|
Guanghui Bridge
The Guanghui Bridge () is a historic stone arch bridge over the Nanshi River in Nanxun, Huzhou, Zhejiang, China. In is backed by the Taoist temple Guanghui Palace. History The current bridge was rebuilt in 1800, in the 5th year of Jiaqing period of the Qing dynasty (1644–1911). It was renovated in 1866, in the reign of Tongzhi Emperor The Tongzhi Emperor (27 April 1856 – 12 January 1875), born Zaichun of the Aisin Gioro clan, was the ninth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the eighth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign, from 1861 to 1875, which effectively laste .... In March 1989, it was inscribed as a municipal cultural preservation unit by the Huzhou Municipal Government. Architecture The bridge measures long, wide, and approximately high. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanghui Bridge Bridges in Zhejiang Arch bridges in China Bridges completed in 1800 Qing dynasty architecture Buildings and structures completed in 1800 1800 in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanxun
Nanxun () is a historic town in Nanxun District of Huzhou, Zhejiang, China. As of the 2007 census it had a population of 119,300 and an area of . Name The name of Nanxun was coined by a combination of the initial Chinese characters of two place' names in the region: "Nanlin" () and "Xunxi" (). History Established in 1252 in the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), Nanxun is located in the northeast of Huzhou city. It was one of the richest towns in Jiangnan from mid-Ming down to mid-Qing dynasties. During this period, with the development of silk industry and rise of commodity economy, it experienced unprecedented prosperity, and developed into the center of China's silk trade at the beginning of 20th century. It became the most prosperous town in Jiangnan region, producing hundreds of magnates. As a popular saying went, "What counts as a city in Huzhou is barely half the size of Nanxun." () Religion The introduction of Christianity into the Nanxun area began in 1860, belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
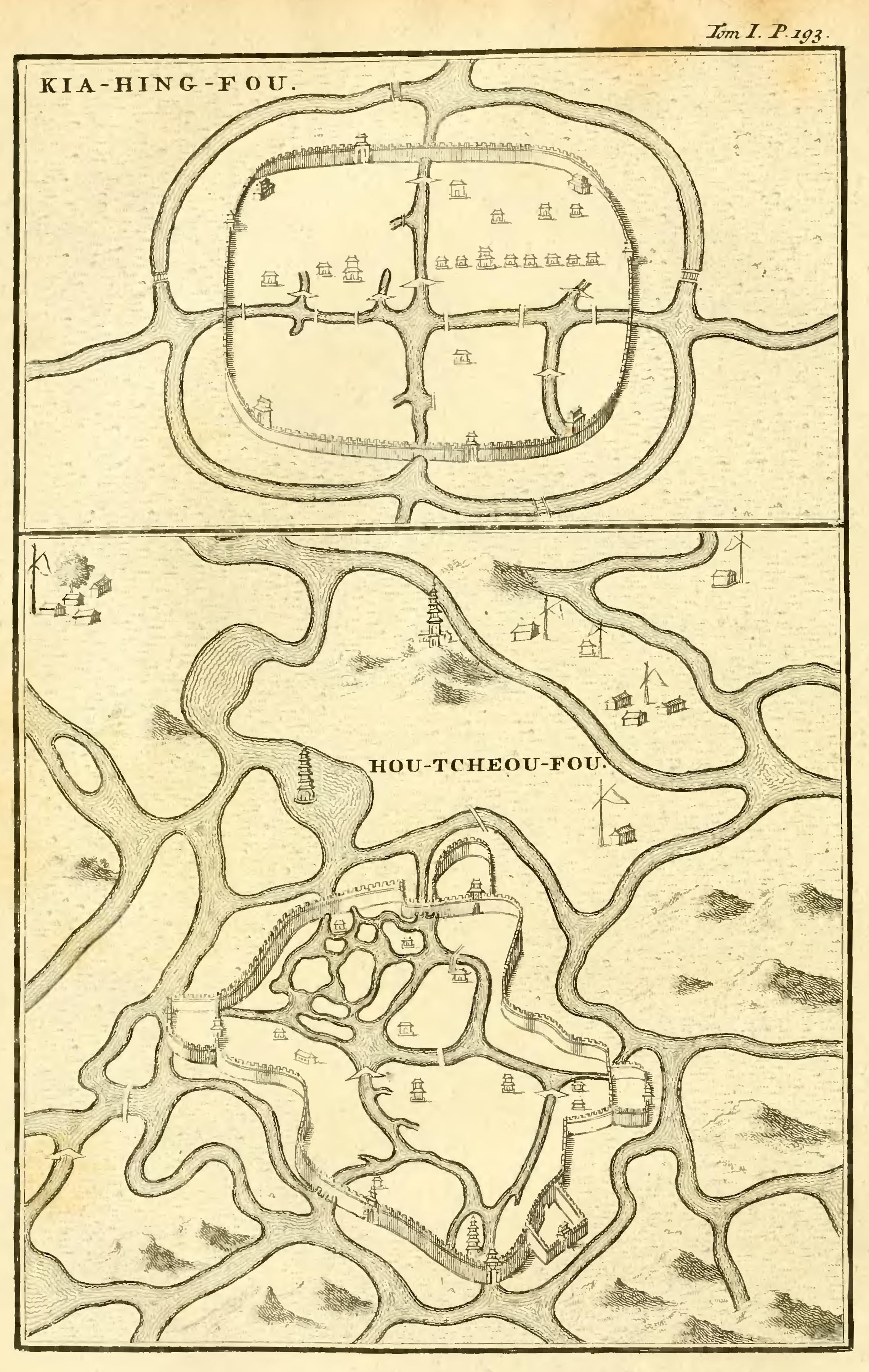
Huzhou
Huzhou (, ; Huzhounese: ''ghou² cieu¹'') is a prefecture-level city in northern Zhejiang province (Hangzhou–Jiaxing–Huzhou Plain, China). Lying south of the Lake Tai, it borders Jiaxing to the east, Hangzhou to the south, and the provinces of Anhui and Jiangsu to the west and north respectively. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,367,579 inhabitants, of whom 1,015,937 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of Wuxing District as Nanxun District is not being conurbated yet. Location Huzhou, in its general aspect, is in the center of the Yangtze River Delta Economic Area, with the city center south of the Chinese third largest freshwater lake Lake Tai. There are transportation links to the provincial capital of Hangzhou away in the south, Jiangsu and Anhui province in the west, and the metropolitan municipality of Shanghai to the northeast. Flowing quietly through the city is the Changxing-Huzhou-Shanghai Channel, it is also referred to as the "Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Jiangsu and Shanghai to the north, Anhui to the northwest, Jiangxi to the west and Fujian to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands. The population of Zhejiang stands at 64.6 million, the 8th highest among China. It has been called 'the backbone of China' due to being a major driving force in the Chinese economy and being the birthplace of several notable persons, including the Chinese Nationalist leader Chiang Kai-shek and entrepreneur Jack Ma. Zhejiang consists of 90 counties (incl. county-level cities and districts). The area of Zhejiang was controlled by the Kingdom of Yue during the Spring and Autumn period. The Qin Empire later annexed it in 222 BC. Under the late Ming dynasty and the Qing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct (a long bridge) may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today. History Possibly the oldest existing arch bridge is the Mycenaean Arkadiko Bridge in Greece from about 1300 BC. The stone corbel arch bridge is still used by the local populace. The well-preserved Hellenistic Eleutherna Bridge has a triangular corbel arch. The 4th century BC Rhodes Footbridge rests on an early voussoir arch. Although true arches were already known by the Etruscans and