|
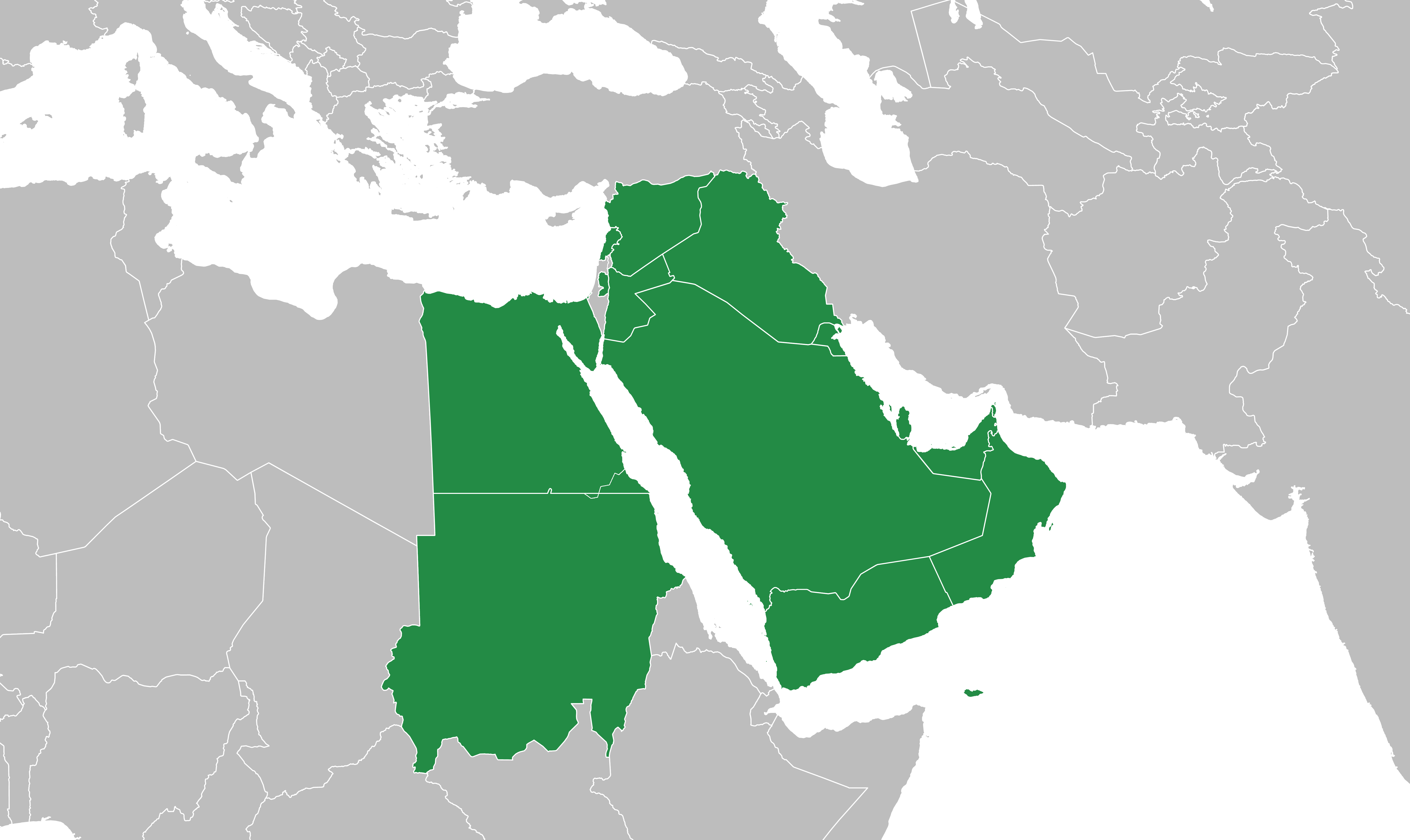
Mashreq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to ''Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part (Cyrenaica) being linked more to Egypt and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashreq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to ''Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part (Cyrenaica) being linked more to Egypt and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab World
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western Asia and Northern Africa, that linguistically or culturally share an Arab identity. A majority of people in these countries are either ethnically Arab or are Arabized, speaking the Arabic language, which is used as the '' lingua franca'' throughout the Arab world. The Arab world is at its minimum defined as the 18 states where Arabic is natively spoken. At its maximum it consists of the 22 members of the Arab League, an international organization, which on top of the 18 states also includes the Comoros, Djibouti, Somalia and the partially recognized state of Palestine. The region stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Indian Ocean in the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union For The Mediterranean
The Union for the Mediterranean (UfM; french: Union pour la Méditerranée, ar, الإتحاد من أجل المتوسط ''Al-Ittiḥād min ajl al-Mutawasseṭ'') is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 16 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Spain. The Union has the aim of promoting stability and integration throughout the Mediterranean region. It is a forum for discussing regional strategic issues, based on the principles of shared ownership, shared decision-making and shared responsibility between the two shores of the Mediterranean. Its main goal is to increase both north–south and South-South inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Arab Economic Unity
The Council of Arab Economic Unity (CAEU) (Arabic: ) was founded by Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Libya, Mauritania, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Tunisia, Syria, United Arab Emirates and Yemen on May 30, 1964, following an agreement in 1957 by the Economic Council of the Arab League. Objectives According to The Economic Unity Agreement approved on June 3, 1957, the Council of Arab Economic Unity desires to "Organize and consolidate economic relations among the States of the Arab League on bases that are consistent with the natural and historical links among them; and to provide the best conditions for flourishing their economies, developing their resources and ensuring the prosperity of their countries." The bases of economic relations between states in the Council of Arab Economic Unity are outlined in Chapter 1, Articles 1 and 2 of The Economic Unity Agreement: Article 1 Article 1 delineates each member state's rights to: # Personal and capital mobility # Free exchange of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi Language
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India. Hindi is the '' lingua franca'' of the Hindi Belt. It is also spoken, to a lesser extent, in other parts of India (usually in a simplified or pidginised variety such as Bazaar Hindustani or Haflong Hindi). Outside India, several ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu Language
Urdu (;"Urdu" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ur, , link=no, ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan, where it is also an official language alongside English language, English. In India, Urdu is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language whose status and cultural heritage is recognized by the Constitution of India; Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian ( classical: , reformed: , , ) is an Indo-European language and an independent branch of that family of languages. It is the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian Highlands, today Armenian is widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by the priest Mesrop Mashtots. The total number of Armenian speakers worldwide is estimated between 5 and 7 million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek (and Phrygian) and Indo-Iranian were dialectally close to each other;''Handbook of Formal Languages'' (1997p. 6 wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French ( Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the ''Organisation internationale de la Francophonie'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Language
Kurdish (, ) is a language or a group of languages spoken by Kurds in the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan and the Kurdish diaspora. Kurdish constitutes a dialect continuum, belonging to Western Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. The main three dialects or languages of Kurdish are Northern Kurdish (), Central Kurdish (), and Southern Kurdish (). A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the Zaza–Gorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds.Kaya, Mehmet. The Zaza Kurds of Turkey: A Middle Eastern Minority in a Globalised Society. The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of Arabic script. The classification of Laki as a dialect of Southern Kurdish or as a fourth language under Kurdish is a matter of debate, but the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubian Languages
The Nubian languages ( ar, لُغَات نُوبِيّة, lughāt nūbiyyah) are a group of related languages spoken by the Nubians. They form a branch of the Eastern Sudanic languages, which is part of the wider Nilo-Saharan phylum. Initially, Nubian languages were spoken throughout much of Sudan, but as a result of Arabization they are today mostly limited to the Nile Valley between Aswan (southern Egypt) and Al Dabbah. Nubian is not to be confused with the various Nuba languages spoken in villages in the Nuba mountains and Darfur. History In the October War, Egypt employed Nubian-speaking Nubian people as code talkers. Languages Rilly (2010) distinguishes the following Nubian languages, spoken by in total about 900,000 speakers: # Nobiin, the largest Nubian language with 545,000 speakers in Egypt, Sudan, and the Nubian diaspora. Previously known by the geographic terms Mahas and Fadicca/Fiadicca. As late as 1863 this language, or a closely related dialect, was known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |