Flory–Huggins solution theory is a
lattice model of the
thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
of
polymer solutions which takes account of the great dissimilarity in
molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
sizes in adapting the usual
expression for the
entropy of mixing
In thermodynamics, the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy when several initially separate systems of different composition, each in a thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium, are mixed without chemical reaction by the ther ...
. The result is an equation for the
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy as the recommended name; symbol is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of Work (thermodynamics), work, other than Work (thermodynamics)#Pressure–v ...
change
for mixing a polymer with a
solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
. Although it makes simplifying assumptions, it generates useful results for interpreting experiments.
Theory
The
thermodynamic equation for the
Gibbs energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy as the recommended name; symbol is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure–volume work, that may be performed by a ther ...
change accompanying mixing at constant
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
and (external)
pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
is
:
A change, denoted by
, is the
value of a
variable for a
solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solu ...
or
mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proporti ...
minus the values for the pure
components
Component may refer to:
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
*System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assembly or software module, within a system considered at a particular level of analysis
* Lumped e ...
considered separately. The objective is to find explicit
formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
s for
and
, the
enthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant extern ...
and
entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
increments associated with the mixing
process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
.
The result obtained by
Flory and
Huggins is
:
The right-hand side is a
function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
of the number of
moles and volume fraction
of
solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
(
component
Component may refer to:
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
*System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assembly or software module, within a system considered at a particular level of analysis
* Lumped e ...
), the number of moles
and volume fraction
of polymer (component
), with the introduction of a parameter
to take account of the
energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
of interdispersing polymer and solvent molecules.
is the
gas constant
The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol or . It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment p ...
and
is the
absolute temperature
Thermodynamic temperature, also known as absolute temperature, is a physical quantity which measures temperature starting from absolute zero, the point at which particles have minimal thermal motion.
Thermodynamic temperature is typically expres ...
. The volume fraction is analogous to the
mole fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the to ...
, but is weighted to take account of the relative sizes of the molecules. For a small solute, the mole fractions would appear instead, and this modification is the innovation due to Flory and Huggins. In the most general case the mixing parameter,
, is a free energy parameter, thus including an entropic component.
Derivation
We first calculate the
''entropy'' of mixing, the increase in the
uncertainty
Uncertainty or incertitude refers to situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown, and is particularly relevant for decision ...
about the locations of the molecules when they are interspersed. In the pure condensed
phases –
solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
and polymer – a molecule exists for any arbitrarily small volume element. The
expression for the
entropy of mixing
In thermodynamics, the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy when several initially separate systems of different composition, each in a thermodynamic state of internal equilibrium, are mixed without chemical reaction by the ther ...
of small molecules in terms of
mole fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the to ...
s is no longer reasonable when the
solute
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are ...
is a
macromolecular
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
chain
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A ...
. We take account of this dis
symmetry
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is Invariant (mathematics), invariant und ...
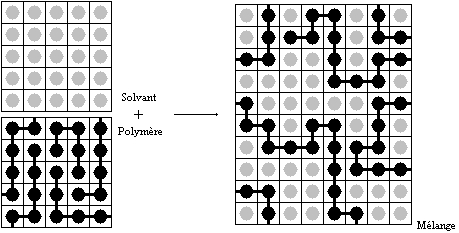
in molecular sizes by assuming that individual polymer segments and individual solvent molecules occupy sites on a
lattice. Each site is occupied by exactly one molecule of the solvent or by one
monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Chemis ...
of the polymer chain, so the total number of sites is
:
where
is the number of solvent molecules and
is the number of polymer molecules, each of which has
segments.
For a
random walk
In mathematics, a random walk, sometimes known as a drunkard's walk, is a stochastic process that describes a path that consists of a succession of random steps on some Space (mathematics), mathematical space.
An elementary example of a rand ...
on a lattice we can calculate the
entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
change (the increase in
spatial uncertainty
Uncertainty or incertitude refers to situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown, and is particularly relevant for decision ...
) as a result of mixing solute and solvent.
:
 Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the
Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the  Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the
Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the