|
Arcobadara
Arcobara (previously identified as Arcobadara (''Arkobadara'', grc, Ἀρκοβάδαρα) Cristian Găzdac, Corneliu Gaiu, Elena Marchiş: "Arcobadara (Ilişua)", Ed. Mega Publishing House, Cluj-Napoca, 2011) was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy. See also * Arcobara (castra) * Dacian davae * List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia * Dacia Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ... * Roman Dacia References Ancient * * Modern * Further reading * Dacian towns Ancient history of Transylvania {{Europe-archaeology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcobara (castra)
Arcobara (previously identified as Arcobadara Cristian Găzdac, Corneliu Gaiu, Elena Marchiş: "Arcobadara (Ilişua)", Ed. Mega Publishing House, Cluj-Napoca, 2011) was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia in the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD. It was unearthed in the village Ilişua (commune Uriu, Romania) in 1978. The fort was edified by ''Ala I Tungrorum Frontoniana''. On the site a significant number of ballista projectiles were discovered: 27 stone projectiles having diameter between 7 and 13.5 cm and weigh up to 2 kg. The artillery was used as defensive, probably located in the fort's towers. These artifacts indicates the presence of ballistarii in this fort. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition ... External linksRoman castra fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uriu
Uriu ( hu, Felőr) is a commune in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Transylvania, Romania Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S .... It is composed of four villages: Cristeștii Ciceului (''Csicsókeresztúr''), Hășmașu Ciceului (''Csicsóhagymás''), Ilișua (''Alsóilosva''), and Uriu. History Natives * Zsófia Torma References Communes in Bistrița-Năsăud County Localities in Transylvania {{BistriţaNăsăud-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
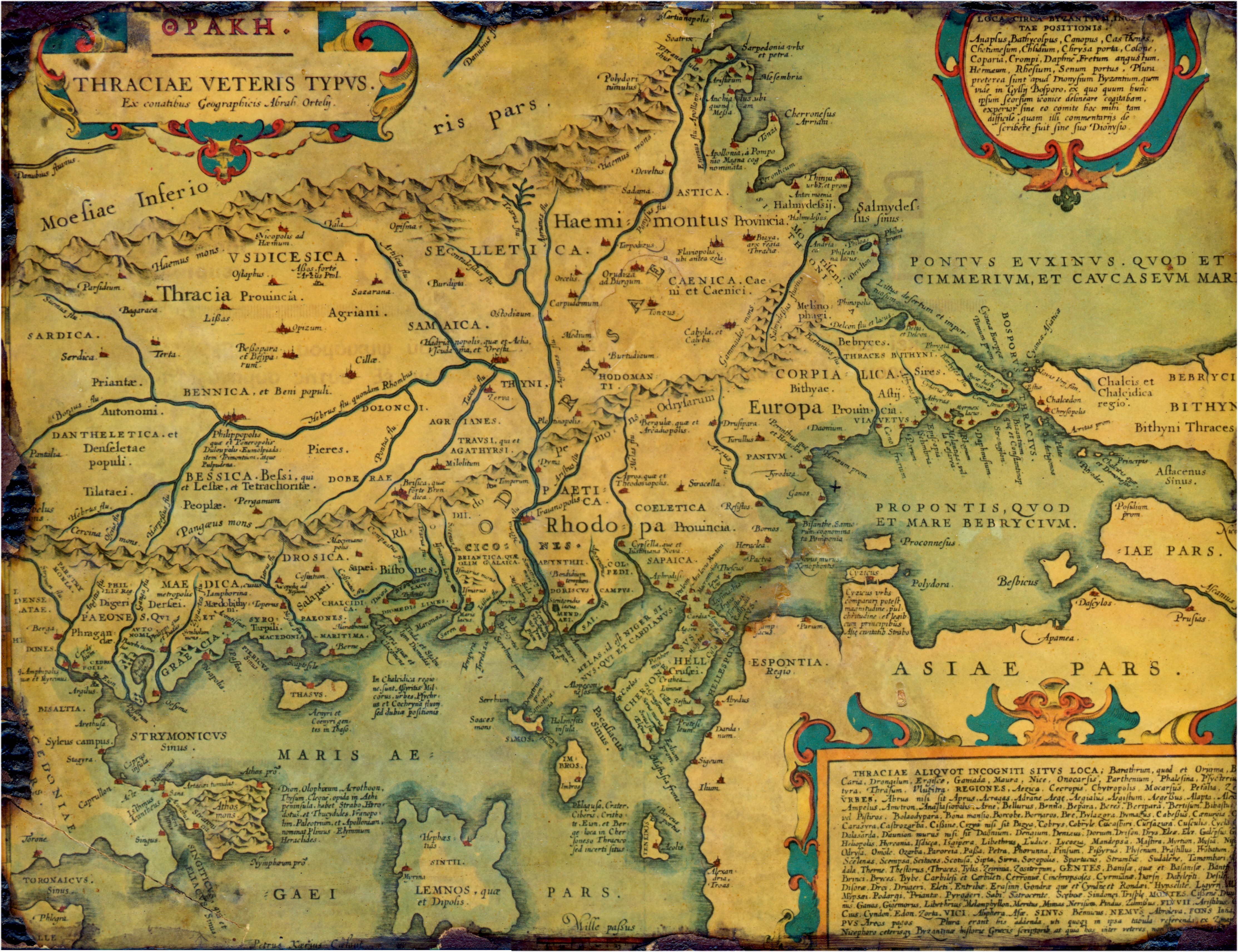
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Towns
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistrița-Năsăud County
Bistrița-Năsăud () is a county (județ) of Romania, in Transylvania, with its capital city at Bistrița. Name In Hungarian language, Hungarian, it is known as ''Beszterce-Naszód megye'', and in German language, German as ''Kreis Bistritz-Nassod''. The name is identical with the county created in 1876, Beszterce-Naszód County ( ro, Comitatul Bistriţa-Năsăud) in the Kingdom of Hungary (the county was recreated in 1940 after the Second Vienna Award, as it became part of Hungary again). Except these, as part of Romania, until 1925 the former administrative organizations were kept when a new county system was introduced. Between 1925–1940 and 1945–1950, most of its territory belonged to the Năsăud County, with smaller parts belonging to the Mureș County, Mureș, Cluj County, Cluj, and Someș County, Someș counties. Demographics On 31 October 2011, it had a population of 277,861 and the population density was . * Romanians – 89.9% * Hungarians in Romania, Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly Temperate climate, temperate-continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Moravian Banovina, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invasion of the Balkans, Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC. Name and etymology Name The Dacians were known as ''Geta'' (plural ''Getae'') in Ancient Greek writings, and as ''Dacus'' (plural ''Daci'') or ''Getae'' in Roman Empire, Roman documents, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dava (Dacian)
''Dava'' (Latinate plural ''davae'') was a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique. Most of these towns are attested by Ptolemy, and therefore date from at least the 1st century CE. The "''dava''" towns can be found as south as Sandanski and Plovdiv. Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae. The Dacians, Getae and their kings were always considered as Thracians by the ancients ( Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius, Appian, Strabo, Herodotus and Pliny the Elder), and were both said to speak the same Thracian language. Etymology Many city names of the Dacians were composed of an initial lexical element (often the tribe name) affixed to ''-dava'', ''-daua'', ''-deva'', ''-deba'', ''-daba'' or ''-dova'' (''*dʰeh₁-'' "to set, place"). Therefore, ''dava'' 'town' d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under Burebista, King Burebista. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last one which is split between Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |