LGBT rights in Ceuta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights in Spain have undergone several significant changes over the last decades to become some of the most advanced in the world. As of the 2020s, Spain is considered one of the most culturally liberal and LGBT-friendly countries in the world.
Among ancient Romans in Spain, sexual interaction between men was viewed as commonplace and marriages between men occurred during the early Roman Empire, but a law against homosexuality was promulgated by Christian emperors Constantius II and Constans, and Roman moral norms underwent significant changes leading up to the 4th century. Laws against sodomy were later established during the legislative period. They were first repealed from the Spanish Code in 1822, but changed again along with societal attitudes towards homosexuality during the Spanish Civil War and

 In 1822, the Kingdom of Spain's first penal code was adopted and same-sex sexual intercourse was legalised. In 1928, under the dictatorship of Miguel Primo de Rivera, the offense of "habitual homosexual acts" was recriminalised in Spain.
In 1822, the Kingdom of Spain's first penal code was adopted and same-sex sexual intercourse was legalised. In 1928, under the dictatorship of Miguel Primo de Rivera, the offense of "habitual homosexual acts" was recriminalised in Spain.
 In 1994, the ''Ley de Arrendamientos Urbanos'' was passed, giving same-sex couples some recognition rights. Registries for same-sex couples were created in all of Spain's 17 autonomous communities: Catalonia (1998),
In 1994, the ''Ley de Arrendamientos Urbanos'' was passed, giving same-sex couples some recognition rights. Registries for same-sex couples were created in all of Spain's 17 autonomous communities: Catalonia (1998),
 Spanish law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, gender identity, HIV status, and "any other personal or social condition or circumstance.” in employment and provision of goods and services. A comprehensive anti-discrimination bill, called the Zerolo Law, was passed by the Cortes Generales on 30 June 2022.
Prior to the Zerolo law, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation had been illegal in the country since 1995 but employment discrimination on the basis of gender identity was not banned nationwide. The first autonomous community to ban such discrimination was
Spanish law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, gender identity, HIV status, and "any other personal or social condition or circumstance.” in employment and provision of goods and services. A comprehensive anti-discrimination bill, called the Zerolo Law, was passed by the Cortes Generales on 30 June 2022.
Prior to the Zerolo law, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation had been illegal in the country since 1995 but employment discrimination on the basis of gender identity was not banned nationwide. The first autonomous community to ban such discrimination was
 In November 2006, the Zapatero Government passed a law that allows transgender people to register under their preferred sex in public documents such as birth certificates, identity cards and passports without undergoing prior surgical change. However a professional diagnosis is still required. The law came into effect on 17 March 2007. In July 2019, the
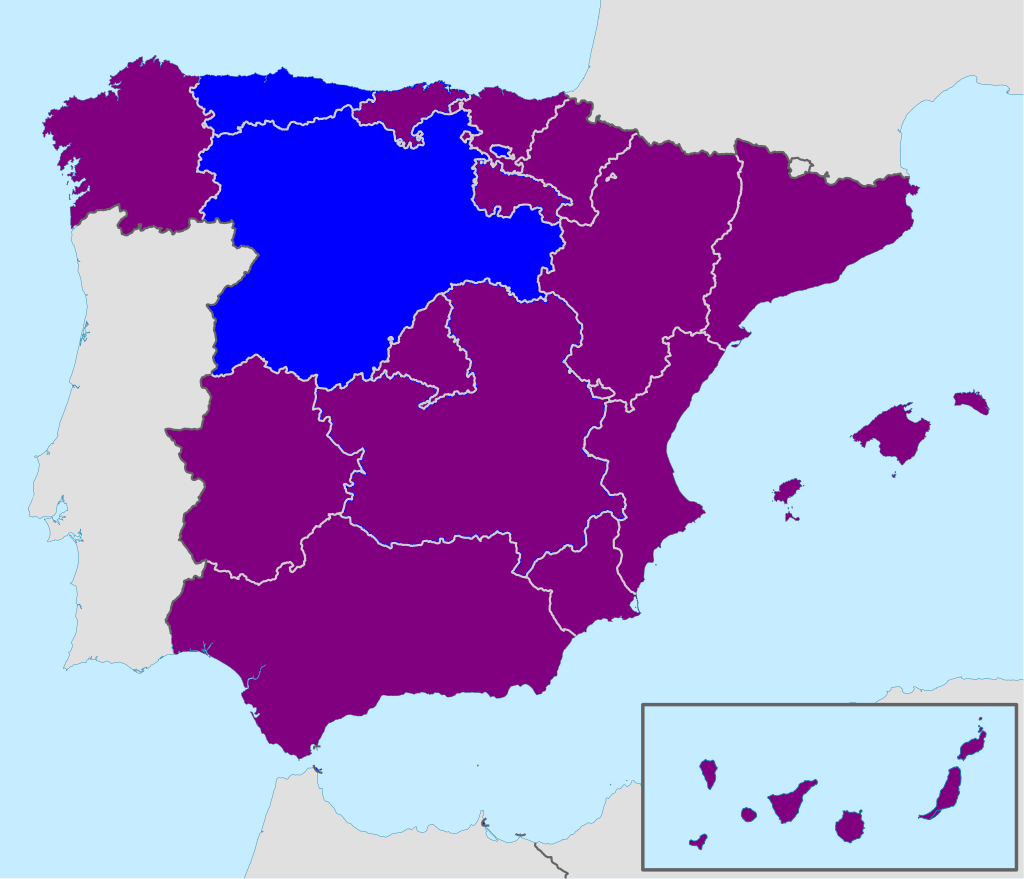
In November 2006, the Zapatero Government passed a law that allows transgender people to register under their preferred sex in public documents such as birth certificates, identity cards and passports without undergoing prior surgical change. However a professional diagnosis is still required. The law came into effect on 17 March 2007. In July 2019, the  Many of Spain's autonomous communities have their own laws which allow trans people to change their legal gender identity. Catalonia (since 2014), Andalucía (since 2014), Valencia (since 2014), Extremadura (since 2015), Balearic Islands (since 2016), Madrid (since 2016), Murcia (since 2016), Navarre (since 2017), Aragón (since 2018), Basque Country (since 2019), Cantabria (since 2020), Canary Islands (since 2021), La Rioja (since 2022), and Castilla-La Mancha (since 2022) allow trans people to self-declare their gender identity. In Galicia, a gender change requires a medical diagnosis.
Intersex infants in Spain may undergo medical interventions to have their sex characteristics altered. Human rights groups consider these surgeries unnecessary and, they argue, should only be performed if the applicant consents to the operation (i.e. has reached the age of 18). Andalusia,
Many of Spain's autonomous communities have their own laws which allow trans people to change their legal gender identity. Catalonia (since 2014), Andalucía (since 2014), Valencia (since 2014), Extremadura (since 2015), Balearic Islands (since 2016), Madrid (since 2016), Murcia (since 2016), Navarre (since 2017), Aragón (since 2018), Basque Country (since 2019), Cantabria (since 2020), Canary Islands (since 2021), La Rioja (since 2022), and Castilla-La Mancha (since 2022) allow trans people to self-declare their gender identity. In Galicia, a gender change requires a medical diagnosis.
Intersex infants in Spain may undergo medical interventions to have their sex characteristics altered. Human rights groups consider these surgeries unnecessary and, they argue, should only be performed if the applicant consents to the operation (i.e. has reached the age of 18). Andalusia,
 The autonomous community of Madrid approved a conversion therapy ban in July 2016. The ban went into effect on 1 January 2017, and applies to medical, psychiatric, psychological and religious groups. In August 2016, an LGBT advocacy group brought charges under the new law against a Madrid woman who offered conversion therapy. In September 2019, the woman was fined 20,000 euros.
Murcia approved a conversion therapy ban in May 2016, which came into effect on 1 June 2016. Unlike the other bans, the Murcia ban only applies to
The autonomous community of Madrid approved a conversion therapy ban in July 2016. The ban went into effect on 1 January 2017, and applies to medical, psychiatric, psychological and religious groups. In August 2016, an LGBT advocacy group brought charges under the new law against a Madrid woman who offered conversion therapy. In September 2019, the woman was fined 20,000 euros.
Murcia approved a conversion therapy ban in May 2016, which came into effect on 1 June 2016. Unlike the other bans, the Murcia ban only applies to
/ref> In January 2019,


 The first gay organisation in Spain was the Spanish Homosexual Liberation Movement (MELH, '' Movimiento Español de Liberación Homosexual'', '' Moviment Espanyol d'Alliberament Homosexual''), which was founded in 1970 in Barcelona. The group also established centers in Madrid and Bilbao. It disbanded in 1973 because of police pressure, but following Franco's death, several members of the group formed the ''Front d'Alliberament Gai de Catalunya'' (FAGC) in 1975 to continue campaigning for LGBT rights. Several more groups were established, including the ''Euskal Herriko Gay-Les Askapen Mugimendua'' in the Basque Country, the ''Frente Homosexual de Acción Revolucionaria'' in Madrid, and the ''Coordinadora de Frentes de Liberación Homosexual de Estado Español'' (COFLHEE), all three in 1977. On 28 June 1977, the FAGC organised the first gay demonstration in Spain in the city of Barcelona with about 4,000 to 5,000 participants. Police repressed the event, with several arrests and injuries. Exactly one year later, the ''Frente de Liberación Homosexual de Castilla'' held a demonstration in Madrid with about 10,000 people. Disagreement within these groups caused many to shut down; many members advocated a more "radical" movement with public demonstrations and many felt the organizations had failed to properly address or campaign for the rights of lesbians and bisexuals. LGBT groups saw an important landmark moment in 1979 with the decriminalisation of homosexuality.
During the 1980s, several LGBT groups and magazines were launched in various cities. The ''
The first gay organisation in Spain was the Spanish Homosexual Liberation Movement (MELH, '' Movimiento Español de Liberación Homosexual'', '' Moviment Espanyol d'Alliberament Homosexual''), which was founded in 1970 in Barcelona. The group also established centers in Madrid and Bilbao. It disbanded in 1973 because of police pressure, but following Franco's death, several members of the group formed the ''Front d'Alliberament Gai de Catalunya'' (FAGC) in 1975 to continue campaigning for LGBT rights. Several more groups were established, including the ''Euskal Herriko Gay-Les Askapen Mugimendua'' in the Basque Country, the ''Frente Homosexual de Acción Revolucionaria'' in Madrid, and the ''Coordinadora de Frentes de Liberación Homosexual de Estado Español'' (COFLHEE), all three in 1977. On 28 June 1977, the FAGC organised the first gay demonstration in Spain in the city of Barcelona with about 4,000 to 5,000 participants. Police repressed the event, with several arrests and injuries. Exactly one year later, the ''Frente de Liberación Homosexual de Castilla'' held a demonstration in Madrid with about 10,000 people. Disagreement within these groups caused many to shut down; many members advocated a more "radical" movement with public demonstrations and many felt the organizations had failed to properly address or campaign for the rights of lesbians and bisexuals. LGBT groups saw an important landmark moment in 1979 with the decriminalisation of homosexuality.
During the 1980s, several LGBT groups and magazines were launched in various cities. The ''
Fiona Govan, Madrid; 4 March 2013; '' The Daily Telegraph'' He also stated that same-sex marriages should not have the same protection under the law as opposite-sex ones, eight years after same-sex marriage was legalized. Among the countries studied by the

 At the beginning of the 20th century, Spanish authors, like Jacinto Benavente,
At the beginning of the 20th century, Spanish authors, like Jacinto Benavente,
 Early representation of homosexuality in Spanish cinema was difficult due to censorship by the Franco regime. The first movie that shows any kind of homosexuality, very discreetly, was ''Diferente'', a musical from 1961, directed by Luis María Delgado. Up to 1977, if homosexuals appeared at all, it was to ridicule them as the "funny effeminate faggot".
During the
Early representation of homosexuality in Spanish cinema was difficult due to censorship by the Franco regime. The first movie that shows any kind of homosexuality, very discreetly, was ''Diferente'', a musical from 1961, directed by Luis María Delgado. Up to 1977, if homosexuals appeared at all, it was to ridicule them as the "funny effeminate faggot".
During the
 During Franco's dictatorship, musicians seldom made any reference to homosexuality in their songs or in public speeches. An exception was the '' copla'' singer Miguel de Molina, openly homosexual and against Franco. De Molina fled to Argentina after being brutally tortured and his shows prohibited. Another exception was Bambino, whose homosexuality was known in flamenco circles. Some songs from Raphael, as "Qué sabe nadie" ("What does anyone know") or "Digan lo que digan" ("Whatever they say"), have frequently been interpreted in a gay light.
In 1974, the folk rock band Cánovas, Rodrigo, Adolfo y Guzmán talked about a lesbian relationship in the song "María y Amaranta" ("María and Amaranta"), that surprisingly was not censored. During the transition to democracy, the duo Vainica Doble sung about the fight of a gay man against the prejudices of his own family in the song "El rey de la casa" ("The king of the house").
Singer-songwriter
During Franco's dictatorship, musicians seldom made any reference to homosexuality in their songs or in public speeches. An exception was the '' copla'' singer Miguel de Molina, openly homosexual and against Franco. De Molina fled to Argentina after being brutally tortured and his shows prohibited. Another exception was Bambino, whose homosexuality was known in flamenco circles. Some songs from Raphael, as "Qué sabe nadie" ("What does anyone know") or "Digan lo que digan" ("Whatever they say"), have frequently been interpreted in a gay light.
In 1974, the folk rock band Cánovas, Rodrigo, Adolfo y Guzmán talked about a lesbian relationship in the song "María y Amaranta" ("María and Amaranta"), that surprisingly was not censored. During the transition to democracy, the duo Vainica Doble sung about the fight of a gay man against the prejudices of his own family in the song "El rey de la casa" ("The king of the house").
Singer-songwriter
 Several openly gay politicians have served in public office in Spain. One of the most prominent gay politicians is
Several openly gay politicians have served in public office in Spain. One of the most prominent gay politicians is
 Sports is traditionally a difficult area for LGBT visibility. Recently though, there have been professional sportswomen and sportsmen who have come out. These include
Sports is traditionally a difficult area for LGBT visibility. Recently though, there have been professional sportswomen and sportsmen who have come out. These include
Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War ...
's regime.
Throughout the late-20th century, the rights of the LGBT community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity became legal once again in 1979 with an equal age of consent
The age of consent is the age at which a person is considered to be legally competent to consent to sexual acts. Consequently, an adult who engages in sexual activity with a person younger than the age of consent is unable to legally claim ...
to heterosexual intercourse. After recognising unregistered cohabitation between same-sex couples countrywide and registered partnerships in certain cities and communities since 1994 and 1997, Spain legalised both same-sex marriage and adoption rights for same-sex couples in 2005. Transgender individuals can change their legal gender without the need for sex reassignment surgery or sterilisation. Discrimination in employment regarding sexual orientation has been banned nationwide since 1995. A broader law prohibiting discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity in employment and provision of goods and services nationwide was passed in 2022. LGBT people are allowed to serve in the military and MSMs can donate blood since 2005.
Spain has been recognised as one of the most culturally liberal and LGBT-friendly countries in the world and LGBT culture has had a significant role in Spanish literature, music, cinema and other forms of entertainment as well as social issues and politics. Public opinion on homosexuality is noted by pollsters as being overwhelmingly positive, with a study conducted by the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
in 2013 indicating that more than 88 percent of Spanish citizens accepted homosexuality, making it the most LGBT-friendly of the 39 countries polled. LGBT visibility has also increased in several layers of society such as the Guardia Civil, army, judicial, and clergy. However, in other areas such as sports, the LGBT community remains marginalised. Spanish film directors such as Pedro Almodóvar have increased awareness regarding LGBT tolerance in Spain among international audiences. In 2007, Madrid hosted the annual Europride celebration and hosted WorldPride in 2017. The cities of Barcelona and Madrid also have a reputation as two of the most LGBT-friendly cities in the world. Gran Canaria is also known worldwide as an LGBT tourist destination.
LGBT history in Spain

Roman Empire
The Romans brought, as with other aspects of their culture, their sexual morality to Spain. Romans were open-minded about their relationships, and sexuality among men was commonplace. Among the Romans, bisexuality seems to have been perceived as the ideal. Edward Gibbon mentions, of the first fifteen emperors, "Claudius was the only one whose taste in love was entirely correct" – the implication being that he was the only one not to take men or boys as lovers. Gibbon based this on Suetonius' factual statement that "He had a great passion for women, but had no interest in men." Suetonius and the other ancient authors actually used this against Claudius. They accused him of being dominated by these same women and wives, of being uxorious, and of being awomaniser
Womanizer may refer to:
* "Womanizer" (term), a promiscuous heterosexual man
* "Womanizer" (song), a 2008 song by Britney Spears
* "Womanizer", a 1977 song by Blood, Sweat & Tears from '' Brand New Day''
* ''Womanizer'', a 2004 album by Absolute ...
.
Marriages between men occurred during the early Roman Empire. These marriages were condemned by law in the Theodosian Code of Christian emperors Constantius and Constans on 16 December 342. Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and ...
, a first-century poet, born and educated in Bílbilis (now Calatayud in Aragon, Spain), but spent most of his life in Rome, attests to same-sex marriages between men during the early Roman Empire. He also characterised Roman life in epigram
An epigram is a brief, interesting, memorable, and sometimes surprising or satirical statement. The word is derived from the Greek "inscription" from "to write on, to inscribe", and the literary device has been employed for over two mille ...
s and poems. In a fictitious first person, he talks about anal and vaginal penetration, and about receiving fellatio from both men and women. He also attests to adult men who played passive roles with other men. He describes, for example, the case of an older man who played the passive role and let a younger slave occupy the active role.
The first recorded marriage between two men occurred during the reign of Emperor Nero, who is reported to have married two other men on different occasions. Roman Emperor Elagabalus is also reported to have done the same. Emperors who were universally praised and lauded by the Romans such as Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Trâiānus Hadriānus ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania B ...
and Trajan openly had male lovers, although it is not recorded whether or not they ever married their lovers. Hadrian's lover, Antinuous, received deification upon his death and numerous statues exist of him today, more than any other non-imperial person.
Among the conservative upper Senatorial classes, status was more important than the person in any sexual relationship. Thus, Roman citizens could penetrate non-citizen males, plebeian (or low class) males, male slaves, boys, eunuchs and male prostitutes just as easily as young female slaves, concubines and female prostitutes. However, no upper class citizen would allow himself to be penetrated by another man, regardless of age or status. He would have to play the active role in any sexual relationship with a man. There was a strict distinction between an active homosexual (who would have sex with men and women) and a passive homosexual (who was regarded as servile and effeminate). This morality was in fact used against Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
, whose allegedly passive sexual interactions with the King of Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Pa ...
, Nicomedes Nicomedes may refer to:
*Nicomedes (mathematician), ancient Greek mathematician who discovered the conchoid
*Nicomedes of Sparta, regent during the youth of King Pleistoanax, commanded the Spartan army at the Battle of Tanagra (457 BC)
*Saint Nicom ...
, were commented everywhere in Rome. However, many people in the upper classes ignored such negative ideas about playing a passive role, as is proved by the actions of the Roman emperors Nero and Elagabalus.
In contrast to the Greeks, evidence for homosexual relationships between men of the same age exists for the Romans. These sources are diverse and include such things as the Roman novel '' Satyricon'', graffiti and paintings found at Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
as well as inscriptions left on tombs and papyri found in Egypt. Generally speaking, however, a kind of pederasty (not unlike the one that can be found among the Greeks) was dominant in Rome. It is important to note, though, that even among heterosexual relationships, men tended to marry women much younger than themselves, usually in their early teens.
Lesbianism was also known, in two forms. Feminine women would have sex with adolescent girls: a kind of female pederasty, and masculine women followed male pursuits, including fighting, hunting and relationships with other women.
The first law against same-sex marriage was promulgated by the Christian emperors Constantius II and Constans. Nevertheless, the Christian emperors continued to collect taxes on male prostitutes until the reign of Anastasius (491–581). In the year 390, Christian emperors Valentinian II, Theodosius I and Arcadius declared homosexual sex to be illegal and those who were guilty of it were condemned to be burned alive in front of the public. Christian Emperor Justinian I (527–565) made homosexuals a scapegoat for problems such as "famines, earthquakes, and pestilences".
As a result of this, Roman morality changed by the 4th century. For example, Ammianus Marcellinus harshly condemned the sexual behaviour of the Taifali, a tribe located between the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
and the Black Sea which practiced the Greek-style pederasty. In 342, emperors Constans and Constantius II introduced a law to punish passive homosexuality (possibly by castration), to which later in 390 Theodosius I would add death by fire to all passive homosexuals that worked in brothel
A brothel, bordello, ranch, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in sexual activity with prostitutes. However, for legal or cultural reasons, establishments often describe themselves as massage parlors, bars, strip clubs, body rub par ...
s. In 438, this law was expanded to include all passive homosexuals, in 533 Justinian punished any homosexual act with castration and death by fire, and in 559 this law became even more strict.
Three reasons have been given for this change of attitude. Procopius, historian at Justinian's court, considered that behind the laws were political motivations, as they allowed Justinian to destroy his enemies and confiscate their properties, and were hardly efficient stopping homosexuality between ordinary citizens. The second reason, and perhaps the more important one, was the rising influence of Christianity in the Roman society, including the Christian paradigm about sex serving solely for reproduction purposes. Colin Spencer, in his book ''Homosexuality: A History'', suggests the possibility that a certain sense of self-preservation in the Roman society after suffering some epidemic such as the Black fever increased the reproductive pressure in individuals. This phenomenon would be combined with the rising influence of Stoicism
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy founded by Zeno of Citium in Athens in the early 3rd century Common Era, BCE. It is a philosophy of personal virtue ethics informed by its system of logic and its views on the natural world, asser ...
in the Empire.
Until the year 313, there was no common doctrine about homosexuality in Christianity, but it is the mistaken belief that Paul had already condemned it as ''contra natura'', though he had no exegetical reason for doing so:
Eventually, the Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical per ...
created a literary ''corpus'' in which homosexuality and sex were condemned most energetically, fighting against a common practice in that epoch's society. On the other hand, homosexuality was identified with heresy, not only because of the pagan traditions, but also due to the rites of some gnostic sects or Manichaeism, which, according to Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Af ...
, practised homosexual rites.
Kingdom of the Visigoths (418–718)
The Germanic peoples had little tolerance for both passive homosexuality and women, whom they considered on the same level as "imbeciles" and slaves, and glorified the warrior camaraderie between men. However, there are reports in Scandinavian countries of feminine and transvestite pastors, and the Nordic gods, the Æsir, including Thor andOdin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered Æsir, god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, v ...
, obtained arcane recognition drinking semen.
In the Early Middle Ages, attitudes toward homosexuality remained constant. There are known cases of homosexual behaviour which did not receive punishment, even if they were not accepted. For example, King Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
on his baptism day confessed to having relationships with other men; or Alcuin, an Anglo-Saxon poet whose verses and letters contain homoerotism.
One of the first legal corpus that considered male homosexuality a crime in Europe was the '' Liber Iudiciorum'' (or ''Lex Visigothorum''). The Visigoth law included in that code (L. 3,5,6) punished sodomy with banishment
Exile is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons and peoples suf ...
and castration
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceut ...
. Within the term "castration" were included all ''sexual crimes'' considered ''unnatural'', such as male homosexuality, anal sex
Anal sex or anal intercourse is generally the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure.Sepages 270–271for anal sex information, anpage 118for information about the clitoris. ...
(heterosexual and homosexual) and zoophilia. Lesbianism was considered sodomy only if it included phallic aids.
It was King Chindasuinth (642–653) who dictated that the punishment for homosexuality should be castration. Such a harsh measure was unheard of in Visigoth laws, except for the cases of Jews practising circumcision. After being castrated, the culprit was given to the care of the local bishop, who would then banish him. If he was married, the marriage was declared void, the dowry was returned to the woman and any possessions distributed among his heirs.
Islamic Spain (718–1492)
The Muslims who invaded and successfully conquered the peninsula in the early 8th century had a noticeably more open attitude to homosexuality than their Visigothic predecessors. In the book ''Medieval Iberia: An Encyclopedia'', Daniel Eisenberg describes homosexuality as "a key symbolic issue throughout the Middle Ages in Iberia", stating that in al-Andalus, homosexual pleasures were indulged in by the intellectual and political elite. There is significant evidence for this. Rulers, such asAbd-ar-Rahman III
ʿAbd al-Rahmān ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn al-Ḥakam al-Rabdī ibn Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Raḥmān al-Dākhil () or ʿAbd al-Rahmān III (890 - 961), was the Umayyad Emir of Córdoba from 912 to 92 ...
, Al-Hakam II, Hisham II
Hisham II or Abu'l-Walid Hisham II al-Mu'ayyad bi-llah (, Abū'l-Walīd Hishām al-Muʾayyad bi-ʾllāh) (son of Al-Hakam II and Subh of Cordoba) was the third Umayyad Caliph of Spain, in Al-Andalus from 976 to 1009, and 1010–13.
Reign
In 9 ...
, and Al Mu'tamid ibn Abbad
Al-Mu'tamid Muhammad ibn Abbad al-Lakhmi ( ar, المعتمد محمد ابن عباد بن اسماعيل اللخمي; reigned c. 1069–1091, lived 1040–1095), also known as Abbad III, was the third and last ruler of the Taifa of Sevi ...
, openly kept male harems, to the point that, to ensure an offspring, a girl had to be disguised as a boy to seduce Al-Hakam II. It was said that male prostitutes charged higher fees and had a higher class of clientele than did their female counterparts. Evidence can also be found in the repeated criticisms of Christians and especially the abundant poetry of homosexual nature. References to both pederasty and love between adult males have been found. Although homosexual practices were never officially condoned, prohibitions against them were rarely enforced, and usually there was not even a pretense of doing so. Sexual activity between men was not seen as a form of identity. Very little is known about lesbian sexual activity during this period.
Kingdom of Spain (1492–1812)
By 1492, the last Islamic kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula, the Emirate of Granada, was invaded and conquered by theCrown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
and the Crown of Aragon. This marked the Christian unification of the Iberian peninsula and the return of Catholic morality. By the early sixteenth century, royal codes decreed death by burning for sodomy and was punished by civil authorities. It fell under the jurisdiction of the Inquisition only in the territories of Aragon, when, in 1524, Clement VII, in a papal brief, granted jurisdiction over sodomy to the Inquisition of Aragon, whether or not it was related to heresy. In Castile, cases of sodomy were not adjudicated, unless related to heresy. The tribunal of Zaragoza distinguished itself for its severity in judging these offences: between 1571 and 1579 more than 100 men accused of sodomy were prosecuted and at least 36 were executed; in total, between 1570 and 1630 there were 534 trials and 102 executions. This does not include, however, those normally executed by the secular authorities.
First French Empire
In 1812, Barcelona wasannexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
into the First French Empire and incorporated into the First French Empire as part of the department Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
(later ''Bouches-de-l'Èbre–Montserrat''), where it remained until it was returned to Spain in 1814. During that time same-sex sexual intercourse was legal in Barcelona.
Kingdom of Spain (1814–1931)
 In 1822, the Kingdom of Spain's first penal code was adopted and same-sex sexual intercourse was legalised. In 1928, under the dictatorship of Miguel Primo de Rivera, the offense of "habitual homosexual acts" was recriminalised in Spain.
In 1822, the Kingdom of Spain's first penal code was adopted and same-sex sexual intercourse was legalised. In 1928, under the dictatorship of Miguel Primo de Rivera, the offense of "habitual homosexual acts" was recriminalised in Spain.
Second Spanish Republic
In 1932, same-sex sexual intercourse was again legalised in Spain.Francoist Spain
At the start of the Spanish Civil War in 1936, the gay poet Federico García Lorca was executed by Nationalist forces. Between 1936 and 1939, right-wing, Catholic forces led byGeneral Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War and thereafter ruled over Spain from 193 ...
took over Spain, and Franco was dictator of the country until his death in 1975. Legal reforms in 1944 and 1963 punished same-sex sexual intercourse as "scandalous public behavior". In 1954, vagrancy laws were modified to declare that homosexuals are "a danger", equating homosexuality with proxenetism ( procuring). The text of the law declared that the measures "are not proper punishments, but mere security measures, set with a doubly preventive end, with the purpose of collective guarantee and the aspiration of correcting those subjects fallen to the lowest levels of morality. This law is not intended to punish, but to correct and reform". However, the way the law was applied was clearly punitive and arbitrary: police would often use the vagrancy laws against suspected political dissenters, using homosexuality (actual or perceived) as a way to go around the judicial guarantees.
However, in other cases, the harassment of gay, bisexual and transgender people was clearly directed at their sexual mores, and homosexuals (mostly men) were sent to special prisons called ''galerías de invertidos'' ("galleries of inverts"). Thousands of homosexual men and women were jailed, put in camps, or locked up in mental institutions under Franco's dictatorship
Francoist Spain ( es, España franquista), or the Francoist dictatorship (), was the period of Spanish history between 1939 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death in 1975, Spani ...
, which lasted for 36 years until his death in 1975. The year Franco died, his regime began to give way to the current constitutional democracy, but in the early 1970s gay prisoners were overlooked by political activism in favour of more "traditional" political dissenters. Some gay activists deplored the fact that reparations were not made until 2008.
However, in the 1960s, a clandestine gay scene began to emerge in Barcelona, and in the countercultural centers of Ibiza
Ibiza (natively and officially in ca, Eivissa, ) is a Spanish island in the Mediterranean Sea off the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. It is from the city of Valencia. It is the third largest of the Balearic Islands, in Spain. Its l ...
and Sitges (a town in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia, that remains a highly popular gay tourist destination). In the late 1960s and the 1970s, a body of gay literature emerged in Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
. Attitudes in greater Spain began to change with the return to democracy after Franco's death through a cultural movement known as La Movida Madrileña. This movement, along with growth of the gay rights movement in the rest of Europe and the Western world, was a large factor in making Spain today one of Europe's most socially tolerant places.
In 1970, Spanish law provided for a three-year prison sentence for those accused of same-sex sexual intercourse.
Kingdom of Spain (1975–present)
Same-sex sexual intercourse was again legalised in Spain in 1979, and is its status today. In December 2001, the Spanish Parliament pledged to wipe clean the criminal records of thousands of gay and bisexual men and women who were jailed during Franco's regime. The decision meant that sentences for homosexuality and bisexuality were taken off police files. Further reparations were made in 2008.Law regarding same-sex sexual activity
Same-sex sexual acts were lawful in Spain from 1822 to 1954, with the exception of the offence of "unusual or outrageous indecent acts with same-sex persons" between the years 1928 and 1932. However, some homosexuals were arrested in the days of the Second Spanish Republic under the ''Ley de Vagos y Maleantes'' ("Vagrants and Common Delinquents Law"). Homosexual acts were made unlawful duringFrancisco Franco
Francisco Franco Bahamonde (; 4 December 1892 – 20 November 1975) was a Spanish general who led the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalist forces in overthrowing the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War ...
's time in power, first by an amendment to the aforementioned law in 1954, and later by the ''Ley de Peligrosidad y Rehabilitación Social'' ("Law on Danger and Social Rehabilitation") in 1970. In 1979, the Adolfo Suárez Government reversed the prohibition of homosexual acts.
A new penal code was introduced in Spain in 1995 which specified an age of consent
The age of consent is the age at which a person is considered to be legally competent to consent to sexual acts. Consequently, an adult who engages in sexual activity with a person younger than the age of consent is unable to legally claim ...
of 12 for all sexual acts, but this was raised to 13 in 1999 and to 16 in 2015.
Recognition of same-sex relationships
 In 1994, the ''Ley de Arrendamientos Urbanos'' was passed, giving same-sex couples some recognition rights. Registries for same-sex couples were created in all of Spain's 17 autonomous communities: Catalonia (1998),
In 1994, the ''Ley de Arrendamientos Urbanos'' was passed, giving same-sex couples some recognition rights. Registries for same-sex couples were created in all of Spain's 17 autonomous communities: Catalonia (1998), Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
(1999), Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
(2000), Castile-La Mancha (2000), Valencia (2001), the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
(2001), Madrid (2001), Asturias (2002), Andalusia (2002), Castile and León
Castile and León ( es, Castilla y León ; ast-leo, Castiella y Llión ; gl, Castela e León ) is an autonomous community in northwestern Spain.
It was created in 1983, eight years after the end of the Francoist regime, by the merging of the ...
(2002), Extremadura (2003), the Basque Country
Basque Country may refer to:
* Basque Country (autonomous community), as used in Spain ( es, País Vasco, link=no), also called , an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain (shown in pink on the map)
* French Basque Country o ...
(2003), the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
(2003), Cantabria (2005), Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
(2008), La Rioja (2010) and Murcia (2018), and in both autonomous cities; Ceuta (1998) and Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was par ...
(2008). These registries grant unmarried couples some benefits, but the effect is mainly symbolic.
Same-sex marriage and adoption were legalised by the Cortes Generales under the administration of Socialist Prime Minister José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero (; born 4 August 1960) is a Spanish politician and member of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE). He was the Prime Minister of Spain being elected for two terms, in the 2004 and 2008 general elections ...
in 2005, making Spain the third country in the world to do so.
Soon after the same-sex marriage bill became law, a member of the Guardia Civil, a military-police force, married his lifelong partner, prompting the organisation to allow same-sex partners to cohabitate in the barracks, the first police force in Europe to accommodate a same-sex partner in a military installation.
Adoption and parenting
Adoption by same-sex couples
Same-sex adoption is the adoption of children by same-sex couples. It may take the form of a joint adoption by the couple, or of the adoption by one partner of the other's biological child ( stepchild adoption).
Joint adoption by same-sex cou ...
has been legal nationwide in Spain since July 2005. Some of Spain's autonomous communities had already legalised such adoptions beforehand, notably Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
in 2000, the Basque Country
Basque Country may refer to:
* Basque Country (autonomous community), as used in Spain ( es, País Vasco, link=no), also called , an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain (shown in pink on the map)
* French Basque Country o ...
in 2003, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
in 2004, Catalonia in 2005 and Cantabria in 2005. Furthermore, in Asturias, Andalusia and Extremadura, same-sex couples could jointly begin procedures to temporarily or permanently take children in care.
Since 2015, married lesbian couples can register both their names on their child(ren)'s certificates. This does not apply to cohabiting couples or couples in de facto unions, where the non-biological mother must normally go through an adoption process to be legally recognized as the child's mother.
Lesbian couples and single women may access in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and assisted reproductive treatments. Prior to 2019, this was mostly in the private sector, where such treatments were much more expensive (around 7,500 euros for IVF). In 2018, following reports that Spain had one of the lowest birth rates in Europe (with reportedly more deaths than births in 2017), measures extending free reproductive treatments for lesbians and single women to public hospitals were announced. The measures took effect in January 2019. Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an arrangement, often supported by a legal agreement, whereby a woman agrees to delivery/labour for another person or people, who will become the child's parent(s) after birth. People may seek a surrogacy arrangement when pregnan ...
is prohibited in Spain regardless of sexual orientation, though surrogacy arrangements undertaken overseas are usually recognized.
In November 2021, an executive order was signed to allow free IVF treatment for single women and women in same-sex relationships throughout Spain. A bill has been formally introduced to implement the decision permanently.
Discrimination protections
 Spanish law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, gender identity, HIV status, and "any other personal or social condition or circumstance.” in employment and provision of goods and services. A comprehensive anti-discrimination bill, called the Zerolo Law, was passed by the Cortes Generales on 30 June 2022.
Prior to the Zerolo law, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation had been illegal in the country since 1995 but employment discrimination on the basis of gender identity was not banned nationwide. The first autonomous community to ban such discrimination was
Spanish law prohibits discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation, gender identity, HIV status, and "any other personal or social condition or circumstance.” in employment and provision of goods and services. A comprehensive anti-discrimination bill, called the Zerolo Law, was passed by the Cortes Generales on 30 June 2022.
Prior to the Zerolo law, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation had been illegal in the country since 1995 but employment discrimination on the basis of gender identity was not banned nationwide. The first autonomous community to ban such discrimination was Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
in 2009. The Basque Country
Basque Country may refer to:
* Basque Country (autonomous community), as used in Spain ( es, País Vasco, link=no), also called , an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain (shown in pink on the map)
* French Basque Country o ...
followed suit in 2012, Andalusia, the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, Catalonia, and Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
in 2014, Extremadura in 2015, Madrid, Murcia, and the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
in 2016, Valencia in April 2017, and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
in January 2019., Cantabria in November 2020 La Rioja in February 2022 and Castilla-La Mancha in May 2022.
Article 4(2) of the ''Workers' Statute'' ( es, link=no, Estatuto de los trabajadores); gl, Estatuto dos traballadores; eu, Langileen Estatutua; ast, Estatutu de los trabayadores reads as follows:
Discrimination in the provisions of goods and services based on sexual orientation and gender identity was not banned nationwide either. The aforementioned autonomous communities all ban such discrimination within their anti-discrimination laws. Discrimination in health services and education based on sexual orientation and gender identity has been banned in Spain since 2011 and 2013, respectively.
Ten autonomous communities also ban discrimination based on sex characteristics, thereby protecting intersex people from discrimination. These autonomous communities are Galicia (2014), Catalonia (2014), Extremadura (2015), the Balearic Islands (2016), Madrid (2016), Murcia (2016), Valencia (2017), Navarre (2017), Andalusia (2018), and Aragon (2019).
Bias-motivated speech and violence
Hate speech on the basis of both sexual orientation and gender identity has been banned since 1995. Additionally, under the country'shate crime
A hate crime (also known as a bias-motivated crime or bias crime) is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership (or perceived membership) of a certain social group or racial demograph ...
law, crimes motivated by the victim's sexual orientation or gender identity, amongst other categories, result in additional legal penalties.
The Secretary of State for Security
The Secretary of State for Security (SES) of Spain is the second-highest-ranking official in the Ministry of the Interior.
The SES is appointed by the Monarch with the advise of the Minister of the Interior. The Secretariat of State for Security ...
reported that instances of violence against LGBT people decreased 4% in 2018. This contrasted with figures from other sources. The ''Observatorio Madrileño'' reported a 7% increase in anti-LGBT violence in Madrid, while the Observatory Against Homophobia of Catalonia () reported a 30% increase in the first few months of 2019.
Since January 2019, teachers and students in Madrid are obliged to report cases of bullying, including against LGBT students.
Military service
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people may serve openly in theSpanish Armed Forces
The Spanish Armed Forces are in charge of guaranteeing the sovereignty and independence of the Kingdom of Spain, defending its territorial integrity and the constitutional order, according to the functions entrusted to them by the Constitution o ...
.
Transgender and intersex rights
 In November 2006, the Zapatero Government passed a law that allows transgender people to register under their preferred sex in public documents such as birth certificates, identity cards and passports without undergoing prior surgical change. However a professional diagnosis is still required. The law came into effect on 17 March 2007. In July 2019, the
In November 2006, the Zapatero Government passed a law that allows transgender people to register under their preferred sex in public documents such as birth certificates, identity cards and passports without undergoing prior surgical change. However a professional diagnosis is still required. The law came into effect on 17 March 2007. In July 2019, the Constitutional Court of Spain
The Constitutional Court ( es, Tribunal Constitucional) is the supreme interpreter of the Spanish Constitution, with the power to determine the constitutionality of acts and statutes made by any public body, central, regional, or local in Spa ...
declared that prohibiting transgender minors from accessing legal gender changes is unconstitutional. The court ruled that transgender minors who are "mature enough" may register their new sex on their identity cards, and struck down the article of the 2007 legislation that limited this possibility only to those over 18. The first minor to change his legal gender did so in December 2019.
A new bill was approved in June 2022 by the Spanish government that would grant permission for people above 16 to change their gender without restrictions, and for people between 12 and 16 under certain conditions.Teenagers between 14 and 16 could do so by requesting approval from their parents (or from a judge if they cannot agree); teenagers between 12 and 14 would require judicial authorisation. The bill was promoted by the left-wing Unidas Podemos
Unidas Podemos (), formerly called Unidos Podemos () and also known in English as United We Can, is a democratic socialist electoral alliance formed by Podemos, United Left, and other left-wing to far-left parties in May to contest the 2016 Spa ...
party, but its approval was initially delayed because the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party opposed, questioning the bill's treatment of transgender teenagers and expressing concerns that it may cause gender inequality. The dispute was resolved when Carmen Calvo, the then Vice President of the government, left the Executive. Lawmakers have yet to approve the bill.
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
, the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
, Extremadura, Madrid, Murcia, Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, and Valencia ban the use of medical interventions on intersex children.
In April 2019, the Catalan Department of Labor, Social Affairs and Families announced that official documents in Catalonia would include the option "non-binary" alongside male and female.
Self-identification national bill
In December 2022, by a vote of 188-150 passed a bill within the Spanish Congress of Deputies to allow transgender individuals "self-identification" on birth certificates at a national level. The bill is awaiting a vote within theSpain Senate
The Senate ( es, Senado) is the upper house of the Cortes Generales, which along with the Congress of Deputies – the lower chamber – comprises the Parliament of the Kingdom of Spain. The Senate meets in the Palace of the Senate in Madrid.
T ...
.
Blood donation
Gay and bisexual men are allowed to donate blood in Spain. For anyone regardless of sexual orientation, the deferral period is six months following the last sexual encounter.Conversion therapy
health professional
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker (sometimes abbreviated HCW) is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician (suc ...
s.
Valencia banned the use of conversion therapies in April 2017. Andalusia followed suit in December 2017, with the law coming into force on 4 February 2018.Ley 8/2017, de 28 de diciembre, para garantizar los derechos, la igualdad de trato y no discriminación de las personas LGTBI y sus familiares en Andalucía/ref> In January 2019,
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
made it an offense to promote and/or perform conversion therapy.
In April 2019, the Government of the Community of Madrid announced it was investigating the Roman Catholic Diocese of Alcalá de Henares
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Alcalá de Henares ( la, Compluten(sis)) is a diocese located in the city of Alcalá de Henares in the Ecclesiastical province of Madrid in Spain.
History
An ancient diocese of '' Complutum'' (the current Alcala d ...
for violating conversion therapy laws. This followed reports that a journalist named Ángel Villascusa posed as a gay man and attended a counselling service provided by the diocese. Villascusa alleged the bishop was running illegal conversion therapy sessions. The bishop was defended by the Catholic Church in Spain. Minister of Health, Consumer Affairs and Social Welfare María Luisa Carcedo
María Luisa Carcedo Roces (born 30 August 1953) is a Spanish doctor, politician and former senator who belongs to the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE). From 2018 to 2020, she served as minister of Health, Consumer Affairs and Social Welf ...
called for a nationwide ban on conversion therapy. She said, "they he Churchare breaking the law therefore, in the first instance, these courses have to be completely abolished. I thought that, in Spain, accepting the various sexual orientations was assumed in all areas, but unfortunately we see that there are still pockets where people are told what their sexual orientation should be".
