Atchison, Topeka And Santa Fe Railroad on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
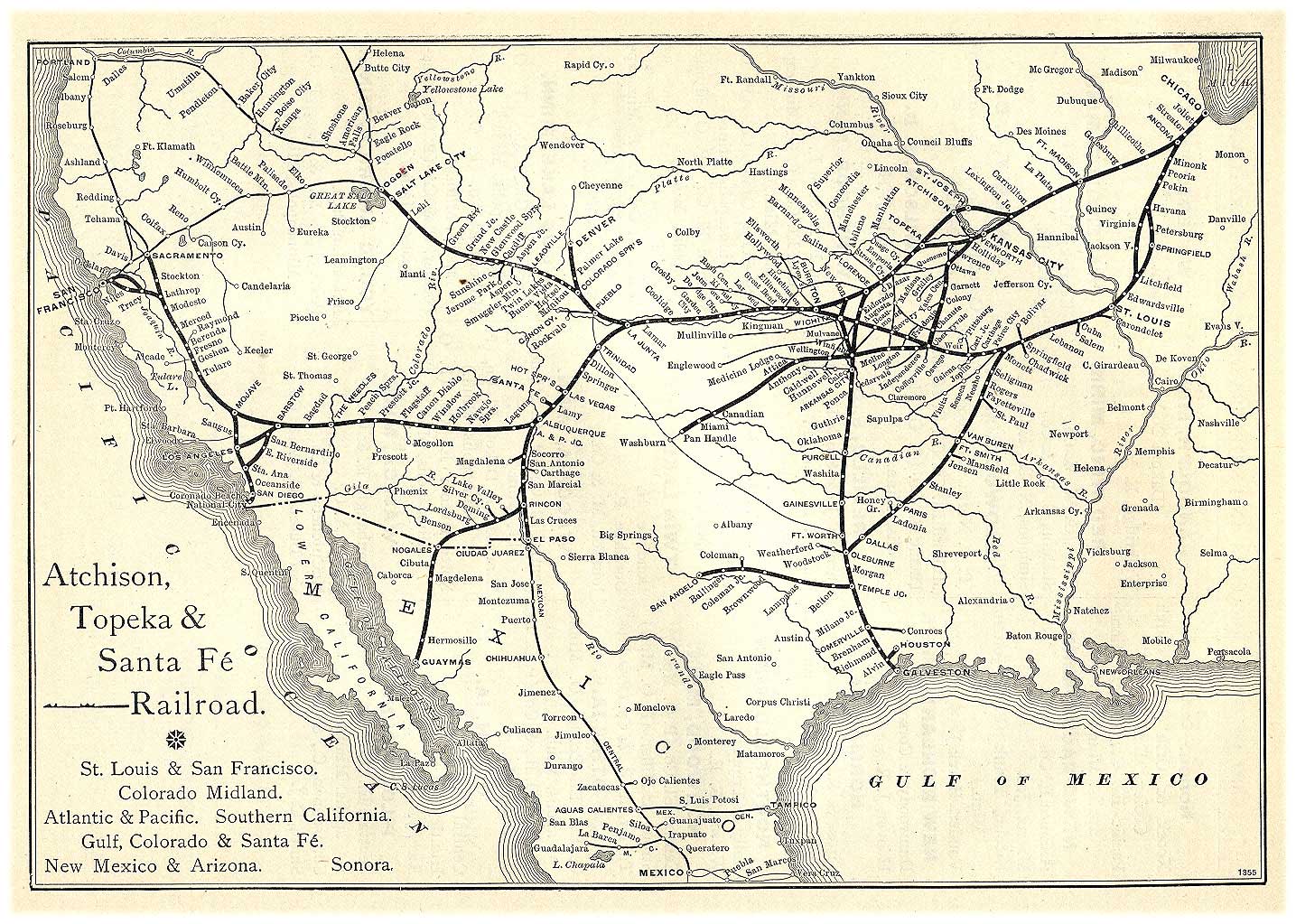
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of


 On , the railway was one of many companies that sponsored attractions in Disneyland with its five-year sponsorship of all Disneyland trains and stations until 1974.
In 1960, AT&SF bought the Toledo, Peoria & Western Railroad (TP&W); then sold a half-interest to the
On , the railway was one of many companies that sponsored attractions in Disneyland with its five-year sponsorship of all Disneyland trains and stations until 1974.
In 1960, AT&SF bought the Toledo, Peoria & Western Railroad (TP&W); then sold a half-interest to the
 AT&SF began to talk mergers in the 1980s. The Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) was a proposed merger between the parent companies of the Southern Pacific and AT&SF announced on December 23, 1983. As part of the joining of the two firms, all rail and non-rail assets owned by Santa Fe Industries and the Southern Pacific Transportation Company were placed under the control of a holding company, the Santa Fe–Southern Pacific Corporation. The merger was subsequently denied by the
AT&SF began to talk mergers in the 1980s. The Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) was a proposed merger between the parent companies of the Southern Pacific and AT&SF announced on December 23, 1983. As part of the joining of the two firms, all rail and non-rail assets owned by Santa Fe Industries and the Southern Pacific Transportation Company were placed under the control of a holding company, the Santa Fe–Southern Pacific Corporation. The merger was subsequently denied by the
 Occasionally, a special train was chartered to make a high-profile run over the Santa Fe's track. These specials were not included in the railroad's regular revenue service lineup, but were intended as one-time (and usually one-way) traversals of the railroad. Some of the more notable specials include:
* '' Cheney Special'':
Occasionally, a special train was chartered to make a high-profile run over the Santa Fe's track. These specials were not included in the railroad's regular revenue service lineup, but were intended as one-time (and usually one-way) traversals of the railroad. Some of the more notable specials include:
* '' Cheney Special'':
 The Santa Fe operated a large and varied fleet of
The Santa Fe operated a large and varied fleet of
 While most of the Santa Fe's steam locomotives were retired and sold for scrap, over fifty were saved and donated to various parks and museums, a handful of which have either been restored to operating condition or are pending future restoration.
Some of the more notable locomotives include:
* 5 (
While most of the Santa Fe's steam locomotives were retired and sold for scrap, over fifty were saved and donated to various parks and museums, a handful of which have either been restored to operating condition or are pending future restoration.
Some of the more notable locomotives include:
* 5 (
 Santa Fe's first set of diesel-electric passenger locomotives was placed in service on the ''Super Chief'' in 1936, and consisted of a pair of blunt-nosed units ( EMC 1800 hp B-B) designated as Nos. 1 and 1A. The upper portion of the sides and ends of the units were painted gold, while the lower section was a dark olive green color; an olive stripe also ran along the sides and widened as it crossed the front of the locomotive.
Riveted to the sides of the units were metal plaques bearing a large "Indian Head" logo, which owed its origin to the 1926 ''
Santa Fe's first set of diesel-electric passenger locomotives was placed in service on the ''Super Chief'' in 1936, and consisted of a pair of blunt-nosed units ( EMC 1800 hp B-B) designated as Nos. 1 and 1A. The upper portion of the sides and ends of the units were painted gold, while the lower section was a dark olive green color; an olive stripe also ran along the sides and widened as it crossed the front of the locomotive.
Riveted to the sides of the units were metal plaques bearing a large "Indian Head" logo, which owed its origin to the 1926 ''' s  In a little over a year, the EMC E1 (a new and improved streamlined locomotive) would be pulling the ''Super Chief'' and other passenger consists, resplendent in the now-famous ''Warbonnet'' paint scheme devised by
In a little over a year, the EMC E1 (a new and improved streamlined locomotive) would be pulling the ''Super Chief'' and other passenger consists, resplendent in the now-famous ''Warbonnet'' paint scheme devised by
 Diesels used as switchers between 1935 and 1960 were painted black, with just a thin white or silver horizontal accent stripe (the sills were painted similarly). The letters "A.T.& S.F." were applied in a small font centered on the sides of the unit, as was the standard blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo. After World War II, diagonal white or silver stripes were added to the ends and cab sides to increase the visibility at grade crossings (typically referred to as the ''Zebra Stripe'' scheme). "A.T.& S.F." was now placed along the sides of the unit just above the accent stripe, with the blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo below.
Due to the lack of abundant water sources in the American desert, the Santa Fe Railway was among the first railroads to receive large numbers of streamlined diesel locomotives for use in freight service, in the form of the EMD FT. For the first group of FTs, delivered between December 1940 and March 1943 (#100–#119), the railroad selected a color scheme consisting of dark blue accented by a pale yellow stripe up the nose, and pale yellow highlights around the cab and along the mesh and framing of openings in the sides of the engine compartment; a thin red stripe separated the blue areas from the yellow.
Diesels used as switchers between 1935 and 1960 were painted black, with just a thin white or silver horizontal accent stripe (the sills were painted similarly). The letters "A.T.& S.F." were applied in a small font centered on the sides of the unit, as was the standard blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo. After World War II, diagonal white or silver stripes were added to the ends and cab sides to increase the visibility at grade crossings (typically referred to as the ''Zebra Stripe'' scheme). "A.T.& S.F." was now placed along the sides of the unit just above the accent stripe, with the blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo below.
Due to the lack of abundant water sources in the American desert, the Santa Fe Railway was among the first railroads to receive large numbers of streamlined diesel locomotives for use in freight service, in the form of the EMD FT. For the first group of FTs, delivered between December 1940 and March 1943 (#100–#119), the railroad selected a color scheme consisting of dark blue accented by a pale yellow stripe up the nose, and pale yellow highlights around the cab and along the mesh and framing of openings in the sides of the engine compartment; a thin red stripe separated the blue areas from the yellow.
 The words SANTA FE were applied in yellow in a 5"–high extended font, and centered on the nose was the "Santa Fe" box logo (initially consisting of a blue cross, circle, and square painted on a solid
The words SANTA FE were applied in yellow in a 5"–high extended font, and centered on the nose was the "Santa Fe" box logo (initially consisting of a blue cross, circle, and square painted on a solid  In 1965, the road took delivery of ten GE U28CG dual-service roadswitcher locomotives equally suited to passenger or fast freight service. These wore a variation of the "Warbonnet" scheme in which the black and yellow separating stripes disappeared. The "Santa Fe" name was emblazoned on the sides in large black letters, using the same stencils used on freight engines; these were soon repainted in red. In 1989, Santa Fe resurrected this version of the "Warbonnet" scheme and applied it to two SDFP45 units, #5992 and #5998. The units were re-designated as #101 and #102 and reentered service on July 4, 1989, as part of the new "Super Fleet" campaign (the first Santa Fe units to be so decorated for freight service). The six remaining FP45 units were thereafter similarly repainted and renumbered. From that point forward, most new locomotives wore red and silver, and many retained this scheme after the Burlington Northern Santa Fe merger, some with "BNSF" displayed across their sides.
For the initial deliveries of factory-new "Super Fleet" equipment, Santa Fe took delivery of the EMD GP60M and General Electric B40-8W which made the Santa Fe the only US Class I railroad to operate new 4-axle (B-B) freight locomotives equipped with the North American Safety Cab intended for high-speed intermodal service.
Several experimental and commemorative paint schemes emerged during the Santa Fe's diesel era. One combination was developed and partially implemented in anticipation of a merger between the parent companies of the Santa Fe and Southern Pacific (SP) railroads in 1984. The red, yellow, and black paint scheme with large yellow block letters on the sides and ends of the units of the proposed Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) has come to be somewhat derisively known among railfans as the ''Kodachrome'' livery, due to the similarity in colors to the boxes containing slide film sold by the Eastman Kodak Company under the same name. Santa Fe units repainted in this scheme were labeled "SF", Southern Pacific units "SP", and some (presumably new) units wore the letters "SPSF". After the ICC's denial of the merger, railfans joked that SPSF really stood for "Shouldn't Paint So Fast."
In 1965, the road took delivery of ten GE U28CG dual-service roadswitcher locomotives equally suited to passenger or fast freight service. These wore a variation of the "Warbonnet" scheme in which the black and yellow separating stripes disappeared. The "Santa Fe" name was emblazoned on the sides in large black letters, using the same stencils used on freight engines; these were soon repainted in red. In 1989, Santa Fe resurrected this version of the "Warbonnet" scheme and applied it to two SDFP45 units, #5992 and #5998. The units were re-designated as #101 and #102 and reentered service on July 4, 1989, as part of the new "Super Fleet" campaign (the first Santa Fe units to be so decorated for freight service). The six remaining FP45 units were thereafter similarly repainted and renumbered. From that point forward, most new locomotives wore red and silver, and many retained this scheme after the Burlington Northern Santa Fe merger, some with "BNSF" displayed across their sides.
For the initial deliveries of factory-new "Super Fleet" equipment, Santa Fe took delivery of the EMD GP60M and General Electric B40-8W which made the Santa Fe the only US Class I railroad to operate new 4-axle (B-B) freight locomotives equipped with the North American Safety Cab intended for high-speed intermodal service.
Several experimental and commemorative paint schemes emerged during the Santa Fe's diesel era. One combination was developed and partially implemented in anticipation of a merger between the parent companies of the Santa Fe and Southern Pacific (SP) railroads in 1984. The red, yellow, and black paint scheme with large yellow block letters on the sides and ends of the units of the proposed Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) has come to be somewhat derisively known among railfans as the ''Kodachrome'' livery, due to the similarity in colors to the boxes containing slide film sold by the Eastman Kodak Company under the same name. Santa Fe units repainted in this scheme were labeled "SF", Southern Pacific units "SP", and some (presumably new) units wore the letters "SPSF". After the ICC's denial of the merger, railfans joked that SPSF really stood for "Shouldn't Paint So Fast."
File:42Richmond yd - Flickr - drewj1946.jpg, ''Warbonnet'' roof details
File:43C at San Diego 04 06 68 sm - Flickr - drewj1946.jpg, ATSF ''San Diegan'' EMD F7 (1968), displaying the "SANTA FE" in black Railroad Roman letters along each side
File:Santa Fe 98.jpg, Santa Fe #98, an EMD FP45 decked out in ''Warbonnet'' colors, including the traditional "cigar band" nose emblem
File:ATSF 681.jpg, Santa Fe #681 in Sealy Texas, June 2001
File:Santa Fe Super Chief.jpg, The L.A.-bound ''Super Chief'' gets its 5-minute pit-stop service in Albuquerque, 1943
File:ATSF Downhhill Caliente Aug 90xRP (7701632638).jpg, ATSF 9542 in ''Kodachrome'' leads other locomotives in ''Freightbonnet (1990)

The Atchison Topeka and Santa Fe
'. Retrieved May 10, 2005. * * ** * * * * Duke, Donald. ''Fred Harvey, civilizer of the American Southwest'' (Pregel Press, 1995); The passenger trains stopped for meals at Fred Harvey restaurants. * Dye, Victoria E. ''All Aboard for Santa Fe: Railway Promotion of the Southwest, 1890s to 1930s'' (University of New Mexico Press, 2007). * * Frailey, Fred W. (1998). ''Twilight of the Great Trains'', p. 108. Waukesha, Wisconsin: Kalmbach Publishing. . * Richard H. Frost, ''The Railroad and the Pueblo Indians: The Impact of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa fe on the Pueblos of the Rio Grande, 1880–1930.'' 2016, Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. * * Goen, Steve Allen (2000). ''Santa Fe in the Lone Star State'' * * Marshall, James Leslie. ''Santa Fe: the railroad that built an empire'' (1945). * * * Pratt School of Engineering, Duke University (2004),
Alumni Profiles: W. John Swartz
'. Retrieved May 11, 2005. * Santa Fe Railroad (1945), ''Along Your Way'', Rand McNally, Chicago. * Santa Fe Railroad (November 29, 1942), ''Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway System Time Tables'', Rand McNally and Company, Chicago. * * Solomon, Brian. ''Santa Fe Railway'' (Voyageur Press, 2003). * * Snell, Joseph W. and Don W. Wilson, "The Birth of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad," (Part One) ''Kansas Historical Quarterly'' (1968) 34#2 pp 113–142
** Snell, Joseph W. and Don W. Wilson, "The Birth of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad," (Part Two) ''Kansas Historical Quarterly'' (1968) 34#3 pp 325–35
*
"Along Your Way", 1946 edition
Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe
photos and other documents on Kansas Memory, the digital portal of the Kansas Historical Society (over 2800 AT&SF items)
Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Company Records
at the Kansas Historical Society, Topeka, Kansas
Russell Crump's Santa Fe Archives
– a very extensive set of resources for Santa Fe history.
Santa Fe Preserved Locomotives
Santa Fe Railway Historical and Modeling Society
official website
article from the May 18, 1947, issue of ''
''Rand, McNally & Co.'s new overland guide to the Pacific Coast''
Chicago: Rand, McNally & Co., 1888. Illustrated guide to the Santa Fe trip circa 1888.
* ttp://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HBS.Baker.EAD:bak00020 Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad Recordsat Baker Library Historical Collections, Harvard Business School
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
Atchison Topeka & Santa Fe (ATSF) All-Time Diesel Roster
{{DEFAULTSORT:Atchison Topeka Santa Fe Railway Former Class I railroads in the United States Predecessors of the BNSF Railway Rail lines receiving land grants Railway companies established in 1895 Railway companies disestablished in 1996 Companies based in Chicago Economy of the Southwestern United States Defunct Arizona railroads Defunct California railroads Defunct Colorado railroads Defunct Illinois railroads Defunct Indiana railroads Defunct Iowa railroads Defunct Kansas railroads Defunct Louisiana railroads Defunct Missouri railroads Defunct Nebraska railroads Defunct Nevada railroads Defunct New Mexico railroads Defunct Oklahoma railroads Defunct Texas railroads Railroads in the Chicago metropolitan area History of Chicago History of San Diego Superfund sites in New Mexico American companies established in 1859 1996 disestablishments in Illinois
Atchison Atchison may refer to:
Places
In the United States:
* Atchison, California, a former settlement
* Atchison, Kansas, a city
* Atchison County, Kansas
* Atchison County, Missouri
People with the surname
*Bob Atchison (born 1941), Canadian drag r ...
and Topeka, Kansas, and Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , Spanish for 'Holy Faith'; tew, Oghá P'o'oge, Tewa for 'white shell water place'; tiw, Hulp'ó'ona, label=Tiwa language, Northern Tiwa; nv, Yootó, Navajo for 'bead + water place') is the capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico. ...
. The railroad reached the Kansas– Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farmland from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress.
