jpg, Manuscript by Wilhelm Busch (undated, late 19th century) File:Bielsko-Biała Teatr Polski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sz (digraph)
Sz is a digraph (orthography), digraph of the Latin script, used in Polish language, Polish, Kashubian language, Kashubian and Hungarian language, Hungarian, and in the Wade–Giles system of Romanization of Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, as well as the Hong Kong Government Cantonese Romanisation, Hong Kong official romanization of Cantonese. Polish In Polish orthography, sz represents a voiceless retroflex fricative . It usually corresponds to š or Sha (Cyrillic), ш in other Slavic languages. It is usually approximated by English speakers with the "sh" sound (and conversely, Polish speakers typically approximate the English digraph ''sh'' with the "sz" sound), although the two sounds are not completely identical. Polish orthography#Digraphs, Like other Polish digraphs, it is not considered a single letter for collation purposes. sz should not be confused with ś (or s followed by i), termed "soft sh", a voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative . Examples of sz (''area, territory' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph () or digram is a pair of character (symbol), characters used in the orthography of a language to write either a single phoneme (distinct sound), or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined. Some digraphs represent phonemes that cannot be represented with a single character in the writing system of a language, like in Spanish ''chico'' and ''ocho''. Other digraphs represent phonemes that can also be represented by single characters. A digraph that shares its pronunciation with a single character may be a relic from an earlier period of the language when the digraph had a different pronunciation, or may represent a distinction that is made only in certain dialects, like the English . Some such digraphs are used for purely etymology, etymological reasons, like in French. In some orthographies, digraphs (and occasionally trigraph (orthography), trigraphs) are considered individual letter (alphabet), letters, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east and north and Switzerland in the west and south. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy headed by the prince of Liechtenstein of the House of Liechtenstein, currently led by Hans-Adam II. It is List of European countries by area, Europe's fourth-smallest country, with an area of just over and a population of 40,023. It is the world's smallest country to border two countries, and is one of the few countries with no debt. Liechtenstein is divided into Municipalities of Liechtenstein, 11 municipalities. Its capital is Vaduz, and its largest municipality is Schaan. It is a member of the United Nations, the European Free Trade Association, and the Council of Europe. It is not a member state of the European Union, but it participates i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |