|
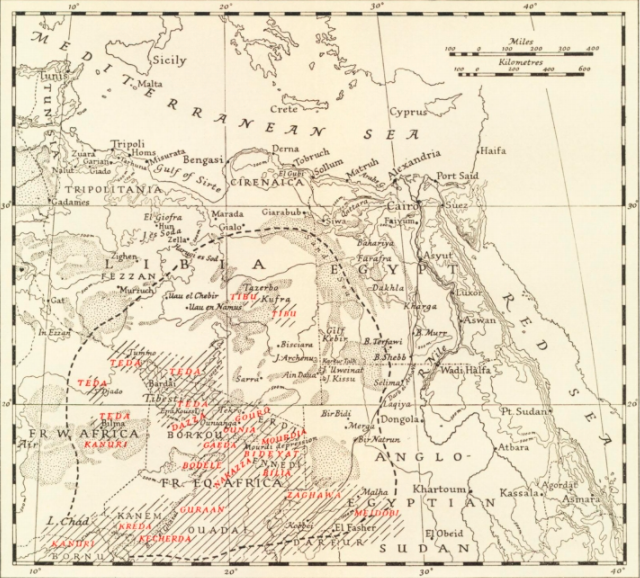
Toubou People
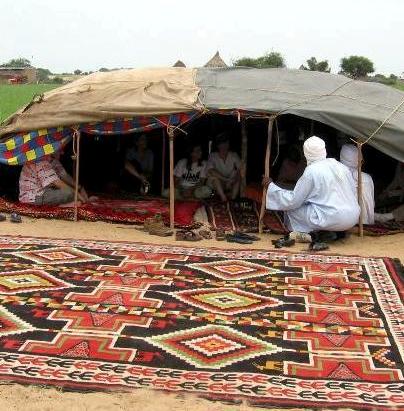
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells. The Toubou are generally divided into two closely related groups: the Teda (or Téda, Toda) and the Dazagara (or Dazzaga, Dazagada, Daza). They are believed to share a common origin and speak the Tebu languages, which are from the Saharan branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Tebu is divided further into two closely related languages, called ''Tedaga'' (Téda Toubou) and ''Dazaga'' (Dazaga Gouran). Of the two groups, the Daza, found to the south of the Teda, are more numerous. The Toubou people are also referred to as the Tabu, Tebu, Tebou, Tibu, Tibbu, Toda, Todga, Todaga, Tubu, Tuda, Tudaga, or Gorane people. The Dazaga are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic Pastoralism
Nomadic pastoralism is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to graze. True nomads follow an irregular pattern of movement, in contrast with transhumance, where seasonal pastures are fixed. However, this distinction is often not observed and the term 'nomad' used for both—and in historical cases the regularity of movements is often unknown in any case. The herded livestock include cattle, water buffalo, yaks, llamas, sheep, goats, reindeer, horses, donkeys or camels, or mixtures of species. Nomadic pastoralism is commonly practised in regions with little arable land, typically in the developing world, especially in the steppe lands north of the agricultural zone of Eurasia. Of the estimated 30–40 million nomadic pastoralists worldwide, most are found in central Asia and the Sahel region of North and West Africa, such as Fulani, Tuaregs, and Toubou, with some also in the Middle East, such as traditionally Bedouins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahr El Gazel (region Of Chad)
Barh El Gazel ( ar, منطقة بحر الغزال, french: Région du Barh El Gazel) is one of the 23 regions of Chad. The region's name may also be written as Barh El Gazal or Bahr el Gazel. Its capital is the town of Moussoro. The region was created in 2008 from the former Barh El Gazel Department of the Kanem Region. Geography The region borders Borkou Region to the north, Batha Region to the east, Hadjer-Lamis Region to the south, and Kanem Region to the west. The region is predominantly grassland, merging into the Sahara Desert in the north. Settlements Moussoro is the regional capital; other major settlements include Chadra, Dourgoulanga, Michemiré and Salal. Demographics As per the census of 2009, the population of the region was 260,865, 46.3% female. The average size of household as of 2009 is 5.90: 5.90 in rural households and 5.80 in urban areas. The total number of households was 43,478: 38,160 in rural areas and 5,318 in urban areas. The number of nomads in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennedi
The Ennedi Plateau is located in the northeast of Chad, in the regions of Ennedi-Ouest and Ennedi-Est. It is considered a part of the group of mountains known as the Ennedi Massif found in Chad, which is one of the nine countries that make up the Sahelian belt that spans the Atlantic Ocean to Sudan. The Ennedi is a sandstone bulwark in the middle of the Sahara, which was formed by erosion from wind and temperature. Many people occupied this area, such as hunters and gatherers (5,000-4,000 cal BC) and pastoralists (beginning 4,000 cal BC). The Ennedi area is also known for its large collection of rock art depicting mainly cattle, as these animals were the main source of financial, environmental, and cultural impact. This art dates back nearly 7,000 years ago. Today, two semi-nomadic groups, mainly of the Muslim religion, have permanent villages in the Ennedi during the rainy months and pass through the area during the dry season. They rely on their herds of camels, donkeys, sheep, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourkou
Borku (french: Borkou) or Borgu (') is a region of Central Africa, mostly in Northern Chad, forming part of the transitional zone between the arid wastes of the Sahara and the fertile lands of the central Sudan. It is bounded N. by the Tibesti Mountains, and is in great measure occupied by lesser elevations belonging to the same system. These hills to the south and east merge into the plains of Ouaddaï and Darfur. South-west, in the direction of Lake Chad, is the Bodele basin. The drainage of the country is to the lake, but the numerous khors with which its surface is scored are mostly dry or contain water for brief periods only. A considerable part of the soil is light sand drifted about by the wind. The irrigated and fertile portions consist mainly of a number of valleys separated from each other by low and irregular limestone rocks. They furnish excellent dates. Barley is also cultivated. The northern valleys are inhabited by a settled population of Gouran stock, known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anakaza Tribe
The Anakaza are name clan of Toubou people branch Daza . Olson, James Stuart (1996); "Anakaza"; ''The Peoples of Africa: An Ethnohistorical Dictionary'', Greenwood Press, pp. 28-29. . One of the largest of Daza subgroups, they are a nomadic people traditionally employed in camel-herding. They are mostly located in the Saharan region of Borkou in northern Chad, they can be found in a vast area from Faya-Largeau to Kirdimi and nomadizing an area which goes from Oum Chalouba to the Djourab and Mortcha.Decalo, Samuel (1987); "Anakaza"; ''Historical Dictionary of Chad'', Scarecrow Press, p. 41. . In modern times out of its ranks was born Hissène Habré, president of Chad between 1982 and 1990, who during his tenure in office gave the key positions to his fellow Daza, favouring among the latters his subgroup. The Anakaza also formed the bulk of his élite unit, the Presidential Guard. Another prominent Anakaza is the current rebel leader Mahamat Nouri. Due to his rebellion in 2006 ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibesti Mountains
The Tibesti Mountains are a mountain range in the central Sahara, primarily located in the extreme north of Chad, with a small portion located in southern Libya. The highest peak in the range, Emi Koussi, lies to the south at a height of and is the highest point in both Chad and the Sahara. Bikku Bitti, the highest peak in Libya, is located in the north of the range. The central third of the Tibesti is of volcanic origin and consists of five volcanoes topped by large depressions: Emi Koussi, Tarso Toon, Tarso Voon, Tarso Yega and Toussidé. Major lava flows have formed vast plateaus that overlie Paleozoic sandstone. The volcanic activity was the result of a continental hotspot that arose during the Oligocene and continued in some places until the Holocene, creating fumaroles, hot springs, mud pools and deposits of natron and sulfur. Erosion has shaped volcanic spires and carved an extensive network of canyons through which run rivers subject to highly irregular flows that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. The Sahel part of Africa includes – from west to east – parts of northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, the extreme south of Algeria, Niger, the extreme north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia. Historically, the western part of the Sahel was sometimes known as the Sudan region (''bilād as-sūdān'' "lands of the Sudan"). This belt was located between the Sahara and the coastal areas of West Africa. There are frequent shortages of food and water due to the dry h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hissène Habré
Hissène Habré (Arabic: ''Ḥusaīn Ḥabrī'', Chadian Arabic: ; ; 13 August 1942 – 24 August 2021), also spelled Hissen Habré, was a Chadian politician and convicted war criminal who served as the 5th president of Chad from 1982 until he was deposed in 1990. A member of Chad's northern population, Habré joined FROLINAT rebels in the first Chadian Civil War against the southern-dominated Chadian government. Due to a rift with fellow rebel commander Goukouni Oueddei, Habré and his Armed Forces of the North rebel army briefly defected to Felix Malloum's government against Oueddei before turning against Malloum, who resigned in 1979. Habré was then given the position of Minister of Defense under Chad's new transitional coalition government, with Oueddei as President. Their alliance quickly collapsed, and Habré's forces overthrew Oueddei in 1982. Having become the country's new president, Habré created a one-party dictatorship ruled by his National Union for Inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goukouni Oueddei
Goukouni Oueddei ( ar, كوكوني عويدي '; born 1944 in Zouar) is a Chadian politician who served as President of Chad from 1979 to 1982. A northerner, Goukouni commanded FROLINAT rebels with Libyan support during the first Chadian Civil War against Chad's southern-dominated government. Upon the rebel victory and the resignation of President Felix Malloum in 1979, he became the new president of Chad's new transitional coalition government by the terms of the Lagos Accord, with rival fellow rebel commander Hissène Habré as defense minister. Goukouni pursued a pro-Libya policy; continued differences with Habré, who opposed Libya, led to him being overthrown by Habré's forces in 1982. He then became the foremost opponent to Habré's new government, and fought against him during the Libyan-Chadian conflict as a Libyan-backed rebel leader. In 1985, due to a supposed rift with his Libyan allies, he went into exile. Biography Goukouni is from the northern half of the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dazaga Language
Daza (also known as Dazaga) is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken by the Daza people inhabiting northern Chad. The Daza are also known as the Gouran (Gorane) in Chad. Dazaga is spoken by around 380,000 people, primarily in the Djurab Desert region and the Borkou region, locally called Haya or Faya-Largeau northern-central Chad, the capital of the Dazaga people. Dazaga is spoken in the Tibesti Mountains of Chad (330,000 speakers), in eastern Niger near N'guigmi and to the north (50,000 speakers). It is also spoken to a smaller extent in Libya and in Sudan, where there is a community of 3,000 speakers in the city of Omdurman. There's also a small diaspora community working in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The two primary dialects of the Dazaga language are Daza and Kara, but there are several other mutually intelligible dialects, including Kaga, Kanobo, Taruge and Azza. It is closely related to the Tedaga language, spoken by the Teda, the other out of the two Toubou people groups, who resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |