|
Plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semisynthetic materials composed primarily of polymers. Their defining characteristic, plasticity, allows them to be molded, extruded, or pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends in plastic demand continue, it is projected that annual global plastic production will exceed 1.3 billion tons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microplastics
Microplastics are "synthetic solid particles or polymeric matrices, with regular or irregular shape and with size ranging from 1 μm to 5 mm, of either primary or secondary manufacturing origin, which are insoluble in water." Microplastics are dangerous to human health and the environment because they contain harmful chemicals which leak into the air, water, and food. Microplastics cause pollution by entering natural ecosystems from a variety of sources, including cosmetics, clothing, construction, renovation, food packaging, and industrial processes. The term ''microplastics'' is used to differentiate from larger, non-microscopic plastic waste. Two classifications of microplastics are currently recognized. Primary microplastics include any plastic fragments or particles that are already 5.0 mm in size or less before entering the environment. These include microfibers from clothing, microbeads, plastic glitter and plastic pellets (also known as nurdles). Seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Plastic Pollution
Marine plastic pollution is a type of Water pollution, marine pollution by Plastic pollution, plastics, ranging in size from large original material such as bottles and bags, down to microplastics formed from the Fragmentation (cell biology), fragmentation of plastic material. Marine debris is mainly discarded human rubbish which floats on, or is suspended in the ocean. Eighty percent of marine debris is Marine debris#Nurdles and plastic bags, plastic. Microplastics and nanoplastics result from the breakdown or photodegradation of plastic waste in surface waters, rivers or oceans. Recently, scientists have uncovered nanoplastics in heavy snow, more specifically about 3,000 tons that cover Switzerland yearly. It is approximated that there is a stock of 86 million tons of plastic marine debris in the worldwide ocean as of the end of 2013, assuming that 1.4% of global plastics produced from 1950 to 2013 has entered the ocean and has accumulated there. Global consumption of plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
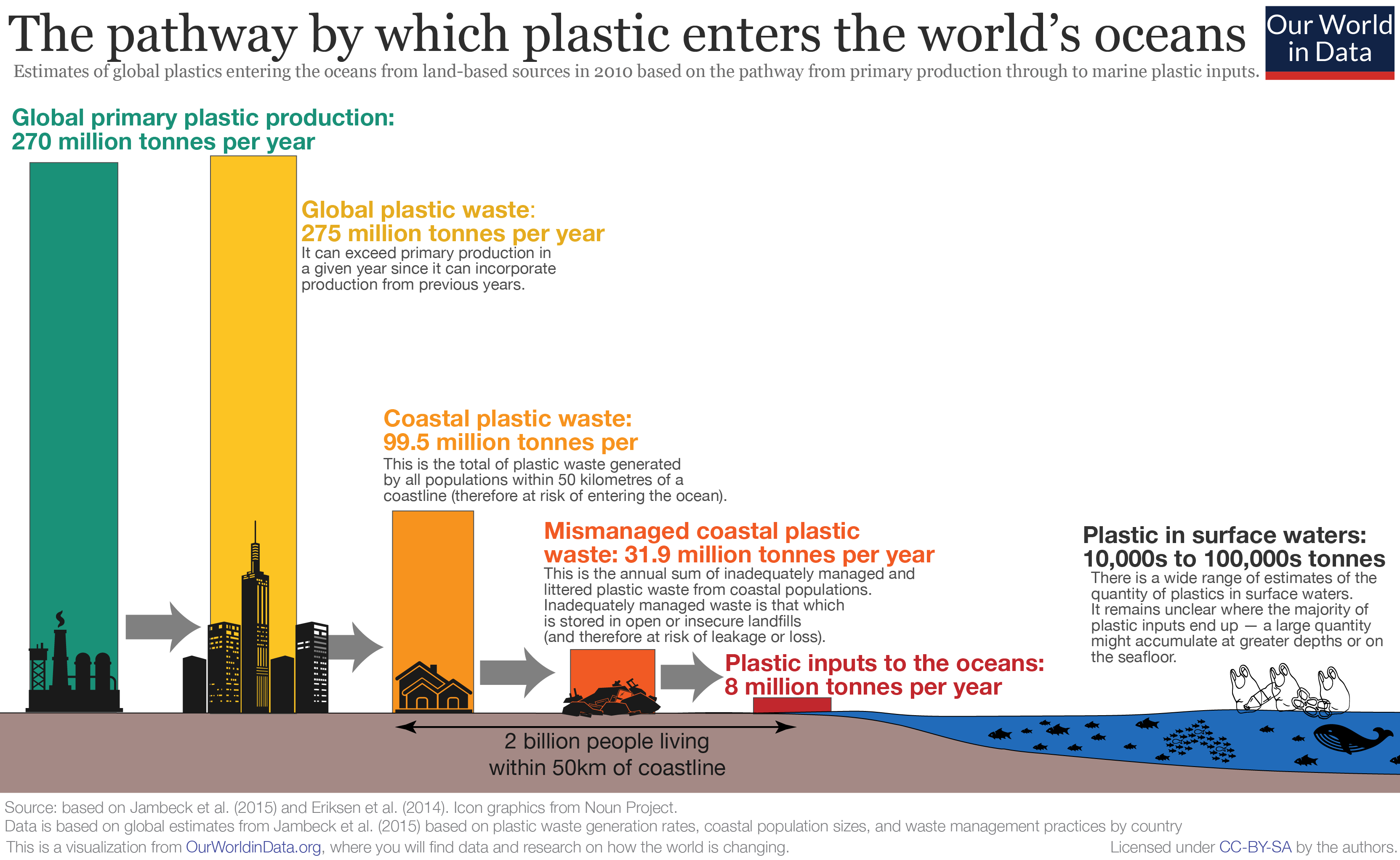
Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat. Plastics that act as pollutants are categorized by size into micro-, meso-, or macro debris. Plastics are inexpensive and durable, making them very adaptable for different uses; as a result, manufacturers choose to use plastic over other materials. However, the chemical structure of most plastics renders them resistant to many natural processes of environmental degradation, degradation and as a result they are slow to degrade. Together, these two factors allow large volumes of plastic to enter the environment as mismanaged waste which persists in the ecosystem and travels throughout food webs. Plastic pollution can afflict land, waterways and oceans. It is estimated that 1.1 to 8.8'' ''million tonnes of plastic waste enters the ocean from coastal communities each year. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Household Items
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polylactic Acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a plastic material. As a thermoplastic polyester (or polyhydroxyalkanoate) it has the backbone formula or . PLA is formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide , the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit. Often PLA is blended with other polymers. PLA can be biodegradable or long-lasting, depending on the manufacturing process, additives and copolymers. PLA has become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources and the possibility to use it for compostable products. In 2022, PLA had the highest consumption volume of any bioplastic of the world, with a share of ca. 26 % of total bioplastic demand. Although its production is growing, PLA is still not as important as traditional commodity polymers like PET or PVC. Its widespread application has been hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible forms. Rigid PVC is used in construction for pipes, doors and windows. It is also used in making plastic bottles, packaging, and bank or membership cards. Adding plasticizers makes PVC softer and more flexible. It is used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, flooring, signage, phonograph records, inflatable products, and in rubber substitutes. With cotton or linen, it is used in the production of canvas. Polyvinyl chloride is a white, brittle solid. It is soluble in ketones, chlorinated solvents, dimethylformamide, THF and DMAc. Discovery PVC was synthesized in 1872 by German chemist Eugen Baumann after extended investigation and experimenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakelite
Bakelite ( ), formally , is a thermosetting polymer, thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in Yonkers, New York, in 1907, and patented on December 7, 1909. Bakelite was one of the first plastic-like materials to be introduced into the modern world and was popular because it could be Molding (process), molded and then hardened into any shape. Because of its electrical nonconductor, nonconductivity and heat-resistant properties, it became a great commercial success. It was used in electrical insulators, radio and telephone casings, and such diverse products as kitchenware, jewelry, pipe stems, children's toys, and firearms. The retro appeal of old Bakelite products has made them collectible. The creation of a synthetic plastic was revolutionary for the chemical industry, which at the time made most of its income f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, cups, jars, etc.). , over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)''n''. PE is usually a mixture of similar polymers of ethylene, with various values of ''n''. It can be ''low-density'' or ''high-density'' and many variations thereof. Its properties can be modified further by crosslinking or copolymerization. All forms are nontoxic as well as chemically resilient, contributing to polyethylene's popularity as a multi-use plastic. However, polyethylene's chemical resilience also makes it a long-lived and decomposition-resistant pollutant when disposed of improperly. Being a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garbage Patch
A garbage patch is a gyre of marine debris particles caused by the effects of ocean currents and increasing plastic pollution by human populations. These human-caused collections of plastic and other debris are responsible for ecosystem and environmental problems that affect marine life, contaminate oceans with toxic chemicals, and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Once waterborne, marine debris becomes mobile. Flotsam can be blown by the wind, or follow the flow of ocean currents, often ending up in the middle of oceanic gyres where currents are weakest. Within garbage patches, the waste is not compact, and although most of it is near the surface of the ocean, it can be found up to more than deep in the water. Patches contain plastics and debris in a range of sizes from microplastics and small scale plastic pellet pollution, to large objects such as fishing nets and consumer goods and appliances lost from flood and shipping loss. Garbage patches grow because of widesp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection Moulding
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refining, refined crude oil. Petroleum is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from anaerobic decay of organic materials from buried prehistoric life, prehistoric organisms, particularly planktons and algae, and 70% of the world's oil deposits were formed during the Mesozoic. Conventional reserves of petroleum are primarily recovered by oil drilling, drilling, which is done after a study of the relevant structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, analysis of the sedimentary basin, and reservoir characterization, characterization of the petroleum reservoir. There are also unconventional (oil & gas) reservoir, unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |