|
Chalconoids Metabolism
Chalconoids Greek language, Greek: χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper", due to its color), also known as ''chalcones'', are natural phenols related to chalcone. They form the central core for a variety of important biological compounds. They show antibacterial, antifungal drug, antifungal, antitumor and anti-inflammatory properties. Some chalconoids demonstrated the ability to block voltage-dependent potassium channels. Chalcones are also natural aromatase inhibitors. Chalcones are aromatic ketones with two phenyl rings that are also intermediates in the synthesis of many biological compounds. The closure of hydroxychalcones causes the Flavonoid biosynthesis, formation of the flavonoid structure. Flavonoids are substances in the plant secondary metabolism with an array of biological activities. Chalconoids are also intermediates in the Auwers synthesis of flavones. Chemical properties Biosynthesis and metabolism Chalcone synthase is an enzyme responsible for the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcone
Chalcone is the organic compound C6H5C(O)CH=CHC6H5. It is an α,β-unsaturated ketone. A variety of important biological compounds are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids. Chemical properties Chalcones have two absorption maxima at 280 nm and 340 nm. Synthesis Chalcone is usually prepared by an aldol condensation between benzaldehyde and acetophenone. : This reaction, which can be carried out without any solvent, is so reliable that it is used in as an example of green chemistry in undergraduate education. Biosynthesis Chalcones and chalconoids are synthesized in plants as secondary metabolites. The enzyme chalcone synthase, a type III polyketide synthase, is responsible for the biosynthesis of these compounds. The enzyme is found in all "higher" (vascular) and several "lower" ( non-vascular) plants. Potential pharmacology Chalcones and their derivatives demonstrate a wide range of biological activities including anti-inflammation. Some 2′-amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auwers Synthesis
The Auwers synthesis is a series of organic reactions forming a flavonol from a coumarone. This reaction was first reported by Karl von Auwers in 1908.K. v. Auwers, E. Auffenberg, "Über Cumaranone und Hydrindone", ''Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges.'', 52, 92-113 (1919) (). The first step in this procedure is an acid catalyzed aldol condensation between benzaldehyde and a 3-cyclooxapentanone to an o-hydroxychalcone. Bromination of the alkene group gives a dibromo-adduct which rearranges to the flavonol by reaction with potassium hydroxide. Mechanism A possible mechanism for the rearrangement step is shown below: See also * Algar–Flynn–Oyamada reaction * Allan–Robinson reaction The Allan–Robinson reaction is the chemical reaction of o-hydroxyaryl ketones with aromatic anhydrides to form flavones (or isoflavones). If aliphatic anhydrides are used, coumarins can also be formed. (See Kostanecki acylation.) : Mechanis ... References {{Organic reactions Heterocycle formi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurones
An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound which is a type of flavonoid. There are two isomers of the molecule, with (''E'')- and (''Z'')-configurations. The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2. In aurone, a chalcone-like group is closed into a 5-membered ring instead of the 6-membered ring more typical of flavonoids. Aurone derivatives Aurone forms the core for a family of derivatives which are known collectively as aurones. Aurones are plant flavonoids that provide yellow color to the flowers of some popular ornamental plants, such as snapdragon and cosmos. Aurones including 4'-chloro-2-hydroxyaurone (C15H11O3Cl) and 4'-chloroaurone (C15H9O2Cl) can also be found in the brown alga ''Spatoglossum variabile''. Most aurones are in a (''Z'')-configuration, which is the more stable configuration according to Austin Model 1 computation, but there are also some in the (''E'')-configurations such as (E)-3'-O-β-d-glucop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin Chalcone
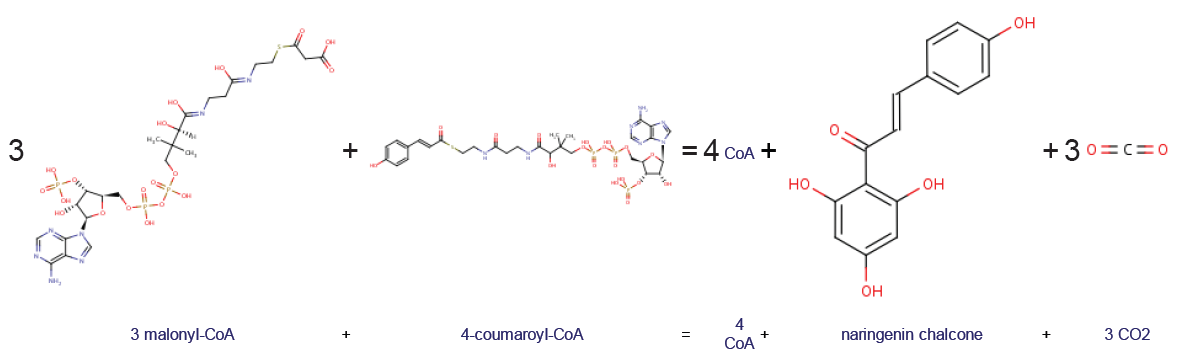
Naringenin chalcone is a common chalconoid (or chalcone, not to be confused with the compound chalcone). It is synthesized from 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA by chalcone synthase (CHS), a key enzyme in the phenylpropanoid pathway. Naringenin chalcone can spontaneously cyclize to naringenin (a flavanone). In plant cells, this process is catalyzed by chalcone isomerase In enzymology, a chalcone isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :a chalcone \rightleftharpoons a flavanone Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, a chalcone, and one product, a flavanone. This enzyme belongs to the .... References Chalconoids {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-coumaroyl-CoA
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include Monolignol, lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids. Biosynthesis and significance It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase: :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A * Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase * Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase * Chalcone synthase * 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase * 6'-Deoxychalcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid. Functions It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and commits them to fatty acid chain synthesis. Malonyl-CoA is formed by carboxylating acetyl-CoA using the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase. One molecule of acetyl-CoA joins with a molecule of bicarbonate,Nelson D, Cox M (2008) ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry''. 5th Ed: p. 806 requiring energy rendered from ATP. Malonyl-CoA is utilised in fatty acid biosynthesis by the enzyme malonyl coenzyme A:acyl carrier protein transacylase (MCAT). MCAT serves to transfer malonate from malonyl-CoA to the terminal thiol of ''holo''-acyl carrier protein (ACP). Polyketide biosynthesis MCAT is also involved in bacterial polyketide biosynthesis. The enzyme MCAT together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP), and a polyketide synthase (PKS) and chain-length f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin-chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcone Isomerase
In enzymology, a chalcone isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :a chalcone \rightleftharpoons a flavanone Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, a chalcone, and one product, a flavanone. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically the class of intramolecular lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is flavanone lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme is also called chalcone-flavanone isomerase. This enzyme participates in flavonoid biosynthesis. The ''Petunia hybrida'' (Petunia) genome contains two genes coding for very similar enzymes, ChiA and ChiB, but only the first seems to encode a functional chalcone isomerase. Structural studies As of late 2007, 7 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes , , , , , , and . Chalcone isomerase has a core 2-layer alpha/beta structure A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Secondary Metabolism
Secondary metabolism produces a large number of specialized compounds (estimated 200,000) that do not aid in the growth and development of plants but are required for the plant to survive in its environment. Secondary metabolism is connected to primary metabolism by using building blocks and biosynthetic enzymes derived from primary metabolism. Primary metabolism governs all basic physiological processes that allow a plant to grow and set seeds, by translating the genetic code into proteins, carbohydrates, and amino acids. Specialized compounds from secondary metabolism are essential for communicating with other organisms in mutualistic (e.g. attraction of beneficial organisms such as pollinators) or antagonistic interactions (e.g. deterrent against herbivores and pathogens). They further assist in coping with abiotic stress such as increased UV-radiation. The broad functional spectrum of specialized metabolism is still not fully understood. In any case, a good balance between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
