Plastic pollution is the accumulation of
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and
microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat.
Plastics that act as
pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oi ...
s are categorized by size into micro-, meso-, or macro debris.
Plastics are inexpensive and durable, making them very adaptable for different uses; as a result, manufacturers choose to use plastic over other materials. However, the chemical structure of most plastics renders them resistant to many natural processes of
degradation and as a result they are slow to degrade.
Together, these two factors allow large volumes of plastic to enter the environment as mismanaged
waste
Waste are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor Value (economics), economic value. A wast ...
which persists in the
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
and travels throughout
food webs.
Plastic pollution can afflict
land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land sur ...
,
waterway
A waterway is any Navigability, navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other ways. A first distinction is ...
s and
ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
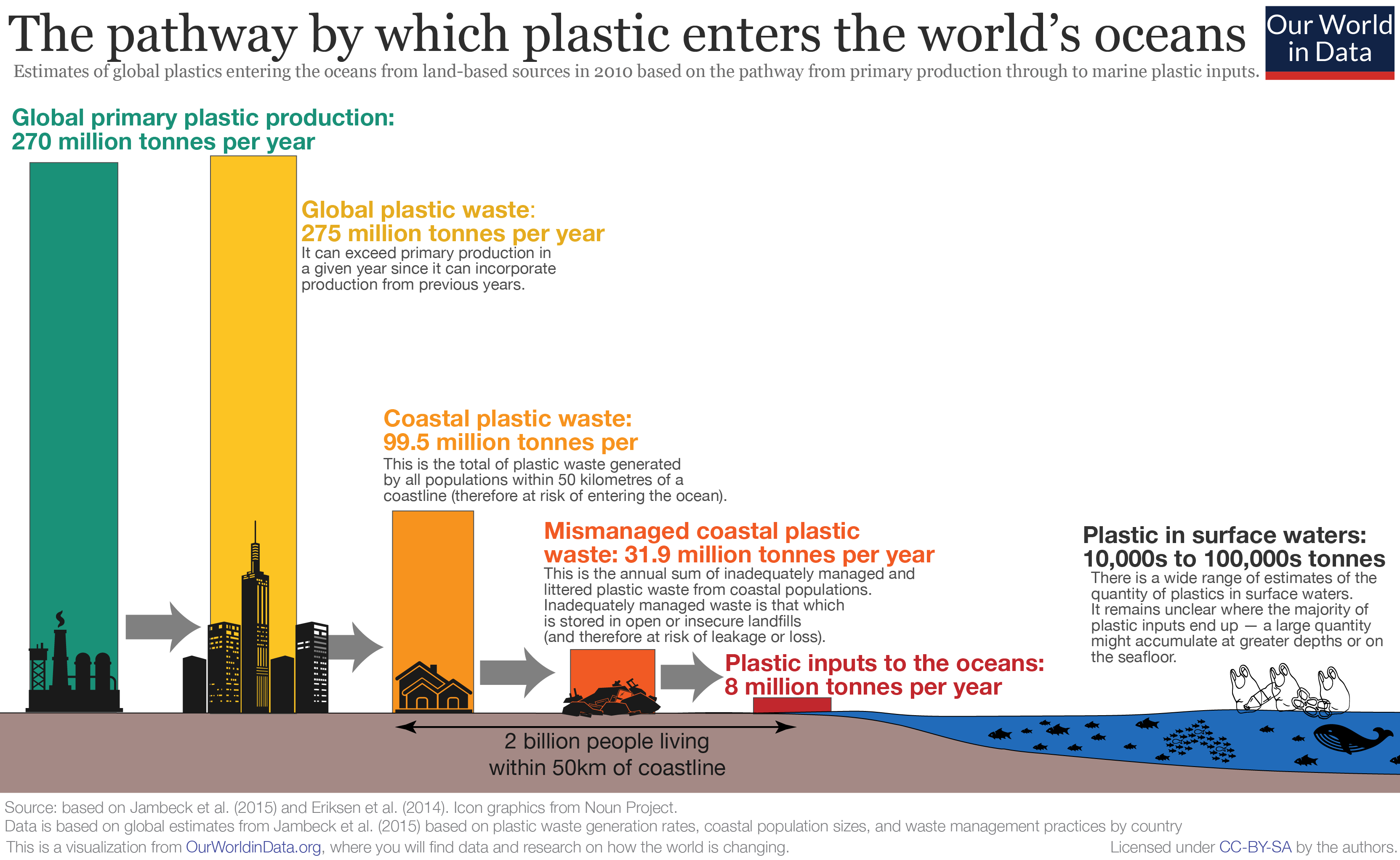
s. It is estimated that 1.1 to 8.8'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste enters the ocean from coastal communities each year.
It is estimated that there is a stock of 86'' ''million tons of plastic
marine debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created solid material that has deliberately or accidentally been released in seas or the ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, freque ...
in the worldwide ocean as of the end of 2013, with an assumption that 1.4% of global plastics produced from 1950 to 2013 has entered the ocean and has accumulated there.
[Jang, Y. C., Lee, J., Hong, S., Choi, H. W., Shim, W. J., & Hong, S. Y. 2015. "Estimating the global inflow and stock of plastic marine debris using material flow analysis: a preliminary approach". ''Journal of the Korean Society for Marine Environment and Energy'', 18(4), 263–27]
/ref> Global plastic production has surged from 1.5'' ''million tons in the 1950s to 335'' ''million tons in 2016, resulting in environmental concerns. A significant issue arises from the inefficient treatment of 79% of plastic products, leading to their release into landfills or natural environments.
Some researchers suggest that by 2050 there could be more plastic than fish in the oceans by weight.physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
. Degraded plastic waste can directly affect humans through direct consumption (i.e. in tap water), indirect consumption (by eating plants and animals), and disruption of various hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
mechanisms.biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
of all land and marine animals combined. A May 2019 amendment to the Basel Convention regulates the exportation/importation of plastic waste, largely intended to prevent the shipping of plastic waste from developed countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
to developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
. Nearly all countries have joined this agreement.[National Geographic, 30 Oct. 2020]
"U.S. Generates More Plastic Trash than Any Other Nation, Report Finds: The Plastic Pollution Crisis Has Been Widely Blamed on a Handful of Asian Countries, But New Research Shows Just How Much the U.S. Contributes"
/ref> On 2 March 2022, in Nairobi, 175 countries pledged to create a legally binding agreement by the end of the year 2024 with a goal to end plastic pollution.COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
due to increased demand for protective equipment and packaging materials. Higher amounts of plastic ended up in the ocean, especially plastic from medical waste and masks.
Causes
 There are differing estimates of how much plastic waste has been produced in the last century. By one estimate, one billion tons of plastic waste have been discarded since the 1950s. Others estimate a cumulative human production of 8.3'' ''billion tons of plastic, of which 6.3'' ''billion tons is waste, with only 9% getting recycled.
There are differing estimates of how much plastic waste has been produced in the last century. By one estimate, one billion tons of plastic waste have been discarded since the 1950s. Others estimate a cumulative human production of 8.3'' ''billion tons of plastic, of which 6.3'' ''billion tons is waste, with only 9% getting recycled.
Types of plastic debris
 There are three major forms of plastic that contribute to plastic pollution: micro-, macro-, and mega-plastics. Mega- and micro plastics have accumulated in highest densities in the Northern Hemisphere, concentrated around urban centers and water fronts. Plastic can be found off the coast of some islands because of currents carrying the debris. Both mega- and macro-plastics are found in packaging, footwear, and other domestic items that have been washed off of ships or discarded in landfills. Fishing-related items are more likely to be found around remote islands.
There are three major forms of plastic that contribute to plastic pollution: micro-, macro-, and mega-plastics. Mega- and micro plastics have accumulated in highest densities in the Northern Hemisphere, concentrated around urban centers and water fronts. Plastic can be found off the coast of some islands because of currents carrying the debris. Both mega- and macro-plastics are found in packaging, footwear, and other domestic items that have been washed off of ships or discarded in landfills. Fishing-related items are more likely to be found around remote islands. Plastic debris is categorized as either primary or secondary. Primary plastics are in their original form when collected. Examples of these would be bottle caps, cigarette butts, and microbeads. Secondary plastics, on the other hand, account for smaller plastics that have resulted from the degradation of primary plastics.
Plastic debris is categorized as either primary or secondary. Primary plastics are in their original form when collected. Examples of these would be bottle caps, cigarette butts, and microbeads. Secondary plastics, on the other hand, account for smaller plastics that have resulted from the degradation of primary plastics.
Microdebris
Microdebris are plastic pieces between 2 mm and 5 mm in size.[Knight 2012, p. 11.][Knight 2012, p. 13.] These micro-plastics can accumulate in the oceans and allow for the accumulation of Persistent Bio-accumulating Toxins such as bisphenol'' ''A, polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It i ...
, DDT, and PCB's which are hydrophobic in nature and can cause adverse health affects.[Knight 2012, p. 12.]
Amounts, locations, tracking, and correlations of the microdebris
A 2004 study by Richard Thompson from the University of Plymouth, UK, found a great amount of microdebris on beaches and in waters in Europe, the Americas, Australia, Africa, and Antarctica.seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
.
Macrodebris
Plastic debris is categorized as macrodebris when it is larger than 20 mm. These include items such as plastic grocery bags.
Plastic production
9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. Of all the plastic discarded so far, 14% has been incinerated and less than 10% has been recycled.
Decomposition of plastics
Plastics themselves contribute to approximately 10% of discarded waste. Many kinds of plastics exist depending on their precursors and the method for their polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. Depending on their chemical composition, plastics and resins have varying properties related to contaminant absorption and adsorption. Polymer degradation takes much longer as a result of saline environments and the cooling effect of the sea. These factors contribute to the persistence of plastic debris in certain environments.bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is Solubility, soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on a ...
. However, due to the increased volume of plastics in the ocean, decomposition has slowed down.
Persistent organic pollutants
It was estimated that global production of plastics is approximately 250 Mt per year. Their abundance has been found to transport persistent organic pollutants, also known as POPs. These pollutants have been linked to an increased distribution of algae associated with red tides.
Commercial pollutants
 In 2019, the group Break Free From Plastic organized over 70,000 volunteers in 51 countries to collect and identify plastic waste. These volunteers collected over "59,000 plastic bags, 53,000 sachets and 29,000 plastic bottles," as reported by ''The Guardian''. Nearly half of the items were identifiable by consumer brands. The most common brands were
In 2019, the group Break Free From Plastic organized over 70,000 volunteers in 51 countries to collect and identify plastic waste. These volunteers collected over "59,000 plastic bags, 53,000 sachets and 29,000 plastic bottles," as reported by ''The Guardian''. Nearly half of the items were identifiable by consumer brands. The most common brands were Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, or Coke, is a cola soft drink manufactured by the Coca-Cola Company. In 2013, Coke products were sold in over 200 countries and territories worldwide, with consumers drinking more than 1.8 billion company beverage servings ...
, Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. ( ) is a Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Switzerland. It has been the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other metrics, since 20 ...
, and Pepsico
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase, New York, Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the f ...
. According to the global campaign coordinator for the project Emma Priestland in 2020, the only way to solve the problem is stopping production of single use plastic and using reusable products instead.
Coca-Cola answered that "more than 20% of our portfolio comes in refillable or fountain packaging", they are decreasing the amount of plastic in secondary packaging.
Nestlé responded that 87% of their packaging and 66% of their plastic packaging can be reused or recycled and by 2025 they want to make it 100%. By that year they want to reduce the consumption of virgin plastic by one third.Altria
Altria Group, Inc. (previously known as Philip Morris Companies, Inc. until 2003) is an American corporation and one of the world's largest producers and marketers of tobacco, cigarettes, and medical products in the treatment of illnesses ca ...
, totaling 24% of the total branded count. 56 companies accounted for over 50% of the branded items.
According to The Plastic Waste Makers index, 55% of plastic waste worldwide is created by 20 companies.
Major plastic waste generator and polluter countries
Plastic waste generation
The United States is the world leader in generating plastic waste, producing an annual 42'' ''million metric tons of plastic waste. Per capita generation of plastic waste in the United States is higher than in any other country, with the average American producing 130.09 kilograms of plastic waste per year. Other high-income countries, such as those of the EU-28 (annual per capita generation 58.56 kg), also have a high per capita plastic waste generation rate. Some high-income countries, such as Japan (annual per capital generation 38.44 kg), produce far less plastic waste per capita.
Plastic pollution
The United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
estimated in 2022 that the worldwide entry of plastic into the ocean was 8'' ''million metric tons of plastic per year. A 2021 study by The Ocean Cleanup estimated that rivers convey between 0.8 and 2.7'' ''million metric tons of plastic into the ocean, and ranked these river's countries. The top ten were, from the most to the least: Philippines, India, Malaysia, China, Indonesia, Myanmar, Brazil, Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Thailand.
Mismanaged plastic waste polluters
In 2018 approximately 513'' ''million tonnes of plastics wind up in the oceans every year out of which the 83,1% is from the following 20 countries: China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
is the most mismanaged plastic waste polluter leaving in the sea the 27.7% of the world total, second Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
with the 10.1%, third Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
with 5.9%, fourth Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
with 5.8%, fifth Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
5.0%, sixth Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
with 3.2%, seventh Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
with 3.0%, eighth Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
with 2.9%, ninth Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
with 2.7%, tenth Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
with 2.5%, eleventh South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
with 2.0%, twelfth India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
with 1.9%, thirteenth Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
with 1.6%, fourteenth Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
with 1.5%, fifteenth Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
with 1.5%, sixteenth Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
with 1.5%, seventeenth Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
with 1.4%, eighteenth Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
with 1.0%, nineteenth North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
with 1.0%, twentieth United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
with 0.9%. The rest of world's countries combined wind up the 16.9% of the mismanaged plastic waste in the oceans, according to a study published by ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'' in 2015.European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
countries combined would rank eighteenth on the list.
Total plastic waste polluters
Around 275'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste is generated each year around the world; between 4.8 million and 12.7'' ''million tonnes is dumped into the sea.Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'', Jambeck ''et al'' (2015).European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
countries combined would rank eighteenth on the list.Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
and the Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
) and eight in Asia (the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
, Indus, Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In t ...
, Yangtze, Hai He
The Hai River (海河, lit. "Sea River"), Postal Map Romanization, also known as the Peiho, ("White River"), or Hai Ho, is a Chinese rivers of China, river connecting Beijing to Tianjin and the Bohai Sea.
During the Song dynasty, the main st ...
, Pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living Exoskeleton, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pear ...
, Mekong and Amur
The Amur River () or Heilong River ( zh, s=黑龙江) is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer Manchuria, Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur ...
) "transport 88–95% of the global plastics load into the sea."
The Caribbean Islands are the biggest plastic polluters per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person".
Social statistics
The term is used in a wide variety of social science, social sciences and statistical research conte ...
in the world. Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
produces 1.5 kilograms of waste per capita per day, is the biggest plastic polluter per capita in the world. At least 0.19 kg per person per day of Trinidad and Tobago's plastic debris end up in the ocean, or for example Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
which generates more than four times the amount of plastic waste per capita as China and is responsible for 1.2 times more improperly disposed plastic waste per capita than China. Of the top thirty global polluters per capita, ten are from the Caribbean region. These are Trinidad and Tobago, Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda is a Sovereign state, sovereign archipelagic country composed of Antigua, Barbuda, and List of islands of Antigua and Barbuda, numerous other small islands. Antigua and Barbuda has a total area of 440 km2 (170 sq mi), ...
, Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis, officially the Federation of Saint Christopher (St Kitts) and Nevis, is an island country consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of the Less ...
, Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
, Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
, Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. Part of the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Saint Vincent ...
, Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. ...
, Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
, Anguilla
Anguilla is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Sa ...
and Aruba
Aruba, officially the Country of Aruba, is a constituent island country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, in the southern Caribbean Sea north of the Venezuelan peninsula of Paraguaná Peninsula, Paraguaná and northwest of Curaçao. In 19 ...
, according to a set of studies summarized by ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine founded by B. C. Forbes in 1917. It has been owned by the Hong Kong–based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments since 2014. Its chairman and editor-in-chief is Steve Forbes. The co ...
'' (2019).
Effects
Effects on the environment
The distribution of plastic debris is highly variable as a result of certain factors such as wind and ocean currents, coastline geography, urban areas, and trade routes. Human population in certain areas also plays a large role in this. Plastics are more likely to be found in enclosed regions such as the Caribbean. It serves as a means of distribution of organisms to remote coasts that are not their native environments. This could potentially increase the variability and dispersal of organisms in specific areas that are less biologically diverse. Plastics can also be used as vectors for chemical contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, wiktionary:Workplace, workplace, etc.
Types of contamina ...
s such as persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals. Plastic pollution has also greatly negatively affected our environment. "The pollution is significant and widespread, with plastic debris found on even the most remote coastal areas and in every marine habitat". This information tells us about how much of a consequential change plastic pollution has made on the ocean and even the coasts.
In January 2022 a group of scientists defined a planetary boundary for "novel entities" (pollution, including plastic pollution) and found it has already been exceeded. According to co-author Patricia Villarubia-Gómez from the Stockholm Resilience Centre, "There has been a 50-fold increase in the production of chemicals since 1950. This is projected to triple again by 2050". There are at least 350,000 artificial chemicals in the world. They have mostly "negative effects on planetary health". Plastic alone contain more than 10,000 chemicals and create large problems. The researchers are calling for limit on chemical production and shift to
Plastic pollution has also greatly negatively affected our environment. "The pollution is significant and widespread, with plastic debris found on even the most remote coastal areas and in every marine habitat". This information tells us about how much of a consequential change plastic pollution has made on the ocean and even the coasts.
In January 2022 a group of scientists defined a planetary boundary for "novel entities" (pollution, including plastic pollution) and found it has already been exceeded. According to co-author Patricia Villarubia-Gómez from the Stockholm Resilience Centre, "There has been a 50-fold increase in the production of chemicals since 1950. This is projected to triple again by 2050". There are at least 350,000 artificial chemicals in the world. They have mostly "negative effects on planetary health". Plastic alone contain more than 10,000 chemicals and create large problems. The researchers are calling for limit on chemical production and shift to circular economy
A circular economy (also referred to as circularity or CE) is a model of resource Production (economics), production and Resource consumption, consumption in any economy that involves sharing, leasing, Reuse, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and ...
, meaning to products that can be reused and recycled.
The problem of ocean plastic debris is ubiquitous. It is estimated that 1.5–4% of global plastics production ends up in the oceans every year, mainly as a result of poor waste management infrastructure and practices combined with irresponsible attitudes to the use and disposal of plastics. The weathering of plastic debris causes its fragmentation into particles that even small marine invertebrates may ingest hence contaminating the food chain. Their small size renders them untraceable to their source and extremely difficult to remove from open ocean environments. In the marine environment, plastic pollution causes "Entanglement, toxicological effects via ingestion of plastics, suffocation, starvation, dispersal, and rafting of organisms, provision of new habitats, and introduction of invasive species are significant ecological effects with growing threats to biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
and trophic relationships. Degradation (changes in the ecosystem state) and modifications of marine systems are associated with loss of ecosystem services and values. Consequently, this emerging contaminant affects the socio-economic aspects through negative impacts on tourism, fishery, shipping, and human health".
Plastic pollution as a cause of climate change
According to the "Plastic and Climate" report, in 2019 production and incineration of plastic contributed greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es in the equivalent of 850'' ''million tonnes of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
() to the atmosphere. In trend, annual emissions from these sources would grow to 1.34'' ''billion tonnes by 2030. By 2050 plastic could emit 56'' ''billion tonnes of greenhouse
A greenhouse is a structure that is designed to regulate the temperature and humidity of the environment inside. There are different types of greenhouses, but they all have large areas covered with transparent materials that let sunlight pass an ...
gas emissions, as much as 14 percent of the earth's remaining carbon budget. Those are emission from production, transportation, incineration, but there are also releases of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
and effects on phytoplankton.
The emissions of methane from plastic decomposition and impact on phytoplankton, were still not known well when the report was released. According to one estimate, plastic floating in the ocean can emit annually 76 Mt methane equal to 2,129 Mt CO2e, based on the 100 years global warming potential
Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, relative to carbon dioxide (). It is expressed as a multiple of warming caused by the same mass of carbon dioxide ( ...
of methane. But these numbers are very preliminary. From one side, it can be an overestimate as it is based on the emissions of LDPE in powder form, the most emission intensive type of plastic in this case and in tropical water where intense radiation increases decomposition. But from the other side it can be an underestimate, as it is not including the decomposition of plastic on land which is probably more emission intensive, the effects on phytoplankton which can be significant, the emissions from submerged plastic. Therefore, the authors prefer to not include them in the official estimate, but to write them in the full report, as a base for further discussion noting the high importance of the problem.
The United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
used 2 different studies to estimate the impact of plastic on climate: according to the first, by the year 2040 the annual emissions from plastic will reach 2.1 GtCO2 and will consume 19% of the 1.5 degrees carbon budget, while the second estimated the emissions in the year 2015 as 1.7 GtCO2 and predicted that by the year 2050 they will reach 6.5 GtCO2, consuming 15% of the carbon budget. The OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
estimated the emissions from plastic as 1.8 GtCO2 (3.7% of total emissions) in 2019 which will rise to 4.3 GtCO2 (4.5% of total emissions) in 2060, without measures to reduce them.
In a 2024 Bloomberg article, the ever-increasing consumption of plastics was highlighted as a critical environmental issue. Global use is projected to reach 1.1 billion metric tons by 2050, up from just 2 million in the 1950s. The plastic industry's greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
are substantial, having emitted 1.8 billion metric tons in 2019, with the potential to exceed 2.5 billion metric tons by 2050 if no changes are made.
With global recycling rates for plastic packaging at a mere 20%, most discarded plastics end up incinerated or in landfills, where they emit methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
as they decompose.
The international community is divided on how to address the plastic issue. Proposals range from national pledges to mandatory production controls, with the latter being supported by entities like the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. However, the recycling solution is under scrutiny due to low success rates. As a result, there's a growing movement towards reducing plastic production and implementing bans on single-use plastics. States like Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
and Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
are taking legislative action with extended producer responsibility laws to ensure that manufacturers are accountable for the lifecycle environmental impact of their products.
Effects of plastic on land
Plastic pollution on land poses a threat to the plants and animals – including humans who are based on the land. Estimates of the amount of plastic concentration on land are between four and twenty three times that of the ocean. The amount of plastic poised on the land is greater and more concentrated than that in the water. Mismanaged plastic waste ranges from 60 percent in East Asia and Pacific to one percent in North America.Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
stated that plastic is often used in agriculture. There is more plastic in the soil than in the oceans. The presence of plastic in the environment hurt ecosystems and human health and pose a threat to food safety.
Chlorinated plastic can release harmful chemicals into the surrounding soil, which can then seep into groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
or other surrounding water sources and also the ecosystem of the world.[Aggarwal,Poonam; (et al.]
Interactive Environmental Education Book VIII
Pitambar Publishing. p. 86. This can cause serious harm to the species that drink the water. A 2025 study confirmed that agricultural soil contain up to 23 times more plastic particles in comparison to the ocean. The particles can be absorbed by the crops through the roots and be eaten by humans. This create different health hazards, especially as the chemicals replacing BPA in the plastic can be more dangerouse than BPA itself.
Effect on flooding
 Plastic waste can clog storm drains, and such clogging can increase flood damage, particularly in urban areas.
Plastic waste can clog storm drains, and such clogging can increase flood damage, particularly in urban areas.Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estim ...
flood risk increases substantially because of plastic waste clogging the already overburdened sewer system.
In tap water
A 2017 study found that 83% of tap water samples taken around the world contained plastic pollutants.United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
was the most polluted, followed by Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. European countries such as the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
had the lowest contamination rate, though still as high as 72%.
In terrestrial ecosystems
Mismanaged plastic waste leads to plastic directly or indirectly entering terrestrial ecosystems.[Li, P., Wang, X., Su, M., Zou, X., Duan, L., & Zhang, H. (2020). Characteristics of plastic pollution in the environment: A Review. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 107(4), 577–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02820-1] There has been a significant increase of microplastic pollution due to the poor handling and disposal of plastic materials.[Mbachu, O., Jenkins, G., Kaparaju, P., & Pratt, C. (2021). The rise of artificial soil carbon inputs: Reviewing microplastic pollution effects in the soil environment. Science of the Total Environment, 780, 146569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146569] In particular, plastic pollution in the form of microplastics now can be found extensively in soil. It enters the soil by settling on the surface and eventually making its way into subsoils.[Chae, Y., & An, Y.-J. (2018). Current research trends on plastic pollution and ecological impacts on the soil ecosystem: A Review. Environmental Pollution, 240, 387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.05.008] These microplastics find their way into plants and animals.[Wei, F., Xu, C., Chen, C., Wang, Y., Lan, Y., Long, L., Xu, M., Wu, J., Shen, F., Zhang, Y., Xiao, Y., & Yang, G. (2022). Distribution of microplastics in the sludge of wastewater treatment plants in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere, 287, 132357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132357]
Effluent and sludge of wastewater contain large amounts of plastics. Wastewater treatment plants do not have a treatment process to remove microplastics which results in plastics being transferred into water and soil when effluent and sludge are applied to land for agricultural purposes.[Yang, J., Li, L., Li, R., Xu, L., Shen, Y., Li, S., Tu, C., Wu, L., Christie, P., & Luo, Y. (2021). Microplastics in an agricultural soil following repeated application of three types of sewage sludge: A field study. Environmental Pollution, 289, 117943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117943] These fibers can be transferred through effluent to land which pollutes soil environments.
Effects of plastic on oceans and seabirds
Marine life
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, aquatic plant, plants, algae, marine fungi, fungi, marine protists, protists, single-celled marine microorganisms, microorganisms ...
is one of the most important when one is affected by plastic pollution. Plastic pollution puts animals' lives in danger and is in constant fear of extinction. Marine wildlife such as seabirds, whales, fish and turtles mistake plastic waste for prey; most then die of starvation as their stomachs become filled with plastic. They also suffer from lacerations, infections, reduced ability to swim, and internal injuries. This evidence tells us how damaged marine wildlife is being affected by plastic pollution, they bring up how many animals mistake plastic for prey and eat it without knowing. "Globally, 100,000 marine mammals die every year as a result of plastic pollution. This includes whales, dolphins, porpoises, seals and sea lions". This evidence tells us the statistics of how many marine mammals really are negatively affected enough to die from plastic pollution.
Effects on freshwater ecosystems
Research into freshwater plastic pollution has been largely ignored over marine ecosystems, comprising only 13% of published papers on the topic.
Plastics make their way into bodies of freshwater, underground aquifers, and moving freshwaters through runoff and erosion of mismanaged plastic waste (MMPW). In some areas, the direct waste disposal into rivers is a remaining factor of historical practices, and has only been somewhat limited by modern legislation.
Impacts on freshwater biodiversity
= Invertebrates
=
A study analyzing ingestion of plastics across a variety of previously published experiments showed that out of the 206 species covered, the majority of papers documented ingestion in fish.nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s of polystyrene, '' Daphnia galeata'' (common water flea) experienced reduced survival within 48 hours as well as reproductive issues. Over a span of 5 days, the amount of pregnant Daphnia decreased by nearly 50%, and less than 20% of exposed embryos survived without any immediate repercussions. Other arthropods, like juvenile stages of insects are susceptible to similar plastic exposure as some spend part of their adolescence fully submerged in a freshwater resource. This similarity in lifestyle to other aquatic invertebrates indicates that insects may experience similar side effects of plastic exposure.
= Vertebrates
=
Plastic exposure in amphibians has mostly been studied in adolescent life stages, when the test subjects are still dependent on an aquatic environment where it can be easier to manipulate variables experimentally. Studies on a common South American freshwater frog, '' Physalaemus cuvieri'' indicated that plastics may have the potential to induce mutagenic and cytotoxic morphological changes. Much more research needs to be done on amphibian response to plastic pollution, especially since amphibians can serve as initial indicator species
A bioindicator is any species (an indicator species) or group of species whose function, population, or status can reveal the qualitative status of the environment. The most common indicator species are animals. For example, copepods and other sma ...
of environmental decline. Freshwater mammals and birds have long been known to have negative interactions with plastic pollution, often resulting in entanglement or suffocation/choking after ingesting. While inflammation within the gastrointestinal tract in both groups has been noted, unfortunately there is little to no data on the toxicological effects of plastic pollutants in these organisms.
Effects on humans
 Compounds that are used in manufacturing pollute the environment by releasing chemicals into the air and water. Some compounds that are used in plastics, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE), are under close statute and might be very harmful. Even though these compounds are unsafe, they have been used in the manufacturing of food packaging, medical devices, flooring materials, bottles, perfumes, cosmetics and much more. Inhalation of microplastics (MPs) have been shown to be one of the major contributors to MP uptake in humans. MPs in the form of dust particles are circulated constantly through ventilation and air conditioning systems indoors.
Compounds that are used in manufacturing pollute the environment by releasing chemicals into the air and water. Some compounds that are used in plastics, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE), are under close statute and might be very harmful. Even though these compounds are unsafe, they have been used in the manufacturing of food packaging, medical devices, flooring materials, bottles, perfumes, cosmetics and much more. Inhalation of microplastics (MPs) have been shown to be one of the major contributors to MP uptake in humans. MPs in the form of dust particles are circulated constantly through ventilation and air conditioning systems indoors.oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
and DNA damage in spermatozoa, causing reduced sperm viability.dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
upon contact with human skin. In many plastics, these toxic chemicals are only used in trace amounts, but significant testing is often required to ensure that the toxic elements are contained within the plastic by inert material or polymer. Children and women during their reproduction age are at most at risk and more prone to damaging their immune as well as their reproductive system from these hormone-disrupting chemicals. Pregnancy and nursing products such as baby bottles, pacifiers, and plastic feeding utensils place infants and children at a very high risk of exposure.
Clinical significance
Due to the pervasiveness of plastic products, most of the human population is constantly exposed to the chemical components of plastics. In the United States, 95% of adults have had detectable levels of BPA in their urine. Exposure to chemicals such as BPA have been correlated with disruptions in fertility, reproduction, sexual maturation, and other health effects.
= Thyroid hormone axis
=
Bisphenol A affects gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
related to the thyroid hormone axis, which affects biological functions such as metabolism and development. BPA can decrease thyroid hormone receptor (TR) activity by increasing TR transcriptional corepressor activity. This then decreases the level of thyroid hormone binding proteins that bind to triiodothyronine. By affecting the thyroid hormone axis, BPA exposure can lead to hypothyroidism.
= Sex hormones
=
BPA can disrupt normal, physiological levels of sex hormones. It does this by binding to globulins that normally bind to sex hormones such as androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s and estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
s, leading to the disruption of the balance between the two. BPA can also affect the metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
or the catabolism of sex hormones. It often acts as an antiandrogen or as an estrogen, which can cause disruptions in gonadal development and sperm production.
= Carotid arteries
=
A recent research found that approximately 58% of patients who underwent vascular surgery for clogged blood vessels were patients with invisible plastic nano particles in their carotid arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
Structure
The common carotid ...
, blocking the blood supply to the brain and neck. The researchers also found that the blood vessels of those with plastic were inflamed, thus putting them at risk of heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retr ...
, strokes, and death.
Another research found that amounts of polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bott ...
were found in the plaque tissues of 150 people who underwent carotid endarterectomy.
= Breast milk
=
A study in 2022 showed that plastic particles were identified in the breast milk of 77% of the sample of healthy mothers. The researchers were concerned with plastic particles jeopardizing the infants’ health during lactation. The Mothers’ consumption of food and drink in plastic packaging and the use of plastic-containing personal hygiene products was recorded. The results showed absence of microplastics, thus scientists considered the omnipresence of microplastics in the environment and the inevitability of them entering the body.
Disease
In 2023, plasticosis, a new disease caused solely by plastics, was discovered in seabirds.
The birds identified as having the disease have scarred digestive tracts from ingesting plastic waste. "When birds ingest small pieces of plastic, they found, it inflames the digestive tract. Over time, the persistent inflammation causes tissues to become scarred and disfigured, affecting digestion, growth and survival."
Reduction efforts
 Efforts to reduce the use of plastics, to promote plastic recycling and to reduce mismanaged plastic waste or plastic pollution have occurred or are ongoing. The first scientific review in the professional academic literature about global plastic pollution in general found that the rational response to the "global threat" would be "reductions in consumption of virgin plastic materials, along with internationally coordinated strategies for
Efforts to reduce the use of plastics, to promote plastic recycling and to reduce mismanaged plastic waste or plastic pollution have occurred or are ongoing. The first scientific review in the professional academic literature about global plastic pollution in general found that the rational response to the "global threat" would be "reductions in consumption of virgin plastic materials, along with internationally coordinated strategies for waste management
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste, together with monitor ...
" – such as banning export of plastic waste unless it leads to better recycling – and describes the state of knowledge about "poorly reversible" impacts which are one of the rationales for its reduction.
Some supermarkets charge their customers for plastic bags, and in some places more efficient reusable or biodegradable materials are being used in place of plastics. Some communities and businesses have put a ban on some commonly used plastic items, such as bottled water and plastic bags. Some non-governmental organizations have launched voluntary plastic reduction schemes like certificates that can be adapted by restaurants to be recognized as eco-friendly among customers.
In January 2019 a "Global Alliance to End Plastic Waste" was created by companies in the plastics industry. The alliance aims to clean the environment from existing waste and increase recycling, but it does not mention reduction in plastic production as one of its targets. Moreover, subsequent reporting has suggested the group is a greenwashing initiative.reusability
In computer programming, reusability describes the quality of a software asset that affects its ability to be used in a software system for which it was ''not'' specifically designed. An asset that is easy to reuse and provides utility is conside ...
. An Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) that should conceive the agreement by the end of the year 2024 was created. The agreement should facilitate the transition to a circular economy, which will reduce GHG emissions by 25%. Inger Andersen, executive director of UNEP called the decision "a triumph by planet earth over single-use plastics".
Biodegradable and degradable plastics
The use of biodegradable plastics has many advantages and disadvantages. Biodegradables are biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
s that degrade in industrial compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and man ...
ers. Biodegradables do not degrade as efficiently in domestic composters, and during this slower process, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
gas may be emitted.biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, ...
s, because they are oil-based, similar to other conventional plastics. These plastics are made to be more degradable through the use of different additives, which help them degrade when exposed to UV rays or other physical stressors.marine pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural, and municipal solid waste, residential waste; particle (ecology), particles; noise; excess carbon dioxi ...
because there is a lack of infrastructure to deal with these new types of plastic, as well as a lack of understanding about them on the part of consumers.
Incineration
Up to 60% of used plastic medical equipment is incinerated rather than deposited in a landfill as a precautionary measure to lessen the transmission of disease. This has allowed for a large decrease in the amount of plastic waste that stems from medical equipment.
Policy
Agencies such as the US Environmental Protection Agency and US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
often do not assess the safety of new chemicals until after a negative side effect is shown. Once they suspect a chemical may be toxic, it is studied to determine the human reference dose, which is determined to be the lowest observable adverse effect level. During these studies, a high dose is tested to see if it causes any adverse health effects, and if it does not, lower doses are considered to be safe as well. This does not take into account the fact that with some chemicals found in plastics, such as BPA, lower doses can have a discernible effect.European Committee for Standardization
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN, ) is a public standards organization whose mission is to foster the economy of the European Single Market and the wider European continent in global trading, the welfare of European citizens an ...
(CEN), lists the standards that plastics must meet, in terms of compostability and biodegradability, in order to officially be labeled as compostable.European Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the 27 member states. It is the largest multilateral financial institution in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt sol ...
Group aims to increase its funding and advisory assistance for ocean cleanup. For example, the Clean Oceans Initiative (COI) was established in 2018. The European Investment Bank, the German Development Bank, and the French Development Agency (AFD) agreed to invest a total of €2'' ''billion under the COI from October 2018 to October 2023 in initiatives aimed at reducing pollution discharge into the oceans, with a special focus on plastics.Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
are some examples, as is solid waste management in Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
and Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
.
Voluntary reduction efforts failing
Major plastic producers continue to lobby governments to refrain from imposing restrictions on plastic production and to advocate for voluntary corporate targets to reduce new plastic output. However, the world's top 10 plastic producers, including The Coca-Cola Company, Nestle SA and PepsiCo have been failing to meet even their own minimum targets for virgin plastic use.
The export of plastic waste from rich countries to poorer countries has been well documented.
Differences between countries in environmental policy and costs relating to taxes, disposal, and transport, are important determinants on legal and illegal international traffic in hazardous and nonhazardous waste
Hazardous waste is waste that must be handled properly to avoid damaging human health or the environment. Waste can be hazardous because it is Toxicity, toxic, Chemical reaction, reacts violently with other chemicals, or is Corrosion, corrosive, ...
and scrap products, including plastics.
= Legally binding plastics treaty
=
Some academics and NGOs believe that a legally binding international treaty to deal with plastic pollution is necessary. They think this because plastic pollution is an international problem, moving between maritime borders, and also because they believe there needs to be a cap on plastic production.
UNEA-5
would lead to a plastics treaty, but the session ended without a legally binding agreement.
In 2022, countries agreed to devise a global plastic pollution treaty by 2024.
Waste import bans
Since around 2017, China, Turkey, Malaysia, Cambodia, and Thailand have banned certain waste imports. It has been suggested that such bans may increase automation and recycling, decreasing negative impacts on the environment.
According to an analysis of global trade data by the nonprofit Basel Action Network, violations of the Basel Convention, active since 1 January 2021, have been rampant during 2021. The U.S., Canada, and the European Union have sent hundreds of millions of tons of plastic to countries with insufficient waste management infrastructure, where much of it is landfilled, burned, or littered into the environment.
Circular economy policies
Laws related to recyclability, waste management, domestic materials recovery facilities, product composition, biodegradability and prevention of import/export of specific wastes may support prevention of plastic pollution. A study considers producer/manufacturer responsibility "a practical approach toward addressing the issue of plastic pollution", suggesting that "Existing and adopted policies, legislations, regulations, and initiatives at global, regional, and national level play a vital role".hyperspectral imaging
Hyperspectral imaging collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifyi ...
and algorithms developed via machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ...
while only an estimated 9% of the estimated 6.3'' ''billion tonnes of plastic waste from the 1950s up to 2018 has been recycled (12% has been incinerated and the rest reportedly being "dumped in landfills or the natural environment").
Collection, recycling and reduction
The two common forms of waste collection include curbside collection and the use of drop-off recycling centers. About 87 percent of the population in the United States (273'' ''million people) have access to curbside and drop-off recycling centers. In curbside collection, which is available to about 63 percent of the United States population (193'' ''million people), people place designated plastics in a special bin to be picked up by a public or private hauling company.
Ocean cleanup
The organization " The Ocean Cleanup" is trying to collect plastic waste from the oceans by nets. There are concerns from harm to some forms of sea organisms, especially neuston
Neuston, also called pleuston, are organisms that live at the surface of a body of water, such as an ocean, estuary, lake, river, wetland or pond. Neuston can live on top of the water surface or submersed just below the water surface. In additio ...
.
Great Bubble Barrier
In the Netherlands, plastic litter from some rivers is collected by a bubble barrier, to prevent plastics from floating into the sea. This so-called 'Great Bubble Barrier' catches plastics bigger than 1 mm.IJssel
The IJssel (; ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour. It more immediatel ...
(2017) and in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
(2019)Katwijk
Katwijk () is a coastal municipality and town in the province of South Holland, which is situated in the mid-western part of the Netherlands.
The Oude Rijn (Utrecht and South Holland), Oude Rijn ("Old Rhine") river flows through the town and i ...
at the end of the river Rhine.
Mapping and tracking
Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
provides graphics about some analyses, including maps, to show sources of plastic pollution
By country/region
Albania
In July 2018, Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
became the first country in Europe to ban lightweight plastic bags.
Australia
It has been estimated that each year, Australia produces around 2.5m tonnes of plastic waste annually, of which about 84% ends up as landfill
A landfill is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, waste was ...
, and around 130,000 tonnes of plastic waste leaks into the environment. Six of the eight states and territories had by December 2021 committed to banning a range of plastics. The federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
's National Packaging Targets created the goal of phasing out the worst of single-use plastics by 2025,[ and under the ''National Plastics Plan 2021'', it has committed "to phase out loose fill and moulded polystyrene packaging by July 2022, and various other products by December 2022.]
Canada
In the year 2022 Canada announced a ban on producing and importing single use plastic from December 2022. The sale of those items will be banned from December 2023 and the export from 2025. The prime minister of Canada Justin Trudeau pledged to ban single use plastic in 2019.
China
China is the biggest consumer of single-use plastics.China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
published a plan to cut 30% of plastic waste in five years. As part of this plan, single use plastic bags and straws will be banned.
European Union
In 2015 the European Union adopted a directive requiring a reduction in the consumption of single use plastic bags per person to 90 by 2019 and to 40 by 2025. In April 2019, the EU adopted a further directive banning almost all types of single use plastic, except bottles, from the beginning of the year 2021.
On 3 July 2021, the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (SUPD, EU 2019/904) went into effect within EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often de ...
. The directive aims to reduce plastic pollution from single-use disposable plastics. It focuses on the 10 most commonly found disposable plastics at beaches, which make up 43% of marine litter (fishing gear another 27%). According to the directive, there is a ban on plastic cotton buds and balloon sticks, plastic plates, cutlery, stirrers and straws, Styrofoam drinks and food packaging (e.g. disposable cups and one-person meals), products made of oxo-degradable plastic, which degrade into microplastics
Microplastics are "synthetic solid particles or polymeric matrices, with regular or irregular shape and with size ranging from 1 μm to 5 mm, of either primary or secondary manufacturing origin, which are insoluble in water." Microplastics a ...
, while cigarette filters, drinking cups, wet wipes, sanitary towels and tampons receive a label indicating the product contains plastic, that it belongs in the trash, and that litter has negative effects on the environment.European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
and the European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body (directorial system) and a symbolic collective head of state, that defines the overall political direction and general priorities of the European Union (EU). It is composed of the he ...
on a revision to the Waste Shipment Regulation, which will cover this matter, was reached on 17 November 2023.
France
In 2021 France banned "free plastic bottles, plastic confetti, and single-use plastic bags", in 2022 restrictions were made on plastic packaging and toys and in the first of January 2023 many types of single use plastic were banned from restaurants that have more than 20 places. Some were concerned the measures will not be implemented well due to the current energy crisis.
India
The government of India decided to ban single use plastics and take a number of measures to recycle and reuse plastic from 2 October 2019.
The Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Government of India, has requested various governmental departments to avoid the use of plastic bottles to provide drinking water during governmental meetings, etc., and to instead make arrangements for providing drinking water that do not generate plastic waste. The state of Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
has restricted the usage of plastic water bottles (in government functions and meetings) and styrofoam products. The state of Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
has banned the usage of plastic water bottles in governmental meetings.
The 2015 National Games of India, organised in Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram ( ), also known as Trivandrum, is the Capital city, capital city of the Indian state of Kerala. As of 2011, the Thiruvananthapuram Municipal Corporation had a population of 957,730 over an area of 214.86 sq. km, making it the ...
, was associated with green protocols. This was initiated by Suchitwa Mission that aimed for " zero-waste" venues. To make the event "disposable-free", there was ban on the usage of disposable water bottles. The event witnessed the usage of reusable tableware and stainless steel tumblers. Athletes were provided with refillable steel flasks. It is estimated that these green practices stopped the generation of 120 tonnes of disposable waste.
The City of Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
in 2016 banned the plastic for all purpose other than for few special cases like milk delivery etc.
The state of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, India effected the Maharashtra Plastic and Thermocol Products ban 23 June 2018, subjecting plastic users to fines and potential imprisonment for repeat offenders.
In the year 2022 India has begun to implement a country wide ban on different sorts of plastic. This is necessary also for achieving the climate targets of the country as in plastic production are used more than 8,000 additives, part of them are thousands times more powerful greenhouse gases than .
Indonesia
In Bali
Bali (English:; Balinese language, Balinese: ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller o ...
, one of the many islands of Indonesia, two sisters, Melati and Isabel Wijsen, made efforts to ban plastic bags in 2019. their organization Bye Bye Plastic Bags had spread to over 50 locations around the world.
Israel
In Israel, two cities: Eilat
Eilat ( , ; ; ) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port of Eilat, port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jordan as the Gulf of Aqaba. The c ...
and Herzliya
Herzliya ( ; , / ) is an affluent List of Israeli cities, city in the Israeli coastal plain, central coast of Israel, at the northern part of the Tel Aviv District, known for its robust start-up and entrepreneurial culture. In it had a populatio ...
, decided to ban the usage of single use plastic bags and cutlery on the beaches. In 2020 Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( or , ; ), sometimes rendered as Tel Aviv-Jaffa, and usually referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the Gush Dan metropolitan area of Israel. Located on the Israeli Mediterranean coastline and with a popula ...
joined them, banning also the sale of single use plastic on the beaches.
Kenya
In August 2017, Kenya has one of the world's harshest plastic bag bans. Fines of $38,000 or up to four years in jail to anyone that was caught producing, selling, or using a plastic bag.
New Zealand
New Zealand announced a ban on many types of hard-to-recycle single use plastic by 2025.
Nigeria
In 2019, The House of Representatives of Nigeria banned the production, import and usage of plastic bags in the country.
Spain
Spain banned several types of single use plastic at the beginning of the year 2023.
Taiwan
In February 2018, Taiwan restricted the use of single-use plastic cups, straws, utensils and bags; the ban will also include an extra charge for plastic bags and updates their recycling regulations and aiming by 2030 it would be completely enforced.
United Kingdom
In January 2019, the Iceland supermarket chain, which specializes in frozen foods, pledged to "eliminate or drastically reduce all plastic packaging for its store-brand products by 2023."
As of 2020, 104 communities achieved the title of "Plastic free community" in United Kingdom; 500 want to achieve it.
After two schoolgirls Ella and Caitlin launched a petition about it, Burger King
Burger King Corporation (BK, stylized in all caps) is an American multinational chain store, chain of hamburger fast food restaurants. Headquartered in Miami-Dade County, Florida, the company was founded in 1953 as Insta-Burger King, a Jacks ...
and McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation, doing business as McDonald's, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain. As of 2024, it is the second largest by number of locations in the world, behind only the Chinese ch ...
in the United Kingdom and Ireland pledged to stop sending plastic toys with their meals. McDonald's pledged to do it from the year 2021. McDonald's also pledged to use a paper wrap for it meals and books that will be sent with the meals. The transmission will begin already in March 2020.
From October 2023 many types of single use plastic will be banned in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
including cutlery and plates. Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
and Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
have already implemented such bans. The new rules entered into force on the first of October, but many are unaware and not prepared for it.
United States
In the beginning of 2024, 12 states and at least 500 municipalities had some kind of plastic bag ban. Three state bans and two city bans alone reduced the amount of plastic bags used in one year approximately by 6'' ''billion.
In 2009, Washington University in St. Louis became the first university in the United States to ban the sale of plastic, single-use water bottles.
In 2009, the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
required all businesses that sell food or alcohol to charge an additional 5 cents for each carryout plastic or paper bag.Kauai
Kauai (), anglicized as Kauai ( or ), is one of the main Hawaiian Islands.
It has an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), making it the fourth-largest of the islands and the 21st-largest island in the United States. Kauai lies 73 m ...
, Maui
Maui (; Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ) is the second largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2). It is the List of islands of the United States by area, 17th-largest in the United States. Maui is one of ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
prohibit non-biodegradable plastic bags at checkout as well as paper bags containing less than 40 percent recycled material. In 2015, Honolulu
Honolulu ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the Consolidated city-county, consolidated City and County of Honol ...
was the last major county approving the ban.Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
ban Styrofoam (polystyrene) containers in May 2019.
In 2019 the Giant Eagle
Giant Eagle, Inc. is an American supermarket chain with stores in Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, Indiana, and Maryland. The company was founded in 1918 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and incorporated on August 31, 1931. ''Supermarket News'' ...
retailer became the first big US retailer that committed to completely phase out plastic by 2025. The first step – stop using single use plastic bags – will begun to be implemented already on January 15, 2020.
In 2019, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
and Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
enacted on legislation. Vermont also restricted single-use straws and polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It i ...
containers.Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
imposed a $0.10 charge on single-use plastic bags at point of sale, and is going to ban them on 1 July 2021.
Vanuatu
On 30 July 2017, Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east o ...
's Independence Day, made an announcement of stepping towards the beginning of not using plastic bags and bottles. This made it one of the first Pacific nations to do so and will start banning the importation of single-use plastic bottles and bags.
Obstruction by major plastic producers
The ten corporations that produce the most plastic on the planet, The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational corporation founded in 1892. It manufactures, sells and markets soft drinks including Coca-Cola, other non-alcoholic beverage concentrates and syrups, and alcoholic beverages. Its stock is lis ...
, Colgate-Palmolive
The Colgate-Palmolive Company, commonly known as Colgate-Palmolive, is an American multinational corporation, multinational consumer products company headquartered on Park Avenue in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The company specializes in ...
, Danone, Mars, Incorporated, Mondelēz International, Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. ( ) is a Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Switzerland. It has been the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other metrics, since 20 ...
, PepsiCo
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational corporation, multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase, New York, Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the f ...
, Perfetti Van Melle, Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/con ...
, and Unilever
Unilever PLC () is a British multinational consumer packaged goods company headquartered in London, England. It was founded on 2 September 1929 following the merger of Dutch margarine producer Margarine Unie with British soap maker Lever B ...
