|
4-Coumaroyl-CoA
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include Monolignol, lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids. Biosynthesis and significance It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase: :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A * Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase * Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase * Chalcone synthase * 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase * 6'-Deoxychalcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naringenin-chalcone Synthase
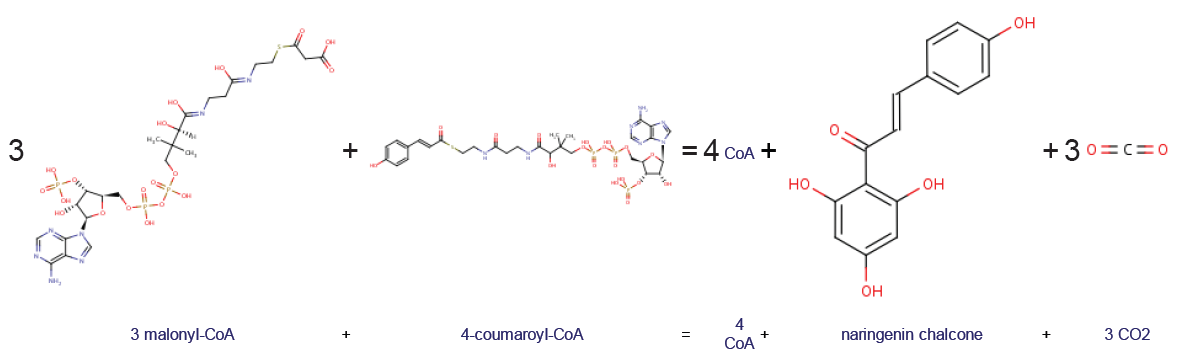
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agmatine N4-coumaroyltransferase
In enzymology, an agmatine N4-coumaroyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4-coumaroyl-CoA + agmatine \rightleftharpoons CoA + N-(4-guanidinobutyl)-4-hydroxycinnamamide Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 4-coumaroyl-CoA and agmatine, whereas its two products are CoA and N-(4-guanidinobutyl)-4-hydroxycinnamamide. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is 4-coumaroyl-CoA:agmatine N4-coumaroyltransferase. Other names in common use include p-coumaroyl-CoA-agmatine N-p-coumaroyltransferase, agmatine coumaroyltransferase, and 4-coumaroyl-CoA:agmatine 4-N-cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trihydroxystilbene Synthase
In enzymology, a trihydroxystilbene synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :3 malonyl-CoA + 4-coumaroyl-CoA \rightleftharpoons 4 CoA + 3,4',5-trihydroxy-stilbene + 4 CO2 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are malonyl-CoA and 4-coumaroyl-CoA, whereas its 3 products are CoA, 3,4',5-trihydroxy-stilbene (resveratrol), and CO2. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, To be specific those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is malonyl-CoA:4-coumaroyl-CoA malonyltransferase (cyclizing). Other names in common use include resveratrol synthase, and stilbene synthase. This enzyme participates in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Structural studies As of late 2007, two structures A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
In enzymology, a shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4-coumaroyl-CoA + shikimate \rightleftharpoons CoA + 4-coumaroylshikimate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 4-coumaroyl-CoA and shikimate, whereas its two products are CoA and 4-coumaroylshikimate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-coumaroyl-CoA:shikimate O-(hydroxycinnamoyl)transferase. This enzyme is also called shikimate hydroxycinnamoyltransferase. This enzyme participates in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes. From amino acids to cinnamates In plants, all phenylpropanoids are derived from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a. phenylalanine/t .... References * * EC 2.3.1 Enzymes of unknow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4-coumaroyl-CoA + a flavonol 3-O- 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="eta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside">eta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside\rightleftharpoons CoA + a flavonol 3-O- 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-_beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="-(4-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)- beta-D-glucoside">-(4-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)- beta-D-glucoside The 3 substrates of this enzyme are 4-coumaroyl-CoA, flavonol, and 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside">3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside, whereas its 4 products are CoA, flavonol Flavonols are a class of flavonoids that have the 3-hydroxyflavone backbone (IUPAC name : 3-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6'-Deoxychalcone Synthase
In enzymology, a 6'-deoxychalcone synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :3 malonyl-CoA + 4-coumaroyl-CoA + NADPH + H+ \rightleftharpoons 4 CoA + isoliquiritigenin + 3 CO2 + NADP+ + H2O The 4 substrates of this enzyme are malonyl-CoA, 4-coumaroyl-CoA, NADPH, and H+, whereas its 5 products are CoA, isoliquiritigenin, CO2, NADP+, and H2O. Deoxychalcone synthase catalyzed activity is involved in the biosynthesis of retrochalcone and certain phytoalexins in the cells of ''Glycyrrhiza echinata'' (Russian licorice) and other leguminous plants. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylpropanoid
The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid. Phenylpropanoids are found throughout the plant kingdom, where they serve as essential components of a number of structural polymers, provide protection from ultraviolet light, defend against herbivores and pathogens, and also mediate plant-pollinator interactions as floral pigments and scent compounds. Hydroxycinnamic acids Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamate
Cinnamic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5-CH=CH- COOH. It is a white crystalline compound that is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many organic solvents. Classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, it occurs naturally in a number of plants. It exists as both a ''cis'' and a ''trans'' isomer, although the latter is more common. Occurrence and production Biosynthesis Cinnamic acid is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of a myriad of natural products including lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. Its biosynthesis involves the action of the enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) on phenylalanine. Natural occurrence It is obtained from oil of cinnamon, or from balsams such as storax. It is also found in shea butter. Cinnamic acid has a honey-like odor; it and its more volatile ethyl ester (ethyl cinnamate) are flavor components in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioesters Of Coenzyme A
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid () and a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. Synthesis The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: :RSNa + R'COCl -> R'COSR + NaCl Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: :CH3C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |