|
Guanghui Palace
Guanghui Palace (), commonly known as Zhang–Wang Temple (), is a Taoist temple located in Nanxun of Huzhou, Zhejiang, China. History The temple was first established in the reign of Yingzong of the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127). In late Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), Zhang Shicheng used the temple as his ''Xinggong'' (). It has been burned down and rebuilt several times, due wars and natural disasters. The current temple was rebuilt in 2003. Architecture The statues of Three Pure Ones The Three Pure Ones (), also translated as the Three Pure Pellucid Ones, the Three Pristine Ones, the Three Divine Teachers, the Three Clarities, or the Three Purities, are the three highest gods in the Taoist pantheon. They are regarded as pure ... are enshrined in the main hall of the temple. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanghui Palace Taoist temples in Zhejiang Buildings and structures in Huzhou Tourist attractions in Huzhou 2003 establishments in China Religious building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of Philosophy, philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of China, Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the ''Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later Zhuangzi (book), writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanxun
Nanxun () is a historic town in Nanxun District of Huzhou, Zhejiang, China. As of the 2007 census it had a population of 119,300 and an area of . Name The name of Nanxun was coined by a combination of the initial Chinese characters of two place' names in the region: "Nanlin" () and "Xunxi" (). History Established in 1252 in the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279), Nanxun is located in the northeast of Huzhou city. It was one of the richest towns in Jiangnan from mid-Ming down to mid-Qing dynasties. During this period, with the development of silk industry and rise of commodity economy, it experienced unprecedented prosperity, and developed into the center of China's silk trade at the beginning of 20th century. It became the most prosperous town in Jiangnan region, producing hundreds of magnates. As a popular saying went, "What counts as a city in Huzhou is barely half the size of Nanxun." () Religion The introduction of Christianity into the Nanxun area began in 1860, belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
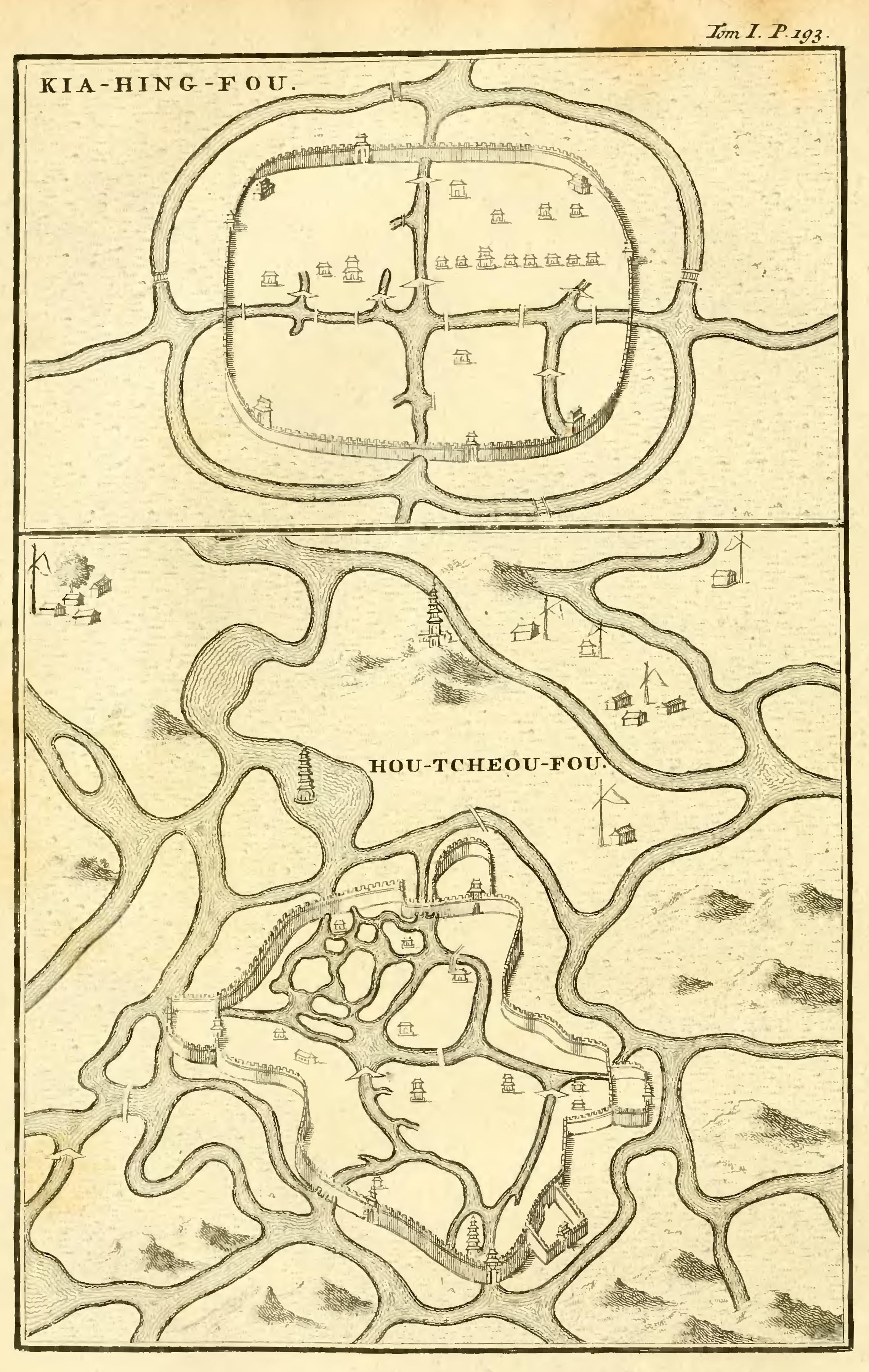
Huzhou
Huzhou (, ; Huzhounese: ''ghou² cieu¹'') is a prefecture-level city in northern Zhejiang province (Hangzhou–Jiaxing–Huzhou Plain, China). Lying south of the Lake Tai, it borders Jiaxing to the east, Hangzhou to the south, and the provinces of Anhui and Jiangsu to the west and north respectively. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,367,579 inhabitants, of whom 1,015,937 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of Wuxing District as Nanxun District is not being conurbated yet. Location Huzhou, in its general aspect, is in the center of the Yangtze River Delta Economic Area, with the city center south of the Chinese third largest freshwater lake Lake Tai. There are transportation links to the provincial capital of Hangzhou away in the south, Jiangsu and Anhui province in the west, and the metropolitan municipality of Shanghai to the northeast. Flowing quietly through the city is the Changxing-Huzhou-Shanghai Channel, it is also referred to as the "Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Jiangsu and Shanghai to the north, Anhui to the northwest, Jiangxi to the west and Fujian to the south. To the east is the East China Sea, beyond which lies the Ryukyu Islands. The population of Zhejiang stands at 64.6 million, the 8th highest among China. It has been called 'the backbone of China' due to being a major driving force in the Chinese economy and being the birthplace of several notable persons, including the Chinese Nationalist leader Chiang Kai-shek and entrepreneur Jack Ma. Zhejiang consists of 90 counties (incl. county-level cities and districts). The area of Zhejiang was controlled by the Kingdom of Yue during the Spring and Autumn period. The Qin Empire later annexed it in 222 BC. Under the late Ming dynasty and the Qing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Architecture
Chinese architecture (Chinese:中國建築) is the embodiment of an architectural style that has developed over millennia in China and it has influenced architecture throughout Eastern Asia. Since its emergence during the early ancient era, the structural principles of its architecture have remained largely unchanged. The main changes involved diverse decorative details. Starting with the Tang dynasty, Chinese architecture has had a major influence on the architectural styles of Japan, Korea, Mongolia, and Vietnam, and minor influences on the architecture of Southeast and South Asia including the countries of Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and the Philippines. Chinese architecture is characterized by bilateral symmetry, use of enclosed open spaces, feng shui (e.g. directional hierarchies), a horizontal emphasis, and an allusion to various cosmological, mythological or in general symbolic elements. Chinese architecture traditionally classifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoist Temple
A Taoist temple (, also called ''dàoguàn'' and , is a place where the Tao is observed and cultivated it is a place of worship in Taoism. Structure and function can vary according to the Taoist school the temple belongs to. For example, ''guàn'' of the Quanzhen School are monasteries where celibate Taoist priests live. The title ''gōng'' () "palace" is often used for large temples built with imperial or governmental patronage. In front of the main gate are the holy statues of Dragon and Tiger. The Three Pure Ones are worshipped inside. Taoist temples are carved with Chinese characters like Fu (blessing), Shou (longevity), Ji (auspicious), reflecting the theme of long and fruitful life. Gallery See also * Taoism * Way of the Celestial Masters * Zhengyi Taoism * Quanzhen Taoism * Chinese ritual mastery traditions * Chinese temple * Cebu Taoist Temple Cebu Taoist Temple ( zh, s=宿雾定光宝殿, t=宿霧定光寶殿, p=Sùwù Dìngguāng Bǎodiàn, poj=Siok-bū Tēng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Yingzong Of Song
Emperor Yingzong of Song (16 February 1032 – 25 January 1067), personal name Zhao Shu, was the fifth emperor of the Song dynasty of China. His original personal name was Zhao Zongshi but it was changed to "Zhao Shu" in 1062 by imperial decree. He reigned from 1063 to his death in 1067. He was succeeded by his eldest son, Emperor Shenzong. Family Background Emperor Yingzong was the 13th son of Zhao Yunrang (趙允讓; 969–1059), who was a first cousin of Emperor Renzong and was posthumously known as "Prince Anyi of Pu" (). Emperor Yingzong's grandfather, Zhao Yuanfen (趙元份; 966–1005), was a younger brother of Emperor Renzong's father, Emperor Zhenzong, and was posthumously known as "Prince Gongjing of Shang" (). Emperor Yingzong's mother, whose maiden family name was Ren (), was the concubine of Zhao Yunrang. She held the title "''Xianjun'' of Xianyou" (). Early life In 1055, Emperor Yingzong's predecessor, Emperor Renzong, became critically ill and started to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan had been enthroned with the Han-style title of Emperor in 1206 and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol-led khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Shicheng
Zhang Shicheng (; 1321-1367), born Zhang Jiusi (), was one of the leaders of the Red Turban Rebellion in the late Yuan dynasty of China. Later, he established the ''Da Zhou'' (大周) kingdom with reigning name "Tianyou" (). Early life Zhang Shicheng was born in what is today the city of Dafeng ( 大丰), Taizhou prefecture, Jiangsu Province. He came from a family of salt shippers, and he himself started out in this trade in Northern Jiangsu, transporting both "legal" and "contraband" salt, as did his brothers Zhang Shiyi (), Zhang Shide (), and Zhang Shixin (). By his generosity he earned the respect of other salt workers who made him their leader when they rebelled against the oppressive government in 1353.Edward L. Farmer, ''Zhu Yuanzhang and Early Ming Legislation: The Reordering of Chinese Society Following the Era of Mongol Rule''. BRILL, 1995. , On Google Books P. 23. Since the 1340s, the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty began to face numerous crises. The Yellow River flooded c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Pure Ones
The Three Pure Ones (), also translated as the Three Pure Pellucid Ones, the Three Pristine Ones, the Three Divine Teachers, the Three Clarities, or the Three Purities, are the three highest gods in the Taoist pantheon. They are regarded as pure manifestation of the Tao and the origin of all sentient beings. The "Three" in Taoism From the Taoist classic ''Tao Te Ching'', it was held that "The Tao produced One; One produced Two; Two produced Three; Three produced All things." It is generally agreed by Taoist scholars that Tao produced One means Wuji produced Taiji, and One produced Two means Taiji produced Yin and Yang r Liangyi () in scholastic term However, the subject of how Two produced Three has remained a popular debate among Taoist Scholars. Most scholars believe that it refers to the Interaction between Yin and Yang, with the presence of Chi, or life force. In religious Taoism, the theory of how Tao produces One, Two, and Three is also explained. In Tao produces One—W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoist Temples In Zhejiang
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the ''Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the Three Treasures: , compassion, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_King_of_Wuyue.jpg)



_-_3_Cash_-_Scott_Semans.jpg)
