Lincolnshire County Council on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a
 During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the
During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the 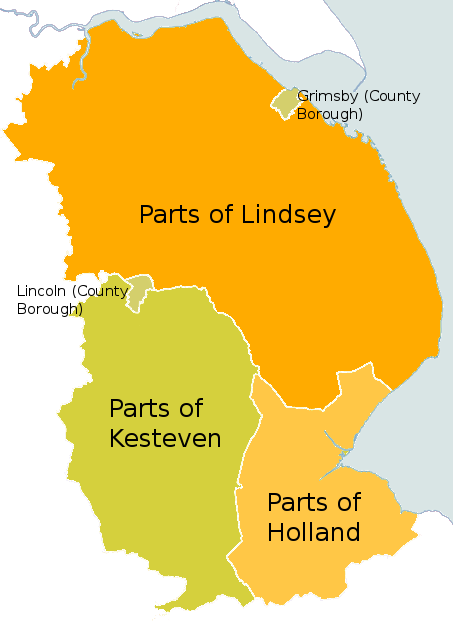 A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of
A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of
File: Belton House 2006 Giano.jpg,
 Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of
Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of
This area covers North Kesteven, Lincoln and West Lindsey. It helps with development and economic planning around the three districts.
 Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by
Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by 
 Most rail services are currently operated by
Most rail services are currently operated by
Northern Lincolnshire and Goole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Some of the larger hospitals in the county include: *
Black Sluice Internal Drainage BoardWitham 4th District IDBLindsey Marsh Drainage Board
, or th
Welland and Deepings Internal Drainage Board



 The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the
The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the
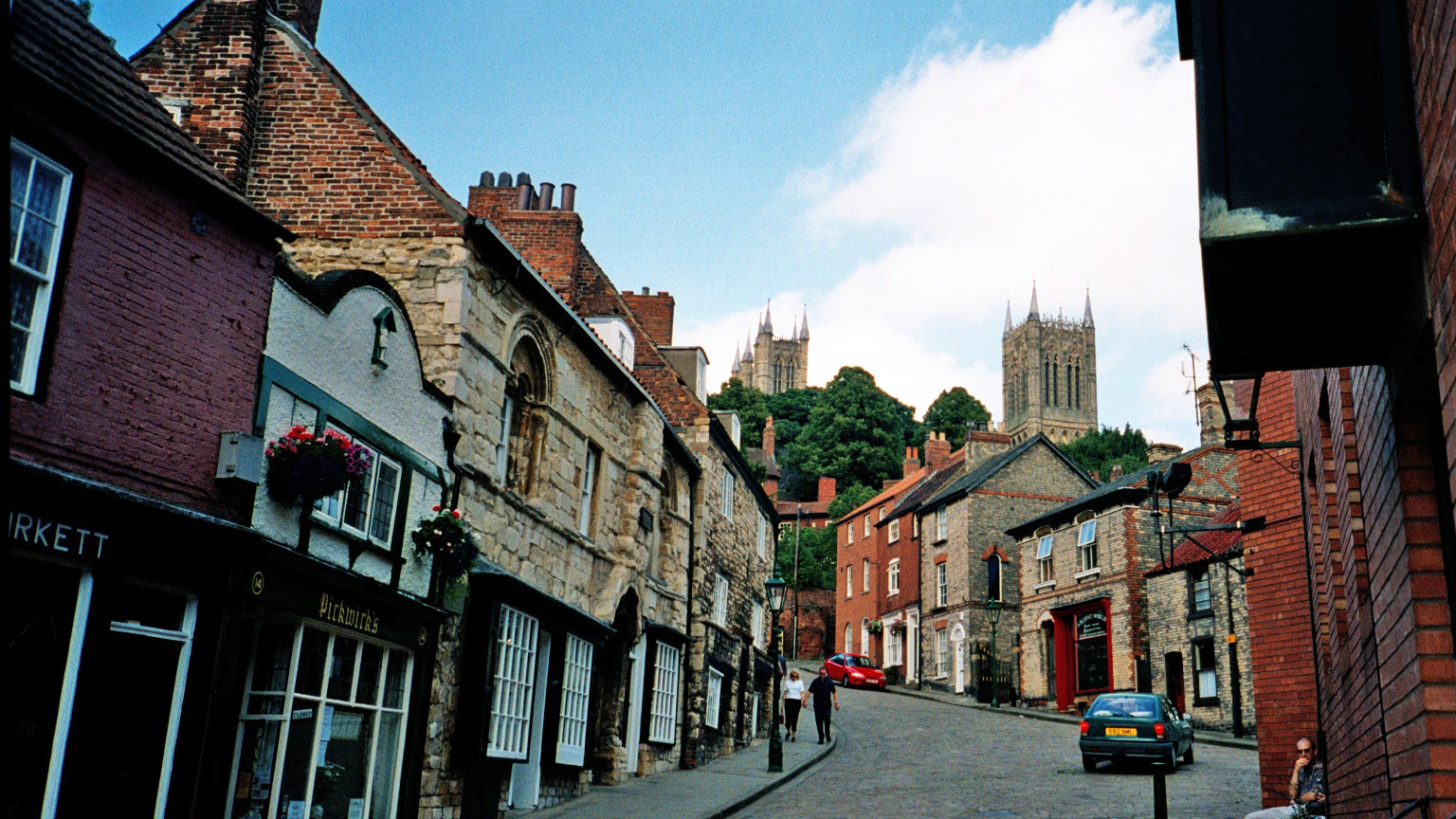
 Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
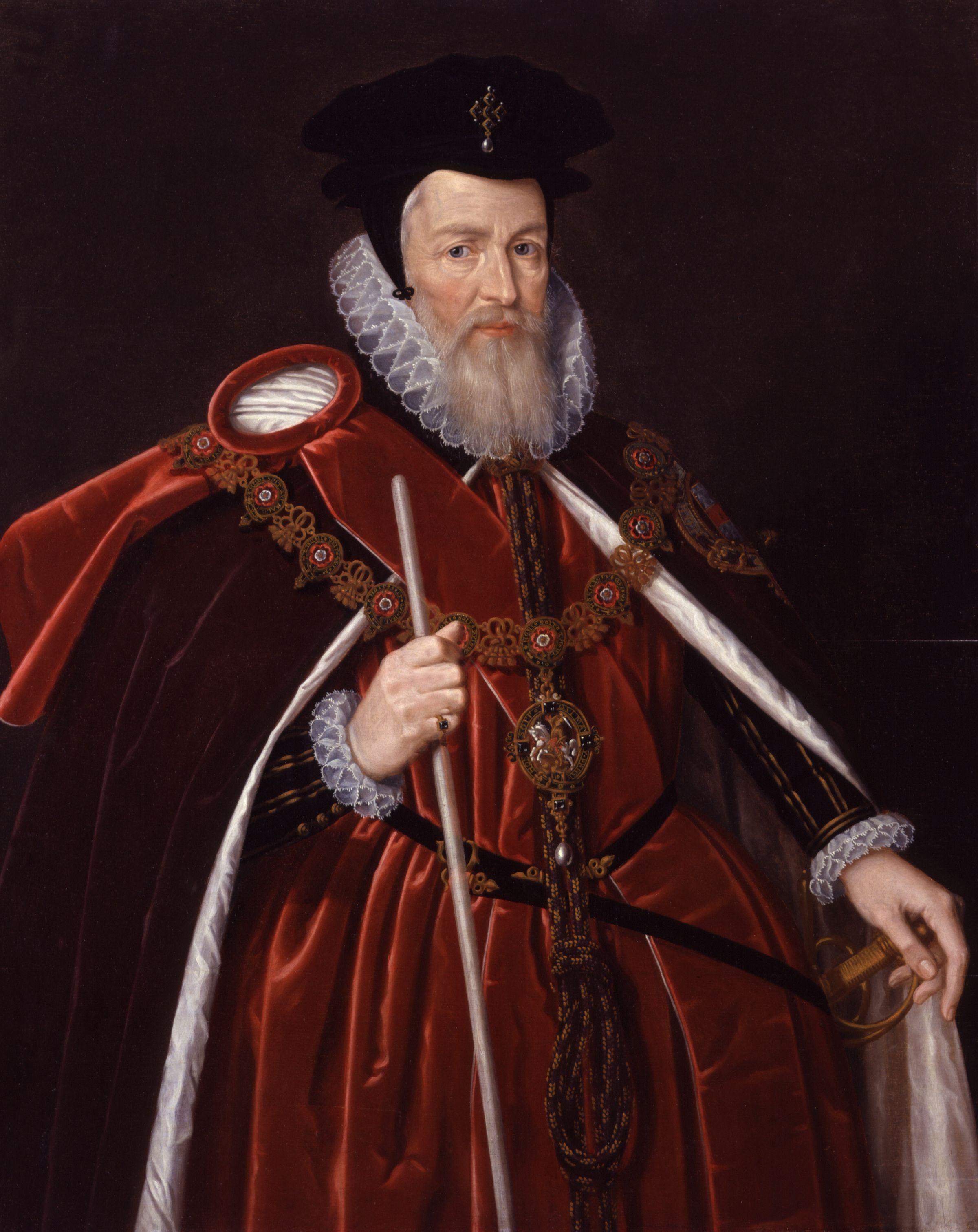
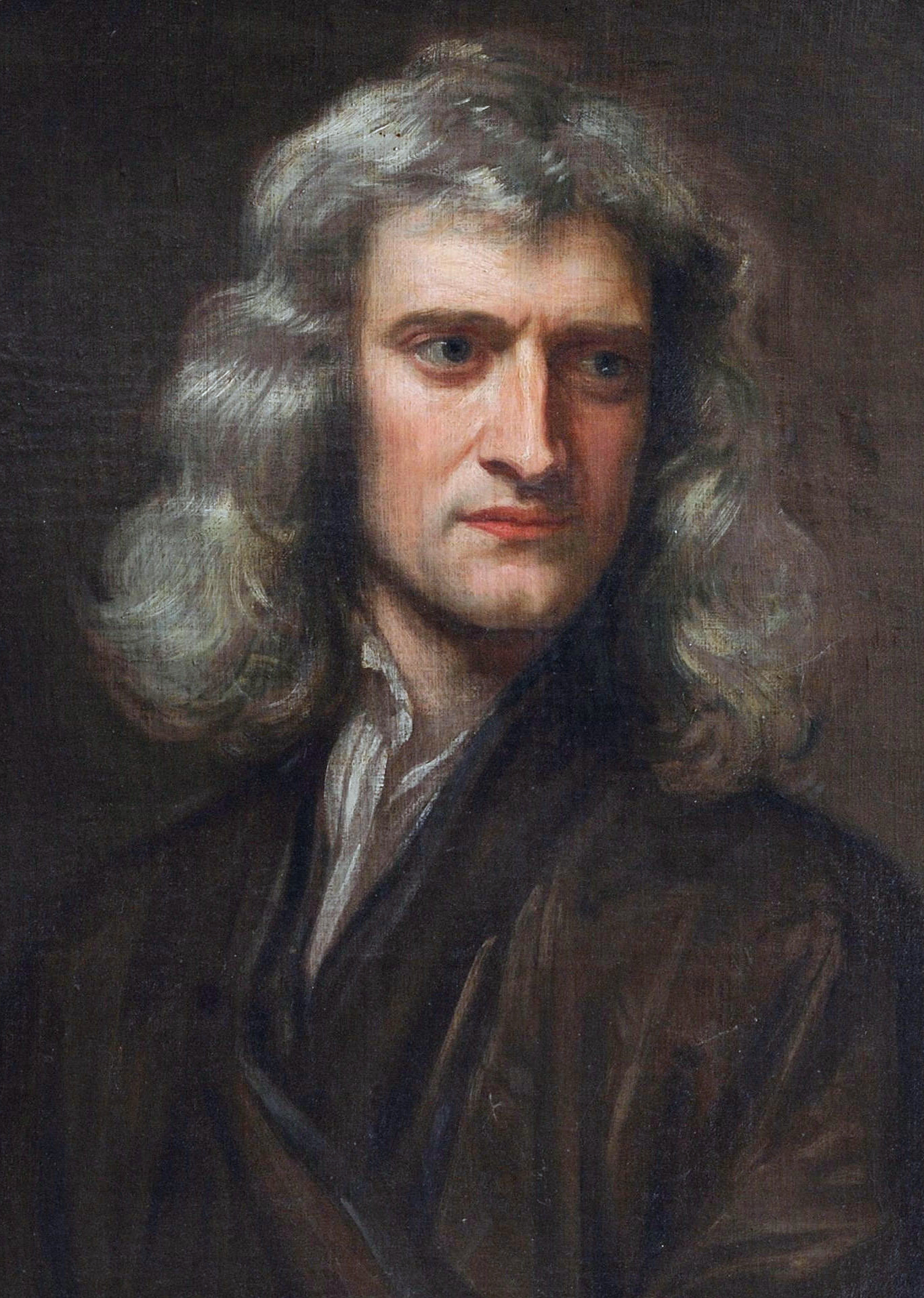






 The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
 Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
* Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with
Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
* Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with
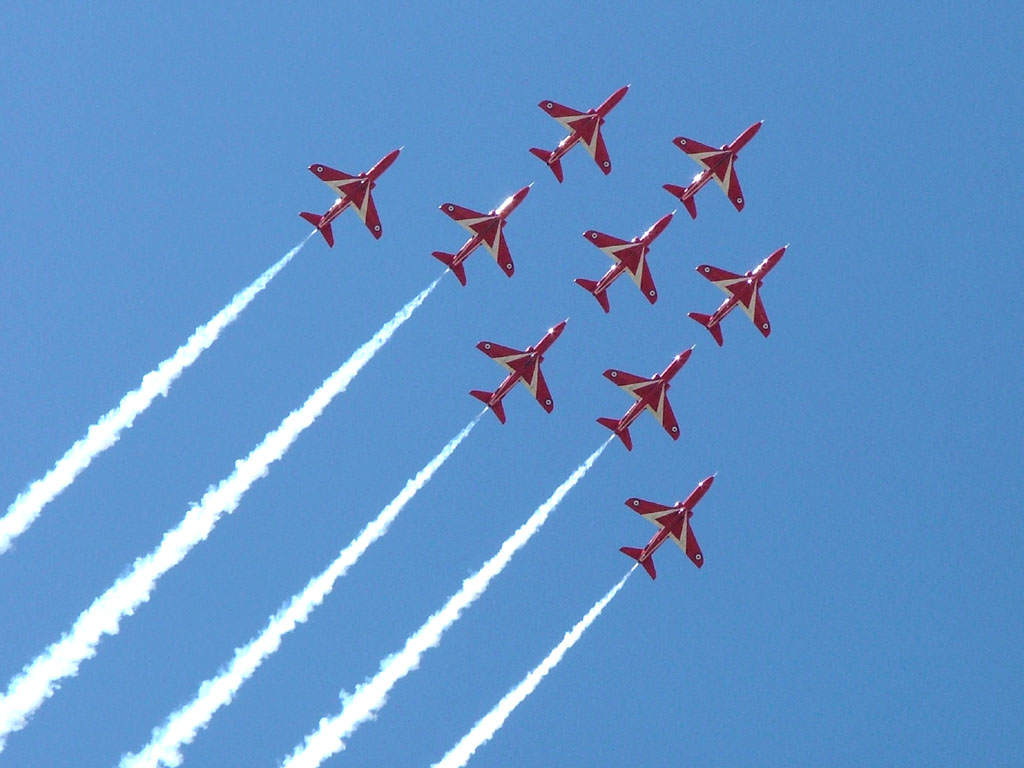 Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The
Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The
Roger Tuby
brings a small funfair to Bourne and then to Spalding in Spring and returns in Autumn at the end of the season. The villages of
 The main sports played in the county are
The main sports played in the county are

 The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "
The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "
which has lost even the unique pose of the carving.
Lincolnshire County Council websiteLincs FM websiteVisitlincolnshire.com
Lindcolne Skipfierde
Lincolnshire'
Anglo-Saxon, Viking and Norman
re-enactment and living history group
Lincolnshire Show official websitePathe newsreel of motor tractors at 1919 agricultural show, thought to be Lincoln show
Images of Lincolnshire
at the English Heritage Archive {{Authority control Lincolnshire, Non-metropolitan counties East Midlands NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Counties of England established in antiquity
county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
in the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, L ...
of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
to the east. It borders Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
to the south-east, Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to t ...
to the south, Rutland
Rutland () is a ceremonial county and unitary authority in the East Midlands, England. The county is bounded to the west and north by Leicestershire, to the northeast by Lincolnshire and the southeast by Northamptonshire.
Its greatest len ...
to the south-west, Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire ...
and Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated Notts.) is a landlocked county in the East Midlands region of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The trad ...
to the west, South Yorkshire
South Yorkshire is a ceremonial and metropolitan county in the Yorkshire and Humber Region of England. The county has four council areas which are the cities of Doncaster and Sheffield as well as the boroughs of Barnsley and Rotherham.
...
to the north-west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire t ...
to the north. It also borders Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It ...
in the south for just , England's shortest county boundary. The county town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
is Lincoln, where the county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
is also based.
The ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
of Lincolnshire consists of the non-metropolitan county
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a county-level entity in England that is not a metropolitan county. The counties typically have populations of 300,000 to 1.8 million. The term ''shire county'' is, however, an unoffi ...
of Lincolnshire and the area covered by the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire
North Lincolnshire is a unitary authority area in Lincolnshire, England, with a population of 167,446 in the 2011 census. The borough includes the towns of Scunthorpe, Brigg, Haxey, Crowle, Epworth, Bottesford, Kirton in Lindsey and Bar ...
and North East Lincolnshire
North East Lincolnshire is a Unitary authority area with borough status in Lincolnshire, England. It borders the borough of North Lincolnshire and districts of West Lindsey and East Lindsey. The population of the district in the 2011 Census w ...
. Part of the ceremonial county is in the Yorkshire and the Humber
Yorkshire and the Humber is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The population in 2011 was 5,284,000 with its largest settlements being Leeds, Sheffield, Bradford, Hull, and York.
It is ...
region of England, and most is in the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, L ...
region. The county is the second-largest of the English ceremonial counties and one that is predominantly agricultural in land use. The county is fourth-largest of the two-tier counties, as the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire are not included.
The county has several geographical sub-regions, including the rolling chalk hills of the Lincolnshire Wolds, the Lincolnshire Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
(south-east Lincolnshire), the Carrs (similar to the Fens but in north Lincolnshire), the industrial Humber Estuary
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the ...
and North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
coast around Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
and Scunthorpe
Scunthorpe () is an industrial town and unparished area in the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire in Lincolnshire, England of which it is the main administrative centre. Scunthorpe had an estimated total population of 82,334 in 2016. A ...
, and in the south-west of the county, the Kesteven Uplands, rolling limestone hills in the district of South Kesteven
South Kesteven is a local government district in Lincolnshire, England, forming part of the traditional Kesteven division of the county. It covers Bourne, Grantham, Market Deeping and Stamford. The 2011 census reports 133,788 people at 1.4 p ...
.
History
 During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the
During pre-Roman times, most of Lincolnshire was inhabited by the Corieltauvi
The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a tribe of people living in Britain prior to the Roman conquest, and thereafter a ''civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is now the English East Midlands. They were ...
people. The language of the area at that time would have been Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, ...
, the precursor to modern Welsh. The name ''Lincoln'' was derived from Lindum Colonia.
Large numbers of Germanic speakers from continental Europe settled in the region following the withdrawal of the Romans. Though these were later identified as Angles, it is unlikely that they migrated as part of an organized tribal group. Thus, the main language of the region quickly became Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
. However, it is possible that Brittonic continued to be spoken in some communities as late as the eighth century.
Modern-day Lincolnshire is derived from the merging of the territory of the Kingdom of Lindsey with that controlled by the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian ...
borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
of Stamford. For some time the entire county was called "Lindsey", and it is recorded as such in the 11th-century ''Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
.'' Later, the name Lindsey was applied to the northern core, around Lincoln. This emerged as one of the three Parts of Lincolnshire
The three parts of the English county of Lincolnshire are or were divisions of the second-largest county in England. Similar in nature to the three ridings of Yorkshire, they existed as local government units until commencement of the Local G ...
, along with the Parts of Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former Provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
in the south-east, and the Parts of Kesteven
The Parts of Kesteven ( or ) are a traditional division of Lincolnshire, England. This division had long had a separate county administration (quarter sessions), along with the two other Parts of Lincolnshire, Lindsey and Holland.
Etymology
T ...
in the south-west, which each had separate Quarter Sessions as their county administrations.
In 1888 when county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irela ...
s were set up, Lindsey, Holland and Kesteven each received separate ones. These survived until 1974, when Holland, Kesteven, and most of Lindsey were unified into Lincolnshire. The northern part of Lindsey, including Scunthorpe
Scunthorpe () is an industrial town and unparished area in the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire in Lincolnshire, England of which it is the main administrative centre. Scunthorpe had an estimated total population of 82,334 in 2016. A ...
Municipal Borough and Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
County Borough, was incorporated into the newly formed non-metropolitan county
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a county-level entity in England that is not a metropolitan county. The counties typically have populations of 300,000 to 1.8 million. The term ''shire county'' is, however, an unoffi ...
of Humberside
Humberside () was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East Riding of Yorkshire, We ...
, along with most of the East Riding of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire t ...
.
 A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of
A local government reform in 1996 abolished Humberside. The land south of the Humber Estuary was allocated to the unitary authorities of North Lincolnshire
North Lincolnshire is a unitary authority area in Lincolnshire, England, with a population of 167,446 in the 2011 census. The borough includes the towns of Scunthorpe, Brigg, Haxey, Crowle, Epworth, Bottesford, Kirton in Lindsey and Bar ...
and North East Lincolnshire
North East Lincolnshire is a Unitary authority area with borough status in Lincolnshire, England. It borders the borough of North Lincolnshire and districts of West Lindsey and East Lindsey. The population of the district in the 2011 Census w ...
. These two areas became part of Lincolnshire for ceremonial purposes, such as the Lord-Lieutenancy, but are not covered by the Lincolnshire police; they are in the Yorkshire and the Humber
Yorkshire and the Humber is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The population in 2011 was 5,284,000 with its largest settlements being Leeds, Sheffield, Bradford, Hull, and York.
It is ...
region.
The remaining districts of Lincolnshire are Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, East Lindsey
East Lindsey is a local government district in Lincolnshire, England. The population of the district council was 136,401 at the 2011 census. The council is based in Manby. Other major settlements in the district include Alford, Wragby, Spils ...
, Lincoln, North Kesteven, South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
, South Kesteven
South Kesteven is a local government district in Lincolnshire, England, forming part of the traditional Kesteven division of the county. It covers Bourne, Grantham, Market Deeping and Stamford. The 2011 census reports 133,788 people at 1.4 p ...
, and West Lindsey. They are part of the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, L ...
region.
The area was shaken by the 27 February 2008 Lincolnshire earthquake
On 27 February 2008 at 00:56:47.8s GMT an earthquake occurred at Market Rasen, Lincolnshire. According to the British Geological Survey the earthquake registered a reading of 5.2 on the Richter scale, with its epicentre 2.5 miles (4&n ...
, reaching between 4.7 and 5.3 on the Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale —also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale—is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Francis Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 p ...
; it was one of the largest earthquakes to affect Britain in recent years.
Lincolnshire is home to Woolsthorpe Manor, birthplace and home of Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, Theology, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosophy, natural philosopher"), widely ...
. He attended The King's School, Grantham. Its library has preserved his signature, carved into a window sill when he was a youth.
Belton House
Belton House is a Grade I listed country house in the parish of Belton near Grantham in Lincolnshire, England, built between 1685 and 1688 by Sir John Brownlow, 3rd Baronet. It is surrounded by formal gardens and a series of avenues leading ...
File: Stump&Ingram.jpeg, Boston Stump
File: Gainsborough Old Hall.jpg, Gainsborough Old Hall
File: Harlaxton manor.jpg, Harlaxton Manor
Harlaxton is a village and civil parish in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. It lies on the edge of the Vale of Belvoir and just off the A607, south-west from Grantham and north-east from Melton Mowbray.
History
A ...
File: Normanby Hall, Lincs (geograph 56340).jpg, Normanby Hall
File: Tattershall Castle, 2006.jpg, Tattershall Castle
File: Thornton Abbey Gatehouse1.jpg, Thornton Abbey
File:Louth Church in 2021.jpg, St James' Church, Louth
St James' Church, Louth is the Anglican parish church of Louth in Lincolnshire, England. It is notable for having the third tallest spire in the whole of the United Kingdom and being the location of the Lincolnshire Rising.
History
The chur ...
Geography
The geographical layout of Lincolnshire is quite extensive and mostly separated by many rivers and rolling countryside. The north of the county begins from where theIsle of Axholme
The Isle of Axholme is a geographical area in England: a part of North Lincolnshire that adjoins South Yorkshire. It is located between the towns of Scunthorpe and Gainsborough, both of which are in the traditional West Riding of Lindsey, an ...
is located near the meeting points of the rivers Ouse
Ouse may refer to:
Places Rivers in England
* River Ouse, Yorkshire
* River Ouse, Sussex
* River Great Ouse, Northamptonshire and East Anglia
** River Little Ouse, a tributary of the River Great Ouse
Other places
* Ouse, Tasmania, a town in Aus ...
and Trent near to the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between ...
. From there, the southside of the Humber esturary forms the border between Lincolnshire and the East Riding of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire t ...
. From there, the south bank of the Humber Estuary where the Humber Bridge crosses the estuary at Barton upon Humber, is used primarily for the shipping ports at Immingham
Immingham is a town, civil parish and ward in the North East Lincolnshire unitary authority of England. It is situated on the south-west bank of the Humber Estuary, and is north-west from Grimsby.
The region was relatively unpopulated and und ...
, New Holland and Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
. From there, the rest of the southern bank forms the Lincolnshire Coast
The coast of Lincolnshire runs for more than down the North Sea coast of eastern England, from the estuary of the Humber (which divides it from East Yorkshire) to the marshlands of the Wash, where it meets Norfolk. This stretch of coastline has lo ...
from Cleethorpes
Cleethorpes () is a seaside town on the estuary of the Humber in North East Lincolnshire, England with a population of 38,372 in 2020. It has been permanently occupied since the 6th century, with fishing as its original industry, then develo ...
to Mablethorpe and then onto Skegness
Skegness ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the East Lindsey District of Lincolnshire, England. On the Lincolnshire coast of the North Sea, the town is east of Lincoln and north-east of Boston. With a population of 19,579 as of 2011, ...
. From Skegness, the rest of the Lincolnshire Coastline forms the sea boundary and border with Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
at the Wash. The coast then at Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
becomes the meeting point of the rivers Welland and Haven.
The rest of the county boundary runs roughly to the point of Sutton Bridge, which is separated from Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
by the River Nene
The River Nene ( or : see below) is a river in the east of England that rises from three sources in Northamptonshire.OS Explorer Map sheet 223, Northampton & Market Harborough, Brixworth & Pitsford Water. The river is about long, about of w ...
which begins to branch off from the North Sea. The border with Lincolnshire to Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to t ...
begins at Crowland
Crowland (modern usage) or Croyland (medieval era name and the one still in ecclesiastical use; cf. la, Croilandia) is a town in the South Holland district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated between Peterborough and Spalding. Crowland ...
, Market Deeping and Stamford which form the southern boundary of the county with both Peterborough
Peterborough () is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, east of England. It is the largest part of the City of Peterborough unitary authority district (which covers a larger area than Peterborough itself). It was part of Northamptonshire unti ...
, Rutland
Rutland () is a ceremonial county and unitary authority in the East Midlands, England. The county is bounded to the west and north by Leicestershire, to the northeast by Lincolnshire and the southeast by Northamptonshire.
Its greatest len ...
and briefly Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It ...
. From there, the border with Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire ...
and Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated Notts.) is a landlocked county in the East Midlands region of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The trad ...
begins at Sleaford
Sleaford is a market town and civil parish in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. Centred on the former parish of New Sleaford, the modern boundaries and urban area include Quarrington to the south-west, Holdingham to the no ...
, Grantham
Grantham () is a market and industrial town in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, situated on the banks of the River Witham and bounded to the west by the A1 road. It lies some 23 miles (37 km) south of the Lincoln a ...
, Lincoln and Gainsborough. From Gainsborough, the border with South Yorkshire
South Yorkshire is a ceremonial and metropolitan county in the Yorkshire and Humber Region of England. The county has four council areas which are the cities of Doncaster and Sheffield as well as the boroughs of Barnsley and Rotherham.
...
begins at Haxey
Haxey is a town and civil parish on the Isle of Axholme in North Lincolnshire, England. It is directly south of Epworth, south-west of Scunthorpe, north-west of Gainsborough, east of Doncaster and north-west of Lincoln, with a population of ...
and Epworth before looping back to the original north of the county near Scunthorpe
Scunthorpe () is an industrial town and unparished area in the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire in Lincolnshire, England of which it is the main administrative centre. Scunthorpe had an estimated total population of 82,334 in 2016. A ...
with East Riding of Yorkshire at the Isle of Axholme and Goole.
Bedrock in Lincolnshire features Jurassic limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
(near Lincoln) and Cretaceous chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
(north-east). The area around Woodhall Spa
Woodhall Spa is a former spa Village and civil parish in Lincolnshire, England, on the southern edge of the Lincolnshire Wolds, south-west of Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, west of Skegness, east-south-east of Lincoln, Lincolnshire, Li ...
and Kirkby on Bain
Kirkby on Bain is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It lies on the River Bain between Horncastle and Coningsby, and just west of the A153 road. Close to the north is the village of Haltham.
...
is dominated by gravel and sand. For much of prehistory, Lincolnshire was under tropical seas, and most fossils found in the county are marine invertebrates. Marine vertebrates have also been found including ichthyosaurus and plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Plesiosaurs first appea ...
.
The highest point in Lincolnshire is Wolds Top (), at Normanby le Wold
Normanby le Wold is a village and civil parish in the West Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is in the Lincolnshire Wolds, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, and about south from the town of Caistor, and north-east from the ...
. Some parts of the Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
may be below sea level. The nearest mountains are in Derbyshire.
The biggest rivers in Lincolnshire are the Trent, running northwards from Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands C ...
up the western edge of the county to the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between ...
estuary, and the Witham, which begins in Lincolnshire at South Witham and runs for through the middle of the county, eventually emptying into the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
at The Wash
The Wash is a rectangular bay and multiple estuary at the north-west corner of East Anglia on the East coast of England, where Norfolk meets Lincolnshire and both border the North Sea. One of Britain's broadest estuaries, it is fed by the riv ...
. The Humber estuary, on Lincolnshire's northern border, is also fed by the River Ouse. The Wash is also the mouth of the Welland, the Nene and the Great Ouse
The River Great Ouse () is a river in England, the longest of several British rivers called "Ouse". From Syresham in Northamptonshire, the Great Ouse flows through Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Cambridgeshire and Norfolk to drain into the W ...
.
Lincolnshire's geography is fairly varied, but consists of several distinct areas:
* Lincolnshire Wolds: area of rolling hills in the north-east of the county designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
* The Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
: dominating the south-east quarter of the county
* The Marshes
The Marshes are an American punk band, from Northampton, Massachusetts, that originally included Colin Sears (drums), Emil Busi (bass, vocals) and Steven Wardlaw (guitar).
Career
Drummer Colin Sears, who was best known for playing with Dag Nast ...
: running along the coast of the county
* Lincoln Edge or Cliff: limestone escarpment running north–south along the western half of the county
Lincolnshire's most well-known nature reserves include Gibraltar Point National Nature Reserve, Whisby Nature Park
Whisby Moor is a small moor situated close to the A46 road, west of North Hykeham, in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England.
Geography
Whisby Moor is situated geographically south-west from Lincoln city centre, with the villag ...
Local Nature Reserve, Donna Nook
Donna Nook is a point on the low-lying coast of north Lincolnshire, England, north of the village of North Somercotes and south of Grimsby. The area, a salt marsh, is used by a number of Royal Air Force stations in Lincolnshire for bombing pra ...
National Nature Reserve, RSPB Frampton Marsh and the Humberhead Peatlands National Nature Reserve. Although the Lincolnshire countryside is intensively farmed, there are many biodiverse wetland areas, as well as rare limewood forests. Much of the county was once wet fenland (see The Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
).
From bones, we can tell that animal species formerly found in Lincolnshire include woolly mammoth, woolly rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a me ...
, wild horse
The wild horse (''Equus ferus'') is a species of the genus ''Equus'', which includes as subspecies the modern domesticated horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') as well as the endangered Przewalski's horse (''Equus ferus przewalskii''). The Europea ...
, wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species i ...
and beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
. Species which have recently returned to Lincolnshire after extirpation include little egret, Eurasian spoonbill, European otter and red kite.
Governance
Lincolnshire County Council isConservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
controlled, as are six of its seven district councils (Lincoln City Council
The City of Lincoln Council is the local authority for the district of Lincoln, in the county of Lincolnshire, England. The council consists of 33 councillors, three for each of the 11 wards in the city. It is currently controlled by the Labour P ...
is controlled by Labour).
Two further districts - North East Lincolnshire
North East Lincolnshire is a Unitary authority area with borough status in Lincolnshire, England. It borders the borough of North Lincolnshire and districts of West Lindsey and East Lindsey. The population of the district in the 2011 Census w ...
and North Lincolnshire
North Lincolnshire is a unitary authority area in Lincolnshire, England, with a population of 167,446 in the 2011 census. The borough includes the towns of Scunthorpe, Brigg, Haxey, Crowle, Epworth, Bottesford, Kirton in Lindsey and Bar ...
- are unitary authorities. They were previously districts of Humberside county from 1974. In 1996, Humberside was abolished along with its county council. However some services in those districts are still shared with the East Riding of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire t ...
ceremonial county, rather than the rest of Lincolnshire.
Lincolnshire is represented by 11 Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MPs). As of the 2019 general election, all 11 constituencies are represented by the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
.
Economy
This is a chart of trend of regional gross value added of Lincolnshire at current basic prices, according to theOffice for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for ...
with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, an ...
.
: includes hunting and forestry
: includes energy and construction
: includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured
Notable businesses based in Lincolnshire include the Lincs FM Group
The Lincs FM Group was the parent company of several Independent Local Radio (ILR) stations. As of Q2 2019 the group had a combined audience of 524,000. It was based in Lincolnshire, in the UK.
History
The Lincs FM Group was formed in the earl ...
, Young's Seafood
Young's Seafood Ltd. is a British producer and distributor of frozen, fresh, and chilled seafood, supplying approximately 40% of all the fish eaten in the United Kingdom every year. It is headquartered in Grimsby, England.
The company as it is ...
, Openfield and the Lincolnshire Co-operative
Lincolnshire Co-op is an independent consumer co-operative which operates in Lincolnshire, and the surrounding counties. The society has over 220 outlets with its principal trading activity being its food stores, funeral homes, florist and cremato ...
(whose membership includes about one quarter of the population of the county).
Agriculture
 Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of
Lincolnshire has long been a primarily agricultural area, and it continues to grow large amounts of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, sugar beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and which is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet ('' Beta vulgaris''). Together ...
, and oilseed rape
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus ''subsp.'' napus''), also known as rape, or oilseed rape, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains a ...
. In south Lincolnshire, where the soil is particularly rich in nutrients, some of the most common crops include potatoes
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern United ...
, cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.&n ...
s, cauliflower
Cauliflower is one of several vegetables in the species ''Brassica oleracea'' in the genus '' Brassica'', which is in the Brassicaceae (or mustard) family. It is an annual plant that reproduces by seed. Typically, only the head is eaten – t ...
s, and onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the on ...
s. Lincolnshire farmers often break world records for crop yields. South Lincolnshire is also home to one of the UK's leading agricultural experiment station
An agricultural experiment station (AES) or agricultural research station (ARS) is a scientific research center that investigates difficulties and potential improvements to food production and agribusiness. Experiment station scientists work with ...
s, located in Sutton Bridge and operated by the Potato Council
AHDB Potatoes, previously known as the Potato Council, is a trade organisation that aims to develop and promote the potato industry in Great Britain. Previously an independent non-departmental public body, it has been a division of the Agricul ...
; Sutton Bridge Crop Storage Research engages in research for the British potato industry.
The Lincoln Longwool is a rare breed of sheep, named after the region, which was developed both for wool and mutton, at least 500 years ago, and has the longest fleece of any sheep breed. The Lincoln Red is an old breed of beef cattle, originating from the county. In the mid 20th century most farms in Lincolnshire moved away from mixed farming to specialise in arable cropping, partly due to cheap wool imports, partly to take advantage of efficiencies of scale and partly because the drier land on the eastern side of England is particularly suitable for arable cropping.
Mechanization
Mechanization is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text a machine is defined as follows:
In some fields, mechanization includes the ...
around 1900 greatly diminished the number of workers required to operate the county's relatively large farms, and the proportion of workers in the agricultural sector dropped substantially during this period. Several major engineering companies developed in Lincoln, Gainsborough and Grantham
Grantham () is a market and industrial town in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, situated on the banks of the River Witham and bounded to the west by the A1 road. It lies some 23 miles (37 km) south of the Lincoln a ...
to support those changes. Among these was Fosters of Lincoln, which built the first tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful ...
, and Richard Hornsby & Sons of Grantham. Most such industrial companies left during late 20th-century restructuring.
Today, immigrant
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, ...
workers, mainly from new member states of the European Union in Central and Eastern Europe, comprise a large component of the seasonal agricultural workforce, particularly in the south of the county. Here more labour-intensive crops are produced, such as small vegetables and cut flowers. This seasonal influx of migrant labour occasionally causes tension between the migrant workforce and local people, in a county which had been relatively unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. Agricultural training is provided at Riseholme College
Riseholme College is a Further Education, Further and Higher Education college in Lincolnshire, specialising in land-based subjects such as Agriculture, Equine and Animal Management.
It is a part of Bishop Burton College and is based across tw ...
and in 2016 the University of Lincoln
, mottoeng = Freedom through wisdom
, established = 1861 – Hull School of Art1905 – Endsleigh College1976 – Hull College1992 – University of Humberside1996 – University of Lincolnshire and Humberside2001 � ...
opened the Lincoln Institute for Agri-Food Technology.
Politics
Services and retail
According to an Intra-governmental Group on Geographic Information (IGGI) study in 2000, the town centres were ranked by area thus (including North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire areas): * Lincoln *Grantham
Grantham () is a market and industrial town in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, situated on the banks of the River Witham and bounded to the west by the A1 road. It lies some 23 miles (37 km) south of the Lincoln a ...
*Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
*Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Scunthorpe
Scunthorpe () is an industrial town and unparished area in the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire in Lincolnshire, England of which it is the main administrative centre. Scunthorpe had an estimated total population of 82,334 in 2016. A ...
(equal)
* Spalding
* Stamford
*Skegness
Skegness ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the East Lindsey District of Lincolnshire, England. On the Lincolnshire coast of the North Sea, the town is east of Lincoln and north-east of Boston. With a population of 19,579 as of 2011, ...
* Louth
*Sleaford
Sleaford is a market town and civil parish in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. Centred on the former parish of New Sleaford, the modern boundaries and urban area include Quarrington to the south-west, Holdingham to the no ...
* Gainsborough
* Brigg
*Cleethorpes
Cleethorpes () is a seaside town on the estuary of the Humber in North East Lincolnshire, England with a population of 38,372 in 2020. It has been permanently occupied since the 6th century, with fishing as its original industry, then develo ...
* Bourne
* Horncastle and Mablethorpe (equal)
Public services
Education
Lincolnshire is one of the few counties in the UK that still uses the 11-plus to decide who may attendgrammar school
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
. As a result, many towns in Lincolnshire have both a grammar school and a secondary modern school. Lincolnshire's rural character means that some larger villages also have primary schools and are served by buses to nearby high schools.
Lincoln itself, however, is primarily non-selective, as is the area within a radius of about seven miles. In this area, almost all children attend comprehensive school
A comprehensive school typically describes a secondary school for pupils aged approximately 11–18, that does not select its intake on the basis of academic achievement or aptitude, in contrast to a selective school system where admission is re ...
s, though it is still possible to opt into the 11-plus system. This gives rise to the unusual result that those who pass the Eleven plus can attend a Grammar School outside the Lincoln Comprehensive area, but those who do not pass still attend a (partly non-selective) Comprehensive school.
Transport
 Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by
Being on the economic periphery of England, Lincolnshire's transport links are poorly developed compared with many other parts of the United Kingdom. The road network in the county is dominated by single carriageway
A single carriageway (British English) or Undivided highway (American English) is a road with one, two or more lanes arranged within a one carriageway with no central reservation to separate opposing flows of traffic. A single-track road has a s ...
A roads
A roads may be
*motorways or freeways, usually where the local word for motorway begins with A (for example, ''Autobahn'' in German; ''Autostrada'' in Italian).
* main roads or highways, in a system where roads are graded A, B and sometimes lower c ...
and local roads (B roads) as opposed to motorways
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
and dual carriageways – the administrative county of Lincolnshire is one of the few UK counties without a motorway, and until several years ago, it was said that there was only about of dual carriageway in the whole of Lincolnshire. The M180 motorway passes through North Lincolnshire, splitting into two dual carriageway trunk roads to the Humber Bridge and Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
, and the A46 is now dual carriageway between Newark-on-Trent
Newark-on-Trent or Newark () is a market town and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district in Nottinghamshire, England. It is on the River Trent, and was historically a major inland port. The A1 road bypasses the town on the line ...
and Lincoln.
The low population density of the county means that the number of railway stations and train services is very low considering the county's large area. Many of the county's railway stations were permanently closed following the Beeching Report of 1963. The most notable reopening has been the line and two stations between Lincoln and Sleaford
Sleaford is a market town and civil parish in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. Centred on the former parish of New Sleaford, the modern boundaries and urban area include Quarrington to the south-west, Holdingham to the no ...
, which reopened within months of the Beeching closure. Most other closed lines in the county were long ago lifted and much of the trackbed has returned to agricultural use.
Prior to 1970, a through train service operated between Cleethorpes
Cleethorpes () is a seaside town on the estuary of the Humber in North East Lincolnshire, England with a population of 38,372 in 2020. It has been permanently occupied since the 6th century, with fishing as its original industry, then develo ...
and London King's Cross
King's Cross railway station, also known as London King's Cross, is a passenger railway terminus in the London Borough of Camden, on the edge of Central London. It is in the London station group, one of the busiest stations in the United Kin ...
via Louth, Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Peterborough
Peterborough () is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, east of England. It is the largest part of the City of Peterborough unitary authority district (which covers a larger area than Peterborough itself). It was part of Northamptonshire unti ...
. The part of this line in Grimsby is now the A16 road
This is a list of roads designated A16. Roads entries are sorted in the countries alphabetical order.
* A16 highway (Australia), a road connecting Port Adelaide and the Adelaide Hills
* A16 motorway (Belgium), a road connecting Mons and Tournai ...
, preventing reinstatement as a railway line, and a small section of the line is now the Lincolnshire Wolds Railway
The Lincolnshire Wolds Railway (LWR) is a heritage railway based at Ludborough station, near Louth, Lincolnshire, England and the only standard gauge steam railway in Lincolnshire open to the public. The line is part of the original Great North ...
, with an extension towards Louth in progress.
A daily through train service operated between Cleethorpes and London King's Cross via Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
, Market Rasen and Lincoln Central
Lincoln railway station (previously Lincoln Central) serves the city of Lincoln in Lincolnshire, England. The station is owned by Network Rail and managed by East Midlands Railway. East Midlands Railway provides the majority of services from th ...
until the late 1980s. The ''Humberlincs Executive'', as the service was known, was operated by an InterCity 125, but was discontinued following the electrification of the East Coast Main Line
The East Coast Main Line (ECML) is a electrified railway between London and Edinburgh via Peterborough, Doncaster, York, Darlington, Durham and Newcastle. The line is a key transport artery on the eastern side of Great Britain running b ...
. Passengers now have to change trains at Newark North Gate when travelling to and from London. However, the East Coast Main Line passes through the western edge of the county and one can catch direct trains to London from Grantham
Grantham () is a market and industrial town in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, situated on the banks of the River Witham and bounded to the west by the A1 road. It lies some 23 miles (37 km) south of the Lincoln a ...
.

East Midlands Railway
Abellio East Midlands Limited, trading as East Midlands Railway (EMR), is a train operating company in England, owned by Abellio, and is the current operator of the East Midlands franchise.
History
In March 2017, the Department for Transport ...
and Northern Trains
Northern Trains, branded as Northern, (legally Northern Trains Limited) is a publicly owned train operating company in England. It is owned by DfT OLR Holdings for the Department for Transport (DfT), after the previous operator Arriva Rail N ...
. London North Eastern Railway
London North Eastern Railway (LNER) is a British train operating company. It is owned by the DfT OLR Holdings for the Department for Transport (DfT). The company's name echoes that of the London and North Eastern Railway, one of the Big Fou ...
and CrossCountry
CrossCountry (legal name XC Trains Limited) is a train operating company in the United Kingdom owned by Arriva UK Trains, operating the Cross Country franchise.
The CrossCountry franchise was restructured by the Department for Transport (DfT ...
have services which pass through the county, with London North Eastern Railway frequently passing and stopping at Grantham on the East Coast Main Line and a service every other hour to Lincoln, while CrossCountry trains stop at Stamford on their way between Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
and Stansted Airport. Stations along the Humber are served by TransPennine Express services between Manchester Airport
Manchester Airport is an international airport in Ringway, Manchester, England, south-west of Manchester city centre. In 2019, it was the third busiest airport in the United Kingdom in terms of passenger numbers and the busiest of those ...
and Cleethorpes. One of the most infrequent services in the UK is in Lincolnshire: the Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire ...
- Gainsborough Central-Cleethorpes line has passenger trains only on a Saturday, with three trains in both directions. This line is, however, used for freight.
On 22 May 2011 East Coast started a Lincoln-London service, initially one train a day each way, and there is a northbound service on a Sunday. This was increased in 2019 to a service every two hours. East Midlands Railway also run a daily (Mon-Sat) service each way between Lincoln and London St Pancras, though this is a stopping service which takes around three hours via Nottingham
Nottingham ( , locally ) is a city and unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east of Sheffield and north-east of Birmingham. Nottingham has links to the legend of Robi ...
, compared to London North Eastern Railway's service to London King's Cross which takes around 1 hour 50 minutes.
The only airport in Lincolnshire is Humberside Airport, near Brigg. East Midlands Airport
East Midlands Airport is an international airport in the East Midlands of England, close to Castle Donington in northwestern Leicestershire, between Loughborough (), Derby () and Nottingham (); Leicester is () to the south and Lincoln () ...
the main airport servicing the East Midlands is within travelling distance of the county. Doncaster Sheffield Airport near Doncaster
Doncaster (, ) is a city in South Yorkshire, England. Named after the River Don, it is the administrative centre of the larger City of Doncaster. It is the second largest settlement in South Yorkshire after Sheffield. Doncaster is situated in ...
is within travelling distance of much of Lincolnshire.
The county's biggest bus companies are Stagecoach Grimsby-Cleethorpes
Stagecoach Grimsby-Cleethorpes is a subdivision of Stagecoach East Midlands that operates buses in and around North East Lincolnshire, England, serving a population of over 150,000. It runs town services in its main hubs of Grimsby and Cleethorpe ...
(formerly Grimsby-Cleethorpes Transport) and Stagecoach in Lincolnshire, (formerly Lincolnshire Road Car). There are several smaller bus companies, including Brylaine of Boston, and Hornsby's of Scunthorpe.
A Sustrans
Sustrans is a United Kingdom-based walking, wheeling and cycling charity, and the custodian of the National Cycle Network.
Its flagship project is the National Cycle Network, which has created of signed cycle routes throughout the United K ...
cycle route runs from Lincoln to Boston in the south of the county.
Health care
TheUnited Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust
United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust is an NHS trust which runs County Hospital Louth, Lincoln County Hospital, Pilgrim Hospital in Boston, Skegness and District Hospital, and Grantham and District Hospital.
The trust established the Path Li ...
is one of the largest trusts in the country, employing almost 4,000 staff and with an annual budget of over £200 million. The north of the county is served by thNorthern Lincolnshire and Goole Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Some of the larger hospitals in the county include: *
Diana Princess of Wales
Diana, Princess of Wales (born Diana Frances Spencer; 1 July 1961 – 31 August 1997) was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of King Charles III (then Prince of Wales) and mother of Princes William and Harry. Her ac ...
Hospital, Grimsby
*Scunthorpe General Hospital
Scunthorpe General Hospital is the main hospital for North Lincolnshire. It is situated on Church Lane in the west of Scunthorpe, off Kingsway (the A18), and north of the railway.
Until the 1970s, it was known as Scunthorpe and District War ...
* Boston Pilgrim Hospital
*Lincoln County Hospital
Lincoln County Hospital is a large district general hospital on the eastern edge of north-east Lincoln, England. It is the largest hospital in Lincolnshire, and offers the most comprehensive services, in Lincolnshire. It is managed by the Unite ...
Since April 1994, Lincolnshire has had an Air Ambulance service
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to definitive care. ...
.
The air ambulance is stationed at RAF Waddington near Lincoln and can reach emergencies in Lincolnshire within 25 minutes. An A&E hospital is only 10 minutes away by helicopter from any accident in Lincolnshire.
Drainage
Separately to the commercial water companies the low-lying parts of the county are drained by various internal drainage boards, such as thBlack Sluice Internal Drainage Board
, or th
Welland and Deepings Internal Drainage Board
Towns and villages
In terms of population, the 12 biggest settlements in the county by population are: * Lincoln (Population: 97,541) *Grimsby
Grimsby or Great Grimsby is a port town and the administrative centre of North East Lincolnshire, Lincolnshire, England. Grimsby adjoins the town of Cleethorpes directly to the south-east forming a conurbation. Grimsby is north-east of L ...
(Population: 88,243)
*Scunthorpe
Scunthorpe () is an industrial town and unparished area in the unitary authority of North Lincolnshire in Lincolnshire, England of which it is the main administrative centre. Scunthorpe had an estimated total population of 82,334 in 2016. A ...
(Population: 82,334)
*Grantham
Grantham () is a market and industrial town in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, situated on the banks of the River Witham and bounded to the west by the A1 road. It lies some 23 miles (37 km) south of the Lincoln a ...
(Population: 44,580)
*Cleethorpes
Cleethorpes () is a seaside town on the estuary of the Humber in North East Lincolnshire, England with a population of 38,372 in 2020. It has been permanently occupied since the 6th century, with fishing as its original industry, then develo ...
(Population: 38,996)
*Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
(Population: 35,124)
* Spalding (Population: 34,613)
* Gainsborough (Population: 22,841)
* Stamford (Population: 19,701)
*Skegness
Skegness ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the East Lindsey District of Lincolnshire, England. On the Lincolnshire coast of the North Sea, the town is east of Lincoln and north-east of Boston. With a population of 19,579 as of 2011, ...
(Population: 19,579)
*Sleaford
Sleaford is a market town and civil parish in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. Centred on the former parish of New Sleaford, the modern boundaries and urban area include Quarrington to the south-west, Holdingham to the no ...
(Population: 17,671)
* Louth (Population, 16,419)
A small part of the Thorne Waste area of the town of Thorne in South Yorkshire, known as the Yorkshire Triangle, currently falls under North Lincolnshire.
Tourism

 The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the
The majority of tourism in Lincolnshire relies on the coastal resorts and towns to the east of the Lincolnshire Wolds. The county has some of the best-known seaside resorts in the United Kingdom, which are a major attraction to visitors from across England, especially the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, L ...
and parts of Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
. There are three main coastal resorts in Lincolnshire and several smaller village resorts.
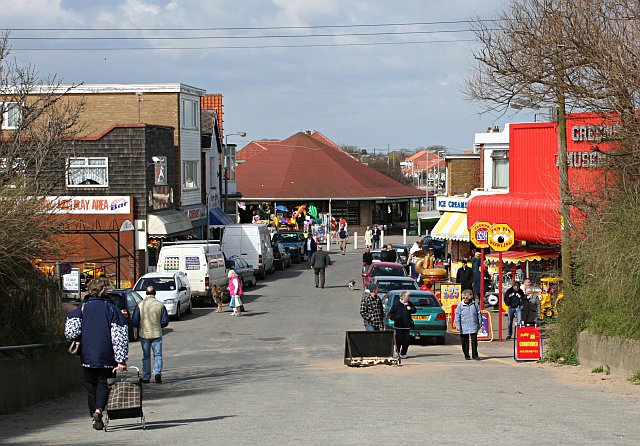
The main county seaside resort of Skegness
Skegness ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the East Lindsey District of Lincolnshire, England. On the Lincolnshire coast of the North Sea, the town is east of Lincoln and north-east of Boston. With a population of 19,579 as of 2011, ...
with its famous Jolly Fisherman mascot and famous slogan "Skegness is so bracing", together with its neighbouring large village coastal resorts of Ingoldmells and Chapel St Leonards, provides the biggest concentration of resorts along the Lincolnshire Coast
The coast of Lincolnshire runs for more than down the North Sea coast of eastern England, from the estuary of the Humber (which divides it from East Yorkshire) to the marshlands of the Wash, where it meets Norfolk. This stretch of coastline has lo ...
, with many large caravan and holiday sites. The resort offers many amusements, beaches, leisure activities and shops, as well as Butlins Skegness, Fantasy Island
''Fantasy Island'' is an American fantasy drama television series created by Gene Levitt. It aired on ABC from 1977 to 1984. The series starred Ricardo Montalbán as the mysterious Mr. Roarke and Hervé Villechaize as his assistant, Tatto ...
, Church Farm Museum, Natureland Seal Sanctuary, Skegness Stadium, Skegness Pier and several well-known local golf courses. There are good road, bus and rail links to the rest of the county.
The second largest group of resorts along the coast is the seaside town of Mablethorpe, famous for its golden sands, and the neighbouring village resorts of Trusthorpe and Sutton-on-Sea. This area also offers leisure activities and has large caravan and holiday sites. But the area is less developed, with fewer amusement arcades and nightclubs, and poorer road links to the rest of the county; but the area offers a more traditional seaside setting.
The third group of resorts includes the seaside town of Cleethorpes
Cleethorpes () is a seaside town on the estuary of the Humber in North East Lincolnshire, England with a population of 38,372 in 2020. It has been permanently occupied since the 6th century, with fishing as its original industry, then develo ...
and the large village resort of Humberston
Humberston is a village and civil parish south of Cleethorpes in North East Lincolnshire, England.
Boundary and population
The village's boundary with Cleethorpes runs along North Sea Lane and Humberston Road. Its population in the 2001 censu ...
within North East Lincolnshire. It has the Cleethorpes Coast Light Railway and Cleethorpes Pier
Cleethorpes Pier is a pleasure pier in the town of Cleethorpes, North East Lincolnshire, England. Opened in 1873 on August Bank Holiday, it originally cost £8,000 and was financed by the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (later ...
along with its local golf courses and caravan and holiday sites, whilst it is also the former site of Pleasure Island Family Theme Park. Cleethorpes is well-served by road and rail; it is easily accessible from the M180 and the TransPennine Express route to Manchester.
Nature is an attraction for many tourists: the south-east of the county is mainly fenland that attracts many species of birds, as do the national nature reserves at Gibraltar Point, Saltfleetby-Theddlethorpe and Donna Nook
Donna Nook is a point on the low-lying coast of north Lincolnshire, England, north of the village of North Somercotes and south of Grimsby. The area, a salt marsh, is used by a number of Royal Air Force stations in Lincolnshire for bombing pra ...
, which also contains a large grey seal
The grey seal (''Halichoerus grypus'') is found on both shores of the North Atlantic Ocean. In Latin Halichoerus grypus means "hook-nosed sea pig". It is a large seal of the family Phocidae, which are commonly referred to as "true seals" o ...
colony which is popular with visitors.
The market towns of the Lincolnshire Wolds Louth, Alford, Horncastle, Caistor and Spilsby
Spilsby is a market town, civil parish and electoral ward in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The town is adjacent to the main A16, east of the county town of Lincoln, north-east of Boston and north-west of Skegnes ...
are also attractive, with several having historically important buildings, such as Alford Manor House
The Manor House is a Listed building, Grade II* listed building which can be found on West street within Alford, Lincolnshire, Alford, Lincolnshire, England. It is believed to be the largest thatched manor house in England and was built to a tradi ...
, St James' Church and Bolingbroke Castle. The Wolds are popular for cycling and walking, with regular events such as the Lincolnshire Wolds Walking Festival.
The city of Lincoln is home to many tourist attractions including Lincoln Castle, Lincoln Cathedral
Lincoln Cathedral, Lincoln Minster, or the Cathedral Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Lincoln and sometimes St Mary's Cathedral, in Lincoln, England, is a Grade I listed cathedral and is the seat of the Anglican Bishop of Lincoln. Construc ...
, The Engine Shed
The Engine Shed is a music and entertainment venue at the University of Lincoln in Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England, and is operated by the University of Lincoln Students' Union. The venue comprises three areas: The Engine Shed, which is the mai ...
, Steep Hill, International Bomber Command Centre
The International Bomber Command Centre (IBCC) is a memorial and interpretation centre telling the story of Bomber Command overlooking the city of Lincoln, in England, the centre opened to the public at the end of January 2018. The official ope ...
and Guildhall and Stonebow among other historical landmarks and listed buildings. The city acts as one of the many tourist centres in the East Midlands Region.
Culture

 Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
Lincolnshire is a rural area where the pace of life is generally much slower than in much of the United Kingdom. Due to the large distances between the towns, many villages have remained very self-contained, with many still having shops, pubs, local halls and local chapels and churches, offering a variety of social activities for residents. Fishing (in the extensive river and drainage system in the fens) and shooting are popular activities. A lot of the culture in Lincoln itself is based upon its history. The Collection is an archaeological museum and art gallery in Lincoln. Lincoln Cathedral also plays a large part in Lincoln's culture, playing host to many events throughout the year, from concert recitals to indoor food markets.
A Lincolnshire tradition was that front doors were used for only three things: a new baby, a bride, and a coffin.
People
Those born in Lincolnshire are sometimes given the nickname of Yellowbellies (often spelt "Yeller Bellies", to reflect the pronunciation of the phrase by the typical Lincolnshire farmer). The origin of this term is debated, but is most commonly believed to derive from the uniform of the10th Regiment of Foot
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
(later the Lincolnshire Regiment) which featured yellow facings. For this reason, the coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
of Lincolnshire County Council is supported by two officers of the regiment.
Notable people






 The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
The following list of notable people associated with Lincolnshire is arranged chronologically by date of birth.
Born before 1701
* Guthlac of Crowland (674–715), Christian saint *Æthelhard
Æthelhard (died 12 May 805) was a Bishop of Winchester then an Archbishop of Canterbury in medieval England. Appointed by King Offa of Mercia, Æthelhard had difficulties with both the Kentish monarchs and with a rival archiepiscopate in sou ...
(8th century-805), Archbishop of Canterbury
* Hereward the Wake (c.1035-c.1072), Anglo-Saxon nobleman
* Lucy of Bolingbroke
Lucy of Bolingbroke or Lucia Thoroldsdottir of Lincoln (died circa 1136) was an Anglo-Norman heiress in central England and, later in life, countess of Chester. Probably related to the old English earls of Mercia, she came to possess extensi ...
(1074–1136), countess of Chester
* Gilbert of Sempringham (c.1085–1190), Saint and Founder of the Gilbertine Order
The Gilbertine Order of Canons Regular was founded around 1130 by Saint Gilbert in Sempringham, Lincolnshire, where Gilbert was the parish priest. It was the only completely English religious order and came to an end in the 16th century at t ...
* Aaron of Lincoln
Aaron of Lincoln (born at Lincoln, England, about 1125, died 1186) was an English Jewish financier. He is believed to have been the wealthiest man in Norman England; it is estimated that his wealth exceeded that of the King. He is first mention ...
(c.1125–1186), financier
* Hugh of Lincoln
Hugh of Lincoln, O.Cart. ( – 16 November 1200), also known as Hugh of Avalon, was a French-born Benedictine and Carthusian monk, bishop of Lincoln in the Kingdom of England, and Catholic saint. His feast is observed by Catholics on 16 Nove ...
(1135/40-1200), Bishop of Lincoln
* Stephen Langton (c.1150–1228), Archbishop of Canterbury
* Nicolaa de la Haye (c.1150–1230), landowner and administrator
* Robert Grosseteste (c.1175–1253), Bishop of Lincoln
* Berechiah de Nicole
Berechiah de Nicole also known as Benedict fil Mosse, (d. after 1270), was a thirteenth-century English Tosafist who lived at Lincoln.
Biography
He was born in the first quarter of the 13th century.Mordechai Yehudah Leib Zakash (ed.)Perushei Rab ...
(c.1210-c.1270), Tosafist
* Eleanor of Castile
Eleanor of Castile (1241 – 28 November 1290) was Queen of England as the first wife of Edward I, whom she married as part of a political deal to affirm English sovereignty over Gascony.
The marriage was known to be particularly close, and ...
(1241–1290), wife of Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vas ...
* Little Saint Hugh of Lincoln
Hugh of Lincoln (1246 – 27 August 1255) was an English boy whose death in Lincoln was falsely attributed to Jews. He is sometimes known as Little Saint Hugh or Little Sir Hugh to distinguish him from the adult saint, Hugh of Lincoln (died ...
(1246–1255), murder victim, falsely attributed to blood libel
Blood libel or ritual murder libel (also blood accusation) is an antisemitic canardTurvey, Brent E. ''Criminal Profiling: An Introduction to Behavioral Evidence Analysis'', Academic Press, 2008, p. 3. "Blood libel: An accusation of ritual mur ...
* Katherine Swynford
Katherine Swynford, Duchess of Lancaster (born Katherine de Roet, – 10 May 1403), also spelled Katharine or Catherine, was the third wife of John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster, the fourth (but third surviving) son of King Edward III.
Daughte ...
(c.1350–1403), third wife of John of Gaunt
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399) was an English royal prince, military leader, and statesman. He was the fourth son (third to survive infancy as William of Hatfield died shortly after birth) of King Edward ...
* Henry IV of England
Henry IV ( April 1367 – 20 March 1413), also known as Henry Bolingbroke, was King of England from 1399 to 1413. He asserted the claim of his grandfather King Edward III, a maternal grandson of Philip IV of France, to the Kingdom of F ...
(1367–1413), King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Baili ...
* Richard Foxe
Richard Foxe (sometimes Richard Fox) ( 1448 – 5 October 1528) was an English churchman, the founder of Corpus Christi College, Oxford. He was successively Bishop of Exeter, Bath and Wells, Durham, and Winchester, and became also Lo ...
(1458–1528), bishop and founder of Corpus Christi College, Oxford
Corpus Christi College (formally, Corpus Christi College in the University of Oxford; informally abbreviated as Corpus or CCC) is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1517, it is the 12t ...
* John Taverner (c1490-1545), composer and organist
* John Whitgift
John Whitgift (c. 1530 – 29 February 1604) was the Archbishop of Canterbury from 1583 to his death. Noted for his hospitality, he was somewhat ostentatious in his habits, sometimes visiting Canterbury and other towns attended by a retinue of 8 ...
(c.1503–1604), Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Just ...
* John Foxe
John Foxe (1516/1517 – 18 April 1587), an English historian and martyrologist, was the author of '' Actes and Monuments'' (otherwise ''Foxe's Book of Martyrs''), telling of Christian martyrs throughout Western history, but particularly the s ...
(c.1516–1587), author of ''Foxe's Book of Martyrs
The ''Actes and Monuments'' (full title: ''Actes and Monuments of these Latter and Perillous Days, Touching Matters of the Church''), popularly known as Foxe's Book of Martyrs, is a work of Protestant history and martyrology by Protestant Engli ...
''
* William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley (1520–1598), Chief Advisor to Queen Elizabeth I
* Anne Askew (1521–1546), Protestant martyr
* William Byrd (1539–1623), composer
* John Smyth (c.1554-c.1612), founder of the Baptist denomination
* Robert Tighe
Robert Tighe (or Teigh or Tyghe, sometimes misspelled Leigh), Deeping, Lincolnshire, (1562-1620) was an English cleric and linguist.
He was educated at both Oxford and Cambridge and served as Archdeacon of Middlesex (1602–1616) and Vicar of t ...
(1562–1620), cleric and linguist
* Francis Meres (1565/1566-1647), churchman and author
* Captain John Smith (1580–1631), leader of the settlement of Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James (Powhatan) River about southwest of the center of modern Williamsburg. It was ...
* John Cotton (1585–1652), clergyman
* Anne Bradstreet
Anne Bradstreet (née Dudley; March 8, 1612 – September 16, 1672) was the most prominent of early English poets of North America and first writer in England's North American colonies to be published. She is the first Puritan figure in ...
(1612–1672), poet
* John Leverett
John Leverett (baptized 7 July 1616 – 16 March 1678/79In the Julian calendar, then in use in England, the year began on 25 March. To avoid confusion with dates in the Gregorian calendar, then in use in other parts of Europe, dates between ...
(1616-1678/79), penultimate governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as th ...
* Simon Patrick (1626–1707), English theologian and bishop
* Sir Isaac Newton (1642–1726), mathematician and physicist
* John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was a self-educated English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the problem of calculating longitude while at sea.
Harrison's solution revo ...
(1693–1776), chronometer innovator
* William Stukeley
William Stukeley (7 November 1687 – 3 March 1765) was an English antiquarian, physician and Anglican clergyman. A significant influence on the later development of archaeology, he pioneered the scholarly investigation of the prehistoric ...
(1687–1765), antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifac ...
Born 1701–1850
*John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
(1703–1791) and Charles Wesley
Charles Wesley (18 December 1707 – 29 March 1788) was an English leader of the Methodist movement. Wesley was a prolific hymnwriter who wrote over 6,500 hymns during his lifetime. His works include "And Can It Be", "Christ the Lord Is Risen T ...
(1707–1788), founders of the Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
movement
* Benjamin Huntsman (1704–1776), inventor of crucible steel
* Thomas Paine
Thomas Paine (born Thomas Pain; – In the contemporary record as noted by Conway, Paine's birth date is given as January 29, 1736–37. Common practice was to use a dash or a slash to separate the old-style year from the new-style year. In th ...
(1737–1809), political activist and philosopher
* Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences.
Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James ...
(1743–1820), botanist and naturalist
* Samuel Eyles Pierce
The Rev. Samuel Eyles Pierce (23 June 1746 in Upottery, Devonshire, England – 10 May 1829 in Clapham, Surrey, England) was an English preacher, theologian, and Calvinist divine. A Dissenter from the Honiton area, Pierce was an evangelical ...
(1746–1829), preacher and theologian
* Thomas Scott (1747–1821), Bible commentator and co-founder of the Church Missionary Society
The Church Mission Society (CMS), formerly known as the Church Missionary Society, is a British mission society working with the Christians around the world. Founded in 1799, CMS has attracted over nine thousand men and women to serve as mission ...
* George Bass (1771-c.1803), explorer of Australia
* Matthew Flinders
Captain Matthew Flinders (16 March 1774 – 19 July 1814) was a British navigator and cartographer who led the first inshore circumnavigation of mainland Australia, then called New Holland. He is also credited as being the first person to ut ...
(1774–1814), navigator and cartographer
* Richard Watson (1781–1833), theologian and Methodist writer
* George Davenport (1783–1845), sailor and frontiersman
* Peter De Wint
Peter De Wint (21 January 1784 – 30 January 1849) was an English landscape painter. A number of his pictures are in the National Gallery, the Victoria and Albert Museum and The Collection, Lincoln. He died in London.
Biography
De Wint w ...
(1784–1849), landscape painter
* Pishey Thompson (1784–1862), publisher and antiquarian writer
* Sir John Franklin (1786–1847), Arctic explorer
* Andreas Kalvos (1792–1869), poet
* Christopher Wordsworth
Christopher Wordsworth (30 October 180720 March 1885) was an English intellectual and a bishop of the Anglican Church.
Life
Wordsworth was born in London, the youngest son of Christopher Wordsworth, Master of Trinity, who was the youngest b ...
(1807–1885), Bishop of Lincoln
* Alfred Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his ...
(1809–1892), poet
* Herbert Ingram (1811–1860), journalist
* Lady Charlotte Guest
Lady Charlotte Elizabeth Guest (née Bertie; 19 May 1812 – 15 January 1895), later Lady Charlotte Schreiber, was an English aristocrat who is best known as the first publisher in modern print format of the ''Mabinogion'', the earliest prose li ...
(1812–1895), businesswoman and Welsh language translator
* George Boole
George Boole (; 2 November 1815 – 8 December 1864) was a largely self-taught English mathematician, philosopher, and logician, most of whose short career was spent as the first professor of mathematics at Queen's College, Cork in ...
(1815–1864), mathematician
* William Marwood
William Marwood (1818 – 4 September 1883) was a hangman for the British government. He developed the technique of hanging known as the " long drop".
Early life
Marwood was born in 1818 in the village of Goulceby, the fifth of ten childre ...
(1818–1883), hangman
* Jean Ingelow (1820–1897), poet
* Charles Frederick Worth
Charles Frederick Worth (13 October 1825 – 10 March 1895) was an English fashion designer who founded the House of Worth, one of the foremost fashion houses of the 19th and early 20th centuries. He is considered by many fashion historians to ...
(1825–1895), fashion designer
* Edward King (1829–1910), Bishop of Lincoln
* Charlotte Alington Barnard
Charlotte Alington Pye Barnard (23 December 1830 in Louth, Lincolnshire – 30 January 1869 in Dover) was an English poet and composer of ballads and hymns, who often wrote under the pseudonym Claribel. She wrote over 100 songs as well as two vol ...
(1830–1869), ballad composer and hymn writer
* Joseph Ruston (1835–1897), engineer and manufacturer
*Arnold Rylott
Arnold Rylott (18 February 1839 – 17 April 1914) was an English cricketer who played for Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) from 1872 to 1888 and for pre-first-class Leicestershire between 1875 and 1890.
Rylott was born in Grantham, Lincolnshi ...
(1839–1914), cricketer for Marylebone Cricket Club
* George Green (Medal of Honor)
George Green (July 16, 1840 – February 10, 1898) was an American soldier who fought in the American Civil War. Green received his country's highest award for bravery during combat, the Medal of Honor. Green's medal was won for his actions in t ...
(1840–1898), Medal of Honor recipient
* Gonville Bromhead
Major Gonville Bromhead VC (29 August 1845 – 9 February 1891) was a British Army officer and recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for valour in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to members of the British armed forces. H ...
(1845–1891), Victoria Cross recipient
* Madge Kendal
Dame Madge Kendal, (born Margaret Shafto Robertson; 15 March 1848 – 14 September 1935) was an English actress of the Victorian and Edwardian eras, best known for her roles in Shakespeare and English comedies. Together with her husband, W. ...
(1848–1935), actress
Born 1851–1950
* Ethel Rudkin (1893–1985), folklorist and archaeologist *Sarah Swift
Dame Sarah Ann Swift, GBE, RRC (22 November 1854, Kirton Skeldyke, Lincolnshire – 27 June 1937, Marylebone) was an English nurse and founder in 1916 of the Royal College of Nursing, thereby introducing Nurse registration.
Early life
Swift was ...
(1854–1937), Royal College of Nursing
The Royal College of Nursing (RCN) is a registered trade union in the United Kingdom for those in the profession of nursing. It was founded in 1916, receiving its royal charter in 1928. Queen Elizabeth II was the patron until her death in 2022. ...
founder
* Frank Bramley
Frank Bramley RA (6 May 1857 – 9 August 1915) was an English post-impressionist genre painter of the Newlyn School.
Personal life
Bramley was born in Sibsey, near Boston, in Lincolnshire to Charles Bramley from Fiskerton also in Lincoln ...
(1857–1915), artist
* Adrian Woodruffe-Peacock
The Reverend (Edward) Adrian Woodruffe-Peacock (23 July 1858 – 3 February 1922) was an English clergyman and ecology, ecologist. He was an early exponent of the ecological approach to natural history recording.
Early life
Woodruffe-Peacock, ...
(1858–1922), clergyman and ecologist
* William Robertson (1860–1933), Field Marshal
* Halford Mackinder (1861–1947), geographer
* Thomas Colclough Watson
Lieutenant Colonel Thomas Colclough Watson VC (11 April 1867 – 15 June 1917) was a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth ...
(1867–1917), Victoria Cross recipient
* Cyril Bland
Cyril Herbert George Bland (23 May 1872 – 1 July 1950) was an English cricketer active from 1897 to 1904 who played for Sussex. He was born in Boston, Lincolnshire, where he was educated at Boston Grammar School, and died at Cowbridge, Boston ...
(1872–1950), cricketer
* William Tritton (1875–1946), tank developer
* Frank Pick (1878–1941), railway administrator
* Sybil Thorndike
Dame Agnes Sybil Thorndike, Lady Casson (24 October 18829 June 1976) was an English actress whose stage career lasted from 1904 to 1969.
Trained in her youth as a concert pianist, Thorndike turned to the stage when a medical problem with her ...
(1882–1976), actress
* Alfred Piccaver (1884–1958), tenor
A tenor is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the countertenor and baritone voice types. It is the highest male chest voice type. The tenor's vocal range extends up to C5. The low extreme for tenors is wide ...
* Arthur Lucan (1885–1954), part of the music hall
Music hall is a type of British theatrical entertainment that was popular from the early Victorian era, beginning around 1850. It faded away after 1918 as the halls rebranded their entertainment as variety. Perceptions of a distinction in Br ...
act Old Mother Riley
Old Mother Riley is a fictional character portrayed from about 1934 to 1954 by Arthur Lucan and from 1954 to the 1980s by Roy Rolland as part of a British music hall act.
Old Mother Riley (full comedy name: Daphne Bluebell Snowdrop Riley) is an ...
* Harold Jackson (VC)
Sergeant Harold Jackson VC (31 May 1892 − 24 August 1918) was a British Army soldier and an English recipient of the Victoria Cross (VC), the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to Brit ...
(1892–1918), Victoria Cross recipient
* Charles Richard Sharpe (1889–1963), Victoria Cross recipient
* Francis Hill (1899–1980), historian
* Frank Whittle (1907–1996), RAF officer
* John George Haigh
John George Haigh (; 24 July 1909 – 10 August 1949), commonly known as the Acid Bath Murderer, was an English serial killer convicted for the murder of six people, although he claimed to have killed nine. Haigh battered to death or shot his ...
(1909–1949), serial killer
* Douglas Bader (1910–1982), RAF flying ace
* James Cobban
Sir James Macdonald Cobban (14 September 1910 – 19 April 1999) was an English educator and headmaster, as well as a prominent lay leader in the Church of England. He was the headmaster of Abingdon School from 1947 to 1970 and is largely c ...
(1910–1999), educator and headmaster
* Chad Varah (1911–2007), priest and " The Samaritans" founder
* Ted Savage
TED may refer to:
Economics and finance
* TED spread between U.S. Treasuries and Eurodollar
Education
* ''Türk Eğitim Derneği'', the Turkish Education Association
** TED Ankara College Foundation Schools, Turkey
** Transvaal Education Depart ...
(1912–1964), footballer
* Guy Gibson
Wing Commander Guy Penrose Gibson, (12 August 1918 – 19 September 1944) was a distinguished bomber pilot in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. He was the first Commanding Officer of No. 617 Squadron, which he led in the "Dam ...
(1918–1944), bomber pilot and Victoria Cross recipient
* Steve Race (1921–2009), musician and broadcaster
* Liz Smith (1921–2016), actress
* Leslie Manser (1922–1942), bomber pilot and Victoria Cross recipient
* Brian Tierney
Brian P. Tierney (born 1957) is an American advertising and public relations executive and former publisher of ''The Philadelphia Inquirer''. Born in Upper Darby Township, Pennsylvania, Tierney is chief executive officer of Brian Communication ...
(1922–2019), historian
* Nicholas Parsons (1923–2020), radio and TV presenter
* Neville Marriner
Sir Neville Marriner, (15 April 1924 – 2 October 2016) was an English violinist and "one of the world's greatest conductors". Gramophone lists Marriner as one of the 50 greatest conductors and another compilation ranks Marriner #14 of the ...
(1924–2016), violinist and conductor
* Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. She was the first female British prime ...
(1925–2013), former Prime Minister
* Elizabeth Jennings (1926–2001), poet
* Brenda Fisher
Brenda Fisher (9 June 1927 – 2 August 2022) was an English long-distance swimmer. In 1951 she broke the women's world record for swimming the English Channel becoming a celebrity and she was given the British Sportswoman of the Year Award.
L ...
(1927–2022), swimmer
* Joan Plowright (born 1929), actress
* Jeff Hall (1929–1959), footballer
* Colin Dexter
Norman Colin Dexter (29 September 1930 – 21 March 2017) was an English crime writer known for his ''Inspector Morse'' series of novels, which were written between 1975 and 1999 and adapted as an ITV television series, ''Inspector Morse'', fr ...
(1930–2017), crime writer
* Bill Podmore (1931–1994), television producer
* Neil McCarthy (1932–1985), actor
* Frank Sargeant (born 1932), retired Anglican bishop
* Mervyn Winfield (1932–2014), cricketer
* Bernard Codd (1934–2013), motorcycle road racer
* Victor Emery (1934–2002), physicist
* Mike Pinner
Michael John Pinner (born 16 February 1934) is an English former amateur footballer who played as a goalkeeper.
Club career
Born in Boston, Pinner spent his early career with Boston Grammar School, Wyberton Rangers, Notts County, Cambridge Univ ...
(born 1934), football goalkeeper
* Bruce Barrymore Halpenny
Bruce Barrymore Halpenny (1937 – 3 May 2015) was an English military historian and author, specialising in airfields and aircraft, as well as ghost stories and mysteries. He was also a broadcaster''Framlington Times'' - Journal of the 390t ...
(born 1937), military historian and author
* Roy Axe
Royden Axe (September 1937 – 5 October 2010) was a British car designer.
Early life and career
Axe was born in Scunthorpe and attended Scunthorpe Grammar School (now St Lawrence Academy).
Axe began his career in 1959 with the Rootes Group wh ...
(1937–2010), car designer
* Barry Spikings
Barry Spikings (born 23 November 1939) is a British film producer who worked in Hollywood. Spikings is best known as a producer of the film, ''The Deer Hunter'' (1978), which won five Academy Awards.
Biography
Spikings was born in Boston, Lincoln ...
(born 1939), Hollywood producer
* John Alderton
John Alderton (born 27 November 1940) is an English actor. He is best known for his roles in '' Upstairs, Downstairs'', '' Thomas & Sarah'', '' Wodehouse Playhouse'', ''Little Miss'' (original television series), '' Please Sir!'', '' No, Hones ...
(born 1940), actor
* John Hurt (1940-2017), actor
* Jo Kendall (1940-2022), actress
* Ted Lewis (1940–1982), crime writer
* Alec Brader
Alec Brader (born 6 October 1942) is an English professional footballer, schoolteacher and youth athletics coach who played as an inside forward. Following his football career he became a schoolteacher teaching Physical Education, Geography, a ...
() (born 1942) professional footballer, schoolteacher and youth athletics coach
* Graham Oates (born 1943), footballer
* John Hargreaves (born 1944), cricketer
* Tony Jacklin (born 1944), golfer
* Roger Scruton (1944–2020), philosopher
* Graham Taylor (1944-2017), footballer, club and England national team manager.
* Chris Wright (born 1944), music industry executive and businessman
* Patricia Hodge (born 1946), actress
* Iain Matthews (born 1946), singer-songwriter and musician
* Philip Priestley (born 1946), former British diplomat
* Richard Budge
Richard John Budge (19 April 1947 – 18 July 2016) was a coal mining entrepreneur and chairman of The Coal Industry Social Welfare Organisations.
Early life
He went to Boston Grammar School in Lincolnshire. He studied Fine Arts at the Universit ...
(1947–2016), coal mining entrepreneur
* Ray Clemence (1948-2020), football goalkeeper
* Jim Broadbent
James Broadbent (born 24 May 1949) is an English actor. He won an Academy Award and a Golden Globe Award for his supporting role as John Bayley in the feature film '' Iris'' (2001), as well as winning a BAFTA TV Award and a Golden Globe for ...
(born 1949), actor
* Geoff Capes (born 1949), shotputter
* Rod Temperton (1949–2016), songwriter, record producer and musician
* Bernie Taupin
Bernard John Taupin (born 22 May 1950) is an English songwriter, singer and visual artist. He is best known for his long-term collaboration with musician Elton John, a songwriting partnership that is one of the most successful in history. Tau ...
(born 1950), songwriter
Born 1951 onwards
*Brian Bolland
Brian Bolland (; born 26 March 1951)Salisbury, Mark, ''Artists on Comic Art'' ( Titan Books, 2000) , p. 11 is a British comics artist. Best known in the United Kingdom as one of the definitive Judge Dredd artists for British comics anthology '' ...
(born 1951), comics artist
* John Ward (born 1951), footballer
* David Ward (born 1953), former Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
(MP)
* Michael Foale (born 1957), astronaut
* Jennifer Saunders (born 1958), actress and comedian
* Chris Woods (born 1959), football goalkeeper
* Lee Chapman
Lee Roy Chapman (born 5 December 1959) is an English former professional footballer who played as a striker from 1978 until 1996, in which he scored over 200 first team goals.
He is best known for spells with Stoke City, Leeds United, Sheff ...
(born 1959), footballer
* Glenn Cockerill
Glenn Cockerill (born 25 August 1959) is an English retired footballer who played more than 700 games in The Football League in a 22-year career. He was a skilled central midfielder renowned for his passing and shooting skills.
Playing career
Co ...
(born 1959), footballer
* Simon Garner (born 1959), footballer
* Alan Moulder (born 1959), record producer, mixing engineer and audio engineer
* John Cridland (born 1961), former Director-General of the Confederation of British Industry
The Confederation of British Industry (CBI) is a UK business organisation, which in total claims to speak for 190,000 businesses, this is made up of around 1,500 direct members and 188,500 non-members. The non members are represented through the 1 ...
(CBI); Chair of Transport for the North
Transport for the North (TfN) is the first statutory sub-national transport body in the United Kingdom. It was formed in 2018 to make the case for strategic transport improvements across the North of England. Creating this body represented an ...
(TfN)
* Bill Dunham (born 1961), former Deputy Commandant General of the Royal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious warfare, amphibious light infantry and also one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighti ...
* Colin McFarlane (born 1961), actor
* Stephen Sackur (born 1964), broadcaster and journalist
* Jonathan Van-Tam
Sir Jonathan Stafford Nguyen-Van-Tam (born 2 February 1964) is a British healthcare professional specialising in influenza, including its epidemiology, transmission, vaccinology, antiviral drugs and pandemic preparedness.
After hospital wor ...
(born 1964), specialist in influenza, and former Deputy Chief Medical Officer for England
In the United Kingdom, a Chief Medical Officer (CMO) is the most senior government advisor on matter relating to health. There are four CMOs in the United Kingdom who are appointed to advise their respective governments:
* His Majesty's Governm ...
* Helen Fospero (born 1966), newsreader and journalist
* Antonio Berardi
Antonio Berardi (born 1968)
''Lincolnshire Ec ...
(born 1968), fashion designer
* ''Lincolnshire Ec ...
Beverley Allitt
Beverley Gail Allitt (born 4 October 1968) is an English serial child killer who was convicted of murdering four children, attempting to murder three other children and causing grievous bodily harm to a further six.
The crimes were committed ...
(born 1968), serial killer
* Samantha Cameron (born 1971), businesswoman and wife of the former Prime Minister David Cameron
* Rae Earl
Rachel Earl (born 13 December 1971) is an English writer and broadcaster. She is best known as the author of the 2007 book ''My Fat, Mad Teenage Diary'', a collection of the diaries she wrote as a teenager which was later adapted into the E4 c ...
(born 1971), author
* Jane Taylor (born 1972), singer and musician
* Robert Webb (born 1972), actor, comedian and writer
* Jonathan Kerrigan
Jonathan Kerrigan (born 14 October 1972) is an English actor well known for various leading roles on TV including '' In The Club'', ''Casualty'', '' Heartbeat'', ''Merseybeat, The Five'' and ''Reach For The Moon''. Films include '' Diana'', ''FL ...
(born 1972), actor
* Paul Palmer (born 1974), swimmer
* Abi Titmuss
Abigail Evelyn Titmuss (born 8 February 1976) is an English actress, television personality and poker player. She is also a former glamour model and nurse.
Early life and education
Born in Newark-on-Trent in Nottinghamshire, Titmuss grew up in ...
(born 1976), poker player and glamour model
* Steve Housham (born 1976), footballer and manager
* Danny Butterfield
Daniel Paul Butterfield (born 21 November 1979) is an English former professional footballer and coach who is currently an assistant head coach at Lincoln City.
Butterfield was born in Boston, Lincolnshire and played between 1997 and 2016 as ...
(born 1979), footballer
* Colin Furze (born 1979), inventor and YouTube personality
* Kelly Adams
Kelly Diane Adams (born 16 October 1979) is an English actress. She has played leading roles in a number of British television series: Mickie Hendrie in the BBC One medical drama series ''Holby City'' (2004–2006) and ''Casualty'' (2005); Emm ...
(born 1979), actress
* Sheridan Smith
Sheridan Caroline Sian Smith OBE (born 25 June 1981) is an English actress, singer and television personality. Smith came to prominence after playing a variety of characters on sitcoms such as ''The Royle Family'' (1999–2000), ''Two Pints of ...
(born 1981), actress
* Paul Mayo
Paul Mayo (born 13 October 1981) is an English former professional footballer, who played as a defender.
He started his professional career with Lincoln City in 1999, and in 2004 after impressing in the clubs recent play-off campaigns he made ...
(born 1981), footballer
* Guy Martin (born 1981), motorcycle racer and television presenter
* Kevin Clifton (born 1982), professional dancer and actor
* Joanne Clifton (born 1983), professional dancer and actress
* Carl Hudson (born 1983), musician
* Ross Edgley (born 1985), extreme adventurer, ultra-marathon sea swimmer and author
* Nicola Roberts
Nicola Maria Roberts (born 5 October 1985) is a British pop singer. She rose to prominence in late 2002 upon winning a place in Girls Aloud, a girl group created through ITV's '' Popstars: The Rivals''. The group's success helped them win the c ...
(born 1985), singer
* Oliver Ryan (born 1985), footballer
* Luke Wright
Luke James Wright (born 7 March 1985) is an English former cricketer. He was a right-handed batsman and a right-arm medium bowler. Wright joined Sussex in 2004, having started his career at Leicestershire. He was named in England's squad for t ...
(born 1985), cricketer
* Lee Frecklington (born 1985), footballer
* Kate Haywood
Kate Emma Haywood (born 1 April 1987) is an English former elite swimmer who competed for Great Britain in the Olympics, FINA world championships, and European championships, and represented England in the Commonwealth Games. She competed predo ...
(born 1987), swimmer
* Sam Clucas (born 1990), footballer
* Georgie Twigg (born 1990), hockey player
* Sophie Wells (born 1990), para-equestrian
* Scott Williams (born 1990), darts player
* Thomas Turgoose
Thomas Aiden Turgoose (born 11 February 1992) is an English actor, best known for his role as Shaun Fields in the film ''This Is England'' (2006), a role he reprises in the ''This Is England'' TV series ''This Is England '86'' (2010), '' This Is ...
(born 1992), actor
* Eliza Butterworth
Eliza Butterworth (born 24 July 1993) is an English actress. She is best known for her role as Queen Aelswith of Wessex in the series ''The Last Kingdom'', and is nominated for best supporting actress in a TV series at the National Film Awards ...
(born 1993), actress
* Patrick Bamford
Patrick James Bamford (born 5 September 1993) is an English professional footballer who plays as a striker for club Leeds United and the England national team.
Bamford began his career at Nottingham Forest, making his debut in December 2011, ...
(born 1993), footballer
* Jack Harvey (born 1993), racing driver
* Hollie Arnold
Hollie Beth Arnold, (born 26 June 1994) is a British Disabled sports, parasport Track and field, athlete competing in category F46 (classification), F46 javelin. Although born in Grimsby, she now lives and trains in Loughborough. She represents ...
(born 1994), javelin thrower
* Ella Henderson (born 1996), singer and songwriter
* Holly Humberstone
Holly Ffion Humberstone (born 17 December 1999) is an English singer-songwriter from Grantham, England. In 2021, she signed a recording contract with Interscope and Polydor Records. Her first EP following the signings, '' The Walls Are Way To ...
(born 1999), singer and songwriter
* Ellis Chapman (born 2001), footballer
Local dialect
In common with most otherNorthern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a r ...
and Midlands dialects in England, "flat" ''a'' is preferred, i.e. over , and also traditionally in words like 'water', pronounced ''watter'' (though such a pronunciation is rarely heard nowadays). Similarly, is usually replaced by . Features rather more confined to Lincolnshire include:
* Elaboration of Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the accent traditionally regarded as the standard and most prestigious form of spoken British English. For over a century, there has been argument over such questions as the definition of RP, whether it is geo ...
English or into a complex triphthong approximating, and often transcribed ''-air-'' or ''-yair-''. For example: 'mate' ; 'beast' ; ''tates'' (potatoes) .
* An equivalent elaboration of standard English – commonly in Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angles, Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Scandinavian York, K ...
– into ''-ooa-''. For example, 'boat' .
* Insertion of an extra schwa
In linguistics, specifically phonetics and phonology, schwa (, rarely or ; sometimes spelled shwa) is a vowel sound denoted by the IPA symbol , placed in the central position of the vowel chart. In English and some other languages, it rep ...
into the standard English diphthong
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech ...
.
* Vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the ...
: 'duck' as a term of endearment or informal address, 'mardy' meaning upset or angry, ''mowt'' (pronounced like 'mout') for 'might', ''while'' as a substitute for standard English 'until', ''frit'' meaning frightened, ''grufty'' meaning dirty or disgusting, and the inimitable salutation ''now then!?'' (hello), sometimes written ''nairn'' to reflect pronunciation.
* In the north-east of the county, around Grimsby and Immingham, the nurse-square merger can be heard, as is also the case along the east coast of Yorkshire and also in Liverpool. Words that take in RP take in these areas.
Lincolnshire has its own dialect "champion", a farmer from the village of Minting called Farmer Wink (real name Robert Carlton), who has produced videos about rural life, narrated in his broad Lincolnshire accent. A resident of Woodhall Spa
Woodhall Spa is a former spa Village and civil parish in Lincolnshire, England, on the southern edge of the Lincolnshire Wolds, south-west of Horncastle, Lincolnshire, Horncastle, west of Skegness, east-south-east of Lincoln, Lincolnshire, Li ...
has published a dictionary of words once prevalent in parts of the county.
Music
Lincolnshire was historically associated with the Lincolnshire bagpipes, instruments derided as coarse and unpleasant in contemporary literature, but noted as very popular in the county. The last player, John Hunsley of Middle Manton, died in 1851, and since then the instrument has been extinct. In 1937, Percy Grainger wrote his '' Lincolnshire Posy'' for wind band. The piece is a compilation of folk songs "musical wildflowers" collected by the composer in and around the county of Lincolnshire.Food
 Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
* Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with
Lincolnshire has a number of local dishes:
* Stuffed chine – this is salted neck-chine of a pig taken from between the shoulder blades, salted for up to ten months and stuffed with parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, ...
(other ingredients are normally kept secret), and served cold.
* Haslet – a type of pork loaf, also flavoured with sage (pronounced HAYSS-let or AYSS-let in Lincolnshire but HAZ-let in many other parts of the country).
*Lincolnshire sausage
Lincolnshire sausages are a distinctive variety of pork sausage developed in and associated with the English county of Lincolnshire.
A widely available variety at most UK butchers and supermarkets, the sausage is commonly dominated by the herb ...
s – most butchers in Lincolnshire have their own secret recipe for these and a competition is held each year to judge the best sausages in the county. Traditional Lincolnshire sausages are made entirely from minced pork, stale bread crumb ( rusk is used nowadays) pepper, sage and salt. The skins should be natural casings which are made from the intestines of either sheep or pig.
* Pork pies – the same pork butchers will take a pride in their unique recipe for pork pies.
* Giblet pie.
* Mutton stuffed with oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
s.
*Plum bread – as with plum pudding
Christmas pudding is sweet dried-fruit pudding traditionally served as part of Christmas dinner in Britain and other countries to which the tradition has been exported. It has its origins in medieval England, with early recipes making use of ...
, plum refers to dried fruit
Dried fruit is fruit from which the majority of the original water content has been removed either naturally, through sun drying, or through the use of specialized dryers or dehydrators. Dried fruit has a long tradition of use dating back to th ...
, namely currants, raisins and sultanas, sometimes soaked in tea.
*Grantham Gingerbread – a hard white ginger biscuit.
*Lincolnshire Poacher cheese
Lincolnshire Poacher is a hard unpasteurised cow's milk cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usua ...
– a cheddar-style cheese produced in Alford. Lincolnshire Poacher has won numerous awards over the years including Supreme Champion at the 1996/7 British Cheese Awards and Best British Cheese at the World Cheese awards in 2001/2.
* Batemans ales – a beer brewed in Wainfleet and served in many pubs in the county and further afield.
*There are several small breweries.
*Grimsby is renowned for its fishing industry, and historically ''Grimsby Fish'' has carried a premium price. Since the decline of the fishing industry following entry to the European Economic Community in the 1970s this is no longer the case, with the majority of fish sold at the town's fish market being brought overland from other ports. However, ''Grimsby Fish'' is still a recognised ''product'', one associated with a particular area that specialises in and has expertise in a particular trade (cf ''Sheffield steel''). In 2009 smoked fish from the town was granted Protected Geographical Indication
Three European Union schemes of geographical indications and traditional specialties, known as protected designation of origin (PDO), protected geographical indication (PGI), and traditional specialities guaranteed (TSG), promote and protect nam ...
by the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
, reflecting the unique smoking methods used by certain local fish companies.
Craft Chocolatiers can be found throughout the county, such as Hansens in Folkingham. In 2013 Redstar Chocolate's ''Duffy's Venezuela Ocumare Milk'' won a gold medal as best bean-to-bar. The factory is in Cleethorpes.
Events
Every year the Lincolnshire Agricultural Society, founded in 1869, stages theLincolnshire Agricultural Show
The Lincolnshire Showground is an agricultural showground and exhibition centre in North Carlton, north of Lincoln in England. It is the chief exhibition centre of the Lincolnshire Agricultural Society, and has been used for large events such ...
. It is held on the Wednesday and Thursday of the last whole week of June at its showground at Grange de Lings, a few miles north of Lincoln on the A15 A15 or A-15 may refer to:
* A15 phases, a crystallographic structure type of certain intermetallic compounds
* A15 road, in several countries
* Antonov A-15, a Soviet glider
* British NVC community A15 (Elodea canadensis community), a British Isles ...
. The show was first held here in 1958. First held around the year 1884, it is one of the largest agricultural shows in the country, and is attended by around 100,000 people over its two days. The showground is in regular use throughout the year for a wide range of other events and functions.
Smaller local agricultural shows, such as the Heckington Show can still be found. Corby Glen
Corby Glen is a village and civil parish in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England. It is approximately south-east of the market town of Grantham and 8 miles (13 km) north west of Bourne.
History
The Church of England par ...
sheep fair has been held since 1238.
 Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The
Each year RAF Waddington is the home to the RAF International Waddington Air Show. The two-day event attracts around 150,000 people and usually takes place during the first weekend of July. Since its inception over 35 countries have participated, with aircraft from around the globe attending the Lincolnshire Base. Beginning 2017, the event will be held at nearby RAF Scampton.
On the Monday before Easter, an unusual auction takes place in Bourne to let the grazing rights of the Whitebread Meadow. Bidding takes place while two boys race toward the Queen's Bridge in Eastgate, the end of which dash is equivalent to the falling of the gavel. The whole affair dates back to the 1742 will of William Clay.
The Haxey Hood
The Haxey Hood is a traditional event in Haxey, North Lincolnshire, England. It consists of a game in which a large football scrum (the "sway") pushes a leather tube (the "hood") to one of four pubs in the town, where it remains until the follo ...
village competition takes place every January, as it has for over 700 years.
Stamford's Mid-Lent fair sees showmen converge on the town the week after Mothering Sunday, with rides and sideshows filling Broad Street, the Sheepmarket and the Meadows for a week. Stalls selling Grantham gingerbread and nougat are a traditional feature. The following week sees them in Grantham, on the way north for the SummerRoger Tuby
brings a small funfair to Bourne and then to Spalding in Spring and returns in Autumn at the end of the season. The villages of
Tetford
Tetford is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England.
History
Tetford is listed as "Tesforde" in the ''Domesday Book'', with a mill, probably on the site of the present 17th-century watermill near the c ...
and Salmonby hold an annual Scarecrow Festival in May every year.
The Belchford
Belchford is a village and civil parish in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. The village is situated approximately north of Horncastle and just to the east of the A153. At the 2011 Census, the population of the parish was ...
Downhill Challenge which is held every two years: soapbox racers race down the hill at up to 30 km/h. The turnout has been up to 1,000.
Lincoln Christmas Market, a street market held throughout the historic area of the city at the start of December, is one of the largest Christmas market
A Christmas market, also known as ''Christkindlmarkt'' (literally: ''Christ Child Market'', but the term "Christkind" usually refers to an angel-like "spirit of Christmas" rather than literally the Christ Child), ''Christkindlesmarkt'', ''Chris ...
s in Europe, attracting over 250,000 people over the four-day event. Around the same time, Christmas lights are turned on in Bourne, Sleaford, Skegness, and other towns.
Throughout the summer the Stamford Shakespeare Company
Stamford Shakespeare Company, a registered charity, is an amateur theatre company presenting an annual season of plays in June, July and August at the Rutland Open Air Theatre in the grounds of Tolethorpe Hall, Rutland.
History
The amateur S ...
presents the Bard's plays in the open-air theatre at Tolethorpe Hall
Tolethope Hall in the parish of Little Casterton, Rutland, England, PE9 4BH is a country house near Stamford, Lincolnshire at . It is now the location of the Rutland Theatre of the Stamford Shakespeare Company. The hall is a Grade II* Listed Bui ...
, which is actually in Rutland
Rutland () is a ceremonial county and unitary authority in the East Midlands, England. The county is bounded to the west and north by Leicestershire, to the northeast by Lincolnshire and the southeast by Northamptonshire.
Its greatest len ...
.
The Spalding Flower Parade was held in late spring every year between 1959 and 2013. Colourful floats decorated with tulip heads competed for a cup.
Sport
 The main sports played in the county are
The main sports played in the county are football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
, cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
and rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
. Lincolnshire does not have a high sporting profile, mainly due to the lack of facilities and high-profile football teams. Probably the most well-known sporting venues in Lincolnshire are Cadwell Park near Louth, where a round of the British Motorbike Championship is held on the last Monday of August every year and the racecourse at Market Rasen
*Three teams from Lincolnshire play in the Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional association football, football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in Association football around the wor ...
: Lincoln City play in Football League One
The English Football League One (often referred to as League One for short or Sky Bet League One for sponsorship purposes, and known as the Football League One from 2004 until 2016) is the second-highest division of the English Football Leag ...
, Grimsby Town play in Football League Two
The English Football League Two (often referred to as League Two for short or Sky Bet League Two for sponsorship purposes, and known as the Football League Two from 2004 until 2016) is the third and lowest division of the English Football L ...
. In non-league football Scunthorpe United
Scunthorpe United Football Club is a professional association football club based in the town of Scunthorpe, Lincolnshire, England. The side currently competes in the National League, the fifth tier of the English football league system. The te ...
play in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
, while Boston United
Boston United Football Club is a semi-professional association football club based in Boston, Lincolnshire, England. The club participates in the National League North, at the sixth tier of the English football league system. The club is known ...
and Gainsborough Trinity play in the Football Conference North. A meeting between any of these clubs is a Lincolnshire derby; the most prominent meeting, having happened across four of the top five tiers of English football, is Lincoln City vs Grimsby Town.
*In cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East Midlands of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea to the east. It borders Norfolk to the south-east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south-we ...
are a minor county and play in the Minor Counties Championship
The NCCA 3 Day Championship (previously the Minor Counties Cricket Championship) is a season-long competition in England and Wales that is contested by the members of the National Counties Cricket Association (NCCA), the so-called national cou ...
.
*In hockey Lindum Hockey Club play in the north of Lincoln.
* Scunthorpe Rugby Club are the most notable rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
team from Lincolnshire, and will play in the fifth level of the English league system in the 2017–18 season. Other notable teams include Market Rasen and Louth RUFC, Lincoln RFC, and Boston Rugby Club.
*Lincolnshire is home to one racecourse, at Market Rasen.
* Cadwell Park is the only motor-racing course in Lincolnshire. There is a speedway track in Scunthorpe, home of the Scunthorpe Scorpions, and stock-car racing at a stadium at Orby, near Skegness
Skegness ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the East Lindsey District of Lincolnshire, England. On the Lincolnshire coast of the North Sea, the town is east of Lincoln and north-east of Boston. With a population of 19,579 as of 2011, ...
.
*Lincolnshire has an American Football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
club, the Lincolnshire Bombers
The Lincolnshire Bombers are a British American football team based in North Hykeham, Lincolnshire, England. The team in its current form was founded in 2005. They currently play in the BAFA NFC South 2 for the 2019 season. The original team ...
, which has existed in its current guise since 2005.
*Lincolnshire is home to the UK roller derby
Roller derby is a roller skating contact sport played by two teams of fifteen members. Roller derby is played by approximately 1,250 amateur leagues worldwide, mostly in the United States.
Game play consists of a series of short scrimmages (jam ...
team, the Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Girls
Lincolnshire Bombers Roller Derby is a flat track roller derby league, based in Lincoln, England. Lincolnshire is a member of the United Kingdom Roller Derby Association (UKRDA) and the Women's Flat Track Derby Association (WFTDA).
League His ...
, which is sponsored by Motörhead
Motörhead () were an English rock band formed in London in 1975 by Lemmy (lead vocals, bass), Larry Wallis (guitar) and Lucas Fox (drums). Lemmy was also the primary songwriter and only constant member. The band are often considered a prec ...
.
Symbols
 The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "
The unofficial anthem of the county is the traditional folk song, "The Lincolnshire Poacher
"The Lincolnshire Poacher" is a traditional English folk song associated with the county of Lincolnshire, and deals with the joys of poaching. It is considered to be the unofficial county anthem of Lincolnshire. It is catalogued as Roud Folk ...
", which dates from around 1776. A version of the song was the theme for BBC Radio Lincolnshire
BBC Radio Lincolnshire is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Lincolnshire.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios near Newport Arch in Lincoln.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly aud ...
for many years.
According to a 2002 marketing campaign by the charity Plantlife, the county flower of Lincolnshire is the common dog-violet
''Viola riviniana'', the common dog-violet, is a species of flowering plant in the family Violaceae, native to Eurasia and Africa. It is also called wood violet and dog violet. It inhabits woodland edges, grassland and shady hedge banks. It is ...
.
In August 2005, BBC Radio Lincolnshire
BBC Radio Lincolnshire is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Lincolnshire.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios near Newport Arch in Lincoln.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly aud ...
and ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine launched a vote for a flag of Lincolnshire
The official flag of Lincolnshire was unveiled at five separate ceremonies across the county on 24 October 2005. The flag was chosen in a popular vote organised by BBC Radio Lincolnshire along with ''Lincolnshire Life'' magazine. The winning entr ...
to represent the county. Six competing designs were voted upon by locals and the winning submission was unveiled in October 2005. Lincoln has its own flag – St George's flag with a Fleur-de-Lys.
The Lincoln Imp
The Lincoln Imp is a grotesque on a wall inside Lincoln Cathedral, England, and it has become the symbol of the city of Lincoln. A legend tells of it being a creature sent to the cathedral by Satan, only to be turned into stone by an angel.
L ...
has symbolised cathedral, city and county for many years. In 2006 it was replaced as the brand of Lincolnshire County Council by the stylised version seen on the header herwhich has lost even the unique pose of the carving.
Media
Press
The county is home to one daily newspaper, the '' Grimsby Telegraph'' which as the name suggests, is published in the town and whose circulation area ostensibly covers North East Lincolnshire, although it reaches as far south as Louth and Alford and as west as Brigg. There are two further weekly papers which used to be published daily until 2011; the '' Lincolnshire Echo'' is published weekly from Lincoln and covers the majority of the county reaching as far north as Louth, and the ''Scunthorpe Telegraph
The ''Scunthorpe Telegraph'' is a local paid-for newspaper published and distributed weekly in Scunthorpe, England. It was launched on 8 September 1937. Prior to the ''Scunthorpe Telegraph''s launch, the town was served by the '' Grimsby Evening ...
'' which covers northern Lincolnshire. All three are ultimately owned by the Daily Mail and General Trust
Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) is a British multinational media company, the owner of the '' Daily Mail'' and several other titles. The 4th Viscount Rothermere is the chairman and controlling shareholder of the company. The head office i ...
.
There are also a number of weekly papers serving individual towns published in the county by Johnston Press
Johnston Press plc was a multimedia company founded in Falkirk, Scotland, in 1767. Its flagship titles included UK-national newspaper the '' i'', ''The Scotsman'', the ''Yorkshire Post'', the ''Falkirk Herald'', and Belfast's ''The News Letter ...
. One of these, the ''Stamford Mercury
The ''Stamford Mercury'' (also the ''Lincoln, Rutland and Stamford Mercury'', the ''Rutland and Stamford Mercury'', and the ''Rutland Mercury'') based in Stamford, Lincolnshire, England, claims to be "Britain's oldest continuously published new ...
'' claims to be Britain's oldest newspaper, although it is now a typical local weekly and no longer covers stories from the whole East Midlands as the archived copies did.
Television
With the exception of a small area to the south-west of the county, Lincolnshire is served from the Belmont transmitter, receiving programmes fromITV Yorkshire
ITV Yorkshire, previously known as Yorkshire Television and commonly referred to as just YTV, is the British television service provided by ITV Broadcasting Limited for the Yorkshire franchise area on the ITV network. Until 1974, this was prima ...
and BBC One
BBC One is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It is the corporation's flagship network and is known for broadcasting mainstream programming, which includes BBC News television bulletins, ...
Yorkshire and Lincolnshire regions.
The BBC has, since 2003, provided the area with its twelfth regional service: BBC Yorkshire and Lincolnshire, carrying a local " Look North" news programme from the main studio in Hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, with input from other studios in Lincoln and Grimsby.
ITV Yorkshire
ITV Yorkshire, previously known as Yorkshire Television and commonly referred to as just YTV, is the British television service provided by ITV Broadcasting Limited for the Yorkshire franchise area on the ITV network. Until 1974, this was prima ...
provides coverage through its evening news programme "Calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a phy ...
". Until late 2008 the station provided a separate edition for the Belmont transmitter (although it was still broadcast from Leeds). From January 2009 the area is now covered by a programme that covers the entire ITV Yorkshire region.
From 1959 to July 1974 ITV programmes were provided by Anglia Television
ITV Anglia, previously known as Anglia Television, is the ITV franchise holder for the East of England. The station is based at Anglia House in Norwich, with regional news bureaux in Cambridge and Northampton. ITV Anglia is owned and operated b ...
(although some coverage could be received from the Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The ...
-based Granada
Granada (,, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada mountains, at the c ...
and ABC Weekend). Based in Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
the company had news offices in Grimsby. Following a transmitter change ITV services were provided by Yorkshire Television. This company kept open the offices in Grimsby and opened further facilities in Lincoln, although both of these closed in the mid-1990s.
South-west Lincolnshire receives BBC East Midlands
BBC East Midlands is the BBC English Region covering Derbyshire (except High Peak, North East Derbyshire and the northern areas of the Derbyshire Dales), Leicestershire, Nottinghamshire (except Bassetlaw), Rutland, southern parts of South Kes ...
and ITV Central which are broadcast from the Waltham-on-the-Wolds Transmitting Station. Although subject to co-channel interference
Co-channel interference or CCI is crosstalk from two different radio transmitters using the same channel. Co-channel interference can be caused by many factors from weather conditions to administrative and design issues. Co-channel interferen ...
from the Waltham transmitter, a small number of households in the southern tip of the county are able to receive regional programming from BBC East and ITV Anglia
ITV Anglia, previously known as Anglia Television, is the ITV franchise holder for the East of England. The station is based at Anglia House in Norwich, with regional news bureaux in Cambridge and Northampton. ITV Anglia is owned and operated ...
.
Many villages just west of the Lincoln Edge cannot get a signal from Belmont due to shadowing and instead get their TV from Emley Moor near Huddersfield.
Radio
The area is covered by several local radio stations including: *BBC Radio Lincolnshire
BBC Radio Lincolnshire is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Lincolnshire.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios near Newport Arch in Lincoln.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly aud ...
Can be heard throughout historic Lincolnshire although its broadcast remit is the present county of Lincolnshire
* BBC Radio Humberside The counties of northern Lincolnshire that were formerly known as South Humberside
* Greatest Hits Radio Lincolnshire Grimsby, Cleethorpes and Immingham
* Heart East Peterborough and South Lincolnshire
* Lincs FM Historic Lincolnshire
*Siren FM
Siren Radio, sometimes known as Siren and formerly as Siren FM, is a community radio station based at the University of Lincoln in the United Kingdom. It broadcasts to the city of Lincoln on 107.3 FM and at its websiteOnline''
History
Launched ...
Lincoln
*Tulip Radio
Tulip Radio was the local community radio station covering the area of Spalding, Lincolnshire, England. The name was linked to Spalding's heavy involvement with the horticulture industry. The town was famous for its tulips, and used to host an ...
Spalding and South Holland
*Viking FM
Viking FM is an Independent Local Radio station based in Sheffield, England, owned and operated by Bauer as part of the Hits Radio network. It broadcasts to the East Riding of Yorkshire and Northern Lincolnshire.
As of September 2022, the s ...
Northern Lincolnshire and the East Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire t ...
, formerly the constituent areas of Humberside
Humberside () was a non-metropolitan and ceremonial county in Northern England from 1 April 1974 until 1 April 1996. It was composed of land from either side of the Humber Estuary, created from portions of the East Riding of Yorkshire, We ...
Military
Air
Because of its flat geography and low population density, Lincolnshire is an ideal place for airfields, and theAir Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of Stat ...
built prolifically with the county hosting nearly seventy separate air bases. It became known as "bomber county". Since the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
most of these airfields or stations were decommissioned, but the RAF retains a significant footprint in Lincolnshire for the air defence of the United Kingdom and aircrew training. For more information on former bases, see List of former RAF stations.
Two major front-line bases located in Lincolnshire are RAF Coningsby
Royal Air Force Coningsby or RAF Coningsby , is a Royal Air Force (RAF) station located south-west of Horncastle, and north-west of Boston, in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is a Main Operating Base of the RAF and ho ...
, which is one of only two RAF Quick Reaction Alert
Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) is state of readiness and '' modus operandi'' of air defence maintained at all hours of the day by NATO air forces. The United States usually refers to Quick Reaction Alert as 'Airspace Control Alert'.
Some non-NATO ...
(QRA) Stations in the United Kingdom and home to the Eurofighter Typhoon
The Eurofighter Typhoon is a European multinational twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter. The Typhoon was designed originally as an air-superiority fighter and is manufactured by a consortium of Airbus, BAE Systems and Leonardo ...
jet fighters, and RAF Waddington, where most of the RAF's Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance aircraft are based. Other stations in Lincolnshire include RAF Cranwell
Royal Air Force Cranwell or more simply RAF Cranwell is a Royal Air Force station in Lincolnshire, England, close to the village of Cranwell, near Sleaford. Among other functions, it is home to the Royal Air Force College (RAFC), which trai ...
, home to all Air Force Basic Officer Training for the Royal Air Force; RAF Scampton
Royal Air Force Scampton or RAF Scampton is a Royal Air Force station located adjacent to the A15 road near to the village of Scampton, Lincolnshire, and north-west of the city of Lincoln, England.
RAF Scampton stands on the site of a Fi ...
, home base to the Red Arrows
The Red Arrows, officially known as the Royal Air Force Aerobatic Team, is the aerobatics display team of the Royal Air Force based at RAF Waddington. The team was formed in late 1964 as an all-RAF team, replacing a number of unofficial team ...
Aerobatic Team and former base of the Avro Vulcan
The Avro Vulcan (later Hawker Siddeley Vulcan from July 1963) is a jet-powered, tailless, delta-wing, high-altitude, strategic bomber, which was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) from 1956 until 1984. Aircraft manufacturer A.V. Roe an ...
nuclear strike V bomber
The "V bombers" were the Royal Air Force (RAF) aircraft during the 1950s and 1960s that comprised the United Kingdom's strategic nuclear strike force known officially as the V force or Bomber Command Main Force. The three models of strategic ...
-force; RAF Barkston Heath
Royal Air Force Barkston Heath or RAF Barkston Heath is a Royal Air Force station near Grantham, Lincolnshire, England.
RAF Barkston Heath has the Naval Element of No. 3 Flying Training School RAF (No. 3 FTS) which, for a period between app ...
, a training airfield; and minor bases such as RAF Kirton in Lindsey
Royal Air Force Kirton in Lindsey or more simply RAF Kirton in Lindsey is a former Royal Air Force station located north of Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England.
It's an RAF habit (inherited from the RFC) to name its bases after the nearest railw ...
, RAF Donna Nook
Donna Nook Air Weapons Range is a Ministry of Defence air weapons range in East Lindsey, Lincolnshire, England. The range, as well as a now defunct airfield and radar station, were previously operated by the Royal Air Force and known as RAF Donn ...
and RAF Digby.
Lincolnshire is also home to two active RAF and NATO-allied air weapons training bombing ranges, located along The Wash
The Wash is a rectangular bay and multiple estuary at the north-west corner of East Anglia on the East coast of England, where Norfolk meets Lincolnshire and both border the North Sea. One of Britain's broadest estuaries, it is fed by the riv ...
and north Lincolnshire coastline— RAF Holbeach active since 1926 (originally part of the former RAF Sutton Bridge station) and Donna Nook
Donna Nook is a point on the low-lying coast of north Lincolnshire, England, north of the village of North Somercotes and south of Grimsby. The area, a salt marsh, is used by a number of Royal Air Force stations in Lincolnshire for bombing pra ...
. The RAF Wainfleet
RAF Wainfleet was a Royal Air Force weapons range on The Wash on the east coast of England near Wainfleet, in the civil parish of Friskney, although the north-east part of the range was in Wainfleet St Mary. Other ranges nearby include RAF Ho ...
range was decommissioned in 2010.
Army
The Army runs Sobraon Barracks, home of 160 (Lincoln) Squadron, Royal Logistic Corps (RLC), as well as Prince William of Gloucester Barracks, Grantham, home to the national specialist logistics units. In November 2016 theMinistry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in state ...
announced that the Grantham site would close in 2020.
Places of interest
See also
*''Outline of England
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to England:
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Its 55,268,100 inhabitants account for more than 84% of the total UK population, while its mainland te ...
''
*Custos Rotulorum of Lincolnshire – List of Keepers of the Rolls for Lincolnshire
*Earl of Lincoln is a title that has been created eight times in the Peerage of England and is currently represented.
*High Sheriff of Lincolnshire
*Lincolnshire (UK Parliament constituency) List of MPs for the Lincolnshire constituency
*Lincs Wind Farm
*Lists
**List of bridges and viaducts in Lincolnshire
**List of churches in Lincolnshire
**List of civil parishes in Lincolnshire
**List of companies in Lincolnshire – Both current and former
**List of forests and woodland in Lincolnshire
**List of monastic houses in Lincolnshire
**List of museums in Lincolnshire
**List of parliamentary constituencies in Lincolnshire
**List of places in Lincolnshire
**List of public art in Lincolnshire
**List of Roman Sites in Lincolnshire, List of Roman sites in Lincolnshire
**List of schools in Lincolnshire
**List of watermills in Lincolnshire
**List of Waterways in Lincolnshire, List of waterways in Lincolnshire
**List of windmills in Lincolnshire
*Lord Lieutenant of Lincolnshire
*Stamford Senior Youth Theatre
*1185 East Midlands earthquake
References
Bibliography
*External links
Lincolnshire County Council website
Lindcolne Skipfierde
Lincolnshire'
Anglo-Saxon, Viking and Norman
re-enactment and living history group
Lincolnshire Show official website
Images of Lincolnshire
at the English Heritage Archive {{Authority control Lincolnshire, Non-metropolitan counties East Midlands NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union Counties of England established in antiquity