LGBT rights movement in Spain

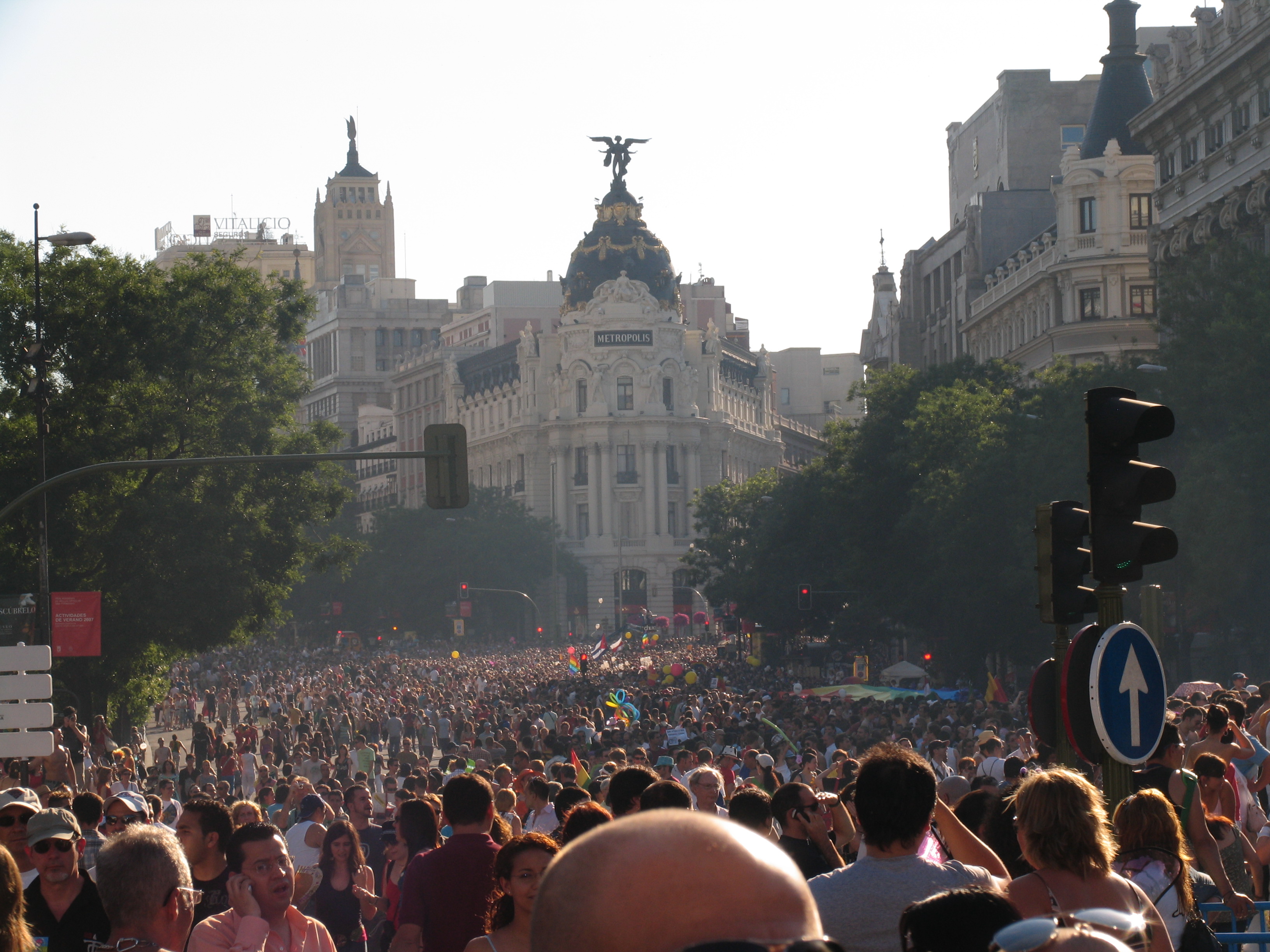
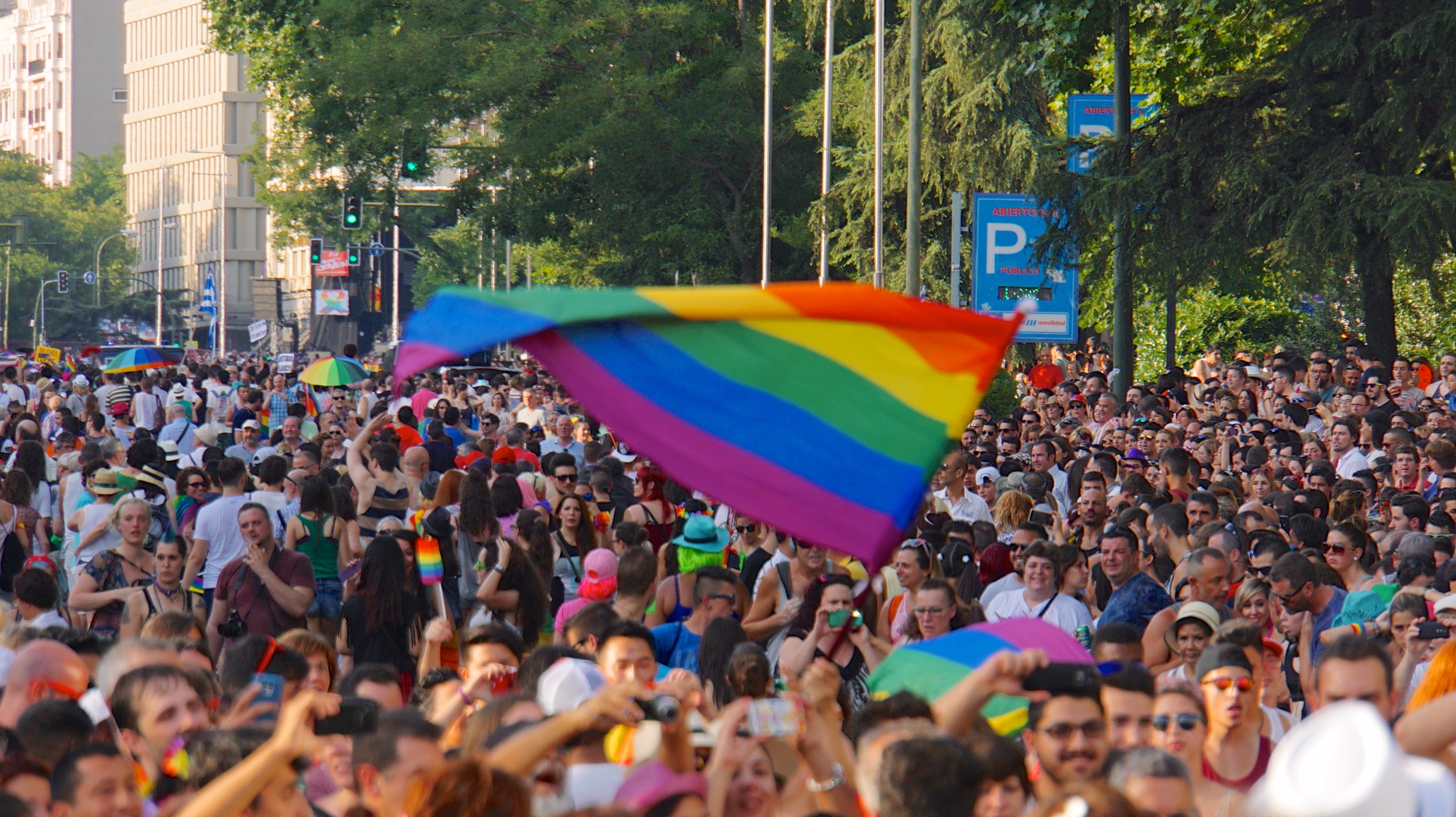
 The first gay organisation in Spain was the Spanish Homosexual Liberation Movement (MELH, '' Movimiento Español de Liberación Homosexual'', '' Moviment Espanyol d'Alliberament Homosexual''), which was founded in 1970 in Barcelona. The group also established centers in Madrid and Bilbao. It disbanded in 1973 because of police pressure, but following Franco's death, several members of the group formed the ''Front d'Alliberament Gai de Catalunya'' (FAGC) in 1975 to continue campaigning for LGBT rights. Several more groups were established, including the ''Euskal Herriko Gay-Les Askapen Mugimendua'' in the Basque Country, the ''Frente Homosexual de Acción Revolucionaria'' in Madrid, and the ''Coordinadora de Frentes de Liberación Homosexual de Estado Español'' (COFLHEE), all three in 1977. On 28 June 1977, the FAGC organised the first gay demonstration in Spain in the city of Barcelona with about 4,000 to 5,000 participants. Police repressed the event, with several arrests and injuries. Exactly one year later, the ''Frente de Liberación Homosexual de Castilla'' held a demonstration in Madrid with about 10,000 people. Disagreement within these groups caused many to shut down; many members advocated a more "radical" movement with public demonstrations and many felt the organizations had failed to properly address or campaign for the rights of lesbians and bisexuals. LGBT groups saw an important landmark moment in 1979 with the decriminalisation of homosexuality.
During the 1980s, several LGBT groups and magazines were launched in various cities. The ''
The first gay organisation in Spain was the Spanish Homosexual Liberation Movement (MELH, '' Movimiento Español de Liberación Homosexual'', '' Moviment Espanyol d'Alliberament Homosexual''), which was founded in 1970 in Barcelona. The group also established centers in Madrid and Bilbao. It disbanded in 1973 because of police pressure, but following Franco's death, several members of the group formed the ''Front d'Alliberament Gai de Catalunya'' (FAGC) in 1975 to continue campaigning for LGBT rights. Several more groups were established, including the ''Euskal Herriko Gay-Les Askapen Mugimendua'' in the Basque Country, the ''Frente Homosexual de Acción Revolucionaria'' in Madrid, and the ''Coordinadora de Frentes de Liberación Homosexual de Estado Español'' (COFLHEE), all three in 1977. On 28 June 1977, the FAGC organised the first gay demonstration in Spain in the city of Barcelona with about 4,000 to 5,000 participants. Police repressed the event, with several arrests and injuries. Exactly one year later, the ''Frente de Liberación Homosexual de Castilla'' held a demonstration in Madrid with about 10,000 people. Disagreement within these groups caused many to shut down; many members advocated a more "radical" movement with public demonstrations and many felt the organizations had failed to properly address or campaign for the rights of lesbians and bisexuals. LGBT groups saw an important landmark moment in 1979 with the decriminalisation of homosexuality.
During the 1980s, several LGBT groups and magazines were launched in various cities. The ''Federación Estatal de Lesbianas, Gays, Transexuales y Bisexuales
The Federación Estatal de Lesbianas, Gays, Transexuales y Bisexuales (FELGTB; en, National Federation of Lesbians, Gays, Transsexuals and Bisexuals) is the main LGBT organisation in Spain. FELGTB is characterised by demanding LGBT rights, at time ...
'' (FELGTB), today Spain's largest LGBT organization, was founded in 1992 from members of the then-former COFLHEE. The groups campaign for legal rights for same-sex couples and LGBT people, societal acceptance, operate counseling centers about topics such as coming out, sex, relationships or health issues, and organize various events and festivals. Several gay villages exist in Spain, including Chueca
Chueca is an area of central Madrid, named after its main square, Plaza de Chueca. It is known as Madrid's gay neighborhood. Plaza de Chueca was named after Spanish composer and author Federico Chueca.
It is located in the administrative ward ...
in Madrid, " Gaixample" in Barcelona, Ibiza
Ibiza (natively and officially in ca, Eivissa, ) is a Spanish island in the Mediterranean Sea off the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. It is from the city of Valencia. It is the third largest of the Balearic Islands, in Spain. Its l ...
, Maspalomas
Maspalomas () is a tourist resort in the south of the island of Gran Canaria, Canary Islands, stretching from Bahía Feliz in the east to Meloneras in the west, including the resort towns of San Agustín and Playa del Inglés and San Fernando. ...
in Gran Canaria, and Sitges.
Nowadays, numerous pride parade
A pride parade (also known as pride march, pride event, or pride festival) is an outdoor event celebrating lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer culture, queer (LGBTQ) social and self-acceptance, achievements, LGBT rights by country o ...
s and other LGBT festivals are held throughout Spain, including Madrid Pride, whose 2019 edition had 400,000 participants according to police, Barcelona, Gran Canaria, Seville, Bilbao, A Coruña, Valencia, Zaragoza, Murcia, Palma de Mallorca
Palma (; ; also known as ''Palma de Mallorca'', officially between 1983–88, 2006–08, and 2012–16) is the capital and largest city of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Balearic Islands in Spain. It is situate ...
, Cartagena, Valladolid, Benidorm
Benidorm is a town and municipality in the province of Alicante, Valencia, on the Mediterranean coast of Spain.
Benidorm has been a tourist destination within Spain since 1925, when its port was extended and the first hotels were built, though ...
, Ibiza, Sitges, Maspalomas, Torremolinos, and many more.
Public opinion
Homosexuality andbisexuality
Bisexuality is a romantic or sexual attraction or behavior toward both males and females, or to more than one gender. It may also be defined to include romantic or sexual attraction to people regardless of their sex or gender identity, whic ...
today are greatly accepted all around the country and intensely in larger and medium cities. That being said, a certain level of discrimination can still be encountered in small villages and among some parts of society.
A Eurobarometer survey published December 2006 showed that 66 percent of Spanish people surveyed supported same-sex marriage and 43 percent supported same-sex couples' right to adopt (EU-wide averages were 44 percent and 33 percent, respectively).
On 4 March 2013, Interior Minister Jorge Fernández Díaz
Jorge Fernández Díaz (born 6 April 1950) is a Spanish politician and a member of the Partido Popular (PP).
Early life and education
Born on 6 April 1950 in Valladolid, he was the son of a military officer and Deputy Inspector-Chief of the B ...
said that due to same-sex marriages the survival of the human species is not guaranteed.Spanish interior minister says 'survival of species' at stake in gay marriage rowFiona Govan, Madrid; 4 March 2013; '' The Daily Telegraph'' He also stated that same-sex marriages should not have the same protection under the law as opposite-sex ones, eight years after same-sex marriage was legalized. Among the countries studied by the
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
in 2013, Spain was rated first in acceptance of homosexuality, with 88% of Spaniards believing that homosexuality should be accepted by society, compared to 11% who disagreed.
In May 2015, PlanetRomeo, an LGBT social network, published its first Gay Happiness Index (GHI). Gay men from over 120 countries were asked about how they feel about society's view on homosexuality, how do they experience the way they are treated by other people and how satisfied are they with their lives. Spain was ranked 13th with a GHI score of 68.
BuzzFeed
BuzzFeed, Inc. is an American Internet media, news and entertainment company with a focus on digital media. Based in New York City, BuzzFeed was founded in 2006 by Jonah Peretti and John S. Johnson III to focus on tracking viral content. Ken ...
conducted a poll in December 2016 across several countries on the acceptance of transgender individuals. Spain ranked the most accepting in most categories, with 87% of those polled believing transgender people should be protected from discrimination, and only 8% believing there is something mentally or physically wrong with them. In addition, 77% believed transgender people should be allowed to use the bathroom that matches their gender identity rather than being forced to use the one of their birth-assigned gender, with over 50% strongly agreeing with this.
The 2015 Eurobarometer found that 84% of Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance peoples, Romance ethnic group native to Spain. Within Spain, there are a number of National and regional identity in Spain, national and regional ethnic identities that reflect the country's complex Hist ...
thought that same-sex marriage should be allowed throughout Europe, 10% were against. The 2019 Eurobarometer showed that 91% of Spaniards believed gay and bisexual people should enjoy the same rights as heterosexual people, and 86% supported same-sex marriage.
LGBT culture
Literature

 At the beginning of the 20th century, Spanish authors, like Jacinto Benavente,
At the beginning of the 20th century, Spanish authors, like Jacinto Benavente, Pedro de Répide
Pedro de Répide Gallegos (8 February 1882 – 16 February 1948) was a Madrid-based writer and journalist.
Biography
Pedro de Répide Gallegos studied law, philosophy and liberal arts at the Complutense University of Madrid, and by the age of ni ...
and Antonio de Hoyos y Vinent, had to choose between ignoring the subject of homosexuality or representing it negatively. The only authors publishing literature with LGBT content were foreigners: Augusto d'Halmar
Augusto Goemine Thomson, who adopted the pseudonym Augusto d’Halmar (April 23, 1882 – January 27, 1950) was a Chilean writer who earned the ''National Prize for Literature'' in 1942.
D’Halmar was the son of Auguste Goemine, a French navi ...
from Chile published ''Pasión y muerte del cura Deusto'', Alfonso Hernández Catá from Cuba published ''El ángel de Sodoma'', and Alberto Nin Frías
Alberto Nin Frías (Montevideo, 9 November 1878 – Suardi, Santa Fe, Argentina, 27 March 1937) was a Uruguayan writer, lecturer and journalist. Among other topics, he is noted for his work on homoeroticism.
Nin Frias also served as a diplomat ...
from Uruguay published ''La novela del renacimiento y otros relatos'', ''La fuente envenenada'', ''Marcos, amador de la belleza'', ''Alexis o el significado del temperamento Urano'' and, in 1933, ''Homosexualismo creador'', the first essay representing homosexuality in a positive light.
Others, such as the authors of the Generation of '27, took refuge in poetry. The gay and bisexual poets of this literary movement were amongst the most influential in Spanish literature: Federico García Lorca, Emilio Prados
Emilio Prados (4 March 1899 - 24 April 1962) was a Spanish poet and editor, a member of the Generation of '27.
Life
Born in the Andalusian city of Málaga in 1899, Prados was offered a place at Madrid's famous Residencia de estudiantes in 1914 a ...
, Luis Cernuda, Vicente Aleixandre and Manuel Altolaguirre. These poets were highly influenced by the great gay authors of the rest of Europe, such as Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
, André Gide, mainly his '' Corydon'', and Marcel Proust
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust (; ; 10 July 1871 – 18 November 1922) was a French novelist, critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel ''In Search of Lost Time'' (''À la recherche du temps perdu''; with the previous Eng ...
. In 1930, Emilio García Gómez
Emilio García Gómez, 1st Count of Alixares (4 June 1905 – 31 May 1995) was a Spanish Arabist, literary historian and critic, whose talent as a poet enriched his many translations from Arabic.
Life
Emilio García Gómez decided to pursue ...
also published his ''Poemas arabigoandaluces'', which included the pederastic poets of Al-Andalus. Around the mid-1930s, there was a slight liberalisation which ended with the beginning of the Spanish Civil War. After the Civil War, with García Lorca assassinated and the majority of gay and bisexual poets in exile, gay culture retired anew to the cryptic poetry of Vicente Aleixandre, who never admitted his homosexuality publicly. Other gay poets of this period are Francisco Brines
Francisco Brines Bañó (22 January 1932 – 20 May 2021) was a Spanish poet.
Biography
Brines was born in Oliva (Valencia). He is regarded as one of the Generation of '50 of Spanish poets, along with Claudio Rodríguez, Jaime Gil de Biedma ...
, Leopoldo María Panero, Juan Gil-Albert and Jaime Gil de Biedma
Jaime Gil de Biedma y Alba (13 November 1929 – 8 January 1990) was a Spanish post-Civil War poet.
He was born in Nava de la Asunción on 13 November 1929. He stopped writing poetry some ten years before his death. He insisted that the charact ...
and, in Córdoba, Vicente Núñez, Pablo García Baena and Juan Bernier, belonging to the ''Cántico'' group.
Authors that appear after the Spanish Transition include Juan Goytisolo
Juan Goytisolo Gay (6 January 1931 – 4 June 2017) was a Spanish poet, essayist, and novelist. He lived in Marrakesh from 1997 until his death in 2017.
He was considered Spain's greatest living writer at the beginning of the 21st century, yet ...
, Luis Antonio de Villena, Antonio Gala
Antonio Gala Velasco (born 2 October 1930) is a Spanish poet, playwright, novelist and writer.
Life and career
Gala was born in Brazatortas, Ciudad Real ( Castile-La Mancha), although he moved very soon to Córdoba and is widely considered an ...
, Terenci Moix
Terenci Moix (; real name Ramon Moix i Meseguer; 5 January 1942, in Barcelona – 2 April 2003, in Barcelona) was a Spanish writer, who wrote in Spanish, and in Catalan. He is also the brother of poet/novelist Ana Maria Moix.
Life and work ...
, Álvaro Pombo
Álvaro Pombo García de los Ríos (born 23 June 1939) is a Spanish poet, novelist and activist.
Born in Santander, Cantabria, he studied at the Complutense University of Madrid and received a Bachelor of Arts in philosophy at Birkbeck, Univers ...
, Vicente Molina Foix
Vicente Molina Foix (born 18 October 1946) is a Spanish writer and film director.
Biography
Born in Elche in 1946, he studied at the Complutense University in Madrid and at the University of London. He taught Spanish literature at the Univer ...
, Antonio Roig, Biel Mesquida, Leopoldo Alas, Vicente García Cervera, Carlos Sanrune, Jaume Cela, Eduardo Mendicutti, Miguel Martín, Lluis Fernández, Víctor Monserrat, Alberto Cardín Benigno Alberto Cardín Garay (Villamayor, 15 January 1948 - Barcelona, 26 January 1992) was a Spanish essayist and anthropologist, and one of the most important gay Spanish activists of the Spanish transition to democracy.Mira 2000:76-77Bueno 1992: ...
, Mariano García Torres, Agustín Gómez-Arcos
Agustin Gomez-Arcos (15 January 1939 – 20 March 1998) was a Spanish writer. He was born in Enix, Spain. He studied law but quit university for theater. However, some of his work was banned in Franco's Spain. He emigrated to London in 1966, th ...
, Óscar Esquivias
Óscar Esquivias (born 28 June 1972 in Burgos, Castile and León, Spain) is a Spanish short-story writer, poet and novelist.
Biography
He studied at the University of Burgos. He was director of the literature magazine ''Calamar, revista de cre ...
, Luisgé Martín and Iñaki Echarte.
No lesbian authors in Spain publicly acknowledged their homosexuality until the 1990s. Gloria Fuertes never wanted her sexual orientation to be public. The first lesbian author to be openly gay was Andrea Luca. Other authors who have treated love between women in their books include Ana María Moix Ana María Moix (12 April 1947 – 28 February 2014) was a Spanish poet, novelist, short story writer, translator and editor. A member of the Novísimos, she was the younger sister of the writer, Terenci Moix.
Moix was born in Barcelona and studie ...
, Ana Rosetti, Esther Tusquets
Esther Tusquets (30 August 1936 – 23 July 2012) was a Spanish publisher, novelist and essayist.
Biography
Tusquets was born in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. Her brother is the architect Òscar Tusquets.
She studied philosophy, literature and ...
, Carmen Riera, Elena Fortún
María de la Encarnación Gertrudis Jacoba Aragoneses y de Urquijo (17 November 1886 in Madrid – 8 May 1952 in Madrid) was a Spanish author of children's literature who wrote under the pen name Elena Fortún. She became famous for '' Celia ...
, Isabel Franc
Isabel Franc (born 1955) is a Spanish writer who signs some of her novels with the pseudonym Lola Van Guardia.
Career
Isabel Franc's works are characterized by humor and being generally focused on the world of female homosexuality. She has also ...
and Lucía Etxebarría
Lucía Etxebarria de Asteinza (7 December 1966 in Valencia) is a Spanish writer, winner of Premio Nadal in 1998 and Premio Planeta de Novela in 2004.
Career
Lucía Etxebarria de Asteinza was born in Valencia in 1966, daughter of José Ignacio ...
, whose novel ''Beatriz y los cuerpos celestes'' won the Nadal Prize
Premio Nadal is a Spanish literary prize awarded annually by the publishing house Ediciones Destino, part of Planeta Group, Planeta. It has been awarded every year on 6 January since 1944. The Josep Pla Award for Catalan literature is given at the ...
in 1998.
Cinema and television
 Early representation of homosexuality in Spanish cinema was difficult due to censorship by the Franco regime. The first movie that shows any kind of homosexuality, very discreetly, was ''Diferente'', a musical from 1961, directed by Luis María Delgado. Up to 1977, if homosexuals appeared at all, it was to ridicule them as the "funny effeminate faggot".
During the
Early representation of homosexuality in Spanish cinema was difficult due to censorship by the Franco regime. The first movie that shows any kind of homosexuality, very discreetly, was ''Diferente'', a musical from 1961, directed by Luis María Delgado. Up to 1977, if homosexuals appeared at all, it was to ridicule them as the "funny effeminate faggot".
During the Spanish transition to democracy
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, the first films appeared where homosexuality was not portrayed in a negative way. Examples are ''La Muerte de Mikel
'' La Muerte de Mikel'' ( en, The Death of Mikel) is a 1984 Spanish film directed by Imanol Uribe, starring Imanol Arias. The film tells in flash back, the story of a gay member of ETA who died under mysterious circumstances.
Plot
The film opens ...
'' from Imanol Uribe
Imanol Uribe (born 28 February 1950) is a Spanish screenwriter and film director. He won the Goya Award for Best Director and Best Screenplay for the 1994 thriller '' Running Out of Time''.
Biography
Born in San Salvador on 28 February 1950 to ...
and ''Ocaña, retrat intermitent'' from Ventura Pons
Ventura Pons Sala (; born 25 July 1945, in Barcelona, Spain) is a Spanish movie director. He mainly directs films in Catalan but also in Spanish and English. Pons has directed 32 feature films and is one of the best-known Catalan film directors ...
. In these films, authors experiment with different visions of gay men: the transvestite in ''Un hombre llamado Flor de Otoño'' (1978), the manly and attractive gay man in ''Los placeres ocultos
''Hidden Pleasures'' ( es, Los placeres ocultos) is a 1977 drama film, directed by Eloy de la Iglesia. The script was written by de la Iglesia, Rafael Sánchez Campoy and Gonzalo Goicoechea with the working title ''La acera de enfrente'' ''(literal ...
'' (1976) from Eloy de la Iglesia
Eloy de la Iglesia (1 January 1944 – 23 March 2006) was a Spanish screenwriter and film director.
De la Iglesia was an outspoken gay socialist filmmaker who is relatively unknown outside Spain despite a prolific and successful career in his ...
, the warring "queen" in ''Gay Club'' (1980), etc. Homosexuality is the center of the plot, and homosexuals are shown as vulnerable, in inner turmoil and in dispute with society.
Beginning in 1985, homosexuality loses primacy on the plot, in spite of still being fundamental. This trend begins with ''La ley del deseo
''Law of Desire'' ( es, link=no, La ley del deseo) is a 1987 Spanish comedy thriller film written and directed by Pedro Almodóvar. Starring Eusebio Poncela as Pablo, Carmen Maura as Tina and Antonio Banderas as Antonio. It was the first film ...
'' (1987) from Pedro Almodóvar and continues with films like ''Tras el cristal
''In a Glass Cage'' ( es, Tras el cristal) is a 1986 Spanish horror film written and directed by Agustí Villaronga, and starring Günter Meisner, Marisa Paredes, and David Sust.Schwartz, ''The Great Spanish Films Since 1950'', p. 193 Inspired by ...
'' (1986) from Agustí Villaronga
Agustí Villaronga Riutort (; 4 March 1953 – 22 January 2023) was a Spanish film director, screenwriter and actor. He directed several feature films, a documentary, three projects for television and three shorts. His film '' Moon Child'' was ...
, ''Las cosas del querer'' (1989) and ''Las cosas del querer 2'' (1995) from Jaime Chávarri. Successful films include '' Perdona bonita, pero Lucas me quería a mí'' (1997), ''Segunda piel
''Second Skin'' ( es, Segunda piel, links=no) is a 1999 Spanish romantic drama film directed by Gerardo Vera, starring Javier Bardem, Jordi Mollà, Ariadna Gil and Cecilia Roth.
Premise
Elena and Alberto, a couple from Madrid, have a happy marria ...
'' (1999), ''Km. 0
''Km. 0'' is a 2000 film Spanish directed by Yolanda García Serrano and Juan Luis Iborra. The plot concerns about several intertwining stories of mistaken identity and coincidental meetings (that may not be coincidental) that take place near t ...
'' (2000), ''Plata quemada
''Burnt Money'' ( es, Plata quemada, links=no) is a 2000 action thriller directed by Marcelo Piñeyro and written by Piñeyro and Marcelo Figueras. Starring Leonardo Sbaraglia, Eduardo Noriega, Pablo Echarri, Leticia Brédice and Ricardo Bartis, ...
'' (2000), '' Los novios búlgaros'' (2003) and ''Cachorro
''Bear Cub'' ( es, Cachorro) is a 2004 Spanish comedy-drama film co-written and directed by Miguel Albaladejo. The plot follows a Bear (gay culture), bearish gay man who ends up looking after his nephew while his sister goes away to India an ...
'' (2004).
Undoubtedly, Spain's best-known LGBT person is Pedro Almodóvar. Almodóvar has often intertwined LGBT themes in his plots, and his films have turned him into one of the most renowned Spanish movie directors. Apart from Almodóvar, Ventura Pons
Ventura Pons Sala (; born 25 July 1945, in Barcelona, Spain) is a Spanish movie director. He mainly directs films in Catalan but also in Spanish and English. Pons has directed 32 feature films and is one of the best-known Catalan film directors ...
and Eloy de la Iglesia
Eloy de la Iglesia (1 January 1944 – 23 March 2006) was a Spanish screenwriter and film director.
De la Iglesia was an outspoken gay socialist filmmaker who is relatively unknown outside Spain despite a prolific and successful career in his ...
are two film directors who have worked on more LGBT themes in their movies. In September 2004, movie director Alejandro Amenábar publicly announced his homosexuality.
There have not been as many Spanish films with a lesbian plot. The most renown may be the comedy '' A mi madre le gustan las mujeres'' (2002), and the romantic drama ''Room in Rome
''Room in Rome'' ( es, Habitación en Roma, links=no) is a 2010 Spanish erotic romantic comedy-drama film directed by Julio Medem starring Elena Anaya and Natasha Yarovenko, depicting the emotional and sexual relations of two women throughou ...
'' (''Habitación en Roma'') (2010).
The most-important LGBT film festivals are LesGaiCineMad in Madrid and the ''Festival internacional de cinema gai i lèsbic de Barcelona'' (FICGLB). There are also many other smaller festivals and shows, including ''Festival del Mar'' in the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
, ''Festival del Sol'' in the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to the African mainland, they are west of Morocc ...
, ''Zinegoak'' in Bilbao, ''LesGaiFestiVal'' in Valencia or ''Zinentiendo'' in Zaragoza.
In 2018, Ángela Ponce
Ángela Maria Ponce Camacho (born 18 January 1991) is a Spanish model and beauty pageant titleholder who won Miss Universe Spain 2018. Ponce made history on 29 June 2018 as the first openly transgender woman to be crowned Miss Spain. She represe ...
became the first transgender woman to win the Miss Universe Spain title, and was the first transgender woman to contest for Miss Universe 2018.
Music
 During Franco's dictatorship, musicians seldom made any reference to homosexuality in their songs or in public speeches. An exception was the '' copla'' singer Miguel de Molina, openly homosexual and against Franco. De Molina fled to Argentina after being brutally tortured and his shows prohibited. Another exception was Bambino, whose homosexuality was known in flamenco circles. Some songs from Raphael, as "Qué sabe nadie" ("What does anyone know") or "Digan lo que digan" ("Whatever they say"), have frequently been interpreted in a gay light.
In 1974, the folk rock band Cánovas, Rodrigo, Adolfo y Guzmán talked about a lesbian relationship in the song "María y Amaranta" ("María and Amaranta"), that surprisingly was not censored. During the transition to democracy, the duo Vainica Doble sung about the fight of a gay man against the prejudices of his own family in the song "El rey de la casa" ("The king of the house").
Singer-songwriter
During Franco's dictatorship, musicians seldom made any reference to homosexuality in their songs or in public speeches. An exception was the '' copla'' singer Miguel de Molina, openly homosexual and against Franco. De Molina fled to Argentina after being brutally tortured and his shows prohibited. Another exception was Bambino, whose homosexuality was known in flamenco circles. Some songs from Raphael, as "Qué sabe nadie" ("What does anyone know") or "Digan lo que digan" ("Whatever they say"), have frequently been interpreted in a gay light.
In 1974, the folk rock band Cánovas, Rodrigo, Adolfo y Guzmán talked about a lesbian relationship in the song "María y Amaranta" ("María and Amaranta"), that surprisingly was not censored. During the transition to democracy, the duo Vainica Doble sung about the fight of a gay man against the prejudices of his own family in the song "El rey de la casa" ("The king of the house").
Singer-songwriter Víctor Manuel
Víctor Manuel San José Sánchez (born July 7, 1947) is a Spanish singer-songwriter.
He has been married to the Spanish singer and actress Ana Belén since 1972. He and his wife are considered symbols of the Spanish Transition, and his songs ...
has included LGBT subjects in several of his songs. In 1980, he released "Quién puso más" ("Who put more?"), a true love story between two men that ends after 30 years. He later mentioned transsexuality in his song "Como los monos de Gibraltar" ("As the monkeys in Gibraltar"), feminine homosexuality in "Laura ya no vive aquí" ("Laura doesn't live here any more") and bisexuality in "No me llames loca" (Don't call me fool/queen).
It was not until the La Movida Madrileña that homosexuality became visible in Spanish music. The duo Pedro Almodóvar and Fabio McNamara usually dressed as women during their concerts, where they sang provocative lyrics. Tino Casal
José Celestino Casal Álvarez, more commonly known as Tino Casal, (11 February 1950, in Tudela Veguín, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain – 22 September 1991, in Madrid, Spain) was a Spanish singer, songwriter and producer, who was active during La ...
never hid his homosexuality and became an icon for many gay people. Nevertheless, it would be the trio Alaska, Nacho Canut y Carlos Berlanga who would be identified from the beginning with the LGBT movement due to their constant references to homosexuality in their lyrics and their concerts. During their time as Dinarama, they recorded the song " ¿A Quién le Importa?" ("Who cares?"), which became a gay anthem in Spain. After the Movida, several artists continued to make music with homosexual themes, such as Fabio McNamara, Carlos Berlanga in "Vacaciones" ("Holiday"), or Luis Miguélez, ex-guitarist of Dinarama and later member of Glamour to Kill.
At the end of the 1980s, Mecano
Mecano was a Spanish pop band formed in 1981 and active until 1992. Mecano became one of the most successful Spanish pop bands of all time. The band is still the best-selling Spanish band, with over 25 million records worldwide. They were consid ...
made a hit with the song " Mujer contra mujer" ("Woman against woman"), clearly defending the love of two women. There were French (" Une femme avec une femme") and Italian ("Per Lei Contro Di Lei") versions. The song was a huge hit in France in 1990 where it reached No. 1 in charts during seven weeks. The song was also a hit in Latin America and is one of the most remembered of the group. They later composed the song "Stereosexual" that talked about bisexuality. In 1988, Tam Tam Go!, in the album "Spanish shuffle", included the song "Manuel Raquel", the only song in Spanish in the album, which told the story of a transsexual. Tino Casal
José Celestino Casal Álvarez, more commonly known as Tino Casal, (11 February 1950, in Tudela Veguín, Oviedo, Asturias, Spain – 22 September 1991, in Madrid, Spain) was a Spanish singer, songwriter and producer, who was active during La ...
included in his 1989 album ''Histeria'' the very explicit song "Que digan misa".
At the beginning of the 1990s, new singer-songwriters also took up the subject, especially Inma Serrano
Inma Serrano is a Spanish singer-songwriter. Serrano was born in Alicante, Spain, in 1968.
She has lived in Alicante, Valencia, Barcelona, and Madrid. In 2003, she created the record label "Cerebro Demente Records". With this record company, she ...
, Javier Álvarez, and Andrés Lewin, but also Pedro Guerra
Pedro Manuel Guerra Mansito (born 2 June 1966 in Güímar, Tenerife) is a Spanish singer-songwriter.
Biography
Guerra is the son of Pedro Guerra Cabrera, the first President of the Canarian Parliament.
He began studying the guitar at the C ...
in his song "Otra forma de sentir" ("Another way of feeling") or Tontxu
Juan Antonio Ipiña (Tontxu) (Bilbao (Spain), August 17, 1973) is a Spanish singer-songwriter.
He worked in the radio station "40 Principales" in Bilbao. Later, he went to Madrid where he started to sing in the café ''Libertad 8.'' There he me ...
in "¿Entiendes?" ("Do you understand?"). Other artists with diverse styles also used the theme, as "El cielo no entiende" ("Heaven doesn't understand") by OBK
OBK is a Spanish synthpop music group from Barcelona (Spain) composed of Jordi Sánchez and Miguel Arjona. The group was famous for introducing the electronic music in Spain in the 1990s (in the early 1980s some Spanish synthpop bands as Azul ...
, "Entender el amor" ("Understand love") by Mónica Naranjo, "El día de año nuevo" ("New Year's Day") by Amaral, "Eva y María" by Materia Prima, "Sacrifícate" by Amistades Peligrosas, "La revolución sexual" by La casa azul, "Ángeles" by Merche, "Como una flor" by Malú, "Da igual" by Taxi, "El que quiera entender que entienda" by Mägo de Oz
Mägo de Oz (Spanish for '' Wizard of Oz'', with a metal umlaut) are a Spanish folk metal band from Begoña, Madrid formed in mid-1988 by drummer Txus di Fellatio.
The band became well known for the strong Celtic feel to their music strengthene ...
, etc.
Indie pop has also treated homosexuality from different points of view, as the band Ellos in the song "Diferentes" ("Different"), or L Kan
L, or l, is the twelfth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Let ...
in "Gayhetera" (Gayhereto). The duo Astrud has been related to gay culture. The leather subculture has the band Gore Gore Gays with themes that range from LGBT demands to explicit sex. Within the indie pop universe, many other bands produce songs almost exclusively for a gay public, especially gay-friendly or with a clear gay content (Nancys Rubias
Nancys Rubias (''Blonde Nancys'') is a Spanish rock-band created in 2004 in Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan are ...
, Lorena C, Spunky, La Terremoto de Alcorcón, Putilatex, Putirecords, Borrachas provincianas, Vanity Bear, Modelé Fatale, Dos Hombres Solos, Postura 69, etc.) and some drag queens have a successful career in music, such as La Prohibida
La Prohibida (in Spanish, ''The Forbidden Woman''), previously "'La Perdida"' (''The Lost Woman'') is the stage name of Amapola López (born Luis Herrero Cortés, 1971), a Spanish pop and electronic music singer.
Life and career 1971-1996: Ear ...
, Nacha la Macha, or La Otxoa.
Politics
 Several openly gay politicians have served in public office in Spain. One of the most prominent gay politicians is
Several openly gay politicians have served in public office in Spain. One of the most prominent gay politicians is Jerónimo Saavedra
Jerónimo Saavedra Acevedo (born 3 July 1936 in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria) is a Spanish politician. He served as President of the Canary Islands twice from 1982 to 1987, and again from 1991 to 1993.
Biography
In 1972 he joined the Spanish So ...
, who served as President of the Canary Islands
The president of the Canary Islands is the head of government of the Canary Islands, one of the 17 autonomous communities of Spain, while the monarch Felipe VI remains the head of state as king of Spain (and therefore of the Canary Islands).
Lis ...
twice from 1982 to 1987 and again from 1991 to 1993. Saavedra came out as gay in 2000. He served as a member of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
until 2004, and was Mayor of Las Palmas from 2007 to 2011. Another prominent gay politician and activist was Pedro Zerolo, who served on the City Council of Madrid until his death in June 2015. Zerolo was known for his LGBT activism and was one of the biggest promoters of the law extending the right to marriage to same-sex couples, leading many to label him a gay icon.
Others include Javier Maroto, formerly serving as mayor of the Basque capital of Vitoria-Gasteiz from 2011 to 2015 and currently serving as senator. Maroto married his fiancé José Manuel Rodríguez in September 2015. The marriage ceremony was attended by Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy. Máximo Huerta
Maximo or Máximo may refer to:
Arts
* Capcom video game series
** '' Maximo: Ghosts to Glory'' (also known as just ''Maximo'')
** ''Maximo vs. Army of Zin'', the sequel to ''Ghosts to Glory''
* Maxïmo Park, a British indie rock band
* Maximu or ...
, Ángeles Álvarez
Ángeles Álvarez Álvarez (born 12 February 1961) is a Spanish politician and feminist activist. She served as a deputy for Madrid from 2011 to 2019. She was also a spokesperson for equality of the PSOE in the Congress of Deputies. She has a lon ...
and Fernando Grande-Marlaska
Fernando Grande-Marlaska Gómez (born 26 July 1962) is a Spanish judge, serving as minister of the Interior since June 2018 under Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez.
Biography Early life and career
Born in Bilbao, he is the son of Avelino Grande, an ...
are other gay politicians who serve/have served in the Cortes Generales. Grande-Marlaska has served as Minister of the Interior
An interior minister (sometimes called a minister of internal affairs or minister of home affairs) is a cabinet official position that is responsible for internal affairs, such as public security, civil registration and identification, emergency ...
since June 2018.
Ada Colau
Ada Colau Ballano (; ; born 3 March 1974) is a Spanish activist and politician who is the current Mayor of Barcelona. On 13 June 2015 she was elected Mayor of Barcelona, the first woman to hold the office, as part of the citizen municipalist pla ...
, elected Mayor of Barcelona
This is a list of mayors of Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. Wi ...
in 2015, revealed her bisexuality in December 2017. Other Catalan gay politicians include Antoni Comín
Antoni Comín, born in Barcelona on March 1971, March 7 1971, is a Catalans, Catalan intellectual and politician from Spain. He is currently the executive vice-president of the Council for the Republic and has been an European Parliament, MEP sin ...
, Santi Vila
Santiago "Santi" Vila i Vicente (born 15 March 1973) is a Catalan historian and politician from Granollers, Spain. He was a member of the Catalan European Democratic Party, and was a councillor at Figueres from 1999 before becoming mayor from 20 ...
and Miquel Iceta.
Carla Antonelli
Carla Delgado Gómez (born 13 July 1959 in Güímar, Tenerife, Canary IslandsGonzález, Maribel (17 May 2009)100 españoles hablan de sexo.'' El Mundo'') is a Spanish actress who uses the stage name Carla Antonelli. She is also a noted LGBT rig ...
, Víctor Casco, Iñigo Lamarca
Íñigo Lamarca Iturbe (born 13 July, 1959) is a Spanish lawyer and served as Ararteko (Ombudsman), of the Basque Country between 2004 and 2014. He previously served as president of GEHITU, and is the first gay man to hold the office.
Life
He wa ...
, Fran Ferri, Jesús Vázquez Abad, Iñaki Oyarzábal, Empar Pineda and Luis Alegre Zahonero
Luis Alegre Zahonero (born 16 March 1977) is a Spanish philosopher and writer, a professor in the Complutense University of Madrid, and a founding member of Podemos.
Biography
Luis Alegre is a researcher and professor of philosophy in the ...
are other openly LGBT politicians, variously serving as mayors or members of regional legislatures. In 2007, Manuela Trasobares won a seat as a councillor in the small Valencian town of Geldo
Geldo is a Municipalities of Spain, municipality of Spain in the Valencian Community, in the province of Castellón (province), Castellón. It has a population of 716 (2005) and an area of 0.50 km².
References
Municipalities in ...
, becoming the first openly transgender Spaniard to hold public office.
Sports
 Sports is traditionally a difficult area for LGBT visibility. Recently though, there have been professional sportswomen and sportsmen who have come out. These include
Sports is traditionally a difficult area for LGBT visibility. Recently though, there have been professional sportswomen and sportsmen who have come out. These include Mapi León
María Pilar León Cebrián (; born 13 June 1995), known as Mapi León, is a Spanish professional women's soccer, footballer who plays as a Defender (association football), defender for Liga F club FC Barcelona Femení, Barcelona and the Spain ...
and Ana Romero
Ana María Romero Moreno (born 14 June 1987), commonly known as Willy, is a Spanish retired footballer who played as a midfielder. She previously represented several teams in Spain's Primera División, including Valencia CF, FC Barcelona, Sevill ...
in football, Víctor Gutiérrez in waterpolo, Carlos Peralta
Carlos Peralta is a Mexican businessman and baseball team owner.
After inheriting the construction business from his father Alejo Peralta, he expanded it into electronics. In 2001, he sold the company's stake in Iusacell to Vodafone for $973 mill ...
in swimming, Marta Mangué
Marta Mangué González (born 23 April 1983) is a Spanish handballer for Bourg-de-Péage Drôme Handball and the Spanish national team.
She was part of the Spanish team that won the bronze medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Mangué played f ...
in handball, Javier Raya
Francisco Javier Raya Buenache (born 20 April 1991) is a Spanish figure skater. He is the 2011 Spanish Figure Skating Championships, Spanish national senior champion and has competed in the free skate at eight ISU Figure Skating Championships, IS ...
in figure skating and Miriam Blasco
Miriam Blasco Soto (born 12 December 1963) is a professional judo competitor, who resides in Alicante, Spain. She competed at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona, Spain where she won the gold medal in Women's Judo in the 57 kg division. ...
in judo.
In February 2019, the far-right party Vox vetoed a motion calling for an official stance against homophobia in sports. The motion, supported by every other political party, required unanimity to be adopted.
Summary table
Notes
See also
*COGAM
Lesbians, Gays, Transsexuals and Bisexuals Collective Organization ( es, Colectivo de Lesbianas, Gays, Transexuales y Bisexuales de Madrid), COGAM is a Spanish Non-governmental organization, non-governmental association stated as a public utilit ...
* Human rights in Spain
* Same-sex marriage in Spain
*First same-sex marriage in Spain
The first same-sex marriage in Spain to take place after the Roman Imperial era occurred on 8 June 1901. Two women, Marcela Gracia Ibeas and Elisa Sánchez Loriga, attempted to get married in A Coruña (Galicia, Spain). To achieve it Elisa had t ...
*LGBT history in Spain This is a list of notable events in the history of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) rights that took place in Spain.
prior to 1600
6th century
* 589 – The Visigothic kingdom in Spain, is converted from Arianism to Catholicism. T ...
* LGBT rights in Europe
* LGBT rights in the European Union
References
External links
* :es:Homosexualidad en España {{DEFAULTSORT:Lgbt Rights in Spain