Despite being chartered to serve the city, the railroad chose to bypass Santa Fe, due to the engineering challenges of the mountainous terrain. Eventually a branch line from Lamy, New Mexico, brought the Santa Fe railroad to its namesake city.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport; at various times, it operated an airline, the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway, and the fleet of Santa Fe Railroad Tugboats. Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not accessible by rail, and ferryboats on the San Francisco Bay allowed travelers to complete their westward journeys to the Pacific Ocean. The AT&SF was the subject of a popular song, Harry Warren
Harry Warren (born Salvatore Antonio Guaragna; December 24, 1893 – September 22, 1981) was an American composer and the first major American songwriter to write primarily for film. He was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Original Song ...
and Johnny Mercer
John Herndon Mercer (November 18, 1909 – June 25, 1976) was an American lyricist, songwriter, and singer, as well as a record label executive who co-founded Capitol Records with music industry businessmen Buddy DeSylva and Glenn E. Wallich ...
's " On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe", written for the film '' The Harvey Girls'' (1946).
The railroad officially ceased operations on December 31, 1996, when it merged with the Burlington Northern Railroad
The Burlington Northern Railroad was a United States-based railroad company formed from a Mergers and acquisitions, merger of four major U.S. railroads. Burlington Northern operated between 1970 and 1996.
Its historical lineage begins in the e ...
to form the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway.
History
Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway



Expansion
 On , the railway was one of many companies that sponsored attractions in Disneyland with its five-year sponsorship of all Disneyland trains and stations until 1974.
In 1960, AT&SF bought the Toledo, Peoria & Western Railroad (TP&W); then sold a half-interest to the
On , the railway was one of many companies that sponsored attractions in Disneyland with its five-year sponsorship of all Disneyland trains and stations until 1974.
In 1960, AT&SF bought the Toledo, Peoria & Western Railroad (TP&W); then sold a half-interest to the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
(PRR). The TP&W cut straight east across Illinois from near Fort Madison, Iowa (Lomax, IL), to a connection with the PRR at Effner, Indiana
Effner is an unincorporated community on the border of the U.S. states of Illinois and Indiana. It lies principally in Iroquois County, Illinois and partially in Newton County, Indiana.
History
Effner was founded ca. 1860 and originally known as ...
(Illinois–Indiana border), forming a bypass around Chicago for traffic moving between the two lines. The TP&W route did not mesh with the traffic patterns Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do busin ...
developed after 1976, so AT&SF bought back the other half, merged the TP&W in 1983, then sold it back into independence in 1989.
Attempted Southern Pacific merger
 AT&SF began to talk mergers in the 1980s. The Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) was a proposed merger between the parent companies of the Southern Pacific and AT&SF announced on December 23, 1983. As part of the joining of the two firms, all rail and non-rail assets owned by Santa Fe Industries and the Southern Pacific Transportation Company were placed under the control of a holding company, the Santa Fe–Southern Pacific Corporation. The merger was subsequently denied by the
AT&SF began to talk mergers in the 1980s. The Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) was a proposed merger between the parent companies of the Southern Pacific and AT&SF announced on December 23, 1983. As part of the joining of the two firms, all rail and non-rail assets owned by Santa Fe Industries and the Southern Pacific Transportation Company were placed under the control of a holding company, the Santa Fe–Southern Pacific Corporation. The merger was subsequently denied by the Interstate Commerce Commission
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was a regulatory agency in the United States created by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887. The agency's original purpose was to regulate railroads (and later trucking) to ensure fair rates, to eliminat ...
(ICC) on the basis that it would create too many duplicate routes.
The companies were so confident the merger would be approved that they began repainting locomotives and non-revenue rolling stock in a new unified paint scheme. While Southern Pacific (railroad) was sold off to Rio Grande Industries, all of the SP's real estate holdings were consolidated into a new company, Catellus Development Corporation, making it California's largest private landowner, of which Santa Fe remained the owner. In the early 1980s, gold was discovered on several properties west of Battle Mountain, Nevada along I-80, on ground owned by the Santa Fe Railroad (formerly SP). The Santa Fe Pacific Corporation (a name correlation of Santa Fe and Southern Pacific) was to develop the properties. They were sold to Newmont during 1997 in preparation for the merger with Burlington Northern). Sometime later, Catellus would purchase the Union Pacific Railroad's interest in the Los Angeles Union Passenger Terminal (LAUPT).
Burlington Northern merger
On September 22, 1995, AT&SF merged withBurlington Northern Railroad
The Burlington Northern Railroad was a United States-based railroad company formed from a Mergers and acquisitions, merger of four major U.S. railroads. Burlington Northern operated between 1970 and 1996.
Its historical lineage begins in the e ...
to form the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway
BNSF Railway is one of the largest freight railroads in North America. One of seven North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that ...
(BNSF). Some of the challenges resulting from the joining of the two companies included the establishment of a common dispatching system, the unionization of AT&SF's non-union dispatchers, and incorporating AT&SF's train identification codes throughout. The two lines maintained separate operations until December 31, 1996, when it officially became BNSF.
:Source: Santa Fe Railroad (1945), ''Along Your Way'', Rand McNally, Chicago, Illinois.
Company officers
Passenger service
AT&SF was widely known for itspassenger train
A passenger train is a train used to transport people along a railroad line. These trains may consist of unpowered passenger railroad cars (also known as coaches or carriages) hauled by one or more locomotives, or may be self-propelled; self pr ...
service in the first half of the 20th century. AT&SF introduced many innovations in passenger rail travel, among these the " Pleasure Domes" of the '' Super Chief'' (billed as the "''...only dome car between Chicago and Los Angeles''" when they were introduced in 1951) and the " Big Dome" Lounge cars and double-decker Hi-Level cars of the '' El Capitan'', which entered revenue service in 1954. The railroad was among the first to add dining cars to its passenger trains, a move which began in 1891, following the examples of the Northern Pacific and Union Pacific railroads. The AT&SF offered food on board in a dining car
A dining car (American English) or a restaurant car (British English), also a diner, is a railroad passenger car that serves meals in the manner of a full-service, sit-down restaurant.
It is distinct from other railroad food service cars that ...
or at one of the many Harvey House restaurants that were strategically located throughout the system.
In general, the same train name was used for both directions of a particular train. The exceptions to this rule included the ''Chicagoan'' and ''Kansas Cityan'' trains (both names referred to the same service, but the ''Chicagoan'' was the eastbound version, while the ''Kansas Cityan'' was the westbound version), and the ''Eastern Express'' and ''West Texas Express''. All AT&SF trains that terminated in Chicago did so at Dearborn Station. Trains terminating in Los Angeles arrived at AT&SF's La Grande Station until May 1939, when Los Angeles Union Passenger Terminal was opened.
The Santa Fe was the only railroad to run trains from Chicago to California on its own tracks. The railway's extensive network was also home to a number of regional services. These generally couldn't boast of the size or panache of the transcontinental trains, but built up enviable reputations of their own nonetheless. Of these, the Chicago-Texas trains were the most famous and impressive. The '' San Diegans,'' which ran from Los Angeles to San Diego, were the most popular and durable, becoming to the Santa Fe what New York City- Philadelphia trains were to the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
. But Santa Fe flyers also served Tulsa, Oklahoma, El Paso, Texas, Phoenix, Arizona (the ''Hassayampa Flyer
The Hassayampa Flyer, also known as the Hassayampa Chief, was a passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway between Ash Fork (later Williams Junction) and Phoenix in Arizona, United States.
History
In 1955, the Sa ...
''), and Denver, Colorado, among other cities not on their main line.
To reach smaller communities, the railroad operated mixed (passenger and freight) trains or gas-electric doodlebug rail cars. The latter were later converted to diesel power, and one pair of Budd Rail Diesel Car
The Budd Rail Diesel Car, RDC, Budd car or Buddliner is a self-propelled diesel multiple unit (DMU) railcar. Between 1949 and 1962, 398 RDCs were built by the Budd Company of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The cars were primarily adop ...
s was eventually added. After World War II, Santa Fe Trailways buses replaced most of these lesser trains. These smaller trains generally were not named; only the train numbers were used to differentiate services.
The ubiquitous passenger service inspired the title of the 1946 Academy-Award-winning Harry Warren
Harry Warren (born Salvatore Antonio Guaragna; December 24, 1893 – September 22, 1981) was an American composer and the first major American songwriter to write primarily for film. He was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Original Song ...
tune " On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe." The song was written in 1945 for the film '' The Harvey Girls'', a story about the waitresses of the Fred Harvey Company's restaurants. It was sung in the film by Judy Garland and recorded by many other singers, including Bing Crosby
Harry Lillis "Bing" Crosby Jr. (May 3, 1903 – October 14, 1977) was an American singer, musician and actor. The first multimedia star, he was one of the most popular and influential musical artists of the 20th century worldwide. He was a ...
. In the 1970s, the railroad used Crosby's version in a commercial.
AT&SF ceased operating passenger trains on May 1, 1971, when it conveyed its remaining trains to Amtrak. These included the ''Super Chief'' / ''El Capitan'', the '' Texas Chief'' and the ''San Diegan'' (though Amtrak reduced the ''San Diegan'' from three round trips to two). Discontinued were the '' San Francisco Chief'', the ex-''Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (, yuf-x-yav, Wi:kaʼi:la, , Southern Paiute language: Paxa’uipi, ) is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a m ...
'', the '' Tulsan'', and a Denver–La Junta local. ATSF had been more than willing to retain the ''San Diegan'' and its famed ''Chiefs.'' However, any railroad that opted out of Amtrak would have been required to operate ''all'' of its passenger routes until at least 1976. The prospect of having to keep operating its less-successful routes, especially the money-bleeding 23/24 (the former ''Grand Canyon'') led ATSF to get out of passenger service altogether.
Amtrak still runs the ''Super Chief'' and ''San Diegan'' today as the '' Southwest Chief'' and '' Pacific Surfliner,'' respectively, although the original routes and equipment have been modified by Amtrak.
Named trains
AT&SF operated the following named trains on regular schedules: * '' The Angel'': San Francisco, California – Los Angeles, California – San Diego, California (this was the southbound version of the ''Saint'') * ''The Angelo
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
'': San Angelo, Texas – Fort Worth, Texas (on the GC&SF)
* ''The Antelope'': Oklahoma City, Oklahoma – Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central ...
* '' Atlantic Express'': Los Angeles, California – Kansas City, Missouri (this was the eastbound version of the ''Los Angeles Express'').
* '' California Express'': Chicago, Illinois – Kansas City, Missouri – Los Angeles, California
* '' California Fast Mail'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California – San Francisco, California
* '' California Limited'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* '' California Special'': Clovis, New Mexico – Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
(with through connections to California via the San Francisco Chief at Clovis)
* '' Cavern'': Clovis, New Mexico – Carlsbad, New Mexico (connected with the ''Scout'').
* ''Centennial State
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
'': Denver, Colorado – Chicago, Illinois
* '' Central Texas Express'': Sweetwater, Texas
Sweetwater is a municipality in and the seat of Nolan County, Texas, United States. It is 123 miles southeast of Lubbock and 40 miles west of Abilene, Texas. Its population was 10,906 at the 2010 census.
History
The town's name "Sweetwater" is t ...
– Lubbock, Texas
Lubbock ( )
is the 10th-most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and the seat of government of Lubbock County. With a population of 260,993 in 2021, the city is also the 85th-most populous in the United States. The city is in the northw ...
* '' Chicagoan'': Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois (this was the eastbound version of the ''Kansas Cityan'' passenger train).
* '' Chicago Express'': Newton, Kansas
Newton is a city in and the county seat of Harvey County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 18,602. Newton is located north of Wichita. The city of North Newton is located immediately north and e ...
– Chicago, Illinois
* '' Chicago Fast Mail'': San Francisco, California – Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois
* '' Chicago-Kansas City Flyer'': Chicago, Illinois – Kansas City, Missouri
* '' The Chief'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* '' Eastern Express'': Lubbock, Texas – Amarillo, Texas (this was the eastbound version of the ''West Texas Express'').
* '' El Capitan'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* '' El Pasoan'': El Paso, Texas – Albuquerque, New Mexico
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
* '' El Tovar'': Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois (via Belen)
* '' Fargo Fast Mail/Express'': Belen, New Mexico
Belén (; es, Belén) is the second most populous city in Valencia County, New Mexico, Valencia County, New Mexico, United States, after its county seat, Los Lunas. The population was 7,360 at the 2020 Census.
Belén is Spanish language, Spanish ...
– Amarillo, Texas – Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois
* ''Fast Fifteen
Fast or FAST may refer to:
* Fast (noun), high speed or velocity
* Fast (noun, verb), to practice fasting, abstaining from food and/or water for a certain period of time
Acronyms and coded Computing and software
* ''Faceted Application of Subje ...
'': Newton, Kansas – Galveston, Texas
Galveston ( ) is a coastal resort city and port off the Southeast Texas coast on Galveston Island and Pelican Island in the U.S. state of Texas. The community of , with a population of 47,743 in 2010, is the county seat of surrounding Galvesto ...
* ''Fast Mail Express
Fast or FAST may refer to:
* Fast (noun), high speed or velocity
* Fast (noun, verb), to practice fasting, abstaining from food and/or water for a certain period of time
Acronyms and coded Computing and software
* ''Faceted Application of Subje ...
'': San Francisco, California (via Los Angeles) – Chicago, Illinois
* '' Golden Gate'': Oakland, California – Bakersfield, California
Bakersfield is a city in Kern County, California, United States. It is the county seat and largest city of Kern County. The city covers about near the southern end of the San Joaquin Valley and the Central Valley region. Bakersfield's populat ...
, with coordinated connecting bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
service to Los Angeles and San Francisco
* '' Grand Canyon Limited'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* ''Hassayampa Flyer
The Hassayampa Flyer, also known as the Hassayampa Chief, was a passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway between Ash Fork (later Williams Junction) and Phoenix in Arizona, United States.
History
In 1955, the Sa ...
'': Phoenix, Arizona – Ash Fork, Arizona (later Williams Junction, Arizona)
* '' The Hopi'': Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois
* '' Kansas Cityan'': Chicago, Illinois – Kansas City, Missouri (this was the westbound version of the ''Chicagoan'' passenger train).
* '' Kansas City Chief'': Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois
* '' Los Angeles Express'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California (this was the westbound version of the ''Atlantic Express'').
* '' The Missionary'': San Francisco, California – Belen, New Mexico – Amarillo, Texas – Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois
* ''Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest federally recognized tribe in the United ...
'': Chicago, Illinois – San Francisco, California (via Los Angeles)
* '' Oil Flyer'': Kansas City, Missouri – Tulsa, Oklahoma, with through sleepers to Chicago via other trains
* ''Overland Limited Overland Limited may refer to:
Trains
* Overland Limited (ATSF train), 1901–1915
* Overland Limited (UP train), 1895–1931
Films
* ''The Overland Limited'' (1925)
* Several short films made in 1899 and 1901:
**''Overland Limited'' (1899)
**''T ...
'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* '' Phoenix Express'': Los Angeles, California – Phoenix, Arizona
* '' The Ranger'': Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois
* '' The Saint'': San Diego, California – Los Angeles, California – San Francisco, California (this was the northbound version of the "Angel")
* ''San Diegan
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
'': Los Angeles, California – San Diego, California
* '' San Francisco Chief'': San Francisco, California – Chicago, Illinois
* '' San Francisco Express'': Chicago, Illinois – San Francisco, California (via Los Angeles)
* ''Santa Fe de Luxe
The ''Santa Fe de Luxe'' was the first extra-fare named passenger train on the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
The ''de Luxe'' (meaning something luxurious, or elegant) started on December 12, 1911, on a seasonal weekly schedule bet ...
'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California – San Francisco, California
* '' Santa Fe Eight'': Belen, New Mexico – Amarillo, Texas – Kansas City, Missouri – Chicago, Illinois
* '' The Scout'': Chicago, Illinois – San Francisco, California (via Los Angeles)
* ''South Plains Express
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
'': Sweetwater, Texas – Lubbock, Texas
* '' Super Chief'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California
* '' The Texan'': Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
– New Orleans, Louisiana (on the GC&SF between Galveston and Houston, then via the Missouri Pacific Railroad between Houston and New Orleans).
* '' Texas Chief'': Galveston, Texas (on the GC&SF) – Chicago, Illinois
* ''Tourist Flyer
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
'': Chicago, Illinois – San Francisco, California (via Los Angeles)
* '' The Tulsan'': Tulsa, Oklahoma – Kansas City, Mo. with through coaches to Chicago, Illinois, via other trains (initially the Chicagoan/Kansas Cityan)
* ''Valley Flyer
The ''Valley Flyer'' was a short-lived named passenger train of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
The all-heavyweight, "semi-streamlined" train ran between Bakersfield and Oakland, California (through California's San Joaquin Vall ...
'': Oakland, California – Bakersfield, California
Bakersfield is a city in Kern County, California, United States. It is the county seat and largest city of Kern County. The city covers about near the southern end of the San Joaquin Valley and the Central Valley region. Bakersfield's populat ...
* '' West Texas Express'': Amarillo, Texas – Lubbock, Texas (this was the westbound version of the ''Eastern Express'').
Special trains
 Occasionally, a special train was chartered to make a high-profile run over the Santa Fe's track. These specials were not included in the railroad's regular revenue service lineup, but were intended as one-time (and usually one-way) traversals of the railroad. Some of the more notable specials include:
* '' Cheney Special'':
Occasionally, a special train was chartered to make a high-profile run over the Santa Fe's track. These specials were not included in the railroad's regular revenue service lineup, but were intended as one-time (and usually one-way) traversals of the railroad. Some of the more notable specials include:
* '' Cheney Special'': Colton, California
Colton is a city in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Nicknamed "Hub City", Colton is located in the Inland Empire region of the state and is a suburb of San Bernardino, California, San Bernardino, approximately south of the cit ...
– Chicago, Illinois (a one-time train that ran in 1895 on behalf of B.P. Cheney, a director of the Santa Fe).
* ''Clarke Special
Clarke is a surname which means "clerk". The surname is of English and Irish origin and comes from the Latin . Variants include Clerk and Clark. Clarke is also uncommonly chosen as a given name.
Irish surname origin
Clarke is a popular surname in ...
'': Winslow, Arizona – Chicago, Illinois (a one-time train that ran in 1904 on behalf of Charles W. Clarke, the son of then-Arizona senator William Andrew Clarke).
* '' David B. Jones Special'': Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois, and on to Lake Forest, Illinois
Lake Forest is a city located in Lake County, Illinois, United States. Per the 2020 census, the population was 19,367. The city is along the shore of Lake Michigan, and is a part of the Chicago metropolitan area and the North Shore. Lake Forest ...
(a one-time, record-breaking train that ran between May 5 to 8, 1923, on behalf of the president of the Mineral Point Zinc Company).
* '' Huntington Special'': Argentine, Kansas – Chicago, Illinois (a one-time train that ran in 1899 on behalf of Collis P. Huntington
Collis Potter Huntington (October 22, 1821 – August 13, 1900) was an American industrialist and railway magnate. He was one of the Big Four of western railroading (along with Leland Stanford, Mark Hopkins, and Charles Crocker) who invested ...
).
* '' H.P. Lowe Special'': Chicago, Illinois – Los Angeles, California (a one-time, record-breaking train that ran in 1903 on behalf of the president of the Engineering Company of America
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
).
* ''Miss Nellie Bly Special
Game board illustrating journalist Nellie Bly's circumnavigation of the globe (1889-1890), in the '' New York World'', 26 January 1890.
''Around the World in Seventy-Two Days'' is an 1890 book by journalist Elizabeth Jane Cochrane, writing und ...
'': San Francisco, California – Chicago, Illinois (a one-time, record-breaking train that ran in 1890 on behalf of Nellie Bly, a reporter for the '' New York World'' newspaper).
* ''Peacock Special
Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera '' Pavo'' and ''Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are refe ...
'': Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois (a one-time train that ran in 1900 on behalf of A.R. Peacock
AR, Ar, or A&R may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Artists and repertoire
Periodicals
* ''Absolute Return + Alpha'', a hedge fund publication
*''The Adelaide Review'', an Australian arts magazine
* ''American Renaissance'' ( ...
, vice-president of the Carnegie Steel and Iron Company).
* '' Scott Special'': Los Angeles, California – Chicago, Illinois (the most well-known of Santa Fe's "specials," also known as the ''Coyote Special'', the ''Death Valley Coyote'', and the ''Death Valley Scotty Special'': a one-time, record-breaking train that ran in 1905, essentially as a publicity stunt).
* ''Wakarusa Creek Picnic Special Wakarusa can refer to several things in the United States:
* Wakarusa, Indiana
* Wakarusa, Kansas
* The Wakarusa River, a tributary of the Kansas River
* The Wakarusa War, part of the Bleeding Kansas violence before the American Civil War
* Wakarus ...
'': Topeka, Kansas – Pauline, Kansas
Pauline is an unincorporated community in Shawnee County, Kansas, United States. Located south of Topeka, it lies next to Forbes Field on southwest Topeka Boulevard. It is occasionally seen as part of the South City Industry Park for Topeka wit ...
(a one-time train that took picnickers on a 30-minute trip, at a speed of , to celebrate the official opening of the line on April 26, 1869).
Signals
The Santa Fe employed several distinctive wayside and crossing signal styles. In an effort to reduce grade crossing accidents, the Santa Fe was an early user of wigwag signals from the Magnetic Signal Company, beginning in the 1920s. They had several distinct styles that were not commonly seen elsewhere. Model 10's, which had the wigwag motor and banner coming from halfway up the mast with the crossbucks on top, were almost unique to the Santa Fe–the Southern Pacific had a few as well. Upper quadrant Magnetic Flagmen were used extensively on the Santa Fe as well–virtually every small town main street and a number of city streets had their crossings protected by these unique wigwags. Virtually all the wigwags were replaced with modern signals by the turn of the 21st century. The railroad was also known for its tall "T-2 style" upper quadrant semaphores which provided traffic control on its lines. Again, the vast majority of these had been replaced by the beginning of the 21st century, with fewer than 50 still remaining in use in New Mexico as of 2015.Paint schemes
Steam locomotives
 The Santa Fe operated a large and varied fleet of
The Santa Fe operated a large and varied fleet of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s. In 1899, the company owned 1036 locomotives. Among them was the 2-10-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. In the United States of America and elsewhere the is ...
"Santa Fe", originally built for the railroad by Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades t ...
in 1903.. The railroad would ultimately end up with the largest fleet of them, at over 300. Aside from the 2-10-2, Santa Fe rostered virtually every type of steam locomotive imaginable, including 4-4-2 Atlantics, 2-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. ...
Moguls, 2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
Consolidations, 2-8-2 Mikados, 2-10-0 Decapods, 2-6-2 Prairies, 4-8-4 Northerns, 4-6-4 Hudsons, 4-6-2 Pacifics, 4-8-2 Mountains, 2-8-4 Berkshires, and 2-10-4 Texas. The railroad also operated a fleet of heavy articulated steam locomotives, including 1158 class 2-6-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and one pair of trailing wheels. ...
s, 2-8-8-0s, 2-10-10-2s, 2-8-8-2
A 2-8-8-2, in the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangements, is an articulated locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. The equivalent UIC classification ...
s, and the rare 4-4-6-2 ''Mallet'' type. The Railroad retired its last steam locomotive in 1959.
During the twentieth century, all but one of these was painted black, with white unit numbers on the sand domes and three sides of the tender. Cab sides were lettered "AT&SF", also in white. The subsidiary Gulf, Colorado and Santa Fe often painted all or part of the smokebox (between the boiler and the headlight) white or silver. In 1940, the circle and cross emblem was applied to the tenders of a few passenger locomotives, but these were all later painted over. After World War II, "Santa Fe" appeared on tender sides of mainline road locomotives in white, above the unit number. Locomotives were delivered from Baldwin with white paint on the wheel rims, but the road did not repaint these "whitewalls" after shopping the locomotives. After World War II, side rods and valve gear were painted chrome yellow. For a short time, Pacific types 1369 and 1376 were semi-streamlined for "Valley Flyer
The ''Valley Flyer'' was a short-lived named passenger train of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
The all-heavyweight, "semi-streamlined" train ran between Bakersfield and Oakland, California (through California's San Joaquin Vall ...
" service, with a unique paint scheme in colors similar to those used on the new passenger diesels. More unique was the two-tone light blue over royal blue scheme of streamlined Hudson type 3460.
Preserved locomotives
 While most of the Santa Fe's steam locomotives were retired and sold for scrap, over fifty were saved and donated to various parks and museums, a handful of which have either been restored to operating condition or are pending future restoration.
Some of the more notable locomotives include:
* 5 (
While most of the Santa Fe's steam locomotives were retired and sold for scrap, over fifty were saved and donated to various parks and museums, a handful of which have either been restored to operating condition or are pending future restoration.
Some of the more notable locomotives include:
* 5 (0-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven. The wheels on the earliest four-coupled locomotives were ...
), located at the California State Railroad Museum
The California State Railroad Museum is a museum in the state park system of California, United States, interpreting the role of the "iron horse" in connecting California to the rest of the nation. It is located in Old Sacramento State Historic ...
in Sacramento, California.
* 132 132 may refer to:
*132 (number)
*AD 132
*132 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 132 BC was a year of the Roman calendar, pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laenas and Rupilius (or, less frequently, year 622 ''Ab ...
(2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
), Built by Baldwin in 1880 and located at the Kansas Museum of History in Topeka. Named for Cyrus K. Holliday. Was used often by the Santa Fe for promotions and special events until it was donated to the Kansas State Historical Society in 1977. It is the second oldest locomotive from the Santa Fe that is preserved close to its original appearance.
* 643
__NOTOC__
Year 643 (Roman numerals, DCXLIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 643 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno D ...
(2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
), Originally built by Hinkley Locomotive Works in 1879 as #73 with a 4-4-0 arrangement. The oldest preserved locomotive of the Santa Fe, although not as originally configured. It was converted by the railroad to a 2-8-0 configuration following an accident in 1897. It had several upgrades over the years while working on the Gulf Division. It was formerly located at the then-new Oklahoma State Fairgrounds, following its donation from the Santa Fe to the people of Oklahoma in 1953. The locomotive was relocated again in 2015 to the Oklahoma Railway Museum in Oklahoma City, where it received a badly needed cleaning and thorough cosmetic restoration, and is currently on display.
* 769
__NOTOC__
Year 769 ( DCCLXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 769 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar er ...
(2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
), located at the Old Coal Mine Museum in Madrid, New Mexico. It is waiting to be moved to the Santa Fe Southern Railway in Santa Fe for future restoration to operating condition.
* 870 (2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
), located at Heritage Park in Santa Fe Springs, California.
* 940 (2-10-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. In the United States of America and elsewhere the is ...
), located at the Union depot in Bartlesville
Bartlesville is a city mostly in Washington County in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The population was 37,290 at the 2020 census. Bartlesville is north of Tulsa and south of the Kansas border. It is the county seat of Washington County. The ...
, Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the nor ...
. It is the only surviving steam locomotive from the Santa Fe with a 2-10-2 wheel arrangement.
* 1010
Year 1010 ( MX) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Africa
* The Nile river in Egypt freezes over.
Asia
* The Lý dynasty is established in Vietnam (or 1 ...
(2-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie.
Overview
The major ...
), located at the California State Railroad Museum
The California State Railroad Museum is a museum in the state park system of California, United States, interpreting the role of the "iron horse" in connecting California to the rest of the nation. It is located in Old Sacramento State Historic ...
in Sacramento, California.
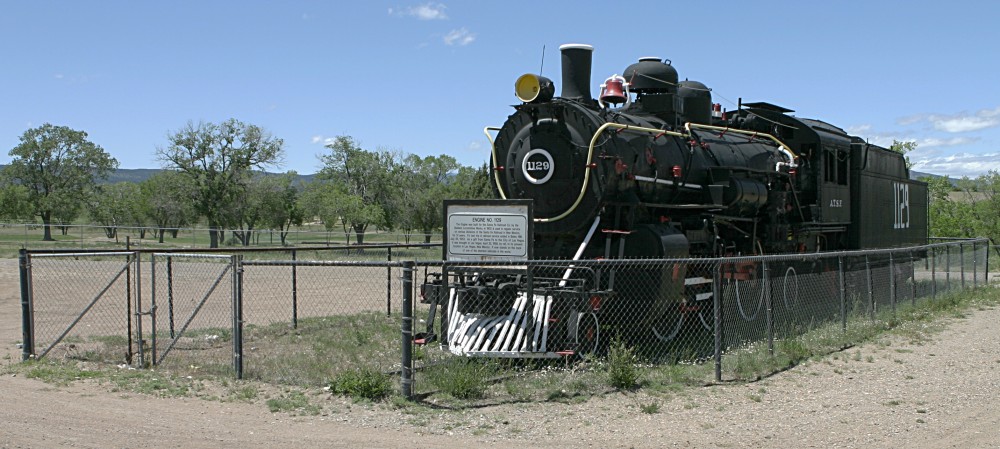
* 1129 (2-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie.
Overview
The major ...
), located at Las Vegas, New Mexico.
* 1316
Year 1316 ( MCCCXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–December
* January 28–March 18 – Llywelyn Bren revolts against English rule in Wales. ...
(4-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The locomotiv ...
), formerly located at Fort Concho
Fort Concho is a former United States Army installation and National Historic Landmark District located in San Angelo, Texas. It was established in November 1867 at the confluence of the North and South Concho Rivers, on the routes of the But ...
, Texas: the sole survivor of the 1309 class was restored to operating condition by the Texas State Railroad in the early 1980s as its No. 500. It is currently displayed at Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
for another restoration for future excursion service.
* 2913 (4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type w ...
), located in Riverview Park at Fort Madison
Fort Madison is a city and a county seat of Lee County, Iowa, United States along with Keokuk, Iowa, Keokuk. Of Iowa's 99 counties, Lee County is the only one with two county seats. The population was 10,270 at the time of the 2020 United State ...
, Iowa.
* 2926 (4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type w ...
), formerly located in Coronado Park in Albuquerque, New Mexico. This locomotive has been undergoing restoration for operational purposes by the New Mexico Steam Locomotive and Rail Historical Society, which has expended 114,000 man-hours and $1,700,000 in donated funds on her restoration since 2002. It has been operational since July 2021.
* 3415 (4-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The locomotiv ...
), formerly located at Eisenhower Park in Abilene, Kansas, until it was acquired by the Abilene and Smoky Valley Railroad and has been restored for excursion service since 2009.
* 3416 (4-6-2), currently preserved at Great Bend, Kansas.
* 3417 (4-6-2), formerly preserved at Hulen Park, in Cleburne, Texas.
* 3423 (4-6-2), located at the Railroad & Heritage Museum in Temple Texas, it is currently preserved.
* 3424 (4-6-2), Preserved in Kinsley, Kansas.
* 3450 (4-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as t ...
), the sole survivor of the 3450 class, this locomotive is the gateway of the RailGiants Train Museum
RailGiants Train Museum is a railroad museum of historic trains located at the Fairplex in Pomona, California, United States.
The museum was closed indefinitely in March 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, but after renovations, it reopen ...
in Pomona
Pomona may refer to:
Places Argentina
* Pomona, Río Negro
Australia
* Pomona, Queensland, Australia, a town in the Shire of Noosa
* Pomona, New South Wales, Australia
Belize
* Pomona, Belize, a municipality in Stann Creek District
Mexico ...
, California.
* 3463 (4-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as t ...
), the sole survivor of the 3460 class, this locomotive is located at the Kansas Expocentre in Topeka, Kansas, waiting for future restoration.
* 3751
Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe 3751 is a class 3751 4-8-4 steam locomotive built in 1927 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Eddystone (Philadelphia), Pennsylvania for the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). 3751 was the first 4-8-4 steam loc ...
(4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type w ...
), the Santa Fe's and Baldwin's very first 4-8-4, was once on display at Viaduct Park near the AT&SF depot in San Bernardino, California. The locomotive was moved out of the park in 1986 to be restored and, after almost 5 years later, No. 3751 made its first run on a 4-day trip from Los Angeles to Bakersfield
Bakersfield is a city in Kern County, California, United States. It is the county seat and largest city of Kern County. The city covers about near the southern end of the San Joaquin Valley and the Central Valley region. Bakersfield's populat ...
and return in December 1991. This trip marked the beginning of No. 3751's career in excursion service. Currently undergoing a federally required 15-year overhaul.
* 3759 (4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and four trailing wheels on two axles. The type w ...
): This locomotive is known for pulling the ''"Farewell to Steam Excursion"'' for the Santa Fe in 1955 before it was donated to the City of Kingman, Arizona, where it is currently on static display. It was almost acquired by the Grand Canyon Railway in the early 1990s.
* 3768 (4-8-4), after retiring in 1958, it was donated to the city of Wichita, Kansas, where it is currently preserved at the Great Plains Museum of Transportation.
* 5000 5000 or ''variation'', may refer to:
In general
* A.D. 5000, the last year of the 5th millennium CE, an exceptional common year starting on Wednesday
* 5000 BCE, a year in the 5th millennium BC
* 5000s AD, a decade, century, millennium in the 6th ...
''Madame Queen'' (2-10-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a locomotive has two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a Bissel truck, ten coupled driving wheels on five axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles, usually in a bogie ...
), the second-oldest preserved steam locomotive with a 2-10-4 wheel arrangement, ''Madame Queen'' is located in Amarillo, Texas, awaiting possible relocation elsewhere.
* 5011 (2-10-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a locomotive has two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a Bissel truck, ten coupled driving wheels on five axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles, usually in a bogie ...
), the first of the 5011 class, is on static display at the National Museum of Transportation in St. Louis, Missouri.
* 5017 (2-10-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a locomotive has two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a Bissel truck, ten coupled driving wheels on five axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles, usually in a bogie ...
), located at the National Railroad Museum in Green Bay, Wisconsin.
* 9005 (0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangemen ...
), located in the historic train depot in Clovis
Clovis may refer to:
People
* Clovis (given name), the early medieval (Frankish) form of the name Louis
** Clovis I (c. 466 – 511), the first king of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler
** Clovis II (c. 634 – c. 657), ...
, New Mexico.
Diesel locomotives
Passenger
Chief
Chief may refer to:
Title or rank
Military and law enforcement
* Chief master sergeant, the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force
* Chief of police, the head of a police department
* Chief of the boa ...
'' " drumhead" logo. "''Super Chief''" was emblazoned on a plaque located on the front. The rooftop was light slate gray, rimmed by a red pinstripe. This unique combination of colors was called the ''Golden Olive'' paint scheme. Before entering service, Sterling McDonald
Sterling may refer to:
Common meanings
* Sterling silver, a grade of silver
* Sterling (currency), the currency of the United Kingdom
** Pound sterling, the primary unit of that currency
Places United Kingdom
* Stirling, a Scottish city who ...
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
Styling Department augmented the look with the addition of red and blue striping along both the sides and ends of the units in order to enhance their appearance.
Leland Knickerbocker Leland may refer to:
Places United States
* Leland, Illinois, a village
* Leland, Iowa, a city
* Leland, Michigan, an unincorporated community and census-designated place
* Leland, Mississippi, a city
* Leland, North Carolina, a town
* Leland, O ...
of the GM Art and Color Section. Its design was protected under a U.S. design patent, granted on November 9, 1937. It is reminiscent of a Native American ceremonial head-dress. The scheme consisted of a red "bonnet" that wrapped around the front of the unit and was bordered by a yellow stripe and black pinstripe. The extent of the bonnet varied according to the locomotive model and was largely determined by the shape and length of the car body. The remainder of the unit was either painted silver or was composed of stainless-steel panels.
All units wore a nose emblem consisting of an elongated yellow "Circle and Cross" emblem with integral "tabs" on the nose and the sides, outlined and accented with black pinstripes, with variances according to the locomotive model. "SANTA FE" was displayed on the horizontal limb of the cross in black, Art Deco-style lettering. This emblem has come to be known as the "cigar band
A cigar band is a loop made of paper or foil fitted around the body of a cigar to denote its brand or variety. Although origins of the device are the subject of several legends, modern historians credit a European immigrant to Cuba named Gustave B ...
" due to its uncanny resemblance to the same. On all but the "Erie-built" units (which were essentially run as a demonstrator set), GE U28CG, GE U30CG, and FP45 units, a three-part yellow and black stripe ran up the nose behind the band.
A "Circle and Cross" motif (consisting of a yellow field, with red quadrants, outlined in black) was painted around the side windows on "as-delivered" E1 units. Similar designs were added to E3s, E6s, the DL109/110 locomotive set, and ATSF 1A after it was rebuilt and repainted. The sides of the units typically bore the words "SANTA FE" in black, 5"– or 9"–high extra extended Railroad Roman letters, as well as the "Indian Head" logo, with a few notable exceptions.
Railway identity on diesel locomotives in passenger service:
Source: Pelouze, Richard W. (1997). ''Trademarks of the Santa Fe Railway.'' The Santa Fe Railway Historical and Modeling Society, Inc., Highlands Ranch, Colorado, pp. 47–50.
In later years, Santa Fe adapted the scheme to its gas-electric " doodlebug" units. The standard for all of Santa Fe's passenger locomotives, the ''Warbonnet'' is considered by many to be the most-recognized corporate logo in the railroad industry. Early after Amtrak's inception in 1971, Santa Fe embarked on a program to repaint the red bonnet on its F units that were still engaged in hauling passenger consists with yellow (also called ''Yellowbonnets'') or dark blue (nicknamed ''Bluebonnets''), as it no longer wanted to project the image of a passenger carrier.
Freight
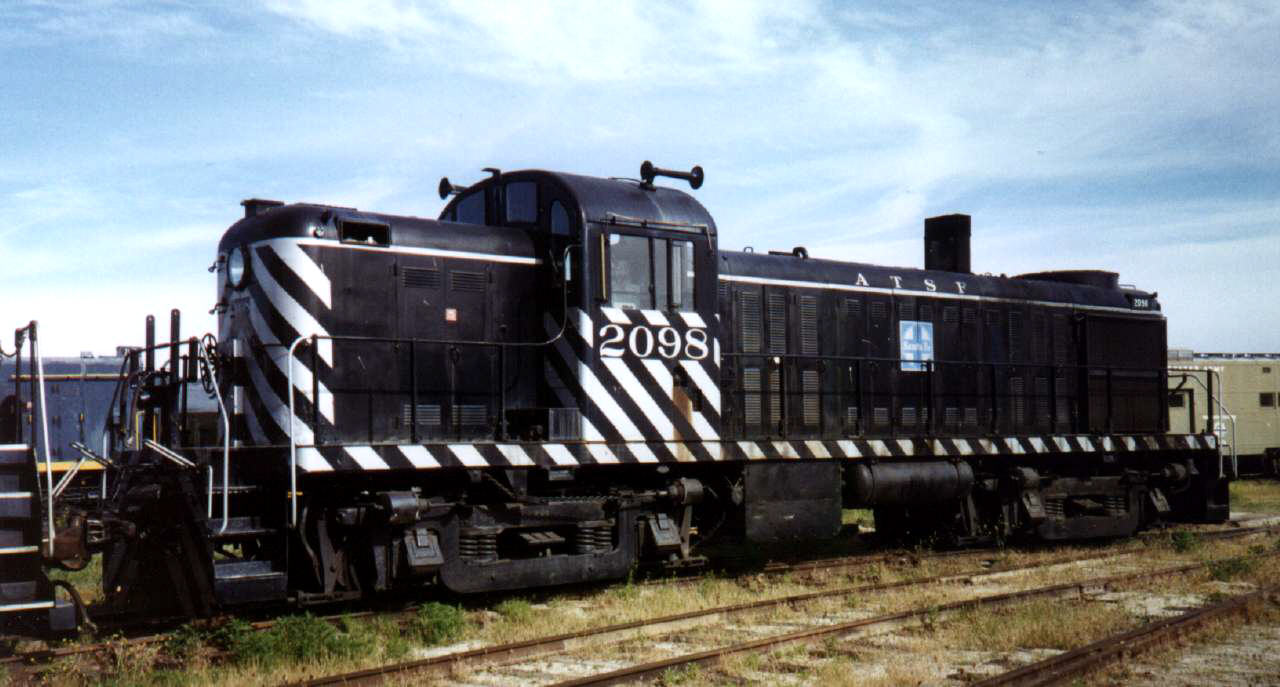
 Diesels used as switchers between 1935 and 1960 were painted black, with just a thin white or silver horizontal accent stripe (the sills were painted similarly). The letters "A.T.& S.F." were applied in a small font centered on the sides of the unit, as was the standard blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo. After World War II, diagonal white or silver stripes were added to the ends and cab sides to increase the visibility at grade crossings (typically referred to as the ''Zebra Stripe'' scheme). "A.T.& S.F." was now placed along the sides of the unit just above the accent stripe, with the blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo below.
Due to the lack of abundant water sources in the American desert, the Santa Fe Railway was among the first railroads to receive large numbers of streamlined diesel locomotives for use in freight service, in the form of the EMD FT. For the first group of FTs, delivered between December 1940 and March 1943 (#100–#119), the railroad selected a color scheme consisting of dark blue accented by a pale yellow stripe up the nose, and pale yellow highlights around the cab and along the mesh and framing of openings in the sides of the engine compartment; a thin red stripe separated the blue areas from the yellow.
Diesels used as switchers between 1935 and 1960 were painted black, with just a thin white or silver horizontal accent stripe (the sills were painted similarly). The letters "A.T.& S.F." were applied in a small font centered on the sides of the unit, as was the standard blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo. After World War II, diagonal white or silver stripes were added to the ends and cab sides to increase the visibility at grade crossings (typically referred to as the ''Zebra Stripe'' scheme). "A.T.& S.F." was now placed along the sides of the unit just above the accent stripe, with the blue and white "Santa Fe" box logo below.
Due to the lack of abundant water sources in the American desert, the Santa Fe Railway was among the first railroads to receive large numbers of streamlined diesel locomotives for use in freight service, in the form of the EMD FT. For the first group of FTs, delivered between December 1940 and March 1943 (#100–#119), the railroad selected a color scheme consisting of dark blue accented by a pale yellow stripe up the nose, and pale yellow highlights around the cab and along the mesh and framing of openings in the sides of the engine compartment; a thin red stripe separated the blue areas from the yellow.
 The words SANTA FE were applied in yellow in a 5"–high extended font, and centered on the nose was the "Santa Fe" box logo (initially consisting of a blue cross, circle, and square painted on a solid
The words SANTA FE were applied in yellow in a 5"–high extended font, and centered on the nose was the "Santa Fe" box logo (initially consisting of a blue cross, circle, and square painted on a solid bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
sheet, but subsequently changed to baked steel sheets painted bronze with the blue identifying elements applied on top). Three thin, pale yellow stripes (known as ''Cat Whiskers'') extended from the nose logo around the cab sides. In January, 1951, Santa Fe revised the scheme to consist of three yellow stripes running up the nose, with the addition of a blue and yellow ''Cigar Band'' (similar in size and shape to that applied to passenger units); the blue background and elongated yellow "SANTA FE" lettering were retained.
The years 1960 to 1972 saw non-streamlined freight locomotives sporting the "Billboard" color scheme (sometimes referred to as the "Bookends" or "Pinstripe" scheme), where the units were predominantly dark blue with yellow ends and trim, with a single yellow accent pinstripe. The words "Santa Fe" were applied in yellow in large bold serif letters (logotype) to the sides of the locomotive below the accent stripe (save for yard switcher
A switcher, shunter, yard pilot, switch engine, yard goat, or shifter is a small railroad locomotive used for manoeuvring railroad cars inside a rail yard in a process known as ''switching'' (US) or ''shunting'' (UK). Switchers are not inten ...
s which displayed the "SANTA FE" in small yellow letters above the accent stripe, somewhat akin to the ''Zebra Stripe'' arrangement).
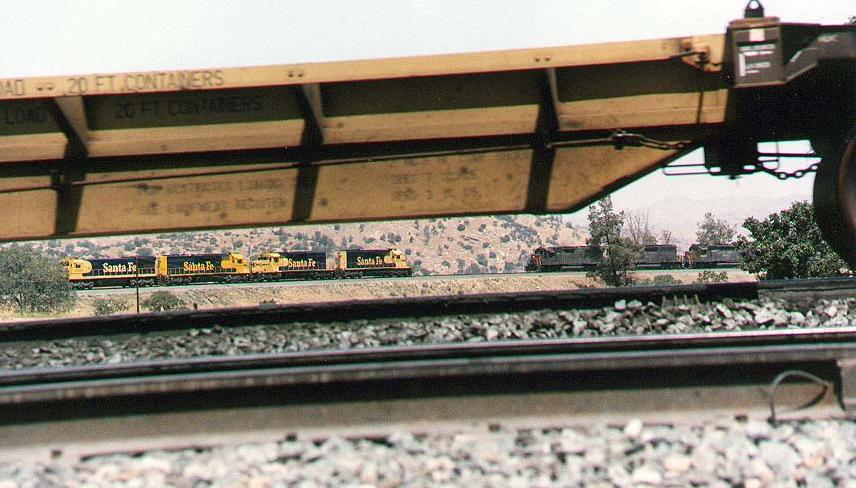
From 1972 to 1996, and even on into the BNSF era, the company adopted a new paint scheme often known among railfans as the "Freightbonnet", which placed more yellow on the locomotives (reminiscent of the company's retired ''Warbonnet'' scheme); the goal again was to ensure higher visibility at grade crossings. The truck assemblies, previously colored black, now received silver paint.
 In 1965, the road took delivery of ten GE U28CG dual-service roadswitcher locomotives equally suited to passenger or fast freight service. These wore a variation of the "Warbonnet" scheme in which the black and yellow separating stripes disappeared. The "Santa Fe" name was emblazoned on the sides in large black letters, using the same stencils used on freight engines; these were soon repainted in red. In 1989, Santa Fe resurrected this version of the "Warbonnet" scheme and applied it to two SDFP45 units, #5992 and #5998. The units were re-designated as #101 and #102 and reentered service on July 4, 1989, as part of the new "Super Fleet" campaign (the first Santa Fe units to be so decorated for freight service). The six remaining FP45 units were thereafter similarly repainted and renumbered. From that point forward, most new locomotives wore red and silver, and many retained this scheme after the Burlington Northern Santa Fe merger, some with "BNSF" displayed across their sides.
For the initial deliveries of factory-new "Super Fleet" equipment, Santa Fe took delivery of the EMD GP60M and General Electric B40-8W which made the Santa Fe the only US Class I railroad to operate new 4-axle (B-B) freight locomotives equipped with the North American Safety Cab intended for high-speed intermodal service.
Several experimental and commemorative paint schemes emerged during the Santa Fe's diesel era. One combination was developed and partially implemented in anticipation of a merger between the parent companies of the Santa Fe and Southern Pacific (SP) railroads in 1984. The red, yellow, and black paint scheme with large yellow block letters on the sides and ends of the units of the proposed Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) has come to be somewhat derisively known among railfans as the ''Kodachrome'' livery, due to the similarity in colors to the boxes containing slide film sold by the Eastman Kodak Company under the same name. Santa Fe units repainted in this scheme were labeled "SF", Southern Pacific units "SP", and some (presumably new) units wore the letters "SPSF". After the ICC's denial of the merger, railfans joked that SPSF really stood for "Shouldn't Paint So Fast."
In 1965, the road took delivery of ten GE U28CG dual-service roadswitcher locomotives equally suited to passenger or fast freight service. These wore a variation of the "Warbonnet" scheme in which the black and yellow separating stripes disappeared. The "Santa Fe" name was emblazoned on the sides in large black letters, using the same stencils used on freight engines; these were soon repainted in red. In 1989, Santa Fe resurrected this version of the "Warbonnet" scheme and applied it to two SDFP45 units, #5992 and #5998. The units were re-designated as #101 and #102 and reentered service on July 4, 1989, as part of the new "Super Fleet" campaign (the first Santa Fe units to be so decorated for freight service). The six remaining FP45 units were thereafter similarly repainted and renumbered. From that point forward, most new locomotives wore red and silver, and many retained this scheme after the Burlington Northern Santa Fe merger, some with "BNSF" displayed across their sides.
For the initial deliveries of factory-new "Super Fleet" equipment, Santa Fe took delivery of the EMD GP60M and General Electric B40-8W which made the Santa Fe the only US Class I railroad to operate new 4-axle (B-B) freight locomotives equipped with the North American Safety Cab intended for high-speed intermodal service.
Several experimental and commemorative paint schemes emerged during the Santa Fe's diesel era. One combination was developed and partially implemented in anticipation of a merger between the parent companies of the Santa Fe and Southern Pacific (SP) railroads in 1984. The red, yellow, and black paint scheme with large yellow block letters on the sides and ends of the units of the proposed Southern Pacific Santa Fe Railroad (SPSF) has come to be somewhat derisively known among railfans as the ''Kodachrome'' livery, due to the similarity in colors to the boxes containing slide film sold by the Eastman Kodak Company under the same name. Santa Fe units repainted in this scheme were labeled "SF", Southern Pacific units "SP", and some (presumably new) units wore the letters "SPSF". After the ICC's denial of the merger, railfans joked that SPSF really stood for "Shouldn't Paint So Fast."

Ferry service
Santa Fe maintained and operated a fleet of three passengerferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
boats (the ''San Pablo'', the ''San Pedro'', and the ''Ocean Wave'') that connected Richmond, California
Richmond is a city in western Contra Costa County, California, United States. The city was municipal corporation, incorporated on August 7, 1905, and has a Richmond, California City Council, city council.
, with San Francisco by water. The ships traveled the eight miles between the San Francisco Ferry Terminal and the railroad's Point Richmond terminal across San Francisco Bay. The service was originally established as a continuation of the company's named passenger train runs such as the ''Angel'' and the ''Saint''. The larger two ships (the ''San Pablo'' and the ''San Pedro'') carried Fred Harvey Company dining facilities.
Rival SP owned the world's largest ferry fleet (which was subsidized by other railroad activities), at its peak carrying 40 million passengers and 60 million vehicles annually aboard 43 vessels. Santa Fe discontinued ferry service in 1933 due to the effects of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
and routed their trains to Southern Pacific's ferry terminal in Oakland
Oakland is the largest city and the county seat of Alameda County, California, United States. A major West Coast port, Oakland is the largest city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, the third largest city overall in the Bay A ...
. The San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge opened in 1936, initiating a slow decline in demand for SP's ferry service, which was eventually discontinued circa 1958; starting in 1938, SF-bound passengers could board buses across the bridge at the Santa Fe Oakland depot (located in Emeryville).
See also
*ATSF 3460 class
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway's 3460 class comprised six 4-6-4 "Super Hudson" type steam locomotives built in 1937 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for service between La Junta, Colorado and Chicago, Illinois, a fairly flat division of ...
* Beep (locomotive)
* CF7
* Corwith Yards, Chicago
* EMD F45
* EMD SDF40-2
The EMD SDP40F was a six-axle C-C diesel–electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division (EMD) from 1973–1974. Based on Santa Fe’s EMD FP45, EMD built 150 for Amtrak, the operator of most intercity passenger trai ...
* Christine Gonzalez
* David L. Gunn
David L. Gunn (born June 21, 1937) is a transportation system administrator who has headed several significant railroads and transit systems in North America. He was director of operations of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA ...
* History of rail transportation in California
* List of defunct railroads of North America
* Santa Fe 3415
Santa Fe 3415 is a preserved class 3400 4-6-2 "Pacific" type steam locomotive built in 1919 by Baldwin for the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. Retired in 1954, it sat in Eisenhower Park in Abilene, Kansas until 1996. At that point, it wa ...
– a restored Pacific type steam locomotive
* Santa Fe 5000
* Santa Fe Refrigerator Despatch
* Santa Fe–Southern Pacific merger
The Santa Fe–Southern Pacific merger was an attempted corporate consolidation of two of the major railroads in the Western United States at the time: the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway and the Southern Pacific Railroad. The approximate ...
* SD26
* Super C
* '' There Goes a Train''
References
Further reading
* * * The Cosmopolitan (February 1893),The Atchison Topeka and Santa Fe
'. Retrieved May 10, 2005. * * ** * * * * Duke, Donald. ''Fred Harvey, civilizer of the American Southwest'' (Pregel Press, 1995); The passenger trains stopped for meals at Fred Harvey restaurants. * Dye, Victoria E. ''All Aboard for Santa Fe: Railway Promotion of the Southwest, 1890s to 1930s'' (University of New Mexico Press, 2007). * * Frailey, Fred W. (1998). ''Twilight of the Great Trains'', p. 108. Waukesha, Wisconsin: Kalmbach Publishing. . * Richard H. Frost, ''The Railroad and the Pueblo Indians: The Impact of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa fe on the Pueblos of the Rio Grande, 1880–1930.'' 2016, Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. * * Goen, Steve Allen (2000). ''Santa Fe in the Lone Star State'' * * Marshall, James Leslie. ''Santa Fe: the railroad that built an empire'' (1945). * * * Pratt School of Engineering, Duke University (2004),
Alumni Profiles: W. John Swartz
'. Retrieved May 11, 2005. * Santa Fe Railroad (1945), ''Along Your Way'', Rand McNally, Chicago. * Santa Fe Railroad (November 29, 1942), ''Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway System Time Tables'', Rand McNally and Company, Chicago. * * Solomon, Brian. ''Santa Fe Railway'' (Voyageur Press, 2003). * * Snell, Joseph W. and Don W. Wilson, "The Birth of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad," (Part One) ''Kansas Historical Quarterly'' (1968) 34#2 pp 113–142
** Snell, Joseph W. and Don W. Wilson, "The Birth of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad," (Part Two) ''Kansas Historical Quarterly'' (1968) 34#3 pp 325–35
*
External links
"Along Your Way", 1946 edition
Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe
photos and other documents on Kansas Memory, the digital portal of the Kansas Historical Society (over 2800 AT&SF items)
Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Company Records
at the Kansas Historical Society, Topeka, Kansas
Russell Crump's Santa Fe Archives
– a very extensive set of resources for Santa Fe history.
Santa Fe Preserved Locomotives
Santa Fe Railway Historical and Modeling Society
official website
article from the May 18, 1947, issue of ''
Life Magazine
''Life'' was an American magazine published weekly from 1883 to 1972, as an intermittent "special" until 1978, and as a monthly from 1978 until 2000. During its golden age from 1936 to 1972, ''Life'' was a wide-ranging weekly general-interest ma ...
'' featuring the Santa Fe fleet.
* James William Steele''Rand, McNally & Co.'s new overland guide to the Pacific Coast''
Chicago: Rand, McNally & Co., 1888. Illustrated guide to the Santa Fe trip circa 1888.
* ttp://nrs.harvard.edu/urn-3:HBS.Baker.EAD:bak00020 Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad Recordsat Baker Library Historical Collections, Harvard Business School
Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
Atchison Topeka & Santa Fe (ATSF) All-Time Diesel Roster
{{DEFAULTSORT:Atchison Topeka Santa Fe Railway Former Class I railroads in the United States Predecessors of the BNSF Railway Rail lines receiving land grants Railway companies established in 1895 Railway companies disestablished in 1996 Companies based in Chicago Economy of the Southwestern United States Defunct Arizona railroads Defunct California railroads Defunct Colorado railroads Defunct Illinois railroads Defunct Indiana railroads Defunct Iowa railroads Defunct Kansas railroads Defunct Louisiana railroads Defunct Missouri railroads Defunct Nebraska railroads Defunct Nevada railroads Defunct New Mexico railroads Defunct Oklahoma railroads Defunct Texas railroads Railroads in the Chicago metropolitan area History of Chicago History of San Diego Superfund sites in New Mexico American companies established in 1859 1996 disestablishments in Illinois