ancient Greeks, the Romans were – as with the vault and the dome – the first to fully realize the potential of arches for bridge construction. A list of Roman bridges compiled by the engineer Colin O'Connor featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct (a long bridge) may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today. History Possibly the oldest existing arch bridge is the Mycenaean Arkadiko Bridge in Greece from about 1300 BC. The stone corbel arch bridge is still used by the local populace. The well-preserved Hellenistic Eleutherna Bridge has a triangular corbel arch. The 4th century BC Rhodes Footbridge rests on an early voussoir arch. Although true arches were already known by the Etruscans and ancient Greeks, the Romans were – as with the vault and the dome – the first to fully realize the potential of arches for bridge construction. A list of Roman bridges compiled by the engineer Colin O'Connor featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanghui Palace
Guanghui Palace (), commonly known as Zhang–Wang Temple (), is a Taoist temple located in Nanxun of Huzhou, Zhejiang, China. History The temple was first established in the reign of Yingzong of the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127). In late Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), Zhang Shicheng used the temple as his ''Xinggong'' (). It has been burned down and rebuilt several times, due wars and natural disasters. The current temple was rebuilt in 2003. Architecture The statues of Three Pure Ones The Three Pure Ones (), also translated as the Three Pure Pellucid Ones, the Three Pristine Ones, the Three Divine Teachers, the Three Clarities, or the Three Purities, are the three highest gods in the Taoist pantheon. They are regarded as pure ... are enshrined in the main hall of the temple. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanghui Palace Taoist temples in Zhejiang Buildings and structures in Huzhou Tourist attractions in Huzhou 2003 establishments in China Religious building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiaqing Emperor
The Jiaqing Emperor (13 November 1760 – 2 September 1820), also known by his temple name Emperor Renzong of Qing, born Yongyan, was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and the fifth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, from 1796 to 1820. He was the 15th son of the Qianlong Emperor. During his reign, he prosecuted Heshen, the corrupt Manchu favorite of his father, and attempted to restore order within the Qing Empire while curbing the smuggling of opium into China. Early years Yongyan was born in the Old Summer Palace, 8 km (5 mi) northwest of the walls of Beijing. His personal name, "Yongyan" (永琰), was later changed to "Yongyan" (顒琰) when he became the emperor. The Chinese character for ''yong'' in his name was changed from the more common 永 to the less common 顒. This novelty was introduced by the Qianlong Emperor, who believed that it was not proper to have a commonly used Chinese character in an emperor's personal name due to the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongzhi Emperor
The Tongzhi Emperor (27 April 1856 – 12 January 1875), born Zaichun of the Aisin Gioro clan, was the ninth List of emperors of the Qing dynasty, Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the eighth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign, from 1861 to 1875, which effectively lasted through his adolescence, was largely overshadowed by the rule of his mother, Empress Dowager Cixi. Although he had little influence over state affairs, the events of his reign gave rise to what historians call the "Tongzhi Restoration", an unsuccessful modernization program. Life The only surviving son of the Xianfeng Emperor and Empress Dowager Cixi, the Tongzhi Emperor was namesake to the attempted political reform initiated by his mother, called the Tongzhi Restoration. His first regnal name was Qixiang (祺祥; Manchu: ''Fengšengge sabingga''), but this name was later changed, as per tradition upon his succession, to "Tongzhi". The regnal name means 'order and prosperity' coming from the Confucian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges In Zhejiang
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Bridges In China
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent collapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_King_of_Wuyue.jpg)
_Bridge_2011.jpg)