, formed a well-financed network that has sabotaged for decades government and community efforts to address the plastic pollution crisis, according to a detailed investigative report by the Changing Markets Foundation. The investigation documents how these companies delay and derail legislation so that they can continue to inundate consumers with disposable plastic packaging. These large plastic producers have exploited public fears of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
to work toward delaying and reversing existing regulation of plastic disposal. Big ten plastic producers have advanced voluntary commitments for plastic waste disposal as a stratagem to deter governments from imposing additional regulations.
PepsiCo faced legal action on 15 November 2023, as the New York attorney general filed a lawsuit. The allegations asserted that the food and beverage giant jeopardized the environment and disseminated deceptive information about its dedication to reducing single-use plastic in packaging. Moreover, a substantial portion of the plastic pollution along the Buffalo River was linked to products manufactured by the company.
Deception of the public about recycling
As early as the early 1970s, petrochemical industry leaders understood that the vast majority of plastic they produced would never be recycled. For example, an April 1973 report written by industry scientists for industry executive states that sorting the hundreds of different kinds plastic is "infeasible" and cost-prohibitive. By the late 1980s, industry leaders also knew that the public must be kept feeling good about purchasing plastic products if their industry was to continue to prosper, and needed to quell proposed legislation to regulate the plastic being sold. So the industry launched a $50'' ''million/year corporate propaganda campaign targeting the American public with the message that plastic can be, and is being, recycled, and lobbied American municipalities to launch expensive plastic waste collection programs, and lobbied U.S. states to require the labeling of plastic products and containers with recycling symbols. They were confident, however, that the recycling initiatives would not end up recovering and reusing plastic in amounts anywhere near sufficient to hurt their profits in selling new "virgin" plastic products because they understood that the recycling efforts that they were promoting were likely to fail. Industry leaders more recently have planned 100% recycling of the plastic they produce by 2040, calling for more efficient collection, sorting and processing.
Action for creating awareness
Earth Day
In 2019, the Earth Day
Earth Day is an annual event on April 22 to demonstrate support for environmental protection. First held on April 22, 1970, it now includes a wide range of events coordinated globally through earthday.org (formerly Earth Day Network) includin ...
Network partnered with Keep America Beautiful and National Cleanup Day for the inaugural nationwide Earth Day CleanUp. Cleanups were held in all 50 states, five US territories, 5,300 sites and had more than 500,000 volunteers.
Earth Day 2020 is the 50th Anniversary of Earth Day. Celebrations will include activities such as the Great Global CleanUp, Citizen Science, Advocacy, Education, and art. This Earth Day aims to educate and mobilize more than one billion people to grow and support the next generation of environmental activists, with a major focus on plastic waste.
World Environment Day
Every year, 5 June is observed as World Environment Day to raise awareness and increase government action on the pressing issue. In 2018, India was host to the 43rd World Environment Day and the theme was "Beat Plastic Pollution", with a focus on single-use or disposable plastic. The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change of India invited people to take care of their social responsibility and urged them to take up green good deeds in everyday life. Several states presented plans to ban plastic or drastically reduce their use.
Other actions
On 11 April 2013 in order to create awareness, artist Maria Cristina Finucci founded The Garbage Patch State at UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
headquarters in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, France, in front of Director General Irina Bokova. This was the first of a series of events under the patronage of UNESCO and of the Italian Ministry of the Environment.
See also
* Burning
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
* Eddy pumping – The role of mesoscale eddies in trapping and transporting plastic in the ocean
* Fiber optic drone
* Great Pacific Garbage Patch – an area with concentrations of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris
* Plastic-eating organisms
* Marine plastic pollution
* Microplastic remediation
* Plasticulture
* Refill (scheme)
* Reverse vending machine
* Rubber pollution
* Nuclear waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. It is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear ...
* Technofossil
Notes
References
Sources
*
*
* Knight, Geof (2012)
Plastic Pollution
Capstone.
*
Further reading
* Colette, Wabnitz & Wallace J. Nichols
Editorial: Plastic Pollution: An Ocean Emergency
3 March 2010. 28 January 2013.
Biodegradable Plastics and Marine Litter. Misconceptions, concerns and impacts on marine environments
2015, United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
(UNEP), Nairobi.
A million bottles a minute: world's plastic binge 'as dangerous as climate change'
''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
''. 28 June 2017.
Guess What's Showing Up In Our Shellfish? One Word: Plastics
NPR. 19 September 2017
Microplastic pollution revealed ‘absolutely everywhere’ by new research
''The Guardian''. 6 March 2019
After bronze and iron, welcome to the plastic age, say scientists
''The Guardian''. 4 September 2019.
Planet Plastic: How Big Oil and Big Soda kept a global environmental calamity a secret for decades
''Rolling Stone''. 3 March 2020.
Plastics an 'unfolding disaster' for US marine life
BBC, 19 November 2020.
* Elizabeth Kolbert, "A Trillion Little Pieces: How plastics are poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
ing us", ''The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. It was founded on February 21, 1925, by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a reporter for ''The New York T ...
'', 3 July 2023, pp. 24–27. "If much of contemporary life is wrapped up in plastic, and the result of this is that we are poisoning our kids, ourselves, and our ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s, then contemporary life may need to be rethought." (p. 27.)
External links
*
{{Authority control
Anthropocene
Pollution
Environmental impact of products
 There are differing estimates of how much plastic waste has been produced in the last century. By one estimate, one billion tons of plastic waste have been discarded since the 1950s. Others estimate a cumulative human production of 8.3'' ''billion tons of plastic, of which 6.3'' ''billion tons is waste, with only 9% getting recycled.
It is estimated that this waste is made up of 81% polymer resin, 13% polymer fibres and 32% polymer additives. In 2018 more than 343'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste were generated, 90% of which was composed of post-consumer plastic waste (industrial, agricultural, commercial and municipal plastic waste). The rest was pre-consumer waste from resin production and manufacturing of plastic products (e.g. materials rejected due to unsuitable colour, hardness, or processing characteristics).
A large proportion of post-consumer plastic waste consists of plastic packaging. In the United States plastic packaging has been estimated to make up 5% of MSW. This packaging includes plastic bottles, pots, tubs and trays, plastic films shopping bags, rubbish bags, bubble wrap, and plastic or stretch wrap and plastic foams e.g. expanded polystyrene (EPS). Plastic waste is generated in sectors including agriculture (e.g. irrigation pipes, greenhouse covers, fencing, pellets, mulch; construction (e.g. pipes, paints, flooring and roofing, insulants and sealants); transport (e.g. abraded tyres, road surfaces and road markings); electronic and electric equipment (e-waste); and pharmaceuticals and healthcare. The total amounts of plastic waste generated by these sectors is uncertain.
Several studies have attempted to quantify plastic leakage into the environment at both national and global levels which have highlight the difficulty of determining the sources and amounts of all plastic leakage. One global study has estimated that between 60 and 99'' ''million tonnes of mismanaged plastic waste were produced in 2015. Borrelle et al. 2020 has estimated that 19–23'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste entered aquatic ecosystems in 2016. while the Pew Charitable Trusts and SYSTEMIQ (2020) have estimated that 9–14'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste ended up in the oceans the same year.
Despite global efforts to reduce the generation of plastic waste, losses to the environment are predicted to increase. Modelling indicates that, without major interventions, between 23 and 37'' ''million tonnes per year of plastic waste could enter the oceans by 2040 and between 155 and 265'' ''million tonnes per year could be discharged into the environment by 2060. Under a business as usual scenario, such increases would likely be attributable to a continuing rise in production of plastic products, driven by consumer demand, accompanied by insufficient improvements in waste management. As the plastic waste released into the environment already has a significant impact on ecosystems, an increase of this magnitude could have dramatic consequences.
The trade in plastic waste has been identified as "a main culprit" of marine litter. Countries importing the waste plastics often lack the capacity to process all the material. As a result, the United Nations has imposed a ban on waste plastic trade unless it meets certain criteria.
There are differing estimates of how much plastic waste has been produced in the last century. By one estimate, one billion tons of plastic waste have been discarded since the 1950s. Others estimate a cumulative human production of 8.3'' ''billion tons of plastic, of which 6.3'' ''billion tons is waste, with only 9% getting recycled.
It is estimated that this waste is made up of 81% polymer resin, 13% polymer fibres and 32% polymer additives. In 2018 more than 343'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste were generated, 90% of which was composed of post-consumer plastic waste (industrial, agricultural, commercial and municipal plastic waste). The rest was pre-consumer waste from resin production and manufacturing of plastic products (e.g. materials rejected due to unsuitable colour, hardness, or processing characteristics).
A large proportion of post-consumer plastic waste consists of plastic packaging. In the United States plastic packaging has been estimated to make up 5% of MSW. This packaging includes plastic bottles, pots, tubs and trays, plastic films shopping bags, rubbish bags, bubble wrap, and plastic or stretch wrap and plastic foams e.g. expanded polystyrene (EPS). Plastic waste is generated in sectors including agriculture (e.g. irrigation pipes, greenhouse covers, fencing, pellets, mulch; construction (e.g. pipes, paints, flooring and roofing, insulants and sealants); transport (e.g. abraded tyres, road surfaces and road markings); electronic and electric equipment (e-waste); and pharmaceuticals and healthcare. The total amounts of plastic waste generated by these sectors is uncertain.
Several studies have attempted to quantify plastic leakage into the environment at both national and global levels which have highlight the difficulty of determining the sources and amounts of all plastic leakage. One global study has estimated that between 60 and 99'' ''million tonnes of mismanaged plastic waste were produced in 2015. Borrelle et al. 2020 has estimated that 19–23'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste entered aquatic ecosystems in 2016. while the Pew Charitable Trusts and SYSTEMIQ (2020) have estimated that 9–14'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste ended up in the oceans the same year.
Despite global efforts to reduce the generation of plastic waste, losses to the environment are predicted to increase. Modelling indicates that, without major interventions, between 23 and 37'' ''million tonnes per year of plastic waste could enter the oceans by 2040 and between 155 and 265'' ''million tonnes per year could be discharged into the environment by 2060. Under a business as usual scenario, such increases would likely be attributable to a continuing rise in production of plastic products, driven by consumer demand, accompanied by insufficient improvements in waste management. As the plastic waste released into the environment already has a significant impact on ecosystems, an increase of this magnitude could have dramatic consequences.
The trade in plastic waste has been identified as "a main culprit" of marine litter. Countries importing the waste plastics often lack the capacity to process all the material. As a result, the United Nations has imposed a ban on waste plastic trade unless it meets certain criteria.
 There are three major forms of plastic that contribute to plastic pollution: micro-, macro-, and mega-plastics. Mega- and micro plastics have accumulated in highest densities in the Northern Hemisphere, concentrated around urban centers and water fronts. Plastic can be found off the coast of some islands because of currents carrying the debris. Both mega- and macro-plastics are found in packaging, footwear, and other domestic items that have been washed off of ships or discarded in landfills. Fishing-related items are more likely to be found around remote islands. These may also be referred to as micro-, meso-, and macro debris.
There are three major forms of plastic that contribute to plastic pollution: micro-, macro-, and mega-plastics. Mega- and micro plastics have accumulated in highest densities in the Northern Hemisphere, concentrated around urban centers and water fronts. Plastic can be found off the coast of some islands because of currents carrying the debris. Both mega- and macro-plastics are found in packaging, footwear, and other domestic items that have been washed off of ships or discarded in landfills. Fishing-related items are more likely to be found around remote islands. These may also be referred to as micro-, meso-, and macro debris.
 Plastic debris is categorized as either primary or secondary. Primary plastics are in their original form when collected. Examples of these would be bottle caps, cigarette butts, and microbeads. Secondary plastics, on the other hand, account for smaller plastics that have resulted from the degradation of primary plastics.
Plastic debris is categorized as either primary or secondary. Primary plastics are in their original form when collected. Examples of these would be bottle caps, cigarette butts, and microbeads. Secondary plastics, on the other hand, account for smaller plastics that have resulted from the degradation of primary plastics.
 In 2019, the group Break Free From Plastic organized over 70,000 volunteers in 51 countries to collect and identify plastic waste. These volunteers collected over "59,000 plastic bags, 53,000 sachets and 29,000 plastic bottles," as reported by ''The Guardian''. Nearly half of the items were identifiable by consumer brands. The most common brands were
In 2019, the group Break Free From Plastic organized over 70,000 volunteers in 51 countries to collect and identify plastic waste. These volunteers collected over "59,000 plastic bags, 53,000 sachets and 29,000 plastic bottles," as reported by ''The Guardian''. Nearly half of the items were identifiable by consumer brands. The most common brands were  Plastic pollution has also greatly negatively affected our environment. "The pollution is significant and widespread, with plastic debris found on even the most remote coastal areas and in every marine habitat". This information tells us about how much of a consequential change plastic pollution has made on the ocean and even the coasts.
In January 2022 a group of scientists defined a planetary boundary for "novel entities" (pollution, including plastic pollution) and found it has already been exceeded. According to co-author Patricia Villarubia-Gómez from the Stockholm Resilience Centre, "There has been a 50-fold increase in the production of chemicals since 1950. This is projected to triple again by 2050". There are at least 350,000 artificial chemicals in the world. They have mostly "negative effects on planetary health". Plastic alone contain more than 10,000 chemicals and create large problems. The researchers are calling for limit on chemical production and shift to
Plastic pollution has also greatly negatively affected our environment. "The pollution is significant and widespread, with plastic debris found on even the most remote coastal areas and in every marine habitat". This information tells us about how much of a consequential change plastic pollution has made on the ocean and even the coasts.
In January 2022 a group of scientists defined a planetary boundary for "novel entities" (pollution, including plastic pollution) and found it has already been exceeded. According to co-author Patricia Villarubia-Gómez from the Stockholm Resilience Centre, "There has been a 50-fold increase in the production of chemicals since 1950. This is projected to triple again by 2050". There are at least 350,000 artificial chemicals in the world. They have mostly "negative effects on planetary health". Plastic alone contain more than 10,000 chemicals and create large problems. The researchers are calling for limit on chemical production and shift to  Plastic waste can clog storm drains, and such clogging can increase flood damage, particularly in urban areas. A buildup of plastic garbage at trash cans raises the water level upstream and may enhance the risk of urban flooding. For example, in
Plastic waste can clog storm drains, and such clogging can increase flood damage, particularly in urban areas. A buildup of plastic garbage at trash cans raises the water level upstream and may enhance the risk of urban flooding. For example, in  Compounds that are used in manufacturing pollute the environment by releasing chemicals into the air and water. Some compounds that are used in plastics, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE), are under close statute and might be very harmful. Even though these compounds are unsafe, they have been used in the manufacturing of food packaging, medical devices, flooring materials, bottles, perfumes, cosmetics and much more. Inhalation of microplastics (MPs) have been shown to be one of the major contributors to MP uptake in humans. MPs in the form of dust particles are circulated constantly through ventilation and air conditioning systems indoors. The large dosage of these compounds are hazardous to humans, destroying the endocrine system. BPA imitates the female's hormone called estrogen. PBD destroys and causes damage to thyroid hormones, which are vital hormone glands that play a major role in the metabolism, growth and development of the human body. MPs can also have a detrimental effect on male reproductive success. MPs such as BPA can interfere with steroid biosynthesis in the male endocrine system and with early stages of spermatogenesis. MPs in men can also create
Compounds that are used in manufacturing pollute the environment by releasing chemicals into the air and water. Some compounds that are used in plastics, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE), are under close statute and might be very harmful. Even though these compounds are unsafe, they have been used in the manufacturing of food packaging, medical devices, flooring materials, bottles, perfumes, cosmetics and much more. Inhalation of microplastics (MPs) have been shown to be one of the major contributors to MP uptake in humans. MPs in the form of dust particles are circulated constantly through ventilation and air conditioning systems indoors. The large dosage of these compounds are hazardous to humans, destroying the endocrine system. BPA imitates the female's hormone called estrogen. PBD destroys and causes damage to thyroid hormones, which are vital hormone glands that play a major role in the metabolism, growth and development of the human body. MPs can also have a detrimental effect on male reproductive success. MPs such as BPA can interfere with steroid biosynthesis in the male endocrine system and with early stages of spermatogenesis. MPs in men can also create  Efforts to reduce the use of plastics, to promote plastic recycling and to reduce mismanaged plastic waste or plastic pollution have occurred or are ongoing. The first scientific review in the professional academic literature about global plastic pollution in general found that the rational response to the "global threat" would be "reductions in consumption of virgin plastic materials, along with internationally coordinated strategies for
Efforts to reduce the use of plastics, to promote plastic recycling and to reduce mismanaged plastic waste or plastic pollution have occurred or are ongoing. The first scientific review in the professional academic literature about global plastic pollution in general found that the rational response to the "global threat" would be "reductions in consumption of virgin plastic materials, along with internationally coordinated strategies for