Arab News Agencies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ,
" ''
 The earliest documented use of the word ''Arab'' in reference to a people appears in the
The earliest documented use of the word ''Arab'' in reference to a people appears in the
 The first written attestation of the ethnonym ''Arab'' occurs in an Assyrian inscription of 853 BCE, where
The first written attestation of the ethnonym ''Arab'' occurs in an Assyrian inscription of 853 BCE, where
DIN 31635 DIN 31635 is a Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) standard for the transliteration of the Arabic alphabet adopted in 1982. It is based on the rules of the Deutsche Morgenländische Gesellschaft (DMG) as modified by the International Orientalist ...
: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora
Arab diaspora (also known as MENA diaspora, as a short version for the Middle East and North Africa diaspora) refers to descendants of the Arab emigrants who, voluntarily or as refugees, emigrated from their native lands to non-Arab countries, ...
is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia
The Tribes of Arabia () or Arab tribes () are the ethnic Arab tribes and clans that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. The tribes of Arabia descend from either one of the two Arab ancestors, Adnan or Qahtan. Arab tribes have historically in ...
. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature
Islamic literature is literature written by Muslim people, influenced by an Islamic cultural perspective, or literature that portrays Islam. It can be written in any language and portray any country or region. It includes many literary forms incl ...
. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
(the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Muslim population.
The first mention of Arabs appeared in the mid-9th century BCE, as a tribal people in eastern and southern Syria and the northern Arabian Peninsula. The Arabs appear to have been under the vassalage of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
, as well as the succeeding Neo-Babylonian
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bein ...
, Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
, Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, and Parthian empires. The Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
, an Arab people, ruled a kingdom near Petra (modern-day Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
) in the 3rd century BCE. Arab tribes, most notably the Ghassanids and the Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
, began to appear in the southern Syrian Desert from the mid-3rd century CE onward, during the middle to later stages of the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
empires. Before the expansion of the Rashidun Caliphate, the term "Arab" referred to any of the both largely nomadic and settled Arabic-speaking people from the Arabian Peninsula, the Syrian Desert, and Lower Mesopotamia, with some even reaching what is now northern Iraq. Since the height of pan-Arabism in the 1950s and 1960s, "Arabs" has been taken to refer to a large number of people whose native regions became part of the Arab world due to the spread of Islam
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territorie ...
, which saw the expansion of Arab tribes and the Arabic language throughout during the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
of the 7th and 8th centuries. These cultural and demographic influences resulted in the subsequent Arabization of the indigenous populations.
The Arabs forged the Rashidun, Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
, Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, and Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
caliphates, whose borders at their zenith reached southern France in the west, China in the east, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
in the north, and Sudan in the south, forming one of the largest land empires in history. In the early 20th century, World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
signalled the beginning of the end of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, a Turkish polity that had ruled much of the Arab world since its conquest of the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
in 1517. The Ottoman defeat in World War I culminated in the 1922 dissolution of the empire and the subsequent partitioning of Ottoman territories, which formed the modern Arab states. Following the adoption of the Alexandria Protocol
The Alexandria Protocol is an agreement signed on 7 October 1944, in Alexandria, by five Arab countries agreeing to the formation of a joint Arab Organization, which led to the formation of the League of Arab States in the following year.
The a ...
in 1944, the Arab League was founded on 22 March 1945.Arab League formed , This Day in History — 3/22/1945" ''
HISTORY
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
''. US: A&E Television Networks
A&E Networks (stylized as A+E NETWORKS) is an American multinational broadcasting company that is a 50–50 joint venture between Hearst Communications and The Walt Disney Company through its General Entertainment Content division. The company o ...
. 2010. Retrieved on 28 April 2014. The Charter of the Arab League endorsed the principle of a unified Arab homeland whilst respecting the individual sovereignty of its member states.
Today, Arabs primarily inhabit the 22 member states of the Arab League. The Arab world stretches around , from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
in the west to the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
in the east and from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
in the north to the Horn of Africa and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
in the southeast. People of non-Arab ethnicities associated with non-Arabic languages also live in these countries, sometimes as a majority; these include Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
, Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ira ...
, Berbers, the Afar people
The Afar ( aa, Qafár), also known as the Danakil, Adali and Odali, are a Cushitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting the Horn of Africa. They primarily live in the Afar Region of Ethiopia and in northern Djibouti, as well as the entire southern co ...
, Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of ...
, and various others. The ties that bind Arabs together are ethnic, linguistic, cultural, historical, identical, nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
, geographical, and political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
. The Arabs have their own customs, language, literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, dance, media, cuisine, dress, society, sports, and mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
, as well as significant influence on Islamic architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic ...
and Islamic art
Islamic art is a part of Islamic culture and encompasses the visual arts produced since the 7th century CE by people who lived within territories inhabited or ruled by Muslim populations. Referring to characteristic traditions across a wide ra ...
. Arabs have greatly influenced and contributed to diverse fields, notably architecture and the arts, language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
, Islamic philosophy
Islamic philosophy is philosophy that emerges from the Islamic tradition. Two terms traditionally used in the Islamic world are sometimes translated as philosophy—falsafa (literally: "philosophy"), which refers to philosophy as well as logic, ...
, mythology, ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concer ...
, literature, politics, business, music, dance, cinema
Cinema may refer to:
Film
* Cinematography, the art of motion-picture photography
* Film or movie, a series of still images that create the illusion of a moving image
** Film industry, the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking
...
, medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
, and technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and Reproducibility, reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in me ...
in ancient and modern history.
Arabs are a diverse group in terms of religious affiliations and practices. In the pre-Islamic era, most Arabs followed polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
religions. However, some tribes had adopted Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
or Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
and a few individuals, known as the '' hanifs'', apparently observed another form of monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfo ...
.*
* Presently, there is a sizable Christian minority in the Arab world. Arab Muslims primarily belong to the Sunni, Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
, Ibadi
The Ibadi movement or Ibadism ( ar, الإباضية, al-Ibāḍiyyah) is a school of Islam. The followers of Ibadism are known as the Ibadis.
Ibadism emerged around 60 years after the Islamic prophet Muhammad's death in 632 AD as a moderate sc ...
, and Alawite denominations. Arab Christians generally follow Eastern Christianity, such as those within the Oriental Orthodox Churches
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent ...
, the Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of t ...
, or the Eastern Protestant Churches.*
* There also exists a small numbers of Arab Jews
Arab Jews ( ar, اليهود العرب '; he, יהודים ערבים ') is a term for Jews living in or originating from the Arab world. The term is politically contested, often by Zionists or by Jews with roots in the Arab world who prefer ...
still living in Arab countries, and a much larger population of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
descended from Arab Jewish communities living in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and various Western countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
, who may or may not consider themselves Arab today. Arabic-speaking Christian minorities in Arab-majority states may also not ethnically identify as Arabs, such as Copts and Assyrians. Other smaller minority religions also exist, such as the Druze and the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the ...
.
Etymology
 The earliest documented use of the word ''Arab'' in reference to a people appears in the
The earliest documented use of the word ''Arab'' in reference to a people appears in the Kurkh Monoliths
The Kurkh Monoliths are two Assyrian stelae that contain a description of the reigns of Ashurnasirpal II and his son Shalmaneser III. The Monoliths were discovered in 1861 by a British archaeologist John George Taylor, who was the British Consu ...
, an Akkadian-language record of the Assyrian conquest of Aram (9th century BCE). The Monoliths used the term to refer to Bedouins of the Arabian Peninsula under King Gindibu, who fought as part of a coalition opposed to Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
. pp. 105, 119, 125–27. Listed among the booty captured by the army of the Assyrian king Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campai ...
in the Battle of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possi ...
(853 BCE) are 1000 camels of "''Gîndibuʾ'' the ''Arbâya''" or " he manGindibu belonging to the ''Arabs''" (''ar-ba-a-a'' being an adjectival nisba
The Arabic language, Arabic word nisba (; also transcribed as ''nisbah'' or ''nisbat'') may refer to:
* Arabic nouns and adjectives#Nisba, Nisba, a suffix used to form adjectives in Arabic grammar, or the adjective resulting from this formation
**c ...
of the noun ''ʿarab'').
The related word ''ʾaʿrāb'' is used to refer to Bedouins today, in contrast to ''ʿarab'' which refers to Arabs in general. Both terms are mentioned around 40 times in pre-Islamic Sabaean inscriptions. The term ''ʿarab'' ('Arab') occurs also in the titles of the Himyarite kings from the time of 'Abu Karab Asad until MadiKarib Ya'fur. According to Sabaean grammar, the term ''ʾaʿrāb'' is derived from the term ''ʿarab''. The term is also mentioned in Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
ic verses, referring to people who were living in Madina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
and it might be a south Arabian loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
into Quranic language.
The oldest surviving indication of an Arab national identity is an inscription made in an archaic form of Arabic in 328 CE using the Nabataean alphabet
The Nabataean script is an abjad (consonantal alphabet) that was used to write Nabataean Aramaic and Nabataean Arabic from the second century BC onwards.Imru' al-Qays ibn 'Amr
Imru' al-Qays ibn 'Amr ( ar, امرؤ القيس بن عمرو) was the second Lakhmid king. His mother was Maria bint 'Amr, the sister of Ka'b al-Azdi. There is debate on his religious affinity: while Theodor Nöldeke noted that Imru' al-Qays ...
as 'King of all the Arabs'. Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
refers to the Arabs in the Sinai, southern Palestine, and the frankincense region (Southern Arabia). Other Ancient-Greek historians like Agatharchides
Agatharchides or Agatharchus ( grc-gre, Ἀγαθαρχίδης or , ''Agatharchos'') of Cnidus was a Greek historian and geographer (flourished 2nd century BC).
Life
Agatharchides is believed to have been born at Cnidus, hence his appellation. A ...
, Diodorus Siculus and Strabo mention Arabs living in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
(along the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
), in Egypt (the Sinai and the Red Sea), southern Jordan (the Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
), the Syrian steppe and in eastern Arabia (the people of Gerrha). Inscriptions dating to the 6th century BCE in Yemen include the term 'Arab'.
The most popular Arab account holds that the word ''Arab'' came from an eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
ous father named Ya'rub
Ya'rub ( ar, يعرب, also spelled ''Yarob'',''Ya'rob'', ''Yarrob'', ''Yarab'' or ''Yaarub'') is an ancient Arabic personal name. He is the grandson of Abir being the son of Qahtan and the ancestor of the Himyarite and Sabaean kings of Yemen.va ...
, who was supposedly the first to speak Arabic. Abu Muhammad al-Hasan al-Hamdani
Abū Muḥammad al-Ḥasan ibn Aḥmad ibn Yaʿqūb al-Hamdānī (279/280-333/334 A.H. / c. 893-945 A.D; ar, أبو محمد الحسن بن أحمد بن يعقوب الهمداني) was an Arab Muslim geographer, chemist, poet, grammarian, his ...
had another view; he states that Arabs were called ''gharab'' ('westerners') by Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
ns because Bedouins originally resided to the west of Mesopotamia; the term was then corrupted into ''arab''.
Yet another view is held by al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
that the word ''Arab'' was initially applied to the Ishmaelites
The Ishmaelites ( he, ''Yīšməʿēʾlīm,'' ar, بَنِي إِسْمَاعِيل ''Bani Isma'il''; "sons of Ishmael") were a collection of various Arabian tribes, confederations and small kingdoms described in Islamic tradition as being des ...
of the Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the bord ...
valley. In Biblical etymology, ''Arab'' (Hebrew: ''arvi'') comes from the desert origin of the Bedouins it originally described (''arava'' means 'wilderness').
The root ''ʿ-r-b'' has several additional meanings in Semitic languages—including 'west, sunset', 'desert', 'mingle', 'mixed', 'merchant' and 'raven'—and are "comprehensible" with all of these having varying degrees of relevance to the emergence of the name. It is also possible that some forms were metathetical from , 'moving around' (Arabic: , 'traverse') and hence, it is alleged, 'nomadic'.
History
Antiquity
Pre-Islamic Arabia refers to the Arabian Peninsula prior to the rise of Islam in the 630s. The study of Pre-Islamic Arabia is important toIslamic studies
Islamic studies refers to the academic study of Islam, and generally to academic multidisciplinary "studies" programs—programs similar to others that focus on the history, texts and theologies of other religious traditions, such as Easter ...
as it provides the context for the development of Islam. Some of the settled communities in the Arabian Peninsula developed into distinctive civilizations. Sources for these civilizations are not extensive, and are limited to archaeological evidence, accounts written outside of Arabia, and Arab oral traditions later recorded by Islamic scholars. Among the most prominent civilizations was Dilmun
Dilmun, or Telmun, ( Sumerian: , later 𒉌𒌇(𒆠), ni.tukki = DILMUNki; ar, دلمون) was an ancient East Semitic-speaking civilization in Eastern Arabia mentioned from the 3rd millennium BC onwards.
Based on contextual evidence, it was ...
, which arose around the 4th millennium BCE and lasted to 538 BCE, and Thamud
The Thamud ( ar, ثَمُوْد, translit=Ṯamūd) were an ancient Arabian tribe or tribal confederation that occupied the northwestern Arabian peninsula between the late-eighth century BCE, when they are attested in Assyrian sources, and the ...
, which arose around the 1st millennium BCE and lasted to about 300 CE. Additionally, from the beginning of the first millennium BCE, Southern Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'A ...
was the home to a number of kingdoms, such as the Sabaean kingdom
The Sabaeans or Sabeans (Sabaean:, ; ar, ٱلسَّبَئِيُّوْن, ''as-Sabaʾiyyūn''; he, סְבָאִים, Səḇāʾīm) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian languag ...
( ar, سَـبَـأ, Saba', Quran 34:15 possibly Sheba
Sheba (; he, ''Šəḇāʾ''; ar, سبأ ''Sabaʾ''; Ge'ez: ሳባ ''Saba'') is a kingdom mentioned in the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament) and the Quran. Sheba features in Jewish, Muslim, and Christian traditions, particularly the Ethiopian Orth ...
), and the coastal areas of Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
were controlled by the Parthian and Sassanians from 300 BCE.
Origins and early history
According to Arab- Islamic-Jewish traditions, Ishmael was father of the Arabs, to be the ancestor of theIshmaelites
The Ishmaelites ( he, ''Yīšməʿēʾlīm,'' ar, بَنِي إِسْمَاعِيل ''Bani Isma'il''; "sons of Ishmael") were a collection of various Arabian tribes, confederations and small kingdoms described in Islamic tradition as being des ...
.
* Both Judaism and Islam see him as the ancestor of Arab peoples.
* Ishmael is recognized by Muslims as the ancestor of several prominent Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
and being the forefather of Muhammad. ''A–Z of Prophets in Islam and Judaism'', Wheeler, ''Ishmael'' Muslims also believe that Muhammad was the descendant of Ishmael that would establish a great nation, as promised by God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
in the Old Testament.
* Genesis 17:20
*
* Ishmael was considered the ancestor of the Northern Arabs and Muhammad was linked to him through the lineage of the patriarch Adnan. Ishmael may also have been the ancestor of the Southern Arabs through his descendant Qahtan.
* Assyrians referred to the Arab Tribes as Ishmaelites, or "Shumu'ilu" as recorded in their inscriptions.
* " Zayd ibn Amr" was another Pre-Islamic figure who refused idolatry and preached monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfo ...
, claiming it was the original belief of their rabsfather Ishmael.
* The tribes of Central West Arabia called themselves the "people of Abraham and the offspring of Ishmael."
 The first written attestation of the ethnonym ''Arab'' occurs in an Assyrian inscription of 853 BCE, where
The first written attestation of the ethnonym ''Arab'' occurs in an Assyrian inscription of 853 BCE, where Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC.
His long reign was a constant series of campai ...
lists a King Gindibu
Gindibu ( Akkadian: ; ) was a king of the Qedarite Arabs.
Reign Background
Gindibu ruled over an Arab kingdom located around the Wādī Sirḥān. The kingdom of Gindibu bordered on the powerful kingdoms of Aram-Damascus and Israel in the wes ...
of ''mâtu arbâi'' (Arab land) as among the people he defeated at the Battle of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possi ...
. Some of the names given in these texts are Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
, while others are the first attestations of Ancient North Arabian dialects. In fact several different ethnonyms are found in Assyrian texts that are conventionally translated "Arab": ''Arabi, Arubu, Aribi'' and ''Urbi''. Many of the Qedarite
The Qedarites ( ar, قيدار, Qaydār) were a largely nomadic ancient Arab tribal confederation centred in the Wādī Sirḥān in the Syrian Desert. Attested from the 8th century BC, the Qedarites formed a powerful polity which expanded its ...
queens were also described as queens of the ''aribi''. The Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Syrian Desert and Arabia. Arab tribes came into conflict with the Assyrians during the reign of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, and he records military victories against the powerful Qedar tribe among others. Old Arabic diverges from Central Semitic by the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE. Medieval Arab
Medieval Arab  Ibn Khaldun's '' Muqaddima'' distinguishes between sedentary Arab Muslims who used to be
Ibn Khaldun's '' Muqaddima'' distinguishes between sedentary Arab Muslims who used to be
 Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts give a clearer picture of the Arabs' emergence. The earliest are written in variants of epigraphic south Arabian '' musnad'' script, including the 8th century BCE Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, the 6th century BCE Lihyanite texts of southeastern Saudi Arabia and the
Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts give a clearer picture of the Arabs' emergence. The earliest are written in variants of epigraphic south Arabian '' musnad'' script, including the 8th century BCE Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, the 6th century BCE Lihyanite texts of southeastern Saudi Arabia and the
'' Syrian Desert and Arabia. Arab tribes came into conflict with the Assyrians during the reign of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, and he records military victories against the powerful Qedar tribe among others. Old Arabic diverges from Central Semitic by the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE.
 Medieval Arab
Medieval Arab genealogist
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kins ...
s divided Arabs into three groups:
# "Ancient Arabs", tribes that had vanished or been destroyed, such as ʿĀd
ʿĀd ( ar, عَادٌ, ') is an ancient tribe mentioned frequently in the Qurʾān.
The tribe's members, referred to as ʿĀdites, formed a prosperous nation until they were destroyed in a violent storm. According to Islamic tradition, the st ...
and Thamud
The Thamud ( ar, ثَمُوْد, translit=Ṯamūd) were an ancient Arabian tribe or tribal confederation that occupied the northwestern Arabian peninsula between the late-eighth century BCE, when they are attested in Assyrian sources, and the ...
, often mentioned in the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
as examples of God's power to vanquish those who fought his prophets.
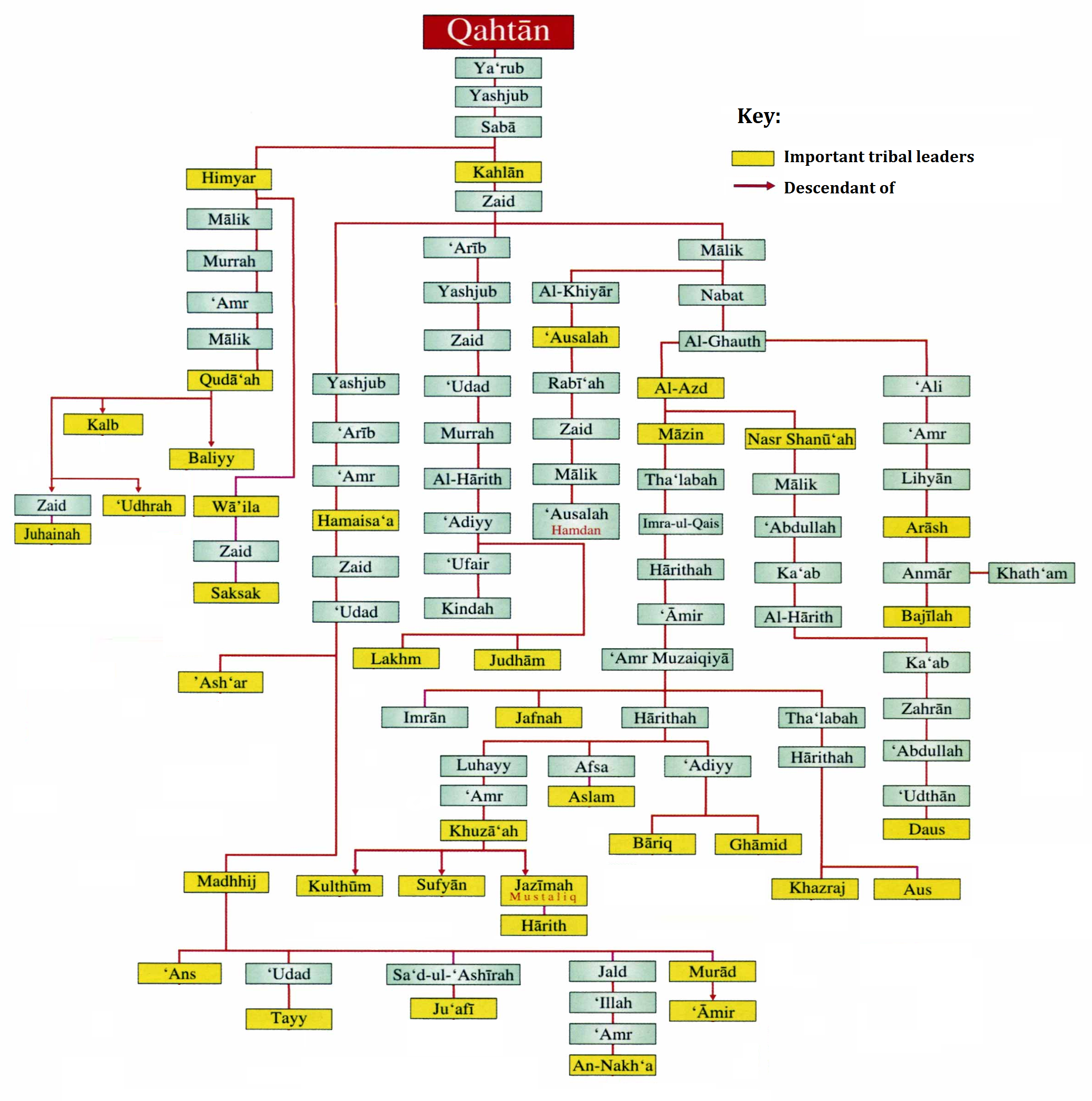
# "Pure Arabs" of South Arabia, descending from Qahtan
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions b ...
. The Qahtanite
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions b ...
s (Qahtanis) are said to have migrated from the land of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
following the destruction of the Ma'rib Dam (''sadd Ma'rib'').
# The "Arabized Arabs" (''mustaʿribah'') of Central Arabia ( Najd) and North Arabia, descending from Ishmael the elder son of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
, through Adnan
Adnan ( ar, عدنان, 'adnān) is the traditional ancestor of the Adnanite Arabs of Northern, Western, Eastern and Central Arabia, as opposed to the Qahtanite Arabs of Southern Arabia who descend from Qahtan. His ancestry can be traced back t ...
(hence, Adnanites
The Adnanites ( ar, عدنانيون) were a tribal confederation of the Ishmaelite Arabs, traces their lineage back to Ismail son of the Islamic prophet and patriarch Ibrahim and his wife Hajar through Adnan, who originate from the Hejaz. Th ...
). The Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
narrates that God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
promised Hagar
Hagar, of uncertain origin; ar, هَاجَر, Hājar; grc, Ἁγάρ, Hagár; la, Agar is a biblical woman. According to the Book of Genesis, she was an Egyptian slave, a handmaiden of Sarah (then known as ''Sarai''), whom Sarah gave to h ...
to beget from Ishmael twelve princes and turn him to a great nation. The Book of Jubilees
The Book of Jubilees, sometimes called Lesser Genesis (Leptogenesis), is an ancient Jewish religious work of 50 chapters (1,341 verses), considered canonical by the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as well as Beta Israel (Ethiopian Jews), where it is ...
claims that the sons of Ishmael intermingled with the 6 sons of Keturah
Keturah ( he, קְטוּרָה, ''Qəṭūrā'', possibly meaning "incense"; ar, قطورة) was a wife (1917 Jewish Publication Society of America translation). "And Abraham took another wife, and her name was Keturah...." and a concubine (191 ...
, from Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
, and their descendants were called Arabs and Ishmaelites
The Ishmaelites ( he, ''Yīšməʿēʾlīm,'' ar, بَنِي إِسْمَاعِيل ''Bani Isma'il''; "sons of Ishmael") were a collection of various Arabian tribes, confederations and small kingdoms described in Islamic tradition as being des ...
:
Assyrian and Babylonian Royal Inscriptions and North Arabian inscriptions from 9th to 6th century BCE, mention the king of Qedar as king of the Arabs and King of the Ishmaelites.
Of the names of the sons of Ishmael the names "Nabat, Kedar, Abdeel, Dumah, Massa, and Teman" were mentioned in the Assyrian Royal Inscriptions as tribes of the Ishmaelites. Jesur was mentioned in Greek inscriptions in the 1st century BCE.
 Ibn Khaldun's '' Muqaddima'' distinguishes between sedentary Arab Muslims who used to be
Ibn Khaldun's '' Muqaddima'' distinguishes between sedentary Arab Muslims who used to be nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic, and Bedouin nomadic Arabs of the desert. He used the term "formerly nomadic" Arabs and refers to sedentary Muslims by the region or city they lived in, as in Yemenis
Yemenis or Yemenites ( ar, يمنيون) are the nationals of Yemen.
Social hierarchy
There is a system of social stratification in Yemen that was officially abolished at the creation of the Republic of Yemen in 1962 but, in practice, this syst ...
. The Christians of Italy and the Crusaders preferred the term Saracens for all the Arabs, Muslims. The Christians of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
used the term Moor to describe all the Arabs and Muslims of that time.
Muslims of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
referred to the nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic tribes of the deserts as the A'raab, and considered themselves sedentary, but were aware of their close racial bonds. The term "A'raab" mirrors the term Assyrians used to describe the closely related nomads they defeated in Syria. The Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
does not use the word , only the nisba
The Arabic language, Arabic word nisba (; also transcribed as ''nisbah'' or ''nisbat'') may refer to:
* Arabic nouns and adjectives#Nisba, Nisba, a suffix used to form adjectives in Arabic grammar, or the adjective resulting from this formation
**c ...
adjective . The Qur'an calls itself , "Arabic", and , "clear". The two qualities are connected for example in Quran 43:2-3, "By the ''clear'' Book: We have made it an ''Arabic'' recitation in order that you may understand". The Qur'an became regarded as the prime example of the , the language of the Arabs. The term '' ʾiʿrāb'' has the same root and refers to a particularly clear and correct mode of speech. The plural noun refers to the Bedouin tribes of the desert who resisted Muhammad, for example in ''at-Tawba
At-Tawbah ( ar, ٱلتوبة, ; The Repentance), also known as Bara'ah ( ar, براءة, ; Repudiation), is the ninth chapter ('' sūrah'') of the Quran. It contains 129 verses ('' āyāt'') and is one of the last Medinan surahs.
This Surah i ...
'' 97,
"the Bedouin are the worst in disbelief
Disbelief (sometimes decapitalized to "disbelief") is a German heavy metal band from Hesse. Their music is rooted in death metal, but has melancholic tendencies.
History
The band was formed in 1990, but did not become one solid line-up fo ...
and hypocrisy".
Based on this, in early Islamic terminology, referred to the language, and to the Arab Bedouins, carrying a negative connotation due to the Qur'anic verdict just cited. But after the Islamic conquest
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territories ...
of the eighth century, the language of the nomadic Arabs became regarded as the most pure by the grammarians following Abi Ishaq, and the term , "language of the Arabs", denoted the uncontaminated language of the Bedouins.
Classical kingdoms
 Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts give a clearer picture of the Arabs' emergence. The earliest are written in variants of epigraphic south Arabian '' musnad'' script, including the 8th century BCE Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, the 6th century BCE Lihyanite texts of southeastern Saudi Arabia and the
Proto-Arabic, or Ancient North Arabian, texts give a clearer picture of the Arabs' emergence. The earliest are written in variants of epigraphic south Arabian '' musnad'' script, including the 8th century BCE Hasaean inscriptions of eastern Saudi Arabia, the 6th century BCE Lihyanite texts of southeastern Saudi Arabia and the Thamudic
Thamudic is a name that refers to ancient Arabic Thamudic tribe language found by nineteenth-century scholars for large numbers of inscriptions in Ancient North Arabian (ANA) alphabets which have not yet been properly studied. These texts are foun ...
texts found throughout the Arabian Peninsula and Sinai (not in reality connected with Thamud
The Thamud ( ar, ثَمُوْد, translit=Ṯamūd) were an ancient Arabian tribe or tribal confederation that occupied the northwestern Arabian peninsula between the late-eighth century BCE, when they are attested in Assyrian sources, and the ...
).
The Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
were nomadic Arabs who moved into territory vacated by the Edomites
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
– Semites who settled the region centuries before them. Their early inscriptions were in Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
, but gradually switched to Arabic, and since they had writing, it was they who made the first inscriptions in Arabic. The Nabataean alphabet
The Nabataean script is an abjad (consonantal alphabet) that was used to write Nabataean Aramaic and Nabataean Arabic from the second century BC onwards.Safaitic inscriptions (beginning in the 1st century BCE) and the many Arabic personal names in  Arabs arrived in the
Arabs arrived in the  Palmyra prospered as part of the Umayyad Caliphate, and its population grew. It was a key stop on the East-West trade route, with a large '' souq'' ( ar, سُـوق,
Palmyra prospered as part of the Umayyad Caliphate, and its population grew. It was a key stop on the East-West trade route, with a large '' souq'' ( ar, سُـوق,
 The Ghassanids,
The Ghassanids,  Greeks and Romans referred to all the nomadic population of the desert in the Near East as Arabi. The Romans called Yemen "
Greeks and Romans referred to all the nomadic population of the desert in the Near East as Arabi. The Romans called Yemen "

 After the death of
After the death of
 In 661, the Rashidun Caliphate fell into the hands of the
In 661, the Rashidun Caliphate fell into the hands of the  Umayyads expanded their Empire westwards capturing North Africa from the Byzantines. Before the Arab conquest, North Africa was conquered or settled by various people including Punics, Vandals and Romans. After the
Umayyads expanded their Empire westwards capturing North Africa from the Byzantines. Before the Arab conquest, North Africa was conquered or settled by various people including Punics, Vandals and Romans. After the

 The Abbasids were the descendants of
The Abbasids were the descendants of  The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the
The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the
 The Fatimid caliphate was founded by al-Mahdi Billah, a descendant of
The Fatimid caliphate was founded by al-Mahdi Billah, a descendant of  It was not until the 11th century that the
It was not until the 11th century that the
 From 1517 to 1918, much of the Arab world was under the suzerainty of the
From 1517 to 1918, much of the Arab world was under the suzerainty of the
 Arabs in modern times live in the Arab world, which comprises 22 countries in
Arabs in modern times live in the Arab world, which comprises 22 countries in
 Today, the main unifying characteristic among Arabs is
Today, the main unifying characteristic among Arabs is
 Arabs in the narrow sense are the indigenous Arabians who trace their roots back to the
Arabs in the narrow sense are the indigenous Arabians who trace their roots back to the  The Arabs of the
The Arabs of the  The Bedouins of western Egypt and eastern Libya are traditionally divided into Saʿada and Murabtin, the Saʿada having higher social status. This may derive from a historical feudal system in which the Murabtin were vassals to the Saʿada.
In Sudan, there are numerous Arabic-speaking tribes, including the
The Bedouins of western Egypt and eastern Libya are traditionally divided into Saʿada and Murabtin, the Saʿada having higher social status. This may derive from a historical feudal system in which the Murabtin were vassals to the Saʿada.
In Sudan, there are numerous Arabic-speaking tribes, including the  The medieval trans-Saharan slave trade in the Sudan drove a wedge between the
The medieval trans-Saharan slave trade in the Sudan drove a wedge between the
 According to the Charter of the Arab League (also known as the ''Pact of the League of Arab States''), the League of Arab States is composed of independent Arab states that are signatories to the Charter.
According to the Charter of the Arab League (also known as the ''Pact of the League of Arab States''), the League of Arab States is composed of independent Arab states that are signatories to the Charter.
 Although all Arab states have Arabic as an official language, there are many non-Arabic-speaking populations native to the Arab world. Among these are Berbers,
Although all Arab states have Arabic as an official language, there are many non-Arabic-speaking populations native to the Arab world. Among these are Berbers,


 There are millions of Arabs living in Europe, mostly concentrated in
There are millions of Arabs living in Europe, mostly concentrated in
The Economist (26 March 2009). Retrieved on 12 July 2013. In
 In 1728, a Russian officer described a group of Arab nomads who populated the Caspian shores of
In 1728, a Russian officer described a group of Arab nomads who populated the Caspian shores of
Arabic as a Minority Language
Walter de Gruyter, 2000; p. 101 The 1888 edition of
by
Characters Персонажи традиционных религиозных представлений азербайджанцев Табасарана.
Stephen Adolphe Wurm et al
Atlas of languages of intercultural communication
Walter de Gruyter, 1996; p. 966 According to the ''History of Ibn Khaldun'', the Arabs that were once in There are only two communities in
There are only two communities in  Afro-Arabs are individuals and groups from
Afro-Arabs are individuals and groups from
 Arabs are mostly Muslims with a Sunni majority and a
Arabs are mostly Muslims with a Sunni majority and a  Today, Sunni Islam dominates in most areas, vastly so in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Shia Islam is dominant among the Arab population in
Today, Sunni Islam dominates in most areas, vastly so in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Shia Islam is dominant among the Arab population in  Christianity had a prominent presence In
Christianity had a prominent presence In
 Arab culture is the culture of the Arabs, from the
Arab culture is the culture of the Arabs, from the
 Another important and unifying characteristic of Arabs is a common
Another important and unifying characteristic of Arabs is a common

 The
The  A large portion of Arabic literature before the 20th century is in the form of
A large portion of Arabic literature before the 20th century is in the form of  Arabic literature and
Arabic literature and

 Arabic art takes on many forms, though it is jewelry, textiles and
Arabic art takes on many forms, though it is jewelry, textiles and  Arabic writing is done from right to left, and was generally written in dark inks, with certain things embellished with special colored inks (red, green, gold). In early Arabic and Early Middle Ages, early Medieval, writing was typically done on parchment made of animal skin. The ink showed up very well on it, and occasionally the parchment was dyed a separate color and brighter ink was used (this was only for special projects). The name given to the form of writing in early times was called Kufic script.
Arabic miniatures (
Arabic writing is done from right to left, and was generally written in dark inks, with certain things embellished with special colored inks (red, green, gold). In early Arabic and Early Middle Ages, early Medieval, writing was typically done on parchment made of animal skin. The ink showed up very well on it, and occasionally the parchment was dyed a separate color and brighter ink was used (this was only for special projects). The name given to the form of writing in early times was called Kufic script.
Arabic miniatures (
 Arabic Architecture has a deep diverse history, it dates to the dawn of the history in
Arabic Architecture has a deep diverse history, it dates to the dawn of the history in
Early Christian and Byzantine Architecture
Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, Penguin Books Ltd., 1965, p. 285. In
 A number of musical instruments used in classical music are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments: the lute was derived from the ''Oud'', the rebec (ancestor of violin) from the ''Maghreb rebab'', the guitar from ''qitara'', which in turn was derived from the Persian Tar (lute), Tar, naqareh, naker from ''naqareh'', adufe from ''Daf, al-duff'', alboka from ''al-buq'', Naffir, anafil from ''al-nafir'', exabeba from ''al-shabbaba'' (flute), atabal (bass drum) from ''al-tabl'', atambal from ''al-tinbal'', the Balaban (instrument), balaban, the castanet from ''kasatan'', Tuna (music), sonajas de azófar from ''sunuj al-sufr'', the Bore (wind instruments), conical bore wind instruments, the xelami from the ''sulami'' or ''fistula'' (flute or Organ pipe, musical pipe),
the shawm and dulzaina from the Reed (instrument), reed instruments ''zamr'' and ''Zurna, al-zurna'', the Galician gaita, gaita from the ''Rhaita, ghaita'', rackett from ''iraqya'' or ''iraqiyya'', Violin, geige (violin) from ''ghichak'',
and the theorbo from the ''tarab''.
During the 1950s and the 1960s, Arabic music began to take on a more Western tone – artists Umm Kulthum, Abdel Halim Hafez, and Shadia along with composers Mohammed Abdel Wahab, Mohamed Abd al-Wahab and Baligh Hamdi pioneered the use of western instruments in Egyptian music. By the 1970s several other singers had followed suit and a strand of Arabic pop was born. Arabic pop usually consists of Western styled songs with Arabic instruments and lyrics. Melodies are often a mix between Eastern and Western. Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical Innovator, pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the
A number of musical instruments used in classical music are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments: the lute was derived from the ''Oud'', the rebec (ancestor of violin) from the ''Maghreb rebab'', the guitar from ''qitara'', which in turn was derived from the Persian Tar (lute), Tar, naqareh, naker from ''naqareh'', adufe from ''Daf, al-duff'', alboka from ''al-buq'', Naffir, anafil from ''al-nafir'', exabeba from ''al-shabbaba'' (flute), atabal (bass drum) from ''al-tabl'', atambal from ''al-tinbal'', the Balaban (instrument), balaban, the castanet from ''kasatan'', Tuna (music), sonajas de azófar from ''sunuj al-sufr'', the Bore (wind instruments), conical bore wind instruments, the xelami from the ''sulami'' or ''fistula'' (flute or Organ pipe, musical pipe),
the shawm and dulzaina from the Reed (instrument), reed instruments ''zamr'' and ''Zurna, al-zurna'', the Galician gaita, gaita from the ''Rhaita, ghaita'', rackett from ''iraqya'' or ''iraqiyya'', Violin, geige (violin) from ''ghichak'',
and the theorbo from the ''tarab''.
During the 1950s and the 1960s, Arabic music began to take on a more Western tone – artists Umm Kulthum, Abdel Halim Hafez, and Shadia along with composers Mohammed Abdel Wahab, Mohamed Abd al-Wahab and Baligh Hamdi pioneered the use of western instruments in Egyptian music. By the 1970s several other singers had followed suit and a strand of Arabic pop was born. Arabic pop usually consists of Western styled songs with Arabic instruments and lyrics. Melodies are often a mix between Eastern and Western. Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical Innovator, pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the
"Lydia Canaan One Step Closer to Rock n' Roll Hall of Fame"
, ''The Daily Star (Lebanon), The Daily Star'', Beirut, 27 April 2016.
 Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in
Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in

 The philosophical thought in the Arab world is heavily influenced by Islamic Philosophy. Schools of Islamic thought include Avicennism and Averroism. The first great Arab thinker in the Islamic tradition is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in
The philosophical thought in the Arab world is heavily influenced by Islamic Philosophy. Schools of Islamic thought include Avicennism and Averroism. The first great Arab thinker in the Islamic tradition is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in
 Science in the medieval Islamic world, Islamic science underwent considerable development during the 8th to 13th centuries CE, a source of knowledge that later spread throughout
Science in the medieval Islamic world, Islamic science underwent considerable development during the 8th to 13th centuries CE, a source of knowledge that later spread throughout  Within a century after Muhammed's death (632 CE), an empire ruled by Arabs was established. It encompassed a large part of the planet, stretching from southern Europe to
Within a century after Muhammed's death (632 CE), an empire ruled by Arabs was established. It encompassed a large part of the planet, stretching from southern Europe to  This era can be identified as the years between 692 and 945,Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 234. and ended when the caliphate was marginalized by local Muslim rulers in Baghdad – its traditional seat of power. From 945 onward until the Sack of Baghdad, sacking of Baghdad by the Mongol invasions, Mongols in 1258, the Caliph continued on as a figurehead, with power devolving more to local amirs.Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 233. The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology. Arabic scientific achievement is not as yet fully understood, but is very large. These achievements encompass a wide range of subject areas, especially Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematics, Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, and Medicine in medieval Islam, medicine. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included Physics in medieval Islam, physics, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy and chemistry, Cosmology in medieval Islam, cosmology, Medieval Islamic ophthalmology, ophthalmology, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and cartography, Sociology in medieval Islam, sociology, and Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology.
Al-Battani (c. 858 – 929; born Harran, Bilad al-Sham) was an Arab astronomer, astrologer and mathematician of the
This era can be identified as the years between 692 and 945,Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 234. and ended when the caliphate was marginalized by local Muslim rulers in Baghdad – its traditional seat of power. From 945 onward until the Sack of Baghdad, sacking of Baghdad by the Mongol invasions, Mongols in 1258, the Caliph continued on as a figurehead, with power devolving more to local amirs.Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 233. The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology. Arabic scientific achievement is not as yet fully understood, but is very large. These achievements encompass a wide range of subject areas, especially Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematics, Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, and Medicine in medieval Islam, medicine. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included Physics in medieval Islam, physics, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy and chemistry, Cosmology in medieval Islam, cosmology, Medieval Islamic ophthalmology, ophthalmology, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and cartography, Sociology in medieval Islam, sociology, and Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology.
Al-Battani (c. 858 – 929; born Harran, Bilad al-Sham) was an Arab astronomer, astrologer and mathematician of the
 Arabic weddings have changed greatly in the past 100 years. Original traditional Arabic weddings are supposed to be very similar to modern-day Bedouin weddings and rural weddings, and they are in some cases unique from one region to another, even within the same Arab world, country. The practice of Marriage, marrying of relatives is a common feature of Arab culture.
In the
Arabic weddings have changed greatly in the past 100 years. Original traditional Arabic weddings are supposed to be very similar to modern-day Bedouin weddings and rural weddings, and they are in some cases unique from one region to another, even within the same Arab world, country. The practice of Marriage, marrying of relatives is a common feature of Arab culture.
In the
The Catholic Encyclopedia, Robert Appleton Company, 1907, Online Edition, K. Night 2003: article Arabia
1894), Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd. * The Arabic language, National Institute for Technology and Liberal Education web page (2006) * * Hooker, Richard. "Pre-Islamic Arabic Culture." WSU Web Site. 6 June 1999. Washington State University. * Owen, Roger. "State Power and Politics in the Making of the Modern Middle East 3rd Ed" Page 57 *
www.LasPortal.org
ArabCultureFund AFAC
{{Authority control Arabs, Tribes of Arabia, Afroasiatic peoples Ancient peoples of the Near East Arab Ethnic groups in Africa Ethnic groups in North Africa Ethnic groups in the Arab world Ethnic groups in the Middle East Muslim communities in Africa Muslim communities in Asia
Nabataean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
inscriptions. From about the 2nd century BCE, a few inscriptions from Qaryat al-Faw
Qaryat Al Faw ( ar, قرية الفاو) was the capital of the first Kingdom of Kinda, Kindah kingdom. It is located about 100 km south of Wadi ad-Dawasir, and about 700 km southwest of Riyadh, the capital city of Saudi Arabia. The Al ...
reveal a dialect no longer considered ''proto-Arabic'', but ''pre-classical Arabic''. Five Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
inscriptions mentioning Arabs have been found at Sumatar Harabesi
Sumatar Harabesi (also, Sumatar Ruins or simply, Sumatar) was an ancient watering place for semi-nomadic peoples located in the Tektek Mountains, southeast of Urfa (Edessa, Mesopotamia) and northeast of Harran, in modern-day Turkey.Lipinski, 199 ...
, one of which dates to the 2nd century CE.
 Arabs arrived in the
Arabs arrived in the Palmyra
Palmyra (; Palmyrene: () ''Tadmor''; ar, تَدْمُر ''Tadmur'') is an ancient city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early secon ...
in the late first millennium BCE. The soldiers of the sheikh Zabdibel, who aided the Seleucids in the battle of Raphia (217 BCE), were described as Arabs; Zabdibel and his men were not actually identified as Palmyrenes in the texts, but the name "Zabdibel" is a Palmyrene name leading to the conclusion that the sheikh hailed from Palmyra. Palmyra was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate after its 634 capture by the Arab general Khalid ibn al-Walid, who took the city on his way to Damascus; an 18-day march by his army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
through the Syrian Desert from Mesopotamia. By then Palmyra was limited to the Diocletian camp. After the conquest, the city became part of Homs Province.
 Palmyra prospered as part of the Umayyad Caliphate, and its population grew. It was a key stop on the East-West trade route, with a large '' souq'' ( ar, سُـوق,
Palmyra prospered as part of the Umayyad Caliphate, and its population grew. It was a key stop on the East-West trade route, with a large '' souq'' ( ar, سُـوق, market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
Geography
*Märket, an ...
), built by the Umayyads, who also commissioned part of the Temple of Bel as a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
. During this period, Palmyra was a stronghold of the Banu Kalb
The Banu Kalb ( ar, بنو كلب) was an Arab tribe which mainly dwelt in the desert between northwestern Arabia and central Syria. The Kalb was involved in the tribal politics of the eastern frontiers of the Byzantine Empire, possibly as early ...
tribe. After being defeated by Marwan II
Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam ( ar, مروان بن محمد بن مروان بن الحكم, Marwān ibn Muḥammad ibn Marwān ibn al-Ḥakam; – 6 August 750), commonly known as Marwan II, was the fourteenth and last caliph of ...
during a civil war in the caliphate, Umayyad contender Sulayman ibn Hisham fled to the Banu Kalb in Palmyra, but eventually pledged allegiance to Marwan in 744; Palmyra continued to oppose Marwan until the surrender of the Banu Kalb leader al-Abrash al-Kalbi in 745. That year, Marwan ordered the city's walls demolished. In 750 a revolt, led by Majza'a ibn al-Kawthar and Umayyad pretender Abu Muhammad al-Sufyani, against the new Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
swept across Syria; the tribes in Palmyra supported the rebels. After his defeat Abu Muhammad took refuge in the city, which withstood an Abbasid assault long enough to allow him to escape.
Late kingdoms
 The Ghassanids,
The Ghassanids, Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
and Kindites
The Kinda ( ar, كِنْدَة, Ancient South Arabian script: 𐩫𐩬𐩵𐩩) were an Arab tribe from South Arabia. As early as the 3rd century CE they served as Bedouin auxiliaries of the Sabaean Kingdom, followed by the Himyarite Kingdom. In ...
were the last major migration of pre-Islamic Arabs out of Yemen to the north. The Ghassanids increased the Semitic presence in then-Hellenized Syria, the majority of Semites were Aramaic peoples. They mainly settled in the Hauran region and spread to modern Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Palestine and Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
.
Arabia Felix
Arabia Felix (literally: Fertile/Happy Arabia; also Ancient Greek: Εὐδαίμων Ἀραβία, ''Eudaemon Arabia'') was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe South Arabia, or what is now Yemen.
Etymology
The term Arabia ...
". The Romans called the vassal nomadic states within the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
''Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province ( la, Provincia Arabia; ar, العربية البترائية; grc, Ἐπαρχία Πετραίας Ἀραβίας) or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Emp ...
'', after the city of Petra, and called unconquered deserts bordering the empire to the south and east Arabia Magna. The Emesene were a Roman client dynasty of Arab priest-kings known to have ruled from Emesa
ar, حمصي, Himsi
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_t ...
, Syria. Roman empress Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of priests ...
, matriarch of the Severan dynasty
The Severan dynasty was a Roman imperial dynasty that ruled the Roman Empire between 193 and 235, during the Roman imperial period. The dynasty was founded by the emperor Septimius Severus (), who rose to power after the Year of the Five Empero ...
of Roman emperors, was one of their descendants.
The Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
as a dynasty inherited their power from the Tanukh
The Tanûkhids ( ar, التنوخيون, transl=al-Tanūḫiyyūn) or Tanukh ( ar, تنوخ, translit=Tanūḫ) or Banū Tanūkh (, romanized as: ) were a confederation of Arab tribes, sometimes characterized as Saracens. They first rose to prom ...
ids, the mid Tigris region around their capital Al-Hira
Al-Hirah ( ar, الحيرة, translit=al-Ḥīra Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq.
History
Kingdom of the Lakhmids
Al-Hirah was a significant city in pre- I ...
. They ended up allying with the Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
against the Ghassanids and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. The Lakhmids contested control of the Central Arabian tribes with the Kindites with the Lakhmids eventually destroying the Kingdom of Kinda
The Kingdom of Kinda ( ar, كِنْدَة الملوك, Kindat al-Mulūk, Royal Kinda) also called the Kindite kingdom, refers to the rule of the Bedouin, nomadic Arab tribes of the Ma'add confederation in north and central Arabia by the Banu Aki ...
in 540 after the fall of their main ally Himyar
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) (fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerite ...
. The Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Sassanids dissolved the Lakhmid dynasty in 602, being under puppet kings, then under their direct control.
The Kindites migrated from Yemen along with the Ghassanids and Lakhmids, but were turned back in Bahrain by the Abdul Qais Rabi'a tribe. They returned to Yemen and allied themselves with the Himyarites who installed them as a vassal kingdom that ruled Central Arabia from "Qaryah Dhat Kahl" (the present-day called Qaryat al-Faw). They ruled much of the Northern/Central Arabian peninsula, until they were destroyed by the Lakhmid king Al-Mundhir, and his son 'Amr.
Medieval period
Arab caliphates
=Rashidun era (632–661)
=Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
in 632, Rashidun armies launched campaigns of conquest, establishing the Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, or Islamic Empire, one of the largest empires in history. It was larger and lasted longer than the previous Arab empire of Queen Mawia or the Aramean
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
-Arab Palmyrene Empire
The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt, ...
. The Rashidun state was a completely new state and unlike the Arab kingdoms of its century such as the Himyarite, Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
or Ghassanids.
=Umayyad era (661–750 & 756–1031)
= In 661, the Rashidun Caliphate fell into the hands of the
In 661, the Rashidun Caliphate fell into the hands of the Umayyad dynasty
Umayyad dynasty ( ar, بَنُو أُمَيَّةَ, Banū Umayya, Sons of Umayya) or Umayyads ( ar, الأمويون, al-Umawiyyūn) were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of Al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In t ...
and Damascus was established as the empire's capital. The Umayyads were proud of their Arab identity and sponsored the poetry and culture of pre-Islamic Arabia. They established garrison towns at Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, Raqqa
Raqqa ( ar, ٱلرَّقَّة, ar-Raqqah, also and ) (Kurdish: Reqa/ ڕەقە) is a city in Syria on the northeast bank of the Euphrates River, about east of Aleppo. It is located east of the Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam. The Hellenistic, ...
, Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
, Kufa
Kufa ( ar, الْكُوفَة ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Currently, Kufa and Najaf a ...
, Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
and Samarra, all of which developed into major cities.
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
Abd al-Malik established Arabic as the Caliphate's official language in 686. This reform greatly influenced the conquered non-Arab peoples and fueled the Arabization of the region. However, the Arabs' higher status among non-Arab Muslim converts and the latter's obligation to pay heavy taxes caused resentment. Caliph Umar II
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz ( ar, عمر بن عبد العزيز, ʿUmar ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz; 2 November 680 – ), commonly known as Umar II (), was the eighth Umayyad caliph. He made various significant contributions and reforms to the society, and ...
strove to resolve the conflict when he came to power in 717. He rectified the disparity, demanding that all Muslims be treated as equals, but his intended reforms did not take effect, as he died after only three years of rule. By now, discontent with the Umayyads swept the region and an uprising occurred in which the Abbasids came to power and moved the capital to Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
.
 Umayyads expanded their Empire westwards capturing North Africa from the Byzantines. Before the Arab conquest, North Africa was conquered or settled by various people including Punics, Vandals and Romans. After the
Umayyads expanded their Empire westwards capturing North Africa from the Byzantines. Before the Arab conquest, North Africa was conquered or settled by various people including Punics, Vandals and Romans. After the Abbasid Revolution
The Abbasid Revolution, also called the Movement of the Men of the Black Raiment, was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE), the second of the four major Caliphates in early Islamic history, by the third, the Abbasid Caliphate ...
, the Umayyads lost most of their territories with the exception of Iberia. Their last holding became known as the Emirate of Córdoba
The Emirate of Córdoba ( ar, إمارة قرطبة, ) was a medieval Islamic kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. Its founding in the mid-eighth century would mark the beginning of seven hundred years of Muslim rule in what is now Spain and Port ...
. It wasn't until the rule of the grandson of the founder of this new emirate that the state entered a new phase as the Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ( ar, خلافة قرطبة; transliterated ''Khilāfat Qurṭuba''), also known as the Cordoban Caliphate was an Islamic state ruled by the Umayyad dynasty from 929 to 1031. Its territory comprised Iberia and parts o ...
. This new state was characterized by an expansion of trade, culture and knowledge, and saw the construction of masterpieces of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
architecture and the library of Al-Ḥakam II which housed over 400,000 volumes. With the collapse of the Umayyad state in 1031 CE, Islamic Spain
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mu ...
was divided into small kingdoms.
= Abbasid era (750–1258 & 1261–1517)
=
 The Abbasids were the descendants of
The Abbasids were the descendants of Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib
Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib ( ar, ٱلْعَبَّاسُبْنُ عَبْدِ ٱلْمُطَّلِبِ, al-ʿAbbās ibn ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib; CE) was a paternal uncle and Sahabi (companion) of Muhammad, just three years older than his ...
, one of the youngest uncles of Muhammad and of the same Banu Hashim clan. The Abbasids led a revolt against the Umayyads and defeated them in the Battle of the Zab effectively ending their rule in all parts of the Empire with the exception of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
. In 762, the second Abbasid Caliph al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ar, أبو جعفر عبد الله بن محمد المنصور; 95 AH – 158 AH/714 CE – 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manṣūr (المنصور) w ...
founded the city of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
and declared it the capital of the Caliphate. Unlike the Umayyads, the Abbasids had the support of non-Arab subjects.
The Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
was inaugurated by the middle of the 8th century by the ascension of the Abbasid Caliphate and the transfer of the capital from Damascus to the newly founded city of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
. The Abbasids were influenced by the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
ic injunctions and hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approva ...
such as "The ink of the scholar is more holy than the blood of martyrs" stressing the value of knowledge. During this period the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
became an intellectual centre for science, philosophy, medicine and education as the Abbasids championed the cause of knowledge and established the " House of Wisdom" () in Baghdad. Rival dynasties such as the Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
s of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
s of al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
were also major intellectual centres with cities such as Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
and Córdoba rivaling Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
.Vartan Gregorian, "Islam: A Mosaic, Not a Monolith", Brookings Institution Press, 2003, pg 26–38
 The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the
The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, who conquered Baghdad in 1258 and killed the Caliph Al-Musta'sim
Abu Ahmad Abdallah ibn al-Mustansir Billah (; 1213 – 20 February 1258), better known by his regnal name al-Musta'sim Billah ( ar, المستعصم بالله, al-Mustaʿṣim billāh, label=none) was the 37th and last caliph of the Abbasid dynas ...
. Members of the Abbasid royal family escaped the massacre and resorted to Cairo, which had broken from the Abbasid rule two years earlier; the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
generals taking the political side of the kingdom while Abbasid Caliphs were engaged in civil activities and continued patronizing science, arts and literature.
=Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171)
= The Fatimid caliphate was founded by al-Mahdi Billah, a descendant of
The Fatimid caliphate was founded by al-Mahdi Billah, a descendant of Fatimah
Fāṭima bint Muḥammad ( ar, فَاطِمَة ٱبْنَت مُحَمَّد}, 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fāṭima al-Zahrāʾ (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, ...
, the daughter of Muhammad, in the early 10th century. Egypt was the political, cultural, and religious centre of the Fatimid empire. The Fatimid state took shape among the Kutama
The Kutama ( Berber: ''Ikutamen''; ar, كتامة) was a Berber tribe in northern Algeria classified among the Berber confederation of the Bavares. The Kutama are attested much earlier, in the form ''Koidamousii'' by the Greek geographer Ptolemy. ...
Berbers, in the West of the North African littoral, in Algeria, in 909 conquering Raqqada
Raqqāda ( ar, رقّادة) is the site of the second capital of the 9th-century dynasty of Aghlabids, located about ten kilometers southwest of Kairouan, Tunisia. The site now houses the National Museum of Islamic Art.
History
In 876, the ni ...
, the Aghlabid
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a ...
capital. In 921 the Fatimids established the Tunisian city of Mahdia
Mahdia ( ar, المهدية ') is a Tunisian coastal city with 62,189 inhabitants, south of Monastir and southeast of Sousse.
Mahdia is a provincial centre north of Sfax. It is important for the associated fish-processing industry, as well as w ...
as their new capital. In 948 they shifted their capital to Al-Mansuriya, near Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( ar, ٱلْقَيْرَوَان, al-Qayrawān , aeb, script=Latn, Qeirwān ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by t ...
in Tunisia, and in 969 they conquered Egypt and established Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
as the capital of their caliphate.
Intellectual life in Egypt during the Fatimid period achieved great progress and activity, due to many scholars who lived in or came to Egypt, as well as the number of books available. Fatimid Caliphs gave prominent positions to scholars in their courts, encouraged students, and established libraries in their palaces, so that scholars might expand their knowledge and reap benefits from the work of their predecessors.Shorter Shi'ite Encyclopaedia, By: Hasan al-Amin, The Fatimids were also known for their exquisite arts. Many traces of Fatimid architecture exist in Cairo today; the most defining examples include Al-Hakim Mosque
The Mosque of al-Hakim ( ar, مسجد الحاكم بأمر الله, Masjid al-Ḥākim bi Amr Allāh), nicknamed al-Anwar ( ar, الانور, lit=the Illuminated), is a historic mosque in Cairo, Egypt. It is named after Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah (98 ...
and the Al-Azhar University.
 It was not until the 11th century that the
It was not until the 11th century that the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
saw a large influx of ethnic Arabs. Starting with the 11th century, the Arab bedouin Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
tribes migrated to the West. Having been sent by the Fatimids to punish the Berber Zirids
The Zirid dynasty ( ar, الزيريون, translit=az-zīriyyūn), Banu Ziri ( ar, بنو زيري, translit=banū zīrī), or the Zirid state ( ar, الدولة الزيرية, translit=ad-dawla az-zīriyya) was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from ...
for abandoning Shias
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
, they travelled westwards. The Banu Hilal quickly defeated the Zirids and deeply weakened the neighboring Hammadids. According to some modern historians. their influx was a major factor in the arabization of the Maghreb. Although Berbers ruled the region until the 16th century (under such powerful dynasties as the Almoravids, the Almohads, Hafsids
The Hafsids ( ar, الحفصيون ) were a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. who ruled Ifriqiya (weste ...
, etc.), the arrival of these tribes eventually helped Arabize much of it ethnically, in addition to the linguistic and political impact on local non-Arabs.
Ottoman Empire
 From 1517 to 1918, much of the Arab world was under the suzerainty of the
From 1517 to 1918, much of the Arab world was under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The Ottomans defeated the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
in Cairo, and ended the Abbasid Caliphate. Arabs did not feel the change of administration because the Ottomans modeled their rule after the previous Arab administration systems.
In 1911, Arab intellectuals and politicians from throughout the Levant formed al-Fatat
Al-Fatat or the Young Arab Society ( ar, جمعية العربية الفتاة, Jam’iyat al-’Arabiya al-Fatat) was an underground Arab nationalist organization in the Ottoman Empire. Its aims were to gain independence and unify various Arab te ...
("the Young Arab Society"), a small Arab nationalist club, in Paris. Its stated aim was "raising the level of the Arab nation to the level of modern nations." In the first few years of its existence, al-Fatat called for greater autonomy within a unified Ottoman state rather than Arab independence from the empire. Al-Fatat hosted the Arab Congress of 1913 in Paris, the purpose of which was to discuss desired reforms with other dissenting individuals from the Arab world. However, as the Ottoman authorities cracked down on the organization's activities and members, al-Fatat went underground and demanded the complete independence and unity of the Arab provinces.Choueiri, pp.166–168.
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, when the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
was overthrown by the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, former Ottoman colonies were divided up between the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and French as League of Nations mandates.
Modern period
 Arabs in modern times live in the Arab world, which comprises 22 countries in
Arabs in modern times live in the Arab world, which comprises 22 countries in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and parts of the Horn of Africa. They are all modern states and became significant as distinct political entities after the fall and defeat and dissolution of the Ottoman Empire (1908–1922)
The dissolution of the Ottoman Empire (1908–1922) began with the Young Turk Revolution which restored the constitution of 1876 and brought in multi-party politics with a two-stage electoral system for the Ottoman parliament. At the same ti ...
.
Identity
Arab identity is defined independently ofreligious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
identity, and pre-dates the spread of Islam
The spread of Islam spans about 1,400 years. Muslim conquests following Muhammad's death led to the creation of the caliphates, occupying a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted by Arab Muslim forces conquering vast territorie ...
, with historically attested Arab Christian kingdoms and Arab Jewish tribes. Today, however, most Arabs are Muslim, with a minority adhering to other faiths, largely Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, but also Druze and Baháʼí.
Paternal descent has traditionally been considered the main source of affiliation in the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
when it comes to membership into an ethnic group or clan.
 Today, the main unifying characteristic among Arabs is
Today, the main unifying characteristic among Arabs is Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, a Central Semitic language
Central Semitic languages are one of the three groups of West Semitic languages, alongside Modern South Arabian languages and Ethiopian Semitic languages.
Central Semitic can itself be further divided into two groups: Arabic and Northwest Semit ...
from the Afroasiatic language family. Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
serves as the standardized
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
and literary
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
variety of Arabic used in writing. The Arabs are first mentioned in the mid-ninth century BCE as a tribal people dwelling in the central Arabian Peninsula subjugated by Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been ...
-based state of Assyria. The Arabs appear to have remained largely under the vassalage of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
(911–605 BCE), and then the succeeding Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bei ...
(605–539 BCE), Persian Achaemenid Empire (539–332 BCE), Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
Macedonian/ Seleucid Empire and Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
.
Arab tribes, most notably the Ghassanids and Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
begin to appear in the south Syrian deserts and southern Jordan from the mid 3rd century CE onwards, during the mid to later stages of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
and Sasanian Empire. Also, before them the Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern L ...
of Jordan and arguably the Emessans, Edessans, and Hatra
Hatra ( ar, الحضر; syr, ܚܛܪܐ) was an ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The city lies northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul.
Hatra was a strongly fortified ...
ns all appear to have been an Aramaic speaking ethnic Arabs who came to rule much of the pre-Islamic fertile crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
often as vassals of the two rival empires, the Sasanian (Persian) and the Byzantine (Eastern Roman). Thus, although a more limited diffusion of Arab culture and language was felt in some areas by these migrant minority Arabs in ''pre-Islamic'' times through Arabic-speaking Christian kingdoms and Jewish tribes, it was only after the rise of Islam in the mid-7th century that Arab culture, people and language began their wholesale spread from the central Arabian Peninsula (including the south Syrian desert) through conquest and trade.
Subgroups
tribes of Arabia
The Tribes of Arabia () or Arab tribes () are the ethnic Arab tribes and clans that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. The tribes of Arabia descend from either one of the two Arab ancestors, Adnan or Qahtan. Arab tribes have historically in ...
and their immediate descendant groups in the Levant and North Africa. Within the people of the Arabian Peninsula, distinction is made between:
* "Perishing Arabs" ( ar, الـعـرب الـبـائـدة), which are ancient tribes about whose history little is known. They include ʿĀd
ʿĀd ( ar, عَادٌ, ') is an ancient tribe mentioned frequently in the Qurʾān.
The tribe's members, referred to as ʿĀdites, formed a prosperous nation until they were destroyed in a violent storm. According to Islamic tradition, the st ...
( ar, عَـاد), Q54:21 Thamûd ( ar, ثَـمُـود), Q7:73-157 Tasm, Jadis, Imlaq and others. Jadis and Tasm perished because of genocide. 'Aad and Thamud perished because of their decadence, as recorded in the Qur'an. Archaeologists have recently uncovered inscriptions that contain references to ''Iram dhāṫ al-'Imād'' ( ar, إِرَم ذَات الـعِـمَـاد, Iram of the Pillars
Iram of the Pillars ( ar, إرَم ذَات ٱلْعِمَاد, ; an alternative translation is ''Iram of the tentpoles''), also called "Irum", "Irem", "Erum", "Ubar", or the "City of the pillars", is considered a lost city, region or tribe men ...
), which was a major city of the 'Aad. Imlaq is the singular form of 'Amaleeq and is probably synonymous to the biblical Amalek.
* "Pure Arabs" ( ar, الـعـرب الـعـاربـة) or Qahtanites
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions ...
from Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, taken to be descended from Ya'rub ibn Yashjub ibn Qahtan and further from Hud
Hud or HUD may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Hud'' (1963 film), a 1963 film starring Paul Newman
* ''Hud'' (1986 film), a 1986 Norwegian film
* ''HUD'' (TV program), or ''Heads Up Daily'', a Canadian e-sports television program
Places
* Hud, Fa ...
.
* "Arabized Arabs" ( ar, الـعـرب الـمـسـتـعـربـة) or Adnanites
The Adnanites ( ar, عدنانيون) were a tribal confederation of the Ishmaelite Arabs, traces their lineage back to Ismail son of the Islamic prophet and patriarch Ibrahim and his wife Hajar through Adnan, who originate from the Hejaz. Th ...
, taken to be the descendants of Ishmael son of Abraham.
Arabians are most prevalent in the Arabian Peninsula, but are also found in large numbers in Mesopotamia ( Arab tribes in Iraq), the Levant and Sinai (Negev Bedouin
The Negev Bedouin ( ar, بدو النقب, ''Badū an-Naqab''; he, הבדואים בנגב, ''HaBedu'im BaNegev'') are traditionally pastoral nomadic Arab tribes ( Bedouin), who until the later part of the 19th century would wander between Sa ...
, Tarabin bedouin), as well as the Maghreb (Eastern Libya, South Tunisia and South Algeria) and the Sudan region.
This traditional division of the Arabs of Arabia may have arisen at the time of the First Fitna. Of the Arabian tribes that interacted with Muhammad
There were several Arabian tribes that interacted with Muhammad.
Introduction
The most prominent of such Arabian tribes were Quraish which were in turn divided into several sub-clans. The Qur'aish sub-clan of Banu Hashim was the clan of Muhammad ...
, the most prominent was the Quraysh. The Quraysh subclan, the Banu Hashim, was the clan of Muhammad. During the early Muslim conquests and the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, the political rulers of Islam were exclusively members of the Quraysh.
The Arab presence in Iran did not begin with the Arab conquest of Persia
The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.
Th ...
in 633 CE. For centuries, Iranian rulers had maintained contacts with Arabs outside their borders, dealt with Arab subjects and client states (such as those of Iraq and Yemen), and settled Arab tribesmen in various parts of the Iranian plateau. It follows that the "Arab" conquests and settlements were by no means the exclusive work of Arabs from the Hejaz and the tribesmen of inner Arabia. The Arab infiltration into Iran began before the Muslim conquests and continued as a result of the joint exertions of the civilized Arabs (ahl al-madar) as well as the desert Arabs (ahl al-wabar). The largest group of Iranian Arabs
Iranian Arabs ( ar, عرب إيران ''ʿArab Īrān''; fa, عربهای ايران ''Arabhāye Irān'') are the Arab inhabitants of Iran who speak Arabic as their native language. In 2008, Iranian Arabs comprised about 1.6 million people, ...
are the Ahwazi Arabs
Khuzestani Arabs () are the largest Arab community in Iran which primarily reside in the western half of the Khuzestan province. This area is known as Ahwaz by the Arab community, and the capital of Khuzestan is Ahvaz. As of 2010, Khuzestani Arab ...
, including Banu Ka'b, Bani Turuf and the Musha'sha'iyyah sect. Smaller groups are the Khamseh
The Khamseh ( fa, ایلات خمسه) is a tribal confederation in the province of Fars in southwestern Iran. It consists of five tribes, hence its name ''Khamseh'', "''the five''". The tribes are partly nomadic, Some are Persian speaking Bass ...
nomads in Fars Province and the Arabs in Khorasan.
 The Arabs of the
The Arabs of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
are traditionally divided into Qays and Yaman tribes
Qays ʿAylān ( ar, قيس عيلان), often referred to simply as Qays (''Kais'' or ''Ḳays'') were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe does not appear to have functioned as a unit in the pre-Islamic e ...
. This tribal division is likewise taken to date to the Umayyad period. The Yemen trace their origin to South Arabia or Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
; they include Banu Kalb
The Banu Kalb ( ar, بنو كلب) was an Arab tribe which mainly dwelt in the desert between northwestern Arabia and central Syria. The Kalb was involved in the tribal politics of the eastern frontiers of the Byzantine Empire, possibly as early ...
, Kinda, Ghassanids, and Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
. Since the 1834 Peasants' revolt in Palestine
The Peasants' Revolt was a rebellion against Egyptian conscription and taxation policies in Palestine. While rebel ranks consisted mostly of the local peasantry, urban notables and Bedouin tribes also formed an integral part of the revolt, wh ...
, the Arabic-speaking population of Palestine has shed its formerly tribal structure and emerged as the Palestinians.
Native Jordanians are either descended from Bedouins (of which, 6% live a nomadic lifestyle),Lowi, Miriam R., ''Water and power: the politics of a scarce resource in the Jordan River basin'', Cambridge University Press, 1995, p.36 or from the many deeply rooted non bedouin communities across the country, most notably Al-Salt
Al-Salt ( ar, السلط ''As-Salt'') is an ancient salt trading city and administrative centre in west-central Jordan. It is on the old main highway leading from Amman to Jerusalem. Situated in the Balqa (region), Balqa highland, about 790–1, ...
city west of Amman which was at the time of Emirate the largest urban settlement east of the Jordan River. Along with indigenous communities in Al Husn, Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Govern ...
, Irbid, Al Karak, Madaba
Madaba ( ar, مادبا; Biblical Hebrew: ''Mēḏəḇāʾ''; grc, Μήδαβα) is the capital city of Madaba Governorate in central Jordan, with a population of about 60,000. It is best known for its Byzantine and Umayyad mosaics, especi ...
, Jerash
Jerash ( ar, جرش ''Ǧaraš''; grc, Γέρασα ''Gérasa'') is a city in northern Jordan. The city is the administrative center of the Jerash Governorate, and has a population of 50,745 as of 2015. It is located north of the capital city ...
, Ajloun, Fuheis and Pella
Pella ( el, Πέλλα) is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It is best-known for serving as the capital city of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon, and was the birthplace of Alexander the Great.
On site of the ancient cit ...
. In Jordan, there is no official census data for how many inhabitants have Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
roots but they are estimated to constitute half of the population, which in 2008 amounted to about 3 million. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics put their number at 3.24 million in 2009.
 The Bedouins of western Egypt and eastern Libya are traditionally divided into Saʿada and Murabtin, the Saʿada having higher social status. This may derive from a historical feudal system in which the Murabtin were vassals to the Saʿada.
In Sudan, there are numerous Arabic-speaking tribes, including the
The Bedouins of western Egypt and eastern Libya are traditionally divided into Saʿada and Murabtin, the Saʿada having higher social status. This may derive from a historical feudal system in which the Murabtin were vassals to the Saʿada.
In Sudan, there are numerous Arabic-speaking tribes, including the Shaigya
The Shaigiya, Shaiqiya, Shawayga or Shaykia () are an Arab or Arabised Nubian tribe. They are part of the Sudanese Arabs and are also one of the three prominent Sudanese Arabs tribes in North Sudan, along with the Ja'alin and Danagla. The trib ...
, Ja'alin
The Ja'alin, Ja'aliya, Ja'aliyin or Ja'al ( ar, جعليون) are an Arab or Arabised Nubian tribe in Sudan. The Ja'alin constitute a large portion of the Sudanese Arabs and are one of the three prominent Sudanese Arab tribes in northern Sudan ...
and Shukria, who are ancestrally related to the Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of ...
. These groups are collectively known as Sudanese Arabs
Sudanese Arabs () are the inhabitants of Sudan who identify as Arabs and speak Arabic as their mother tongue. Part of them are descendants of Arabs who migrated to Sudan from the Arabian Peninsula, although the rest have been described as Arabiz ...
. In addition, there are other Afroasiatic-speaking populations, such as Copts and Beja.
 The medieval trans-Saharan slave trade in the Sudan drove a wedge between the
The medieval trans-Saharan slave trade in the Sudan drove a wedge between the Arabized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
Sudanese and the non-Arabized Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-sp ...
Sudanese populations. It has contributed to ethnic conflict in the region, such as the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile
The Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile is an armed conflict in the Sudanese southern states of South Kordofan and Blue Nile between the Sudanese Army (SAF) and Sudan People's Liberation Movement-North (SPLM-N), a northern affilia ...
, Northern Mali conflict, or the Boko Haram insurgency.
The Arabs of the Maghreb are descendants of Arabian tribes of Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
, the Banu Sulaym and the Maqil
The Banu Ma'qil ( ar, بنو معقل) was an Arab nomadic tribe that originated in South Arabia. The tribe emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa with the Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym tribes in the 11th century. They mainly settled in and ...
native of Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
and of other tribes native to Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
. Arabs and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
-speakers inhabit plains and cities. The Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
spent almost a century in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
before moving to Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and another century later some moved to Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, it is logical to think that they are mixed with inhabitants of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and with Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
.
Demographics
The total number of Arabic speakers living in theArab nations
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western As ...
is estimated at 366 million by the CIA Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
(as of 2014). The estimated number of Arabs in countries outside the Arab League is estimated at 17.5 million, yielding a total of close to 384 million.
Arab world
 According to the Charter of the Arab League (also known as the ''Pact of the League of Arab States''), the League of Arab States is composed of independent Arab states that are signatories to the Charter.
According to the Charter of the Arab League (also known as the ''Pact of the League of Arab States''), the League of Arab States is composed of independent Arab states that are signatories to the Charter.
Toubou
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. They live either as herders and nomads or as ...
, Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Assyrians, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ira ...
. Additionally, many Arab countries in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
have sizable non-Arab immigrant populations (10–70%). Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
, Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it ...
, United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia ( The Middle East). It is located at t ...
and Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
have a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
speaking minority. The same countries also have Hindi-Urdu
Hindustani (; Devanagari: ,
*
*
*
* ; Perso-Arabic: , , ) is the '' lingua franca'' of Northern and Central India and Pakistan. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu. Thus, the lang ...
speakers and Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or othe ...
as sizable minority. Balochi speakers are a good size minority in Oman. Additionally, countries like Bahrain, UAE, Oman and Kuwait have significant non-Arab and non-Muslim minorities (10–20%) like Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
from South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
The table below shows the distribution of populations in the Arab world, as well as the official language(s) within the various Arab states.
Arab diaspora

Arab diaspora
Arab diaspora (also known as MENA diaspora, as a short version for the Middle East and North Africa diaspora) refers to descendants of the Arab emigrants who, voluntarily or as refugees, emigrated from their native lands to non-Arab countries, ...
refers to descendants of the Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
who, voluntarily or as refugees, emigrated from their native lands in non-Arab countries, primarily in East Africa, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, North America, Australia and parts of South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
, the Caribbean, and West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
. According to the International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers.
The IOM w ...
, there are 13 million first-generation Arab migrants in the world, of which 5.8 million reside in Arab countries. Arab expatriates contribute to the circulation of financial and human capital in the region and thus significantly promote regional development. In 2009, Arab countries received a total of 35.1 billion USD in remittance in-flows and remittances sent to Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
from other Arab countries are 40 to 190 per cent higher than trade revenues between these and other Arab countries. The 250,000 strong Lebanese community in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
is the largest non-African group in the region. Arab traders have long operated in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
and along the East Africa's Swahili coast. Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
was once ruled by Omani
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
Arabs. Most of the prominent Indonesians, Malaysians
Malaysians are nationals and citizens who are identified with the country of Malaysia. Although citizens make up the majority of Malaysians, non-citizen residents and overseas Malaysians may also claim a Malaysian identity.
The country is h ...
, and Singaporeans
Singaporeans, or the Singaporean people, refers to citizens or people who identify with the sovereign island city-state of Singapore. Singapore is a multi-ethnic, multi-cultural and multi-lingual country. Singaporeans of Chinese, Malay, Indi ...
of Arab descent are Hadhrami people
The Hadhrami ( ar, حضرمي, ḥaḍramī, singular) or Hadharem ( ar, حضارم, ḥaḍāram, plural) are an Arab ethnic group indigenous to the Hadhramaut region in South Arabia around Eastern Yemen, western Oman, and southern Saudi Arabia ...
with origins in southern Arabia in the Hadramawt
Hadhramaut ( ar, حَضْرَمَوْتُ \ حَضْرَمُوتُ, Ḥaḍramawt / Ḥaḍramūt; Hadramautic: 𐩢𐩳𐩧𐩣𐩩, ''Ḥḍrmt'') is a region in South Arabia, comprising eastern Yemen, parts of western Oman and southern Saud ...
coastal region.
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
(about 6,000,000 in 2005). Most Arabs in France
Arabs in France are those parts of the Arab diaspora who have immigrated to France, as well as their descendants. Subgroups include Algerians in France, Moroccans in France, Mauritanians in France, Tunisians in France and Refugees of the Syri ...
are from the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
but some also come from the Mashreq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the n ...
areas of the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
. Arabs in France form the second largest ethnic group after ethnically French people.France's ethnic minorities: To count or not to countThe Economist (26 March 2009). Retrieved on 12 July 2013. In
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Arabs first arrived on the southern island of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
in the 9th century. The largest modern societies on the island from the Arab world are Tunisians and Moroccans, who make up 10.9% and 8% respectively of the foreign population of Sicily, which in itself constitutes 3.9% of the island's total population. The modern Arab population of Spain numbers 1,800,000, and there have been Arabs in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
since the early 8th century when the Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
created the state of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
. In Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
the Arab population numbers over 1,000,000, in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
between 366,769 and 500,000, and in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
between 250,000 and 750,000). In addition, Greece is home to people from Arab countries who have the status of refugees (e.g. refugees of the Syrian civil war). In the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
180,000, and in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
121,000. Other European countries
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the regions of Europe, various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, ...
are also home to Arab populations, including Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Switzerland, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
. As of late 2015, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
had a total population of 78.7 million, with Syrian refugees accounting for 3.1% of that figure based on conservative estimates. Demographics indicated that the country previously had 1,500,000 to 2,000,000 Arab residents, so Turkey's Arab population is now 4.5 to 5.1% of the total population, or approximately 4–5 million people.

Arab immigration to the United States Arab immigration to the United States began before the United States achieved independence in 1776. Since the first major wave of Arab immigration in the late 19th century, the majority of Arab immigrants have settled in or near large cities. Roug ...
began in sizable numbers during the 1880s. Today, it is estimated that nearly 3.7 million Americans trace their roots to an Arab country. Arab Americans
Arab Americans ( ar, عَرَبٌ أَمْرِيكِا or ) are Americans of Arab ancestry. Arab Americans trace ancestry to any of the various waves of immigrants of the countries comprising the Arab World.
According to the Arab American Ins ...
are found in every state, but more than two thirds of them live in just ten states: California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
, New York, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
. Metropolitan Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
are home to one-third of the population. Contrary to popular assumptions or stereotypes, the majority of Arab Americans are native-born, and nearly 82% of Arabs in the U.S. are citizens. Arab American Population Highlights Arab American Institute Foundation Arabs immigrants began to arrive in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
in small numbers in 1882. Their immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
was relatively limited until 1945, after which time it increased progressively, particularly in the 1960s and thereafter. According to the website "Who are Arab Canadians
Arab Canadians (french: Arabo-Canadiens) come from all of the countries of the Arab world. According to the 2021 Census, there were 694,015 Canadians, or 1.87%, who claimed Arab ancestry. According to the 2011 Census there were 380,620 Canadia ...
," Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, the Canadian city with the largest Arab population, has approximately 267,000 Arab inhabitants.
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
has the largest Arab population outside of the Arab World
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
. Latin America is home to anywhere from 17–25 to 30 million people of Arab descent, which is more than any other diaspora region in the world. The Brazilian and Lebanese governments claim there are 7 million Brazilians of Lebanese descent. Also, the Brazilian government claims there are 4 million Brazilians of Syrian descent. According to research conducted by IBGE in 2008, covering only the states of Amazonas, Paraíba, São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the Ga ...
, Rio Grande do Sul, Mato Grosso and Distrito Federal
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they ...
, 0.9% of white Brazilian respondents said they had family origins in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
. Other large Arab communities includes Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
(about 4,500,000) The interethnic marriage in the Arab community, regardless of religious affiliation, is very high; most community members have only one parent who has Arab ethnicity. Colombia (over 3,200,000), Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
(over 1,600,000), Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
(over 1,100,000), Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
(over 800,000), and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, particularly El Salvador, and Honduras (between 150,000 and 200,000). is the fourth largest in the world after those in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, and Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
. Arab Haitians (a large number of whom live in the capital) are more often than not, concentrated in financial areas where the majority of them establish businesses.
Mughan
Mughan plain ( az, Muğan düzü, مغان دوزو; ) is a plain stretching from northwestern Iran to the southern part of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The highest density of irrigation canals is in the section of the Mughan plain which lies in ...
(in present-day Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
) and spoke a mixed Turkic-Arabic language.Genko, A. ''The Arabic Language and Caucasian Studies''. USSR Academy of Sciences Publ. Moscow-Leningrad. 8–109 It is believed that these groups migrated to the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
in the 16th century.Zelkina, AnnaArabic as a Minority Language
Walter de Gruyter, 2000; p. 101 The 1888 edition of
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
also mentioned a certain number of Arabs populating the Baku Governorate of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.Baynes, Thomas Spencer (ed). "Transcaucasia." Encyclopædia Britannica. 1888. p. 514 They retained an Arabic dialect
The varieties (or dialects or vernacular languages) of Arabic, a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family originating in the Arabian Peninsula, are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. There are considerable variatio ...
at least into the mid-19th century,Golestan-i Iramby
Abbasgulu Bakikhanov
Abbasgulu agha Bakikhanov ( az, Abbasqulu ağa Bakıxanov) (21 June 1794, Amirjan – 31 May 1847, Wadi Fatima, near Jeddah), Abbas Qoli Bakikhanov, or Abbas-Qoli ibn Mirza Mohammad (Taghi) Khan Badkubi was an Azerbaijani writer, historian, journa ...
. Translated by Ziya Bunyadov
Ziya Musa oglu Bunyadov ( az, Ziya Bünyadov sometimes spelled in English as Zia Buniatov or Bunyatov) (21 December 1923, Astara – 21 February 1997, Baku) was an Azerbaijani historian, academician, and Vice-President of the National Academy o ...
. Baku: 1991, p. 21 there are nearly 30 settlements still holding the name ''Arab'' (for example, Arabgadim, Arabojaghy, Arab-Yengija, etc.). From the time of the Arab conquest of the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
, continuous small-scale Arab migration from various parts of the Arab world occurred in Dagestan. The majority of these lived in the village of Darvag, to the north-west of Derbent
Derbent (russian: Дербе́нт; lez, Кьвевар, Цал; az, Дәрбәнд, italic=no, Dərbənd; av, Дербенд; fa, دربند), formerly romanized as Derbend, is a city in Dagestan, Russia, located on the Caspian Sea. It i ...
. The latest of these accounts dates to the 1930s. Most Arab communities in southern Dagestan underwent linguistic Turkicisation
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization ( tr, Türkleştirme) describes a shift whereby populations or places received or adopted Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly ...
, thus nowadays Darvag is a majority- Azeri village.Seferbekov, RuslanCharacters Персонажи традиционных религиозных представлений азербайджанцев Табасарана.
Stephen Adolphe Wurm et al
Atlas of languages of intercultural communication
Walter de Gruyter, 1996; p. 966 According to the ''History of Ibn Khaldun'', the Arabs that were once in
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
have been either killed or have fled the Tatar invasion of the region, leaving only the locals.History of Ibn Khaldun However, today many people in Central Asia identify as Arabs. Most Arabs of Central Asia are fully integrated into local populations, and sometimes call themselves the same as locals (for example, Tajiks
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Taj ...
, Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
) but they use special titles to show their Arab origin such as Sayyid
''Sayyid'' (, ; ar, سيد ; ; meaning 'sir', 'Lord', 'Master'; Arabic plural: ; feminine: ; ) is a surname of people descending from the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandsons, Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali, sons of Muhamma ...
, Khoja
The Khojas ( sd}; gu, ખોજા, hi, ख़ोजा) are a mainly Nizari Isma'ili Shia community of people originating in Gujarat, India.
Derived from the Persian Khwaja, a term of honor, the word Khoja is used to refer to Lohana Rajp ...
or Siddiqui
Siddiqui ()( Romanized: Ṣiddīqī ) are a South Asian Muslim Sheikh community found mainly in India and Pakistan and in expatriate communities in Saudi Arabia and the Middle East region. They claim to be the descendants of Abu Bakr, the first ...
.Arabic As a Minority Language By Jonathan Owens, pg. 184 There are only two communities in
There are only two communities in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
which self-identify as Arabs, the Chaush of the Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
region and the Chavuse of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. These groups are largely descended from Hadhrami migrants who settled in these two regions in the 18th century. However, neither community still speaks Arabic, although the Chaush have seen re-immigration to Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
and thus a re-adoption of Arabic. In South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, where Arab ancestry is considered prestigious, many communities have origin myths that claim Arab ancestry. Several communities following the Shafi'i madhab (in contrast to other South Asian Muslims who follow the Hanafi madhab) claim descent from Arab traders like the Konkani Muslims
Konkani Muslims (or ''Kokani'' Muslims) are an ethnoreligious subgroup of the Konkani people of the Konkani region along the west coast of India, who practice Islam. ''Nawayath'' Muslims from the North Canara district of Karnataka have similar ...
of the Konkan region, the Mappilla
Mappila Muslim, often shortened to Mappila, formerly anglicized as Moplah/Mopla and historically known as Jonaka/Chonaka Mappila or Moors Mopulars/Mouros da Terra and Mouros Malabares, in general, is a member of the Muslim community of same n ...
of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
, and the Labbai
Labbay (Labbai, Labba, Labbabeen, Lebbay, Lebbai), is a Muslim trading community in southern India found throughout the southern Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala.
Etymology
''Labbay'' means "Here I am", and is used as a title ...
and Marakkar
Marakkar/Maricar/Marecar/Marikkar/Markiyar/Marican/Marecan (Malayalam:Marakkar; Tamil: Marrakayar)( Sinhalese: Marakkala), is a South Asian Muslim community found in parts of the Indian states of Kerala (The Malabar Coast), Tamil Nadu (the Palk ...
of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
and a few Christian groups in India that claim and have Arab roots are situated in the state of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South ...
. South Asian Iraqi biradri may have records of their ancestors who migrated from Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
in historical documents. The Sri Lankan Moors are the third largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka, constituting 9.23% of the country's total population. Some sources trace the ancestry of the Sri Lankan Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
to Arab traders who settled in Sri Lanka at some time between the 8th and 15th centuries.
There are about 5,000,000 Native Indonesians
Native Indonesians, also known as ''Pribumi'' (), are Indonesians whose ancestral roots lie mainly in the archipelago, distinguished from Indonesians of known (partial) foreign descent, like Chinese Indonesians (Tionghoa), Arab Indonesians, Indi ...
with Arab ancestry. Arab Indonesians
Arab Indonesians ( ar, عربٌ إندونيسيون) or ''Hadharem'' (; sing., ''Hadhrami'', ), informally known as Jama'ah, and until the 20th century known as Codjas or Kodjas, note the work was also published in the Hague and Utrecht simulta ...
are mainly of Hadrami descent.
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
who are of partial Arab descent. Most Afro-Arabs inhabit the Swahili Coast in the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
region, although some can also be found in parts of the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
. Large numbers of Arabs migrated to West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
, particularly Côte d'Ivoire (home to over 100,000 Lebanese), Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
(roughly 30,000 Lebanese), Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
(roughly 10,000 Lebanese today; about 30,000 prior to the outbreak of Sierra Leone Civil War, civil war in 1991), Liberia, and Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
. Since the end of the civil war in 2002, Lebanese traders have become re-established in Sierra Leone. The Arabs of Chad occupy northern Cameroon and Nigeria (where they are sometimes known as Shuwa), and extend as a belt across Chad and into Sudan, where they are called the Baggara
The Baggāra ( ar, البَقَّارَة "heifer herder") or Chadian Arabs are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile ri ...
grouping of Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
ethnic groups inhabiting the portion of Africa's Sahel. There are 171,000 in Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
, 150,000 in Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesCentral African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR; ; , RCA; , or , ) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to the north, Sudan to the northeast, South Sudan to the southeast, the DR Congo to the south, the Republic of th ...
.
Religion
Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
minority, one exception being the Ibadi
The Ibadi movement or Ibadism ( ar, الإباضية, al-Ibāḍiyyah) is a school of Islam. The followers of Ibadism are known as the Ibadis.
Ibadism emerged around 60 years after the Islamic prophet Muhammad's death in 632 AD as a moderate sc ...
s, who predominate in Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
.See, for example:
*
* Arab Christians generally follow Eastern Churches
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus, Northeast Africa, the Fertile Crescent and ...
such as the Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
and Greek Catholic The term Greek Catholic Church can refer to a number of Eastern Catholic Churches following the Byzantine (Greek) liturgy, considered collectively or individually.
The terms Greek Catholic, Greek Catholic church or Byzantine Catholic, Byzantine Ca ...
churches, though a minority of Protestant Church
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
followers also exists. There are also Arab communities consisting of Druze and Baháʼís.
Before the coming of Islam, most Arabs followed a pagan religion with a number of deities, including Hubal
In Arabian mythology, Hubal ( ar, هُبَل) was a god worshipped in pre-Islamic Arabia, notably by the Quraysh at the Kaaba in Mecca. The god's idol was a human figure believed to control acts of divination, which was performed by tossing ar ...
, Wadd
Wadd ( ar, وَدّ) (Ancient South Arabian script: 𐩥𐩵) is a pre-Islamic Arabian god. He was the national god of the Minaeans of South Arabia, and the snake was associated with him. It is also called Waddum and Wadd'ab.
In Islamic tr ...
, Allāt, Manat, and Uzza. A few individuals, the '' hanifs'', had apparently rejected polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, t ...
in favor of monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfo ...
unaffiliated with any particular religion. Some tribes had converted to Christianity or Judaism. The most prominent Arab Christian kingdoms were the Ghassanid and Lakhmid kingdoms. When the Himyarite king converted to Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
in the late 4th century, the elites of the other prominent Arab kingdom, the Kindites
The Kinda ( ar, كِنْدَة, Ancient South Arabian script: 𐩫𐩬𐩵𐩩) were an Arab tribe from South Arabia. As early as the 3rd century CE they served as Bedouin auxiliaries of the Sabaean Kingdom, followed by the Himyarite Kingdom. In ...
, being Himyirite vassals, apparently also converted (at least partly). With the expansion of Islam, polytheistic Arabs were rapidly Islamized
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
, and polytheistic traditions gradually disappeared.
 Today, Sunni Islam dominates in most areas, vastly so in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Shia Islam is dominant among the Arab population in
Today, Sunni Islam dominates in most areas, vastly so in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Shia Islam is dominant among the Arab population in Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
and southern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
while northern Iraq is mostly Sunni. Substantial Shia populations exist in Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, northern Syria and Al-Batinah Region in Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
. There are small numbers of Ibadi
The Ibadi movement or Ibadism ( ar, الإباضية, al-Ibāḍiyyah) is a school of Islam. The followers of Ibadism are known as the Ibadis.
Ibadism emerged around 60 years after the Islamic prophet Muhammad's death in 632 AD as a moderate sc ...
and non-denominational Muslims
Non-denominational Muslims () are Muslims who do not belong to, do not self-identify with, or cannot be readily classified under one of the identifiable Islamic schools and branches.
Non-denominational Muslims are found primarily in Central Asi ...
too. The Druze community is concentrated in Lebanon, Syria, Israel and Jordan. Many Druze claim independence from other major religions in the area and consider their religion more of a philosophy. Their books of worship are called Kitab Al Hikma (Epistles of Wisdom). They believe in reincarnation and pray to five messengers from God. In Israel, the Druze have a ''status aparte'' from the general Arab population, treated as a separate ethno-religious community.
 Christianity had a prominent presence In
Christianity had a prominent presence In pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia ( ar, شبه الجزيرة العربية قبل الإسلام) refers to the Arabian Peninsula before the emergence of Islam in 610 CE.
Some of the settled communities developed into distinctive civilizations. Informatio ...
among several Arab communities, including the Bahrani people
The Baharna ( ar, بحارنة) are the indigenous Shia Muslim inhabitants of Bahrain who inhabited the area before the arrival of Sunni Muslim Arab tribes from Najd, particularly by Banu Utbah in the 18th century which the Bahraini royal fam ...
of Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
, the Christian community of Najran, in parts of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, and among certain northern Arabian tribes such as the Ghassanids, Lakhmids
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capita ...
, Taghlib
The Banu Taghlib (), also known as Taghlib ibn Wa'il, were an Arab tribe that originated in Najd (central Arabia), but later migrated and inhabited the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) from the late 6th century onward. Their parent tribe was the Rabi ...
, Banu Amela
Banu 'Amilah ( ar, بَنُو عَامِلَة, '), also spelled Amelah, were an Arab tribe that inhabited the historic region of Jabal Amel in present day Southern Lebanon. Lebanese Shia Muslims of Southern Lebanon hail the tribe as their progeni ...
, Banu Judham, Tanukhids
The Tanûkhids ( ar, التنوخيون, transl=al-Tanūḫiyyūn) or Tanukh ( ar, تنوخ, translit=Tanūḫ) or Banū Tanūkh (, romanized as: ) were a confederation of Arab tribes, sometimes characterized as Saracens. They first rose to prom ...
and Tayy
, location = 2nd century CE–10th century: Jabal Tayy and Syrian Desert
10th century–16th century: Jabal Tayy, Syrian Desert, Jibal al-Sharat, al-Balqa, Palmyrene Steppe, Upper Mesopotamia, Northern Hejaz, Najd
, parent_tribe = Madh ...
. In the early Christian centuries, Arabia was sometimes known as ''Arabia heretica'', due to its being "well known as a breeding-ground for heterodox interpretations of Christianity." Christians make up 5.5% of the population of Western Asia and North Africa. A sizeable share of those are Arab Christians proper, and affiliated Arabic-speaking populations of Copts and Maronites. In Lebanon, Christians number about 40.5% of the population. In Syria, Christians make up 10% of the population. In West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
and in Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
, Christians make up 8% and 0.7% of the populations, respectively. In Egypt, Coptic Christians number about 10% of the population. In Iraq, Christians constitute 0.1% of the population. In Israel, Arab Christians constitute 2.1% (roughly 9% of the Arab population). Arab Christians make up 8% of the population of Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
. Most North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
n Arabs are Christian, so are about half of the Arabs in Australia who come particularly from Lebanon, Syria and Palestine. One well known member of this religious and ethnic community is Saint Abo, martyr and the patron saint of Tbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of approximately 1.5 million p ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. Arab Christians also live in holy Christian cities such as Nazareth, Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
and the Christian Quarter
The Christian Quarter ( ar, حارة النصارى, ''Ḥārat al-Naṣārā''; he, הרובע הנוצרי, ''Ha-Rova ha-Notsri'') is one of the four quarters of the walled Old City of Jerusalem, the other three being the Jewish Quarter, ...
of the Old City of Jerusalem and many other villages with holy Christian sites.
Culture
 Arab culture is the culture of the Arabs, from the
Arab culture is the culture of the Arabs, from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
in the west to the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
in the north to the Horn of Africa and the Indian Ocean in the southeast. The various religions the Arabs have adopted throughout their history and the various empires and kingdoms that have ruled and took lead of the Arabian civilization have contributed to the ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
and formation of modern Arab culture. Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
, literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, gastronomy
Gastronomy is the study of the relationship between food and culture, the art of preparing and serving rich or delicate and appetizing food, the cooking styles of particular regions, and the science of good eating. One who is well versed in gastr ...
, art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, spirituality, philosophy and mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in ...
are all part of the cultural heritage of the Arabs.
Arabs share basic belief
Basic beliefs (also commonly called foundational beliefs or core beliefs) are, under the epistemological view called foundationalism, the axioms of a belief system.
Categories of beliefs
Foundationalism holds that all beliefs must be justifi ...
s and values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of something or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live (normative ethics in ethics), or to describe the significance of di ...
that cross national and social class boundaries. Social attitudes have remained constant because Arab society is more conservative and demands conformity from its members.
Language
 Another important and unifying characteristic of Arabs is a common
Another important and unifying characteristic of Arabs is a common language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
is a Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
of the Afro-Asiatic Family. Evidence of its first use appears in accounts of wars in 853 BCE. It also became widely used in trade and commerce. Arabic also is a liturgical
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
language of 1.7 billion Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
.
Arabic is one of six official languages of the United Nations
The Official Languages of the United Nations are the six languages that are used in UN meetings and in which all official UN documents are written. In the six languages, four are the official language or national language of permanent members ...
. It is revered as the language that God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
chose to reveal the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
.
Arabic has developed into at least two distinct forms. Classical Arabic is the form of the Arabic language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
used in literary texts from Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
and Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
times (7th to 9th centuries). It is based on the medieval dialects of Arab tribes
The Tribes of Arabia () or Arab tribes () are the ethnic Arab tribes and clans that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. The tribes of Arabia descend from either one of the two Arab ancestors, Adnan or Qahtan. Arab tribes have historically inhabit ...
. Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
(MSA) is the direct descendant used today throughout the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
in writing and in formal speaking, for example, prepared speeches, some radio broadcasts, and non-entertainment content, while the lexis
Lexis may refer to:
* Lexis (linguistics), the total bank of words and phrases of a particular language, the artifact of which is known as a lexicon
*Lexis (Aristotle), a complete group of words in a language
*LexisNexis, part of the LexisNexis onl ...
and stylistics of Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
are different from Classical Arabic. Colloquial Arabic, an informal spoken language, varies by dialect from region to region; various forms of the language are in use today and provide an important force for Arab cohesion.
Mythology

Arabic mythology
Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia included indigenous Arabian polytheism, ancient Semitic religions, Christianity, Judaism, Mandaeism, and Iranian religions such as Zoroastrianism, and Manichaeism, and rarely Buddhism.
Arabian polytheism, the d ...
comprises the ancient beliefs of the Arabs. Prior to Islam the Kaaba of Mecca was covered in symbols representing the myriad demons, djinn, demigods, or simply tribal gods and other assorted deities which represented the polytheistic culture of pre-Islamic. It has been inferred from this plurality an exceptionally broad context in which mythology could flourish. The most popular beasts and demons of Arabian mythology are Bahamut
Bahamut, or Bahamoot ( ; ar, بهموت), is a monster that lies deep below, underpinning the support structure that holds up the earth, according to Zakariya al-Qazwini.
In this conception of the world, the earth is shouldered by an angel, w ...
, Dandan, Falak, Ghoul
A ghoul ( ar, غول, ') is a demon-like being or monstrous humanoid. The concept originated in pre-Islamic Arabian religion, associated with graveyards and the consumption of human flesh. Modern fiction often uses the term to label a cert ...
, Hinn, Jinn
Jinn ( ar, , ') – also Romanization of Arabic, romanized as djinn or Anglicization, anglicized as genies (with the broader meaning of spirit or demon, depending on sources)
– are Invisibility, invisible creatures in early Arabian mytho ...
, Karkadann
The Karkadann (Arabic كركدن ''karkadann'' or ''karkaddan'' from ''Kargadan'', Persian language, Persian: كرگدن) is a mythical creature said to have lived on the grassy plains of India and Iran, Persia.
The word ''kargadan'' also means ...
, Marid
''Marid'' ( ar, مارد ') is a type of devil in Islamic traditions. The Arabic word meaning ''rebellious'' is applied to such supernatural beings.
In Arabic sources Etymology
The word ''mārid'' is an active participle of the root ''m-r-d'' ...
, Nasnas, Qareen, Roc, Shadhavar
Shâd'havâr (Arabic: شادهوار) or Âras (آرس) is a legendary creature from medieval Muslim bestiaries resembling a unicorn. Al-Qazwini said that it lives in the country of '' Rūm'' (Byzantium) and that it has one horn with 42 hollow bra ...
, Werehyena
Were-hyena is a neologism coined in analogy to werewolf for therianthropy involving hyenas. It is common in the folklore of the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the Near East as well as some adjacent territorie ...
and other assorted creatures which represented the profoundly polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
environment of pre-Islamic.
The most obvious symbol of Arabian mythology is the Jinn
Jinn ( ar, , ') – also Romanization of Arabic, romanized as djinn or Anglicization, anglicized as genies (with the broader meaning of spirit or demon, depending on sources)
– are Invisibility, invisible creatures in early Arabian mytho ...
or genie. Jinns are supernatural beings of varying degrees of power. They possess free will (that is, they can choose to be good or evil) and come in two flavors. There are the Marids, usually described as the most powerful type of Jinn. These are the type of genie with the ability to grant wishes to humans. However, granting these wishes is not free. The Quran says that the ''jinn'' were created from "mārijin min nar" (''smokeless fire'' or ''a mixture of fire''; scholars explained, this is the part of the flame, which mixed with ''the blackness of fire''). They are not purely spiritual, but are also physical in nature, being able to interact in a tactile manner with people and objects and likewise be acted upon. The ''jinn'', humans, and angels
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles incl ...
make up the known sapient creations of God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
.
A ghoul
A ghoul ( ar, غول, ') is a demon-like being or monstrous humanoid. The concept originated in pre-Islamic Arabian religion, associated with graveyards and the consumption of human flesh. Modern fiction often uses the term to label a cert ...
is a monster
A monster is a type of fictional creature found in horror, fantasy, science fiction, folklore, mythology and religion. Monsters are very often depicted as dangerous and aggressive with a strange, grotesque appearance that causes terror and fe ...
or evil spirit
Evil, in a general sense, is defined as the opposite or absence of good. It can be an extremely broad concept, although in everyday usage it is often more narrowly used to talk about profound wickedness and against common good. It is generally ...
in Arabic mythology
Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia included indigenous Arabian polytheism, ancient Semitic religions, Christianity, Judaism, Mandaeism, and Iranian religions such as Zoroastrianism, and Manichaeism, and rarely Buddhism.
Arabian polytheism, the d ...
, associated with graveyards and consuming human flesh, demonic being believed to inhabit burial grounds and other deserted places. In ancient Arabic folklore, ghūls belonged to a diabolic class of jinn (spirits) and were said to be the offspring of Iblīs, the prince of darkness in Islam. They were capable of constantly changing form, but their presence was always recognizable by their unalterable sign—ass's hooves. which describes the ''ghūl'' of Arabic folklore. The ''ghul'' is a devilish type of jinn
Jinn ( ar, , ') – also Romanization of Arabic, romanized as djinn or Anglicization, anglicized as genies (with the broader meaning of spirit or demon, depending on sources)
– are Invisibility, invisible creatures in early Arabian mytho ...
believed to be sired by Iblis
Iblis ( ar, إِبْلِيس, translit=Iblīs), alternatively known as Eblīs, is the leader of the devils () in Islam. According to the Quran, Iblis was thrown out of heaven, after he refused to prostrate himself before Adam. Regarding the o ...
.
Literature
 The
The Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
, the main holy book
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They differ from literature by being a compilation or discussion of beliefs, mythologies, ritual prac ...
of Islam, had a significant influence on the Arabic language, and marked the beginning of Islamic literature
Islamic literature is literature written by Muslim people, influenced by an Islamic cultural perspective, or literature that portrays Islam. It can be written in any language and portray any country or region. It includes many literary forms incl ...
. Muslims believe it was transcribed in the Arabic dialect of the Quraysh, the tribe of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
. As Islam spread, the Quran had the effect of unifying and standardizing Arabic.
Not only is the Qur'an the first work of any significant length written in the language, but it also has a far more complicated structure than the earlier literary works with its 114 ''suwar
A ''surah'' (; ar, سورة, sūrah, , ), is the equivalent of "chapter" in the Qur'an. There are 114 ''surahs'' in the Quran, each divided into '' ayats'' (verses). The chapters or ''surahs'' are of unequal length; the shortest surah ('' Al-K ...
'' (chapters) which contain 6,236 '' ayat'' (verses). It contains injunction
An injunction is a legal and equitable remedy in the form of a special court order that compels a party to do or refrain from specific acts. ("The court of appeals ... has exclusive jurisdiction to enjoin, set aside, suspend (in whole or in pa ...
s, narrative
A narrative, story, or tale is any account of a series of related events or experiences, whether nonfictional (memoir, biography, news report, documentary, travel literature, travelogue, etc.) or fictional (fairy tale, fable, legend, thriller (ge ...
s, homilies
A homily (from Greek ὁμιλία, ''homilía'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered ex ...
, parable
A parable is a succinct, didactic story, in prose or verse, that illustrates one or more instructive lessons or principles. It differs from a fable in that fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as characters, w ...
s, direct addresses from God, instructions and even comments on how the Qu'ran will be received and understood. It is also admired for its layers of metaphor as well as its clarity, a feature which is mentioned in An-Nahl
The Bee (Arabic: الْنَّحْل; ''an-nahl'') is the 16th chapter (''sūrah'') of the Qur'an, with 128 verses ('' āyāt''). It is named after honey bees mentioned in verse 68, and contains a comparison of the industry and adaptability of h ...
, the 16th surah.
Al-Jahiz
Abū ʿUthman ʿAmr ibn Baḥr al-Kinānī al-Baṣrī ( ar, أبو عثمان عمرو بن بحر الكناني البصري), commonly known as al-Jāḥiẓ ( ar, links=no, الجاحظ, ''The Bug Eyed'', born 776 – died December 868/Jan ...
(born 776, in Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
– December 868/January 869) was an Arab prose writer and author of works of literature, Mu'tazili
Muʿtazila ( ar, المعتزلة ', English: "Those Who Withdraw, or Stand Apart", and who called themselves ''Ahl al-ʿAdl wa al-Tawḥīd'', English: "Party of ivineJustice and Oneness f God); was an Islamic group that appeared in early Islamic ...
theology, and politico-religious polemics. A leading scholar in the Abbasid Caliphate, his canon includes two hundred books on various subjects, including Arabic grammar
Arabic grammar or Arabic language sciences ( ar, النحو العربي ' or ar, عُلُوم اللغَة العَرَبِيَّة ') is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with ...
, zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
, poetry, lexicography, and rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
. Of his writings, only thirty books survive. Al-Jāḥiẓ was also one of the first Arabian writers to suggest a complete overhaul of the language's grammatical system, though this would not be undertaken until his fellow linguist Ibn Maḍāʾ
Abu al-Abbas Ahmad bin Abd al-Rahman bin Muhammad bin Sa'id bin Harith bin Asim al-Lakhmi al-Qurtubi, better known as Ibn Maḍāʾ ( ar, ابن مضاء; 1116–1196) was an Arab Muslim polymath from Córdoba in Islamic Spain. Kees Versteegh ...
took up the matter two hundred years later.
There is a small remnant of pre-Islamic poetry
Arabic poetry ( ar, الشعر العربي ''ash-shi‘ru al-‘Arabīyyu'') is the earliest form of Arabic literature. Present knowledge of poetry in Arabic dates from the 6th century, but oral poetry is believed to predate that.
Arabic poetry ...
, but Arabic literature predominantly emerges in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, during the Golden Age of Islam
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. Literary Arabic is derived from Classical Arabic, based on the language of the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
as it was analyzed by Arabic grammarians
Arabic grammar or Arabic language sciences ( ar, النحو العربي ' or ar, عُلُوم اللغَة العَرَبِيَّة ') is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with ...
beginning in the 8th century.
 A large portion of Arabic literature before the 20th century is in the form of
A large portion of Arabic literature before the 20th century is in the form of poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings i ...
, and even prose from this period is either filled with snippets of poetry or is in the form of '' saj'' or rhymed prose.
The ''ghazal
The ''ghazal'' ( ar, غَزَل, bn, গজল, Hindi-Urdu: /, fa, غزل, az, qəzəl, tr, gazel, tm, gazal, uz, gʻazal, gu, ગઝલ) is a form of amatory poem or ode, originating in Arabic poetry. A ghazal may be understood as a ...
'' or love poem had a long history being at times tender and chaste and at other times rather explicit. In the Sufi
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ...
tradition the love poem would take on a wider, mystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
and religious
Religion is usually defined as a social system, social-cultural system of designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morality, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sacred site, sanctified places, prophecy, prophecie ...
importance. Arabic epic literature
Arabic epic literature encompasses epic poetry and epic fantasy in Arabic literature. Virtually all societies have developed Folklore, folk tales encompassing tales of heroes. Although many of these are legends, many are based on real events and ...
was much less common than poetry, and presumably originates in oral tradition, written down from the 14th century or so. Maqama
''Maqāmah'' (مقامة, pl. ''maqāmāt'', مقامات, literally "assemblies") are an (originally) Arabic prosimetric literary genre which alternates the Arabic rhymed prose known as '' Saj‘'' with intervals of poetry in which rhetorical ...
or rhymed prose Rhymed prose is a literary form and literary genre, written in unmetrical rhymes. This form has been known in many different cultures. In some cases the rhymed prose is a distinctive, well-defined style of writing. In modern literary traditions ...
is intermediate between poetry and prose
Prose is a form of written or spoken language that follows the natural flow of speech, uses a language's ordinary grammatical structures, or follows the conventions of formal academic writing. It differs from most traditional poetry, where the f ...
, and also between fiction and non-fiction. Maqama
''Maqāmah'' (مقامة, pl. ''maqāmāt'', مقامات, literally "assemblies") are an (originally) Arabic prosimetric literary genre which alternates the Arabic rhymed prose known as '' Saj‘'' with intervals of poetry in which rhetorical ...
was an incredibly popular form of Arabic literature, being one of the few forms which continued to be written during the decline of Arabic in the 17th and 18th centuries.
 Arabic literature and
Arabic literature and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
declined significantly after the 13th century, to the benefit of Turkish and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
. A modern revival took place beginning in the 19th century, alongside resistance against Ottoman rule. The literary revival is known as ''al-Nahda
The Nahda ( ar, النهضة, translit=an-nahḍa, meaning "the Awakening"), also referred to as the Arab Awakening or Enlightenment, was a cultural movement that flourished in Arabic-speaking regions of the Ottoman Empire, notably in Egypt, ...
'' in Arabic, and was centered in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
. Two distinct trends can be found in the ''nahda'' period of revival. The first was a neo-classical movement which sought to rediscover the literary traditions of the past, and was influenced by traditional literary genres—such as the ''maqama
''Maqāmah'' (مقامة, pl. ''maqāmāt'', مقامات, literally "assemblies") are an (originally) Arabic prosimetric literary genre which alternates the Arabic rhymed prose known as '' Saj‘'' with intervals of poetry in which rhetorical ...
''—and works like ''One Thousand and One Nights
''One Thousand and One Nights'' ( ar, أَلْفُ لَيْلَةٍ وَلَيْلَةٌ, italic=yes, ) is a collection of Middle Eastern folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age. It is often known in English as the ''Arabian ...
''. In contrast, a modernist movement began by translating Western modernist works—primarily novels—into Arabic. A tradition of modern Arabic poetry
Arabic poetry ( ar, الشعر العربي ''ash-shi‘ru al-‘Arabīyyu'') is the earliest form of Arabic literature. Present knowledge of poetry in Arabic dates from the 6th century, but oral poetry is believed to predate that.
Arabic poetry ...
was established by writers such as Francis Marrash, Ahmad Shawqi
Ahmed Shawqi (also written Chawki; ar, أحمد شوقي, , ; ; 1868–1932), nicknamed the Prince of Poets ( ar, أمير الشعراء ''Amīr al-Shu‘arā’''), was an Arabic poet laureate, to the Arabic literary tradition.
Life
Raised ...
and Hafiz Ibrahim
Hafez Ibrahim ( ar, حافظ إبراهيم, ; 1871–1932) was a well known Egyptian poet of the early 20th century. He was dubbed the "Poet of the Nile", and sometimes the "Poet of the People", for his political commitment to the poor. His p ...
. Iraqi poet Badr Shakir al-Sayyab
Badr Shakir al Sayyab ( ar, بدر شاكر السياب) (December 24, 1926 in Jaykur, near Basra – December 24, 1964 in Kuwait) was a leading Iraqi poet, well known throughout the Arab world and one of the most influential Arab poets of all ti ...
is considered to be the originator of free verse in Arabic poetry
Arabic poetry ( ar, الشعر العربي ''ash-shi‘ru al-‘Arabīyyu'') is the earliest form of Arabic literature. Present knowledge of poetry in Arabic dates from the 6th century, but oral poetry is believed to predate that.
Arabic poetry ...
.
Gastronomy

Arabic cuisine
Arab cuisine ( ar, المطبخ العربي) is the cuisine of the Arabs, defined as the various regional cuisines spanning the Arab world, from the Maghreb to the Fertile Crescent and the Arabian Peninsula. These cuisines are centuries old an ...
is the cuisine of the Arab people. The cuisines are often centuries old and reflect the culture of great trading in spices, herbs, and foods. The three main regions, also known as the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, the Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the n ...
, and the Khaleej have many similarities, but also many unique traditions. These kitchens have been influenced by the climate, cultivating possibilities, as well as trading possibilities. The kitchens of the Maghreb and Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
are relatively young kitchens which were developed over the past centuries. The kitchen from the Khaleej region is a very old kitchen. The kitchens can be divided into the urban
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
and rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are describ ...
kitchens.
Arab cuisine
Arab cuisine ( ar, المطبخ العربي) is the cuisine of the Arabs, defined as the various regional cuisines spanning the Arab world, from the Maghreb to the Fertile Crescent and the Arabian Peninsula. These cuisines are centuries old an ...
mostly follows one of three culinary traditions – from the Maghreb, the Levant or Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
. In the Maghreb countries (Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
) traditional main meals are tajine
A tajine or tagine ( ar, طاجين) is a North African dish, named after the earthenware pot in which it is cooked. It is also called or .
Etymology
The Arabic () is derived from the Berber 'shallow earthen pot', from Ancient Greek () ' ...
s or dishes using couscous
Couscous ( '; ber, ⵙⴽⵙⵓ, translit=Seksu) – sometimes called kusksi or kseksu – is a Maghrebi dish of small steamed granules of rolled durum wheat semolina that is often served with a stew spooned on top. Pearl millet, sorghum, ...
. In the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
(Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and Syria) main meals usually start with mezze
Meze or mezza (, ) is a selection of small dishes served as appetizers in the Levantine cuisine, Levant, Turkish cuisine, Turkey, Greek cuisine, Greece, the Balkan cuisine, Balkans, the Caucasian cuisine, Caucasus and Iranian cuisine, Iran. It i ...
– small dishes of dips and other items which are eaten with bread. This is typically followed by skewers of grilled lamb or chicken. Gulf cuisine, tends to be more highly spiced with more use of rice. Sometimes a lamb is roasted and served whole.
One will find the following items in most dishes; cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfa ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
(in coastal areas), garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
, lamb
Lamb or The Lamb may refer to:
* A young sheep
* Lamb and mutton, the meat of sheep
Arts and media Film, television, and theatre
* ''The Lamb'' (1915 film), a silent film starring Douglas Fairbanks Sr. in his screen debut
* ''The Lamb'' (1918 ...
(or veal), mild to hot sauce
In cooking, a sauce is a liquid, cream, or semi-solid food, served on or used in preparing other foods. Most sauces are not normally consumed by themselves; they add flavor, moisture, and visual appeal to a dish. ''Sauce'' is a French word t ...
s, mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ...
, onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent i ...
, sesame
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
, yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in t ...
, spices
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garni ...
due to heavy trading between the two regions. Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
, thyme
Thyme () is the herb (dried aerial parts) of some members of the genus ''Thymus'' of aromatic perennial evergreen herbs in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are relatives of the oregano genus ''Origanum'', with both plants being mostly indigenou ...
(or oregano), turmeric
Turmeric () is a flowering plant, ''Curcuma longa'' (), of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae, the rhizomes of which are used in cooking. The plant is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asi ...
, a variety of fruits (primarily citrus) and vegetables such as cucumbers, eggplants, lettuce, tomato, Capsicum annuum, green pepper, green beans, zucchini and parsley.
Art
 Arabic art takes on many forms, though it is jewelry, textiles and
Arabic art takes on many forms, though it is jewelry, textiles and architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
that are the most well-known. It is generally split up by different eras, among them being History of the Arabic alphabet, early Arabic, early medieval, late medieval, Arabic, late Arabic, and finally, current Arabic. One thing to remember is that many times a particular style from one era may continue into the next with few changes, while some have a drastic transformation. This may seem like a strange grouping of art mediums, but they are all closely related.
 Arabic writing is done from right to left, and was generally written in dark inks, with certain things embellished with special colored inks (red, green, gold). In early Arabic and Early Middle Ages, early Medieval, writing was typically done on parchment made of animal skin. The ink showed up very well on it, and occasionally the parchment was dyed a separate color and brighter ink was used (this was only for special projects). The name given to the form of writing in early times was called Kufic script.
Arabic miniatures (
Arabic writing is done from right to left, and was generally written in dark inks, with certain things embellished with special colored inks (red, green, gold). In early Arabic and Early Middle Ages, early Medieval, writing was typically done on parchment made of animal skin. The ink showed up very well on it, and occasionally the parchment was dyed a separate color and brighter ink was used (this was only for special projects). The name given to the form of writing in early times was called Kufic script.
Arabic miniatures (Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
: الْمُنَمْنَمَات الْعَرَبِيَّة, ''Al-Munamnamāt al-ʿArabīyah'') are small paintings on paper, usually book or manuscript illustrations but also sometimes separate artworks that occupy entire pages. The earliest example dates from around 690 AD, with a flourishing of the art from between 1000 and 1200 AD in the Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliphate. The art form went through several stages of evolution while witnessing the fall and rise of several Caliphate, Islamic caliphates. Arab miniaturists absorbed Chinese art, Chinese and Persian art, Persian influences brought by the Mongol invasion of the Middle East, Mongol destructions, and at last, got totally assimilated and subsequently disappeared due to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman occupation of the Arab world. Nearly all forms of Islamic miniatures (Persian miniatures, Ottoman miniatures and Mughal miniatures) owe their existences to Arabic miniatures, as Arab patrons were the first to demand the production of illuminated manuscripts in the Caliphate, it wasn't until the 14th century that the artistic skill reached the non-Arab regions of the Caliphate.''La Peinture arabe''
Despite the considerable changes in Arabic miniature style and technique, even during their last decades, the early Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Arab influence could still be noticed. Arabic miniature artists include Ismail al-Jazari, who illustrated his own ''Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices,''al-Jazari, ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices: Kitáb fí ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiyya'', transl. & anno. Donald Hill, Donald R. Hill. (1973), Springer Science+Business Media. and the Abbasid artist, Yahya ibn Mahmud al-Wasiti, Yahya Al-Wasiti, who probably lived in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
in the late Abbasid era (12th to 13th-centuries), was one of the pre-eminent exponents of the Baghdad school. In 1236-1237, he is known to have transcribed and illustrated the book, ''Maqamat Badi' az-Zaman al-Hamadhani, Maqamat'' (also known as the ''Assemblies'' or the ''Sessions''), a series of anecdotes of social satire written by Al-Hariri of Basra. The narrative concerns the travels of a middle-aged man as he uses his charm and eloquence to swindle his way across the Arabic world.
With most surviving Arabic manuscripts in western museums, Arabic miniatures occupy very little space in modern Arab culture.
Arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foliate ornament, typically using leaves, derived from stylised half-palmettes, which were combined with spiralling stems". It usually consists of a single design which can be 'tiled' or seamlessly repeated as many times as desired.
Architecture
pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia ( ar, شبه الجزيرة العربية قبل الإسلام) refers to the Arabian Peninsula before the emergence of Islam in 610 CE.
Some of the settled communities developed into distinctive civilizations. Informatio ...
and includes various styles from the Nabataean architecture to the old yet still used architecture in various regions of the Arab world. Each of it phases largely
an extension of the earlier phase, it left also heavy impact on the Islamic architecture, architecture of other nations. Arab Architecture also encompasses a wide range of both secular and religious styles from the History of Islam, foundation of Islam to the present day. Some parts of its religious architectures raised by Muslim Arabs were influenced by cultures of Roman architecture, Roman, Byzantine architecture, Byzantine, Persian architecture, Persian and cultures of other lands which the Early Muslim conquests, Arab conquered in the 7th and 8th centuries.Krautheimer, RichardEarly Christian and Byzantine Architecture
Yale University Press Pelican History of Art, Penguin Books Ltd., 1965, p. 285. In
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Arab-Norman culture#Norman-Arab-Byzantine architecture, Arab-Norman architecture combined Occidental features, such as the Classical pillars and friezes, with typical Arabic decorations and calligraphy. The principal Islamic architectural types are: the Mosque, the Tomb, the Palace and the Fort. From these four types, the vocabulary of Islamic architecture is derived and used for other buildings such as public baths, fountains and domestic architecture.Copplestone, p.149
Music
Arabic music, while independent and flourishing in the 2010s, has a long history of interaction with many other regional musical styles and genres. It is an amalgam of the music of the Arab people in the Arabian Peninsula and the music of all the peoples that make up theArab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
today. Pre-Islamic Arab music was similar to that of Ancient Middle Eastern music. Most historians agree that there existed distinct forms of music in the Arabian peninsula in the pre-Islamic period between the 5th and 7th century CE. Arabic poetry, Arab poets of that "Jahili poets", meaning "the poets of the period of ignorance"—used to recite poems with a high notes. It was believed that Genie, Jinns revealed poems to poets and music to musicians. By the 11th century, al-Andalus, Islamic Iberia had become a center for the manufacture of instruments. These goods spread gradually throughout France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, influencing French troubadours, and eventually reaching the rest of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
. The English words lute, rebec, and naqareh, naker are derived from Arabic oud, Rebab, rabab, and naqareh.
 A number of musical instruments used in classical music are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments: the lute was derived from the ''Oud'', the rebec (ancestor of violin) from the ''Maghreb rebab'', the guitar from ''qitara'', which in turn was derived from the Persian Tar (lute), Tar, naqareh, naker from ''naqareh'', adufe from ''Daf, al-duff'', alboka from ''al-buq'', Naffir, anafil from ''al-nafir'', exabeba from ''al-shabbaba'' (flute), atabal (bass drum) from ''al-tabl'', atambal from ''al-tinbal'', the Balaban (instrument), balaban, the castanet from ''kasatan'', Tuna (music), sonajas de azófar from ''sunuj al-sufr'', the Bore (wind instruments), conical bore wind instruments, the xelami from the ''sulami'' or ''fistula'' (flute or Organ pipe, musical pipe),
the shawm and dulzaina from the Reed (instrument), reed instruments ''zamr'' and ''Zurna, al-zurna'', the Galician gaita, gaita from the ''Rhaita, ghaita'', rackett from ''iraqya'' or ''iraqiyya'', Violin, geige (violin) from ''ghichak'',
and the theorbo from the ''tarab''.
During the 1950s and the 1960s, Arabic music began to take on a more Western tone – artists Umm Kulthum, Abdel Halim Hafez, and Shadia along with composers Mohammed Abdel Wahab, Mohamed Abd al-Wahab and Baligh Hamdi pioneered the use of western instruments in Egyptian music. By the 1970s several other singers had followed suit and a strand of Arabic pop was born. Arabic pop usually consists of Western styled songs with Arabic instruments and lyrics. Melodies are often a mix between Eastern and Western. Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical Innovator, pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the
A number of musical instruments used in classical music are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments: the lute was derived from the ''Oud'', the rebec (ancestor of violin) from the ''Maghreb rebab'', the guitar from ''qitara'', which in turn was derived from the Persian Tar (lute), Tar, naqareh, naker from ''naqareh'', adufe from ''Daf, al-duff'', alboka from ''al-buq'', Naffir, anafil from ''al-nafir'', exabeba from ''al-shabbaba'' (flute), atabal (bass drum) from ''al-tabl'', atambal from ''al-tinbal'', the Balaban (instrument), balaban, the castanet from ''kasatan'', Tuna (music), sonajas de azófar from ''sunuj al-sufr'', the Bore (wind instruments), conical bore wind instruments, the xelami from the ''sulami'' or ''fistula'' (flute or Organ pipe, musical pipe),
the shawm and dulzaina from the Reed (instrument), reed instruments ''zamr'' and ''Zurna, al-zurna'', the Galician gaita, gaita from the ''Rhaita, ghaita'', rackett from ''iraqya'' or ''iraqiyya'', Violin, geige (violin) from ''ghichak'',
and the theorbo from the ''tarab''.
During the 1950s and the 1960s, Arabic music began to take on a more Western tone – artists Umm Kulthum, Abdel Halim Hafez, and Shadia along with composers Mohammed Abdel Wahab, Mohamed Abd al-Wahab and Baligh Hamdi pioneered the use of western instruments in Egyptian music. By the 1970s several other singers had followed suit and a strand of Arabic pop was born. Arabic pop usually consists of Western styled songs with Arabic instruments and lyrics. Melodies are often a mix between Eastern and Western. Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical Innovator, pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
O'Connor, Tom"Lydia Canaan One Step Closer to Rock n' Roll Hall of Fame"
, ''The Daily Star (Lebanon), The Daily Star'', Beirut, 27 April 2016.
Spirituality
 Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in
Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia ( ar, شبه الجزيرة العربية قبل الإسلام) refers to the Arabian Peninsula before the emergence of Islam in 610 CE.
Some of the settled communities developed into distinctive civilizations. Informatio ...
. Deity, Gods and goddesses, including Hubal
In Arabian mythology, Hubal ( ar, هُبَل) was a god worshipped in pre-Islamic Arabia, notably by the Quraysh at the Kaaba in Mecca. The god's idol was a human figure believed to control acts of divination, which was performed by tossing ar ...
and the goddesses al-Lat, al-Lāt, Al-'Uzzá and Manāt, were worshipped at local shrines, such as the Kaaba in Mecca, whilst Arabs in the south, in what is today's Yemen, worshipped various gods, some of which represented the Sun or Moon. Different theories Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia#Mecca, have been proposed regarding the role of Allah in Meccan religion. Many of the physical descriptions of the pre-Islamic gods are traced to Cult image, idols, especially near the Kaaba, which is said to have contained up to 360 of them. Until about the fourth century, almost all Arabs practised polytheistic religions. Although significant Judaism, Jewish and Christian minorities developed, polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, t ...
remained the dominant belief system in pre-Islamic Arabia.
The religious beliefs and practices of the nomadic bedouin were distinct from those of the settled tribes of towns such as Mecca. Nomadic religious belief systems and practices are believed to have included fetishism, totemism and veneration of the dead but were connected principally with immediate concerns and problems and did not consider larger Philosophy, philosophical questions such as the afterlife. Settled urban Arabs, on the other hand, are thought to have believed in a more complex Pantheon (religion), pantheon of deities. While the Meccans and the other settled inhabitants of the Hejaz worshipped their gods at permanent shrines in towns and oases, the bedouin practised their religion on the move.
Philosophy

 The philosophical thought in the Arab world is heavily influenced by Islamic Philosophy. Schools of Islamic thought include Avicennism and Averroism. The first great Arab thinker in the Islamic tradition is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in
The philosophical thought in the Arab world is heavily influenced by Islamic Philosophy. Schools of Islamic thought include Avicennism and Averroism. The first great Arab thinker in the Islamic tradition is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in Kufa
Kufa ( ar, الْكُوفَة ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000. Currently, Kufa and Najaf a ...
and Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
(modern day Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
). After being appointed by the Abbasid Caliphs to translate Greeks, Greek scientific and philosophical texts into Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, he wrote a number of original treatises of his own on a range of subjects, from metaphysics and ethics to mathematics and pharmacology.
Much of his Philosophy, philosophical output focuses on Theology, theological subjects such as the nature of God, the soul and Prophecy, prophetic knowledge. Doctrines of the Arabic philosophers of the 9th–12th century who influenced medieval Scholasticism in Europe. The Arabic tradition combines Aristotelianism and Neoplatonism with other ideas introduced through Islam. Influential thinkers include the non-Arabs al-Farabi and Avicenna. The Arabic philosophic literature was translated into Hebrew and Latin, this contributed to the development of modern European philosophy. The Arabic tradition was developed by Moses Maimonides and Ibn Khaldun.
Science
 Science in the medieval Islamic world, Islamic science underwent considerable development during the 8th to 13th centuries CE, a source of knowledge that later spread throughout
Science in the medieval Islamic world, Islamic science underwent considerable development during the 8th to 13th centuries CE, a source of knowledge that later spread throughout Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and greatly influenced both medical practice and education. The language of recorded science was Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
. Scientific treatises were composed by thinkers originating from across the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
. These accomplishments occurred after Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
united the Arab tribes
The Tribes of Arabia () or Arab tribes () are the ethnic Arab tribes and clans that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. The tribes of Arabia descend from either one of the two Arab ancestors, Adnan or Qahtan. Arab tribes have historically inhabit ...
and the spread of Islam beyond the Arabian peninsula.
 Within a century after Muhammed's death (632 CE), an empire ruled by Arabs was established. It encompassed a large part of the planet, stretching from southern Europe to
Within a century after Muhammed's death (632 CE), an empire ruled by Arabs was established. It encompassed a large part of the planet, stretching from southern Europe to North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
to Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and on to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. In 711 CE, Arab Muslims invaded southern Spain; al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
was a center of Arabic scientific accomplishment. Soon after, Sicily too joined the greater islamic world. Another center emerged in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
from the Abbasids, who ruled part of the Muslim world, Islamic world during a historic period later characterized as the "Islamic Golden Age, Golden Age" (∼750 to 1258 CE).
 This era can be identified as the years between 692 and 945,Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 234. and ended when the caliphate was marginalized by local Muslim rulers in Baghdad – its traditional seat of power. From 945 onward until the Sack of Baghdad, sacking of Baghdad by the Mongol invasions, Mongols in 1258, the Caliph continued on as a figurehead, with power devolving more to local amirs.Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 233. The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology. Arabic scientific achievement is not as yet fully understood, but is very large. These achievements encompass a wide range of subject areas, especially Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematics, Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, and Medicine in medieval Islam, medicine. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included Physics in medieval Islam, physics, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy and chemistry, Cosmology in medieval Islam, cosmology, Medieval Islamic ophthalmology, ophthalmology, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and cartography, Sociology in medieval Islam, sociology, and Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology.
Al-Battani (c. 858 – 929; born Harran, Bilad al-Sham) was an Arab astronomer, astrologer and mathematician of the
This era can be identified as the years between 692 and 945,Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 234. and ended when the caliphate was marginalized by local Muslim rulers in Baghdad – its traditional seat of power. From 945 onward until the Sack of Baghdad, sacking of Baghdad by the Mongol invasions, Mongols in 1258, the Caliph continued on as a figurehead, with power devolving more to local amirs.Marshall Hodgson, ''The Venture of Islam; Conscience and History in a World Civilisation Vol 1''. The University of Chicago, 1974, pg. 233. The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology. Arabic scientific achievement is not as yet fully understood, but is very large. These achievements encompass a wide range of subject areas, especially Mathematics in medieval Islam, mathematics, Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, and Medicine in medieval Islam, medicine. Other subjects of scientific inquiry included Physics in medieval Islam, physics, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy and chemistry, Cosmology in medieval Islam, cosmology, Medieval Islamic ophthalmology, ophthalmology, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and cartography, Sociology in medieval Islam, sociology, and Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology.
Al-Battani (c. 858 – 929; born Harran, Bilad al-Sham) was an Arab astronomer, astrologer and mathematician of the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
. His work is considered instrumental in the development of science and astronomy. One of Al-Battani's best-known achievements in astronomy was the determination of the solar year as being 365 days, 5 hours, 46 minutes and 24 seconds which is only 2 minutes and 22 seconds off.
In Islamic mathematics, mathematics, al-Battānī produced a number of Trigonometry, trigonometrical relationships:
::
::
He also solved the equation sin ''x'' = ''a'' cos ''x'' discovering the formula:
::
He gives other trigonometric formulae for right-angled triangles such as:
::
Al-Battānī used Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi, al-Marwazi's idea of Trigonometric function, tangents ("shadows") to develop equations for calculating tangents and cotangents, compiling tables of them. He also discovered the reciprocal functions of secant and cosecant, and produced the first table of cosecants, which he referred to as a "table of shadows" (in reference to the shadow of a gnomon), for each degree from 1° to 90°.
Using these trigonometrical relationships, Al-Battānī created an equation for finding the qibla, which Muslims must face in each of the five prayers they practice every day. The equation he created did not give accurate directions, as it did not take into account the fact that Earth is a sphere. The relationship Al-Battānī used was fairly precise when a person is in Mecca, or close to Mecca, but resulted in more and more inaccurate results as one gets more distant from Mecca. However, it was still a widely used method at the time. The equation is as follows:
Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) used experimentation to obtain the results in his ''Book of Optics'' (1021), an important development in the history of scientific method, history of the scientific method. He combined observations, experiments and Rationality, rational arguments to support his intromission theory of visual perception, vision, in which Ray (optics), rays of light are emitted from objects rather than from the eyes. He used similar arguments to show that the ancient Emission theory (vision), emission theory of vision supported by Ptolemy and Euclid (in which the eyes emit the rays of light used for seeing), and the ancient intromission theory supported by Aristotle (where objects emit physical particles to the eyes), were both wrong.
Al-Zahrawi, regarded by many as the greatest surgeon of the middle ages. His surgical treatise "Al-Tasrif, De chirurgia" is the first illustrated surgical guide ever written. It remained the primary source for surgical procedures and instruments in Europe for the next 500 years. The book helped lay the foundation to establish surgery as a scientific discipline independent from medicine, earning al-Zahrawi his name as one of the founders of this field.
Other notable Arabic contributions include among other things: the pioneering of organic chemistry by Jābir ibn Hayyān, establishing the science of cryptology and cryptanalysis by al-Kindi, the development of analytic geometry by Ibn al-Haytham, the discovery of the pulmonary circulation by Ibn al-Nafis, the discovery of the itch mite parasite by Ibn Zuhr, the first use of irrational numbers as an algebraic objects by Abū Kāmil, the first use of the positional decimal fractions by Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi, al-Uqlidisi, the development of the Arabic numerals and an early History of mathematical notation, algebraic symbolism in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, the Thabit number and amicable numbers#Thābit ibn Qurra theorem, Thābit theorem by Thābit ibn Qurra, the discovery of several new List of trigonometric identities, trigonometric identities by Ibn Yunus and al-Battani, the mathematical proof for Ceva's theorem by Yusuf al-Mu'taman ibn Hud, Ibn Hűd, the first accurate Lunar theory, lunar model by Ibn al-Shatir, the invention of the torquetum by Jabir ibn Aflah, the invention of the universal astrolabe and the equatorium by al-Zarqali, the first description of the crankshaft by al-Jazari, the anticipation of the inertia concept by Averroes, the discovery of the Reaction (physics), physical reaction by Avempace, the identification of more than 200 new plants by Ibn al-Baitar the Arab Agricultural Revolution, and the Tabula Rogeriana, which was the most accurate world map in pre-modern times by al-Idrisi.Bacharach, 2006, p. 140.
The birth of the University institution can be traced to this development, as several universities and educational institutions of the Arab world such as the University of Al Quaraouiyine, Al Azhar University, and University of Ez-Zitouna, Al Zaytuna University are considered to be the oldest in the world. Founded by Fatima al-Fihri, Fatima al Fihri in 859 as a mosque, the University of Al Quaraouiyine in Fez, Morocco, Fez is the oldest existing, continually operating and the first Academic degree, degree awarding educational institution in the world according to UNESCO and Guinness World Records and is sometimes referred to as the oldest university.
There are many scientific Influence of Arabic on other languages, Arabic loanwords in Western European languages, including :wikt:English terms derived from Arabic, English, mostly via Old French. This includes List of Arabic star names, traditional star names such as Aldebaran, scientific terms like '':wikt:alchemy, alchemy'' (whence also '':wikt:chemistry, chemistry''), '':wikt:algebra, algebra'', '':wikt:algorithm, algorithm'', '':wikt:alcohol, alcohol'', '':wikt:alkali, alkali'', '':wikt:cipher, cipher'', '':wikt:zenith, zenith'', etc.
Under Ottoman rule, cultural life and science in the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
declined. In the 20th and 21st centuries, Arabs who have won important science prizes include Ahmed Zewail and Elias Corey (Nobel Prize), Michael DeBakey and Alim Louis Benabid, Alim Benabid (Lasker Award), Omar M. Yaghi (Wolf Prize), Huda Zoghbi (Shaw Prize), Zaha Hadid (Pritzker Prize), and Michael Atiyah (both Fields Medal and Abel Prize). Rachid Yazami was one of the co-inventors of the lithium-ion battery, and Tony Fadell was important in the development of the iPod and the iPhone.
Wedding and marriage
 Arabic weddings have changed greatly in the past 100 years. Original traditional Arabic weddings are supposed to be very similar to modern-day Bedouin weddings and rural weddings, and they are in some cases unique from one region to another, even within the same Arab world, country. The practice of Marriage, marrying of relatives is a common feature of Arab culture.
In the
Arabic weddings have changed greatly in the past 100 years. Original traditional Arabic weddings are supposed to be very similar to modern-day Bedouin weddings and rural weddings, and they are in some cases unique from one region to another, even within the same Arab world, country. The practice of Marriage, marrying of relatives is a common feature of Arab culture.
In the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
today between 40% and 50% of all marriages are consanguineous or between close family members, though these figures may vary among Arab nations. In Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, around 40% of the population Cousin marriage, marry a cousin. A 1992 survey in Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
found that 32% were married to a first cousin; a further 17.3% were married to more distant relatives. 67% of marriages in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
are between close relatives as are 54% of all marriages in Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
, whereas 18% of all Lebanon, Lebanese were between blood relatives. Due to the actions of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
and the Rightly Guided Caliphs, marriage between cousins is explicitly allowed in Islam and the Quran, Qur'an itself does not discourage or forbid the practice.Surah, Surah chapter 4, verse 23 Nevertheless, opinions vary on whether the phenomenon should be seen as exclusively based on Islamic practices as a 1992 study among Arabs in Jordan did not show significant differences between Arab Christians, Christian Arabs or Arab Muslims, Muslim Arabs when comparing the occurrence of consanguinity.
Genetics
See also
* Arab Union *Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
* List of Arabs
* List of Arab companies, Lists of Arab companies
* North African Arabs
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Touma, Habib Hassan. ''The Music of the Arabs''. Portland, Oregon: Amadeus P, 1996. . * Lipinski, Edward. ''Semitic Languages: Outlines of a Comparative Grammar'', 2nd ed., Orientalia Lovanensia Analecta: Leuven 2001 * Kees Versteegh, ''The Arabic Language'', Edinburgh University Press (1997)The Catholic Encyclopedia, Robert Appleton Company, 1907, Online Edition, K. Night 2003: article Arabia
1894), Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd. * The Arabic language, National Institute for Technology and Liberal Education web page (2006) * * Hooker, Richard. "Pre-Islamic Arabic Culture." WSU Web Site. 6 June 1999. Washington State University. * Owen, Roger. "State Power and Politics in the Making of the Modern Middle East 3rd Ed" Page 57 *
Further reading
* Price-Jones, David. ''The Closed Circle: an Interpretation of the Arabs''. Pbk. ed., with a new preface by the author. Chicago: I. R. Dee, 2002. xiv, 464 p. * Ankerl, Guy. ''Coexisting Contemporary Civilizations: Arabo-Muslim, Bharati, Chinese, and Western.'' INU PRESS, Geneva, 2000. . *External links
www.LasPortal.org
ArabCultureFund AFAC
{{Authority control Arabs, Tribes of Arabia, Afroasiatic peoples Ancient peoples of the Near East Arab Ethnic groups in Africa Ethnic groups in North Africa Ethnic groups in the Arab world Ethnic groups in the Middle East Muslim communities in Africa Muslim communities in Asia